Abstract
Deep learning has demonstrated remarkable accuracy analyzing images for cancer detection tasks in recent years. The accuracy that has been achieved rivals radiologists and is suitable for implementation as a clinical tool. However, a significant problem is that these models are black-box algorithms therefore they are intrinsically unexplainable. This creates a barrier for clinical implementation due to lack of trust and transparency that is a characteristic of black box algorithms. Additionally, recent regulations prevent the implementation of unexplainable models in clinical settings which further demonstrates a need for explainability. To mitigate these concerns, there have been recent studies that attempt to overcome these issues by modifying deep learning architectures or providing after-the-fact explanations. A review of the deep learning explanation literature focused on cancer detection using MR images is presented here. The gap between what clinicians deem explainable and what current methods provide is discussed and future suggestions to close this gap are provided.
1. Introduction
Deep learning has grown both in terms of research along with private and public sector application in recent years. A part of this growth is the application of deep learning algorithms to big data in the healthcare sector [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11] as depicted in Figure 1. These algorithms have demonstrated results suitable for clinical implementation but explanation remains a barrier for wide-spread clinical adoption.
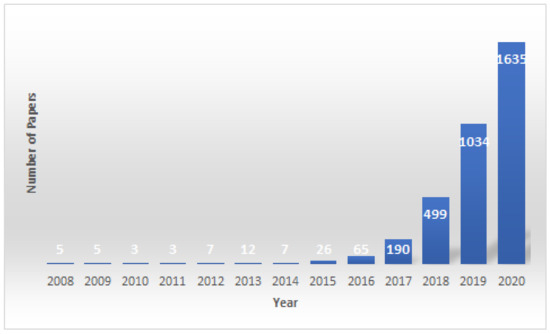
Figure 1.
This figure shows the number of published papers using deep learning models to predict cancer risk, classification, prediction and detection per year since 2008. The data were collected using keyword searches through PubMed.
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that has grown in recent years due to the advances in computational power and the access to large datasets. Deep learning has proven to be successful in a wide breadth of applications [12,13,14,15,16]. There are three main categories of deep learning algorithms which are supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning fits a non-linear function using features as input data and labels as output data where the labels, or outputs, are known when training the algorithm. Common supervised deep learning algorithms are convolutional neural networks and recurrent neural networks. These algorithms are commonly used for classification tasks such as classifying lesions as benign or malignant. Unsupervised learning on the other hand does not use labeled output data. It is looking for patterns in the input data distribution. Some examples of unsupervised deep learning are generative adversarial networks and autoencoders. These are used for tasks such as data compression and data augmentation. The final category is reinforcement learning. In reinforcement learning, a reward function is defined and the neural network optimizes its weights to maximize the reward function.
Deep neural networks consist of an input layer, output layer, and many hidden layers in the middle. Each layer consists of neurons which are inspired by how neurons in the brain process information. Each neuron has a weight that is updated using a technique called gradient descent during the training process. The weights of the network are optimized by minimizing a cost function. Nonlinearities are applied between layers to fit nonlinear functions from the input data to the output. Due to this, neural networks are able to model complex mappings. After training, the model is able to classify unseen data.
Deep learning has achieved high performance for numerous types of cancers. The authors of [17] demonstrated accuracy up to 98.42 for breast cancer detection. In [18], they found that they could detect lung cancer with up to 97.67 using deep transfer learning. In the fall of 2018, researchers at Seoul National University Hospital and College of Medicine developed a machine learning algorithm called Deep Learning based Automatic Detection (DLAD) to analyze chest radiographs and detect abnormal cell growth, such as potential cancers. In [19], the algorithm’s performance was compared to multiple physician’s detection abilities on the same images and outperformed 17 of 18 doctors. These results demonstrate the potential for using deep learning to aid medical practitioners. Despite this performance, adoption of these systems in clinical environments has been stunted due to lack of explainability.
Deep learning techniques are considered black boxes as depicted in Figure 2. Explainability attempts to mitigate the black box nature of these algorithms. Explainability is needed for a variety of reasons. First, there are legal and ethical requirements along with laws and regulations that are required for deep learning cancer detection systems to be implemented in a clinical setting. An example of a regulation is the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requiring organizations that use patient data for classifications and recommendations to provide on-demand explanations [20]. The inability to provide such explanations on demand may result in large penalties for the organizations involved. There are also monetary incentives associated with explainable deep learning models. Beyond ethical and legal issues, clinicians and patients need to be able to trust the classifications provided by these systems [21]. Explanation is also needed for trust and transparency [22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. Explanation methods attempts to show the reasoning behind the model’s classification therefore building a degree of trust between the system, clinician, and patient. This can reduce the number of misinformed results that would be a possible consequence of non-explainable systems. Finally, explainable deep learning systems will provide the clinician with additional usefulness such as localization and segmentation of the lesion location [29,30,31,32]. How explanability brings value to the end user is depicted in Figure 3.
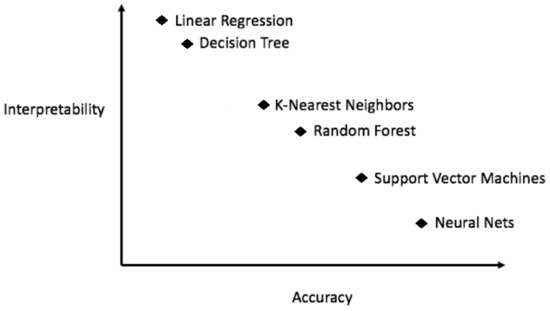
Figure 2.
In general, more accurate models are less explainable.
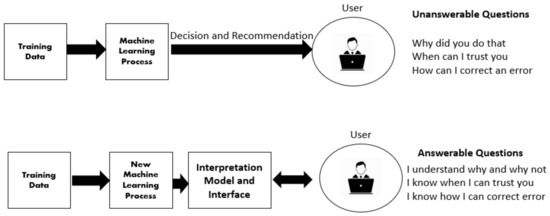
Figure 3.
How explanation methods provide value to the end user.
Explainable and interpretable are used interchangeably in parts of the literature [33] yet they are defined separately in others. This work will use the terms are used interchangeably. There is not an agreed upon definition of explainability. As Lipton mentioned, “the term explainability holds no agreed upon meaning, and yet machine learning conferences frequently publish papers which wield the term in a quasi-mathematical way”. This demonstrates the ambiguity of term and the need for a formal definition. That is outside the scope of this work but for the context of this paper, we adopt the [34] definition of explainability which is, “explainability is the degree to which a human can understand the cause of a decision”.
We conducted an extensive literature review by examining relevant papers from six major academic databases. A keyword based search was used to select papers, it consists of searching for index keywords based on common variations in literature of the terms “explainable”, “transparency”, “black box”, “understandable”, “comprehensible”, and “explainable” and its union with a set of terms related to deep learning cancer detection including “deep learning”, “machine learning” and “convolutional neural network”. The research was restricted to articles published between 2012 and 2020 with one exception published in 1991. The papers were skimmed and then filtered by quality and relevancy. More papers were then added by using a snowballing strategy that consists of using the reference list of the selected papers to identify additional papers.
The contributions of this review are three fold. First, this work will focus on explainability for cancer detection using MRI images. Second, we provide a thorough overview of the current approaches to measure explainability that are commonly used in the literature and why this is important for medical explainability. There is not an universally agreed upon metric for an explanation. This review will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of metrics commonly found in the literature. Third, this review will discuss papers related to what clinicians consider important for explanation systems. This highlights a gap between ML researchers who design the algorithms and clinicians who are the end users. This paper attempts to discuss direction for closing that gap.
This paper is organized in the following way. First, a general taxonomy of explanation approaches for deep learning cancer detection systems is described. Second, current measures for explanation quality are examined and analyzed. Third, we discuss explanation techniques applied to cancer detection deep learning models. Finally, it will conclude with a discussion with suggested future directions in section four and five respectively.
2. Background
Although the research volume is expanding rapidly around explainability [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62] a review focusing on image intepretability within the context of deep learning cancer detection systems is missing. Indeed, there are existing research studies of deep learning explainability for medical applications [63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74] in the literature as well as review articles. Notably, [75,76]. The survey of Tjoa and Guan reviews post-hoc explanation methods for medical applications. The review looks at medical explainability as a whole. The authors provide future directions such as including textual explanation and propose creating a authoritative body to oversee algorithmic explainability. In the review by [76], the authors provide a review of explainable deep learning models for medical imaging analysis. The authors discuss medical applications of brain, breast, retinal, skin, CT, and X-ray images. In contrast to the previously noted reviews, this review focuses solely on analyzing medical images for cancer detection while discussing the gap between clinicians and ML researchers.
2.1. Taxonomy
There are various proposed taxonomies to classify explanation methods [77,78,79]. Generally, these classification systems are task dependent therefore there is not an universally accepted taxonomy for explanation methods. This section will outline how explanation methods are grouped throughout this paper which is guided by the taxonomy by the authors of [78].
2.1.1. Local vs. Global
Local explanation refers to providing explanations for individual samples. This approach is useful when explanations for individual patients are of interest. An example of this is SHAP [80,81] which provides explanations for single classifications. On the other hand, global explanation refers to providing explanation for a group of samples or the entire model. This shows the overall feature importance for a group of patients. An example of global explanations are Global Model Explanation via Recursive Partitioning [82] and Garson’s Algorithm [83] for depicting feature importance.
2.1.2. Data Modality Specific vs. Data Modality Agnostic
Data modality specific refers to explanation methods that are only applicable for a certain data type. For example, some methods only work with MR images and some methods only work for tabular clinical records. An example of a method that only works for images is Grad-CAM [84] which does not apply to other data modalities such as textual or tabular data. These data modality specific approaches are usually coupled with model-specific explanation approaches. For example, some explanation methods use feature maps from convolution operations to calculate what information the model uses to make a prediction. Data modality agnostic refers to explanation methods that work for any data type. An example of this is LIME [85] which can provide explanations for image, tabular, and textual data. These are useful for clinical implementation due to the ability to handle a wide range of data used to make clinical decisions. These methods commonly use surrogate or perturbation based approaches to create a general approach for model explanation.
2.1.3. Ad-Hoc vs. Post-Hoc
For ad-hoc explanation methods, the model itself is designed to be intrinsically explainable. Common current approaches are limiting learned features to only explainable features or by altering the optimization procedure to focus on optimizing for explainability rather than accuracy. The goal of this approach is to design a deep learning model that is inherently explainable and opposes the notion that there is a trade off between accuracy and explainability. On the contrary, post-hoc explanation techniques provide explanations after the classification is made. These are more common in the literature due to ease of implementation. Some refer to these as diagnostic methods [86] due to their utility for diagnosing and their apparent limitations for providing a complete explanation for the end user. Examples of these are saliency maps [87,88], Grad-CAM [84], Respond-CAM [89], and SHAP [80] where the explanation is provided after-the-fact.
2.1.4. Model Agnostic vs. Model Specific
Model agnostic refers to explanation methods that are able to explain any model and are not restrained to a certain type (e.g., SHAP). A common approach for model-agnostic methods is to change the inputs and measure the corresponding change in output. Then to use this to determine what change in inputs produces the greatest change in outputs. Model specific explanation methods only work with a specific model. For example, Grad-CAM [84] produces feature visualizations for convolutional neural networks, but does not work with LSTMs. These methods often use certain aspects of model architecture, for example feature maps produced from graph convolutions.
2.1.5. Attribution vs. Non-Attribution
The majority of proposed explanation techniques are attribution based methods. Attribution methods attempt to calculate the inputs of the neural network that are the most important with regards to the network’s result. This can be broken further into two categories: perturbation based approaches and back-propagation based approaches. Perturbation based techniques estimate the most important features by removing one, calculating change in class score, and repeating for all features. It uses this to calculate the attribution of each feature. It then ranks feature importance by attribution. An example of this is SHAP. These are usually inefficient due to having to compute many iterations. Gradient-based methods conduct a similar procedure except with a single forward or backwards pass. Some of these methods provide only positive contributions (e.g., CAM) and some provide positive and negative contributions (e.g., DeepLIFT). In general, these methods produce results faster due to having to perform only one pass.
2.2. Measures for Explanations
There are various approaches for measuring the quality of an explanation which range from computing an intersection over union (IOU) score to conducting user studies. Measuring the quality of explanation is challenging because of the importance of the context the method is used for along with the non-triviality of defining what a good explanation is. For example, measuring explanation methods for cancer detection could have different criteria then explanation methods for insurance risk prediction. Therefore, in addition to testing explanation methods in a general way, it is important to consider the context of potential applications. This is especially important for cancer explanation methods due to high-risk nature of the predictions.
2.2.1. What Defines a High-Quality Explanation
The question what defines a high-quality explanation is an important first question to consider. There are studies that attempt to explore this question [90,91,92]. One question that is important is the time taken to understand the explanation. Ideally, the explanation is thorough enough to convey the necessary information yet concise enough that is to be understood in a timely manner. The authors of [91] explore this by asking what makes explanations explainable in the context of verification. The authors conduct an user study and identify what kind of increases in complexity have the greatest effect on the time it takes for humans to verify the rationale, and which seem relatively insensitive. Another factor to consider is the question who will be the end user of the algorithm. The end user of the deep learning system should guide the approach to evaluation. Designing explanation techniques for clinical settings require different explanations than designing explanation for robotics. A paper published in 2018 by [92] discusses the different roles involving explanation techniques and how the explanations differs depending on what role you are providing the explanation for. They show that an explanation for one role should be measured differently for other roles. This sounds trivial but is often ignored. For example, measuring explanations for doctors should have different criteria than measuring explanations for patients receiving the diagnosis or engineers designing the system. Consequentially, this suggests the need to test explanations on a variety of human subjects to evaluate for whom the explanations fail and for whom the explanation provides adequate information. For example, the explanation can be thorough and complete for a clinicians but fail for a patient when ideally it should address the needs of each end user. A limitation of the current literature is the lack of studies that verify explanation methods with a population of radiologists or doctors. To the best of our knowledge, there is not any studies that incorporate radiologists into the design process of deep learning explanation algorithms. The majority of human-studies involved general, non-specialized individuals recruited through a crowd-sourcing service such as Amazon Mechanical Turk [93]. The authors of [94] also highlight the importance of keeping the end-user in mind when defining what is explainable and how to measure it. It is also essential to have quantitative measures to be able to compare different methodologies quantitatively when qualitative measures fail. A paper published by the authors of [95] propose Remove and Retrain (ROAR) to quantitatively compute feature importance. ROAR ranks feature importance, removes these the features ranked as most important, and then retrains the model and measures the difference during testing. This method is widely used but there still lacks a standard procedure for quantitatively measuring explanation performance. For measuring qualitatively, Doshi-Velez and Kim discuss factors related to qualitative assessment. First, what are explanations composed of? For example, feature importance or examples from the training? It other words, what units are being used to provide an explanation. Second, what are the number of units that explanations are composed of? If the explanation finds similar training examples to provide an explanation, does it just provide the most relevant examples or all? Third, if there is only a select few examples how are these ordered and what determines that criteria? If they are ranked in terms of similarity how is similarity defined? Or if they are ranked in terms of feature importance, how do you measure feature importance? Fourth, how do you show the interaction among these units in a human-digestible way? Fifth, how do you quantitatively show the uncertainty in an explanation? While there is no silver bullet for measuring explanation quality, these are all important questions to consider when evaluating the quality of an explanation and choosing a metric to measure results.
2.2.2. Methods to Measure Explanation Quality
This next section will discuss approaches to measure explanation quality commonly used in the literature. These are broken into two types: human-based evaluation and proxy-based evaluation. Human-based studies design an experiment where participants are recruited and asked to fill out a questionnaire about different explanation methods. This data is then analyzed in an attempt to answer a question regarding the different explanation methods (e.g., which one is more concise). The participants are usually recruited using a crowd-sourcing service if non-specialized participants are acceptable. If specialized participants are needed, for example doctors, the authors usually recruit a cohort from local or regional organizations. Out of the papers reviewed for this survey 73 percent use proxy-based and 27 percent conduct human studies. This statistics highlights a need for more human-verified explanation techniques. This section will discuss human-based and proxy-based methods to measure explanation quality.
“Human-based” can be broken down into two more categories which are specific tasks or general tasks. For specific tasks, studies can be designed to evaluate specific applications. An example of this would be explaining predictions for ICU duration. The other category is when the application is more general or not known. This is when the desire is to test the explanation method in a general setting. An example of this is Grad-CAM++ [93], SHAP [80], or LIME [85] which all were tested with randomized human studies using Amazon Mechanical Turk. The authors produced heatmaps for 5 classes in the ImageNet testing set totaling 250 images. These maps, along with their corresponding original image, were shown to 13 human subjects and asked which explanation algorithm invoked more trust in the underlying model. They consider the algorithm with more votes the model with greater trustworthiness.
Sometimes designing and carrying out human studies is infeasible or inconvenient due to various reasons such as IRB, recruitment, or funding. There are also cases where human-based studies do not measure what is desired. In these studies a formal definition of explanation is used as a proxy for explanation quality. The non-triviality here is choosing what proxy is best to be used. Some examples are showing increased performance for a method that has been deemed explainable based on human studies or showing that method performs better with respect to certain regularizers. An example of this approach is Saliency Maps which measure explanation quality using a localization task on benchmark datasets.
3. Explanation Methods for Deep Learning Cancer Detection Models
This section is separated into two sub-sections. First, post-hoc explanation methods will be discussed. The second section will discuss ad-hoc methods. Ad-hoc methods aim to develop intrinsically explainable deep learning systems as opposed to providing after-the-fact explanations.
Explainability for deep learning models within a medical context is essential to create safe and responsible systems suitable for clinical implementation. Explainability attempts to alleviate risk and build trust [96,97]. There are numerous papers published each year regarding explainability and interpretability for healthcare [98]. This section will further discuss some of these works regarding image explanation methods for cancer detection.
3.1. Post-Hoc
A majority of deep learning cancer detection models utilize post-hoc methodologies due to their ease of implementation. Post-hoc methods can be used to analyze the learned features of the model and to diagnose overfitting. This provides a feedback loop for the researcher and allows them to improve the model. It also shows the discriminative areas of the image. This section will review recent studies that apply post-hoc explanation methods to breast cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer, brain cancer, and liver cancer.
The predecessor for post-hoc techniques such as Respond-CAM, Pyramid-CAM, Grad-CAM, Grad-CAM+, and Grad-CAM++ is class activation maps (CAM) which generates a heatmap using global average pooling. In [99] the method shows the region of the image used the identify the label by outputting the spatial average of the feature maps of each unit at the last layer. It was tested as weakly supervised segmentation on the ILSVRC dataset with a top 5 error rate of 37.1 percent which is only 3 percent away from the top score.
CAM is formally defined as the following. Let represent the activation of unit k in the last convolutional layer at spatial location . The result of performing global average pooling is = therefore for a given class, c, the input to the softmax, is where is the weight corresponding to class c for unit k. Essentially, indicates the importance of for class c. Finally the output of the softmax for class c, is given by By plugging into the class score, , we obtain
The authors define as the class activation map for class c, where each spatial element is given by
A further developed version of CAM is Grad-CAM. In [84], Grad-CAM calculates the gradients of the class score with respect to the activation of the feature maps which are globally average pooled over the width and height dimensions. This is followed by a weighted combination which is passed through a ReLU function. This works best with the final layer because of the larger receptive field compared to the beginning layers. It was evaluated using the ImageNet localization challenge and outperforms CAM with a top-5 error of 10.89 percent. It achieves an IoU score of 49.6 percent on the PASCAL VOC 2012 segmentation data set. They also used a human study and found Grad-CAM outperforms guided backpropagation by 16.79 percent.
In order to obtain the class-discriminative localization map Grad-CAM of width u and height v for any class c, we first compute the gradient of the score for class c, (before the softmax), with respect to feature map activations of a convolutional layer, i.e., . These gradients flowing back are global-average-pooled over the width and height dimensions (indexed by i and j respectively) to obtain the neuron importance weights :
During computation of while backpropagating gradients with respect to activations, the exact computation amounts to successive matrix products of the weight matrices and the gradient with respect to activation functions till the final convolution layer that the gradients are being propagated to. Hence, this weight represents a partial linearization of the deep network downstream from A, and captures the importance of feature map k for a target class c. We perform a weighted combination of forward activation maps, and follow it by a ReLU to obtain,
The authors of [29] propose a modified version of CAM called pyramid gradient-based class activation.they used PG-CAM a densely connected encoder decoder-based feature pyramid network (DC-FPN) as a backbone structure, and extracts a multi-scale Grad-CAM that captures hierarchical features of a tumor. Mathmatically, PG-CAM is defined as follows.
where is the unit of the feature map , is a GradCAM generated from the feature maps delivered from each scale p, and the PG-CAM aggregating the GradCAMs will consequently contain information on multiple scales of the feature pyramid.
Integrated gradients has became popular due to its ability to explain models that use different data modalities. This is in addition its ease of use, theoretical foundation, and computational efficiency. Formally, Integrated Gradients is defined as follows
where i is the feature, x is the input, is the baseline, and interpolation constant to perturb features by. Note that this integral is often approximated due to computational costs and numerical limits.
Occlusion is a simple to perform model agnostic approach which reveals the feature importance of a model. It can reveal if a model is overfitting and learning irrelevant features as in the case of adversarial examples. Adversarial examples are inputs designed to cause the model to make a false decision. In that case, the model misclassifies the image (say malignant as benign) despite the presence of discriminating feature occluding all features (pixels) one-by-one and running the forward pass each time can be computationally expensive and can take several hours per image. It is common to use patches of sizes such as 5 × 5, 10 × 10, or even larger depending on the size of the target features and computational resources available.
CAM and Grad-CAM calculate the change in class score based on features extracted by the model. These two methods then visualize the features that cause the largest change in class score. On the other hand, occlusion occludes part of the image and then calculates the change in class score using the occluded image. It repeats this for many patches of the image and the patch that produces the largest change in class score is deemed the most important. Both methods produce a heatmap highlighting the most discriminative areas of the image. Therefore, the largest difference between the two techniques is how the they compute the most discriminative area of the image. The disadvantage of occlusion is that it is computationally expensive and takes longer to compute than CAM or Grad-CAM. The advantage of Grad-CAM and CAM is that they can compute their results in one pass instead of many passes like occlusion techniques. The disadvantage of Grad-CAM and CAM is that they only take into account the feature maps therefore could produce misleading results whereas occlusion takes into account different patches of the image. A summary of these methods is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Post-Hoc explanation techniques for cancer classification.
3.1.1. Brain Cancer
The authors of [100] attempt to incorporate explainability into the model before training. The authors assess the advantages of implementing features to increase explainability early in the development process, by training a neural network to differentiate between MRI slices containing either a vestibular schwannoma, a glioblastoma, or no tumor. They report that after training to detect explainable features, the network highlights more explainable regions.
In [29] PG-CAM to Grad-CAM was compared and it was found that PG-CAM outperformed Grad-CAM by delivering a 23 percent higher localization accuracy for the validation set.
3.1.2. Liver Cancer
A CNN was developed to classify liver lesions by [101]. To interpret the network, the authors visualized the activations of the last convolution layer. The authors calculated a feature score for each feature by hindering the network to utilize that feature and observing the difference in class score. They tested if the network was able to discover explainable radiological features. The model obtained a PPV of 76.5 ± 2.2 in identifying the 1–4 correct radiological features for the 60 manually labeled test lesions.
3.1.3. Breast Cancer
Deep learning has achieved remarkable accuracy for the detection and segmentation of breast cancer [102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111]. Detection in Mammography using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks by the author of [112] employee deep convolutional neural networks to localize classifications and masses in mammogram images without training directly on the full images. The authors implement a VGGNet architecture and report an accuracy of 92.53. The network was train by using images cropped around a ROI and then tested on the original, unaltered images. The authors then apply Grad-CAM.
A Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) aims to minimize the tumor size before surgery. Predicting response to NAC could reduce toxicity and delays to effective intervention. The authors of [113] implement a CNN to predict response using DCE-MRI images and then produce Grad-CAM heatmaps for post-hoc explanation. They report accuracy ranging from 0.69 to 0.88.
3.1.4. Prostate Cancer
Deep learning has also shown great success for prostate cancer [114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126]. The authors of [127] implement a convolution feature extractor followed by a SVM classifier for the task of detecting prostate cancer. They report an AUC of 0.86 for T2W images and 0.93 for ADC images. After prediction the authors generate CAM heatmaps for the MRI images to show localization of prostate lesions.
The authors of [32] demonstrated the ability to localize prostate lesions in T2W transverse images using Grad-CAM. The authors used MRI images for classification as well as tabular data such as weight, height, and age from ProstateX dataset. Deep learning techniques were used for classification. After classification GradCAM, Saliency Maps, LIME and Deep-SHAP were used to provide post-hoc explanations. They reports results of an average error of 6.93 pixels. The authors also made the qualitative observation that different explanation methods highlight different aspects of the resulting classification.
3.1.5. Lung Cancer
The authors of [128] described the goal of their paper “To explain predictions of a deep residual convolutional network for characterization of lung nodule by analyzing heat maps.” The authors used occlusion to systematically block regions of a nodule and map drops in malignancy risk score to generate clinical attribution heatmaps on 103 nodules from Lung Image Database Consortium image collection and Image Database Resource Initiative (LIDC-IDRI) dataset, which were analyzed by a thoracic radiologist. They report an accuracy of 85 percent for classification and qualitatively access their explanation results.
The authors of [129] applied XAI visualization to gain an insight into the features learned by a DCNN trained to classify estrogen receptor status (ER+ vs. ER−) based on dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCEMRI) of the breast. The authors developed a network that utilized “transfer-trained dual-domain DCNN architecture derived from the AlexNet model trained on ImageNet data that received the spatial (across the volume) and dynamic (across the acquisition sequence) components of each DCE-MRI ROI as input”. The authors implemented integrated gradients as a post-hoc explanation technique. They observed that the CNN learned relevant features from the spatial and dynamic domains. They note there were differences in the contributing features from the two domains.
3.2. Ad-Hoc
Ad-Hoc explanation techniques modify the training procedure and/or network architecture to learn explainable features. An additional proposed approach to learn explainable features was the work by the authors of [130] using supervised iterative descent. The authors’ approach learns explainable features for image registration by incorporating a shared modality-agnostic feature space and using segmentations to derive a weak supervisory signal for registration. The authors report their experiments “demonstrate that these features can be plugged into conventional iterative optimizers and are more robust than state-of-the-art hand-crafted features for aligning MRI and CT images”. This is significant with respect to medical imaging because of the multi-modality aspect which is common to medical imaging.
The authors of [131] propose a two part explainable deep learning network. One part extracts features and predicts while the other part generates an explanation. The authors create a mathematical model to extract high-level explainable features. The explanation model reports information such as what are the most important features, what is their rank, and how does each one influence the prediction.
Capsule networks have been recently utilized due to the impression they are more explainable compared to CNN [132]. The authors of [133] state that convolutions neural networks struggle with explainability therefore they propose explainable capsules, or X-Caps. X-Caps utilize a capsule network architecture that is designed to be inherently explainable. The authors design to capsule network to learn an explainable feature space by encoding high-level visual attributes within the vectors of a capsule network to perform explainable image-based diagnosis. The authors report accuracy similar to that of unexplainable models demonstrating accuracy and explainability are not mutually exclusive. The authors define a routing sigmoid as follow.
where are the routing coefficients determined by the dynamic routing algorithm for child capsule i to parent capsule j and the initial logits, are the prior probabilities that the prediction vector for capsule i should be routed to parent capsule j.
Let the critical response maps for a given CT scan slice image x for each prediction c be computed via back-propagation from the last layer of the last explainable sequencing cell in the proposed SISC radiomic sequencer. The notation used in this study is based on the study done by the authors of [134] for consistency. The last layer in the explainable sequencing cell at the end of the proposed SISC radiomic sequencer contains nodes, equal to the number of possible predictions (i.e., benign and malignant). The output activations of this layer are followed by global average pooling and then a softmax output layer. So, to create the critical maps for each possible prediction, the back-propagation starts with the individual prediction nodes in the last layer to the input space. For a single layer l, The deconvoluted output response is given by,
where is the feature map and is the kernel of layer l. the symbol ∗ represents the convolution operator. Therefore, the critical response map , for a given prediction c is defined as,
where is the unpooling operation and is the convolution operation at the last layer with kernel replaced by zero except at the cth location corresponding to the prediction c.
The majority of ad-hoc explanation techniques attempt to learn an explainable feature space using modifications to traditional architectures that vary from modifying loss functions to modifying the procedure for computing convolutional features. Some papers argue the best approach is to move away from convolutional neural networks to capsule networks due to greater explainability with similar predictive performance though data is limited [133].
3.2.1. Brain Cancer
A capsule network trained to recognize explainable radionomic features was proposed by the authors of [132]. The explainability of capsule networks is studied. The authors’ results show that the radiomics features extracted by Capsule networks can not only distinguish between the tumor types, but also show considerable correlation with hand-crafted features, which are more acceptable and reliable from a physician’s point of view.
3.2.2. Lung Cancer
The authors of [135] proposed An explainable Deep Hierarchical Semantic Convolutional Neural Network for Lung Nodule Malignancy Classification in 2018. The proposed network provides two levels of output. One level contains the low-level, explainable features for radiologists and the second level provides a high-level malignancy prediction score. They incorporate both of these tasks in their loss function therefore optimizing the network parameters for both levels mentioned above. The authors use the LIDC dataset which contains annotated lung nodule characteristics. The network achieves a test AUC of 0.856. For the semantic, explainable features task they achieved mean accuracy of 0.908, 0.725, 0.719, 0.834 and 0.552; mean AUC score of 0.930, 0.776, 0.803, 0.850 and 0.568; mean sensitivity of 0.930, 0.758, 0.673, 0.855 and 0.552; and mean specificity of 0.763, 0.632, 0.796, 0.636 and 0.554 for calcification, margin, subtlety, texture, and sphericity, respectively.
Another approach is SISC: End-to-end explainable Discovery Radiomics-Driven Lung Cancer Prediction via Stacked explainable Sequencing Cells was proposed by the authors of [134]. They implement an end-to-end system that automatically discovers semantically meaningful radiomic features using radiomic sequencers. The radiomic sequencer being discovered possesses a deep architecture comprised of stacked explainable sequencing cells (SISC). The network produces an AUC score of 89.06.
3.2.3. Breast Cancer
DeepMiner was proposed by [136] in 2018. Their framework attempts to discover explainable representations and build explanations using these representations for medical purposes, specifically breast cancer. An advantage to this approach is there is no need to train on full medical reports. They attempt to analyze the individual units rather than train a network to output a medical report. Their network is composed of three phase. First, they crop patches of the mammogram image. They then train a network using these cropped patches. Second, they have human experts annotate the units from this network. Third, they generate explanations by ranking the annotated units. The utilize transfer learning and obtain a AUC for 0.838 for normal patches, 0.802 for benign patches, and 0.872 for malignant patches. They test the explanation quality by using the Greedy Matching Score to compare the generated explanations with the explanations in the ground truth resulting in a score of 0.627.
In general, ad-hoc techniques provide more advantageous explanations compared to post-hoc techniques due to their inherently explainable design. One can argue that this makes the explanations more trustworthy. The disadvantage of ad-hoc techniques is their accuracy and scalability. When altering deep learning architectures to be inherently explainable there is usually an amount of accuracy lost. Also, the scalability of ad-hoc methods comes into question. In general, there are claims of post-hoc techniques not being as trustworthy since they are attempting to explain inherently unexplainable models. However, they do not suffer from the accuracy and scalability problems the ad-hoc methods do. See Table 2 for an overview of both post-hoc and ad-hoc methods.

Table 2.
Explanation Techniques for Deep Learning Cancer Detection.
4. Discussion
There has been significant research progress with regards to explainable deep learning cancer detection systems. The majority of methods utilized in the literature are local, post-hoc methods that are usually model and data specific. Current research demonstrate a trajectory heading towards explainable deep learning for cancer diagnosis, but there is still work to be done to fully realize the implementation of these systems in a clinical setting.
When a methodology provides an obviously wrong explanation it is important to be able to probe more to find out what went wrong. There is little research around this area despite being important for clinical implementation. This would help alleviate misclassification errors and provide greater insight to the clinician. Being able to quantify uncertainity in explanations is important for clinicians as well. This would give the clinician a gauge for the amount of trust to have in an explanation. This would also help alleviate potential errors introduce by explanation techniques.
Since the end user of explainability approaches for cancer detection will be clinicians and their patients, it is essential to take into account what they consider to be explainable. This is an important aspect that is often ignored by explanation studies. Most algorithms are measured using quantitative methods such as log loss or human studies of non-clinicians recruited from a service such as Amazon Mechanical Turk. There is a need to incorporate clinicians into the design process of these algorithms and to evaluate the algorithms with the doctors that will be using them. There are studies that attempt to design clinical visualization development and evaluation with clinicians and researchers. The authors of [139] introduce Clinical-Vis which is an EHR visualization based prototype system for task-focused design evaluation of interactions between healthcare providers (HCPs) and EHRs. They design a study where they recruit 14 clinicians. They compare the clinicians interaction with their systems against a baseline system. They qualitatively analyzed the differences between systems by having the clinicians think out loud during the assigned tasks. The authors also conducted a survey after the task was complete and analyzed the surveys. The measured time taken to arrive at a decision, accuracy of decision, confidence in decision, and TLX scores which the authors define as “Self-reported mental demand, physical demand, effort level, hurriedness, success and discouragement on a scale of 0–10”. Overall, they found their system performed above baseline across all measures. The authors of [59] perform an iterative design of an explanation system for recurrent neural networks (RNN) including machine learning researchers and clinicians. They use feedback from clinicians while designing the algorithm. They evaluate it using a mixture of techniques including quantitative, qualitative, and case-studies. To the best of our knowledge, there are no studies such as this for explanation techniques. There is a study that interviews a cohort of clinicians to gain insight on what they consider to be explainable deep learning. The authors of [86] interviewed 10 clinicians belonging to two groups—Intensive Care Unit and Emergency Department. The goal of this study was to shed light on what clinicians look for in explainable machine learning and developing a metric to measure it. The authors interviewed each clinician for 45–60 min. They proposed the clinician’s notions of explainability to determine what each clinician understood by the term and what he/she expected from ML models in their specific clinical setting. They designed an hypothetical scenario regarding the use of an explainable deep learning system to gain insights into what the clinicians looked for in explainable systems. The authors found that the clinicians viewed explainability as a means of justifying their clinical decision-making (for instance, to patients and colleagues) in the context of the model’s prediction. The clinicians desired to understand the clinically relevant model features that align with current evidence-based medical practice. The implemented system/model needs to provide clinicians with information about the context within which the model operates and promote awareness of situations where the model may fall short (e.g., model did not use specific history or did not have information around certain aspect of a patient). Models that lacked accuracy were deemed suitable as long as an explanation of the prediction was provided. The authors state a quote that stood out was ”the variables that have derived the decision of the model” and mentioned it was brought up by 3 ICU, 1 ED clinicians which is also identified in. The authors report that the clinical thought process for acting on predictions of any assistive tool appears to consist of two primary steps following presentation of the model’s prediction: (i) understanding, and (ii) rationalizing the predictions. The clinicians stated they wanted to see both global and local explanations. Clinicians found finding similar training examples to be useful is certain applications such as diagnosis but not as much in other cases. The clinicians reported one of the most sought after features was a measure for uncertainty. ‘Patient trajectories that are influential in driving model predictions’ was reported to be an important aspect of model explanation. These studies provide direction for future algorithmic development as well as a call for more research regarding the clinical performance of current explanation techniques.
Future Directions
There are numerous works that propose novel explanation methods but little focus on what makes an explanation suitable for the context it will applied. This is essential for domains such as cancer diagnosis. Furthermore, more studies are needed to identify what clinicians deem explainable and use these insights as a measuring stick for explanation methods for deep learning cancer detection systems. Another important direction is using these insights to derive quantitative explanation metrics. The majority of metrics used to measure explanation quality are designed without clinicians involved. To create explanation techniques suitable for clinician integration is is necessary to measure them in a way guided by end-user criteria. Explanation techniques also can be useful to extract clinically relevant features. There are studies that use explanation techniques to localize lesions but these models do not extract information such as shape, volume, area, and other relevant characteristics. A future opportunity is to extract these features without computationally expensive segmentation. With this, clinicians do not need to extract these features manually. If explanation techniques are implemented into clinical settings, the system can automatically extract these characteristics for the clinicians thus aiding in the diagnosis process.
The common approach for providing an explanation for image classification is to produce a heatmap showing the most discriminative region. More work needs to be done to provide greater insight than using this direct approach. For example, it would provide more insight if explanation methods could should why a classification was not made and quantify the uncertainity of the explanation. Being able to reason for and against is also important to provide greater insight and explainability. More studies should be conducted on where current methods fail and why. This would provide the community more insight on how to create more robust explanation methods. It would also provide greater confidence the methods we currently have.
Currently, the majority of cancer detection studies utilize post-hoc techniques. As stated in [33,140] it is advantageous to develop intrinsically explainable (i.e., ad-hoc) deep learning models. Post-hoc explanation methods may be useful for diagnosing the deep network model but the insight gained is unsubstantial. A model suited for clinical implementation should be fully explainable with the predictive power of modern deep learning approaches. Post-hoc methods only explain where the network is looking which is not enough information for high stakes decision making. Post-hoc methods are fragile and easily manipulated [141,142] and can provide misleading results which hinders clinical implementation. Some approaches attempting ad-hoc models were discussed in the paper with results that show that intrinsically explainable models can achieve accuracy similar to that of unexplainable models. More research is needed to verify this and evaluate the clinical performance.
5. Conclusions
A review on explainability techniques for cancer detection using MRI images was presented. Different evaluation methods for these methods were discussed with their respective significance. In addition to this, what clinicians deem to be explainable was also discussed along with the gap between what current methods provide versus what clinicians want. The importance of designing explanation methods with this in mind was highlighted. A critical analysis and suggestions for future work were then presented to conclude and future efforts were suggested based on the current state of the literature.
In summary, there is a need to incorporate clinicians in the design process for these algorithms and a need to build intrinsically explainable deep learning algorithms for cancer detection. The majority of explanation techniques are designed for general use and do not incorporate context. This is important for clinical use cases due to the unique, high-risk environment. It is important to evaluate proposed methods alongside clinicians to determine the clinical strengths and weaknesses of the methods. This has the potential to help guide future efforts. Furthermore, there is a need to go beyond basic visualization of the discriminative regions. Some promising future directions include quantifying the explanation uncertainty, providing counter examples, and designing ad-hoc models that are intrinsically explainable.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors received no funding for this work.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- Kooi, T.; van Ginneken, B.; Karssemeijer, N.; den Heeten, A. Discriminating solitary cysts from soft tissue lesions in mammography using a pretrained deep convolutional neural network. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akselrod-Ballin, A.; Karlinsky, L.; Alpert, S.; Hasoul, S.; Ben-Ari, R.; Barkan, E. A Region Based Convolutional Network for Tumor Detection and Classification in Breast Mammography, in Deep Learning and Data Labeling for Medical Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Kano, T.; Koyasu, H.; Li, S.; Zhou, X.; Hara, T.; Matsuo, M.; Fujita, H. Automated assessment of breast tissue density in non-contrast 3D CT images without image segmentation based on a deep CNN. In Medical Imaging 2017: Computer-Aided Diagnosis; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10134. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Wu, T.; Li, J.; Zheng, B.; Ruan, L.; Shang, D.; Patel, B. SD-CNN: A shallow-deep CNN for improved breast cancer diagnosis. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2018, 70, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Fan, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, L. Discriminating between benign and malignant breast tumors using 3D convolutional neural network in dynamic contrast enhanced-MR images. In Medical Imaging 2017: Imaging Informatics for Healthcare, Research, and Applications; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10138. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, A.S.; Marcon, M.; Ghafoor, S.; Wurnig, M.C.; Frauenfelder, T.; Boss, A. Deep Learning in Mammography: Diagnostic Accuracy of a Multipurpose Image Analysis Software in the Detection of Breast Cancer. Investig. Radiol. 2017, 52, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Zhi, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y. Artificial intelligence in healthcare past, present and future. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, T.-C.; Huang, Y.-S.; Chen, R.-T.; Huang, C.-S.; Chang, R.-F. Tumor Detection in Automated Breast Ultrasound Using 3-D CNN and Prioritized Candidate Aggregation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langlotz, C.P.; Allen, B.; Erickson, B.J.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Bigelow, K.; Flanders, T.S.C.A.E.; Lungren, M.P.; Mendelson, D.S.; Rudie, J.D.; Wang, G.; et al. A Roadmap for Foundational Research on Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging. Radiology 2019, 291, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhou, B.; Chen, D. Convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection or diagnosis in medical image analysis: An overview. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 6536–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooi, T.; Litjens, G.; van Ginneken, B.; Gubern-Mérida, A.; Sánchez, C.I.; Mann, R.; den Heeten, A.; Karssemeijer, N. Large scale deep learning for computer aided detection of mammographic lesions. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 35, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsisi, M.; Tran, M.-Q.; Mahmoud, K.; Lehtonen, M.; Darwish, M.M.F. Deep Learning-Based Industry 4.0 and Internet of Things towards Effective Energy Management for Smart Buildings. Sensors 2021, 21, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 8689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zintgraf, L.M.; Cohen, T.S.; Adel, T.; Welling, M. Visualizing deep neural network decisions: Prediction difference analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Elsisi, M.; Mahmoud, K.; Lehtonen, M.; Darwish, M.M.F. Reliable Industry 4.0 Based on Machine Learning and IoT for Analyzing, Monitoring, and Securing Smart Meters. Sensors 2021, 21, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.N.; Mahmoud, K.; Lehtonen, M.; Darwish, M.M.F. Promising MPPT Methods Combining Metaheuristic, Fuzzy-Logic and ANN Techniques for Grid-Connected Photovoltaic. Sensors 2021, 21, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Islam, N.; Jan, Z.; Din, I.U.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. A novel deep learning based framework for the detection and classification of breast cancer using transfer learning. Pattern Recognition. Letters 2019, 125, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shakeel, P.M.; Burhanuddin, M.A. Mohamad Ishak Desa, Lung cancer detection from CT image using improved profuse clustering and deep learning instantaneously trained neural networks. Measurement 2019, 145, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.G.; Park, S.; Hwang, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Jin, K.N.; Lim, K.Y.; Vu, T.H.; Sohn, J.H.; Hwang, S.; Goo, J.M.; et al. Development and Validation of Deep Learning-based Automatic Detection Algorithm for Malignant Pulmonary Nodules on Chest Radiographs. Radiology 2019, 290, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoofnagle, C.J.; Sloot, B.V.; Borgesius, F.Z. The European Union general data protection regulation: What it is and what it means. Inf. Commun. Technol. Law 2019, 28, 65–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, A.; Langs, G.; Denk, H.; Zatloukal, K.; Müller, H. Causability and explainability of artificial intelligence in medicine. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2019, 9, e1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.; Wu, S.; Zaldivar, A.; Barnes, P.; Vasserman, L.; Hutchinson, B.; Spitzer, E.; Raji, I.D.; Gebru, T. Model cards for model reporting. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.03993. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Rodriguez, V.; Grossman Liu, L.V.; Mitchell, E.G.; Averitt, A.; Bear Don’t Walk, O.; Bhave, S.; Sun, T.; Thangaraj, P. Columbia DBMI CMS AI Challenge Team. Engendering Trust and Usability in Clinical Prediction of Unplanned Admissions: The CLinically Explainable Actionable Risk (CLEAR) Model. In Proceedings of the Conference on Machine Learning for Health (MLHC), Stanford, CA, USA, 16–18 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Solar-Lezama, A.; Singh, R. Interpreting neural network judgments via minimal, stable, and symbolic corrections. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems NIPS2018, Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 4879–4890. [Google Scholar]
- Nolan, M.E.; Cartin-Ceba, R.; Moreno-Franco, P.; Pickering, B.; Herasevich, V. A Multisite Survey Study of EMR Review Habits, Information Needs, and Display Preferences among Medical ICU Clinicians Evaluating New Patients. Appl. Clin. Inform. 2017, 8, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, I.; Noack, A.; Guzman-Nateras, L.; Dou, D.; Li, B.; Huan, J. NormLime: A New Feature Importance Metric for Explaining Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.04200. [Google Scholar]
- Hegselmann, S.; Volkert, T.; Ohlenburg, H.; Gottschalk, A.; Dugas, M.; Ertmer, C. An Evaluation of the Doctor-explainability of Generalized Additive Models with Interactions. In Proceedings of the 5th Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, PMLR, Vienna, Austria, 7–8 August 2020; Volume 126, pp. 46–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kowsari, K.; Jafari Meimandi, K.; Heidarysafa, M.; Mendu, S.; Barnes, L.; Brown, D. Text Classification Algorithms: A Survey. Information 2019, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Park, C.; Yoon, S. Robust Tumor Localization with Pyramid Grad-CAM. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.11393. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, Y.; Lee, H.H.; Park, C.; Tama, B.A.; Kim, J.S.; Cheung, D.Y.; Chung, W.C.; Cho, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-M.; Choi, M.-G.; et al. An Improved Classification and Localization Approach to Small Bowel Capsule Endoscopy Using Convolutional Neural Network. Dig. Endosc. Off. J. Jpn. Gastroenterol. Endosc. Soc. 2021, 33, 598–607. [Google Scholar]
- Sumeet ShindeTanay ChouguleJitender SainiMadhura Ingalhalika. HR-CAM: Precise Localization of Pathology Using Multi-Level Learning in CNNs. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. In Proceedings of the MICCAI 2019, 22nd International Conference, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; Part IV. pp. 298–306. [Google Scholar]
- Gulum, M.A.; Trombley, C.M.; Kantardzic, M. Multiple Explanations Improve Deep Learning Transparency for Prostate Lesion Detection. In Proceedings of the DMAH 2020, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 31 August–4 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zachary, C.L. The mythos of model interpretability. Commun. ACM 2018, 61, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tim, M. Explanation in Artificial Intelligence: Insights from the Social Sciences, arXiv e-prints, Computer Science—Artificial Intelligence. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.07269. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, M.; Chen, E.; He, J.; Kim, B.; Gershman, S.; Doshi-Velez, F. How do Humans Understand Explanations from Machine Learning Systems? An Evaluation of the Human-explainability of Explanation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1902.00006. [Google Scholar]
- Hicks, S.; Riegler, M.; Pogorelov, K.; Anonsen, K.V.; de Lange, T.; Johansen, D.; Jeppsson, M.; Randel, K.R.; Eskeland, S.L.; Halvorsen, P.; et al. Dissecting Deep Neural Networks for Better Medical Image Classification and Classification Understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE 31st International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Karlstad, Sweden, 18–21 June 2018; pp. 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Beck, M.W.; Winkler, D.A.; Huang, B.; Sib, A.W.; Goyal, H. Opening the black box of neural networks: Methods for interpreting neural network models in clinical applications. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, U.; Ravikumar, P.; Moura, J.M.F. Building Human-Machine Trust via Interpretability. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 9919–9920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ravi, S.; Singh, V. Adaptive Activation Thresholding: Dynamic Routing Type Behavior for Interpretability in Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–3 November 2019; pp. 4937–4946. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Bau, D.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Interpreting Deep Visual Representations via Network Dissection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 2131–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakab, T.; Gupta, A.; Bilen, H.; Vedaldi, A. Self-Supervised Learning of Interpretable Keypoints From Unlabelled Videos. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–18 June 2020; pp. 8784–8794. [Google Scholar]
- Donglai, W.; Bolei, Z.; Antonio, T.; William, F. Understanding Intra-Class Knowledge Inside CNN. Computer Science—Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1507.02379. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Creager, E.; Goldenberg, A.; Duvenaud, D. Explaining Image Classifiers by Counterfactual Generation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations ICLR, 2019, Ernest N. Morial Convention Center, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Song, L. Learn to Explain Efficiently via Neural Logic Inductive Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1910.02481. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.J.; Augustin, M.; Fritz, M.; Schiele, B. Towards Reverse-Engineering Black-Box Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the ICLR: 2018, Vancouver Convention Center, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T. Gaining Free or Low-Cost Transparency with explainable Partial Substitute. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1802.04346. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Wattenberg, M.; Gilmer, J.; Cai, C.J.; Wexler, J.; Viégas, F.B.; Sayres, R. Explainability Beyond Feature Attribution: Quantitative Testing with Concept Activation Vectors (TCAV). In Proceedings of the ICML, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Song, L.; Wainwright, M.; Jordan, M. Learning to Explain: An Information-Theoretic Perspective on Model explanation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.07814. [Google Scholar]
- Singla, S.; Wallace, E.; Feng, S.; Feizi, S. Understanding Impacts of High-Order Loss Approximations and Features in Deep Learning explanation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.00407. [Google Scholar]
- Schwab, P.; Karlen, W. CXPlain: Causal Explanations for Model explanation under Uncertainty. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.12336. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Huang, S.; Tao, Y.; Xing, X.; Lin, L. Explaining Deep Learning Models-A Bayesian Non-parametric Approach. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.03422. [Google Scholar]
- Lage, I.; Ross, A.; Gershman, S.J.; Kim, B.; Doshi-Velez, F. Human-in-the-Loop explainability Prior. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.11571. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Melis, D.; Jaakkola, T. Towards Robust explainability with Self-Explaining Neural Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.07538. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Li, O.; Barnett, A.; Su, J.; Rudin, C. This Looks Like That: Deep Learning for Explainable Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the NeurIPS: 2019, Vancouver Convention Center, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shrikumar, A.; Greenside, P.; Kundaje, A. Learning Important Features Through Propagating Activation Differences. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.02685. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, S.J.; Hanser, T.; Howlin, B.; Krause, P.; Vessey, J.D. Feature combination networks for the explanation of statistical machine learning models: Application to Ames mutagenicity. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elish, M.C. The Stakes of Uncertainty: Developing and Integrating Machine Learning in Clinical Care. In Proceedings of the 2018 EPIC Proceedings, Oxford, UK, 7 July 2018; University of Oxford–Oxford Internet Institute: Oxford, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.M.; Teredesai, E.C. Interpretable Machine Learning in Healthcare. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI), New York, NY, USA, 4–7 June 2018; p. 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.C.; Choi, M.J.; Kim, J.T.; Choi, E.; Kim, Y.B.; Kwon, S.; Sun, J.; Choo, J. RetainVis: Visual Analytics with explainable and Interactive Recurrent Neural Networks on Electronic Medical Records. Proc. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2019, 25, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, R.C.; Vedaldi, A. Explainable explanations of black boxes by meaningful perturbation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 27–29 October 2017; pp. 3449–3457. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, A.; Montavon, G.; Lapuschkin, S.; Muller, K.; Samek, W. Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation for Neural Networks with Local Renormalization Layers. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning (ICANN 2016), Barcelona, Spain, 6–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Montavon, G.; Bach, S.; Binder, A.; Samek, W.; Müller, K. Explaining nonlinear classification decisions with deep Taylor decomposition. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 65, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshawi, R.; Al-Mallah, M.H.; Sakr, S. On the explainability of machine learning-based model for predicting hypertension. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, W.; Oakden-Rayner, L.; Gustavo, C.; Andrew, P.B.; Lyle, J.P. Producing radiologist-quality reports for explainable artificial intelligence. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.00340. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, X.A.; Gao, G. Outlining the Design Space of Explainable Intelligent Systems for Medical Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the ACM IUI 2019, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 20 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.; Zuo, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Yin, M.; Lu, K. Interpretable Classification from Skin Cancer Histology Slides Using Deep Learning: A Retrospective Multicenter Study. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.06156. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Roa, A.; Arevalo, J.; Madabhushi, A.; González, F. A Deep Learning Architecture for Image Representation, Visual explainability and Automated Basal-Cell Carcinoma Cancer Detection. In Proceedings of the MICCAI International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Nagoya, Japan, 22–26 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Weber, C.; Grossman, R.; Khan, A.A. Evaluating and interpreting caption prediction for histopathology images. In Proceedings of the 5th Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, in PMLR, Online Metting, 7–8 August 2020; Volume 126, pp. 418–435. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.; Kim, Y.; Mallavarapu, T.; Oh, J.H.; Kang, M. Explainable deep neural network for cancer survival analysis by integrating genomic and clinical data. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hussaini, I.; Xiao, C.; Westover, M.B.; Sun, J. SLEEPER: Interpretable Sleep staging via Prototypes from Expert Rules. In Proceedings of the 4th Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, in PMLR, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 9–10 August 2019; Volume 106, pp. 721–739. [Google Scholar]
- Essemlali, A.; St-Onge, E.; Descoteaux, M.; Jodoin, P. Understanding Alzheimer disease’s structural connectivity through explainable AI. In Proceedings of the Third Conference on Medical Imaging with Deep Learning, PMLR, Montreal, QC, Canada, 6–8 July 2020; Volume 121, pp. 217–229. [Google Scholar]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cao, R.; Zhu, D. Vispi: Automatic Visual Perception and explanation of Chest X-rays. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.05190. [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu, I.; Cordero-Grande, L.; Edwards, A.; Hajnal, J.; Modat, M.; Deprez, M. Interpretable Convolutional Neural Networks for Preterm Birth Classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.00071. [Google Scholar]
- Tjoa, E.; Guan, C. A Survey on Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Toward Medical XAI. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sengupta, S.; Lakshminarayanan, V. Explainable Deep Learning Models in Medical Image Analysis. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, A.B.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Ser, J.D.; Bennetot, A.; Tabik, S.; Barbado, A.; Garcia, S.; Gil-Lopez, S.; Molina, D.; Benjamins, R.; et al. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, Taxonomies, Opportunities and Challenges toward Responsible AI. Inf. Fusion 2020, 58, 82–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Murdoch, W.J.; Yu, B. Hierarchical explanations for neural network predictions. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1806.05337. [Google Scholar]
- Adadi, A.; Berrada, M. Peeking inside the black-box: A survey on Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI). IEEE Access 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A unified approach to interpreting model classifications. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’17), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa, I.P.; Rebuzzi Vellasco, M.B.; da Silva, E.C. Local explainable Model-Agnostic Explanations for Classification of Lymph Node Metastases. Sensors 2019, 19, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Rangarajan, A.; Ranka, S. Global Model Interpretation Via Recursive Partitioning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 20th International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 16th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 4th International Conference on Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), Exeter, UK, 28–30 June 2018; pp. 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garson, G.D. Interpreting neural network connection weights. Artif. Intell. Expert 1991, 6, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Cogswell, M.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2019, 128, 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. Why should i trust you? Explaining the classifications of any classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Tonekaboni, S.; Joshi, S.; McCradden, M.D.; Goldenberg, A. What Clinicians Want: Contextualizing Explainable Machine Learning for Clinical End Use. In Proceedings of the 4th Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, Online Metting, 7–8 August 2020; Volume 106, pp. 359–380. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Deep inside convolutional networks: Visualising image classification models and saliency maps. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6034. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Seo, J.; Jeon, S.; Koo, J.; Choe, J.; Jeon, T. Why are Saliency Maps Noisy? Cause of and Solution to Noisy Saliency Maps. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4149–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhou, B.; Wang, K.; Jiang, R.; Xu, M. Respond-CAM: Analyzing Deep Models for 3D Imaging Data by Visualizations; Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI: Granada, Spain, 2018; pp. 485–492. [Google Scholar]
- Doshi-Velez, F.; Been, K. Towards A Rigorous Science of explainable Machine Learning. Machine Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.08608. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, B.; Silva, M.S.; Hardie, R.; Kueterman, N.K.; Ali, R.A. Understanding Deep Neural Network Predictions for Medical Imaging Applications. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.09621. [Google Scholar]
- Tomsett, R.J.; Braines, D.; Harborne, D.; Preece, A.; Chakraborty, S. Interpretable to Whom? A Role-based Model for Analyzing Interpretable Machine Learning Systems. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.07552. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhay, A.; Sarkar, A.; Howlader, P.; Balasubramanian, V.N. Grad-CAM++: Generalized Gradient-Based Visual Explanations for Deep Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preece, A.D.; Harborne, D.; Braines, D.; Tomsett, R.; Chakraborty, S. Stakeholders in Explainable AI. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.00184. [Google Scholar]
- Hooker, S.; Erhan, D.; Kindermans, P.; Kim, B. A Benchmark for explainability Methods in Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the NeurIPS, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cassel, C.K.; Jameton, A.L. Dementia in the elderly: An analysis of medical responsibility. Ann. Intern. Med. 1981, 94, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croskerry, P.; Cosby, K.; Graber, M.L.; Singh, H. Diagnosis: Interpreting the Shadows; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; 386p, ISBN 9781409432333. [Google Scholar]
- Kallianos, K.; Mongan, J.; Antani, S.; Henry, T.; Taylor, A.; Abuya, J.; Kohli, M. How far have we come? Artificial intelligence for chest radiograph interpretation. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Learning Deep Features for Discriminative Localization. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 Jun–1 July 2016; pp. 2921–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windisch, P.; Weber, P.; Fürweger, C.; Ehret, F.; Kufeld, M.; Zwahlen, D.; Muacevic, A. Implementation of model explainability for a basic brain tumor detection using convolutional neural networks on MRI slices. Neuroradiology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Hamm, C.A.; Savic, L.J.; Ferrante, M.; Schobert, I.; Schlachter, T.; Lin, M.; Weinreb, J.C.; Duncan, J.S.; Chapiro, J.; et al. Deep learning for liver tumor diagnosis part II: Convolutional neural network explanation using radiologic imaging features. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 3348–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giger, M.L.; Karssemeijer, N.; Schnabel, J.A. Breast image analysis for risk assessment, detection, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 15, 327–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samala, R.K.; Chan, H.P.; Hadjiiski, L.M.; Cha, K.; Helvie, M.A. Deep-learning convolution neural network for computer-aided detection of microcalcifications in digital breast tomosynthesis. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2016: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, San Diego, CA, USA, 27 February–3 March 2016; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9785, p. 97850Y. [Google Scholar]
- Posada, J.G.; Zapata, D.M.; Montoya, O.L.Q. Detection and Diagnosis of Breast Tumors using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the XVII Latin American Conference on Automatic Control, Medellín, Colombia, 13–15 October 2016; pp. 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Dhungel, N.; Carneiro, G.; Bradley, A.P. The Automated Learning of Deep Features for Breast Mass Classification from Mammograms. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Proceedings of the MICCAI 2016 19th International Conference, Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016; Part I; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samala, R.K.; Chan, H.-P.; Hadjiiski, L.; Helvie, M.A.; Richter, C.D.; Cha, K.H. Breast Cancer Diagnosis in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Effects of Training Sample Size on Multi-Stage Transfer Learning Using Deep Neural Nets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samala, R.K.; Chan, H.P.; Hadjiiski, L.; Helvie, M.A.; Wei, J.; Cha, K. Mass detection in digital breast tomosynthesis: Deep convolutional neural network with transfer learning from mammography. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Zheng, H.; Wang, S. A Radiomics Approach with CNN for Shear-wave Elastography Breast Tumor Classification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wu, N.; Phang, J.; Park, J.; Liu, K.; Tyagi, S.; Heacock, L.; Kim, S.G.; Moy, L.; Cho, K.; et al. An explainable classifier for high-resolution breast cancer screening images utilizing weakly supervised localization. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.07613. [Google Scholar]
- Saffari, N.; Rashwan, H.A.; Abdel-Nasser, M.; Kumar Singh, V.; Arenas, M.; Mangina, E.; Herrera, B.; Puig, D. Fully Automated Breast Density Segmentation and Classification Using Deep Learning. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Abdel-Nasser, M.; Akram, F.; Rashwan, H.A.; Sarker, M.M.K.; Pandey, N.; Romani, S.; Puig, D. Breast Tumor Segmentation in Ultrasound Images Using Contextual-Information-Aware Deep Adversarial Learning Framework. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 162, 113870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, J.; Bu, Q.; Liu, F.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Y.; Lv, Y. Breast Mass Detection in Digital Mammogram Based on Gestalt Psychology. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 4015613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, R.; Chin, C.; Karcich, J.; Liu, M.Z.; Chang, P.; Mutasa, S.; Van Sant, E.P.; Wynn, R.T.; Connolly, E.; Jambawalikar, S. Prior to Initiation of Chemotherapy, Can We Predict Breast Tumor Response? Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks Approach Using a Breast MRI Tumor Dataset. J. Digit Imaging 2019, 32, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Shinde, A.; Liu, A.; Glaser, S.; Lyou, Y.; Yuh, B.; Wong, J.; Amini, A. Machine Learning—Based explanation and Visualization of Nonlinear Interactions in Prostate Cancer Survival. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2020, 4, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, X.; Hu, S.; Li, X.; Zou, Q.; Li, Y. A transfer learning approach for classification of clinical significant prostate cancers from mpMRI scans. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2017: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Orlando, FL, USA, 11–16 February 2017; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10134, p. 101344F. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Li, J.; Sarma, K.V.; Ho, K.C.; Shen, S.; Knudsen, B.S.; Gertych, A.; Arnold, C.W. Path R-CNN for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Gleason Grading of Histological Images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.D.; Yan, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, M.; Hu, B.; Yang, G. Computer-aided diagnosis of prostate cancer using a deep convolutional neural network from multiparametric MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 48, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Cheng, D.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Cheng, K.T. Automated Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer in mp-MRI Images Based on an End-to-End Deep Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishioka, J.; Matsuoka, Y.; Uehara, S.; Yasuda, Y.; Kijima, T.; Yoshida, S.; Yokoyama, M.; Saito, K.; Kihara, K.; Numao, N.; et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of prostate cancer on magnetic resonance imaging using a convolutional neural network algorithm. BJU Int. 2018, 122, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, S.A.; Bonekamp, D.; Schlemmer, H.; Yaqubi, K.; Hohenfellner, M.; Hadaschik, B.; Radtke, J.; Maier-Hein, K. Adversarial Networks for the Detection of Aggressive Prostate Cancer. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.08014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Min, H.L.; Wang, L.; Cheng, K.T. Co-trained convolutional neural networks for automated detection of prostate cancer in multi-parametric MRI. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.K.; Hewitt, S.M. Nuclear Architecture Analysis of Prostate Cancer via Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18526–18533. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Weinreb, J.; Han, J.; Li, Q.; Kong, X.; Yan, Y.; Ke, Z.; Luo, B.; Liu, T.; et al. Searching for prostate cancer by fully automated magnetic resonance imaging classification: Deep learning versus non-deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zheng, H.; Feng, Y.; Li, W. Prostate Cancer Diagnosis using Deep Learning with 3D Multiparametric MRI. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2017: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Orlando, FL, USA, 11–16 February 2017; Volume 10134, p. 1013428. [Google Scholar]
- Le, M.H.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Cheng, K.T.; Yang, X. Automated diagnosis of prostate cancer in multi-parametric MRI based on multimodal convolutional neural networks. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 6497–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akatsuka, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sekine, T.; Numata, Y.; Morikawa, H.; Tsutsumi, K.; Yanagi, M.; Endo, Y.; Takeda, H.; Hayashi, T.; et al. Illuminating Clues of Cancer Buried in Prostate MR Image: Deep Learning and Expert Approaches. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Le, H.M.; Chen, J.; Cheng, K.T.T.; Wang, L. Joint Detection and Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer in Multi-Parametric MRI Based on Multimodal Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, 20th International Conference, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–13 September 2017; pp. 426–434. [Google Scholar]
- Venugopal, V.K.; Vaidhya, K.; Murugavel, M.; Chunduru, A.; Mahajan, V.; Vaidya, S.; Mahra, D.; Rangasai, A.; Mahajan, H. Unboxing AI-Radiological Insights Into a Deep Neural Network for Lung Nodule Characterization. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasopoulos, Z.; Samala, R.K.; Chan, H.P.; Hadjiiski, L.; Paramagul, C.; Helvie, M.A.; Neal, C. H Explainable AI for medical imaging: Deep-learning CNN ensemble for classification of estrogen receptor status from breast MRI. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2020: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Oxford, UK, 20–21 January 2020; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11314, p. 113140Z. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blendowski, M.; Heinrich, M.P. Learning explainable multi-modal features for alignment with supervised iterative descent. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Medical Imaging with Deep Learning, in PMLR, London, UK, 8–10 July 2019; Volume 102, pp. 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Pintelas, E.; Liaskos, M.; Livieris, I.E.; Kotsiantis, S.; Pintelas, P. Explainable Machine Learning Framework for Image Classification Problems: Case Study on Glioma Cancer Prediction. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, P.; Plataniotis, K.N.; Mohammadi, A. Capsule Networks’ explainability for Brain Tumor Classification Via Radiomics Analyses. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 3816–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaLonde, R.; Torigian, D.; Bagci, U. Encoding Visual Attributes in Capsules for Explainable Medical Diagnoses. In Proceedings of the MICCAI: 2020, Online, 4–8 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sankar, V.; Kumar, D.; David, A.C.; Taylor, G.W.; Wong, A. SISC: End-to-End explainable Discovery Radiomics-Driven Lung Cancer Prediction via Stacked explainable Sequencing Cells. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 145444–145454. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.; Han, S.; Aberle, D.; Bui, A.; Hsu, W. An Interpretable Deep Hierarchical Semantic Convolutional Neural Network for Lung Nodule Malignancy Classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 128, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, B.; Peck, D.; Hsieh, S.; Dialani, V.; Lester, W. Mackey and Genevieve Patterson DeepMiner: Discovering explainable Representations for Mammogram Classification and Explanation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.12323. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, P.; Shu, C.; Goubran, R. Abnormality Detection in Mammography using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Rome, Italy, 11–13 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, S.H.; Cheng, M.; Tao, Y.B.; Wang, Y.F.; Juengpanich, S.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Jiang, Y.K.; Yan, Y.Y.; Lu, W.; Lue, J.M.; et al. Deep Learning for Accurate Diagnosis of Liver Tumor Based on Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Clinical Data. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, M.; Pushkarna, M.; Wexler, J.; Johnson, J.; Varghese, P. ClinicalVis: Supporting Clinical Task-Focused Design Evaluation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.05798. [Google Scholar]
- Rudin, C. Please Stop Explaining Black Box Models for High Stakes Decisions. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.10154. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, N.; Gaw, N.; Singh, P.; Chang, K.; Aggarwal, M.; Chen, B.; Hoebel, K.; Gupta, S.; Patel, J.; Gidwani, M.; et al. Assessing the (Un)Trustworthiness of Saliency Maps for Localizing Abnormalities in Medical Imaging. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.02766. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Shen, H.; Ji, S.; Luo, X.; Wang, T. Interpretable Deep Learning under Fire. In Proceedings of the 29th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 20), Boston, MA, USA, 12–14 August 2020; pp. 1659–1676. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).