Three-Dimensional Printed Silicone Bite Blocks for Radiotherapy of Head and Neck Cancer—A Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
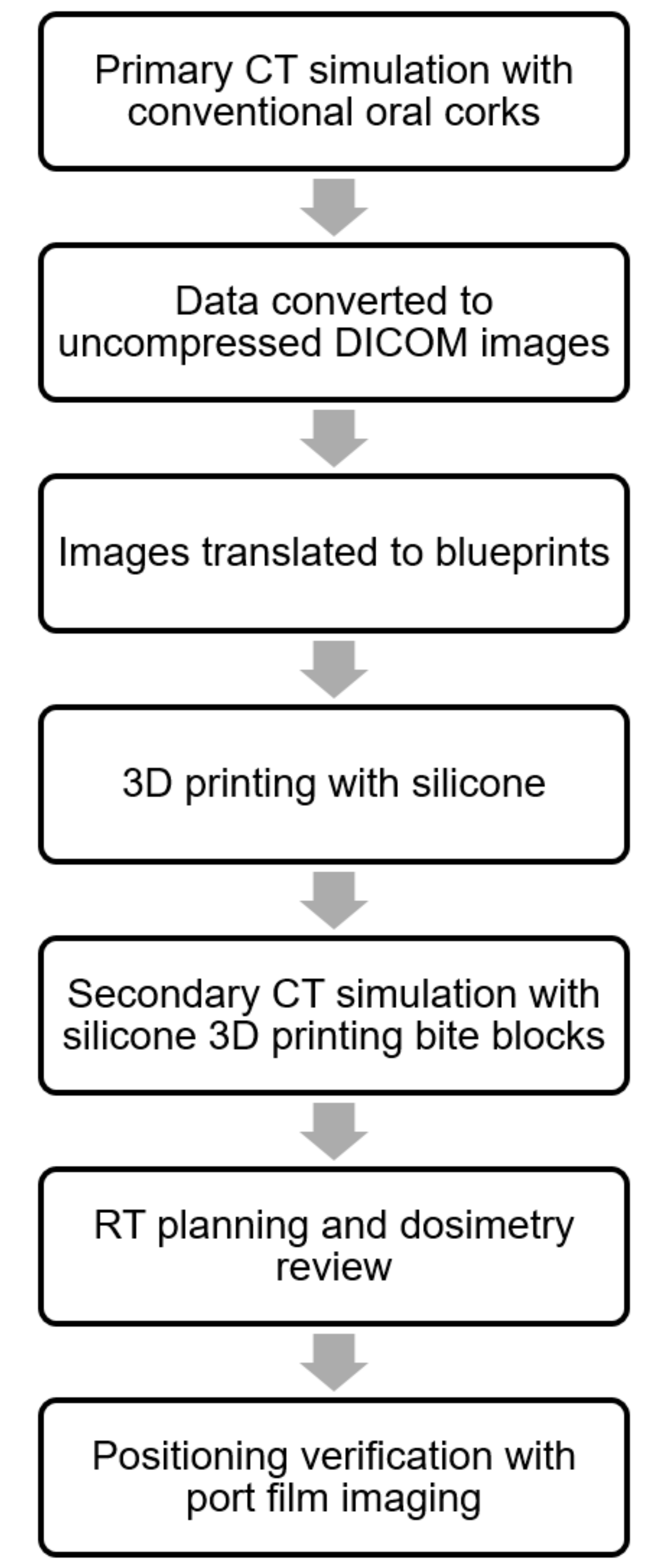
2.1. Development of Treatment Process
2.2. Materials of 3D Printed Bite Blocks
2.3. Patients
2.4. Computed Tomography (CT) Simulation
2.5. 3D Printing Process
2.6. RT Design
2.7. RT Planning
2.8. Dosimetric Comparison
2.9. Images Verification
2.10. Ethical Statement
3. Results
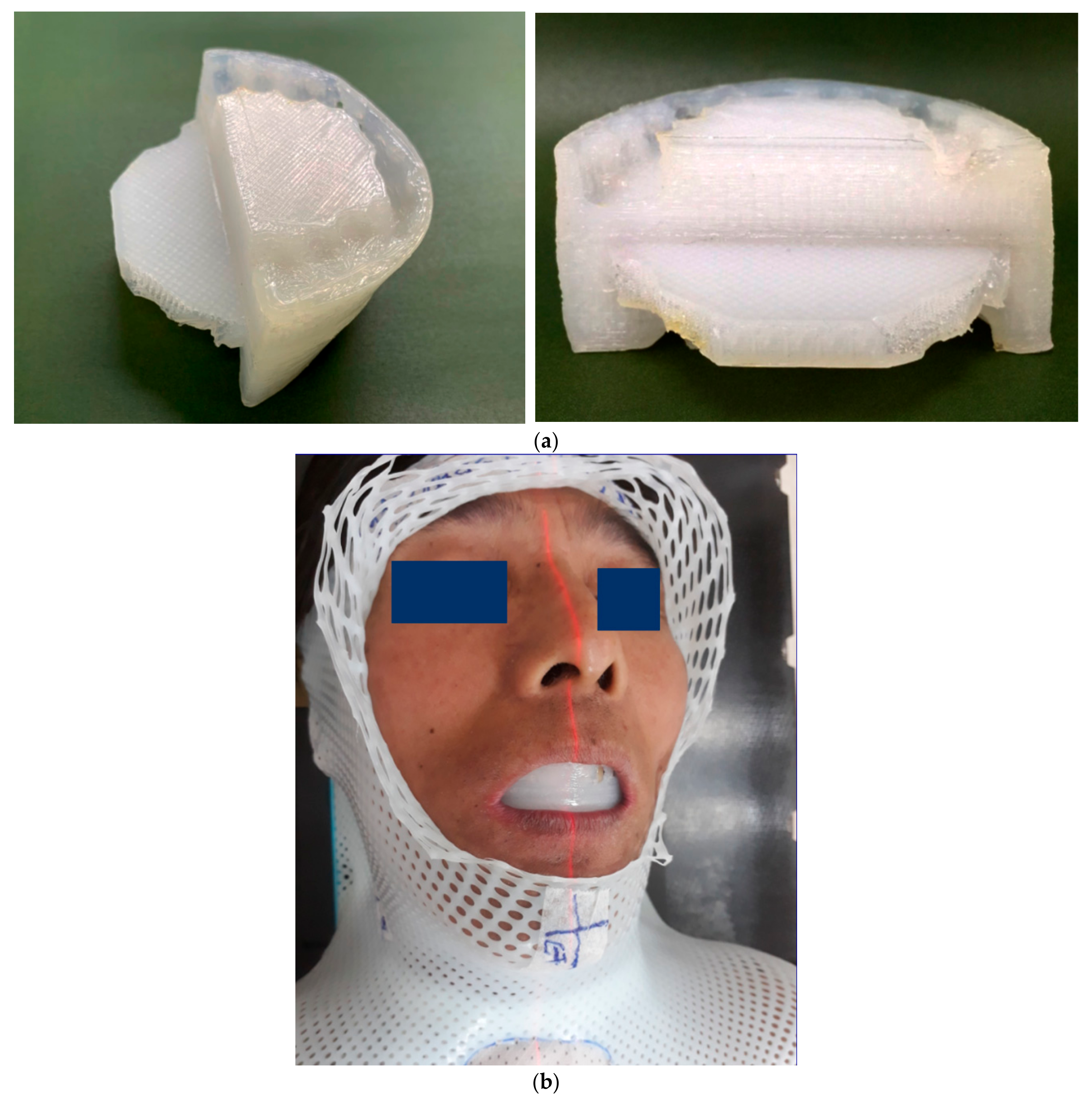
3.1. Special Consideration of the Unique Technology of 3D Printing Bite Blocks
3.1.1. Conformal to Occlusal Surface
3.1.2. Immobilization of the Tongue without Gag Reflex
3.1.3. Elastic and Firm Texture that Supports Opening of the Mouth
3.1.4. Smooth Surface with Tolerable Intraoral Tactility
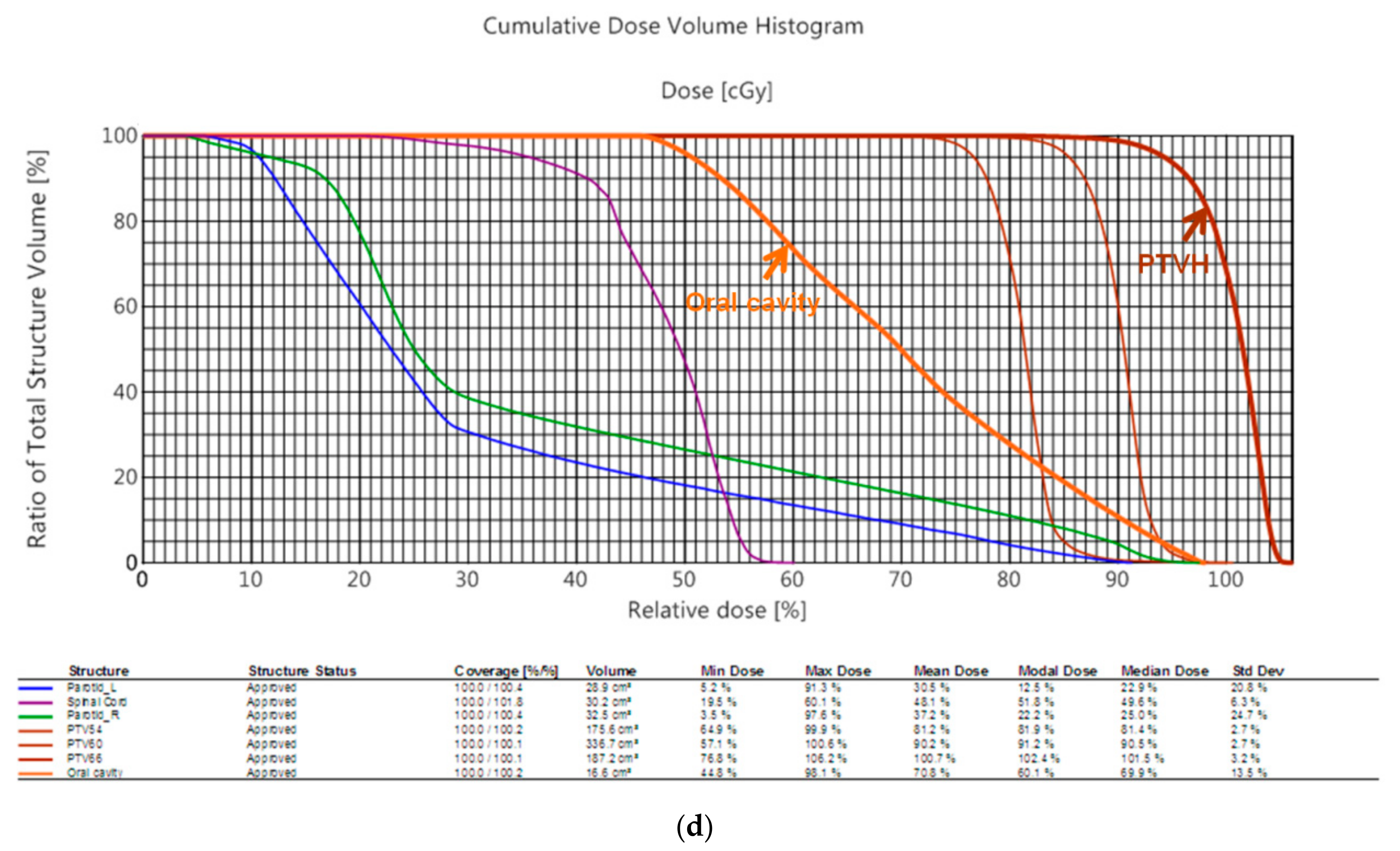
3.2. Dosimetric Comparison
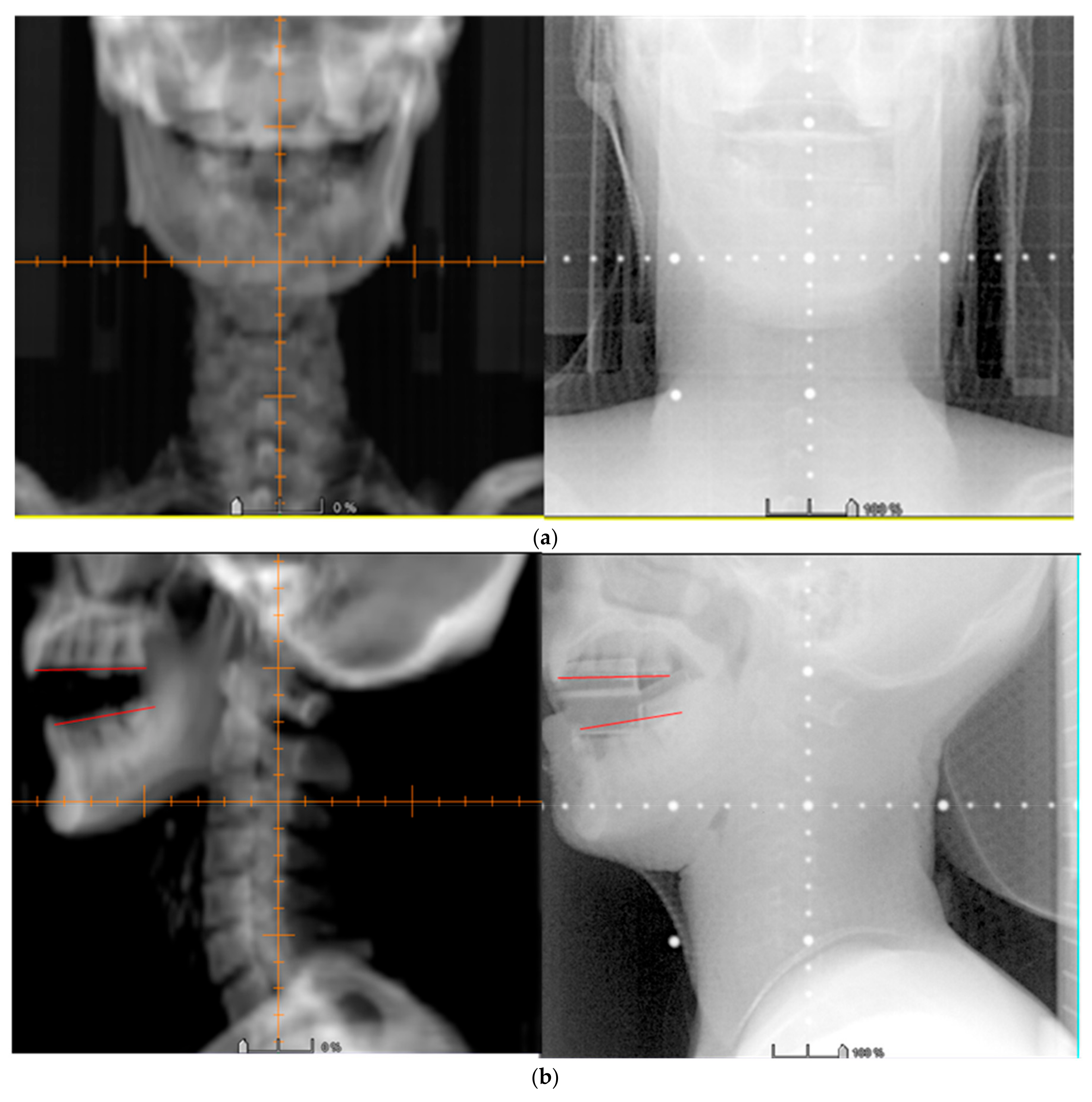
3.3. Image Verification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, N.; Fedewa, S.; Chen, A.Y. Epidemiology and demographics of the head and neck cancer population. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 30, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, C.J.; Hsu, W.L.; Lou, P.J.; Zhu, C.; Pan, J.; Shen, H.; et al. Tobacco smoking, alcohol drinking, betel quid chewing, and the risk of head and neck cancer in an East Asian population. Head Neck 2019, 41, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignon, J.P.; le Maitre, A.; Maillard, E.; Bourhis, J. Meta-analysis of chemotherapy in head and neck cancer (MACH-NC): An update on 93 randomised trials and 17,346 patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2009, 92, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, P.; Bourhis, J.; Lacas, B.; Posner, M.R.; Vermorken, J.B.; Hernandez, J.J.C.; Bourredjem, A.; Calais, G.; Paccagnella, A.; Hitt, R.; et al. Taxane-cisplatin-fluorouracil as induction chemotherapy in locally advanced head and neck cancers: An individual patient data meta-analysis of the meta-analysis of chemotherapy in head and neck cancer group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2854–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollows, P.; Hayter, J.P.; Vasanthan, S. The Leicester radiotherapy bite block: An aid to head and neck radiotherapy. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 39, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oita, M.; Ohmori, K.; Obinata, K.; Kinoshita, R.; Onimaru, R.; Tsuchiya, K.; Suzuki, K.; Nishioka, T.; Ohsaka, H.; Fujita, K.; et al. Uncertainty in treatment of head-and-neck tumours by use of intraoral mouthpiece and embedded fiducials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 64, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Anton, M.; Vorwerk, H. Dose uncertainty in radiotherapy of patients with head and neck cancer measured by in vivo ESR/alanine dosimetry using a mouthpiece. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robar, J.L.; Moran, K.; Allan, J.; Clancey, J.; Joseph, T.; Chytyk-Praznik, K.; MacDonald, R.L.; Lincoln, J.; Sadeghi, P.; Rutledge, R. Intrapatient study comparing 3D printed bolus versus standard vinyl gel sheet bolus for postmastectomy chest wall radiation therapy. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 8, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craft, D.; Balter, P.; Woodward, W.; Kry, S.; Salehpour, M.; Howell, R. Design and feasibility of 3D printed tissue compensators for postmastectomy radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, S184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefner, M.F.; Giesel, F.L.; Mattke, M.; Rath, D.; Wade, M.; Kuypers, J.; Preuss, A.; Kauczor, H.U.; Schenk, J.P.; Debus, J.; et al. 3D-Printed masks as a new approach for immobilization in radiotherapy–a study of positioning accuracy. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loja, M.; Craveiro, D.; Vieira, L.; Sousa, E.; Rodrigues, J.; Portal, R. Radiotherapy-customized head immobilization masks: From modeling and analysis to 3D printing. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2019, 30, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tino, R.; Yeo, A.; Leary, M.; Brandt, M.; Kron, T. A systematic review on 3D-printed imaging and dosimetry phantoms in radiation therapy. Technol. Cancer. Res. Treat. 2019, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grehn, M.; Stille, M.; Ziemann, C.; Cremers, F.; Rades, D.; Buzug, T.M. A new phantom for individual verification of the dose distribution in precision radiotherapy for head-and-neck cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 6931–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deasy, J.O.; Moiseenko, V.; Marks, L.; Chao, K.C.; Nam, J.; Eisbruch, A. Radiotherapy dose–volume effects on salivary gland function. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, S58–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodin, N.P.; Kabarriti, R.; Garg, M.K.; Guha, C.; Tome, W.A. Systematic review of normal tissue complication models relevant to standard fractionation radiation therapy of the head and neck region published after the QUANTEC reports. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 100, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrone, J.R.; Alves, F.A.; Prado, J.D.; Boccaletti, K.W.; Sereno, M.P.; Silva, M.L.; Jaguar, G.C. Impact of intraoral stent on the side effects of radiotherapy for oral cancer. Head Neck 2013, 35, E213–E217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kil, W.J.; Kulasekere, C.; Derrwaldt, R.; Bugno, J.; Hatch, C. Decreased radiation doses to tongue with “stick-out” tongue position over neutral tongue position in head and neck cancer patients who refused or could not tolerate an intraoral device (bite-block, tongue blade, or mouthpiece) due to trismus, gag reflex, or discomfort during intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 53029. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Musha, A.; Saitoh, J.; Shirai, K.; Kubota, Y.; Shimada, H.; Abe, T.; Komatsu, Y.; Komatsu, S.; Ohno, T.; Nakano, T.; et al. Customized mouthpieces designed to reduce tongue mucositis in carbon-ion radiotherapy for tumours of the nasal and paranasal sinuses. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudoh, T.; Ikushima, H.; Kudoh, K.; Furutani, S.; Kawanaka, T.; Kubo, A.; Takamaru, N.; Tamatani, T.; Miyamoto, Y. Effectiveness of newly developed water-equivalent mouthpiece during external beam radiotherapy for oral cancer. Ann. Carcinog. 2017, 2, 1007. [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa, H.; Koto, M.; Ebner, D.K.; Takagi, R.; Hayashi, K.; Tsuji, H.; Kamada, T. A custom-made mouthpiece incorporating tongue depressors and elevators to reduce radiation-induced tongue mucositis during carbon-ion radiation therapy for head and neck cancer. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 8, e27–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.S.; Oh, D.; Ju, S.G.; Ahn, Y.C.; Na, C.H.; Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, C.C. Development of a semi-customized tongue displacement device using a 3D printer for head and neck IMRT. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaid, M.; Bajaj, N.; Burrows, H.; Mathew, R.; Dai, A.; Wilke, C.T.; Palasi, S.; Hergenrother, R.; Chung, C.; Fuller, C.D.; et al. Creating customized oral stents for head and neck radiotherapy using 3D scanning and printing. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamori, H.; Sumida, I.; Tsujimoto, T.; Shimamoto, H.; Murakami, S.; Ohki, M. Evaluation of mouthpiece fixation devices for head and neck radiotherapy patients fabricated in PolyJet photopolymer by a 3D printer. Phys. Med. 2019, 58, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

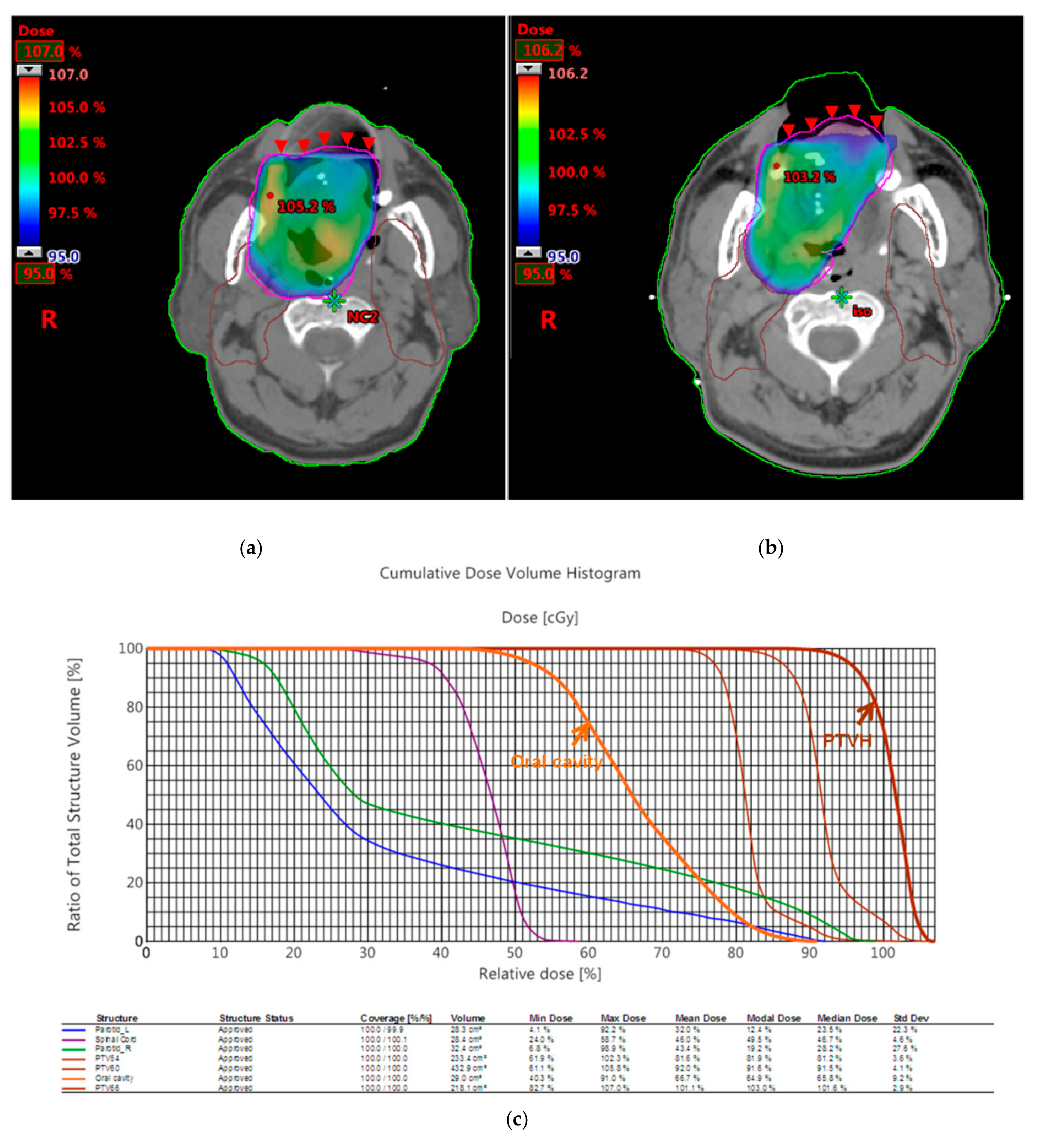
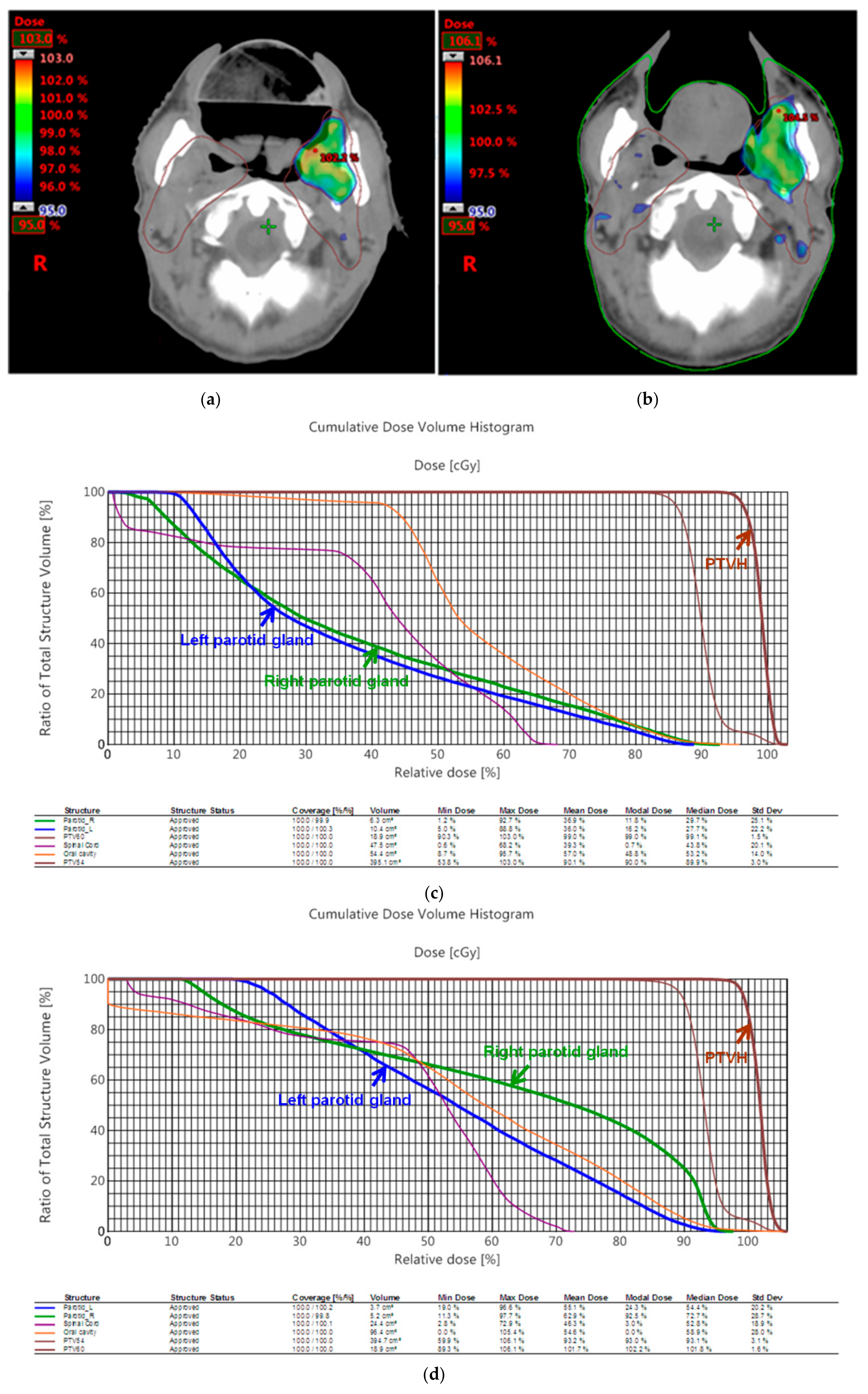
| Patient 1 | 3D Printed Bite Blocks | Conventional Oral Corks |
|---|---|---|
| PTV D100% | 95% | 95% |
| PTVmax | 107% | 106.2% |
| PTVmin | 82.7% | 76.8% |
| CI | 0.96 | 0.94 |
| HI | 1.13 | 1.12 |
| Median dose of oral cavity | 45.7 Gy | 48.6 Gy |
| Patient 2 | 3D Printed Bite Blocks | Conventional Oral Corks |
|---|---|---|
| PTV D100% | 98% | 97% |
| PTVmax | 103% | 106.1% |
| PTVmin | 90.3% | 89.3% |
| CI | 0.99 | 1.00 |
| HI | 1.08 | 1.12 |
| V26 of right parotid gland | 38% | 70% |
| V26 of left parotid gland | 34% | 68% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-C.; Chu, C.-M.; Tai, H.-C.; Hou, T.-C.; Chen, F.Y.-S.; Chi, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-J. Three-Dimensional Printed Silicone Bite Blocks for Radiotherapy of Head and Neck Cancer—A Preliminary Study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051688
Huang Y-M, Lee J-C, Chu C-M, Tai H-C, Hou T-C, Chen FY-S, Chi C-W, Chen Y-J. Three-Dimensional Printed Silicone Bite Blocks for Radiotherapy of Head and Neck Cancer—A Preliminary Study. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(5):1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051688
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yu-Ming, Jehn-Chuan Lee, Chien-Ming Chu, Hung-Chi Tai, Tien-Chi Hou, Fred Yi-Shueh Chen, Chih-Wen Chi, and Yu-Jen Chen. 2020. "Three-Dimensional Printed Silicone Bite Blocks for Radiotherapy of Head and Neck Cancer—A Preliminary Study" Applied Sciences 10, no. 5: 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051688
APA StyleHuang, Y.-M., Lee, J.-C., Chu, C.-M., Tai, H.-C., Hou, T.-C., Chen, F. Y.-S., Chi, C.-W., & Chen, Y.-J. (2020). Three-Dimensional Printed Silicone Bite Blocks for Radiotherapy of Head and Neck Cancer—A Preliminary Study. Applied Sciences, 10(5), 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051688






