Analysis of Salt Mixture Contamination on Insulators via Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
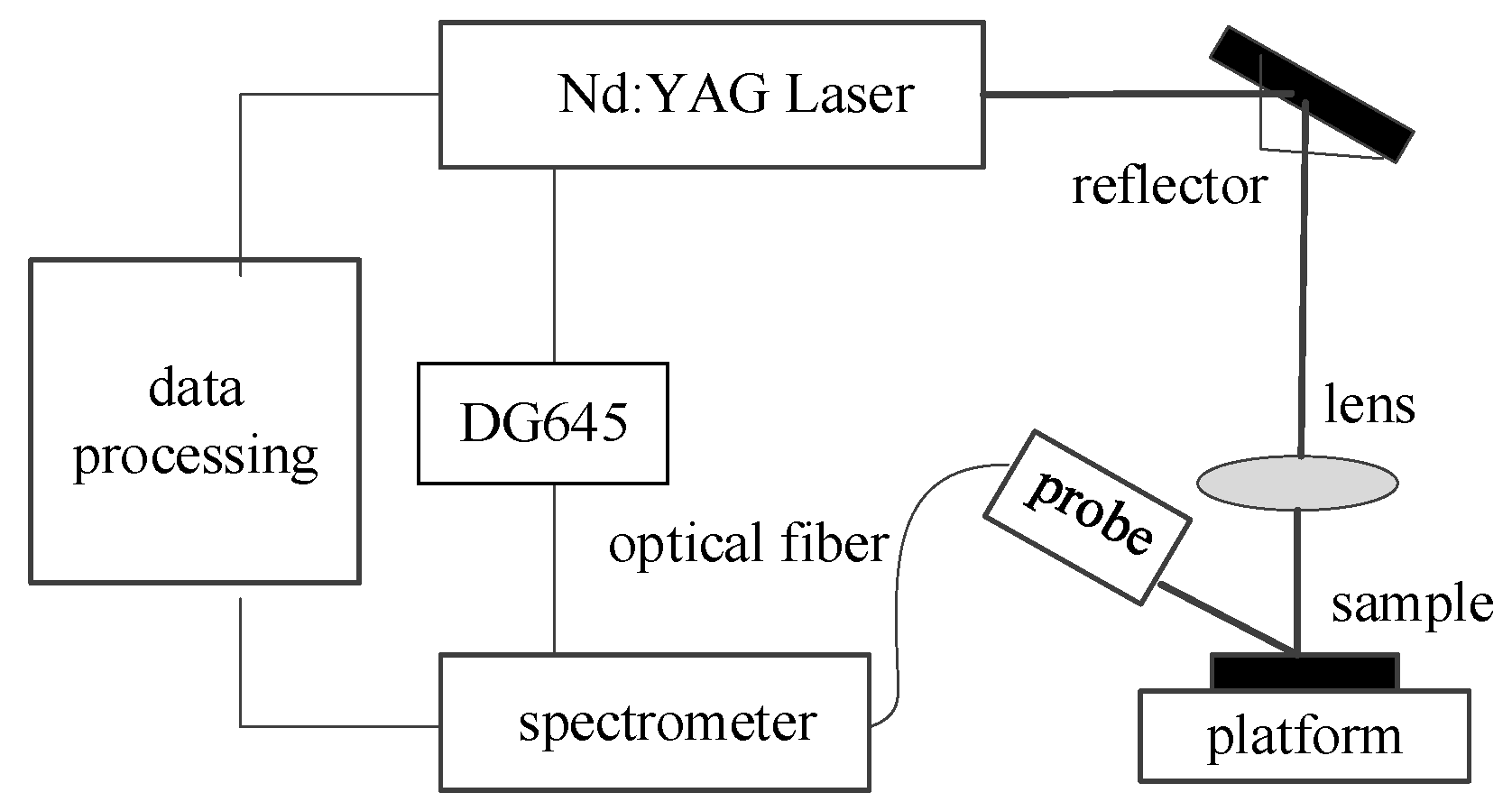
2. Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
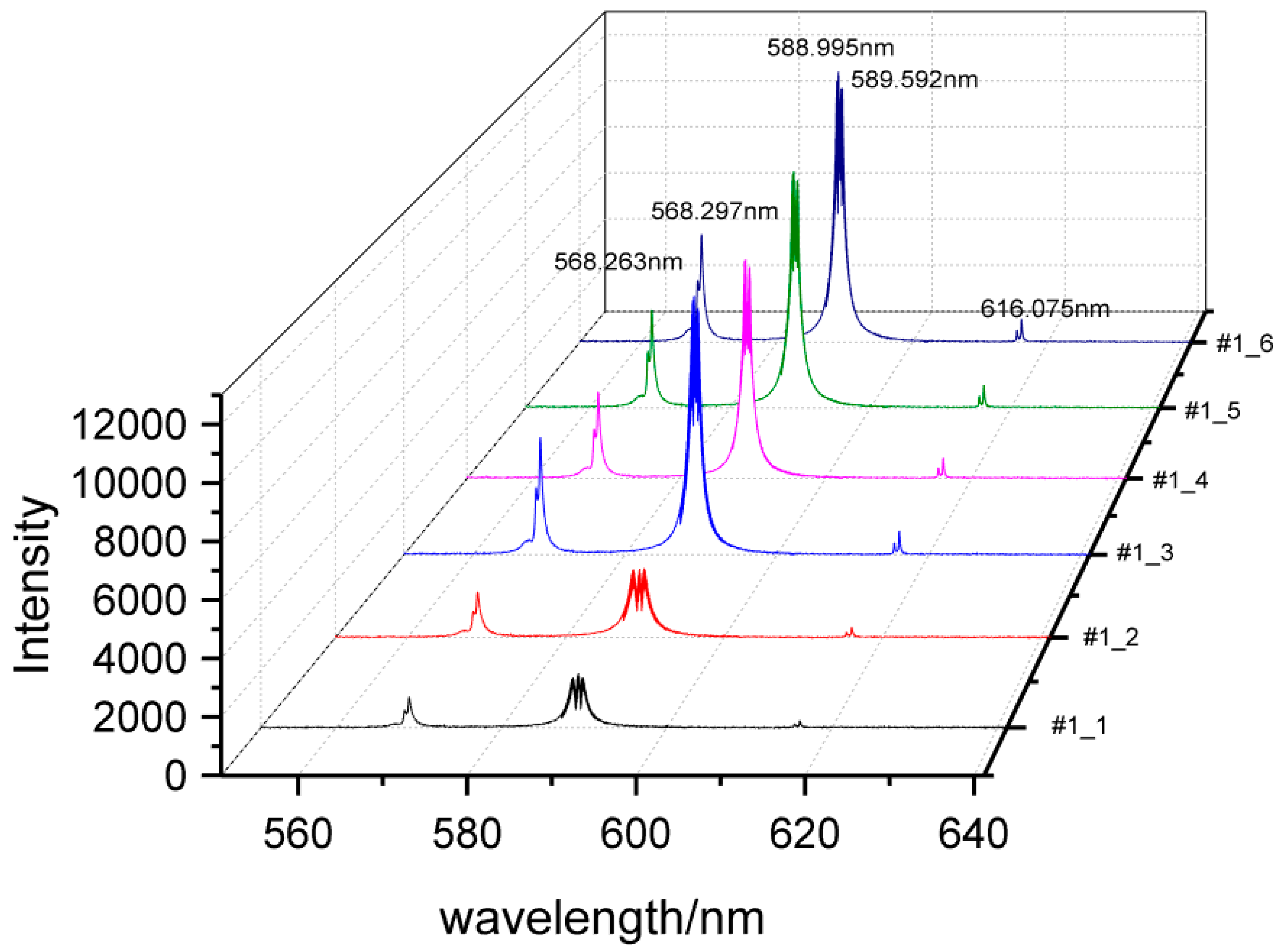
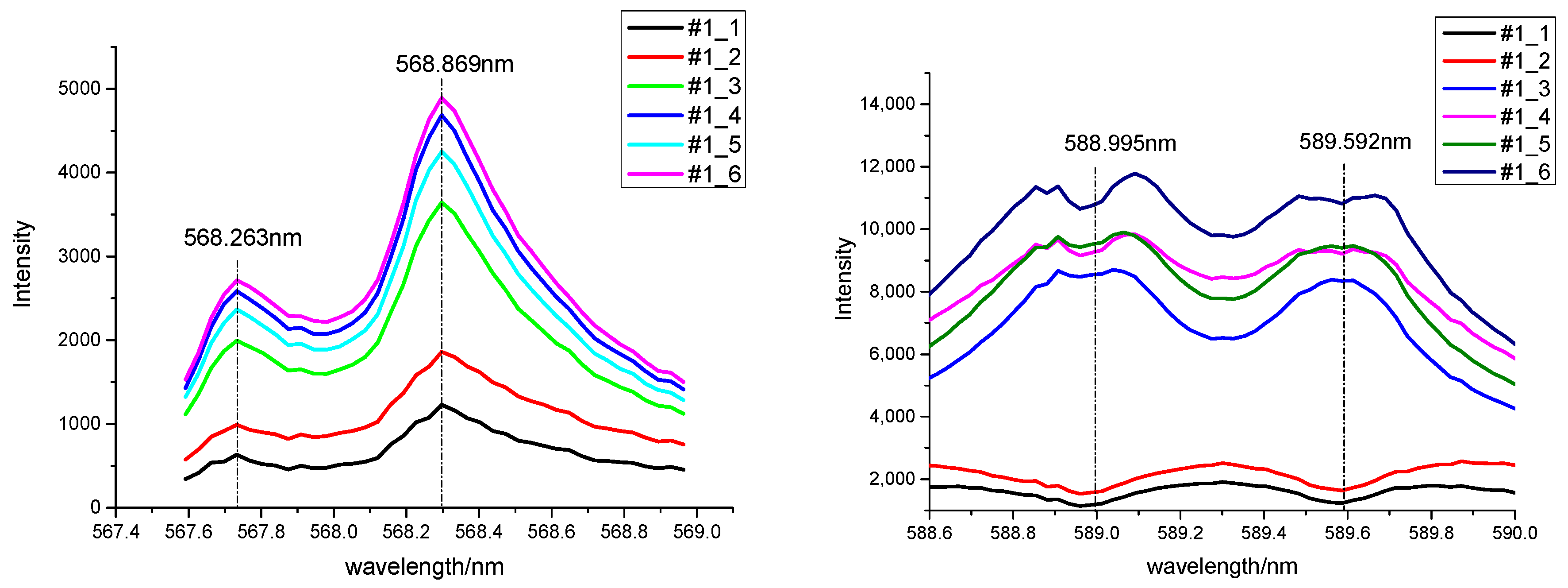
3.1. Spectral Characteristics for Na2CO3 and NaHCO3
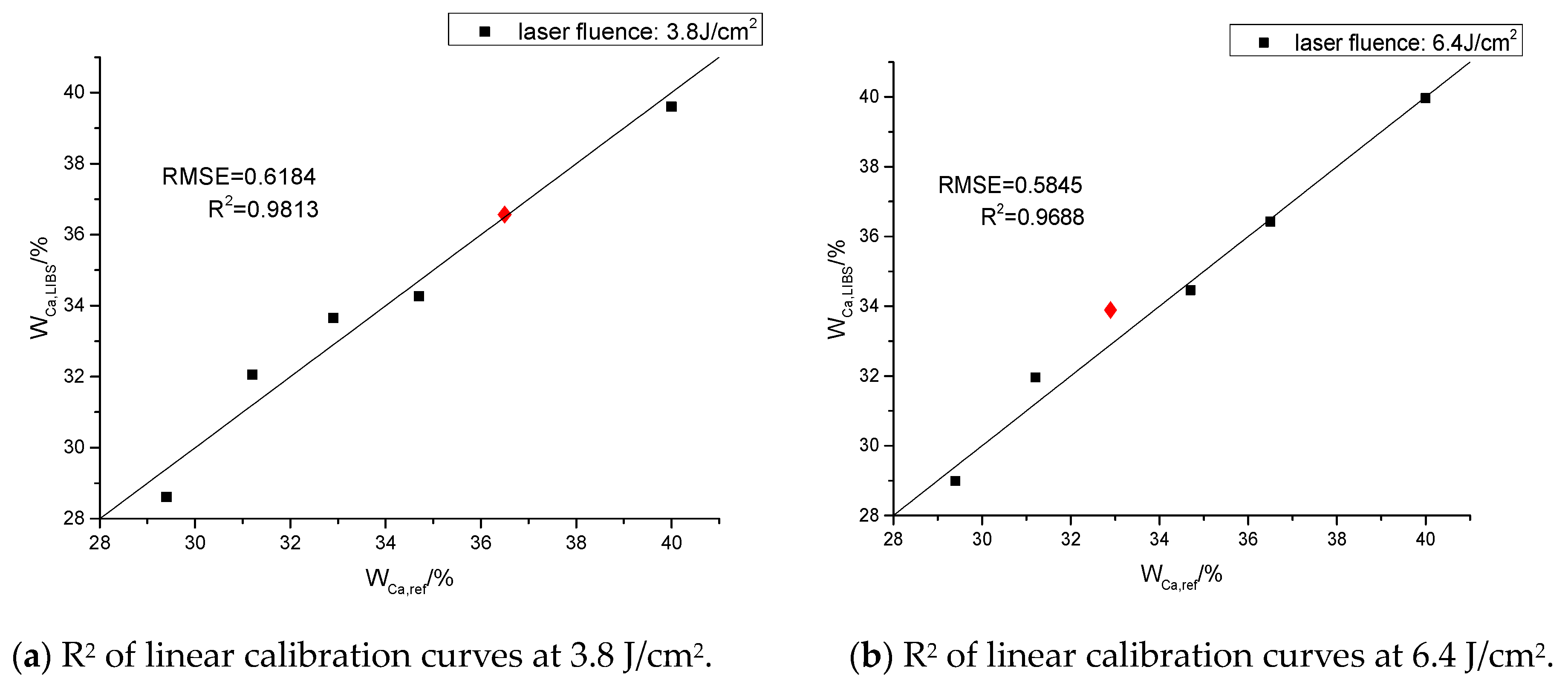
3.2. Characteristic Spectra of CaCO3 and CaSO4
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Du, B. Dynamic formation mechanism of water droplet and induced surface discharges on silicone rubber composites. High Volt. 2019, 4, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, S.; Fan, J.; Guan, Z. Development of composite insulators in China. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1999, 6, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcelroy, A.J.; Lyon, W.J.; Phelps, J.D.; Woodson, H.H. Insulators with contaminated surfaces, part I: Field conditions and their laboratory simulation. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1970, 8, 1848–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodson, H.H.; Mcelroy, A.J. Insulators with contaminated surfaces, part II: Modeling of discharge mechanisms. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1970, 8, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Arai, N.; Shimoda, O.; Holte, K. Contaminated insulators-chemical dependence of flashover voltages and salt migration. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1974, 5, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courreges-Lacoste, G.B.; Ahlers, B.; Perez, F.R. Combined Raman spectrometer/laser-induced breakdown spectrometer for the next ESA mission to Mars. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2007, 68, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremers, D.A.; Multari, R.A.; Knight, A.K. Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy, Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry: Applications, Theory and Instrumentation; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.-Q.; Zhao, Y.-R.; Liu, F.; He, Y. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy coupled with multivariate chemometrics for variety discrimination of soil. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Song, L.; Liu, P. Experimental study of vacuum degree online detection of vacuum interrupter based on laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. High Volt. Appar. 2017, 3, 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Gojani, A.B.; Gornushkin, I.B.; Wang, X. Investigation of laser-induced plasma at varying pressure and laser focusing. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2018, 150, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, H.; Liu, D.; Yang, A.; Liu, P.; Gao, L.; Ding, H.; Wang, W.; Rong, M. A pilot study on the vacuum degree online detection of vacuum interrupter using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 44LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, X.; Chen, P.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, R.; Lv, Q. Metal Contamination Distribution Detection in High-Voltage Transmission Line Insulators by Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS). Sensors 2018, 18, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, C.; Jia, Z. Ablation properties and elemental analysis of silicone rubber using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2016, 44, 2766–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hong, X.; Chen, P.; Zhao, C.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Lv, Q.; Huang, R.; Liu, S. In-situ and quantitative analysis of aged silicone rubber materials with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. High Volt. 2018, 3, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.S.; Vasa, N.J.; Sarathi, R. Remote surface pollutant measurement by adopting a variable stand-off distance based laser induced spectroscopy technique. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 435504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, D.W.; Omenetto, N. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), part II: Review of instrumental and methodological approaches to material analysis and applications to different fields. Appl. Spectrosc. 2012, 66, 347–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tognoni, E.; Palleschi, V.; Corsi, M.; Cristoforetti, G. Quantitative micro-analysis by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: A review of the experimental approaches. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2002, 57, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, T.-B.; Hou, Z.-Y.; Zhou, W.-D.; Lu, J.-D.; Ding, H.-B.; Zeng, X.-Y. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in China. Front. Phys. 2014, 9, 419–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST. National Institute of Standards and Technology, U.S. Department of Technology Database. Available online: http://www.physics.nist.gov (accessed on 8 February 2020).
- Cremers, D.A.; Radziemski, L.J. Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy; John Wilkey & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.P.; Thakur, S.N. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
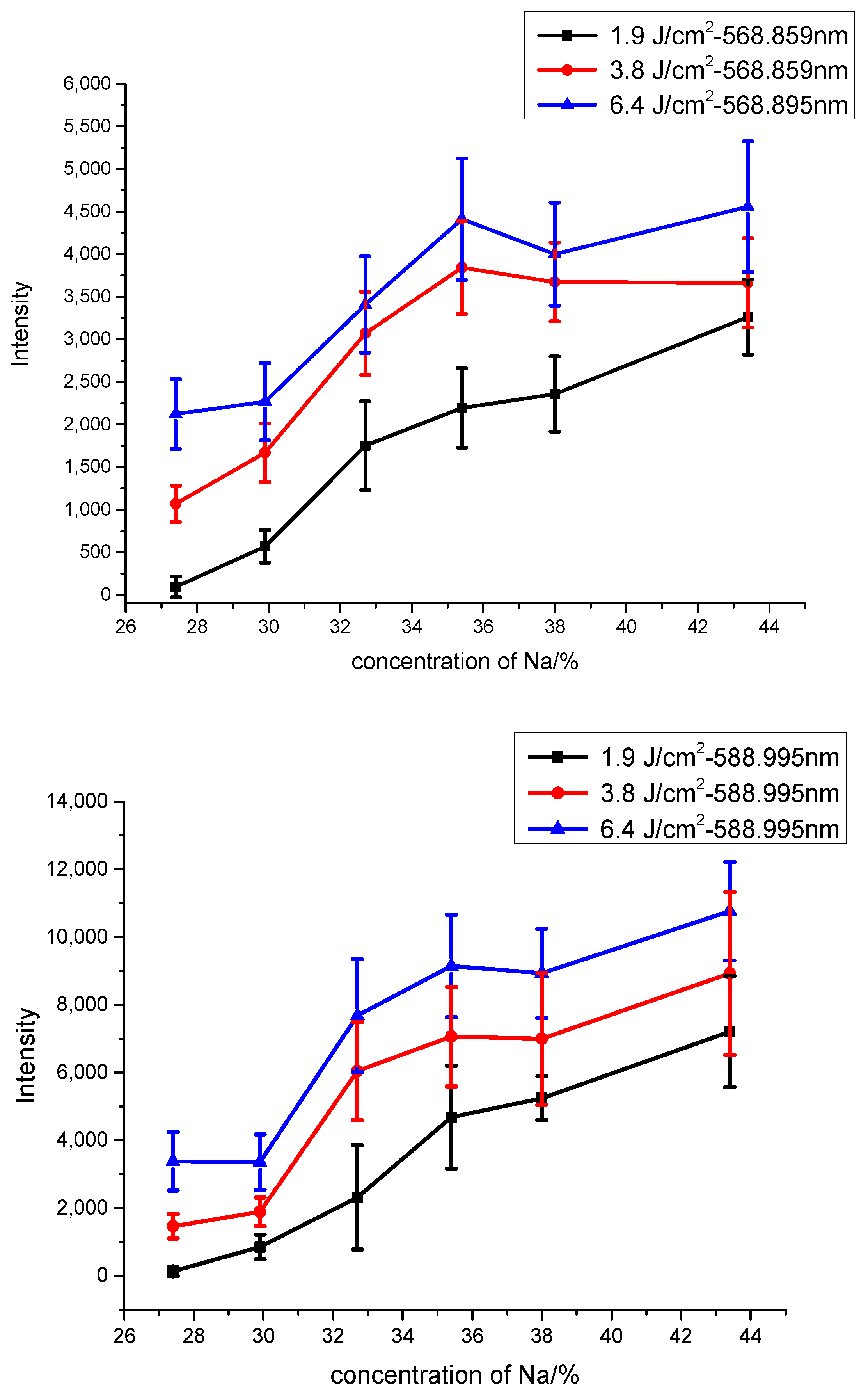
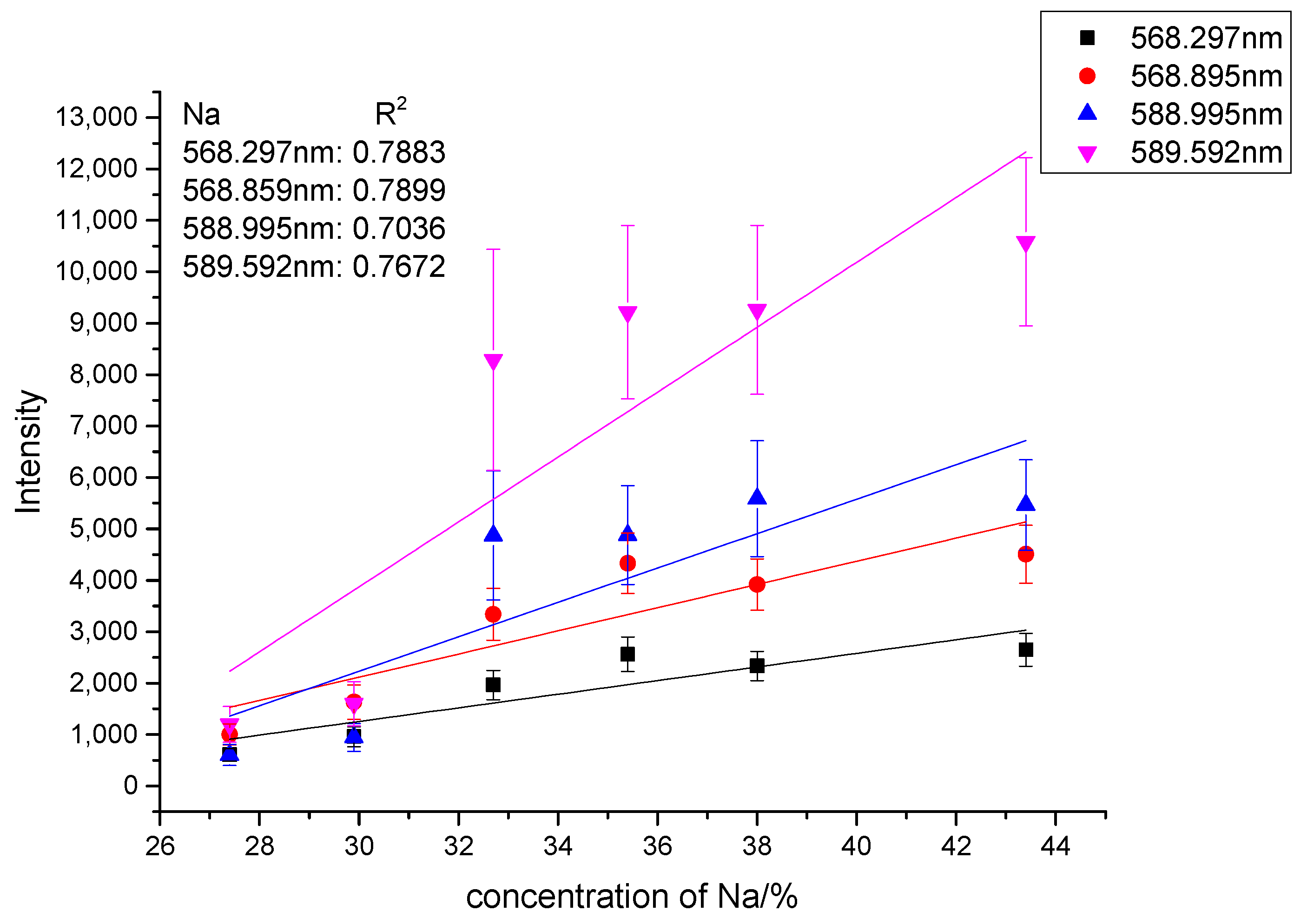
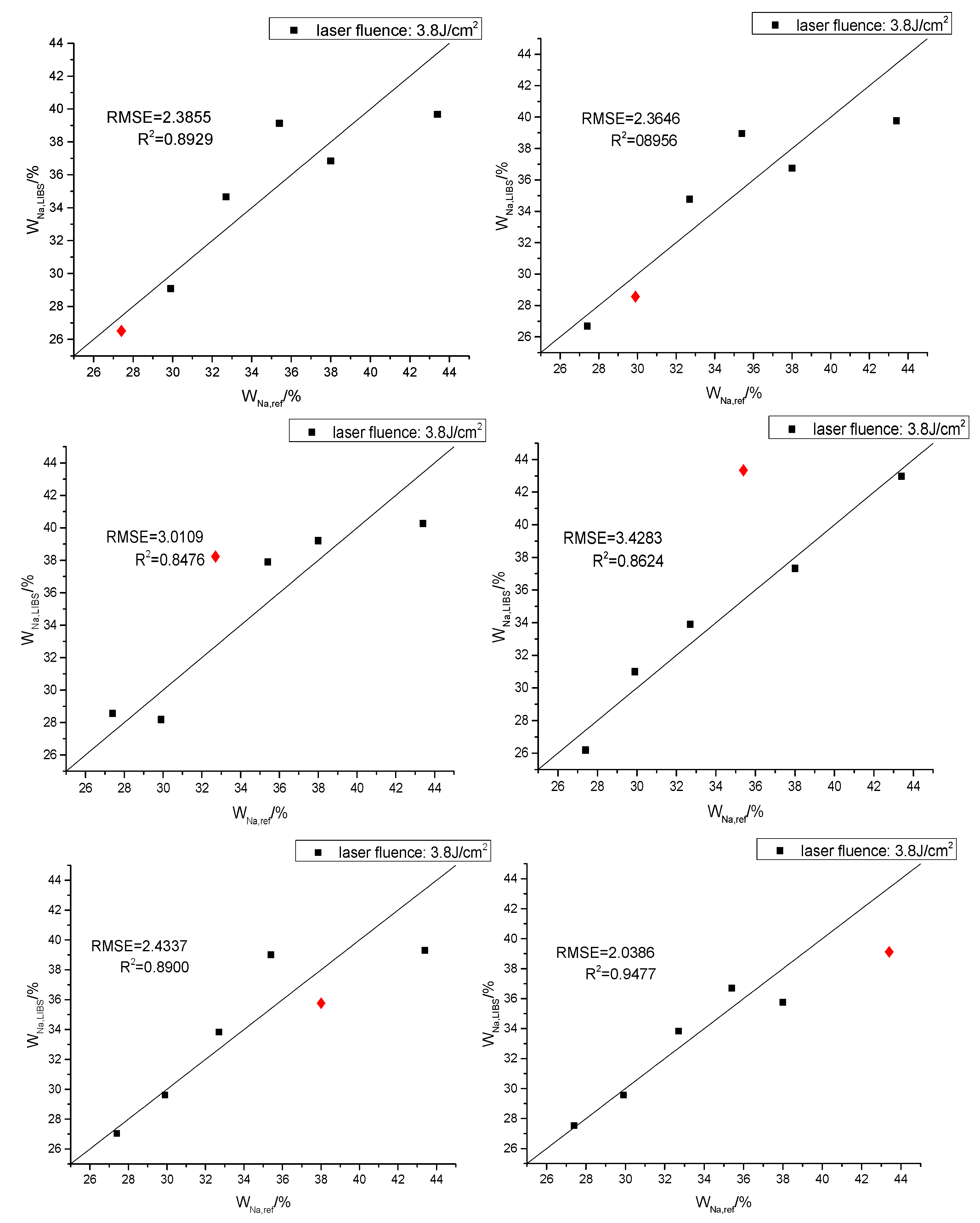
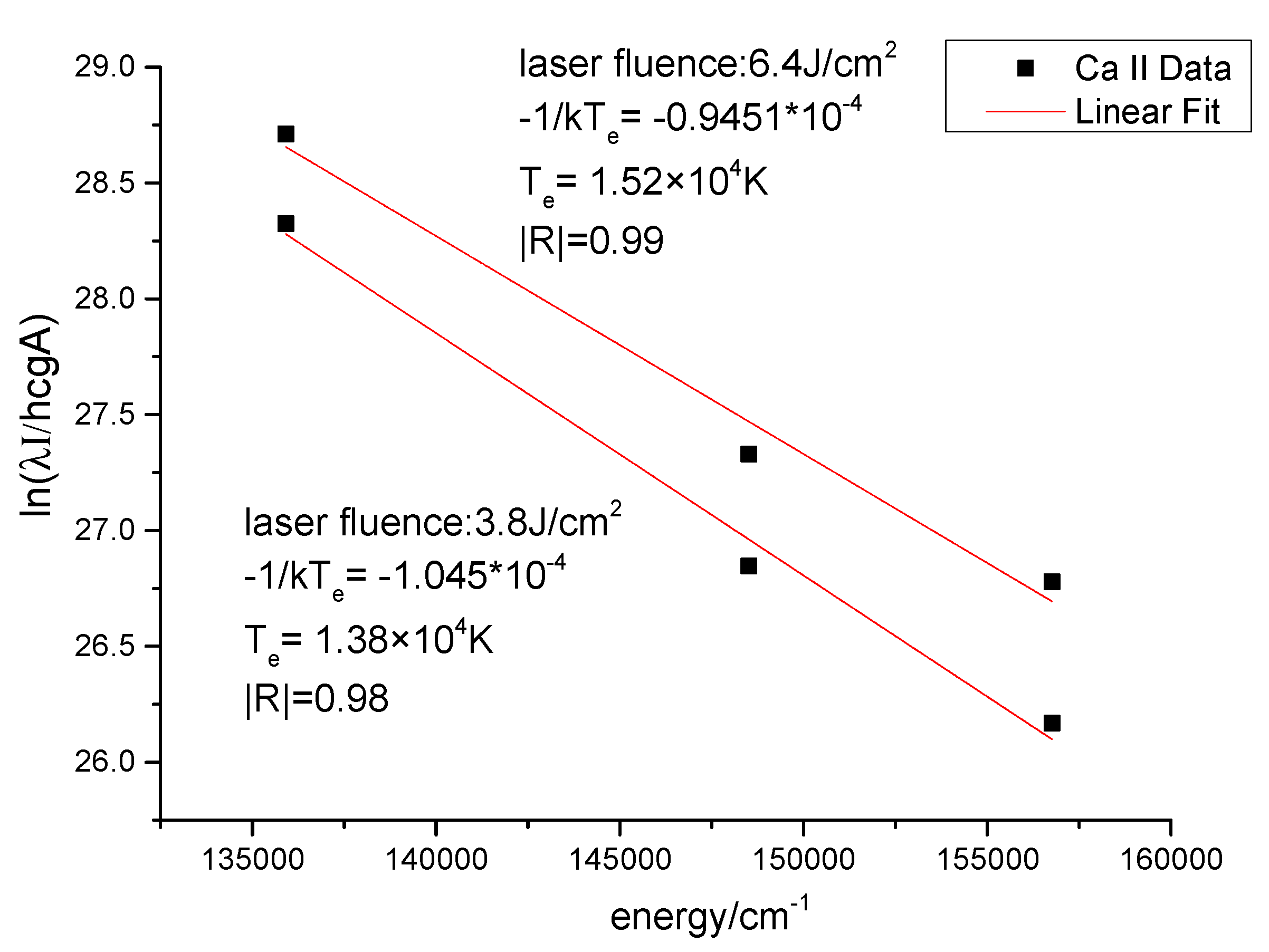
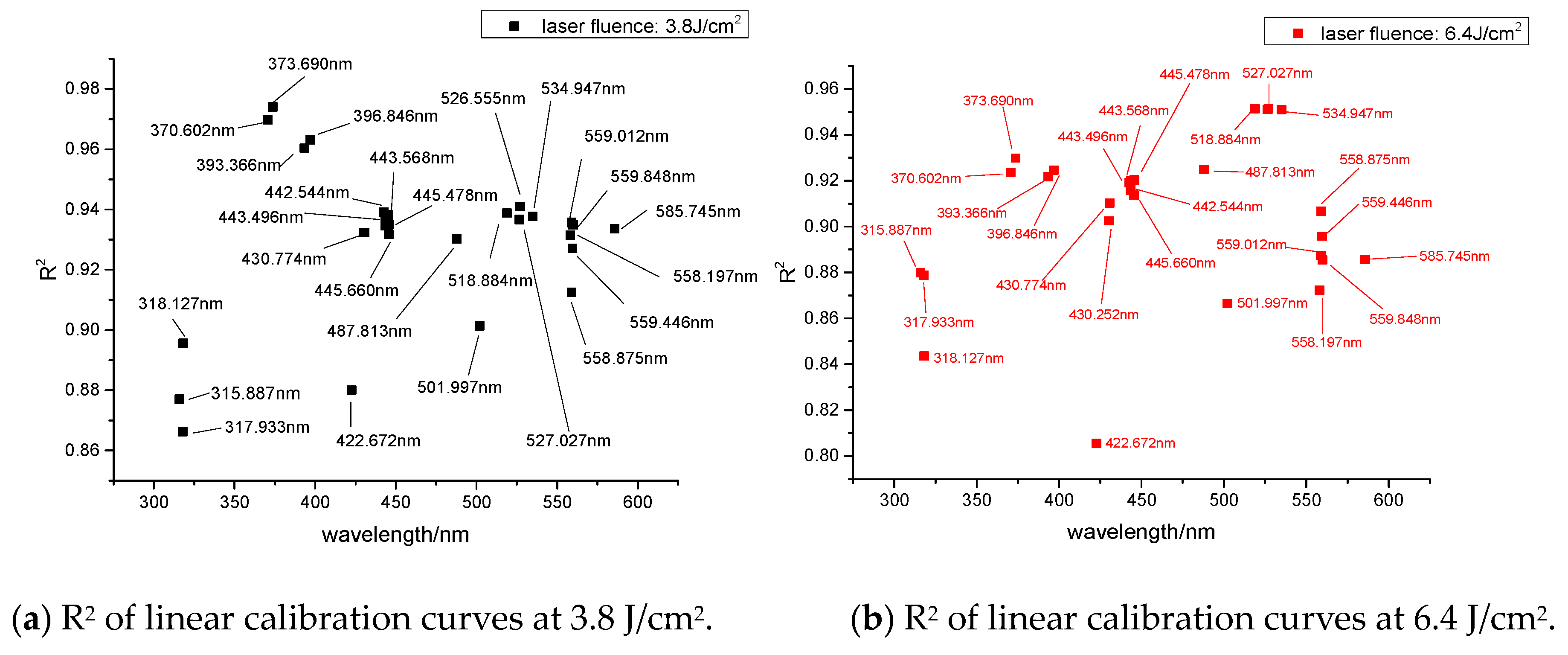
| Sample Number | Na/% | Na2CO3/g | NaHCO3/g | Weight/g | Ratio of Na (Na2CO3:NaHCO3) |
| #1-1 | 27.4 | 0 | 1.500 | 1.5 | 0:1 |
| #1-2 | 29.9 | 0.250 | 1.250 | 1.5 | 0.317:1 |
| #1-3 | 32.7 | 0.500 | 1.000 | 1.5 | 0.792:1 |
| #1-4 | 35.4 | 0.750 | 0.750 | 1.5 | 1.584:1 |
| #1-5 | 38.0 | 1.000 | 0.500 | 1.5 | 3.168:1 |
| #1-6 | 43.4 | 1.5 | 0 | 1.5 | 1:0 |
| Sample Number | Ca/% | CaSO4/g | CaCO3/g | Weight/g | Ratio of Ca (CaSO4:CaCO3) |
| #2-1 | 29.4 | 1.5 | 0 | 1.5 | 1:0 |
| #2-2 | 31.2 | 1.250 | 0.250 | 1.5 | 3.675:1 |
| #2-3 | 32.9 | 1.000 | 0.500 | 1.5 | 1.470:1 |
| #2-4 | 34.7 | 0.750 | 0.750 | 1.5 | 0.735:1 |
| #2-5 | 36.5 | 0.500 | 1.000 | 1.5 | 0.368:1 |
| #2-6 | 40.0 | 0 | 1.500 | 1.5 | 0:1 |
| Element | Na I | Na I | Na I | Na I | Na I |
| Wavelength/nm | 568.263 | 568.859 | 589.592 | 588.995 | 616.075 |
| Element | Ca II | Ca II | Ca II | Ca II | Ca I |
| Wavelength/nm | 315.886 | 317.933 | 393.366 | 396.846 | 422.672 |
| Species | Wavelength/nm | Em/cm−1 | Amn/107s−1 | gm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca II | 392.065 | 148515 | 3.3 | 9 |
| 504.133 | 135910 | 1.6 | 5 | |
| 534.516 | 156767 | 1.1 | 13 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Qin, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, Z. Analysis of Salt Mixture Contamination on Insulators via Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072617
Lu S, Wang X, Wang T, Qin X, Wang X, Jia Z. Analysis of Salt Mixture Contamination on Insulators via Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(7):2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072617
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Shan, Xinwei Wang, Tianzheng Wang, Xinran Qin, Xilin Wang, and Zhidong Jia. 2020. "Analysis of Salt Mixture Contamination on Insulators via Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy" Applied Sciences 10, no. 7: 2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072617
APA StyleLu, S., Wang, X., Wang, T., Qin, X., Wang, X., & Jia, Z. (2020). Analysis of Salt Mixture Contamination on Insulators via Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Applied Sciences, 10(7), 2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072617





