Source Separation Using Dilated Time-Frequency DenseNet for Music Identification in Broadcast Contents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Baseline
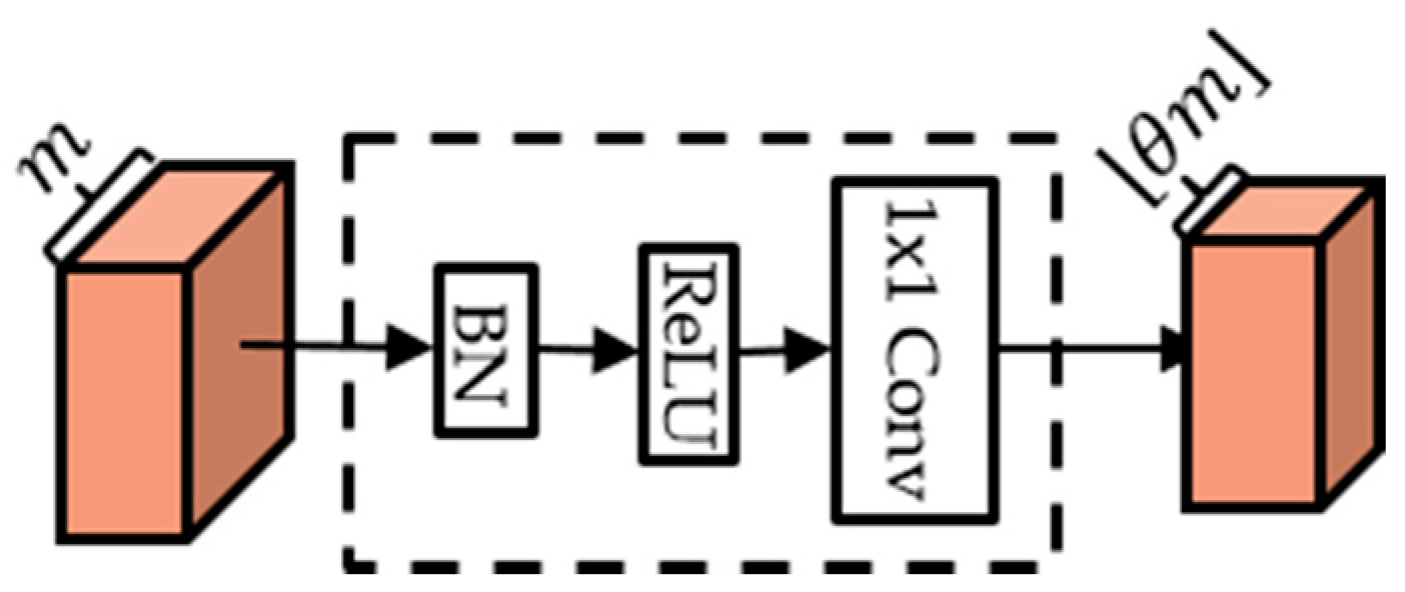
2.1. DenseNet
2.2. Multi-Scale DenseNet for Audio Source Separation
3. Proposed Architecture for Source Separation
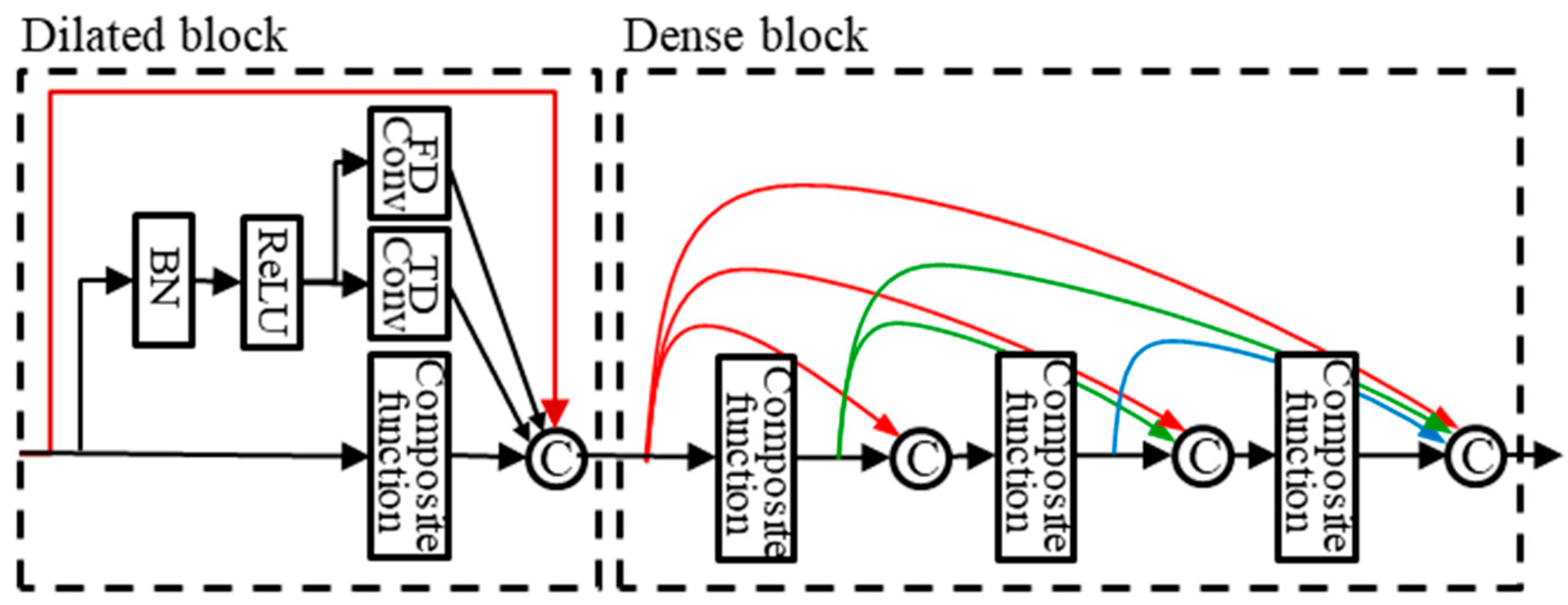
3.1. Multi-Band Block
3.2. Dilated Dense Block
3.3. Dropout
3.4. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Singing Voice-Separation Experiment
4.1.1. Dataset
4.1.2. Setup
4.1.3. Separation Results
4.2. Music Identification Experiment
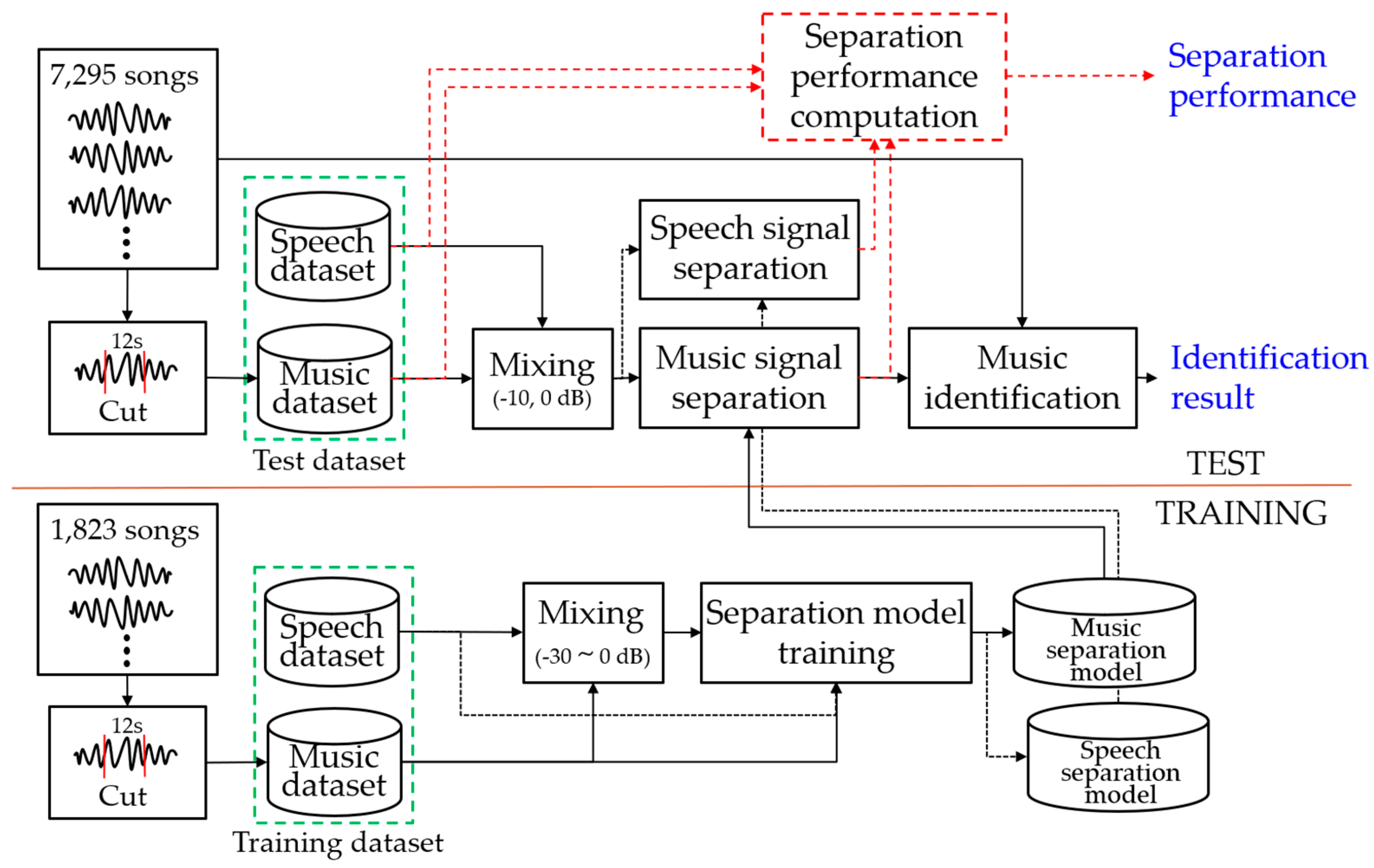
4.2.1. Dataset
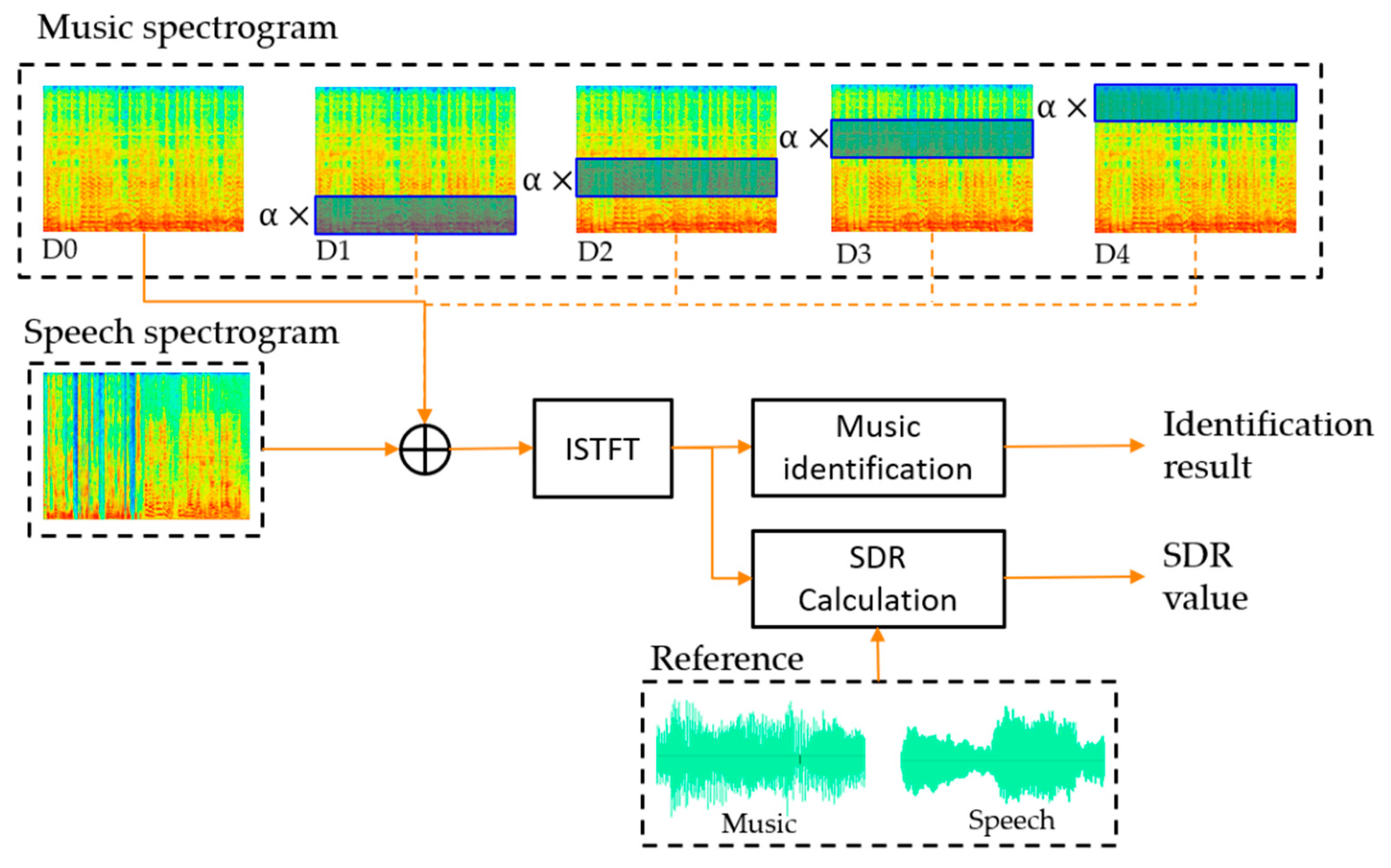
4.2.2. Mixing
4.2.3. Setup
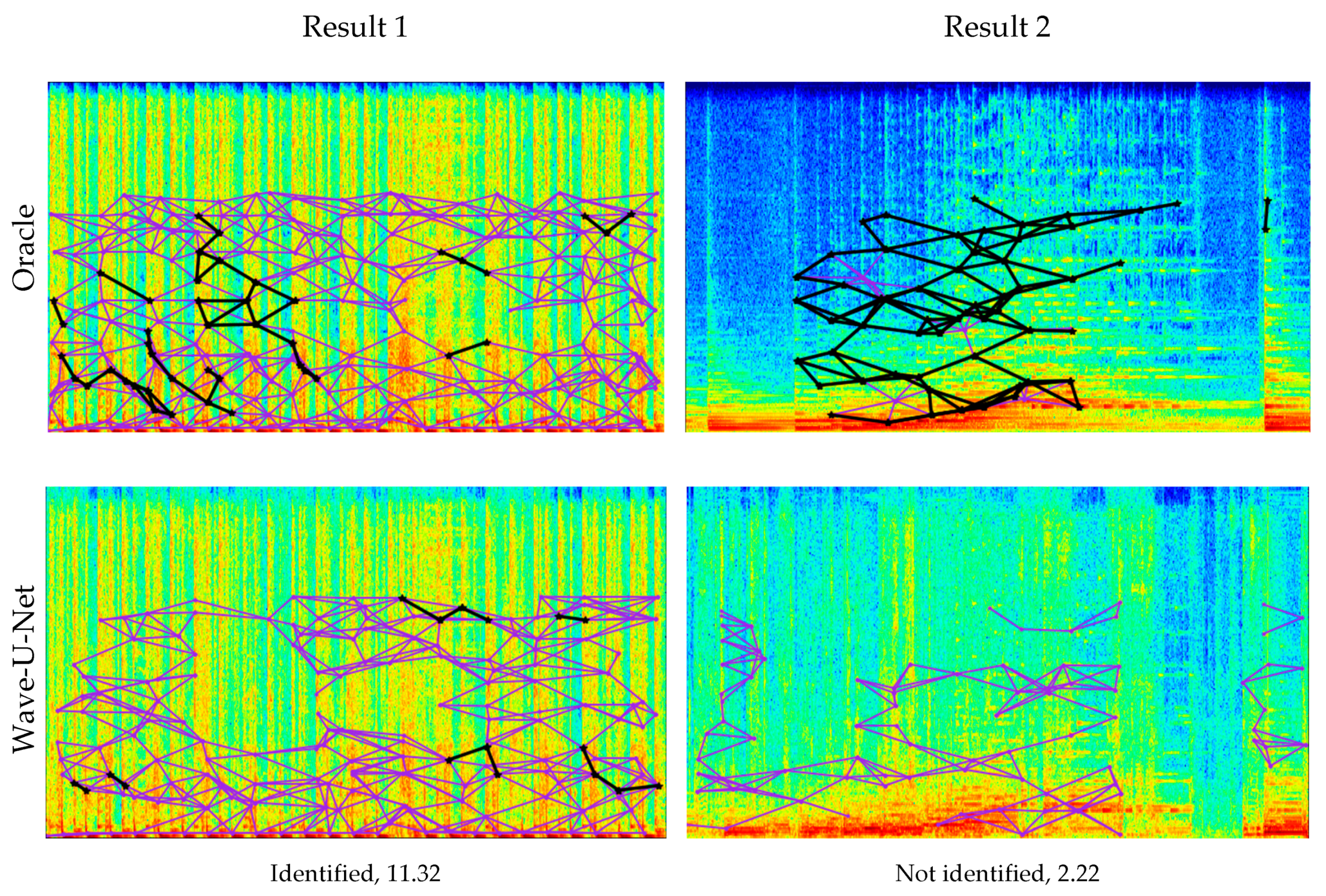
4.2.4. Music Identification Results
4.2.5. Signal-to-Distortion Ratio (SDR) Comparison of Distortion in the Spectrogram Frequency Band
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Layers | Parameter | Output Size |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-band 1 (, ) | 33, 27 | 51212827 |
| Dilated Dense 1 (, , ) | 12, 4, 0 | 512128111 |
| Compression ( | 0.25 | 51212827 |
| Down-sampling | 22 average pooling | 2566427 |
| Dilated Dense 2 (, , ) | 12, 4, 0 | 25664111 |
| Compression ( | 0.25 | 2566427 |
| Down-sampling | 22 average pooling | 1283227 |
| Dilated Dense 3 (, , ) | 12, 4, 0 | 12832111 |
| Compression ( | 0.25 | 1283227 |
| Down-sampling | 22 average pooling | 641627 |
| Dilated Dense 4 (, , ) | 12, 4, 0 | 6416111 |
| Compression ( | 0.25 | 641627 |
| Up-sampling | 22 transposed convolution | 1283227 |
| Concatenate | Dilated Dense 3 | 1283254 |
| Dilated Dense 5 (, , ) | 12, 4, 0.2 | 12832138 |
| Compression ( | 0.25 | 1283234 |
| Up-sampling | 22 transposed convolution | 2566434 |
| Concatenate | Dilated Dense 2 | 2566461 |
| Dilated Dense 6 (, , ) | 12, 4, 0.2 | 25664145 |
| Compression ( | 0.25 | 2566436 |
| Up-sampling | 22 transposed convolution | 51212836 |
| Concatenate | Dilated Dense 1 | 51212863 |
| Dilated Dense 7 (, , ) | 12, 4, 0.2 | 512128147 |
| Compression ( | 0.25 | 51212836 |
| Dilated Dense 8 (, , ) | 4, 2, 0.2 | 51212844 |
| Compression ( | 0.25 | 51212811 |
| Multi-band 2 (, ) | 33, 9 | 5121289 |
| BN-ReLU | - | (same) |
| Conv (, ) | 33, 1 | 5121281 |
| ReLU | - | (same) |
References
- Vincent, E.; Bertin, N.; Gribonval, R.; Bimbot, F. From blind to guided audio source separation: How models and side information can improve the separation of sound. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2014, 31, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvärinen, A.; Oja, E. Independent component analysis: Algorithms and applications. Neural Netw. 2000, 13, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.D.; Seung, H.S. Algorithms for non-negative matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–8 December 2001; pp. 556–562. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev, P.; Theis, F.; Cichocki, A. Sparse component analysis and blind source separation of underdetermined mixtures. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2005, 16, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, A.J.; Roma, G.; Plumbley, M.D. Deep karaoke: Extracting vocals from musical mixtures using a convolutional deep neural network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Latent Variable Analysis and Signal Separation (LVA/ICA), Liberec, Czech Republic, 25–28 August 2015; pp. 429–436. [Google Scholar]
- Grais, E.; Sen, M.; Erdogan, H. Deep neural networks for single channel source separation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 3734–3738. [Google Scholar]
- Nugraha, A.A.; Liutkus, A.; Vincent, E. Multichannel music separation with deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Budapest, Hungary, 29 August–2 September 2015; pp. 1748–1752. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlich, S.; Giron, F.; Mitsufuji, Y. Deep neural network based instrument extraction from music. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brisbane, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; pp. 2135–2139. [Google Scholar]
- Le Roux, J.; Hershey, J.; Weninger, F. Deep NMF for speech separation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brisbane, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; pp. 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Sawada, H.; Mukai, R.; Araki, S.; Makino, S. A robust and precise method for solving the permutation problem of frequency-domain blind source separation. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2004, 12, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-S.; Kim, M.; Hasegawa-Johnson, M.; Smaragdis, P. Deep learning for monaural speech separation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 1562–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlich, S.; Porcu, M.; Giron, F.; Enenkl, M.; Kemp, T.; Takahashi, N.; Mitsufuji, Y. Improving music source separation based on deep neural networks through data augmentation and network blending. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 261–265. [Google Scholar]
- Jansson, A.; Humphrey, E.; Montecchio, N.; Bittner, R.; Kumar, A.; Weyde, T. Singing voice separation with deep U-Net convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), Montreal, MT, Canada, 4–8 November 2017; pp. 745–751. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Kim, T.; Lee, K.; Kwak, N. Music source separation using stacked hourglass networks. In Proceedings of the International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), Paris, France, 23–27 September 2018; pp. 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, N.; Mitsufuji, Y. Multi-scale multi-band DenseNets for audio source separation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA), New Paltz, NY, USA, 15–18 October 2017; pp. 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Weinberger, K.Q.; Maaten, L. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–30 June 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Stoller, D.; Ewert, S.; Dixon, S. Wave-u-net: A multi-scale neural network for end-to-end audio source separation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.03185. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, N.; Goswami, N.; Mitsufuji, Y. MMDenseLSTM: An efficient combination of convolutional and recurrent neural networks for audio source separation. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Acoustic Signal Enhancement (IWAENC), Tokyo, Japan, 17–20 September 2018; pp. 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, N.; Agrawal, P.; Goswami, N.; Mitsufuji, Y. PhaseNet: Discretized phase modeling with deep neural networks for audio source separation. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 2713–2717. [Google Scholar]
- Hubel, D.H.; Wiesel, T.N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat’s visual cortex. J. Physiol. 1962, 160, 106–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.S.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.E.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Juan, PR, USA, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, B.Y.; Heo, W.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, O.W. Music detection from broadcast contents using convolutional neural networks with a Mel-scale kernel. EURASIP J. Audio Speech Music Process. 2019, 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Glorot, X.; Bordes, A.; Bengio, Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS), Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 11–13 April 2011; pp. 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Dumoulin, V.; Visin., F. A guide to convolution arithmetic for deep learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.07285. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.E.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Liutkus, A.; Stöter, F.; Rafii, Z.; Kitamura, D.; Rivet, B.; Ito, N.; Ono, N.; Fontecave, J. The 2016 signal separation evaluation campaign. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Latent Variable Analysis and Signal Separation (LVA/ICA), Grenoble, France, 21–23 February 2017; pp. 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, E.; Gribonval, R.; Fevotte, C. Performance measurement in blind audio source separation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2006, 14, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A. An industrial strength audio search algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), Baltimore, MD, USA, 26–30 October 2003; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- WebRTC. Available online: https://github.com/wiseman/py-webrtcvad (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Audfpint. Available online: https://github.com/dpwe/audfprint (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Wave-U-Net. Available online: https://github.com/f90/Wave-U-Net (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Ward, D.; Mason, R.D.; Kim, C.; Stöter, F.R.; Liutkus, A.; Plumbley, M. SiSEC 2018: State of the art in musical audio source separation-subjective selection of the best algorithm. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Intelligent Music Production, Huddersfield, UK, 14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]






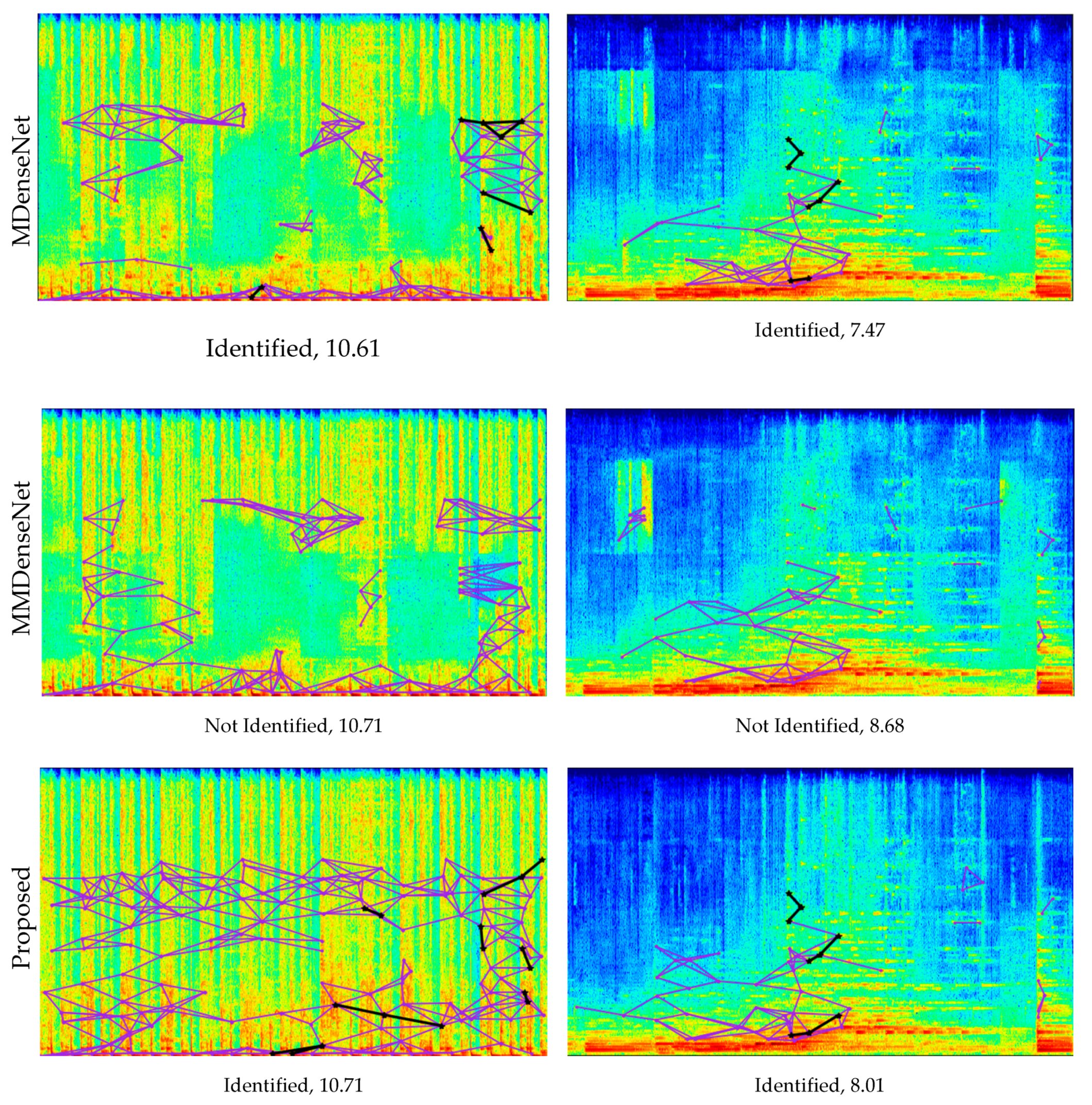
| Signal | Vocals | Accompaniment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistics | SDR | SIR | SAR | SDR | SIR | SAR | |
| Architecture | |||||||
| A1 (MDenseNet) | 4.93 | 12.98 | 6.22 | 11.48 | 16.74 | 13.45 | |
| A2 (MMDenseNet) | 5.61 | 13.43 | 6.57 | 11.97 | 16.84 | 13.96 | |
| A3 (MMDenseLSTM) | 5.78 | 13.57 | 6.87 | 12.03 | 16.44 | 14.22 | |
| A4 (A1 + MB) | 5.31 | 13.51 | 6.30 | 11.62 | 16.24 | 13.38 | |
| A5 (A3 + TDConv) | 5.51 | 14.27 | 6.47 | 11.73 | 16.86 | 13.50 | |
| A6 (A3 + FDConv) | 5.26 | 13.50 | 6.48 | 11.71 | 17.82 | 13.21 | |
| A7 (A3 + 2DConv) | 5.46 | 13.82 | 6.42 | 11.81 | 17.67 | 13.07 | |
| A8 (A3 + T-FDConv) | 5.90 | 14.56 | 6.90 | 12.03 | 17.16 | 13.48 | |
| Method | Vocals | Accompaniment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DeepNMF [9] | - | 2.75 | 8.90 |
| FNN [8] | - | 4.47 | 11.12 |
| BLSTM [12] | 30.03 | 4.86 | 11.26 |
| SH-4stack [14] | 34.18 | 5.45 | 12.14 |
| MMDenseNet [15] | 0.33 | 6.00 | 12.10 |
| MMDenseLSTM [20] | 1.22 | 6.31 | 12.73 |
| Our method | 0.48 | 6.25 | 12.58 |
| Separated Signal | Music | Speech | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | 0 dB | −10 dB | 0 dB | −10 dB | |||||||||
| Statistics | SDR | SIR | SAR | SDR | SIR | SAR | SDR | SIR | SAR | SDR | SIR | SAR | |
| Architecture | |||||||||||||
| U-Net | 6.24 | 11.51 | 8.54 | 3.18 | 10.72 | 4.63 | 5.66 | 9.10 | 9.36 | 13.65 | 16.97 | 17.04 | |
| Wave-U-Net | 6.33 | 14.19 | 7.54 | 2.97 | 13.15 | 3.70 | 6.02 | 10.32 | 8.97 | 14.24 | 18.70 | 16.66 | |
| MDenseNet | 6.98 | 13.23 | 8.63 | 3.84 | 11.32 | 5.14 | 6.57 | 10.80 | 9.42 | 14.45 | 18.63 | 17.01 | |
| MMDenseNet | 7.15 | 13.43 | 8.86 | 4.04 | 11.48 | 5.35 | 6.77 | 10.92 | 9.58 | 14.53 | 18.74 | 17.07 | |
| MMDenseLSTM | 7.40 | 13.34 | 9.22 | 4.13 | 11.21 | 5.54 | 7.68 | 12.36 | 10.02 | 14.98 | 19.41 | 17.33 | |
| Proposed | 7.72 | 13.74 | 9.45 | 4.44 | 11.72 | 5.72 | 7.63 | 12.29 | 9.98 | 15.00 | 19.39 | 17.34 | |
| SNR | 0 dB | −10 dB | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | |||
| Mix | 43.38 | 4.59 | |
| U-Net | 42.33 | 19.38 | |
| Wave-U-Net | 54.77 | 26.89 | |
| MDenseNet | 52.57 | 28.44 | |
| MMDenseNet | 49.66 | 26.67 | |
| MMDenseLSTM | 67.94 | 44.96 | |
| Proposed | 71.91 | 48.03 | |
| Oracle | 95.92 | ||
| Distortion | Mean SDR (dB) | Identification Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| D0 | −0.01 | 48.9 |
| D1 | −8.53 | 42.9 |
| D2 | −0.30 | 40.9 |
| D3 | −0.10 | 40.6 |
| D4 | −0.05 | 40.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heo, W.-H.; Kim, H.; Kwon, O.-W. Source Separation Using Dilated Time-Frequency DenseNet for Music Identification in Broadcast Contents. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051727
Heo W-H, Kim H, Kwon O-W. Source Separation Using Dilated Time-Frequency DenseNet for Music Identification in Broadcast Contents. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(5):1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051727
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeo, Woon-Haeng, Hyemi Kim, and Oh-Wook Kwon. 2020. "Source Separation Using Dilated Time-Frequency DenseNet for Music Identification in Broadcast Contents" Applied Sciences 10, no. 5: 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051727
APA StyleHeo, W.-H., Kim, H., & Kwon, O.-W. (2020). Source Separation Using Dilated Time-Frequency DenseNet for Music Identification in Broadcast Contents. Applied Sciences, 10(5), 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051727




