Abstract
New fabrication methods are strongly demanded for the development of thin-film saturable absorbers with improved optical properties (absorption band, modulation depth, nonlinear optical response). In this sense, we investigate the performance of indium nitride (InN) epitaxial layers with low residual carrier concentration (<1018 cm−3), which results in improved performance at telecom wavelengths (1560 nm). These materials have demonstrated a huge modulation depth of 23% and a saturation fluence of 830 µJ/cm2, and a large saturable absorption around −3 × 104 cm/GW has been observed, attaining an enhanced, nonlinear change in transmittance. We have studied the use of such InN layers as semiconductor saturable absorber mirrors (SESAMs) for an erbium (Er)-doped fiber laser to perform mode-locking generation at 1560 nm. We demonstrate highly stable, ultrashort (134 fs) pulses with an energy of up to 5.6 nJ.
1. Introduction
In recent years, significant progress has been made on the fabrication of ultrafast fiber lasers (delivering extremely short pulses, in the order of picoseconds or femtoseconds), which have become the key element for multiple applications, such as optical communications, material processing, laser micromachining [1,2,3,4,5], etc. These reliable, flexible, and compact sources have found applications not only in industrial processes but also in the medical (biological photonics [6,7,8]) or military (radar systems [9,10]) fields. In order to generate laser pulses, two different techniques are applied, namely Q-switching or mode-locking operation, both based on the insertion of a variable attenuator, e.g., a saturable absorber (SA), within the laser resonator cavity [11,12]. For both techniques, we can distinguish between active or passive operation modes, with passive approaches presenting advantages in terms of simplicity, low cost, and stability. Several nonlinear elements have been tested as variable attenuators, such as semiconductor-based SAs [13,14], carbon nanotubes [15], or nonlinear polarization-rotators [16], among others. Because of their low saturation intensity and extensive modulation depth, semiconductor SA elements are widely used in commercial lasers [17]. However, semiconductor SAs have also demonstrated some limitations, such as narrow working bandwidth and low damage threshold. Therefore, new fabrication methods should be explored to counteract these effects, since they are critical to implementing high-power, ultrafast pulsed lasers [18,19]. It is known, for instance, that semiconductor SAs are highly dependent on structural defects, such as impurities, vacancies, or grain boundaries [20,21,22,23]. It is therefore remarkable to improve the crystal quality as a way of enhancing its optical performance in terms of the absorption band, modulation depth, or saturation intensity [24,25,26].
Among semiconductor SAs, indium nitride (InN) has demonstrated remarkable advantages in comparison to other semiconductors, due to its low bandgap energy (0.65–0.9 eV) and the possibility of extending the emission wavelength from infrared to ultraviolet region when using InN and its alloys with GaN or AlN [27,28]. Furthermore, InN epitaxial layers have demonstrated high thermal stability and huge nonlinear behavior at telecom wavelengths [29,30]. For this material, the reduction of the residual carrier concentration is a challenge, since structural defects and incorporation of common impurities like oxygen or hydrogen results in efficient n-type doping [28]. Recent progress in molecular beam epitaxy has led to InN epitaxial layers with a residual carrier concentration below 1018 cm−3, which results in an absorption edge energy below 0.7 eV at room temperature [30]. It is hence interesting to study this material as a saturable absorber at 1560 nm.
In this work, we report on the application of InN layers as saturable absorbers in a laser cavity in mode-locked operation at 1560 nm. We show that a reduction of the free carrier concentration leads to an enhancement of the nonlinear optical response. We demonstrate saturable and non-saturable absorption coefficients of 4 × 104 cm−1 and −3 × 104 cm/GW, respectively, a modulation depth of 23%, and saturation attained for a power density of 4 GW/cm2. This material was inserted in a fiber laser cavity, delivering pulses with an ultrashort pulse duration of 134.4 fs and energies of up to 5.6 nJ. These results make InN a promising candidate as a saturable absorber for ultrafast laser applications in the telecom range.
2. Material Characterization
InN epitaxial layers were deposited by plasma-assisted molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) on a commercial GaN-on-sapphire template. The growth temperature was 450 °C, and the growth rate was 290 nm/h. During the deposition, the In/N flux ratio was 1.2. The indium (In) flux was interrupted along the growth every 10 min to consume the excess In on the sample surface and prevent the accumulation of In droplets there as well [22]. Two samples with different InN thicknesses were investigated: samples S1 and S2, with InN thicknesses of 360 nm and 780 nm, respectively. The thickness of the GaN-on-sapphire template was 4 µm/350 µm in both samples. Previously reported 1 µm-thick InN samples [26] with higher residual doping (samples S0 and S0′) were included in this analysis for comparison purposes. For the reference samples, the growth rate was 280 nm/h, and growth interruptions under nitrogen performed every 5 min.
An optical transmittance spectrum of the samples under study is shown in the inset of Figure 1. The linear transmission at the operation wavelength of the laser (1560 nm) was 23%, 9%, 16%, and 3% for samples S0, S0′, S1, and S2, respectively. Hence, the linear absorption coefficients were estimated at for S0, for S0′, and for samples S1 and S2. Furthermore, we have calculated the semiconductor bandgap energy from Tauc’s plots [31,32]. The obtained results, shown in Figure 1, evidence a redshift for samples S1 and S2, whose bandgap energies have been fitted to 0.69 eV and 0.67 eV, respectively, in comparison to 0.8 eV and 0.77 eV in the reference samples S0 and S0′, respectively. From the bandgap energies, the carrier concentration is estimated below cm3 for S1 and S2, 4–5 cm3 for S0′, and higher than cm3 for S0 [33]. The smaller bandgap energy in S1 and S2 can be attributed to the reduction of the Burstein–Moss effect, due to a lower carrier concentration, and therefore to an improvement of the crystal quality because of a higher control of the growth conditions related to the time intervals of N deposition [34].
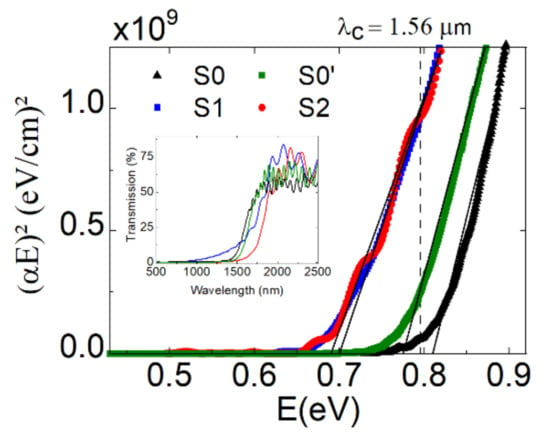
Figure 1.
Tauc’s plot for direct electronic transitions, i.e., representation of (αE)2 versus energy (E), for samples S0 (black line), S0′ (green line), S1 (blue line), and S2 (red line). The vertical dashed line indicates the operation wavelength of the laser. The inset shows the transmission of each sample as a function of the incident wavelength.
The nonlinear transmission of the SAs was measured by the open-aperture Z-scan technique [35], depicted in Figure 2a, which allows for determination of the intensity-dependent, nonlinear absorption properties (α2) for each sample. The SAs are excited by an ultrafast, mode-locked fiber laser with a pulse width of 250 fs, beam waist () of 8.5 µm, and a Rayleigh distance () of 223.2 µm (characterized by the knife-edge technique [36,37]), operating at 1560 nm with a repetition rate of 5.6 MHz. The transmitted signal is monitored by a Ge photodiode (Detector B, Thorlabs SM05PD6A) as the sample moves gradually along the propagation direction on a motorized translation stage. A power meter detects the output power of the reference beam in Detector A (Thorlabs PM100USB), in order to control possible oscillations of the laser. The laser beam has a maximum peak power of 40 kW, which corresponds to an energy fluence of 7 mJ/cm2 incident on the sample surface.
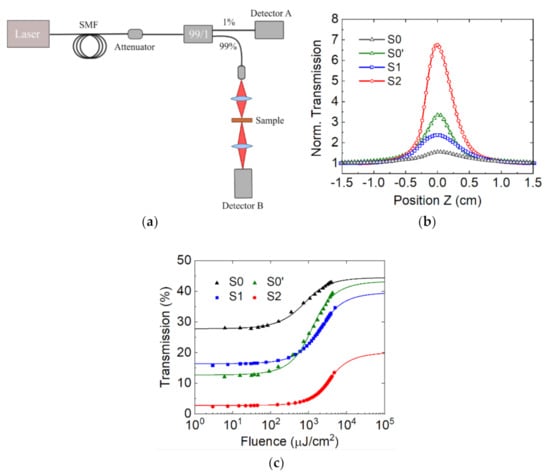
Figure 2.
(a) Schematic description of the setup for Z-scan measurements. (b) Normalized nonlinear transmission change as a function of the focal distance for the case of maximum incident pulse energy (40 kW). (c) Evolution of the nonlinear transmittance versus the incident pulse fluence at 1560 nm. Solid lines are fitting curves to Equation (2).
Figure 2b shows the transmission increase concerning the linear transmission for the maximum light intensity (40 kW), and as a function of the sample position (relative to the focus z = 0), fitted by [38,39].
where T is the transmission, is the intensity of the incident pulse; is the effective length of the InN layer; z is the position of the sample, with respect to the focal point; and the Rayleigh distance. The extracted nonlinear absorption coefficients are = , , , and cm/GW for samples S0, S0′, S1, and S2, respectively.
A study of the nonlinear transmission at the focal point and as a function of the variable impinging fluence is shown in Figure 2c, together with a fit to the following equation [14]:
where and correspond to the saturable and non-saturable transmittance coefficients respectively; is the fluence, estimated from the spatial characteristics of the incident beam (beam radius and Rayleigh distance); and represents the saturated fluence. The parameters extracted from the fits are listed in Table 1. The modulation depth (MD), calculated as Tns − Tlin, was 23.2% for S1 and 17.3% for S2, while S0 and S0′ have modulation depths of 16.7% and 30.6%, respectively. A higher saturable absorption response was obtained for samples S1 and S2 compared to reference samples S0 and S0′, as shown in Figure 2b. The maximum nonlinear transmission change ΔT, calculated as the ratio between the non-saturable and linear transmission coefficients, was obtained for S1 (241%) and S2 (715%), which means at least a two-fold improvement for S0 and S0′. Note that the reduced transmission change in S1 with respect to S2 is due to the smaller InN layer thickness, and thus to a higher coefficient (16.4% for S1 and 2.8% for S2).

Table 1.
Nonlinear optical parameters calculated from the fitting formula (2) to the experimental data for the different samples.
As depicted in Figure 2c, the samples have a saturable absorption behavior at high input fluences. This difference can be explained by the reduction of the bandgap attained in samples S1 and S2 compared to previous results. In order to achieve the optical bleaching of samples S1 and S2 (maximum transmission), a higher excitation fluence is required. This implies that the damage threshold of samples S1 and S2 may be higher than for reference samples S0 and S0′, and hence there is a wider operation energy region.
As it is shown in Figure 2c, these materials tolerate high-incident fluence. In our experimental setup, the damage threshold value could not be measured, due to the peak power limitation of the laser cavity. Our group has recently reported the highest value of incident energy fluence achievable for this type of passive mode-locked lasers (1 TW/cm2) without performing any apparent damage to the bulk InN saturable absorber [40], denoting the viability of these materials for high-power, ultrafast applications. This suggests promising results as saturable absorbers in ultrafast lasers.
3. Pulsed Laser Operation
The above-described InN saturable absorbers were inserted in a home-built, Er-doped, fiber ring laser cavity for mode-locked operation, as depicted in Figure 3a. The saturable absorber was placed in a free-space region on a reflection configuration. A 300 nm-thick aluminum layer was deposited on the InN film by radio-frequency sputtering at room temperature, to create a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror (SESAM). A commercial, erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) acted as the gain medium (Accelink, TV series), with a maximum output power of 24 dBm and 16 m of erbium-doped fiber, with a normal group velocity dispersion of 0.016 ps2/m. In this experiment, a variable optical attenuator is inserted to control the optical losses within the laser cavity. In order to maximize the optical power onto the sample, a 70/30 optical fiber coupler was included, so that 70% of the signal was recirculated inside the cavity, whereas the remaining 30% was the laser output. This configuration has demonstrated the best results for this type of laser cavity [29], in comparison to a transmitted configuration, as described in previous results [30]. The laser cavity had a total length of 38 m, from which 22 m corresponded to single-mode fiber (SMF) with anomalous dispersion (−0.021 ps2/m). It should be noticed that due to the bulk structure and small thickness, small Fabry–Pérot oscillations in the transmission measurement were measured for the InN semiconductor (inset of Figure 1), which yielded a negligible group-velocity dispersion (GVD) coefficient compared to the ones obtained for SMF and EDF. Thus, the laser cavity behaves as a dispersion-managed cavity [41,42], with a net dispersion coefficient of −0.21 ps2, operating in the anomalous dispersion regime.
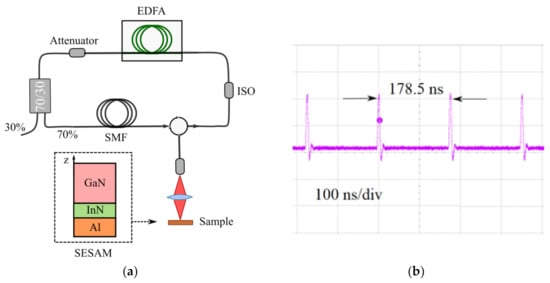
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic set-up of the erbium (Er)-doped, mode-locked fiber laser, using InN as a saturable absorber. (b) Oscilloscope trace for fundamental mode-locking operations at 5.6 MHz.
Due to the wurtzite structure of the saturable absorber, no polarization controller was added to the laser cavity, as the material is polarized independently for light impinging along its z-axis [43].
Therefore, a highly stable, mode-locked, pulsed laser was obtained inside the laser cavity, delivering Gaussian stretched pulses with a repetition rate of 5.6 MHz, as expected for strong dispersion-managed cavities [42]. Figure 3b shows the corresponding oscilloscope trace of the mode-locked pulse train, with a time interval between consecutive pulses of 178.5 ns, which coincides with the optical round trip of the fiber laser cavity working at the fundamental state, i.e., no harmonic generation was observed. The laser cavity length was increased in up to 1.05 km, obtaining Gaussian pulses at the fundamental mode without generating amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) noise from the EDFA. Higher harmonic generation has been detected for longer cavities, modifying the pulse profile at the output, as described in [40]. The corresponding signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) was characterized by a radio frequency (RF) spectrum analyzer, obtaining a value of >45 dB [29]. No side-peaks were observed in the RF spectrum between consecutive pulses, which proves the stability of the laser cavity in the mode-locking regime.
An analysis of the laser properties was performed for each sample, as a function of the output power of the laser cavity. For that purpose, the gain power of the EDFA remained constant while varying the linear losses inside the cavity through the variable optical attenuator, and thus, the energy applied to the saturable absorber. In this experiment, a second fiber coupler with a 99/1 ratio, inserted at the output of the laser cavity, monitored the average power and the autocorrelation and spectrum figures for each value of optical power inside the cavity. More details related to the measurement method can be found in [30]. In order to better understand the saturable absorber properties of the proposed InN materials, those properties have been compared to the best performance in our previous work (sample S0′) [29].
Inserting sample S1, an ultrafast, mode-locking generation was obtained for an intracavity pump power higher than 35 mW. The maximum output power of the laser cavity (minimum attenuation) was 31.6 mW, which corresponded to a peak power and pulse energy of 25.5 kW and 5.6 nJ, respectively, at an intracavity pump power of 73.7 mW. Figure 4a,b shows the autocorrelation trace and the optical spectrum, which yields a pulse duration of 156.3 fs in the autocorrelation trace (fitted to a Gaussian pulse shape and measured as the full width at half-maximum (FWHM) of the optical pulse, i.e., fs, where τAC = 221 fs is the pulse duration of the autocorrelation function), and there is a 3 dB spectral bandwidth of 26.4 nm at 1564 nm. A 0.648 constant has been applied to transform the autocorrelation (AC) temporal width to the pulse profile, as in reference [44].
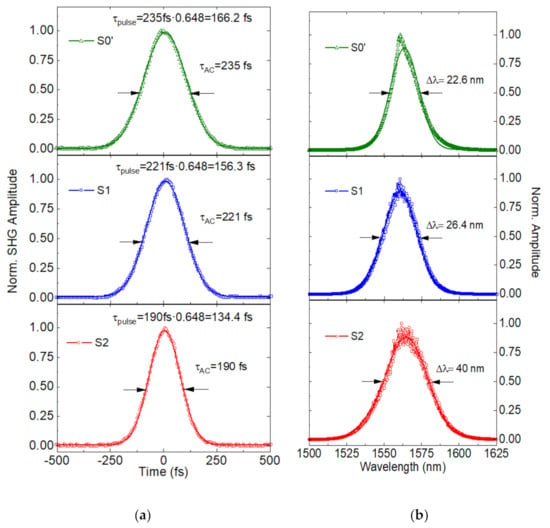
Figure 4.
(a) Mode-locked autocorrelation trace for reference sample (S0′) and modified saturable absorbers (SAs) (S1 and S2) with a Gaussian fitting function, i.e., the pulse duration of the autocorrelation function (τAC) = 235 fs for S0′, τAC = 221 fs for S1, and τAC = 190 fs for S2. (b) Optical spectrum of each sample centered in 1560 nm and fitted to a Gaussian function (22.6 nm for reference sample S0′, 25.4 nm for S1, and 40 nm for S2), with a pump power of 70 mW within the laser cavity.
This corresponds to a time–bandwidth product (TBP; measured as Δτ·Δυ, where τ is the pulse duration and υ the optical frequency) of 0.49. This implies that the pulse is not in the transform-limited situation, i.e., the optical pulses are slightly chirped. No Kelly sidebands have been observed in the optical spectrum, which denotes the weak intracavity nonlinearity and dispersion of the fiber laser [42].
By using S2, a readily highly stable pulsed laser was obtained when the intracavity pump power was higher than 38.5 mW. In the case of maximum pump power (70 mW), the output pulse had an optical power of 30 mW, developing a peak power of 28.2 kW and a 5.4 nJ pulse energy. Concerning the pulse duration of the autocorrelation function, it was estimated at 134.4 fs with a Gaussian fit ( fs where τAC = 190 fs), and the optical bandwidth at 3 dB decay was 40 nm, centered at a wavelength of 1569 nm. In this case, a more chirped pulse was obtained with TBP = 0.62.
Therefore, a reduction of the temporal duration was obtained for samples S1 and S2 concerning reference sample S0′ (166.2 fs), while the optical bandwidth increased from 22.6 nm (S0′) to 40 nm (S2). Also, Figure 4b shows a redshift of the central wavelength in S1 (1564 nm) and S2 (1569 nm) for the reference sample S0′ (1560 nm), which can be explained by the enhancement of the saturable absorption coefficient, and thus to the reduction of the carrier concentration by means of the higher control of the growth conditions during the fabrication process.
4. Discussion
The above-described results show that the reduced carrier concentration in the InN layers leads to an improvement of their performance as saturable absorbers. An enhancement of the output peak power and the energy per optical pulse (28.2 kW and 5.4 nJ) has been observed compared to the reference sample S0′ (22.3 kW and 5.2 nJ). Also, the pulse duration is shorter (134.4 fs) than that obtained for S0′ (166.2 fs) [29].
The reduction of the pulse duration, and thus the widening in the optical frequency domain, may be associated with a higher saturable absorption coefficient in S1 and S2. The enhanced nonlinear response can induce high-order nonlinear effects in the optical pulse, generating chirped pulses, which could also explain the spectral redshift in S1 and S2 observed in Figure 4b. The difference between samples S1 and S2 in terms of pulse duration and optical bandwidth is related to the variation in the active layer thickness [25]. On the other hand, a higher optical fluence has to be employed to achieve the optical bleaching of samples S1 and S2, expanding the energy operation range and thus denoting the viability of these materials for high-power applications in the telecom range.
None of these samples has displayed any sign of optical damage, even for the maximum intracavity intensity (31.6 mW of average output power implicates 73.7 mW in the resonator and a fluence of 10.5 mJ/cm2 on the saturable absorber).
In this work, a pulse duration of 134.4 fs (obtained directly from the autocorrelation trace) and an optical bandwidth of 40 nm was obtained for the best performance (S2), which is among the shortest values compared to similar fiber laser saturable absorbers. The large nonlinear effects and the high damage threshold level of the optimized, InN-based semiconductors presented above make InN SAs a promising candidate for ultrafast laser applications, such as biophotonic imaging [45] or surface micromachining [46], among others.
New types of saturable absorbers with high efficiency, compactness, and easy fabrication are currently being investigated for pulsed laser generation [47,48,49]. These saturable absorbers, also denoted as two-dimensional (2D) materials, are constituted by a few layers of atoms grown in one direction while keeping the crystal quality. In this regard, 2D materials have exhibited great results in nonlinear optics [50,51], biomedicine [52], and optoelectronics [53], due to their dimensionality and optical properties. In this sense, graphene [54,55], topological insulators (TIs) [56,57], transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) [58,59,60], and black phosphorus [61,62], are the most studied 2D materials for ultrafast fiber laser generation. Recently, some 2D materials, such as MXene [63], bismuthene [64], or antimonene [65] have emerged due to its attractive physical properties, allowing ultrafast recoveries, broad bandwidths, or low saturation fluences. However, the development of novel 2D materials with promising nonlinear optical properties is still a challenge, i.e., presenting damage thresholds below the 2 mJ/cm2, which yields some limitations in the ultrafast laser energy per pulse. Fabrication methods that monitor material deposition and the controllable optical properties of 2D materials are still an outstanding goal. Table 2 summarizes the optical properties of the modified, InN-based saturable absorbers compared to some 2D materials in erbium-doped, mode-locked fiber lasers.

Table 2.
Optical properties of mode-locked, erbium-doped fiber lasers, using two-dimensional (2D) materials as saturable absorbers (SA) at telecom wavelengths.
The results obtained in this work are comparable to those obtained for black phosphorus [61], bismuthene [64], or graphene [55], which have reported the narrowest pulse in a dispersion compensation fiber-ring cavity. Nevertheless, due to the limitations in the modulation depth coefficient, some new materials are being investigated, such as topological insulators, transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), and MXenes. The observed modulation depth and saturation intensities of the InN-based saturable absorbers are comparable to those reported for graphene or MXene in the high-power regime. Furthermore, compared to 2D materials, InN obtained the highest value of output power, and hence, the energy per optical pulse with a value of 28.2 kW and a 5.4 nJ. Compared with previous work [29], the pulse duration of the modified SA has decreased considerably, while the nonlinear saturable absorption increased two times. Therefore, these materials have demonstrated huge advantages in the high-power, ultrafast regime in comparison to other saturable absorbers.
5. Conclusions
In summary, reducing the residual carrier concentration in InN below 1018 cm−3 results in an enhancement of the nonlinear absorption at 1560 nm. Thus, we have demonstrated an InN epitaxial layer, with a thickness of 780 nm, that displays a saturable intensity of 4.4 GW/cm2, a modulation depth of 17.3%, and a nonlinear absorption coefficient in up to −3 × 104 cm/GW, and which has been observed attaining an enhanced nonlinear change in transmittance (715% of transmission change). This suggests promising results as saturable absorbers in ultrafast lasers. Based on this saturable absorber, an ultrafast fiber laser was developed with a pulse duration of 134.4 fs and peak power up to 28.2 kW. The InN-based SESAM has demonstrated not only some advantages in terms of ease of fabrication, robustness, and crystalline quality, but also a higher achievable peak power in comparison with other materials. These results make InN a promising candidate for the production of commercial saturable absorbers in the telecom spectral range.
Author Contributions
Material development, E.M.; formal analysis, L.M.; investigation, L.M., M.J.-R. and F.B.N.; data curation, L.M. and M.J.-R.; writing—original draft preparation, L.M.; writing—review and editing, E.M., M.G.-H. and F.B.N.; supervision, E.M., M.G.-H. and F.B.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Comunidad de Madrid, grant number S2018/NMT-4326; by the Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades, grant number RTI2018-097957-B-C31; and the Ministerio de Economía, Industria y Competitividad, Gobierno de España, with grant number TEC2015-71127-C2-2-R.
Acknowledgments
Authors want to thank S. Fernández from Centro de Investigaciones Energéticas, Medioambientales y Tecnológicas (CIEMAT) for the transmittance measurements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hirao, M.; Tsuji, S.; Mizuishi, K.; Doi, A.; Nakamura, M. Long wavelength InGaAsP/InP lasers for optical fiber communication systems. J. Opt. Commun. 1980, 1, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Heidt, A.M.; Simakov, N.; Jung, Y.; Daniel, J.M.O.; Alam, S.U.; Richardson, D.J. Diode-pumped wideband thulium-doped fiber amplifiers for optical communications in the 1800–2050 nm window. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 26450–26455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wise, F. Recent advances in fibre lasers for nonlinear microscopy. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, V.; Ibrahim, T.A.; Absil, P.P.; Johnson, F.G.; Grover, R.; Ho, P.-T. Optical signal processing using nonlinear semiconductor microring resonators. J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2002, 8, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattass, R.; Mazur, E. Femtosecond laser micromachining in transparent materials. Nat. Photonics 2008, 2, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, F.; Jackson, S.; Shang, X.; Arafin, S.; Yang, H. Mid-infrared Lasers for medical applications: Introduction to the feature issue. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 6255–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirk, M.D.; Molian, P.A. A review of ultrashort pulsed laser ablation of materials. J. Laser Appl. 1998, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccheo, S. Fiber lasers for medical diagnostics and treatments: State of the art, challenges and future perspectives. In Proceedings of the Optical Fibers and Sensors for Medical Diagnostics and Treatment Applications XVII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 23 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Samson, B. Military applications of lasers. In Fiber Lasers: Basics, Technology, and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 299–311. [Google Scholar]
- Anderberg, B.; Wolbarsht, M.L. Laser Weapons: The Dawn of a New Military Age, 1st ed.; Springer US Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 1992; p. 244. [Google Scholar]
- Garmire, E.; Yariv, A. Laser mode-locking with saturable absorbers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1967, 3, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, U. Recent developments in compact ultrafast lasers. Nature 2003, 424, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, U.; Weingarten, K.J.; Kartner, F.X. Semiconductor saturable absorber mirrors (SESAM’s) for femtosecond to nanosecond pulse generation in solid-state lasers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 1996, 2, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiml, M.; Grange, R.; Keller, U. Optical characterization of semiconductor saturable absorbers. Appl. Phys. B 2004, 79, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, D.; Sun, Z.; Hasan, T.; Cho, W.B.; Wang, F.; Torrisi, F.; Ferrari, A.C. 74-fs nanotube-mode-locked fiber laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.Y.; Zhao, L.M. Generation of 47-fs directly from and erbium-doped fiber laser. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haefner, C.L.; Bayramian, A.; Betts, S.; Bopp, R.; Cupal, S.J.; Drouin, M.; Erlandson, A.; Horáček, J.; Horner, J.; Jarboe, J.; et al. High average power, diode pumped petawatt laser systems: A new generation of lasers enabling precision science and commercial applications. In Proceedings of the SPIE Research Using Extreme Light: Entering New Frontiers with Petawatt-Class Lasers III, Prague, Czech Republic, 26 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, K.; Lee, C.; Zhang, H.; He, J. Recent progress in 2D material-based saturable absorbers for all solid-state pulsed bulk lasers. Laser Photonics Rev. 2020, 14, 1900240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Safaei, R.; Rezayi, M.; Amiri, I.S. Novel D-shaped fiber fabrication method for saturable absorber application in the generation of ultra-short pulses. Laser Phys. Lett. 2017, 14, 085001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, R.B.; Smith, D.L. Dependence of the saturation intensity of p-type germanium on impurity concentration and residual absorption at 10.59 μm. Solid State Commun. 1980, 33, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Chen, K.; Chen, Z.; Chen, W.; Gui, X.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Xu, J.B. Centimeter-Scale CVD growth of highly crystalline single-layer MoS2 film with spatial homogeneity and the visualization of grain boundaries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12073–12078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potin, V.; Ruterana, P.; Nouet, G.; Pond, R.C.; Morkoç, H. Mosaic growth of GaN on (0001) sapphire: A high-resolution electron microscopy and crystallographic study of threading dislocations from low-angle to high-angle grain boundaries. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 5587–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruterana, P.; Potin, V.; Barbaray, B.; Nouet, G. Growth defects in GaN layers on top of (0001) sapphire: A geometrical investigation of the misfit effect. Philos. Mag. A 2000, 80, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruterana, P.; Syrkin, A.L.; Monroy, E.; Valcheva, E.; Kirilov, K. The microstructure and properties of InN layers. Phys. Status Solidi C 2010, 7, 1301–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteagudo-Lerma, L.; Valdueza-Felip, S.; Núñez-Cascajero, A.; Ruiz, A.; González-Herráez, M.; Monroy, E.; Naranjo, F.B. Morphology and arrangement of InN nanocolumns deposited by radio-frequency sputtering: Effect of the buffer layer. J. Cryst. Growth 2016, 434, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, F.B.; Kandaswamy, P.K.; Valdueza-Felip, S.; Calvo, V.; González-Herráez, M.; Martín-López, S.; Corredera, P.; Méndez, J.A.; Mutta, G.R.; Lacroix, B.; et al. Nonlinear absorption of InN/InGaN multiple-quantum-well structures at optical telecommunication wavelengths. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 031902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, A.G.; Hashimoto, A.; Yamamoto, A. Indium nitride (InN): A review on growth, characterization, and properties. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 2779–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Walukiewicz, W.; Yu, K.M.; Ager, J.W., III; Haller, E.E.; Lu, H.; Schaff, W.J.; Saito, Y.; Nanishi, Y. Unusual properties of the fundamental band gap of InN. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Rodríguez, M.; Monroy, E.; González-Herráez, M.; Naranjo, F.B. Ultrafast fiber laser using InN as saturable absorber mirror. J. Light. Technol. 2018, 36, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy, L.; Jiménez-Rodríguez, M.; Ruterana, P.; Monroy, E.; González-Herráez, M.; Naranjo, F.B. Effect of the residual doping on the performance of InN epilayers as saturable absorbers for ultrafast lasers at 1.55 µm. Opt. Mater. Express 2019, 9, 2785–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J. Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous Ge and Si. Mater. Res. Bull. 1968, 3, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viezbicke, B.D.; Patel, S.; Davis, B.E.; Birnie, D.P. Evaluation of the Tauc method for optical absorption edge determination: ZnO thin films as a model system. Phys. Status Solidi B 2015, 252, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Walukiewicz, W.; Li, S.X.; Armitage, R.; Ho, J.C.; Weber, E.R.; Haller, E.E.; Lu, H.; Schaff, W.J.; Barcz, A.; et al. Effects of electron concentration on the optical absorption edge of InN. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 2805–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.; Jones, R.E.; Li, S.X.; Yu, K.M.; Walukiewicz, W. Electron mobility in InN and III-alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik-bahae, M.; Said, A.A.; Wei, T.H.; Hagan, D.J.; Vanstryland, E.W. Sensitive measurement of optical nonlinearities using a single beam. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 1990, 26, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, J.A.; Hubbard, W.M.; Mandeville, G.D.; de la Clavière, B.; Franke, E.A.; Franke, J.M. Technique for fast measurement of gaussian laser beam parameters. Appl. Opt. 1971, 10, 2775–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, M.A.; Silva, R.; de Lima, E.; Pereira, D.P.; de Oliveira, P.C. Measurement of Gaussian laser beam radius using the knife-edge technique: Improvement on data analysis. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapple, P.B.; Staromlynska, J.; Hermann, J.A.; Mckay, T.J.; Mcduff, R.G. Single-Beam Z-scan: Measurement techniques and analysis. J. Nonlinear Opt. Phys. Mater. 1997, 6, 251–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, M.S.; Muhammad, A.S.; Rashid, S.A.; Mahdi, M.A. Frequency and duty cycle modulation optimization in minimizing thermal accumulation effect in Z-scan measurement with high-repetition-rate laser. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallazzi, F.; Jimenez-Rodriguez, M.; Monroy, E.; Corredera, P.; González-Herráez, M.; Naranjo, F.B.; Castañón, J.D.A. Megawatt peak-power femtosecond ultralong ring fibre laser with InN SESAM. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe and European Quantum Electronics Conference, Munich, Germany, 23–27 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Ippen, E.P.; Haus, H.A.; Nelson, L.E. 77-fs pulse generation from a stretched-pulse mode-locked all-fiber ring laser. Opt. Lett. 1993, 18, 1080–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turitsyn, S.K.; Bale, B.G.; Fedoruk, M.P. Dispersion-managed solitons in fibre systems and lasers. Phys. Rep. 2012, 521, 135–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Rodríguez, M.; Monteagudo-Lerma, L.; Monroy, E.; González-Herráez, M.; Naranjo, F.B. Widely power-tunable polarization-independent ultrafast mode-locked fiber laser using bulk InN as saturable absorber. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 5366–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diels, J.M.; Fontaine, J.J.; McMichael, I.A.; Simoni, F. Control and measurement of ultrashort pulse shapes (in amplitude and phase) with femtosecond accuracy. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnola, P.J.; Wei, M.; Lewis, A.; Loew, L.M. High-Resolution nonlinear optical imaging of live cells by second harmonic generation. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 3341–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, N.H. Femtosecond laser micromachining: Current status and applications. Riken Rev. 2003, 50, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, R.I.; Kelleher, E.J.R. 2D saturable absorbers for fibre lasers. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 1440–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Mao, D.; Zhao, J. Recent progress of pulsed fiber lasers based on transition-metal dichalcogenides and black phosphorus saturable absorbers. Nanophotonics 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Yin, K.; Wang, C.; You, J.; Ouyang, H.; Miao, R.; Zhang, C.; Wei, K.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; et al. Ultrafast fiber lasers mode-locked by two-dimensional materials: Review and prospect. Photonics Res. 2020, 8, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autere, A.; Jussila, H.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lipsanen, H.; Sun, Z. Nonlinear optics with 2D layered materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eibl, M.; Weng, D.; Hakert, H.; Kolb, J.P.; Pfeiffer, T.; Hundt, J.E.; Huber, R.; Karpf, S. Wavelength agile multi-photon microscopy with a fiber amplified diode laser. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 6273–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Venugopalan, V. Mechanisms of pulsed laser ablation of biological tissues. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 577–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, O.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wee, A.T.S. Van der Waals stacked 2D layered materials for optoelectronics. 2D Mater. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ni, Z.; Yan, Y.; Shen, Z.X.; Loh, K.P.; Tang, D.Y. Atomic-layer graphene as a saturable absorber for ultrafast pulsed lasers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3077–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotor, J.; Pasternak, I.; Krajewska, A.; Strupinski, W.; Sobon, G. Sub-90 fs a stretched-pulse mode-locked fiber laser based on a graphene saturable absorber. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 27503–27508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Lin, R.; Ruan, S.; Liu, A.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Guo, C.; Hu, J. A practical topological insulator saturable absorber for mode-locked fiber laser. Sci Rep. 2005, 5, 8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, X.; Liu, M.; Zhao, N.; Luo, A.; Luo, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.; Wen, S. Femtosecond pulse generation from a topological insulator mode-locked fiber laser. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 6868–6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, J.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Jhon, Y.M.; Lee, J.H. Femtosecond harmonic mode-locking of a fiber laser at 3.27 GHz using a bulk-like, MoSe2-based saturable absorber. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 10575–10589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Liu, M.L.; Yang, Y.; Hou, H.; Ma, G.; Lei, M.; Wei, Z.Y. Tungsten diselenide for mode-locked erbium-doped fiber lasers with short pulse duration. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Liu, M.L.; Liu, B.; Quhe, R.G.; Lei, M.; Fang, S.B.; Teng, H.; Wei, Z.Y. Nonlinear optical properties of MoS2-WS2 heterostructure in fiber lasers. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 6689–6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotor, J.; Sobon, G.; Macherzynski, W.; Paletko, P.; Abramski, K.M. Black phosphorus saturable absorber for ultrashort pulse generation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 051108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Hu, G.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.; Albrow-Owen, T.; Howe, R.C.T.; Wu, T.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Hasan, T. 102 fs pulse generation from a long-term stable, inkjet-printed black phosphorus-mode-locked fiber laser. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 12506–12513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, S.; Liang, W.; Luo, S.; He, Z.; Ge, Y.; Wang, H.; Cao, R.; Zhang, F.; Wen, Q.; et al. Broadband nonlinear photonics in few-layer MXene Ti3C2Tx (T = F, O, or OH). Laser Photonics Rev. 2018, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Wang, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Huang, H.; Zhang, F.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, H. Sub-200 fs soliton mode-locked fiber laser based on bismuthene saturable absorber. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 22750–22760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumera, M.; Sofer, Z. 2D monoelemental arsenene, antimonene, and bismuthene: Beyond black phosphorus. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).