Navigated 3D Ultrasound in Brain Metastasis Surgery: Analyzing the Differences in Object Appearances in Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Abstract
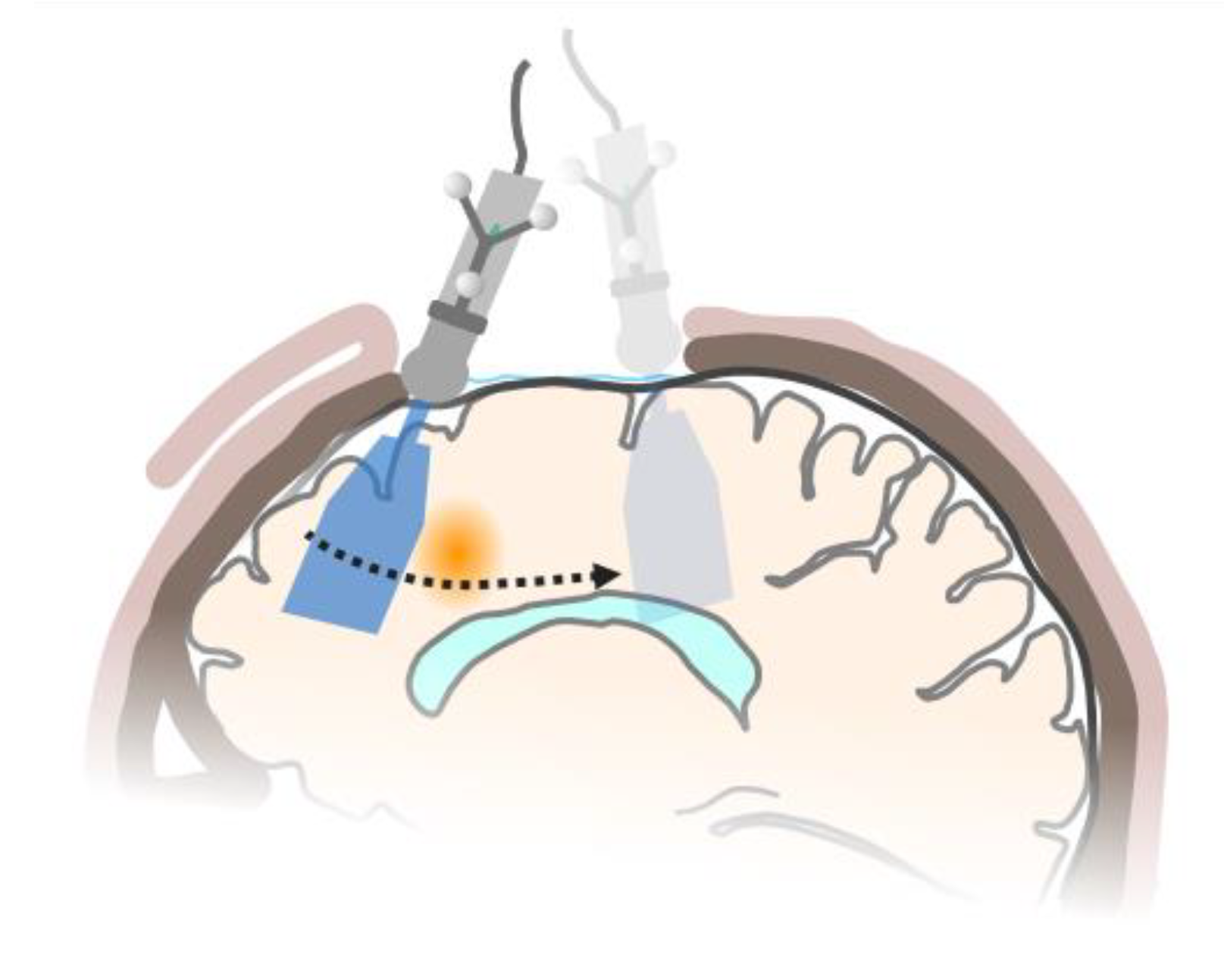
1. Introduction
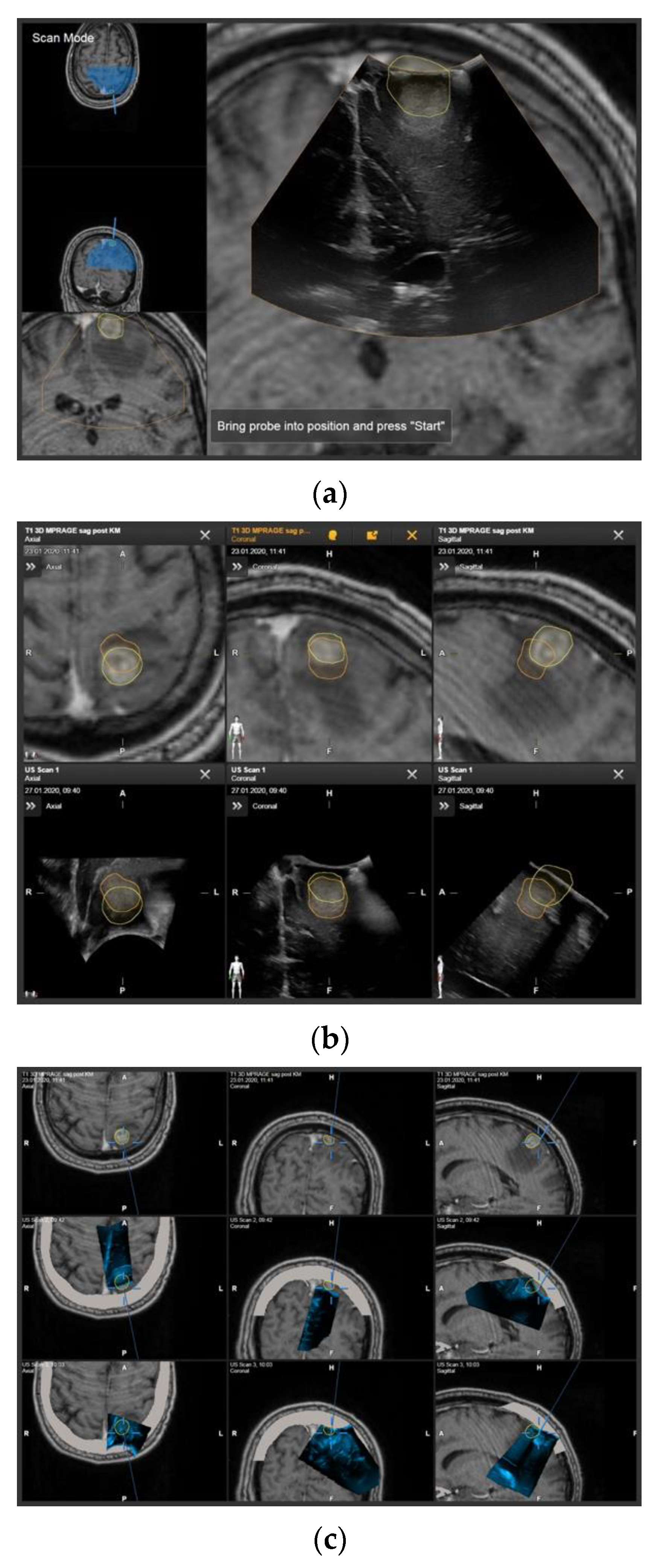
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Tumor Object Characteristics
3.3. Influence of Registration
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Tabouret, E.; Chinot, O.; Metellus, P.; Tallet, A.; Viens, P.; Goncalves, A. Recent trends in epidemiology of brain metastases: An overview. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 4655–4662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davis, F.G.; Dolecek, T.A.; McCarthy, B.J.; Villano, J.L. Toward determining the lifetime occurrence of metastatic brain tumors estimated from 2007 United States cancer incidence data. Neuro-Oncology 2012, 14, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauko, A.; Rauf, Y.; Ahluwalia, M.S. Medical management of brain metastases. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2020, 2, vdaa015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankey, E.W.; Tsvankin, V.; Grabowski, M.M.; Nayar, G.; Batich, K.A.; Risman, A.; Champion, C.D.; Salama, A.K.S.; Goodwin, C.R.; Fecci, P.E. Operative and peri-operative considerations in the management of brain metastasis. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 6809–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soffietti, R.; Abacioglu, U.; Baumert, B.; Combs, S.E.; Kinhult, S.; Kros, J.M.; Marosi, C.; Metellus, P.; Radbruch, A.; Villa Freixa, S.S.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of brain metastases from solid tumors: Guidelines from the European Association of Neuro-Oncology (EANO). Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelbaum, M.A.; Suh, J.H. Resectable brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, S.; Maier, A.; Ostermeier, M.; Fahrig, R. Intraoperative Imaging Modalities and Compensation for Brain Shift in Tumor Resection Surgery. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2017, 2017, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimsky, C.; Ganslandt, O.; Cerny, S.; Hastreiter, P.; Greiner, G.; Fahlbusch, R. Quantification of, visualization of, and compensation for brain shift using intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.W.; Hartov, A.; Kennedy, F.E.; Miga, M.I.; Paulsen, K.D. Intraoperative brain shift and deformation: A quantitative analysis of cortical displacement in 28 cases. Neurosurgery 1998, 43, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, P.J.; Kall, B.A.; Goerss, S.; Earnest, F.T. Computer-assisted stereotaxic laser resection of intra-axial brain neoplasms. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 64, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorward, N.L.; Alberti, O.; Velani, B.; Gerritsen, F.A.; Harkness, W.F.; Kitchen, N.D.; Thomas, D.G. Postimaging brain distortion: Magnitude, correlates, and impact on neuronavigation. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 88, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.L.; Maurer, C.R., Jr.; Maciunas, R.J.; Barwise, J.A.; Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Wang, M.Y. Measurement of intraoperative brain surface deformation under a craniotomy. Neurosurgery 1998, 43, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audette, M.A.; Siddiqi, K.; Peters, T.M. Level-Set Surface Segmentation and Fast Cortical Range Image Tracking for Computing Intrasurgical Deformations. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI’99, Proceeding of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Cambridge, UK, 19–22 September, 1999; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 788–797. [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz, C.R.; Bonsanto, M.M.; Knauth, M.; Tronnier, V.M.; Albert, F.K.; Staubert, A.; Kunze, S. Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging to update interactive navigation in neurosurgery: Method and preliminary experience. Comput. Aided Surg. 1997, 2, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimsky, C.; Ganslandt, O.; Hastreiter, P.; Fahlbusch, R. Intraoperative compensation for brain shift. Surg. Neurol. 2001, 56, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, A.; Black, P.M.; Gering, D.T.; Westin, C.F.; Mehta, V.; Pergolizzi, R.S., Jr.; Ferrant, M.; Warfield, S.K.; Hata, N.; Schwartz, R.B.; et al. Serial intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging of brain shift. Neurosurgery 2001, 48, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimsky, C.; Ganslandt, O.; von Keller, B.; Romstock, J.; Fahlbusch, R. Intraoperative high-field-strength MR imaging: Implementation and experience in 200 patients. Radiology 2004, 233, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinertsen, I.; Lindseth, F.; Askeland, C.; Iversen, D.H.; Unsgard, G. Intra-operative correction of brain-shift. Acta Neurochir. 2014, 156, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, W.F.; Knake, J.E.; McGillicuddy, J.E.; Lillehei, K.O.; Silver, T.M. Intraoperative use of real-time ultrasonography in neurosurgery. J. Neurosurg. 1982, 57, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knake, J.E.; Chandler, W.F.; McGillicuddy, J.E.; Silver, T.M.; Gabrielsen, T.O. Intraoperative sonography for brain tumor localization and ventricular shunt placement. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1982, 139, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, R.; Bi, W.L.; Pieper, S.; Frisken, S.; Kapur, T.; Wells, W., III; Golby, A.J. Applications of Ultrasound in the Resection of Brain Tumors. J. Neuroimaging 2017, 27, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronningsaeter, A.; Kleven, A.; Ommedal, S.; Aarseth, T.E.; Lie, T.; Lindseth, F.; Lango, T.; Unsgard, G. SonoWand, an ultrasound-based neuronavigation system. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohue, S.; Kumon, Y.; Nagato, S.; Kohno, S.; Harada, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Kikuchi, K.; Miki, H.; Ohnishi, T. Evaluation of intraoperative brain shift using an ultrasound-linked navigation system for brain tumor surgery. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2010, 50, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsgaard, G.; Ommedal, S.; Muller, T.; Gronningsaeter, A.; Nagelhus Hernes, T.A. Neuronavigation by intraoperative three-dimensional ultrasound: Initial experience during brain tumor resection. Neurosurgery 2002, 50, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronnier, V.M.; Bonsanto, M.M.; Staubert, A.; Knauth, M.; Kunze, S.; Wirtz, C.R. Comparison of intraoperative MR imaging and 3D-navigated ultrasonography in the detection and resection control of lesions. Neurosurg. Focus 2001, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munkvold, B.K.R.; Jakola, A.S.; Reinertsen, I.; Sagberg, L.M.; Unsgard, G.; Solheim, O. The Diagnostic Properties of Intraoperative Ultrasound in Glioma Surgery and Factors Associated with Gross Total Tumor Resection. World Neurosurg. 2018, 115, e129–e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, G.E.; Lamborn, K.R.; Berger, M.S. Coregistration accuracy and detection of brain shift using intraoperative sononavigation during resection of hemispheric tumors. Neurosurgery 2003, 53, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeau, R.M.; Fenster, A.; Peters, T.M. Intraoperative US in interactive image-guided neurosurgery. Radiographics 1998, 18, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letteboer, M.M.; Willems, P.W.; Viergever, M.A.; Niessen, W.J. Brain shift estimation in image-guided neurosurgery using 3-D ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, A.G.; Kumar, N.K.; Chacko, G.; Athyal, R.; Rajshekhar, V. Intraoperative ultrasound in determining the extent of resection of parenchymal brain tumours—a comparative study with computed tomography and histopathology. Acta Neurochir. 2003, 145, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerganov, V.M.; Samii, A.; Akbarian, A.; Stieglitz, L.; Samii, M.; Fahlbusch, R. Reliability of intraoperative high-resolution 2D ultrasound as an alternative to high-field strength MR imaging for tumor resection control: A prospective comparative study. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerganov, V.M.; Samii, A.; Giordano, M.; Samii, M.; Fahlbusch, R. Two-dimensional high-end ultrasound imaging compared to intraoperative MRI during resection of low-grade gliomas. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 18, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rygh, O.M.; Selbekk, T.; Torp, S.H.; Lydersen, S.; Hernes, T.A.; Unsgaard, G. Comparison of navigated 3D ultrasound findings with histopathology in subsequent phases of glioblastoma resection. Acta Neurochir. 2008, 150, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsgaard, G.; Selbekk, T.; Brostrup Muller, T.; Ommedal, S.; Torp, S.H.; Myhr, G.; Bang, J.; Nagelhus Hernes, T.A. Ability of navigated 3D ultrasound to delineate gliomas and metastases—comparison of image interpretations with histopathology. Acta Neurochir. 2005, 147, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carl, B.; Bopp, M.; Sass, B.; Nimsky, C. Intraoperative computed tomography as reliable navigation registration device in 200 cranial procedures. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the Amount of Ecologic Association Between Species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.H.; Warfield, S.K.; Bharatha, A.; Tempany, C.M.; Kaus, M.R.; Haker, S.J.; Wells, W.M., III; Jolesz, F.A.; Kikinis, R. Statistical validation of image segmentation quality based on a spatial overlap index. Acad. Radiol. 2004, 11, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, J.; Klein, J.; Dammann, P.; Wrede, K.; Gembruch, O.; Moltz, J.H.; Meine, H.; Sure, U.; Kikinis, R.; Miller, D. Automatic and efficient MRI-US segmentations for improving intraoperative image fusion in image-guided neurosurgery. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 22, 101766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttenlocher, D.P.; Klanderman, G.A.; Rucklidge, W.J. Comparing Images Using the Hausdorff Distance. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1993, 15, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flusser, J.; Suk, T. A moment-based approach to registration of images with affine geometric distortion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, K.; Graessl, A.; Rieger, J.; Lysiak, D.; Huelnhagen, T.; Winter, L.; Heidemann, R.; Lindner, T.; Hadlich, S.; Zimpfer, A.; et al. Diffusion-sensitized ophthalmic magnetic resonance imaging free of geometric distortion at 3.0 and 7.0 T: A feasibility study in healthy subjects and patients with intraocular masses. Investig. Radiol. 2015, 50, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivukangas, J.; Louhisalmi, Y.; Alakuijala, J.; Oikarinen, J. Ultrasound-controlled neuronavigator-guided brain surgery. J. Neurosurg. 1993, 79, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, N.; Dohi, T.; Iseki, H.; Takakura, K. Development of a frameless and armless stereotactic neuronavigation system with ultrasonographic registration. Neurosurgery 1997, 41, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschberg, H.; Unsgaard, G. Incorporation of ultrasonic imaging in an optically coupled frameless stereotactic system. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 1997, 68, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prada, F.; del Bene, M.; Mattei, L.; Lodigiani, L.; DeBeni, S.; Kolev, V.; Vetrano, I.; Solbiati, L.; Sakas, G.; DiMeco, F. Preoperative magnetic resonance and intraoperative ultrasound fusion imaging for real-time neuronavigation in brain tumor surgery. Ultraschall Med. 2015, 36, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunn, K.E.; Paulsen, K.D.; Roberts, D.W.; Kennedy, F.E.; Hartov, A.; West, J.D. Displacement estimation with co-registered ultrasound for image guided neurosurgery: A quantitative in vivo porcine study. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2003, 22, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.J.; Perrin, D.P.; Vasilyev, N.V.; Marx, G.R.; Del Nido, P.J.; Howe, R.D. Real-time image-based rigid registration of three-dimensional ultrasound. Med. Image Anal. 2012, 16, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coupe, P.; Hellier, P.; Morandi, X.; Barillot, C. 3D Rigid Registration of Intraoperative Ultrasound and Preoperative MR Brain Images based on Hyperechogenic Structures. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2012, 2012, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canalini, L.; Klein, J.; Miller, D.; Kikinis, R. Segmentation-based registration of ultrasound volumes for glioma resection in image-guided neurosurgery. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 1697–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackerseder, J.; Göbl, R.; Navab, N.; Hennersperger, C. Fully Automatic Segmentation of 3D Brain Ultrasound: Learning from Coarse Annotations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08655. [Google Scholar]
- Risholm, P.; Pieper, S.; Samset, E.; Wells, W.M., III. Summarizing and visualizing uncertainty in non-rigid registration. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2010, 13 Pt 2, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]



| Case | Age [Years] | Sex | Localization | Diagnosis/ Primary Tumor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 59.5 | male | left frontal | melanoma |
| 2 | 73.3 | male | right frontal | ADC, colon |
| 3 | 32.7 | male | left frontal | melanoma |
| 4 | 64.2 | male | cerebellar | ADC, lung |
| 5 | 50.7 | female | left temporal | ADC, lung |
| 6 | 69.0 | male | right parieto-occipital | ADC, gall bladder |
| 7 | 78.1 | male | cerebellar | RCC |
| 8 | 76.6 | female | left occipital | ADC, lung |
| 9 | 79.1 | male | right frontal | RCC |
| 10 | 62.8 | female | left frontal | ADC, lung |
| 11 | 57.2 | female | left frontal | CA, CUP |
| 12 | 59.2 | female | cerebellar | ADC, lung |
| 13 | 62.8 | female | left frontal | NEC, lung |
| 14 | 56.7 | female | left frontal | melanoma |
| 15 | 67.3 | female | left parietal | RCC |
| 16 | 72.8 | male | right insular | ADC, GI |
| 17 | 74.1 | female | left occipital | ADC, colon |
| 18 | 71.1 | male | cerebellar | RCC |
| 19 | 56.0 | male | left frontal | melanoma |
| 20 | 28.6 | female | right frontal | mammary CA (NST) |
| 21 * | 53.5 | male | right frontal | NEC, lung |
| 22 | 50.5 | female | right occipital | melanoma |
| 23 | 59.5 | male | left parietal | ADC, lung |
| 24 | 51.2 | female | cerebellar | NEC, lung |
| 25 | 65.3 | female | left temporo-parietal | ADC, lung |
| 26 | 74.6 | female | left occipital | ADC, colon |
| 27 | 71.5 | male | left frontal | ADC, esophagus |
| 28 | 78.2 | male | left temporal | melanoma |
| 29 | 67.6 | female | left parietal | NEC, lung |
| 30 | 69.5 | female | cerebellar | ADC, lung |
| 31 | 55.4 | female | right frontal | ADC, lung |
| 32 | 70.7 | male | right frontal | ADC, lung |
| 33 | 41.8 | female | right frontal | mammary ADC |
| 34 | 69.7 | male | right parietal | mammary ADC |
| 35 | 58.6 | male | left CN | melanoma |
| 36 | 58.6 | male | left frontal | ADC, lung |
| 37 * | 64.9 | female | left frontal | ADC, lung |
| Case | Tumor Volume MRI [cm3] | Tumor Volume US [cm3] | Dice Coefficient * | Hausdorff Distance [mm] | Center of Gravity ** [mm] | Target Registration Error [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.11 | 5.63 | 0.44 | 9.33 | 7.28 | 0.58 |
| 2 | 5.84 | 5.34 | 0.68 | 7.33 | 4.56 | 0.45 |
| 3 | 23.90 | 23.80 | 0.84 | 8.41 | 2.42 | 1.51 |
| 4 | 1.19 | 1.14 | 0.73 | 4.50 | 1.95 | 1.21 |
| 5 | 1.95 | 1.96 | 0.83 | 2.45 | 1.49 | 0.56 |
| 6 | 9.96 | 9.63 | 0.73 | 11.11 | 3.91 | 0.53 |
| 7 | 3.42 | 3.10 | 0.78 | 4.39 | 1.96 | 0.93 |
| 8 | 6.95 | 7.90 | 0.85 | 4.29 | 1.30 | 0.78 |
| 9 | 9.63 | 9.83 | 0.83 | 5.73 | 2.63 | 0.63 |
| 10 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 0.21 | 6.00 | 4.84 | 0.93 |
| 11 | 77.70 | 77.60 | 0.88 | 8.10 | 2.56 | 0.41 |
| 12 | 8.52 | 9.87 | 0.84 | 4.89 | 1.89 | 0.66 |
| 13 | 31.00 | 30.40 | 0.68 | 15.30 | 7.98 | 0.87 |
| 14 | 9.39 | 9.93 | 0.56 | 10.55 | 7.85 | 0.33 |
| 15 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 6.42 | 4.07 | 0.79 |
| 16 | 34.40 | 32.40 | 0.87 | 6.29 | 2.58 | 0.92 |
| 17 | 11.1 | 10 | 0.72 | 9.60 | 4.44 | 0.45 |
| 18 | 28.10 | 26.30 | 0.86 | 6.02 | 1.94 | 0.72 |
| 19 | 12.00 | 10.90 | 0.73 | 8.78 | 5.09 | 0.56 |
| 20 | 6.24 | 5.59 | 0.46 | 9.12 | 5.44 | 0.41 |
| 22 | 42.40 | 41.00 | 0.64 | 11.70 | 7.13 | 1.11 |
| 23 | 1.71 | 1.38 | 0.38 | 8.60 | 6.52 | 0.68 |
| 24 | 14.30 | 13.90 | 0.77 | 6.60 | 3.26 | 1.58 |
| 25 | 19.90 | 20.20 | 0.85 | 6.77 | 0.72 | 1.16 |
| 26 | 6.73 | 7.69 | 0.71 | 9.15 | 2.61 | 0.80 |
| 27 | 4.62 | 3.62 | 0.74 | 7.59 | 3.18 | 1.13 |
| 28 | 36.60 | 36.50 | 0.85 | 9.75 | 1.92 | - |
| 29 | 3.38 | 3.27 | 0.76 | 5.24 | 1.28 | 1.02 |
| 30 | 9.71 | 8.80 | 0.84 | 5.12 | 1.44 | - |
| 31 | 0.61 | 0.65 | 0.00 | 13.83 | 12.26 | - |
| 32 | 10.50 | 10.20 | 0.82 | 11.02 | 1.41 | 1.06 |
| 33 | 6.57 | 5.58 | 0.75 | 11.31 | 3.00 | 1.40 |
| 34 | 3.54 | 3.21 | 0.76 | 11.05 | 1.36 | 1.55 |
| 35 | 28.80 | 33.30 | 0.81 | 7.81 | 2.96 | 0.37 |
| 36 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 0.32 | 8.53 | 5.47 | 0.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saß, B.; Carl, B.; Pojskic, M.; Nimsky, C.; Bopp, M. Navigated 3D Ultrasound in Brain Metastasis Surgery: Analyzing the Differences in Object Appearances in Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7798. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217798
Saß B, Carl B, Pojskic M, Nimsky C, Bopp M. Navigated 3D Ultrasound in Brain Metastasis Surgery: Analyzing the Differences in Object Appearances in Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(21):7798. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217798
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaß, Benjamin, Barbara Carl, Mirza Pojskic, Christopher Nimsky, and Miriam Bopp. 2020. "Navigated 3D Ultrasound in Brain Metastasis Surgery: Analyzing the Differences in Object Appearances in Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging" Applied Sciences 10, no. 21: 7798. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217798
APA StyleSaß, B., Carl, B., Pojskic, M., Nimsky, C., & Bopp, M. (2020). Navigated 3D Ultrasound in Brain Metastasis Surgery: Analyzing the Differences in Object Appearances in Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Applied Sciences, 10(21), 7798. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217798








