Developing Hybrid Machine Learning Models for Estimating the Unconfined Compressive Strength of Jet Grouting Composite: A Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Machine Learning Algorithms
2.1. Applied ML Algorithms
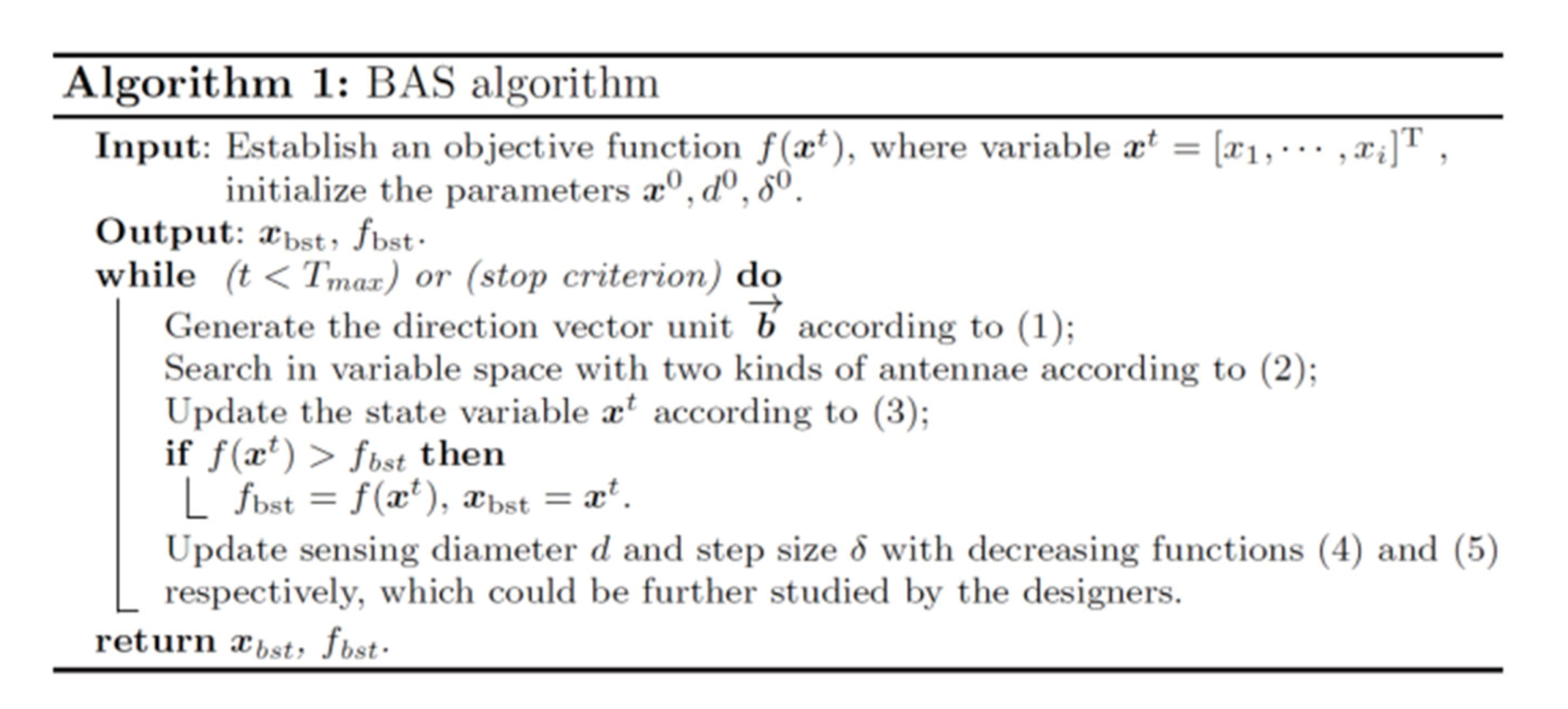
2.2. Beetle Antennae Search Algorithm (BAS)
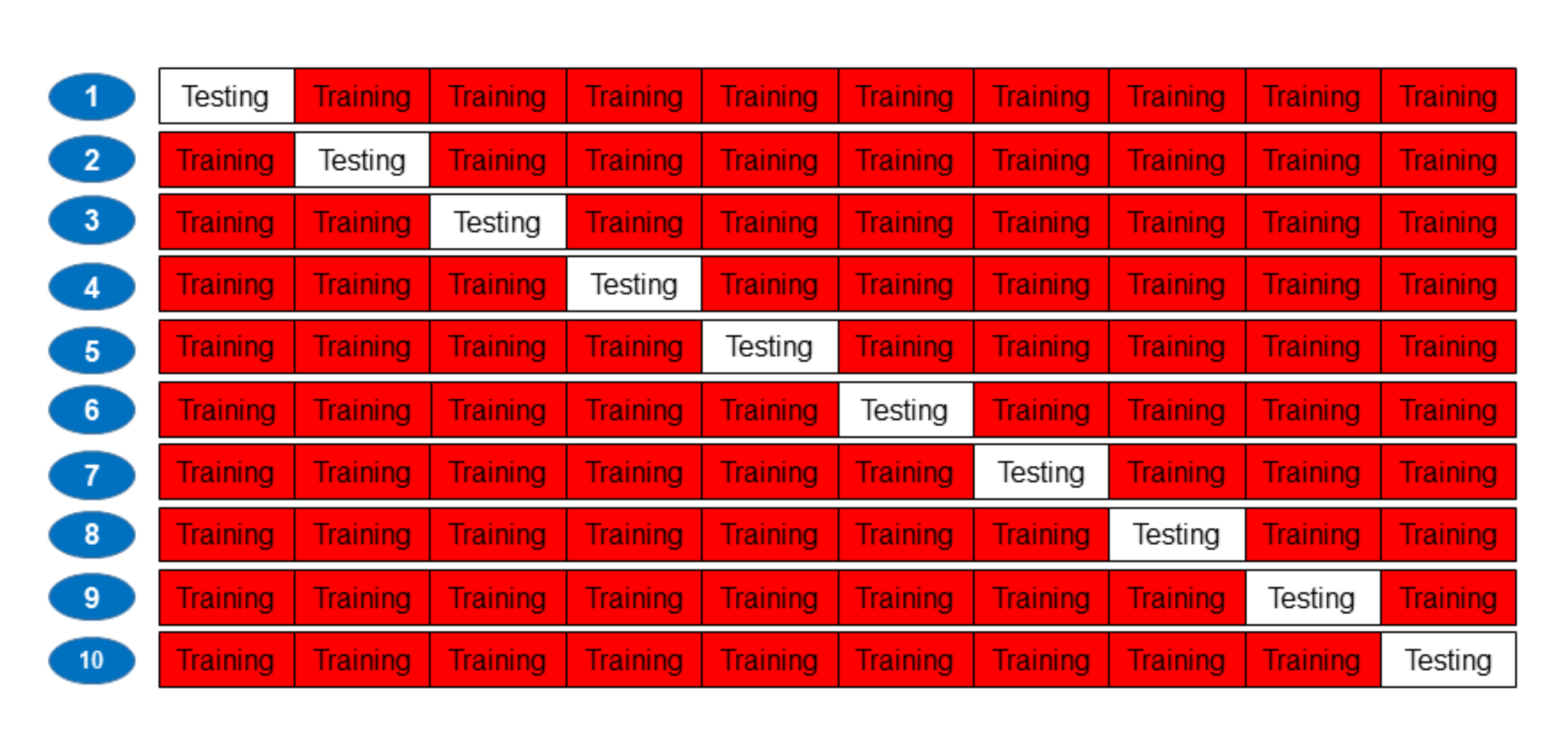
2.3. K-Fold Cross-Validation
2.4. Hyper-Parameter Tuning
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Specimen Preparation
- (1)
- Preparation of the grout. Cementitious or chemical binders were fully mixed with water and accelerator to achieve the designed cementitious grout or chemical grout.
- (2)
- Creation of coal-grout composite mixes. The raw coal was then mixed with the cementitious grout or chemical grout by a mixer (HJW-60) for about 5 min and 1 min, respectively.
- (3)
- Casting of coal-grout composites. The pre-produced coal-grout composite mixes were poured into a rectangular mold. After compaction, the model was placed in a curing chamber for 4 hours (coal-chemical grout only), and 1, 7, 14, and 28 days, respectively. The environment conditions were at approximately 20 °C and 90% humidity.
- (4)
- Sampling method for fabricating standard specimens. The core-drilling machine (HZ-20) was used to obtain the cylindrical specimens (of 50 mm and 100 mm in diameter and height, respectively) from the casted specimen. To ensure the flatness and parallelism, a grinding machine was utilized.
3.3. UCS Test
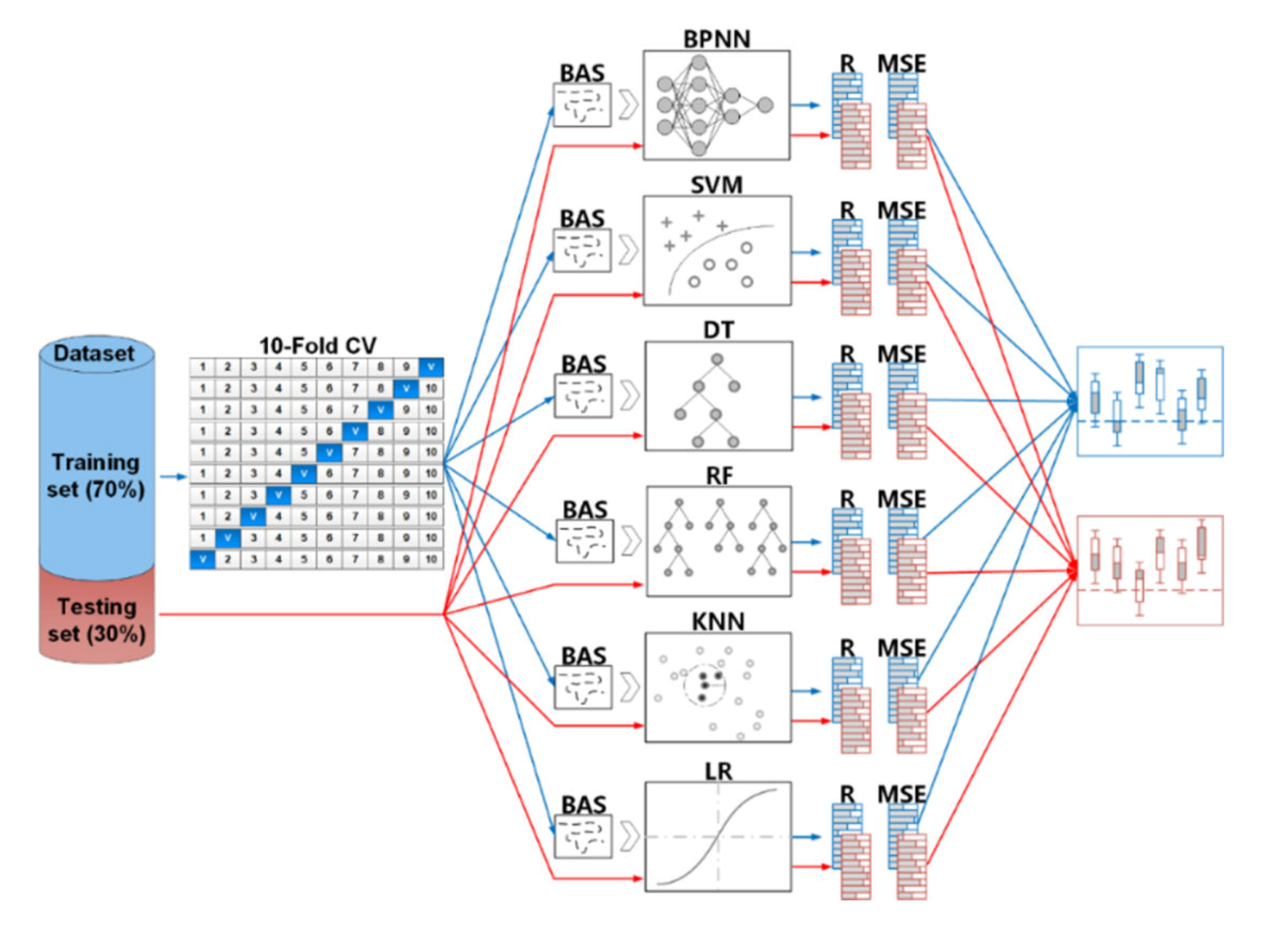
3.4. Dataset Partition
4. Results and Discussion
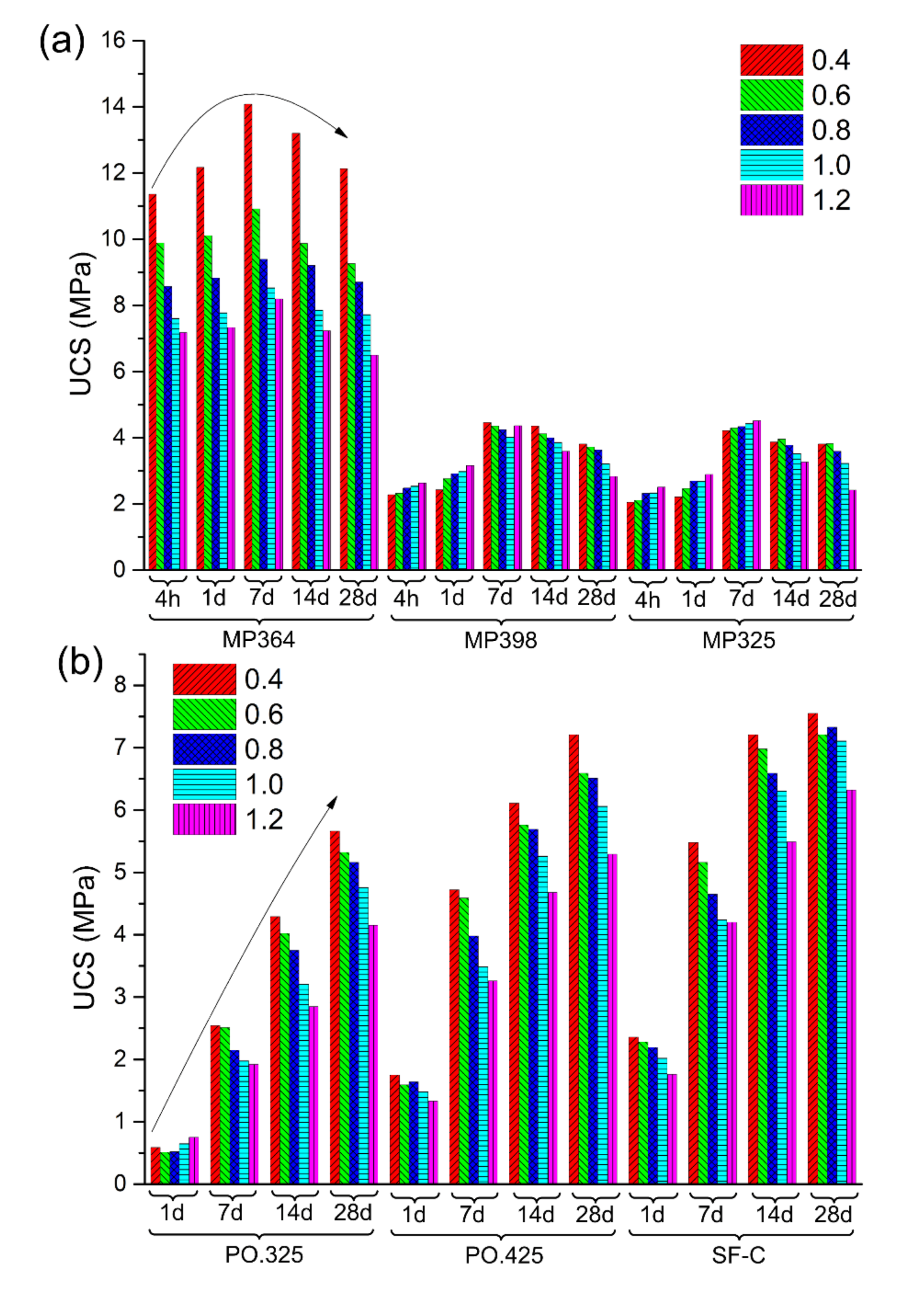
4.1. UCS Results of Coal-Grout Composites
4.2. Results of Hyper-Parameters Tuning
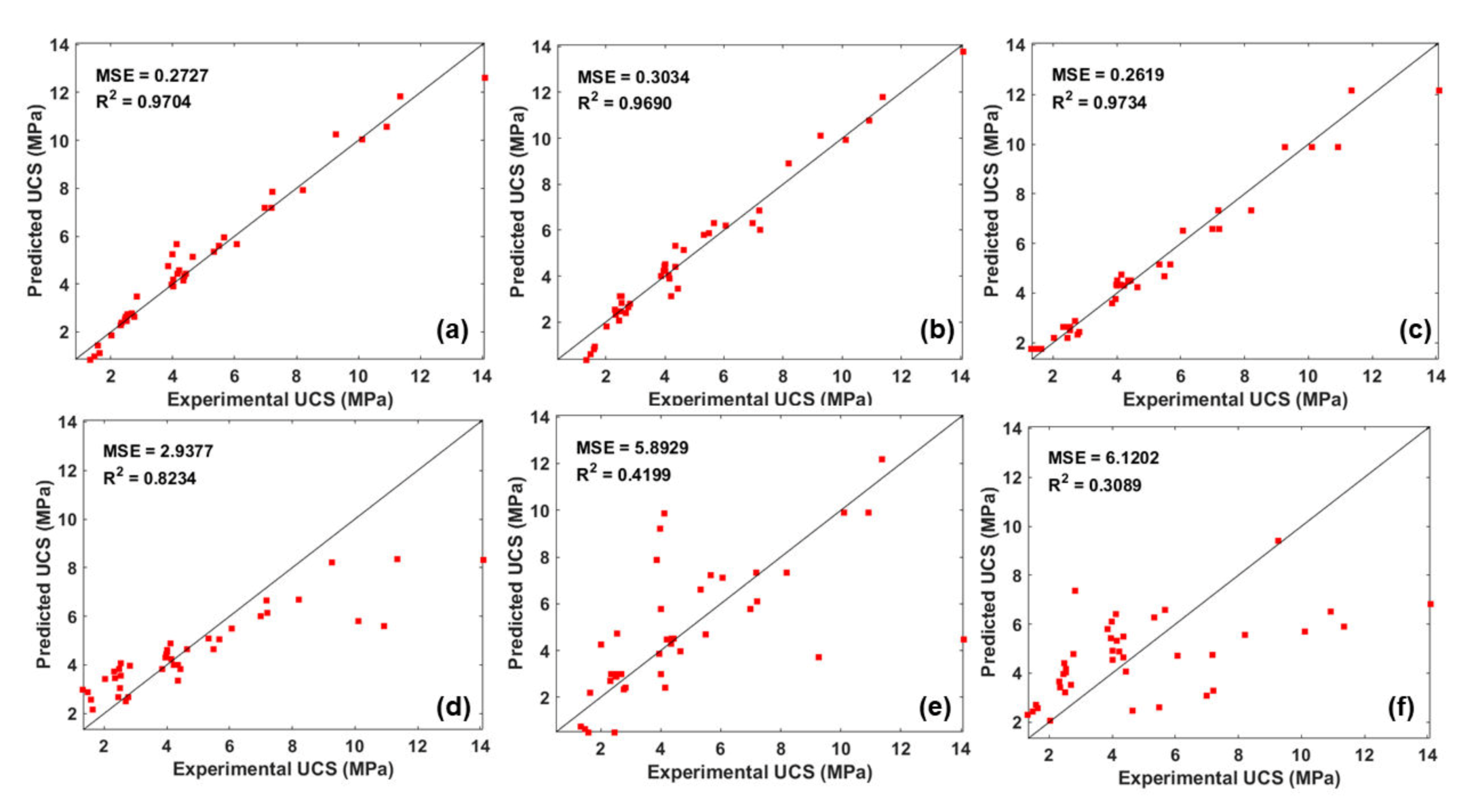
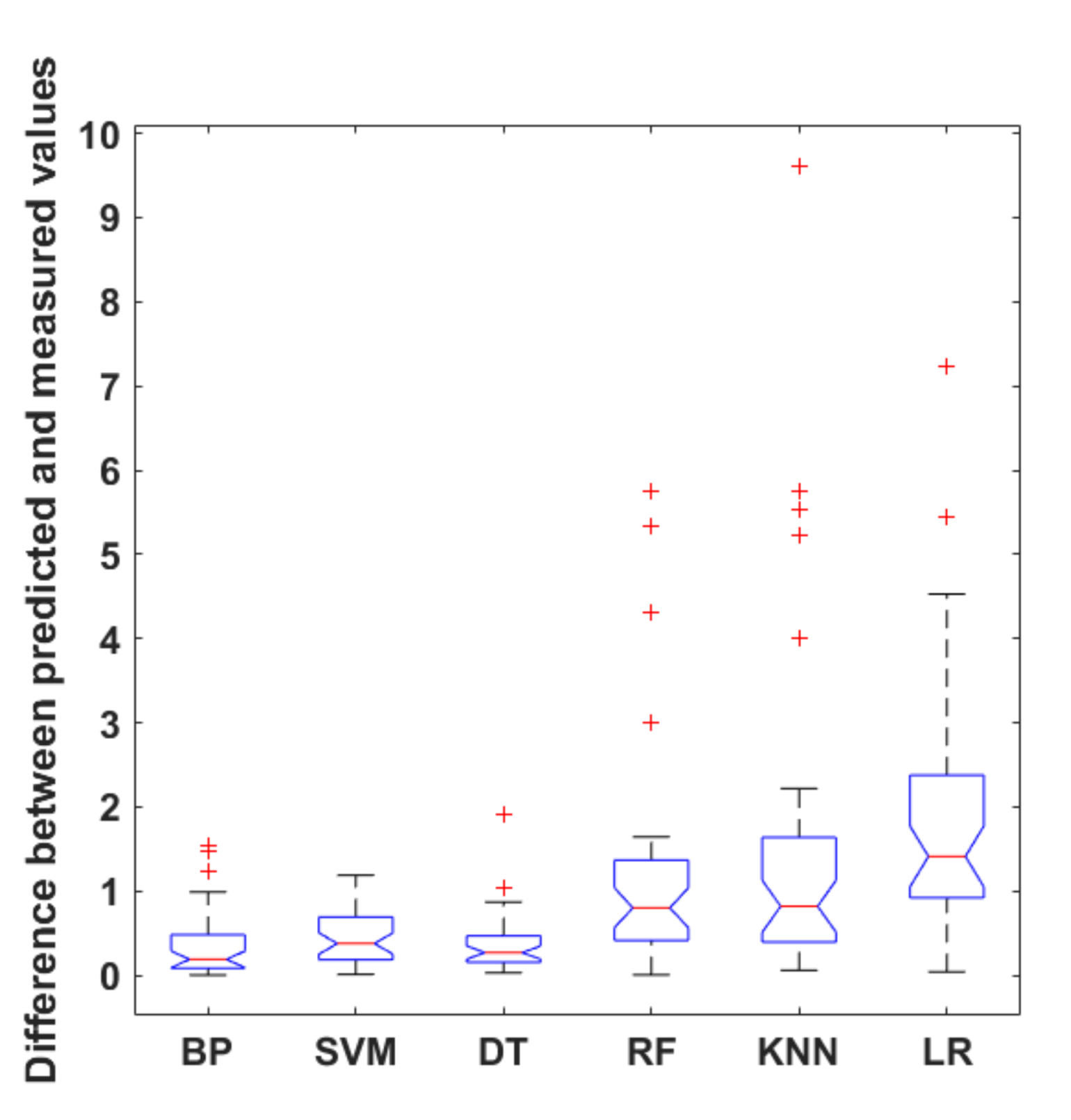
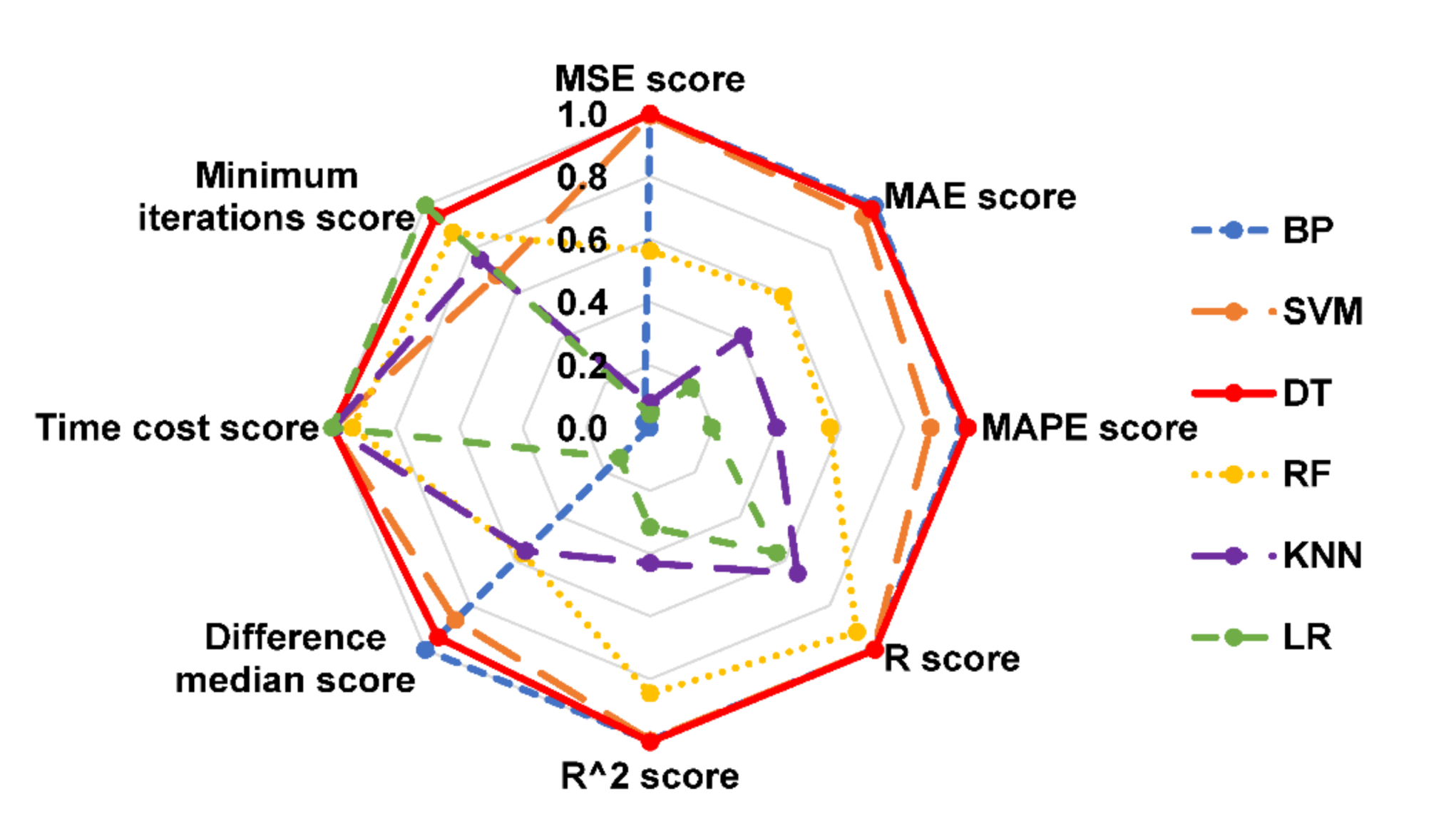
4.3. Comparison of Integrated ML Algorithms
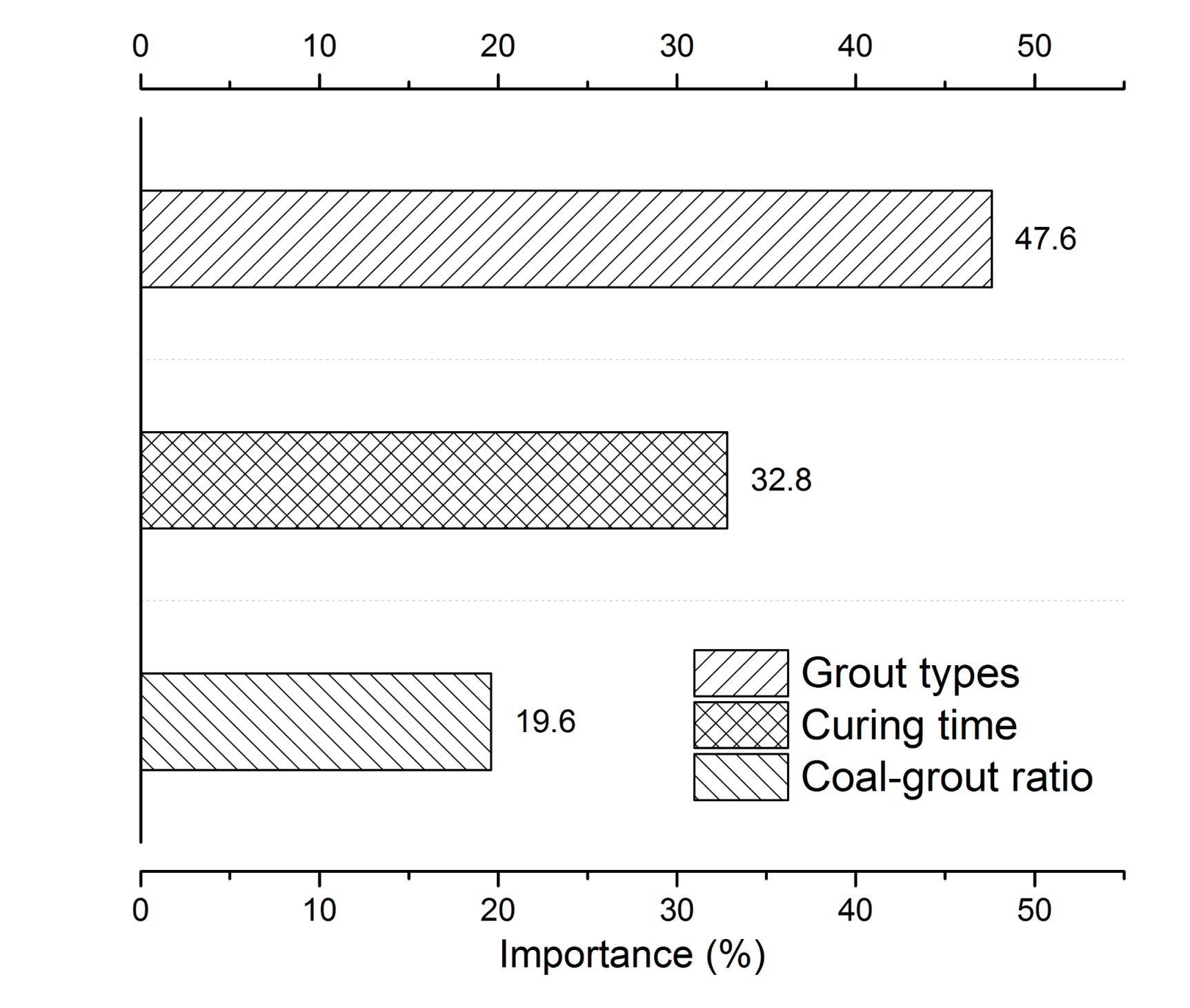
4.4. Analysis of the Variable Importance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| JG | Jet grouting |
| UCS | Unconfined compressive strength |
| ML | Machine learning |
| BPNN | Back-propagation neural network |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| DT | Decision tree |
| RF | Random forest |
| KNN | K-nearest neighbors |
| LR | Logistic regression |
| BAS | Beetle antennae search algorithm |
| CV | Cross-validation |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
| R | Correlation coefficient |
| P.O 32.5 | Portland cement P.O 32.5 |
| P.O 42.5 | Portland cement P.O 42.5 |
| SF-C | Superfine cement |
| RMSE | Root-mean-square error |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
| MAPE | Mean absolute percentage error |
References
- Croce, P.; Flora, A.; Modoni, G. Jet Grouting: Technology, Design and Control; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; ISBN 041552640X. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Shao, Z. Study on the effect of flexible layer on support structures of tunnel excavated in viscoelastic rocks. J. Eng. Mech. 2019, 145, 4019077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzner, C. Grouting of Rock and Soil; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; ISBN 9054106344. [Google Scholar]
- Yahiro, T.; Yoshida, H. Induction grouting method utilizing high speed water jet. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Moscow, Russia, 6–11 August 1973; Volume 4, pp. 359–362. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Qian, D. Prediction of the Strength of Rubberized Concrete by an Evolved Random Forest Model. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 5198583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Basarir, H.; Karrech, A.; Azadi, M.R. Laboratory evaluation of shear strength properties for cement-based grouted coal mass. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Qian, D. Stability Control for the Rheological Roadway by a Novel High-Efficiency Jet Grouting Technique in Deep Underground Coal Mines. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J. Investigation on jet grouting support strategy for controlling time-dependent deformation in the roadway. Energy Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Qian, D. Experimental and numerical investigation on a novel support system for controlling roadway deformation in underground coal mines. Energy Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basarir, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, G. Gateway stability analysis by global-local modeling approach. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2019, 113, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitake, I.; Nakagawa, K.; Mitsui, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ikeda, A. An evaluation method of ground improvement by jet grouting. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 2004, 19, 496–497. [Google Scholar]
- Nikbakhtan, B.; Ahangari, K. Field study of the influence of various jet grouting parameters on soilcrete unconfined compressive strength and its diameter. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2010, 47, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinoco, J.; Correia, A.G.; Cortez, P. A novel approach to predicting Young’s modulus of jet grouting laboratory formulations over time using data mining techniques. Eng. Geol. 2014, 169, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.H.; Lee, Y.; Chew, S.-H.; Yong, K.Y. Strength and modulus of marine clay-cement mixes. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2005, 131, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.S.; Liao, J.J.; Sze, S.C. An empirical strength criterion for jet grouted soilcrete. Eng. Geol. 1994, 37, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, B.S.; Sivapullaiah, P.V.; Suresh, S.; Omkar, S.N. Prediction of unconfined compressive strength of soft grounds using computational intelligence techniques: A comparative study. Comput. Geotech. 2006, 33, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiá, M.; Olmo, I.F.; Irabien, A. Neural network prediction of unconfined compressive strength of coal fly ash-cement mixtures. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asheghi, R.; Shahri, A.A.; Zak, M.K. Prediction of uniaxial compressive strength of different quarried rocks using metaheuristic algorithm. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 8645–8659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahri, A.A.; Larsson, S.; Johansson, F. Updated relations for the uniaxial compressive strength of marlstones based on P-wave velocity and point load index test. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2016, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Fourie, A. Cemented paste backfill for mineral tailings management: Review and future perspectives. Miner. Eng. 2019, 144, 106025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Ma, G.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Nener, B. Determination of Young’s modulus of jet grouted coalcretes using an intelligent model. Eng. Geol. 2019, 252, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Jiang, C. Optimized neural network using beetle antennae search for predicting the unconfined compressive strength of jet grouting coalcretes. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2019, 43, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, G.; Huang, Y.; Aslani, F.; Nener, B. Modelling uniaxial compressive strength of lightweight self-compacting concrete using random forest regression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 210, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, G. Prediction of permeability and unconfined compressive strength of pervious concrete using evolved support vector regression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 207, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Tuyen, T.T.; Shirzadi, A.; Pham, B.T.; Shahabi, H.; Omidvar, E.; Amini, A.; Entezami, H.; Prakash, I.; Phong, T. Van Development of a novel hybrid intelligence approach for landslide spatial prediction. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloop, M.R.; Kumar, D.; Samui, P.; Gabr, A.R.; Hu, J.W.; Jin, X.; Roy, B. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm-Extreme Learning Machine (PSO-ELM) model for predicting resilient modulus of stabilized aggregate bases. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.; Nguyen, H.; Dou, J.; Zhou, J. A comparative study of PSO-ANN, GA-ANN, ICA-ANN, and ABC-ANN in estimating the heating load of buildings’ energy efficiency for smart city planning. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heermann, P.D.; Khazenie, N. Classification of multispectral remote sensing data using a back-propagation neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearst, M.A.; Dumais, S.T.; Osuna, E.; Platt, J.; Scholkopf, B. Support vector machines. IEEE Intell. Syst. Their Appl. 1998, 13, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, Y.; Mason, L. The alternating decision tree learning algorithm. In Proceedings of the ICML, Bled, Slovenia, 27–30 June 1999; Volume 99, pp. 124–133. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, K.S.; Nguyen, T.Q. An adaptable k -nearest neighbors algorithm for MMSE image interpolation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnapuram, B.; Carin, L.; Figueiredo, M.A.T.; Hartemink, A.J. Sparse multinomial logistic regression: Fast algorithms and generalization bounds. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, S. BAS: Beetle Antennae Search Algorithm for Optimization Problems. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10724. [Google Scholar]
- Braga-Neto, U.; Hashimoto, R.; Dougherty, E.R.; Nguyen, D.V.; Carroll, R.J. Is cross-validation better than resubstitution for ranking genes? Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R.J. An Introduction to the Bootstrap; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; ISBN 0412042312. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, D.L. Fuzzy clustering with spatial constraints. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Rochester, NY, USA, 22–25 September 2002; Volume 2, p. II. [Google Scholar]
- Braga-Neto, U.; Dougherty, E. Bolstered error estimation. Pattern Recognit. 2004, 37, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M. Cross-validatory choice and assessment of statistical predictions. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1974, 111–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Runger, G.C.; Hubele, N.F. Engineering Statistics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 0470526947. [Google Scholar]
- Shlesinger, M.F. Search research. Nature 2006, 443, 281–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlyukevich, I. Lévy flights, non-local search and simulated annealing. J. Comput. Phys. 2007, 226, 1830–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, G.M.; Afanasyev, V.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Murphy, E.J.; Prince, P.A.; Stanley, H.E. Lévy flight search patterns of wandering albatrosses. Nature 1996, 381, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akın, M.; Akın, M.; Çiftçi, A.; Beril Bayram, B. The Effect of Jet-Grouting on the Cyclic Stress Ratio (Csr) for the Mitigation of Liquefaction. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mutluhan_Akin/publication/289534049_THE_EFFECT_OF_JET-GROUTING_ON_THE_CYCLIC_STRESS_RATIO_CSR_FOR_THE_MITIGATION_OF_LIQUEFACTION/links/568fa81408ae78cc05195e6a/THE-EFFECT-OF-JET-GROUTING-ON-THE-CYCLIC-STRESS-RATIO-CSR-FOR-THE-MITIGATION-OF-LIQUEFACTION.pdf (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- Mathey, M.; Merwe, J.N. van der development of coal-crete as a composite analogue material for coal in mechanical laboratory studies and for mine backfill purpose m. Mathey Van der Merwe 2015, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- AASTM C39. Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. ASTM Int. 2001. Available online: https://www.astm.org/Standards/C39 (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- Reeves, C.R. Training Set Selection in Neural Network Applications. In Proceedings of the Artificial Neural Nets and Genetic Algorithms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 476–478. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, M.M.; Illingworth, W.T. A Practical Guide to Neural Nets; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Tabor, D. Principles of adhesion—Bonding in cement and concrete. In Adhesion Problems in the Recycling of Concrete; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; pp. 63–87. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, J.J.; Johari, M.A.M.; Mazloom, M. Effect of admixtures on the setting times of high-strength concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2000, 22, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniraj, S.R.; Havanagi, V.G. Compressive strength of cement stabilized fly ash-soil mixtures. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, A.M.; Brooks, J.J. Concrete Technology; Longman Scientific & Technical: New York, UK, 1987; ISBN 0582988594. [Google Scholar]
- Frigge, M.; Hoaglin, D.C.; Iglewicz, B. Some implementations of the boxplot. Am. Stat. 1989, 43, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, K.E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tague, N.R. The Quality Toolbox; ASQ Quality Press: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2005; Volume 600. [Google Scholar]



| Algorithms | Parameter | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| BPNN | hidden_layer_num | Hidden layers numbers. |
| hidden_layer_size | Neurons in hidden layers. | |
| SVM | C | Penalty term coefficient. |
| gamma | Gamma in gaussian kernel. | |
| DT | min_samples_split | Minimum sample numbers for an internal node. |
| min_samples_leaf | Minimum sample number for a leaf node. | |
| RF | tree_num | The number of trees. |
| min_samples_leaf | Minimum sample numbers for a leaf node. | |
| KNN | neighbors_num | Neighbor sample numbers. |
| Grout Types | W-C/A:B | Coal-Grout Ratio | Curing Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cementitious grout | P.O 32.5 | 1:1 | 0.4:1, 0.6:1, 0.8:1, 1:1, 1.2:1 | 4 h 1,1 day, 7 days, 14 days, 28 days |
| P.O 42.5 | ||||
| SF-C | ||||
| Chemical grout | MP 364 | |||
| MP 398 | ||||
| MP 325 | ||||
| Variable | Min | Max | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal-grout ratio | 0.4 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.28 |
| Curing time (days) | 0.17 | 28 | 10.03 | 10.26 |
| Grout types | 1.0 | 6.0 | 3.5 | 1.71 |
| UCS (MPa) | 0.51 | 14.08 | 4.79 | 2.77 |
| Algorithms | Parameter | Restriction | Empirical Scope | Initial Value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPNN | hidden_layer_num | >0, integer | [1,4] | {1,2,3,4} | 1 |
| hidden_layer_size | >0, integer | [1,20] | 30, (20,10), (20,10,10), (10,10,10,10) | 15 | |
| SVM | C | real number | [0.1,1000] | 16 | 451 |
| gamma | real number | [0.001,100] | 16 | 3.15 | |
| DT | min_samples_split | >0, integer >min_samples_ leaf*2 | [1,10] | 25 | 1 |
| min_samples_leaf | >0, integer | [2,10] | 50 | 2 | |
| RF | tree_num | >0, integer | [1,10] | 40 | 7 |
| min_samples_leaf | >0, integer | [1,10] | 40 | 1 | |
| KNN | neighbors_num | >0, integer | [1,10] | 30 | 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J. Developing Hybrid Machine Learning Models for Estimating the Unconfined Compressive Strength of Jet Grouting Composite: A Comparative Study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051612
Sun Y, Li G, Zhang J. Developing Hybrid Machine Learning Models for Estimating the Unconfined Compressive Strength of Jet Grouting Composite: A Comparative Study. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(5):1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051612
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yuantian, Guichen Li, and Junfei Zhang. 2020. "Developing Hybrid Machine Learning Models for Estimating the Unconfined Compressive Strength of Jet Grouting Composite: A Comparative Study" Applied Sciences 10, no. 5: 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051612
APA StyleSun, Y., Li, G., & Zhang, J. (2020). Developing Hybrid Machine Learning Models for Estimating the Unconfined Compressive Strength of Jet Grouting Composite: A Comparative Study. Applied Sciences, 10(5), 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051612







