An Improved Biocompatible Probe for Photoacoustic Tumor Imaging Based on the Conjugation of Melanin to Bovine Serum Albumin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
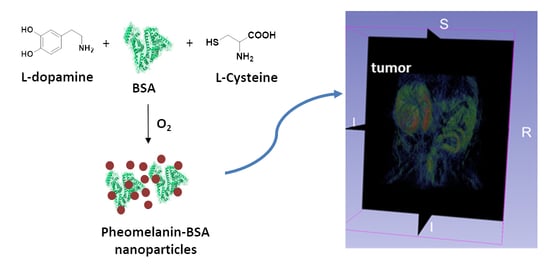
2.1. Synthesis of Melanin-BSA Conjugates and PheoBSA-FITC Conjugates
2.2. Cell Line and Animal Models
2.3. In Vitro Characterization of Melanin-BSA Conjugates
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. PheoBSA-FITC In Vivo Biodistribution Test
2.6. In Vivo Photoacoustic Imaging
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Melanin-BSA Conjugates
3.2. PheoBSA Conjugate D In Vivo Biodistribution and Tumor Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bell, A.G. On the production and reproduction of sound by light. Am. J. Sci. 1880, 20, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zackrisson, S.; van de Ven, S.M.; Gambhir, S.S. Light in and sound out: Emerging translational strategies for photoacoustic imaging. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 979–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, S.L. Optical properties of biological tissues: A review. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, R37–R61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, M.; Buehler, A.; Aguirre, J.; Ntziachristos, V. Three-dimensional multispectral optoacoustic mesoscopy reveals melanin and blood oxygenation in human skin in vivo. J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohndiek, S.E.; Sasportas, L.S.; Machtaler, S.; Jokerst, J.V.; Hori, S.; Gambhir, S.S. Photoacoustic Tomography Detects Early Vessel Regression and Normalization During Ovarian Tumor Response to the Antiangiogenic Therapy Trebananib. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1942–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijblom, M.; Piras, D.; Brinkhuis, M.; van Hespen, J.C.; van den Engh, F.M.; van der Schaaf, M.; Klaase, J.M.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; Steenbergen, W.; Manohar, S. Photoacoustic image patterns of breast carcinoma and comparisons with Magnetic Resonance Imaging and vascular stained histopathology. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijblom, M.; Klaase, J.M.; van den Engh, F.M.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; Steenbergen, W.; Manohar, S. Imaging tumor vascularization for detection and diagnosis of breast cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 10, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffels, I.; Morscher, S.; Helfrich, I.; Hillen, U.; Lehy, J.; Burton, N.C.; Sardella, T.C.; Claussen, J.; Poeppel, T.D.; Bachmann, H.S.; et al. Metastatic status of sentinel lymph nodes in melanoma determined noninvasively with multispectral optoacoustic imaging. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 317ra199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Zhu, R.; Song, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, X. Photoacoustic Imaging: Contrast Agents and Their Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1805875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Beard, P.C.; Bohndiek, S.E. Contrast agents for molecular photoacoustic imaging. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Huang, L.; Jiang, M.S.; Jiang, H. Contrast agents for photoacoustic and thermoacoustic imaging: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 23616–23639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, R.E.; Rochford, J. Molecular Photoacoustic Contrast Agents: Design Principles & Applications. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 1175–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luke, G.P.; Yeager, D.; Emelianov, S.Y. Biomedical applications of photoacoustic imaging with exogenous contrast agents. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Wang, S.; Reinecke, D.; Kiser, W.; Kruger, R.A.; DeGrado, T.R. Synthesis and evaluation of near-infrared (NIR) dye-herceptin conjugates as photoacoustic computed tomography (PCT) probes for HER2 expression in breast cancer. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beziere, N.; Lozano, N.; Nunes, A.; Salichs, J.; Queiros, D.; Kostarelos, K.; Ntziachristos, V. Dynamic imaging of PEGylated indocyanine green (ICG) liposomes within the tumor microenvironment using multi-spectral optoacoustic tomography (MSOT). Biomaterials 2015, 37, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozza, M.; Blasi, F.; Valbusa, G.; Oliva, P.; Cabella, C.; Buonsanti, F.; Cordaro, A.; Pizzuto, L.; Maiocchi, A.; Poggi, L. Photoacoustic imaging of integrin-overexpressing tumors using a novel ICG-based contrast agent in mice. Photoacoustics 2018, 11, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Huang, S.W.; Day, K.C.; O’Donnell, M.; Agayan, R.R.; Day, M.A.; Kopelman, R.; Ashkenazi, S. Indocyanine-green-embedded PEBBLEs as a contrast agent for photoacoustic imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 044020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrauto, G.; Carniato, F.; Di Gregorio, E.; Tei, L.; Botta, M.; Aime, S. Large photoacoustic effect enhancement for ICG confined inside MCM-41 mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Zerda, A.; Zavaleta, C.; Keren, S.; Vaithilingam, S.; Bodapati, S.; Liu, Z.; Levi, J.; Smith, B.R.; Ma, T.J.; Oralkan, O.; et al. Carbon nanotubes as photoacoustic molecular imaging agents in living mice. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, M.; Swierczewska, M.; Green, D.; Sitharaman, B.; Wang, L.V. Single-walled carbon nanotubes as a multimodal-thermoacoustic and photoacoustic-contrast agent. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 034018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Xing, D.; Ou, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhou, F. Photoacoustic molecular imaging with antibody-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes for early diagnosis of tumor. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 021008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Huang, Q.; Ku, G.; Wen, X.; Zhou, M.; Guzatov, D.; Brecht, P.; Su, R.; Oraevsky, A.; Wang, L.V.; et al. Photoacoustic imaging of living mouse brain vasculature using hollow gold nanospheres. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2617–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, X. Gold nanoparticles for photoacoustic imaging. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 299–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.H.; Kim, C.; Cobley, C.M.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L.V. Near-infrared gold nanocages as a new class of tracers for photoacoustic sentinel lymph node mapping on a rat model. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, E.; Li, Y.; Monaco, I.; Guo, W.; Maturi, M.; Menichetti, L.; Armanetti, P.; Martin, R.C.; Comes Franchini, M. A novel theranostic gold nanorods- and Adriamycin-loaded micelle for EpCAM targeting, laser ablation, and photoacoustic imaging of cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1877–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Beziere, N.; Song, L.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, D.; Chi, C.; Yang, X.; Guo, H.; Diot, G.; et al. DNA-Nanostructure-Gold-Nanorod Hybrids for Enhanced In Vivo Optoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10000–10007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanetti, P.; Flori, A.; Avigo, C.; Conti, L.; Valtancoli, B.; Petroni, D.; Doumett, S.; Cappiello, L.; Ravagli, C.; Baldi, G.; et al. Spectroscopic and photoacoustic characterization of encapsulated iron oxide super-paramagnetic nanoparticles as a new multiplatform contrast agent. Spectrochim. Acta. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 199, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkes, J.M.; Zhu, L.; Bahukhandi, S.B.; Rueping, M.; Kiessling, F.; Banala, S. Photoacoustic Imaging Probes Based on Tetrapyrroles and Related Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banala, S.; Fokong, S.; Brand, C.; Andreou, C.; Krautler, B.; Rueping, M.; Kiessling, F. Quinone-fused porphyrins as contrast agents for photoacoustic imaging. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6176–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokerst, J.V.; Van de Sompel, D.; Bohndiek, S.E.; Gambhir, S.S. Cellulose Nanoparticles are a Biodegradable Photoacoustic Contrast Agent for Use in Living Mice. Photoacoustics 2014, 2, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekkoury, A.; Nunes, A.; Gateau, J.; Symvoulidis, P.; Feuchtinger, A.; Beziere, N.; Ovsepian, S.V.; Walch, A.; Ntziachristos, V. High-Resolution Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography of the Vascularization and Constitutive Hypoxemia of Cancerous Tumors. Neoplasia 2016, 18, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razansky, D.; Ntziachristos, V. Optical and Optoacoustic Imaging. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2020, 216, 155–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haedicke, K.; Agemy, L.; Omar, M.; Berezhnoi, A.; Roberts, S.; Longo-Machado, C.; Skubal, M.; Nagar, K.; Hsu, H.T.; Kim, K.; et al. High-resolution optoacoustic imaging of tissue responses to vascular-targeted therapies. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaszewski, M.R.; Gehrung, M.; Joseph, J.; Quiros-Gonzalez, I.; Disselhorst, J.A.; Bohndiek, S.E. Oxygen-Enhanced and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Optoacoustic Tomography Provide Surrogate Biomarkers of Tumor Vascular Function, Hypoxia, and Necrosis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5980–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagel, M.D. Science to practice: Can photoacoustic imaging be used to monitor tumor oxygenation and the effects of antivascular chemotherapies? Radiology 2015, 275, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmire, M.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Clearance properties of nano-sized particles and molecules as imaging agents: Considerations and caveats. Nanomedicine 2008, 3, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.T.; Li, M.L.; Zhang, H.F.; Maslov, K.; Stoica, G.; Wang, L.V. Three-dimensional imaging of skin melanoma in vivo by dual-wavelength photoacoustic microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 34032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffels, I.; Dissemond, J.; Pöppel, T.; Schadendorf, D.; Klode, J. Intraoperative Fluorescence Imaging for Sentinel Lymph Node Detection: Prospective Clinical Trial to Compare the Usefulness of Indocyanine Green vs Technetium Tc 99m for Identification of Sentinel Lymph Nodes. JAMA Surg. 2015, 150, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, B.; Armanetti, P.; Sanità, G.; Vitiello, G.; Lamberti, A.; Calì, G.; Pezzella, A.; Luciani, G.; Menichetti, L.; Luin, S.; et al. Silver-nanoparticles as plasmon-resonant enhancers for eumelanin’s photoacoustic signal in a self-structured hybrid nanoprobe. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 102, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorow, H.; Tribl, F.; Halliday, G.; Gerlach, M.; Riederer, P.; Double, K.L. Neuromelanin in human dopamine neurons: Comparison with peripheral melanins and relevance to Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005, 75, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K. Chemistry of mixed melanogenesis—Pivotal roles of dopaquinone. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucca, F.A.; Segura-Aguilar, J.; Ferrari, E.; Muñoz, P.; Paris, I.; Sulzer, D.; Sarna, T.; Casella, L.; Zecca, L. Interactions of iron, dopamine and neuromelanin pathways in brain aging and Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 155, 96–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; Cheng, K.; Hu, X.; Ma, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, M.; Lu, X.; Xing, L.; Huang, W.; Gambhir, S.S.; et al. Transferring biomarker into molecular probe: Melanin nanoparticle as a naturally active platform for multimodality imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15185–15194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liopo, A.; Oraevsky, A. Methods and Compositions for Carrier Agents and Clearing Agents Used in Optoacoustic Imaging Systems. U.S. Patent No. 9,615,750, 11 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liopo, A.; Su, R.; Oraevsky, A.A. Melanin nanoparticles as a novel contrast agent for optoacoustic tomography. Photoacoustics 2015, 3, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repenko, T.; Fokong, S.; De Laporte, L.; Go, D.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T.; Kuehne, A.J. Water-soluble dopamine-based polymers for photoacoustic imaging. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6084–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, D.L.; Stefania, R.; Callari, C.; De Rose, F.; Rolle, R.; Conti, L.; Consolino, L.; Arena, F.; Aime, S. Water Soluble Melanin Derivatives for Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Photoacoustic Imaging of Tumor Vasculature and Response to Antiangiogenic Therapy. Adv. Health Mater. 2017, 6, 1600550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, K.Y.; Kang, J.; Pyo, J.; Lim, J.; Chang, J.H.; Lee, J.K. pH-Induced aggregated melanin nanoparticles for photoacoustic signal amplification. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 14448–14456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Ren, X.; Ai, K.; Chen, X.; Lu, L. Targeted polydopamine nanoparticles enable photoacoustic imaging guided chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy of tumor. Acta Biomater 2017, 47, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Su, H.; Cai, J.; Cheng, D.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Liu, S.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A Multifunctional Platform for Tumor Angiogenesis-Targeted Chemo-Thermal Therapy Using Polydopamine-Coated Gold Nanorods. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 10404–10417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sheng, D.; Wang, D.; Yao, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, Z.; Deng, L.; Chen, Y. Bioinspired Multifunctional Melanin-Based Nanoliposome for Photoacoustic/Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Efficient Photothermal Ablation of Cancer. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1591–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, D.L.; Stefania, R.; Aime, S.; Oraevsky, A. Melanin-Based Contrast Agents for Biomedical Optoacoustic Imaging and Theranostic Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, E.; Engelen, M.; Monzani, E.; Sturini, M.; Girotto, S.; Bubacco, L.; Zecca, L.; Casella, L. Synthesis and structural characterization of soluble neuromelanin analogs provides important clues to its biosynthesis. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 18, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsyboulski, D.A.; Liopo, A.V.; Su, R.; Ermilov, S.A.; Bachilo, S.M.; Weisman, R.B.; Oraevsky, A.A. Enabling in vivo measurements of nanoparticle concentrations with three-dimensional optoacoustic tomography. J. Biophotonics 2014, 7, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.; Ermilov, S.A.; Liopo, A.V.; Oraevsky, A.A. Three-dimensional optoacoustic imaging as a new noninvasive technique to study long-term biodistribution of optical contrast agents in small animal models. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 101506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.G.; Weis, J.A.; Gayzik, F.S.; Thomas, A.; Chiba, A.; Gurcan, M.N.; Topaloglu, U.; Samykutty, A.; McNally, L.R. Applying dynamic contrast enhanced MSOT imaging to intratumoral pharmacokinetic modeling. Photoacoustics 2018, 11, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupple, C.W.; Morscher, S.; Burton, N.C.; Pagel, M.D.; McNally, L.R.; Cardenas-Rodriguez, J. A light-fluence-independent method for the quantitative analysis of dynamic contrast-enhanced multispectral optoacoustic tomography (DCE MSOT). Photoacoustics 2018, 10, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, K.; Yoshida, K.; Yoshioka, K.; Aki, S.; Yoneda, N.; Inoue, D.; Kitao, A.; Ogi, T.; Kozaka, K.; Minami, T.; et al. Photoacoustic imaging of tumour vascular permeability with indocyanine green in a mouse model. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2018, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, E.; Taruttis, A.; Beziere, N.; Lutich, A.A.; Razansky, D.; Ntziachristos, V. Optical imaging of cancer heterogeneity with multispectral optoacoustic tomography. Radiology 2012, 263, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolayev, V.; Dean-Ben, X.L.; Mandal, S.; Ntziachristos, V.; Razansky, D. Simultaneous visualization of tumour oxygenation, neovascularization and contrast agent perfusion by real-time three-dimensional optoacoustic tomography. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Razansky, D.; Dean-Ben, X.L. Model-Based Reconstruction of Large Three-Dimensional Optoacoustic Datasets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2020, 39, 2931–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Capozza, M.; Stefania, R.; Rosas, L.; Arena, F.; Consolino, L.; Anemone, A.; Cimino, J.; Longo, D.L.; Aime, S. An Improved Biocompatible Probe for Photoacoustic Tumor Imaging Based on the Conjugation of Melanin to Bovine Serum Albumin. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8313. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238313
Capozza M, Stefania R, Rosas L, Arena F, Consolino L, Anemone A, Cimino J, Longo DL, Aime S. An Improved Biocompatible Probe for Photoacoustic Tumor Imaging Based on the Conjugation of Melanin to Bovine Serum Albumin. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(23):8313. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238313
Chicago/Turabian StyleCapozza, Martina, Rachele Stefania, Luisa Rosas, Francesca Arena, Lorena Consolino, Annasofia Anemone, James Cimino, Dario Livio Longo, and Silvio Aime. 2020. "An Improved Biocompatible Probe for Photoacoustic Tumor Imaging Based on the Conjugation of Melanin to Bovine Serum Albumin" Applied Sciences 10, no. 23: 8313. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238313
APA StyleCapozza, M., Stefania, R., Rosas, L., Arena, F., Consolino, L., Anemone, A., Cimino, J., Longo, D. L., & Aime, S. (2020). An Improved Biocompatible Probe for Photoacoustic Tumor Imaging Based on the Conjugation of Melanin to Bovine Serum Albumin. Applied Sciences, 10(23), 8313. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238313