Abstract
Respiration and heartbeat are basic indicators of the physiological state of human beings. Frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) radar can sense micro-displacement in the human body surface without contact, and is used for vital-sign (respiration and heartbeat) monitoring. For the extraction of vital-sign, it is essential to select the target range containing vital-sign information. In this paper, we exploit the coherency of phase in different range-bins of FMCW radar to effectively select the range-bins that contain accurate signals for remote monitoring of human respiration and heartbeat. To quantify coherency, the spatial phase coherency (SPC) index is introduced. The experimental results show that the SPC can select a range-bin containing more accurate vital-sign signals than conventional methods. This result demonstrates that the proposed method is accurate for monitoring of vital signs by using FMCW radar.
1. Introduction
Respiration and heartbeat can provide the basic physiological state of human beings, and can be used as healthcare indicators or in clinical diagnosis [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Traditionally, stretch sensors [7], pneumotachographs [6,8], photoplethysmographs [9,10], and electrocardiographs [11,12] have been used to measure respiration and heartbeat. However, traditional monitoring sensors that are attached to the body can cause discomfort and restrict behavior. Radar can detect micro-displacement in the human body surface without contact [13,14,15], and this ability has been exploited for contactless monitoring of vital signs (VSs). Radar can monitor VSs continuously, and without contact, so the monitoring system has been applied in various applications such as medical care surveillance for severe burns or infectious diseases [16,17], driver assistance [18,19], sleep monitoring for sudden infant death syndrome, apnea detection [20,21,22], and homecare for the elderly [23,24,25]. In particular, frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) radar, which has ranging capability, can spatially separate VSs from clutters [26,27]. Additionally, FMCW radar uses a millimeter-wave band, and therefore has the advantages of small sizes and low power consumption. Therefore, FMCW radar has been widely used for contactless monitoring of VSs [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36].
Methods to extract VSs from the FMCW radar signal are generally divided into spectral analysis and range-bin selection [37,38,39,40,41]. The discrete Fourier transform (DFT) is mostly used for spectral analysis, which is a range analysis of the FMCW signal. The results of DFT at each range (or spectral) bin, namely magnitude and phase, contain information about displacement of the target. Information pertaining to respiration and heartbeat exists in specific range-bins, such as range-bins near the abdomen or thorax for respiration [39,42], and range-bins near the neck for heartbeat [43], so the range-bin that includes the VSs must be selected precisely. In conventional methods, the magnitude or phase in a single range-bin is used to search for the range-bin that includes the VSs [37,38,39], or signals in multiple range-bins are integrated [40]. The method in [37] uses the coherency between magnitude and phase as a criterion for range-bin selection, and therefore enables more accurate selection of range-bins that contain information about VSs, compared to the methods in [38,39,40], which exploit the extent of magnitude, phase fluctuation, or integrated phase. However, the magnitude does not give an accurate measurement of VSs, so range-bins that contain inaccurate information on VSs may be selected. When a range-bin that contains inaccurate VS information is selected, the accuracy of the measurement of VSs degrades. Therefore, range-bin that contains accurate VS information must be selected exactly.
This paper introduces a range-bin selection criterion that exploits coherency of the phase in multiple range-bins to select a range-bin that contain an accurate VS signal. Considering the radar signal model, phase is preferred for measuring the VS displacement to magnitude. In addition, respiration and heartbeat occur in spatially-various parts of the body, so the displacement with vital periods observed simultaneously in various range-bins is expected to be respiration or heartbeat. Thus, spatial phase information is used for range-bin selection instead of using magnitude, as in [37,38]. A spatial phase coherency (SPC) index was devised to quantify the coherency between displacements in spatially different range-bins. Then, a pair of range-bins that had the highest SPC was selected for vital extraction. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method selects range-bins that contain more accurate respiration and heartbeat than the bins selected by using conventional methods.
2. Methods
2.1. FMCW Radar Signal Model
The FMCW radar transmits a radio wave that has linearly-increasing frequency. The transmitted signal is mixed with the received signal, then subjected to low-pass filtering, to obtain the intermediate frequency (IF) signal, [26,27]:
where t is the scan time, n is the sampling time in a chirp, r is the range, is the beat frequency, is the magnitude, and is the phase.
contains the range information in . DFT is applied to at each to calculate and , which contain displacement information of the target at r. When a target exists in range-bin r, the signal model in [37] for and are
where is the baseline magnitude, is the center frequency, and c is the lightspeed.
Moreover, with regard to the small displacement in the target, the displacement affects and , as
However, in (2) is valid for an isotropic antenna model. In general, radar uses directional antennas and should be modeled considering antenna gain G, radar cross section , and effective area [44,45], as
According to the conventional studies [46,47], changes by respiratory activity. Considering the results, G, , and in (4) could change by VS displacement, . Therefore, in (4) is difficult to describe for unlike in (3). Considering the model in (3) and (4), the relationship between and is not clear, whereas is linearly proportional to . With regard to VS measurements, is the displacement of the body surface caused by respiration and heartbeat, and measures displacement more precisely than does.
2.2. Vital-Sign Measurement
Figure 1 shows the experimental settings for FMCW radar based VS measurements. As shown in Figure 1a, subjects comfortably sat on a chair facing the radar about 1 m apart. The distance between parts of body and the radar depends on the build of subjects, but generally distance to the abdomen was about 0.6~0.8 m, and distance to the neck was about 0.9~1.0 m. The FMCW radar used for recording was BTS60 [48] (bitsensing Inc., Seoul, Korea ) shown in Figure 1b. To obtain ground truth of VSs, a Neulog Respiration Monitor Belt logger sensor (Neulog Inc., Rishon Lezion, Israel) was wrapped around the abdomen, and the ECG electrodes of a PolyG-A (Laxtha Inc., Daejeon, Korea) were attached to both wrists and the right ankle.

Figure 1.
Vital-sign measurement using FMCW radar. (a) Experimental settings for vital measurement; (b) FMCW radar.
Figure 2 shows VS signals measured by FMCW radar. and for respiration and heartbeat are shown in Figure 2a,b. Because of high range-resolution of the radar, displacements in various parts of body are reflected in different range-bins. To identify the range-bin where the VS displacement exists, the temporal correlation coefficient [49] between at each range-bin and referenced VS signals was calculated as shown in Figure 2c,d. According to the conventional studies, respiration can be measured near the abdomen or thorax [39,42], and heartbeat can be measured where the skin is thin, such as neck [43]. In our experiments, the correlation between and referenced respiration signal was high between and m, which is near the subject’s abdomen. The correlation between and referenced heartbeat signal was high between to m which is near the subject’s neck.

Figure 2.
Measured vital-sign signals. (a,b) and of respiration and heartbeat, (c,d) temporal correlation coefficient between and referenced vital-sign, and (e,f) respiration and heartbeat in several range-bins.
In Figure 2e,f, the extracted VSs (respiration and the heartbeat) from various range bins corresponding to high and low correlation with referenced signals are compared. m in Figure 2e is highly correlated with referenced respiration, but m is not. m in Figure 2f shows a high correlation with a referenced heartbeat; however, m does not. At m in Figure 2e and m in Figure 2f, nor are associated with referenced VSs.
To summarize, respiration and heartbeat signals can be observed in multiple range-bins of , which is more accurate and reliable than . In addition, displacement of VSs exists in certain range-bins, so the range-bin that contains accurate displacement of VSs must be chosen.
2.3. Spatial Phase Coherency
To select the range-bins that contain displacement of VSs, we introduce a new method that selects range-bins by considering the coherency between over multiple range-bins. As shown in Figure 2, displacement by VSs is spatially distributed in multiple range-bins, and the displacement is simultaneously observed in the of the range-bins. Thus, the coherency between in range-bins that contain VS displacement should be high. Coherency is our criterion for selecting a range-bin that contain vital information, and an SPC index to quantify coherency was devised, as in (5).
where the mean of over t is eliminated beforehand, and is the standard deviation of .
Then, the pair of range-bins that have the highest SPC value are selected as the VS target range , as in (6):
To test whether SPC could measure coherency, signals were generated and SPC was applied. Figure 3a shows generated . To generate , peak points of sinusoids were detected, the location of peak points were disordered by uniform noise, and the points were interpolated. From to , the boundary of uniform distribution was expanded to generate further disorder. Figure 3b shows the SPC between and in other range-bins. As was disordered from to , the SPC decreased.

Figure 3.
Generated signal and SPC. (a) Generated , and (b) SPC with respect to .
As shown in Figure 4, SPC was applied to a real FMCW radar signal shown in Figure 4a,b and the capability of SPC in selecting the range-bins that contain vital information was tested. Figure 4c,d shows the calculated SPC. The SPCs for respiration and heartbeat were high for range-bins where was spatially coherent such as m in Figure 4a, and m in Figure 4b. In addition, maximum SPC at each range-bin was compared to the correlation coefficient between and referenced VSs. The SPC and correlation coefficient represented similar trends over the range, and both indices had maximum values at the same range-bin. Figure 4e,f shows and in the pair of range-bins that had the highest SPC. For respiration, and in Figure 4e are coherent, and are in proportion with the referenced respiration. For heartbeat, and in Figure 4f are coherent, and are proportional to the referenced heartbeat. However, the in the same range-bins does not show VS displacement.

Figure 4.
SPC and extracted vital-sign signals. (a,b) and for respiration and heartbeat, (c,d) SPCs, for respiration and heartbeat, and (e,f) extracted respiration and heartbeat.
To summarize, displacement by VSs was represented in several range-bins of ; accurate respiration and heartbeat signals were extracted by selecting a pair of range-bins that had the highest SPC.
3. Results
3.1. Data Acquisition
The radar and referenced VS signals of 20 subjects (15 men and 5 women) were recorded. The subjects sat on a chair facing the radar apart about 1 m. Depending on subjects, the distance between body parts and radar can be varied. However, the distance to the abdomen was generally 0.6~0.8 m and the distance to the neck was 0.9~1.0 m. Thus, we set the searching boundary of the target range bin to 0.5~1.2 m. Each subject was well informed about the entire process and purpose of recording, and agreed to the recording. All subjects had normal vital rates, and rested for least 5 min before the recording process. The recording lasted 2 min for each subject.
3.2. Computation Process
The recorded data were processed using MATLAB R2015a (MathWorks Inc., Natick, MA, USA). and were calculated using the built-in fast Fourier transform function, and the Hamming window was applied to to prevent spectral distortion. To reconstruct the continuous phase variation, phase unwrapping was applied to . To reduce the time complexity, the boundary of the human target was set by reference to the variance of ; this process suppresses stationary clutter [50]. Then, considering that normal adults’ respiratory rate is 14~20 respiration per minute (RPM), and heart rate is 60~100 beats per minute (BPM) [51,52], inside the boundary, was filtered at 0.1~0.4 Hz for respiration, and 0.8~1.7 Hz for heartbeat. For each pair of range-bins, the SPC was calculated and was selected. Then, in the selected range-bins was averaged to calculate vital rates using the zero-crossing detection [53]. The vital rates were represented as RPM for respiration and BPM for heartbeat. For continuous monitoring of vital rates, they were extracted every second using s of time-windowed data. For comparison with conventional methods, the vital rates of conventional methods were calculated in the same way as the proposed method, except for the range-bin selection. Conventional methods were implemented as followed equations. The method in [37] selects a range-bin, which has the highest coherency between magnitude and phase, as
where is the standard deviation of .
The method in [38] selects a range-bin, which has the maximum magnitude of range-profile considering the reflected power from the target as in (8). The range profile, is calculated by Fourier transform as in (9)
where for , and is bandwidth and N is the number of samples in a chirp.
The method in [39] selects a range-bin, which has the maximum phase fluctuation as
where DC offset of P(t,r) is removed in advance.
The method in [40] uses a range-integrated phase, for VS measurements as
3.3. Vital-Sign Accuracy
The accuracy of the VSs in the range-bins that was selected by the proposed and conventional methods were examined and compared.
Figure 5 shows extracted VS signals depending on range-bin selection methods. As shown in Figure 5, the proposed method selected the pair of range-bins for which showed the coherency and correlations between and referenced VSs were high. However, in the same range-bins, m in Figure 5a and m in Figure 5d do not represent respiration or heartbeat, although m in Figure 5b and m in Figure 5c are proportional to referenced heartbeat or respiration. Although represented vital displacement as in Figure 5b,c, was not reliable in measuring VS displacement as in Figure 5a,d. Consequently, the accuracy of VSs extracted by method in [37] varied among the subjects. Furthermore, both and of methods in [38,39,40] had inaccurate information about both respiration and heartbeat considering the correlation with the reference.
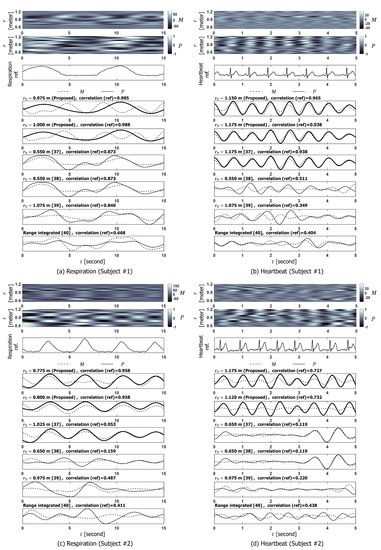
Figure 5.
Extracted vital signs. (a,b) Extracted respiration and heartbeat signals for subject#1, and (c,d) extracted respiration and heartbeat signals for subject#2.
Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the results of continuous vital monitoring using the proposed method for 20 subjects. For most subjects, the estimated VS rates were consistent with the reference. However, due to the unexpected body movements or spectral overlapping of respiration and heart rhythms, there were some subjects whose estimated VS rates show large variation from the reference data at some time points.

Figure 6.
Comparison of the extracted respiration rate using the proposed method with the referenced ground truth for 20 subjects.

Figure 7.
Comparison of the extracted heart rate using the proposed method with the referenced ground truth for 20 subjects.
For each subject, 105 vital rates were obtained and 2100 vital rates were totally obtained from the all subjects. Figure 8 depicts scatter plots of the estimated vital rates compared to the ground truth. Diagonal patterns are observed in the scatter plots of the proposed method, indicating that estimated vital rates are close to the ground truth. Moreover, we evaluated the accuracy of the estimated vital-sign rates as the mean error , correctness o, and correlation coefficient with ground truth for the various time window, as shown in Figure 9.

Figure 8.
Comparison of radar based vital rates with reference. (a) Respiration rate, and (b) heart rate.

Figure 9.
Extracted vital rates for various time window, . (a) Respiration rate, and (b) heart rate.
The measures averaged absolute difference between estimated vital rates and ground truth, as in (12):
where is total number of vital rates, x is estimated vital rates, and y is referenced vital rates.
The o calculates the proportion of the estimated vital rates of which the error compared to the ground truth is within the boundaries [37,40], as in (13).
where , RPM for respiration and BPM for heartbeat.
The measures the correlation between the estimated vital rates and ground truth [49], as in (14):
where and are mean of x and y, and and are standard deviation of x and y.
For both respiration and heartbeat, the vital rates extracted from the proposed method show higher accuracy than conventional methods with respect to , o, and regardless of length of the time window.
4. Discussion
SPC was introduced to select a range-bin containing accurate VS displacement, and VS signals were extracted from in a selected pair of range-bins that had the highest SPC. The range-bins selected by the proposed method had more accurate VS displacement than those selected by the conventional methods. For some subjects, estimated vital rates deviated at some time intervals due to the unknown artifacts, presumably caused by body motion, respiration harmonics, or subject dependency. For future works, the range-bin tracking logic [54,55] or the cancellation of respiration harmonic [56] can be applied to improve the stability of VS monitoring. Moreover, considering the FMCW radar is widely used for multi-target monitoring because of its ranging capability, the proposed SPC needs to be expanded to multi-target VS monitoring.
5. Conclusions
Depending on the range-bin selection, the accuracy of the extracted respiration and heartbeat varied. To select an appropriate range-bin that contains accurate VS signals, a range-bin selection method that used SPC was proposed. The method utilized spatial information of the phase, which is more reliable than the magnitude in VS monitoring. In experimental results, the accuracy of VS extraction for 20 subjects was shown. The range-bins that had the highest SPC contained accurate vital information. Furthermore, the proposed method selected the range-bins that contain more accurate-respiration and heartbeat signals than the bins selected by conventional methods. Quantitative evaluations of , o, and , demonstrated that the proposed method was superior to the conventional methods. The proposed method can extract accurate VS signals from the FMCW radar signal, and therefore will be useful for applications in healthcare monitoring.
Although the proposed method selected the range-bins that contain more accurate-respiration and heartbeat signals than the bins selected by conventional methods, the results were obtained from the situation when subjects sat on a chair facing the radar apart about 1 m. For the rigorous quantification of the performance, the proposed method needs to be evaluated with freely moving subjects located at various distances.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-I.C. and H.S.; methodology, H.-I.C.; software, H.-I.C.; validation, W.-J.S.; formal analysis, H.-I.C.; investigation, H.S.; resources, W.-J.S.; data curation, H.-I.C.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-I.C.; writing—review and editing, H.-C.S.; visualization, H.-I.C. and H.-C.S.; supervision, W.-J.S.; project administration, H.-C.S.; funding acquisition, H.-C.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT), Korea, under the ITRC (Information Technology Research Center) support program (IITP-2021-2020-0-01602) supervised by the IITP (Institute for Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kelly, C. Respiratory rate 1: Why measurement and recording are crucial. Nurs. Times 2018, 114, 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cretikos, M.A.; Bellomo, R.; Hillman, K.; Chen, J.; Finfer, S.; Flabouris, A. Respiratory rate: The neglected vital sign. Med. J. Aust. 2008, 188, 657–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfe, S. The importance of respiratory rate monitoring. Br. J. Nurs. 2019, 28, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, D.; Paulo Silva Cunha, J. Wearable health devices—Vital sign monitoring, systems and technologies. Sensors 2018, 18, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakria, P.; Tripathi, N.; Kitipawang, P. A real-time health monitoring system for remote cardiac patients using smartphone and wearable sensors. Int. J. Telemed. Appl. 2015, 2015, 373474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Khalidi, F.Q.; Saatchi, R.; Burke, D.; Elphick, H.; Tan, S. Respiration rate monitoring methods: A review. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2011, 46, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegan, J.D.; Zhang, J.; Chu, M.; Nguyen, T.; Park, S.J.; Paul, A.; Kim, J.; Bachman, M.; Khine, M. Skin-mountable stretch sensor for wearable health monitoring. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17295–17303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, Y.; von Maltzahn, W.W.; Neuman, M.R.; Bronzino, J.D. Clinical Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shelley, K.H. Photoplethysmography: Beyond the calculation of arterial oxygen saturation and heart rate. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 105, S31–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, K.; Tamura, T.; Miike, H. Monitoring of heart and respiratory rates by photoplethysmography using a digital filtering technique. Med. Eng. Phys. 1996, 18, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, M.B. Understanding Electrocardiography; Elsevier Health Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Baltazar, R.F. Basic and Bedside Electrocardiography; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, V.C. The Micro-Doppler Effect in Radar; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Lin, J. Microwave Noncontact Motion Sensing and Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 230. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Lubecke, V.M.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lin, J. A review on recent advances in Doppler radar sensors for noncontact healthcare monitoring. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 2046–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Matsui, T.; Kawahara, H.; Ichiki, H.; Shimizu, J.; Kondo, Y.; Gotoh, S.; Yura, H.; Takase, B.; Ishihara, M. A non-contact vital sign monitoring system for ambulances using dual-frequency microwave radars. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2009, 47, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisa, S.; Pittella, E.; Piuzzi, E. A survey of radar systems for medical applications. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2016, 31, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, G.; Lenhard, T.; Will, C.; Koelpin, A. Microwave interferometer radar-based vital sign detection for driver monitoring syst. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), Heidelberg, Germany, 27–29 April 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.K. Wireless vital signal tracking for drivers using micro-doppler seatback radar. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th IFIP International Conference on New Technologies, Mobility and Security (NTMS), Paris, France, 26–28 February 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Sun, L.; Tian, T.; Huang, Z.; Clancy, E. Real-time non-contact infant respiratory monitoring using UWB radar. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 16th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Hangzhou, China, 18–21 October 2015; pp. 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, X.; Weiss, M.D.; Lin, J. Verification of a non-contact vital sign monitoring system using an infant simulator. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 4836–4839. [Google Scholar]
- Ziganshin, E.; Numerov, M.; Vygolov, S. UWB baby monitor. In Proceedings of the 2010 5th International Conference on Ultrawideband and Ultrashort Impulse Signals, Sevastopol, Ukraine, 6–10 September 2010; pp. 159–161. [Google Scholar]
- Diraco, G.; Leone, A.; Siciliano, P. A radar-based smart sensor for unobtrusive elderly monitoring in ambient assisted living applications. Biosensors 2017, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Kagawa, M.; Kubota, M.; Kurita, A. Development of a practicable non-contact bedside autonomic activation monitoring system using microwave radars and its clinical application in elderly people. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2013, 27, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postolache, O.; Girao, P.; Pinheiro, E.; Madeira, R.; Pereira, J.D.; Mendes, J.; Postolache, G.; Moura, C. Multi-usage of microwave Doppler radar in pervasive healthcare systems for elderly. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Hangzhou, China, 10–12 May 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Stove, A.G. Linear FMCW radar techniques. In IEE Proceedings F (Radar and Signal Processing); IET: London, UK, 1992; Volume 139, pp. 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Brooker, G.M. Understanding millimetre wave FMCW radars. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Sensing Technology, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 21–23 November 2005; pp. 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Pohl, A.; Jaeschke, T.; Czaplik, M.; Köny, M.; Leonhardt, S.; Pohl, N. A novel ultra-wideband 80 GHz FMCW radar system for contactless monitoring of vital signs. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 4978–4981. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Kurata, M.; Inaba, T. FMCW radar for small displacement detection of vital signal using projection matrix method. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Lee, K.K. Low-complexity joint extrapolation-MUSIC-based 2D parameter estimator for vital FMCW radar. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 19, 2205–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, A.; Blanch, S.; Aguasca, A.; Romeu, J.; Broquetas, A. Collimated beam FMCW radar for vital sign patient monitoring. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 67, 5073–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, G.; Piuzzi, E.; Pittella, E.; Pisa, S. An FMCW radar for localization and vital signs measurement for different chest orientations. Sensors 2020, 20, 3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, B.H.; Park, J.K.; Kim, S.W.; Yook, J.G. A resolution enhancement technique for remote monitoring of the vital signs of multiple subjects using a 24 GHz bandwidth-limited FMCW radar. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, M.; Ren, A.; Tian, Z. Remote monitoring of human vital signs based on 77-GHz mm-wave FMCW radar. Sensors 2020, 20, 2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Yang, C.L. Simultaneous detection of multi-target vital signs using EEMD algorithm based on FMCW radar. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Biomedical Conference (IMBioC), Nanjing, China, 6–8 May 2019; Volume 1, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Turppa, E.; Kortelainen, J.M.; Antropov, O.; Kiuru, T. Vital Sign Monitoring Using FMCW Radar in Various Sleeping Scenarios. Sensors 2020, 20, 6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.I.; Song, H.; Shin, H.C. Target range selection of FMCW radar for accurate vital information extraction. IEEE Access 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Ferreras, J.M.; Wang, J.; Peng, Z.; Li, C.; Gómez-García, R. Fmcw-radar-based vital-sign monitoring of multiple patients. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Biomedical Conference (IMBioC), Nanjing, China, 6–8 May 2019; Volume 1, pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, M.; Shaker, G.; De Almeida, J.C.M.; Morita, P.P.; Safavi-Naeini, S. Remote monitoring of human vital signs using mm-Wave FMCW radar. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54958–54968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, B.H.; Park, J.K.; Yook, J.G. A novel vital-sign sensing algorithm for multiple subjects based on 24-GHz FMCW Doppler radar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.I.; Seul, J.; Shin, H.C. Vital information extraction using FMCW radar. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), Bangkok, Thailand, 13–16 January 2021; pp. 636–639. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.; Nian, Y.; Gong, Y. Novel signal processing method for vital sign monitoring using FMCW radar. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 33, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Lee, Y.; Choi, Y.W.; Heo, R.; Park, H.K.; Cho, S.H.; Cho, S.H.; Lim, Y.H. Preclinical evaluation of a noncontact simultaneous monitoring method for respiration and carotid pulsation using impulse-radio ultra-wideband radar. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H. Fundamental Principles of Radar; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mahafza, B.R. Introduction to Radar Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Piuzzi, E.; D’Atanasio, P.; Pisa, S.; Pittella, E.; Zambotti, A. Complex radar cross section measurements of the human body for breath-activity monitoring applications. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 2247–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aardal, Ø.; Hamran, S.E.; Berger, T.; Hammerstad, J.; Lande, T.S. Radar cross section of the human heartbeat and respiration in the 500MHz to 3GHz band. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 6–19 January 2011; pp. 422–425. [Google Scholar]
- Bitsensing. BTS60. Available online: http://bitsensing.com/pdf/Technical_Specification_InCabinRadar_miniV.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Benesty, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Cohen, I. Pearson correlation coefficient. In Noise Reduction in Speech Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Gu, C.; Inoue, T.; Li, C. A hybrid FMCW-interferometry radar for indoor precise positioning and versatile life activity monitoring. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2014, 62, 2812–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Model, D. Making Sense of Clinical Examination of the Adult Patient: Hands-on Guide; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Taktak, A.; Ganney, P.; Long, D.; Axell, R. Clinical Engineering: A Handbook for Clinical and Biomedical Engineers; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Petrović, V.L.; Janković, M.M.; Lupšić, A.V.; Mihajlović, V.R.; Popović-Božović, J.S. High-accuracy real-time monitoring of heart rate variability using 24 GHz continuous-wave Doppler radar. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 74721–74733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Pi, Z.; Liu, B. TROIKA: A general framework for heart rate monitoring using wrist-type photoplethysmographic signals during intensive physical exercise. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 62, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalan, M.; Santra, A.; Will, C. Improved contactless heartbeat estimation in FMCW radar via Kalman filter tracking. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2020, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Javaid, A.Q.; Weitnauer, M.A. Harmonic Path (HAPA) algorithm for non-contact vital signs monitoring with IR-UWB radar. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 31 October–2 November 2013; pp. 146–149. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).