Blockchain-Based Secure Data Storage for Distributed Vehicular Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Problem Statement
1.3. Contributions
- we proposed a blockchain-based VN for reliable data sharing between resource constrained ordinary nodes,
- to store the huge data generated by smart vehicles, a distributed file system, i.e., IPFS is used,
- all the transactions are automated and the reviews are checked using smart contracts,
- Proof of Work (PoW) is replaced with Proof of Authority (PoA) to reduce latency and increase throughput of the system,
- cryptocurrency based incentive mechanism is proposed for edge vehicle nodes. If a valid service is provided by an edge vehicle node, then it is awarded with some incentive,
- caching technique is introduced in edge vehicle nodes to optimize the cost of the proposed system,
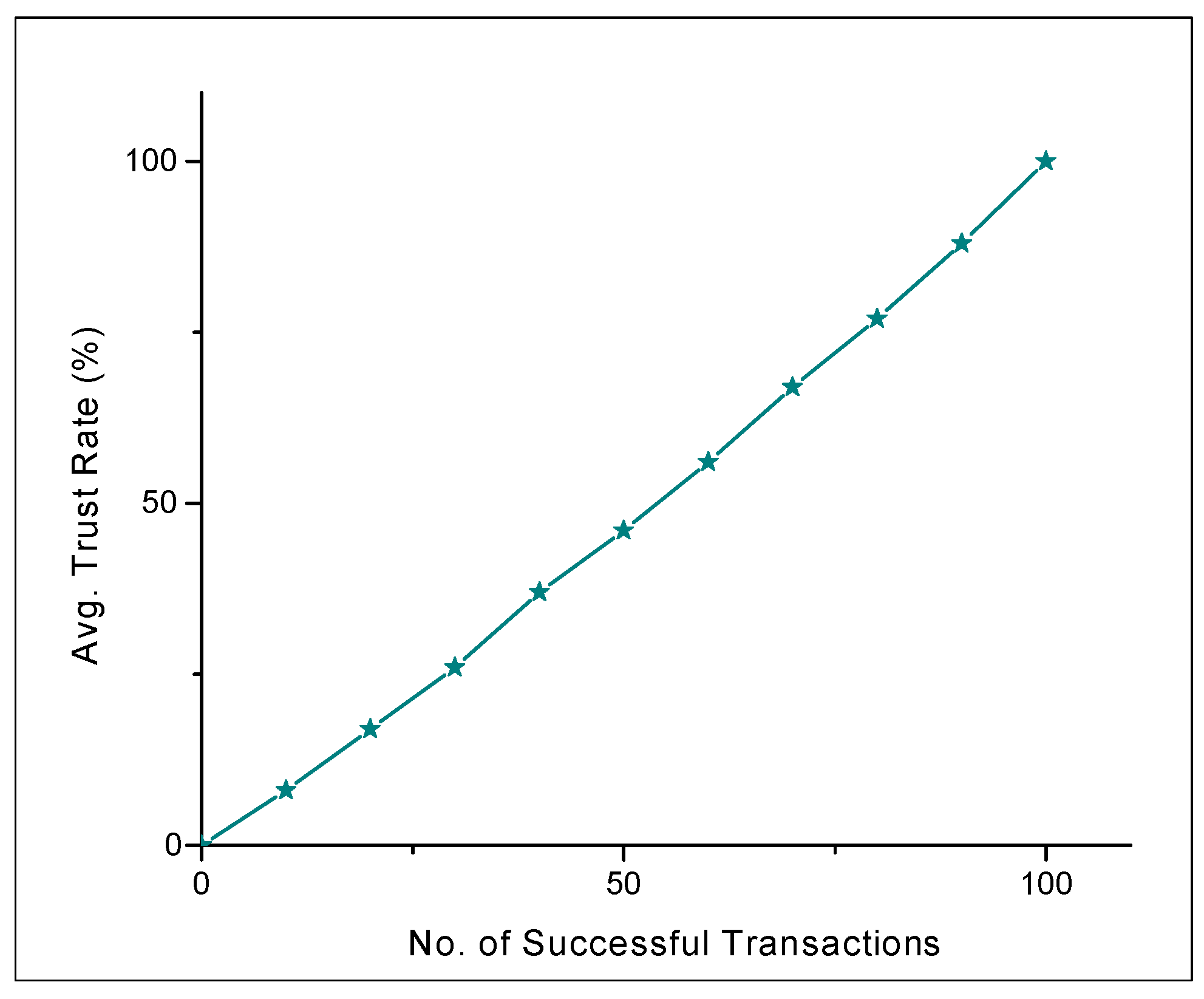
- Intelligent Vehicle Trust Point (IVTP) is introduced to calculate the trust values of ordinary vehicle nodes and
- to share data in a secure manner, a cryptographic mechanism: symmetric key encryption/decryption, is used.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Blockchain in IoT
2.2. Blockchain in Healthcare
2.3. Blockchain in Wireless Sensor Network (WSN)
3. Proposed System Model
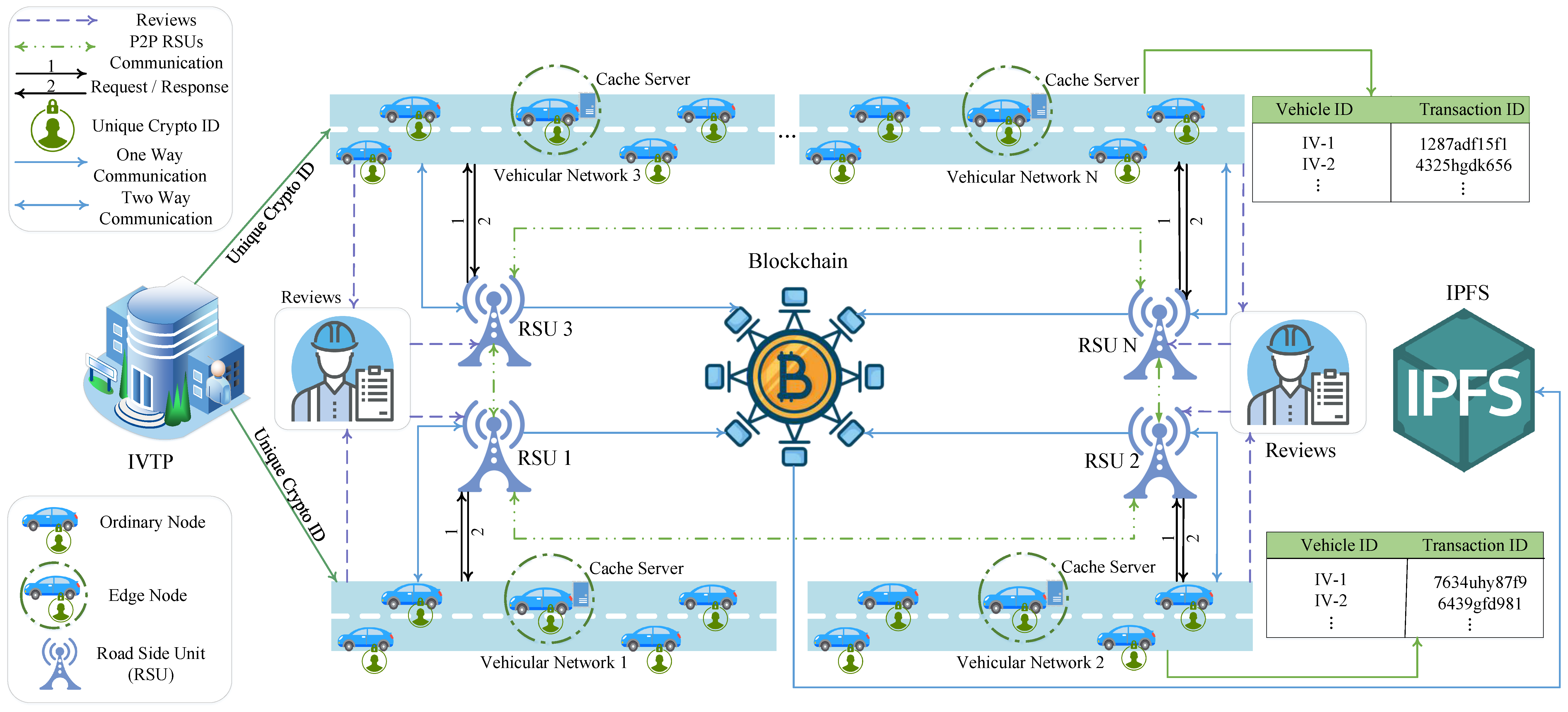
3.1. Architecture Overview
3.2. Edge Node Model Overview
3.3. Incentive Mechanism in VN
| Algorithm 1: Algorithm of Service and Incentive Provisioning in VN. |
 |
3.4. RSU Overview
3.5. Authentication of VN
3.6. Caching and IPFS
3.7. Workflow of Proposed System
| Algorithm 2: Algorithm of Data Storage in IPFS. |
 |
4. Simulations and Results
4.1. Simulation Environment
4.1.1. Remix Integrated Development Environment (Remix IDE)
4.1.2. Ganache
4.1.3. MetaMask
4.1.4. System Specification
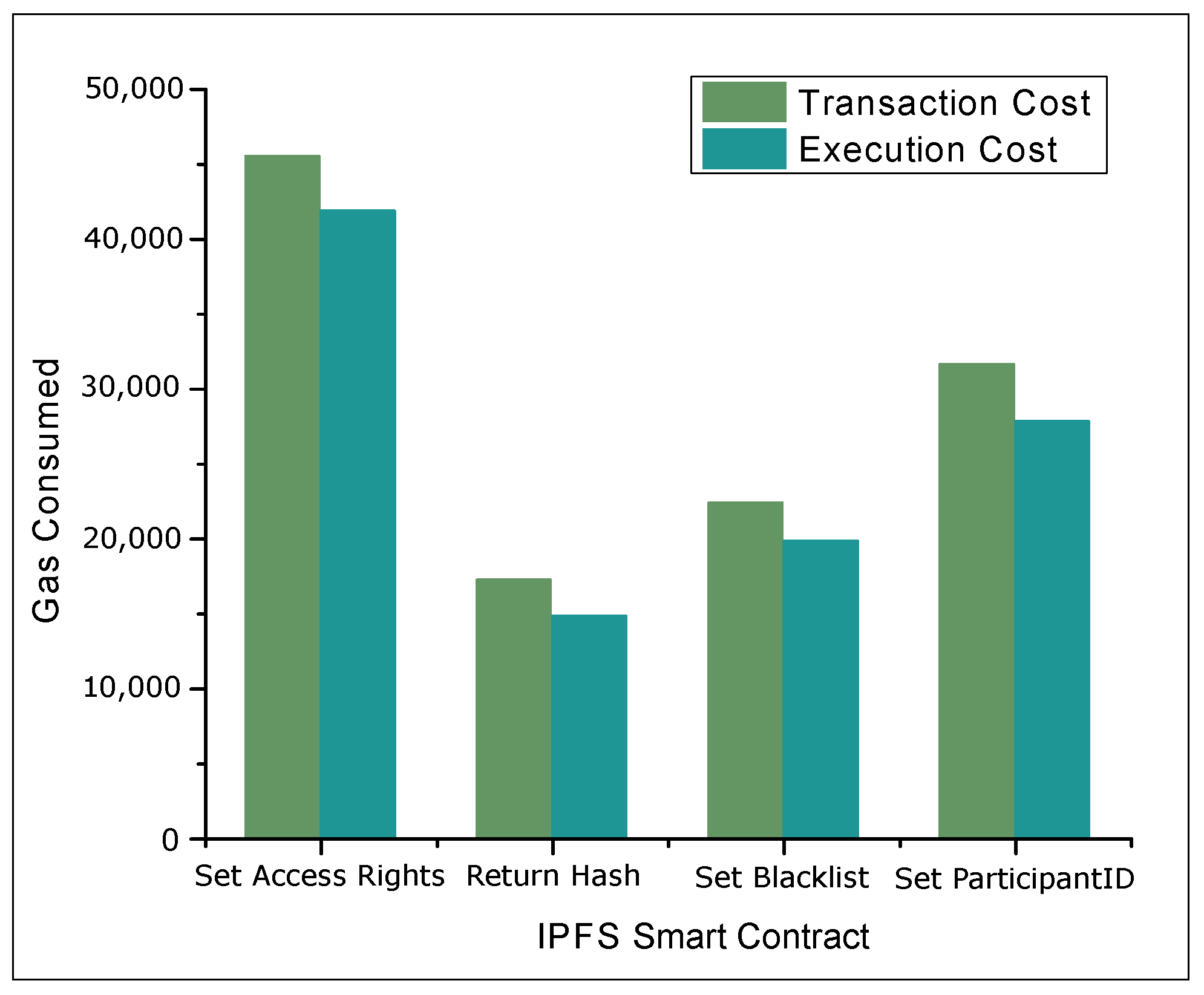
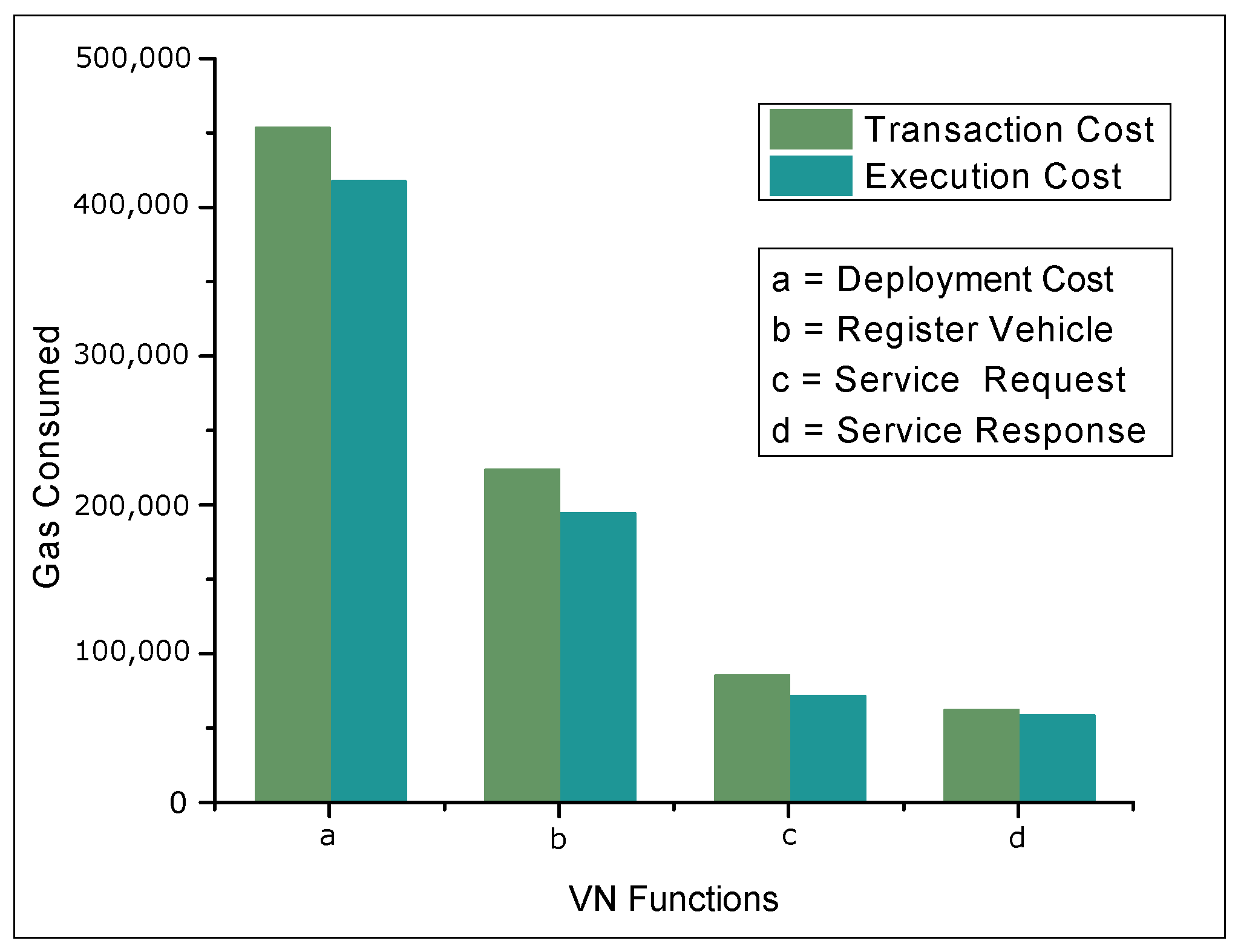
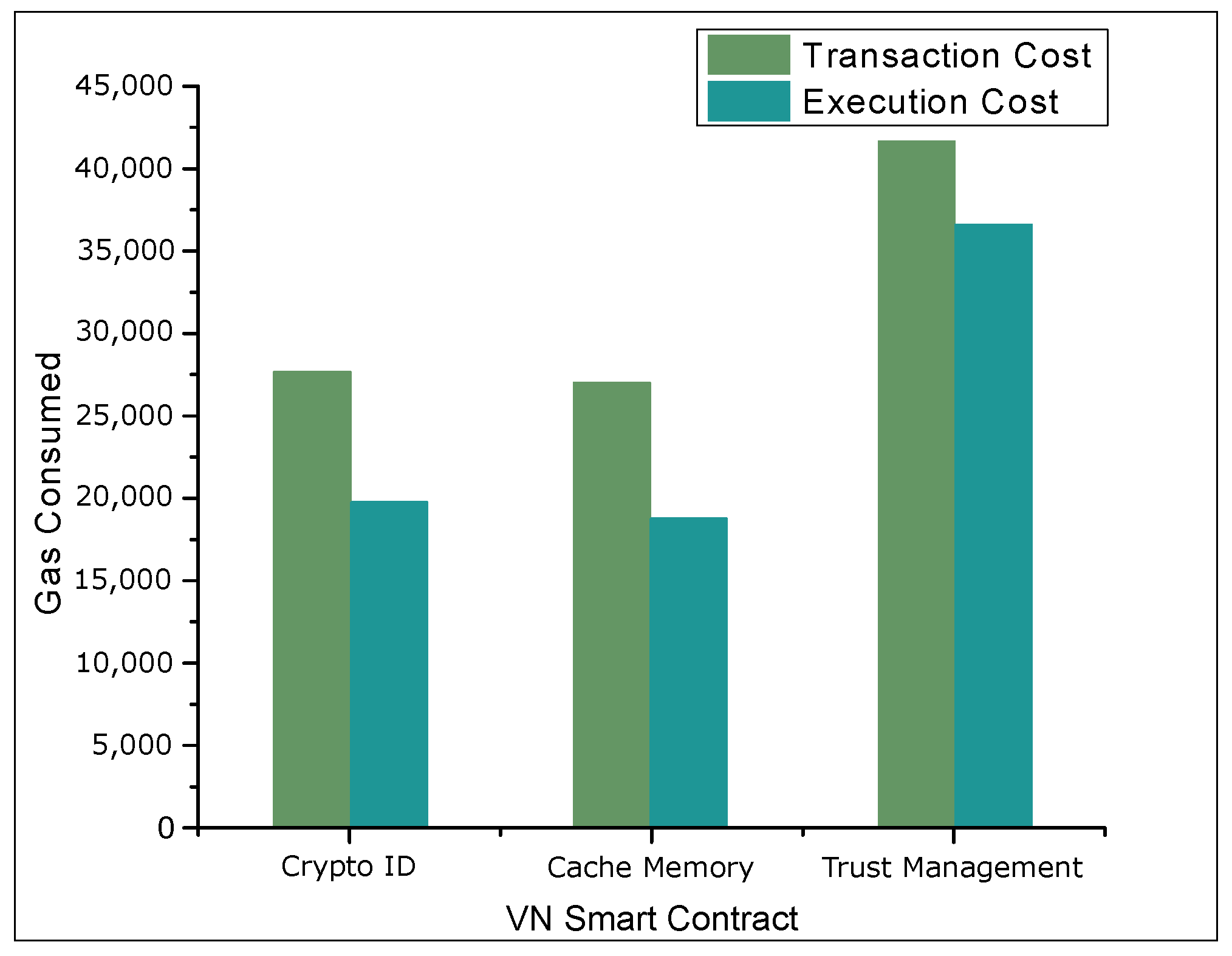
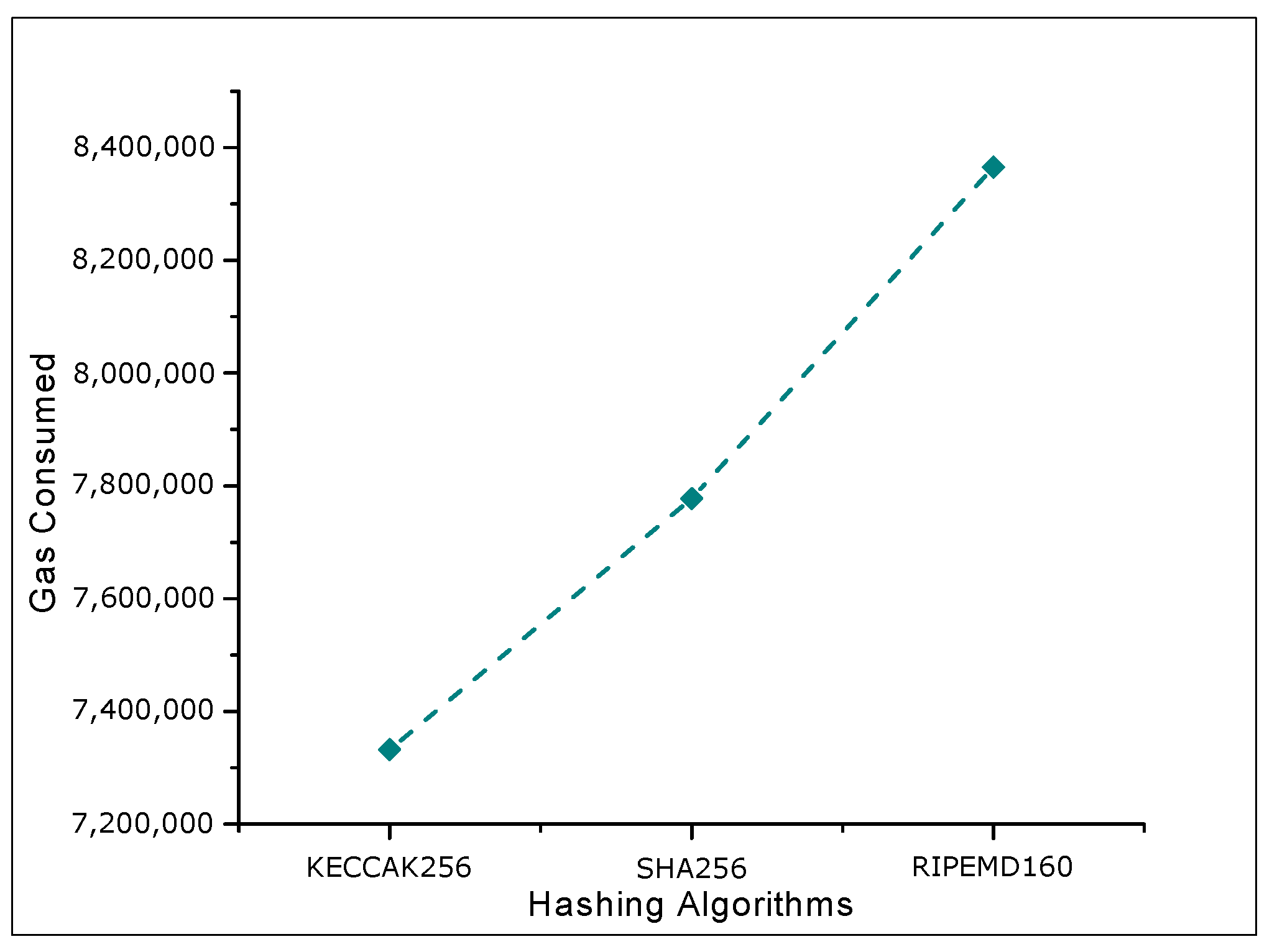
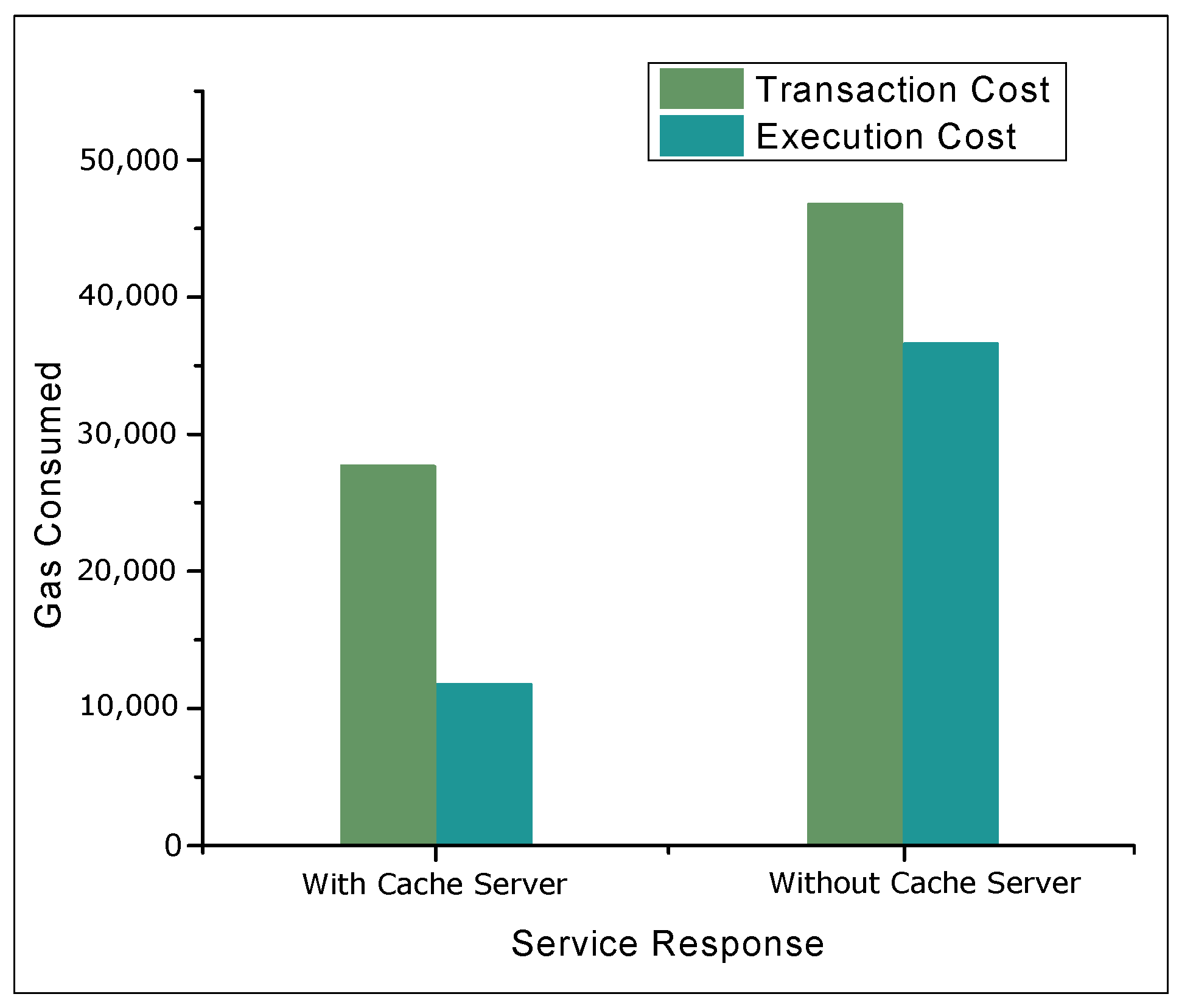
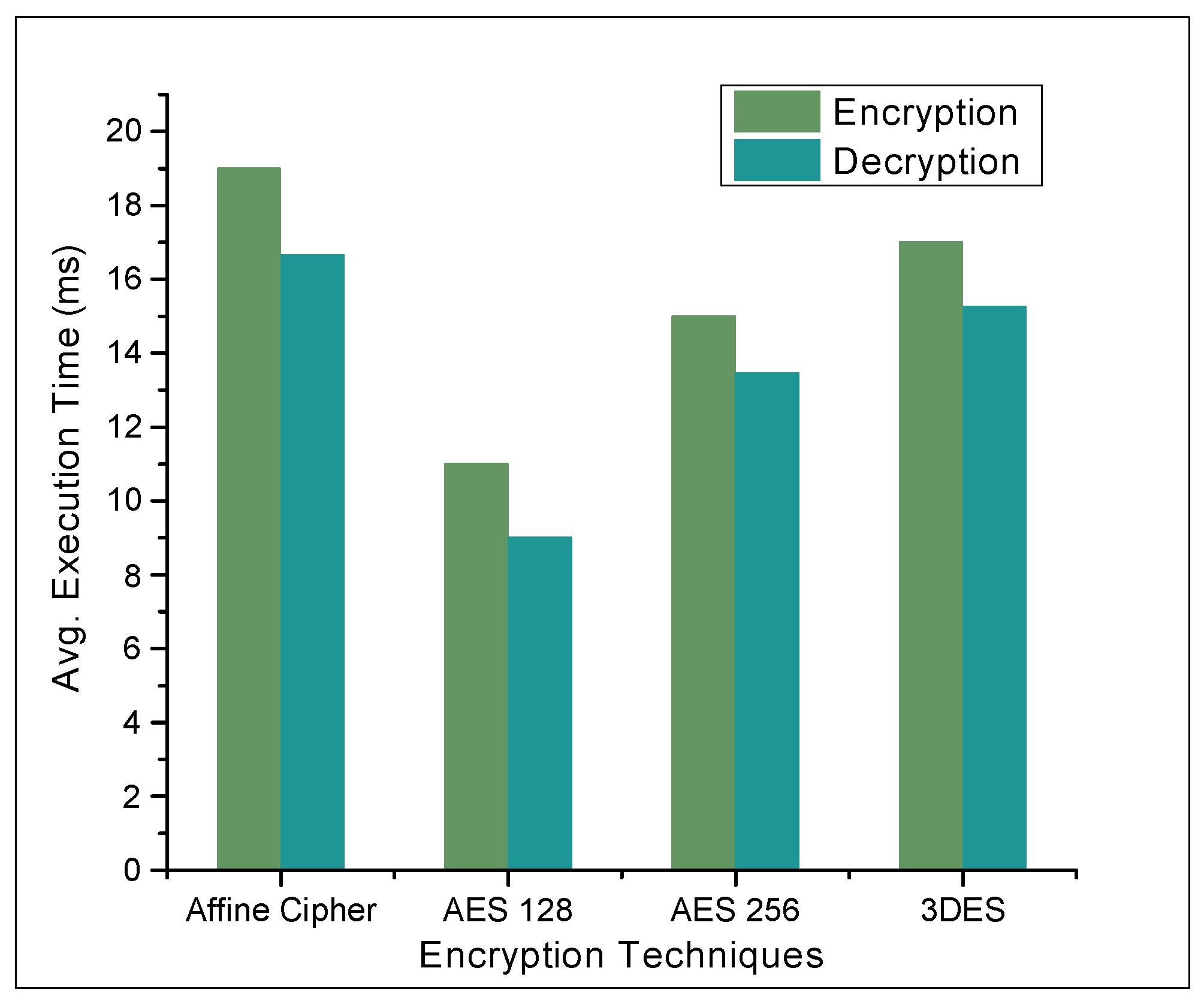
4.2. Results and Discussions
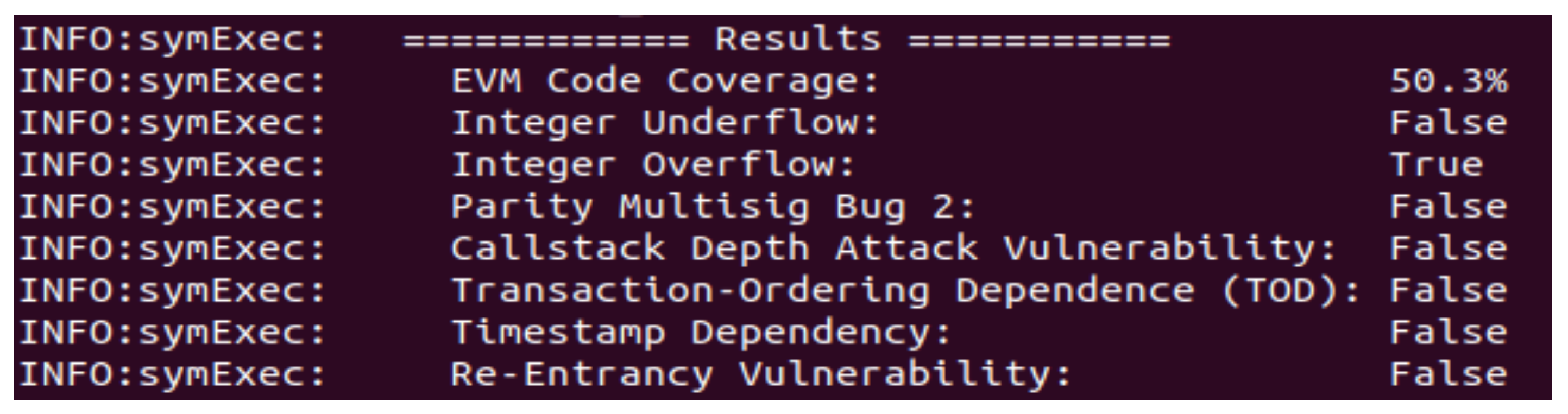
4.3. Security Analysis of the Proposed System
4.4. Attacker Model
4.4.1. Forgery Attack
4.4.2. Man-in-the-Middle Attack
4.4.3. Identity Revealing Attack
4.5. Propositions
4.6. Security Features of Proposed System
4.6.1. Data Integrity
4.6.2. Privacy Preservation
4.6.3. Data Confidentiality
4.6.4. Single Point of Failure
4.6.5. Availability
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABE | Attribute Based Encryption |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CSI | Channel State Information |
| DAC | Distributed Autonomous Corporation |
| D2D | Device to Device |
| DApps | Decentralized Applications |
| E-health | Electronic health |
| EMR | Electronic Medical Record |
| IDE | Integrated Development Environment |
| IPFS | Interplanetary File System |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| IoV | Internet of Vehicles |
| IVTP | Intelligent Vehicle Trust Point |
| IV | Intelligent Vehicle |
| IDE | Integrated Development Environment |
| PDP | Provable Data Possession |
| PoA | Proof of Authority |
| PoW | Proof of Work |
| P2P | Peer to Peer |
| P2M | Person to Machine |
| PHI | Personal Health Information |
| SDN | Software Defined Networking |
| WSN | Wireless Sensor Network |
| V2R | Vehicle to Road Side Unit |
| V2V | Vehicle to Vehicle |
| VN | Vehicular Network |
References
- Hartenstein, H.; Laberteaux, K. VANET: Vehicular Applications and Inter-Networking Technologies; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2010; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Allied Market Research. Autonomous Vehicle Market by Level of Automation. 2018. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/autonomous-vehicle-market (accessed on 18 November 2019).
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. 2018. Available online: Https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2019).
- Rehman, M.; Javaid, N.; Awais, M.; Imran, M.; Naseer, N. Cloud based Secure Service Providing for IoTs using Blockchain. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBCOM 2019), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 9–13 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, O.; Javaid, N.; Awais, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Imran, M.; Guizani, M. A Blockchain Model for Fair Data Sharing in Deregulated Smart Grids. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 9–13 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, M.; Khan, Z.A.; Javed, M.U.; Zohaib, M.; Iftikhar, U.M.; Bux, I.; Javaid, N. A blockchain-based distributed vehicular network architecture for smart cities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications, Caserta, CE, Italy, 15–17 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.K.; Moon, S.Y.; Park, J.H. Block-VN: A distributed blockchain-based vehicular network architecture in smart City. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 13, 184–195. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, T.; Almogren, A.; Akbar, M.; Zuair, M.; Ullah, I.; Javaid, N. Data Sharing System Integrating Access Control Mechanism using Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts for IoT Devices. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, J.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C. Towards secure network computing services for lightweight clients using blockchain. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Park, J.H. Blockchain-based hybrid network architecture for the smart city. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 86, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Tao, M.; Zhang, J.; Hong, X.; Yuan, R. Blockchain-based credibility verification method for IoT entities. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. A blockchain-based framework for data sharing with fine-grained access control in decentralized storage systems. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 38437–38450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Cao, J.; Li, C.; Fan, K.; Li, H. A Novel Attribute-Based Access Control Scheme Using Blockchain for IoT. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 38431–38441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Hui, P.; Jin, D. Blockchain-based data sharing system for ai-powered network operations. J. Commun. Inf. Netw. 2018, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wen, J. The IoT electric business model: Using blockchain technology for the internet of things. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2017, 10, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kim, S. Branch based blockchain technology in intelligent vehicle. Comput. Netw. 2018, 145, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Fang, H.; Wang, H. Blockchain-based internet of vehicles: Distributed network architecture and performance analysis. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 4640–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, K.; Lei, L.; Zheng, K.; Leung, V.C. Blockchain-based decentralized trust management in vehicular networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, T.A.; Ali, I.; Javaid, N.; Shafiq, M. Secure Service Provisioning Scheme for Lightweight IoT Devices with a Fair Payment System and an Incentive Mechanism based on Blockchain. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Lin, X. Towards secure and privacy-preserving data sharing in e-health systems via consortium blockchain. J. Med. Syst. 2018, 42, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ji, S.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Wang, J. Incentive mechanism of data storage based on blockchain for wireless sensor networks. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushch, S.; Prieto-Castrillo, F. A rolling blockchain for a dynamic WSNs in a smart city. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.11399. [Google Scholar]
- Di, L.; Tang, Y. Blockchain consensus based user access strategies in D2D networks for data-intensive applications. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 72683–72690. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Song, W.S.; Gim, G.Y. An empirical analysis on medical information sharing model based on blockchain. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Res. 2019, 9, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Du, J. Electronic medical record security sharing model based on blockchain. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Cryptography, Security and Privacy, Kuala Lampur, Malaysia, 19–21 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, A.D.; Srivastava, G.; Dhar, S.; Singh, R. A decentralized privacy-preserving healthcare blockchain for iot. Sensors 2019, 19, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.; Al-zahrani, F.A.; Khalid, R.; Javaid, N.; Qamar, A.M.; Afzal, M.K.; Shafiq, M. A secure data sharing platform using blockchain and interplanetary file system. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, W. Ethereum: A secure decentralised generalised transaction ledger. Ethereum Proj. Yellow Pap. 2014, 151, 1–32. [Google Scholar]

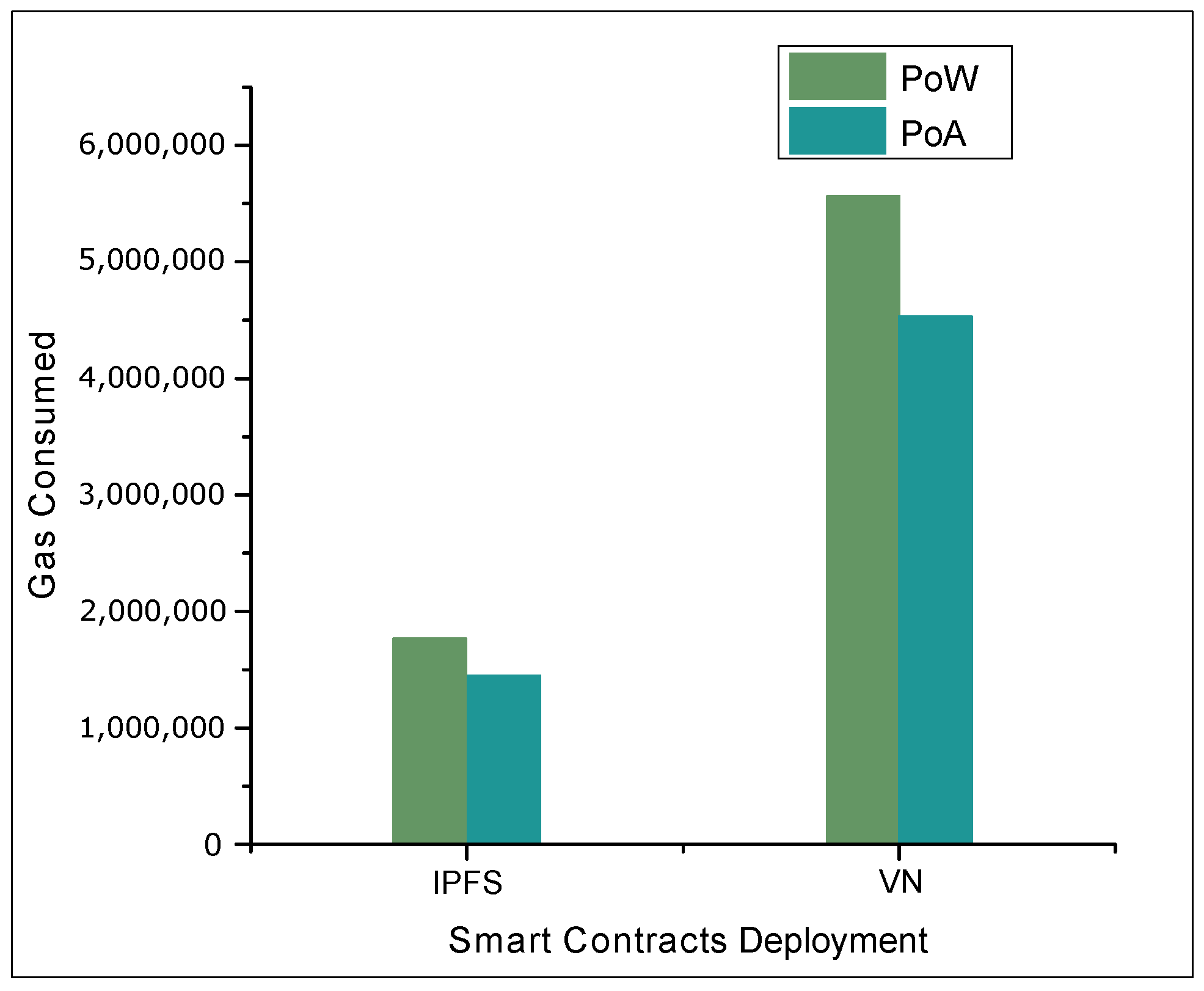

| Domain | Problem Identified | Proposed Solution | Technique | Results | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VN [7] | Insecure communication in large scale VN | Vehicular ad-hoc network for scalable VN | Not explicit | Scalability of the system is achieved | Limited resource sharing scenario |
| IoT [9] | Insecure service provisioning for IoT | Secure service provisioning mechanism | Blockchain with PoA consensus algorithm | Secure service provisioning achieved | Service charging is not considered |
| IoT [10] | Optimization of the system performance | Blockchain-based hybrid network architecture | Hybrid architecture with Argon2 based PoW | Reduction in computational time | Efficient deployment of edge node is not considered |
| IoT [11] | Credibility verification in IoT | Blockchain-based credibility verification method | Self organization blockchain structure | Response time and storage capacity are optimized | Complete decentralization is not achieved |
| IoT [12] | Authentication of IoT | Attribute based access control mechanism | Blockchain-based access control mechanism | Secure access control policies achieved | Users attribute revocation is not considered |
| IoT [13] | Security and authentication | Decentralized access control mechanism | Blockchain and Attribute based access control | Scalability and robustness achieved | No real-time scenario is considered |
| IoT [14] | Secure data sharing scenario | Efficient access control and permission levels | Data chain and behaviour chain is used for data sharing | Security and privacy preserving data sharing systems | Proposed system is designed only for a single system |
| IoT [15] | Third party involvement | DAC | Blockchain with e-trading system | Secure trading environment | Designed only for two commodities |
| IV [16] | Authentication and trust of vehicles | Dynamic traffic rates | IVTP | Large number of vehicles are handled | Temporal complexity faced |
| IoV [17] | Real-time response in V2V communication | Blockchain-based VN | Blockchain with PoW | Storage capacity is optimized | No real-time traffic conditions are considered |
| VN [18] | Trust management system for VN | Bayesian inference model | Blockchain with PoW | Trust value is calculated | Privacy preservation is not considered |
| IoT [19] | Computational power of lightweight clients | Fair payment scheme with secure service provisioning | Blockchain with PoA | Service provisioning cost is reduced | No security check on lightweight clients and service providers |
| Healthcare [20] | Security of the medical data | E-health management system | Blockchain with PoW | Scalability is achieved | Proposed system is designed for a limited scenario |
| WSN [21] | Optimizing data storage in wireless nodes | Incentive mechanism for data storage | Blockchain with PDP | Data storage capacity is optimized | Two blockchains are used |
| WSN [22] | Data storage and computational complexity | Rolling blockchain concept | PoW is not used | Secure data storage achieved | No security analysis done |
| Cellular network [23] | Authentication of CSI | Blockchain-based data intensive system | Blockchain for cellular network | Spectra efficiency is improved | Only handles non-cooperative mobile users |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javed, M.U.; Rehman, M.; Javaid, N.; Aldegheishem, A.; Alrajeh, N.; Tahir, M. Blockchain-Based Secure Data Storage for Distributed Vehicular Networks. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062011
Javed MU, Rehman M, Javaid N, Aldegheishem A, Alrajeh N, Tahir M. Blockchain-Based Secure Data Storage for Distributed Vehicular Networks. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(6):2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062011
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaved, Muhammad Umar, Mubariz Rehman, Nadeem Javaid, Abdulaziz Aldegheishem, Nabil Alrajeh, and Muhammad Tahir. 2020. "Blockchain-Based Secure Data Storage for Distributed Vehicular Networks" Applied Sciences 10, no. 6: 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062011
APA StyleJaved, M. U., Rehman, M., Javaid, N., Aldegheishem, A., Alrajeh, N., & Tahir, M. (2020). Blockchain-Based Secure Data Storage for Distributed Vehicular Networks. Applied Sciences, 10(6), 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062011






