Utilisation of Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition in Conjunction with Cyclostationary Technique for Wind Turbine Gearbox Fault Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. Cyclic Spectral Analysis
2.2. Empirical Mode Decomposition
3. Measurement Setup
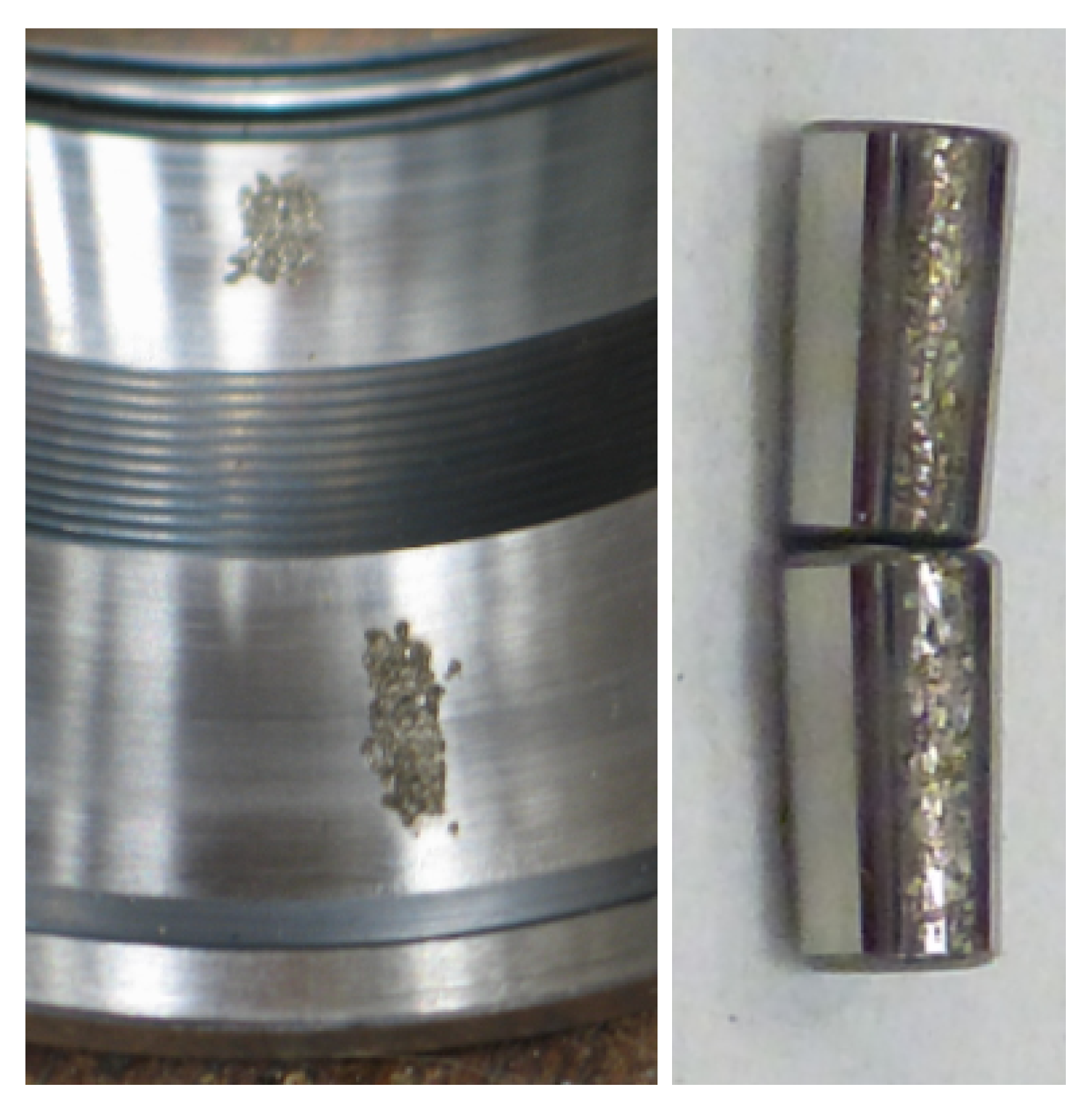
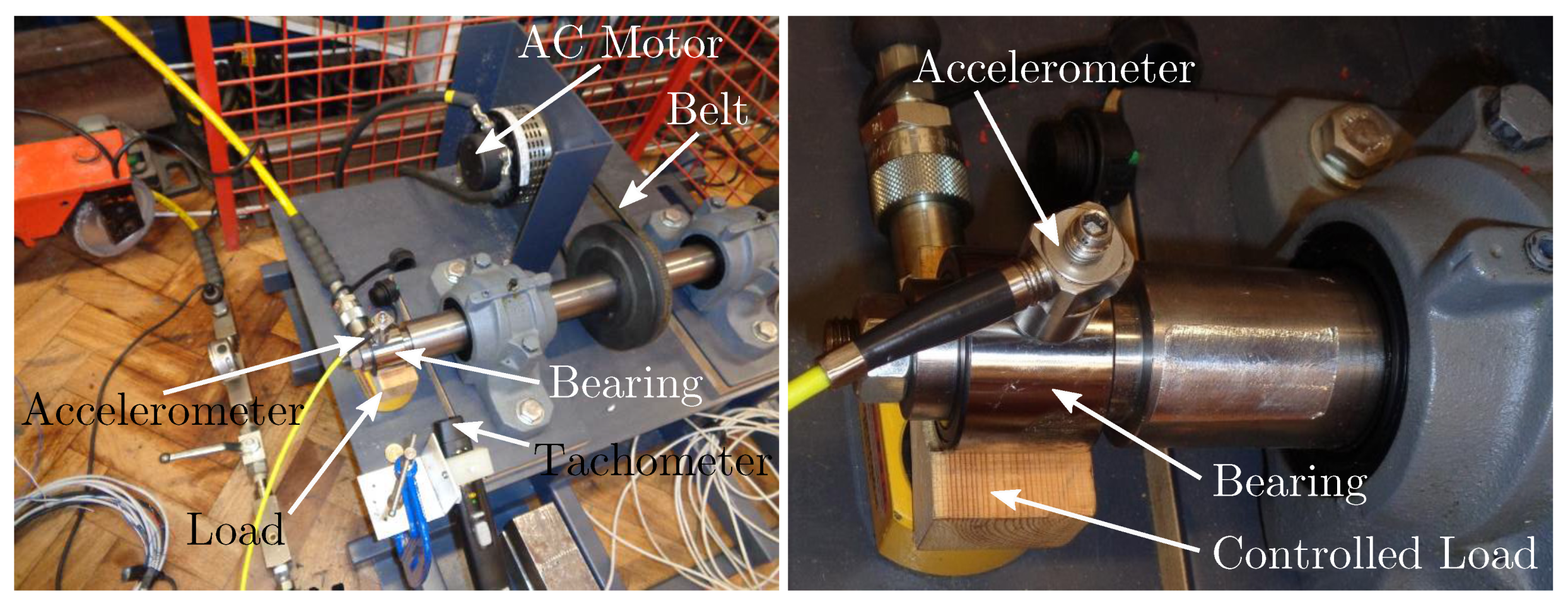
3.1. Rolling Element Test Rig
3.2. Tidal Turbine Gearbox Test Rig
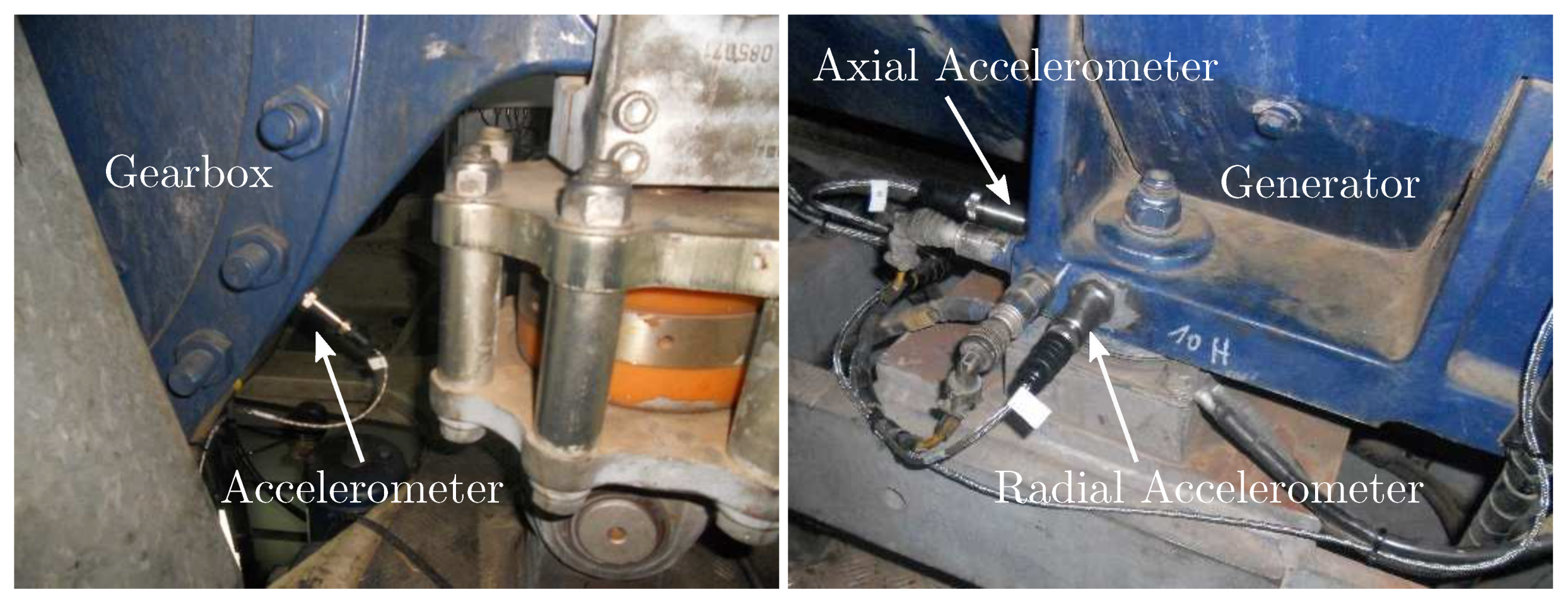
3.3. Wind Turbine Gearbox
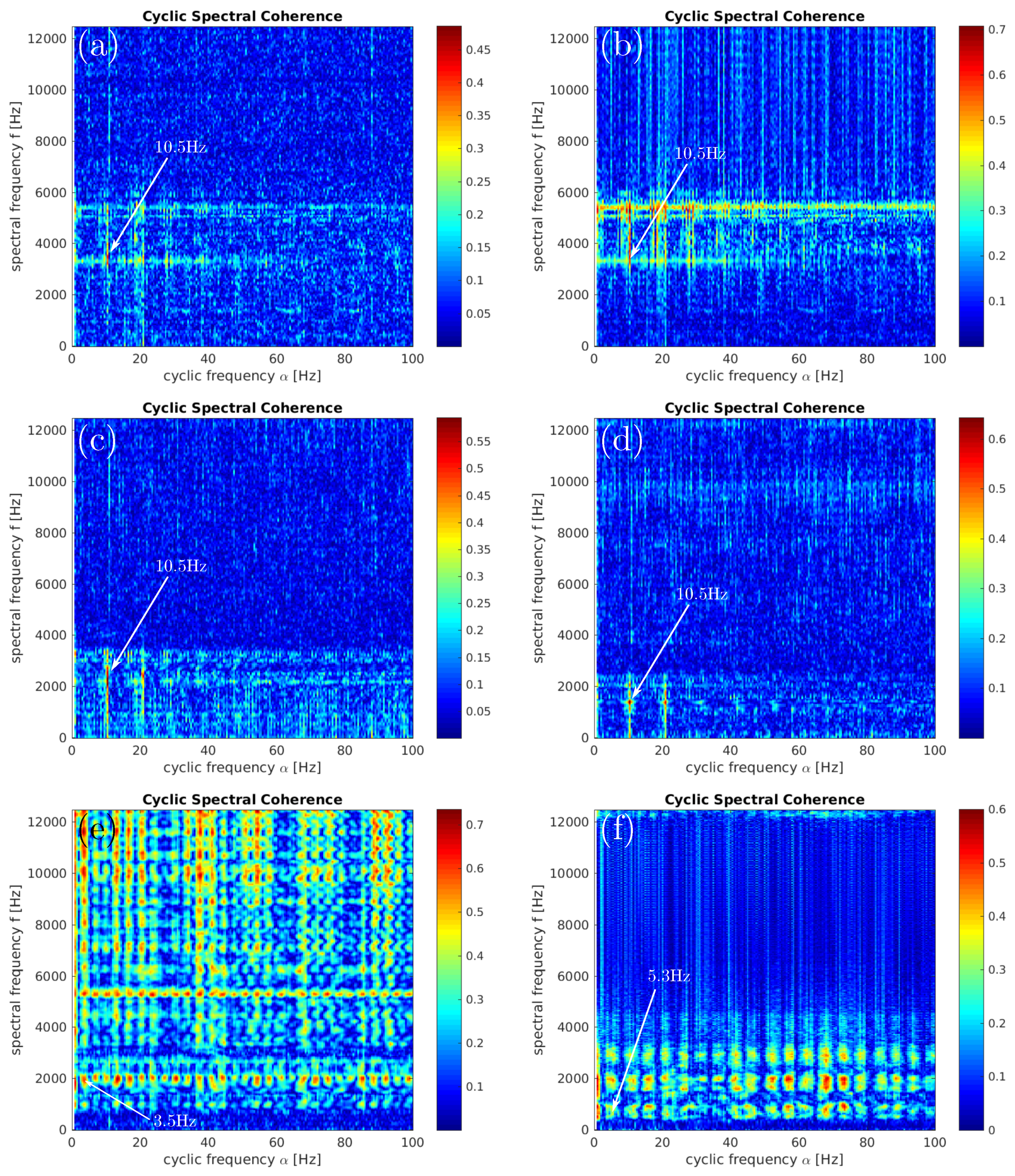
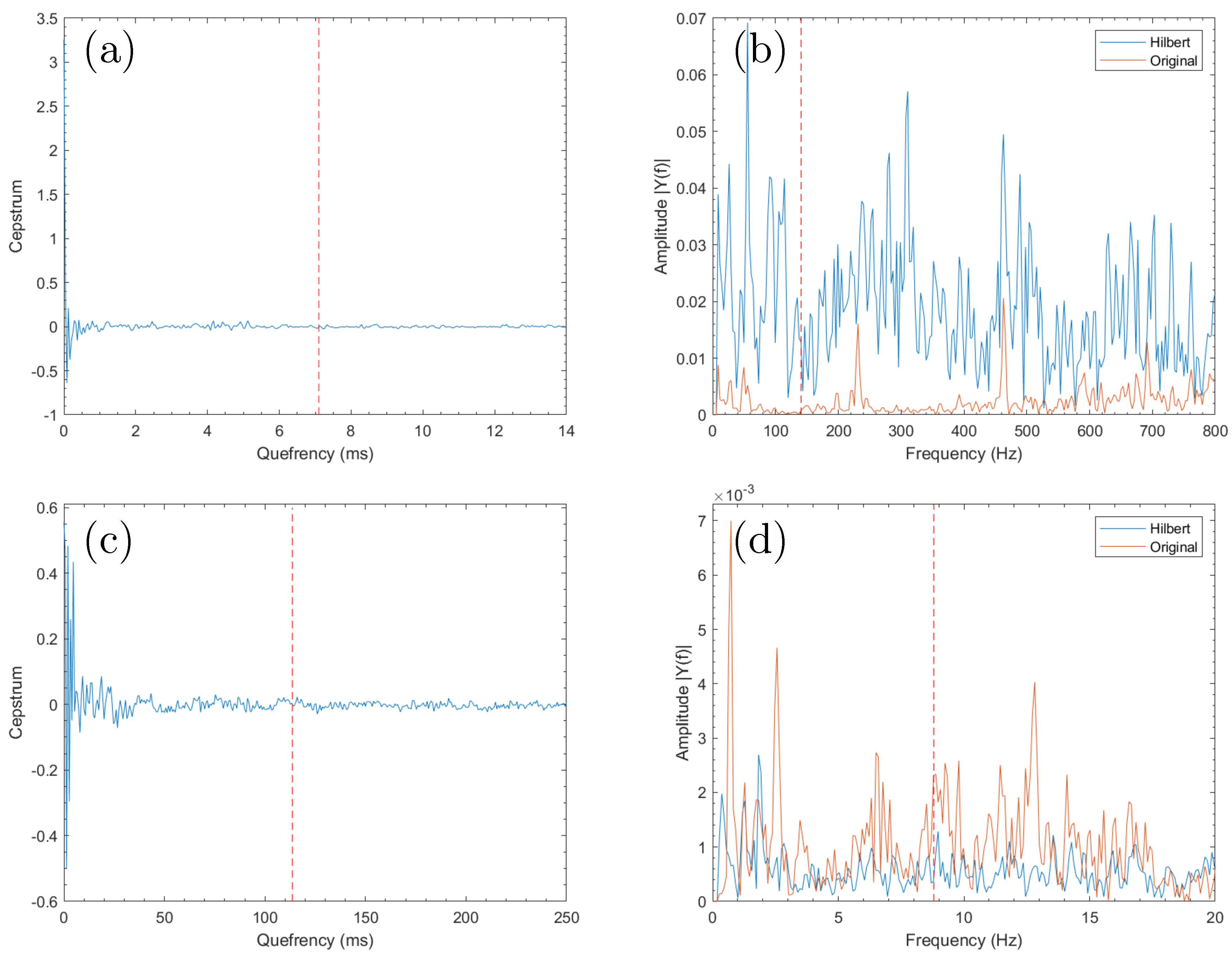
4. Results and Discussions
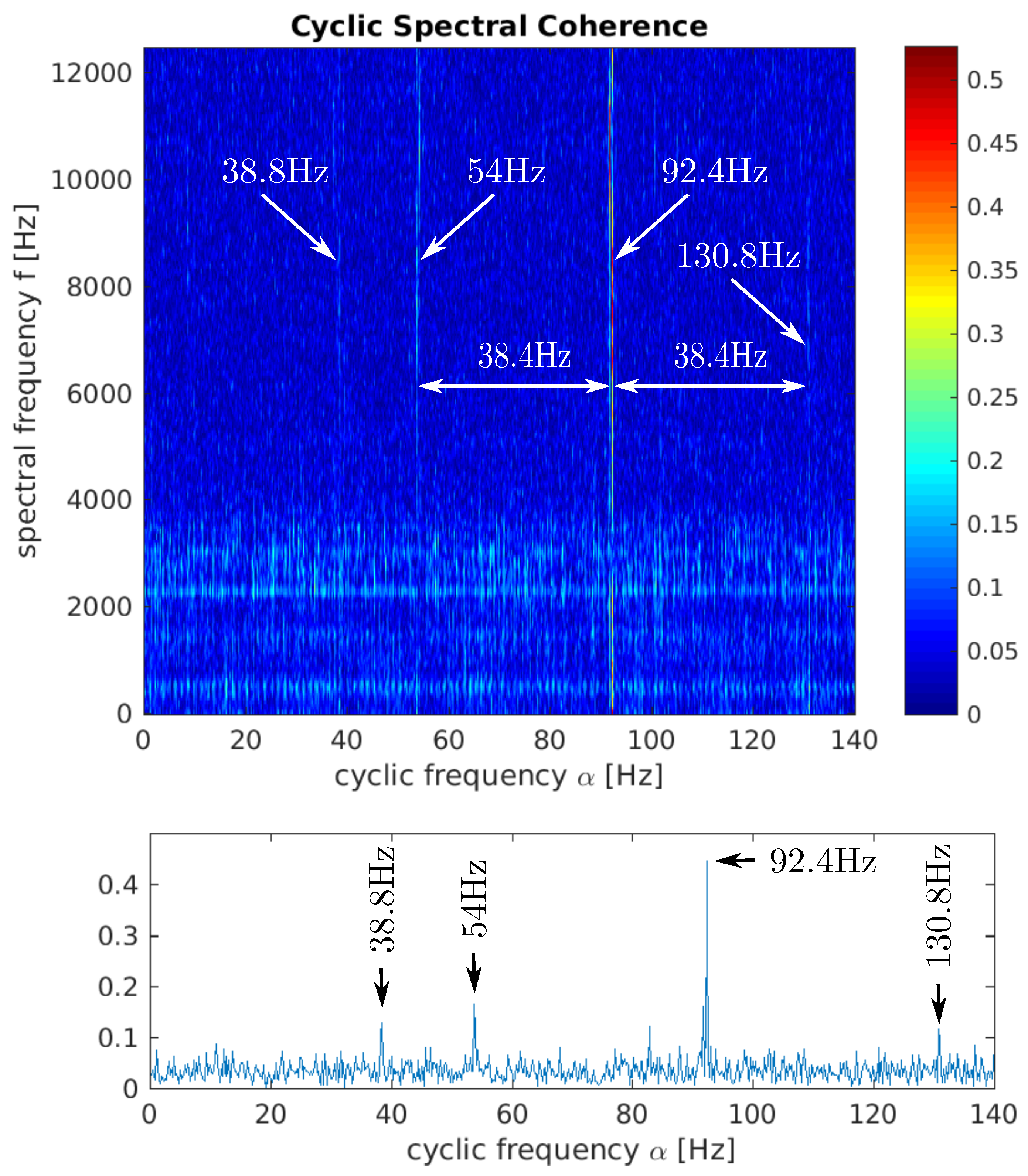
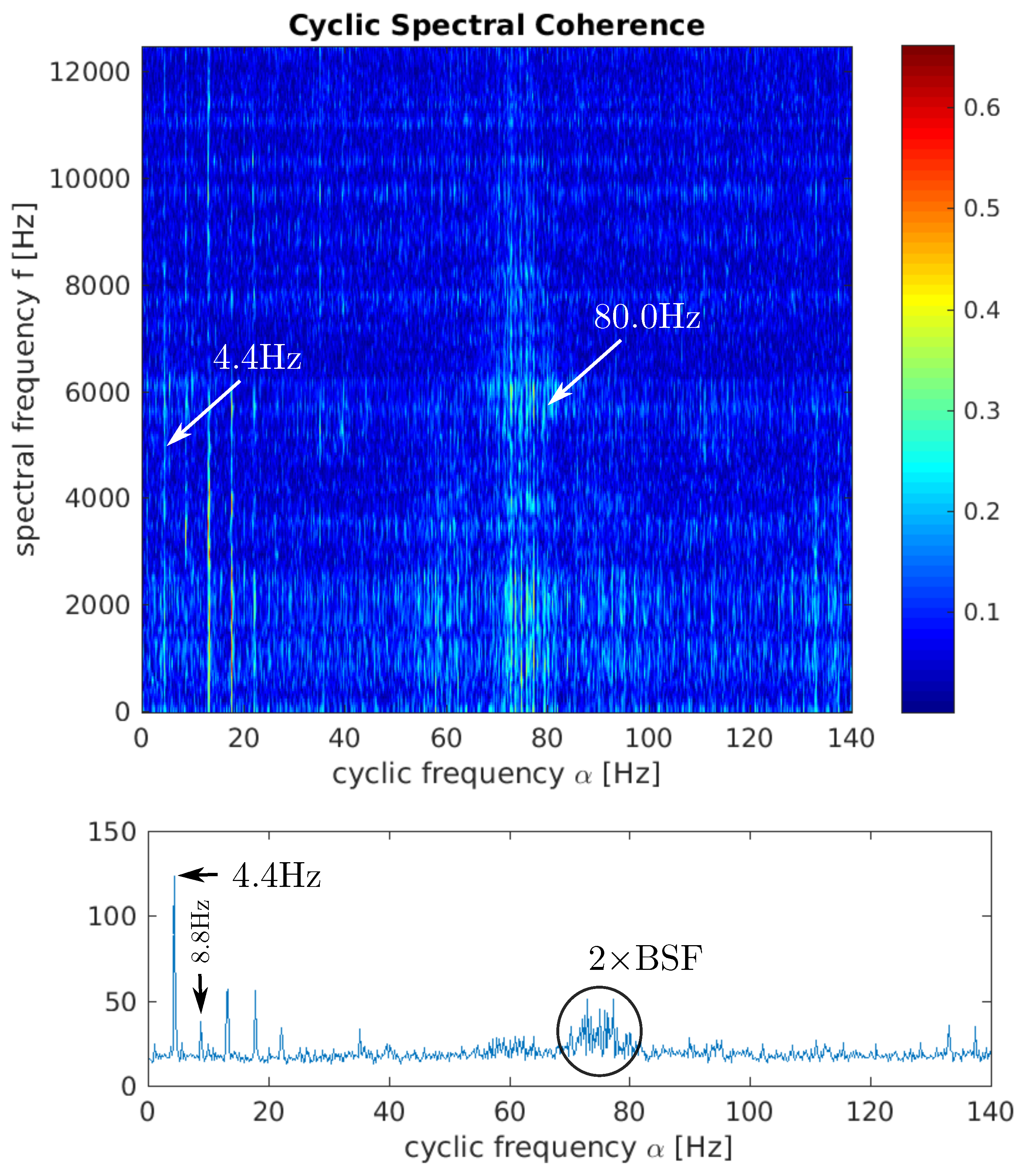
4.1. Rolling Element Analysis
4.2. Simplified Gearbox Analysis
4.3. Wind Turbine Gearbox Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPFI | Ball Pass Frequency of Inner race |
| BPFO | Ball Pass Frequency of Outer race |
| BSF | Ball Spin Frequency |
| EEMD | Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| EMD | Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| FTF | Fundamental Train Frequency |
| GM | Gear-mesh |
| GAPF | Gear Assembly Phase Frequency |
| IMF | Intrinsic Mode Function |
References
- Global Wind Statistics. Global Wind Report 2019. Available online: https://gwec.net/global-wind-report-2019 (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Barszcz, T. Vibration-Based Condition Monitoring of Wind Turbines, 1st ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.M.P.; Márquez, F.P.G.; Tobias, A.; Papaelias, M. Wind turbine reliability analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 23, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, F.P.G.; Tobias, A.M.; Pérez, J.M.P.; Papaelias, M. Condition monitoring of wind turbines: Techniques and methods. Renew. Energy 2012, 46, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Roshanmanesh, S.; Hayati, F.; Junior, V.J.; Wang, T.; Hajiabady, S.; Li, X.; Basoalto, H.; Dong, H.; Papaelias, M. Improving the reliability of industrial multi-MW wind turbines. Insight-Non Test. Cond. Monit. 2017, 59, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ferrando Chacon, J.L.; Andicoberry, E.A.; Kappatos, V.; Papaelias, M.; Selcuk, C.; Gan, T.H. An experimental study on the applicability of acoustic emission for wind turbine gearbox health diagnosis. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2016, 35, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Pelka, K.; Puls, S.; Poech, M.H.; Mertens, A.; Bartschat, A.; Tegtmeier, B.; Broer, C.; Wenske, J. Exploring the Causes of Power-Converter Failure in Wind Turbines based on Comprehensive Field-Data and Damage Analysis. Energies 2019, 12, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, V.J.; Zhou, J.; Roshanmanesh, S.; Hayati, F.; Hajiabady, S.; Li, X.; Dong, H.; Papaelias, M. Evaluation of damage mechanics of industrial wind turbine gearboxes. Insight-Non Test. Cond. Monit. 2017, 59, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Kaa, G.; van Ek, M.; Kamp, L.M.; Rezaei, J. Wind turbine technology battles: Gearbox versus direct drive-opening up the black box of technology characteristics. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 153, 119933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chu, F. Cyclostationary Analysis for Gearbox and Bearing Fault Diagnosis. Shock Vib. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Chen, J. Investigation into various techniques of cyclic spectral analysis for rolling element bearing diagnosis under influence of gear vibrations. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 364, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Lage, Y.; Soua, S.; Wang, B.; Gan, T.H. Vestas V90-3MW wind turbine gearbox health assessment using a vibration-based condition monitoring system. Shock Vib. 2016, 2016, 6423587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.A. (Ed.) An Introduction to Cyclostationary Signals. In Cyclostationarity in Communication and Signal Processing; IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Chapter 1; pp. 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Giannakis, G.B. Cyclostationary Signal Analysis. In The Digital Signal Processing Handbook; Madisetti, V.K., Williams, D.B., Eds.; IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Chapter 17. [Google Scholar]
- Ishak, G.; Raad, A.; Antoni, J. Analysis of Vibration Signals Using Cyclostationary Indicators; Institute of Technology of Chartres: Chartres, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Antoni, J. Cyclic spectral analysis in practice. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 597–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Long, S.R.; Shen, Z. The Mechanism for Frequency Downshift in Nonlinear Wave Evolution. In Advances in Applied Mechanics; Academic Press: London, UK, 1996; Volume 32, pp. 59–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R. A New View of Nonlinear Water Waves: The Hilbert Spectrum. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1999, 31, 417–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizhner, S.; Blank, K.; Flatley, T.; Huang, N.E.; Patrick, D.; Hestnes, P. On the Hilbert-Huang Transform Theoretical Developments. 2005. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?R=20050210067 (accessed on 20 April 2018).
- Huang, N.E. Introduction to the Hilbert-huang Transform and Its Related Mathematical Problems. In Hilbert-Huang Transform and Its Applications, 2nd ed.; Huang, N.E., Shen, S.S.P., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2014; Chapter 1; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Lin, J.; He, Z.; Zuo, M.J. A review on empirical mode decomposition in fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 35, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition: A Noise-Assisted Data Analysis Method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Speed | Characteristic Frequency (Hz) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRM | Hz | FTF | BPFO | BPFI | BSF |
| 600 | 10 | 4.4 | 92.3 | 117.7 | 40.0 |
| Feature | Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|
| Output Shaft | 12.5 |
| 3rd Stage Gear-mesh | 337.5 |
| Interim Shaft | 3.55 |
| 2nd Stage Gear-mesh | 35.5 |
| Slow Shaft | 0.83 |
| 1st Stage Gear-mesh | 11.6 |
| 1st GAPF | 5.8 |
| Input Shaft | 0.18 |
| Speed | Characteristic Frequency (Hz) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRM | Hz | FTF | BPFO | BPFI | BSF |
| 60 | 1.00 | 0.405 | 5.676 | 8.323 | 2.550 |
| 64 | 1.07 | 0.433 | 6.057 | 8.881 | 2.721 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roshanmanesh, S.; Hayati, F.; Papaelias, M. Utilisation of Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition in Conjunction with Cyclostationary Technique for Wind Turbine Gearbox Fault Detection. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3334. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093334
Roshanmanesh S, Hayati F, Papaelias M. Utilisation of Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition in Conjunction with Cyclostationary Technique for Wind Turbine Gearbox Fault Detection. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(9):3334. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093334
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoshanmanesh, Sanaz, Farzad Hayati, and Mayorkinos Papaelias. 2020. "Utilisation of Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition in Conjunction with Cyclostationary Technique for Wind Turbine Gearbox Fault Detection" Applied Sciences 10, no. 9: 3334. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093334
APA StyleRoshanmanesh, S., Hayati, F., & Papaelias, M. (2020). Utilisation of Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition in Conjunction with Cyclostationary Technique for Wind Turbine Gearbox Fault Detection. Applied Sciences, 10(9), 3334. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093334






