Evaluation of the Built-Up Area Dynamics in the First Ring of Cluj-Napoca Metropolitan Area, Romania by Semi-Automatic GIS Analysis of Landsat Satellite Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
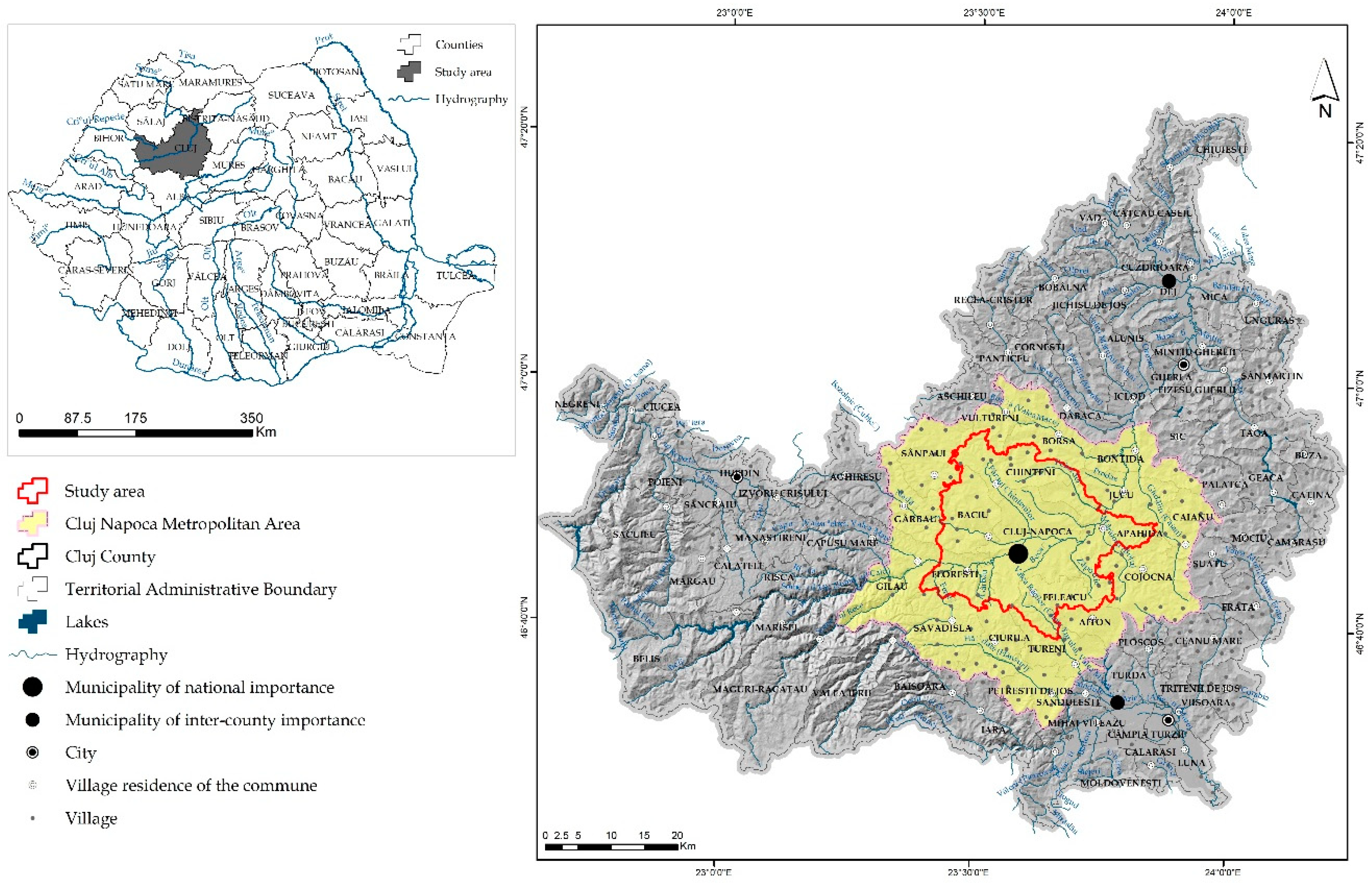
Case Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pre-Processing (Corrections and Calibrations)
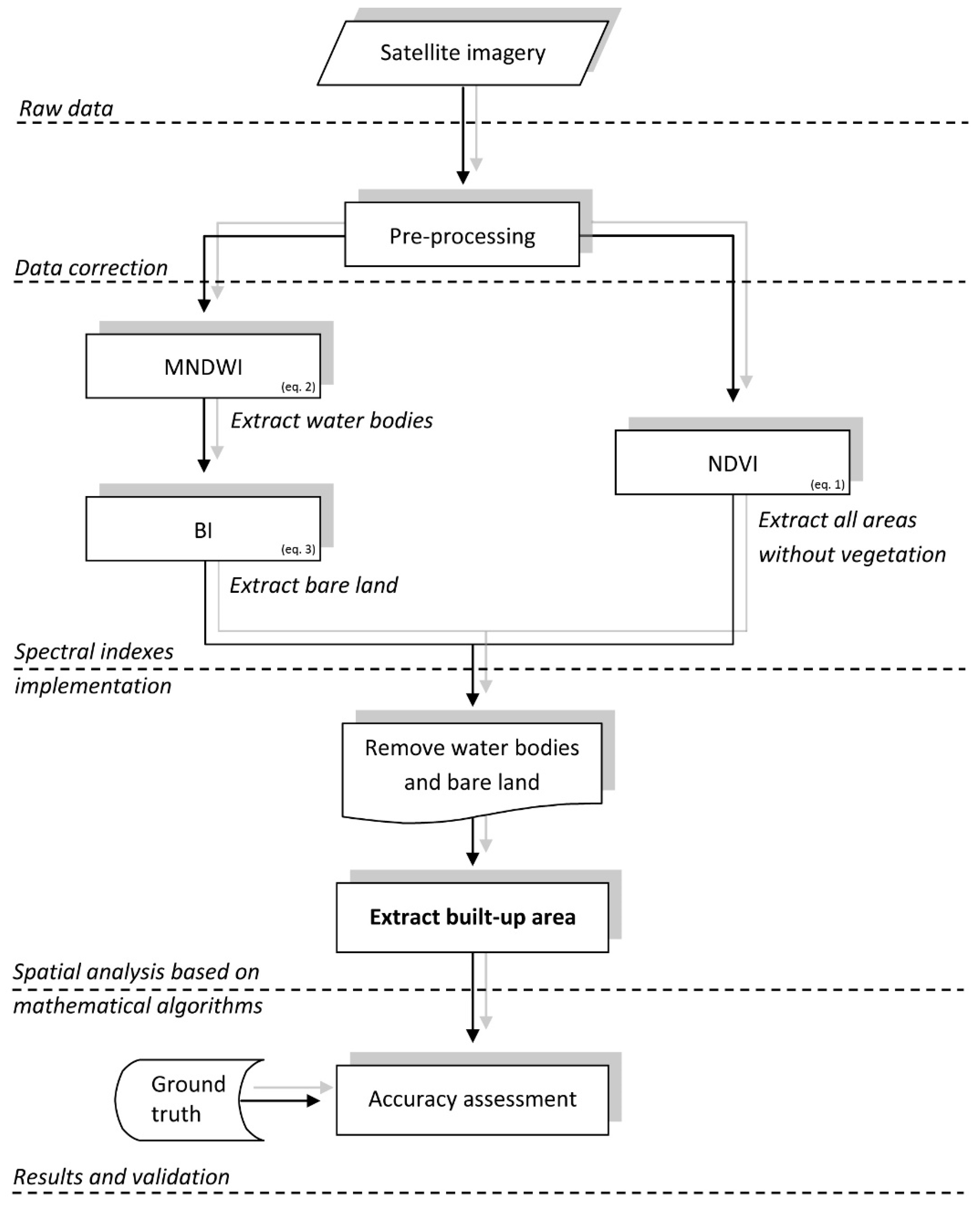
2.2. Method
3. Results
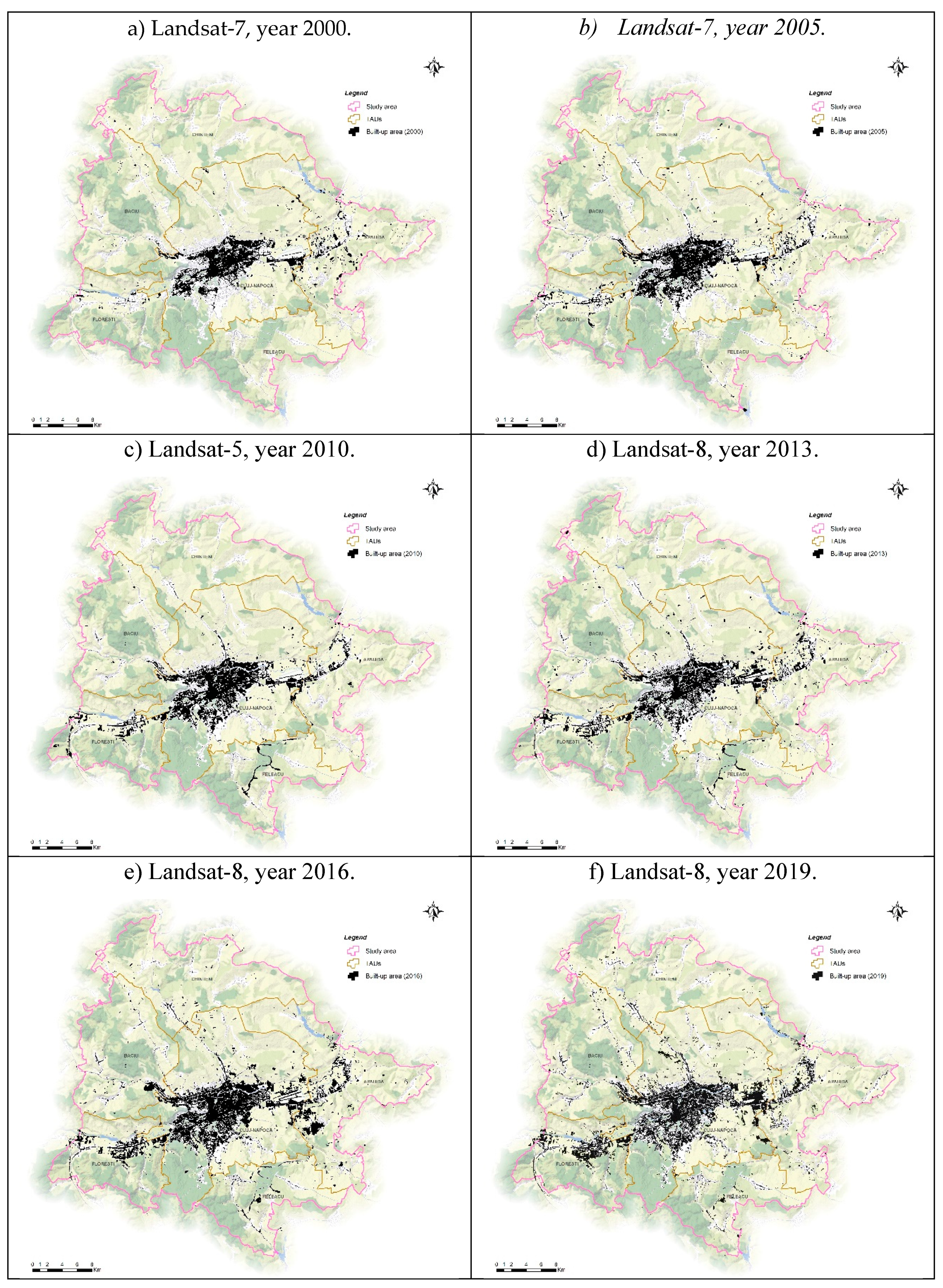
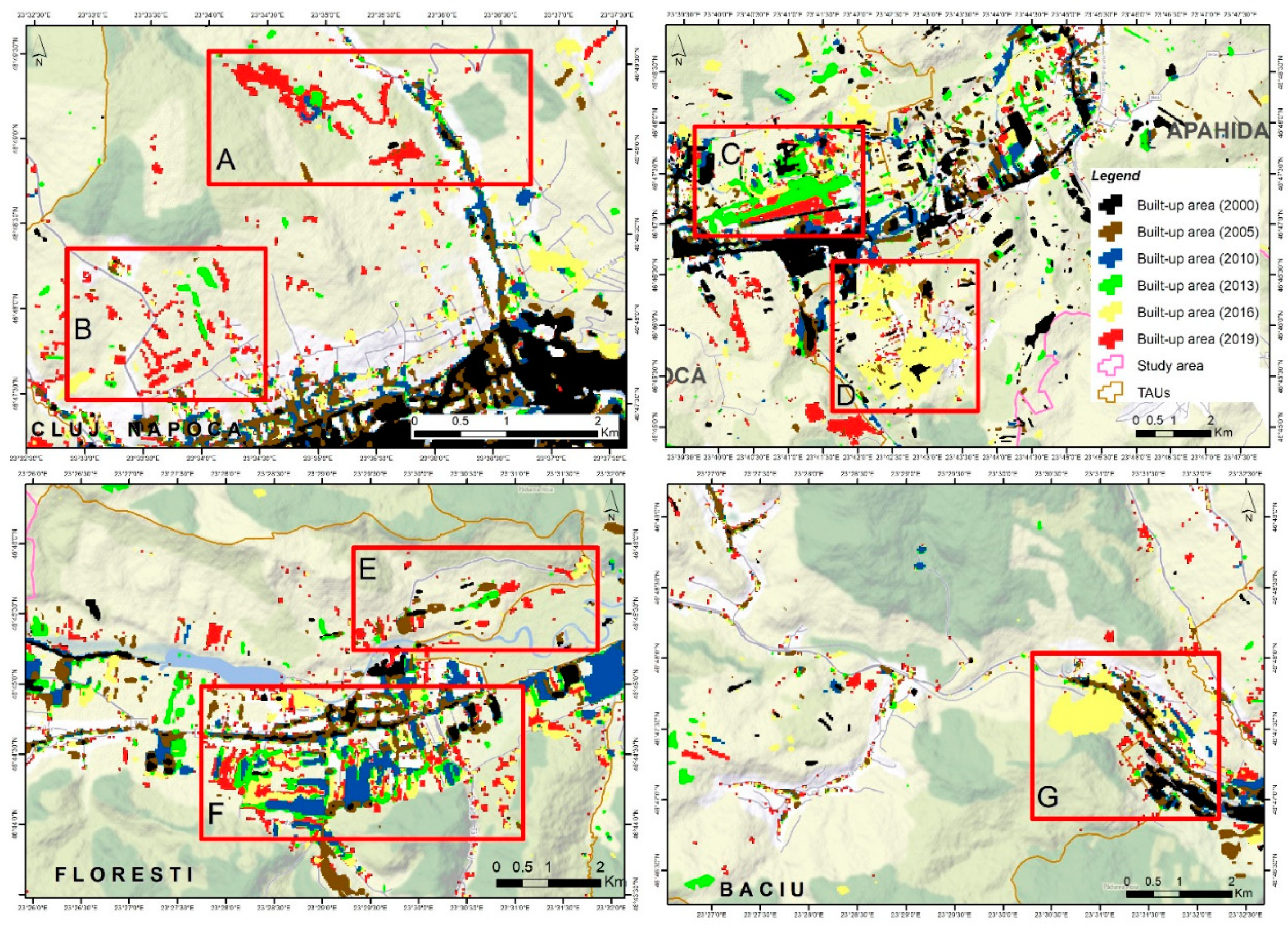
3.1. Built-Up Area Dynamics
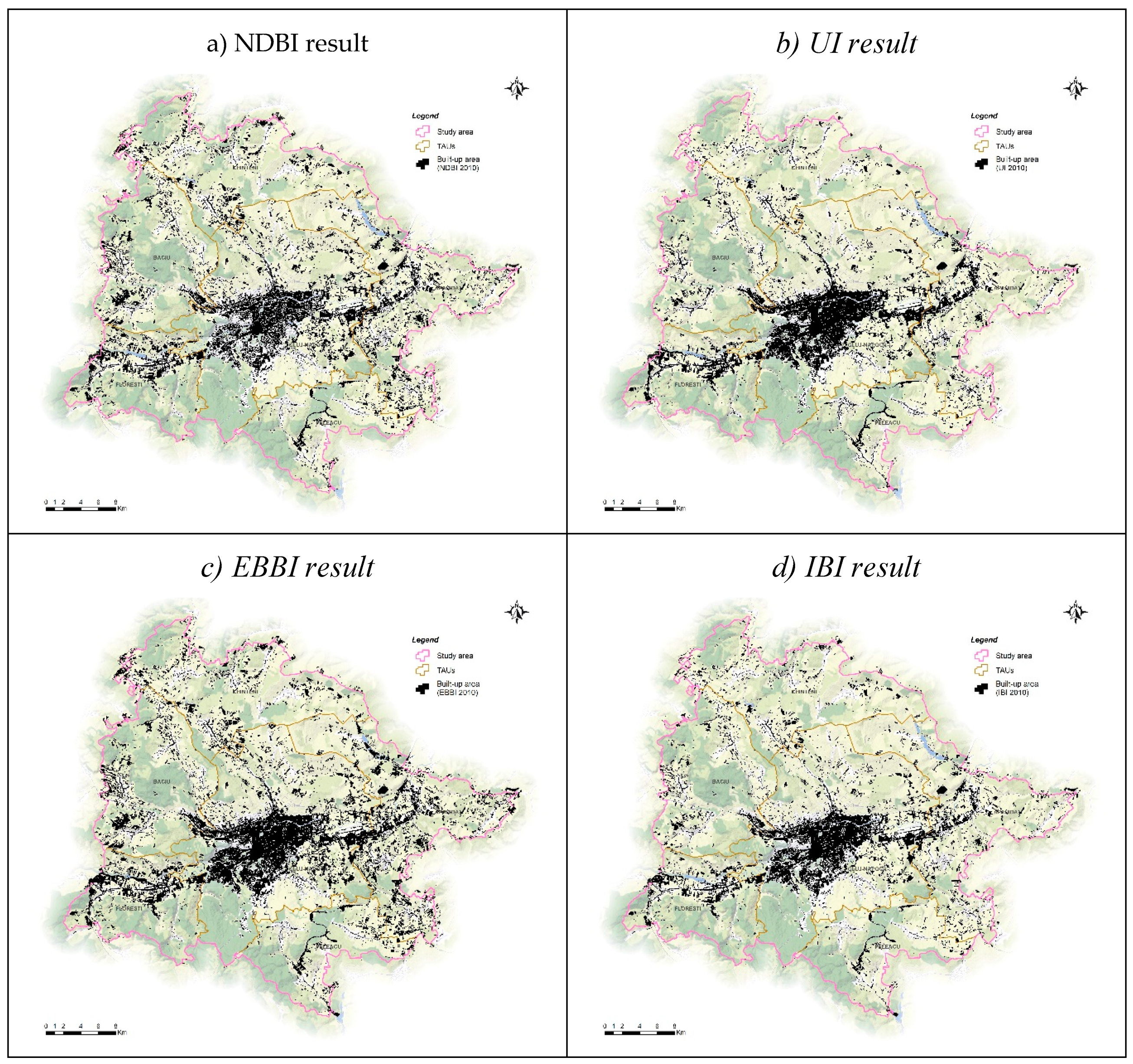
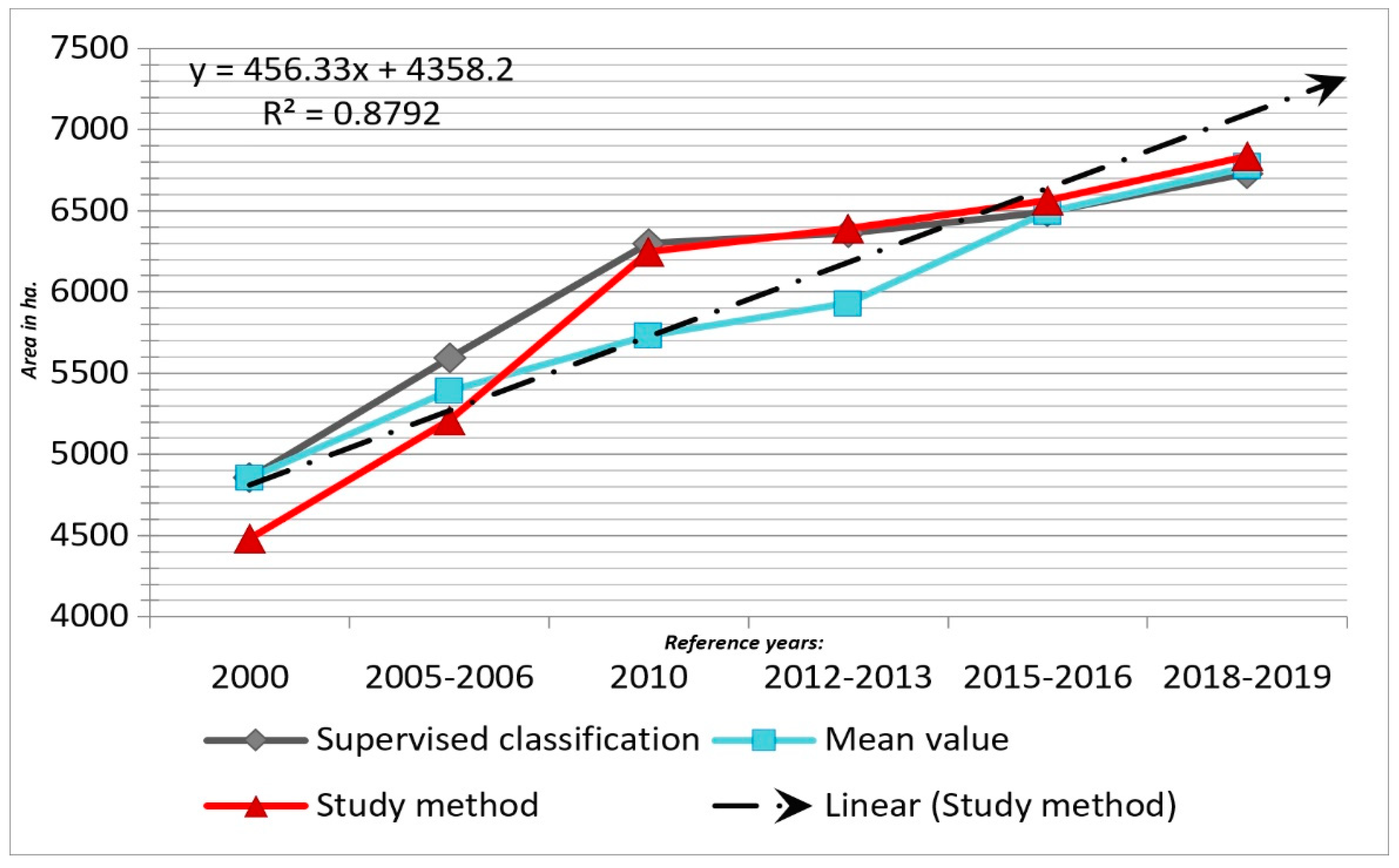
3.2. Comparison with Urban Related Indices
3.3. Accuracy Assessment
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masek, J.G.; Lindsay, F.E.; Goward, S.N. Dynamics of urban growth in the Washington DC metropolitan area, 1973–1996, from Landsat observations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 3473–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpade, C.; Man, T.; Petrea, D.; Corpade, A.-M.; Moldovan, C. Changes in landscape structure induced by transportation projects in Cluj-Napoca periurban area using GIS. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 9, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kil, J.; Kowalczyk, C.; Moldovan, C. Comparison of changes in urbanized area in Poland and Romania. Transylv. Rev. 2018, 17, 56–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, R.K.; Seto, K.C.; Schneider, A.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, W. Climate response to rapid urban growth: Evidence of a human-induced precipitation deficit. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebotari, S.; Cristea, M.; Moldovan, C.; Zubașcu, F. Renewable Energy’s Impact on Rural Development in Northwestern Romania. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roşca, S.; Bilaşco, Ş.; Petrea, D.; Fodorean, I.; Vescan, I.; Filip, S. Application of landslide hazard scenarios at annual scale in the Niraj River basin (Transylvania Depression, Romania). Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 1573–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Bilaşco, Ş.; Roşca, S.; Fodorean, I.; Vescan, I.; Filip, S.; Petrea, D. Quantitative evaluation of the risk induced by dominant geomorphological processes on different land uses, based on GIS spatial analysis models. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 12, 311–324. [Google Scholar]
- Bilasco, S.; Roşca, S.; Petrea, D.; Vescan, I.; Fodorean, I.; Filip, S. 3D Reconstruction of Landslides for the Acquisition of Digital Databases and Monitoring Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Landslides Based on GIS Spatial Analysis and UAV Techniques. In Spatial Modeling in GIS and R for Earth and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier, Hamid Reza Pourghasemi, Candan Gokceoglu: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 451–465. [Google Scholar]
- Sestras, P.; Bilasco, S.; Roşca, S.; Naș, S.; Bondrea, M.; Gâlgău, R.; Vereş, I.; Salagean, T.; Spalevic, V.; Cimpeanu, S. Landslides Susceptibility Assessment Based on GIS Statistical Bivariate Analysis in the Hills Surrounding a Metropolitan Area. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonghong, H.; Gensuo, J. Influence of land use change on urban heat island derived from multi-sensor data. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 30, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar]
- PATJCluj.ro. Available online: https://www.patjcluj.ro/rezultatele/studii-de-fundamentare/studiul-de-fundamentare-privind-riscurile-naturale.html?fbclid=IwAR3fAyA2sV-qgb4BQ1dtjanCzsLXSHgo2BhQ2pQCySvyfjvOQhuPNa7vaDM (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- European Environment Agency-Urban sprawl in Europe. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/urban-sprawl-in-europe (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Śleszyński, P.; Gibas, P.; Sudra, P. The Problem of Mismatch between the CORINE Land Cover Data Classification and the Development of Settlement in Poland. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepeška, T.; Wojkowski, J.; Wałęga, A.; Młyński, D.; Radecki-Pawlik, A.; Olah, B. Urbanization—Its Hidden Impact on Water Losses: Prądnik River Basin, Lesser Poland. Water 2020, 12, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Z.; Wang, L.; Che, M.; Hou, S. Effects of Different Urbanization Levels on Land Surface Temperature Change: Taking Tokyo and Shanghai for Example. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wu, X.; Cheng, X. The Analysis of the Urban Sprawl Measurement System of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, Based on Deep Learning and Neural Network Algorithm. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, J.A.G.; Schwick, C. Improving the measurement of urban sprawl: Weighted Urban Proliferation (WUP) and its application to Switzerland. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 38, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhira, H.S.; Kaup, J.; Ramachandra, T.V. Urban Sprawl Pattern Recognition and Modeling Using GIS, Map India Conference. 2003. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237816205 (accessed on 15 November 2017).
- Bueno-Suárez, C.; Coq-Huelva, D. Sustaining What Is Unsustainable: A Review of Urban Sprawl and Urban Socio-Environmental Policies in North America and Western Europe. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monalisha, M.; Kamal, K.M.; Subudhi, A.P. Urban Sprawl Mapping and Land Use Change Analysis Using Remote Sensing and GIS. 2011. Available online: https://geospatialworldforum.org/2011/proceeding/pdf/Monalisha.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- Banzhaf, E.; Netzband, M. Monitoring Urban Land Use Changes with Remote Sensing Techniques. Appl. Urban Ecol. A Glob. Framew. 2011, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenli, H.; Huiping, L.; Qingzu, L.; Qingxiang, J.; Junping, L.; Hua, L. Detection and Prediction of Land Use Change in Beijing Based on Remote Sensing and GIS. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Westen, C.J. Remote Sensing and GIS for Natural Hazards Assessment and Disaster Risk Management. Treatise Geomorphol. 2013, 3, 259–298. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, W.G.; Jasmine, C.; Elizabeth, F.; Duncan, T. Assessment and Prediction of Natural Hazards from Satellite Imagery. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2007, 31, 459–470. [Google Scholar]
- Matei, I.; Pacurar, I.; Rosca, S.; Bilasco, S.; Sestras, P.; Rusu, T.; Jude, E.T.; Tăut, F.D. Land Use Favourability Assessment Based on Soil Characteristics and Anthropic Pollution. Case Study Somesul Mic Valley Corridor, Romania. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarez, V.; Helen, F.; Marais-Sicre, C.; Baup, F. In-Season Mapping of Irrigated Crops Using Landsat 8 and Sentinel-1 Time Series. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claus, R.; Mushtaq, H. Toronto’s Urban Heat Island-Exploring the Relationship between Land Use and Surface Temperature. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, H. Estimating Urban Heat Island Effects on the Temperature Series of Uccle (Brussels, Belgium) using Remote Sensing Data and a Land Surface Scheme. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2773–2784. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Wang, X.R.; Wang, X.J.; Ma, W.C.; Zhang, H. Remote sensing evaluation of urban heat island and its spatial pattern of the Shanghai metropolitan area, China. Ecol. Complex 2009, 6, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weier, J.; Herring, D. Measuring Vegetation (NDVI & EVI). 2000. Available online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/MeasuringVegetation/measuring_vegetation_1.php (accessed on 30 September 2017).
- Santi, G.; Bertolazzi, A.; Leporelli, E.; Turrini, U.; Croatto, G. Green Systems Integrated to the Building Envelope: Strategies and Technical Solution for the Italian Case. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shair, I.M. GIS and Remote Sensing in urban transportation planning: A case study of Birkenhead. Auckland 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sieczka, A.; Bujakowski, F.; Falkowski, T.; Koda, E. Morphogenesis of a Floodplain as a Criterion for Assessing the Susceptibility to Water Pollution in an Agriculturally Rich Valley of a Lowland River. Water 2018, 10, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luscier, J.D.; Thompson, W.L.; Wilson, J.M.; Gorham, B.E.; Drăguţ, L.D. Using digital photographs and object- based image analysis to estimate percent ground cover in vegetation plots. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2006, 4, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, B.; Zhang, Y.; Dillabaugh, C. Landsat Urban Mapping Based on a Combined Spectral-Spatial Methodology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A New Index for Delineating Built-Up Land Features in Satellite Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4269–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Hostert, P.; Gruebner, O.; Van Der Linden, S. Mapping Megacity Growth with Multi-Sensor Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, P.; Chen, Y. Dynamic monitoring of land-use/land-cover change and urban expansion in Shenzhen using Landsat imagery from 1988 to 2015. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 38, 5388–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunyang, H.; Peijun, S.; Dingyong, X.; Yuanyuan, Z. Improving the normalized difference built-up index to map urban built-up areas using a semi-automatic segmentation approach. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 1, 213–221. [Google Scholar]
- Harig, O.; Burghardt, D.; Hecht, R. A Supervised Approach to Delineate Built-Up Areas for Monitoring and Analysis of Settlements. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.; Roberts, D.; Dennison, P.; Hess, L. Sub-pixel mapping of urban land cover using multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis: Manaus, Brazil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.; Cuizhen, W.; Cheng, Z.; Aijun, S.; Chengren, X.; Jinge, W.; Junqi, L. Mapping Urban Bare Land Automatically from Landsat Imagery with a Simple Index. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 249–263. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y. Monitoring the seasonal bare soil areas in Beijing using multitemporal TM images. In International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 3379–3382. [Google Scholar]
- As-syakur, A.R.; Adnyana, I.W.; Arthana, I.W.; Nuarsa, I.W. Enhanced Built Up and Bareness Index (EBBI) for Mapping Built-Up and Bare Land in an Urban Area. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 2957–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Geological Survey. NDVI, the Foundation for Remote Sensing Phenology. 2015. Available online: https://phenology.cr.usgs.gov/ndvi_foundation.php (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Jiang, Z.; Huete, A.R.; Didan, K.; Miura, T. Development of a two-band Enhanced Vegetation Index without a blue band. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3833–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.C. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. Modification of normalized difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.-M.; Chen, X. Use of normalized difference bareness index in quickly mapping bare areas from TM/ETM+. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. (IGARSS) 2005, 3, 1666–1668. [Google Scholar]
- Koc, D.S.; Turker, M. Automatic building detection and delineation from high resolution space images using model-based approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 33, 4193–4218. [Google Scholar]
- USGS: Spectral Characteristics Viewer. Available online: https://landsat.usgs.gov/spectral-characteristics-viewer (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Moran, M.S.; Jackson, R.D.; Slater, P.N.; Teillet, P.M. Evaluation of simplified procedures for retrieval of land surface reflectance factors from satellite sensor output. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 41, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Paolini, L. Land surface temperature retrieval from LANDSAT TM 5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsat Science: Landsat 7. Available online: https://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/landsat-7/ (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Lee, K.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.-G.; Kim, Y. Determination of the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) with Top-of-Canopy (TOC) Reflectance from a KOMPSAT-3A Image Using Orfeo ToolBox (OTB) Extension. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Yung, Y.K. Evaluation of atmospheric correction models and Landsat surface reflectance product in an urban coastal environment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6271–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Amparan, J.A.; Villarreal-Guerrero, F.; Martinez-Salvador, M.; Manjarrez-Domínguez, C.; Santellano-Estrada, E.; Pinedo-Alvarez, A. Atmospheric and Radiometric Correction Algorithms for the Multitemporal Assessment of Grasslands Productivity. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Summary of Current Radiometric Calibration Coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+ and EO-1 ALI Sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspersen, P.S.; Fensholt, R.; Drews, M. Using Landsat Vegetation Indices to Estimate Impervious Surface Fractions for European Cities. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8224–8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaiah, M.; Avtar, R.; Rahman, M.M. Land Cover Influences on LST in Two Proposed Smart Cities of India: Comparative Analysis Using Spectral Indices. Land 2020, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Yin, K.; Tang, L. A Feature-Based Approach of Decision Tree Classification to Map Time Series Urban Land Use and Land Cover with Landsat 5 TM and Landsat 8 OLI in a Coastal City, China. Isprs Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, T.A.; Hassan, Q.K.; Ishaq, S.; Batool, M.; Butt, H.J.; Jabbar, H. Investigative Spatial Distribution and Modelling of Existing and Future Urban Land Changes and Its Impact on Urbanization and Economy. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 105. [Google Scholar]
- USGS: What are the band designations for the Landsat satellites? Available online: https://landsat.usgs.gov/what-are-band-designations-landsat-satellites (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Li, S.; Chen, X. A new bare-soil index for rapid mapping developing areas using Landsat 8 data. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2014. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Technical Commission IV Symposium, Suzhou, China, 14–16 May 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yao, Z.; Weijun, G.; Dian, Z. The Investigation of Urbanization and Urban Heat Island in Beijing Based on Remote Sensing. Proc. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 216, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilaşco, S.; Govor, C.; Roşca, S.; Vescan, I.; Filip, S.; Fodorean, I. GIS model for identifying urban areas vulnerable to noise pollution: Case study. Front. Earth Sci. 2016, 11, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roșca, S.; Șimonca, V.; Bilașco, Ș.; Vescan, I.; Fodorean, I.; Petrea, D. The Assessment of Favorability and Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Pinus Mugo in the Romanian Carpathians Using GIS Technology and Landsat Images. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bălteanu, D.; Micu, M.; Jurchescu, M.; Malet, J.-P.; Sima, M.; Kucsicsa, G.; Dumitrică, C.; Petrea, D.; Mărgărint, M.C.; Bilaşco, S.T.; et al. National-scale landslide susceptibility map of Romania in a European methodological framework. Geomorphology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čurović, Ž.; Čurović, M.; Spalević, V.; Janic, M.; Sestras, P.; Popović, S.G. Identification and Evaluation of Landscape as a Precondition for Planning Revitalization and Development of Mediterranean Rural Settlements—Case Study: Mrkovi Village, Bay of Kotor, Montenegro. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, R.; Heiko, B.; Gaylan, R.; Faqe, I.; Hasan, M.H.; James, W.; Bashir, A.; Sa’ad, I.; Peshawa, M.N. Applying Built-Up and Bare-Soil Indices from Landsat 8 to Cities in Dry Climates. Land 2018, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, S.B.; Nitin, K.T. Built-up area extraction using Landsat 8 OLI imagery. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2014, 51, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
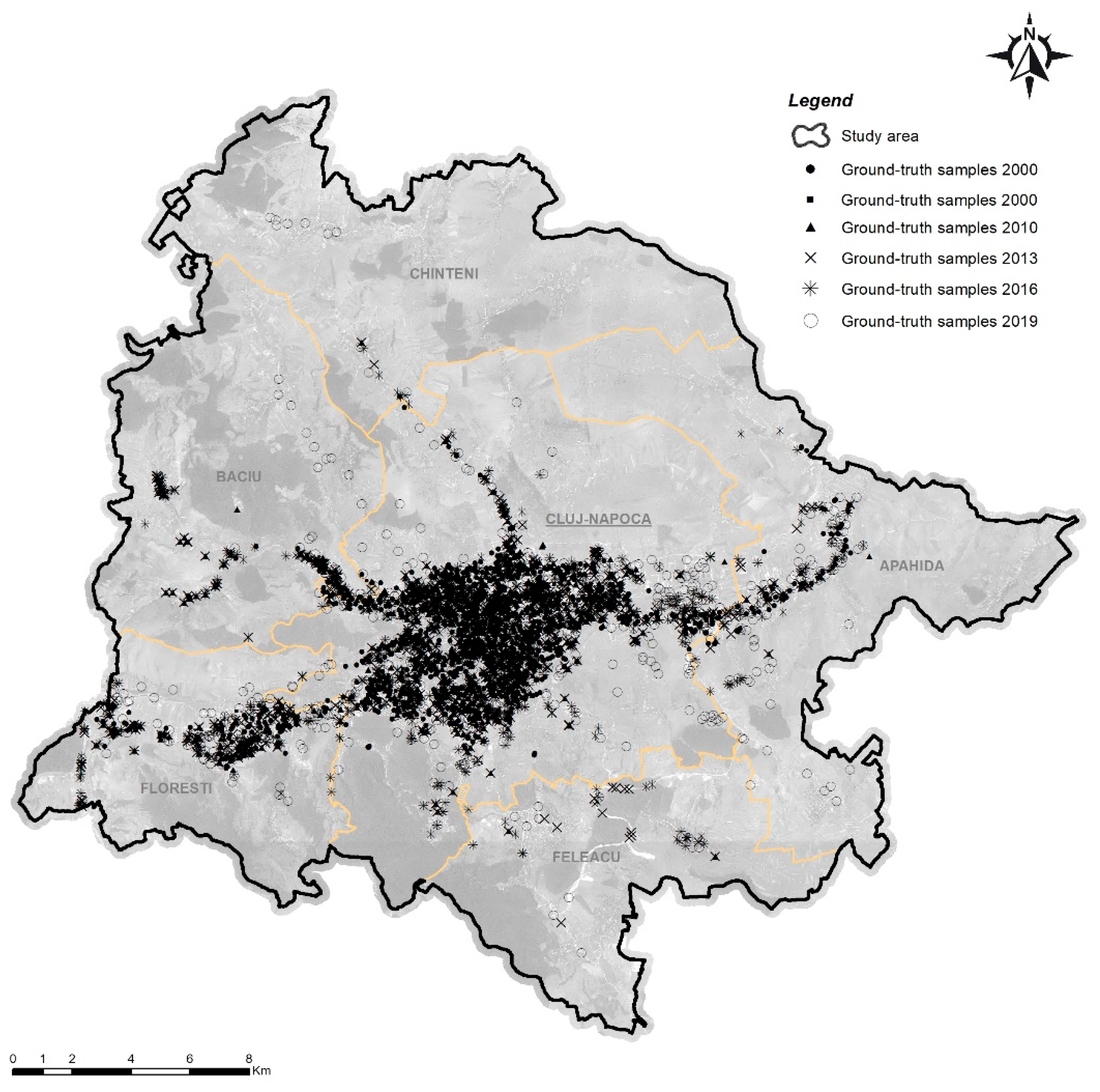
| Capture Date | Scene | Sensor | Bands | Spatial Resolution (m) | Cloud Amount (%) | RMSE (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) 2000-08-22 | Landsat-7 | ETM+ | 8 | 30 | 1 | 2.323 |
| (b) 2005-10-07 | Landsat-7 | ETM+ | 7 | 30 | 0 | 5.079 |
| (c) 2010-08-26 | Landsat-5 | TM | 7 | 30 | 12 | 4.062 |
| (d) 2013-08-02 | Landsat-8 | OLI&TIRS | 11 | 30 | 3.21 | 7.477 |
| (e) 2016-08-26 | Landsat-8 | OLI&TIRS | 11 | 30 | 0.48 | 6.783 |
| (f) 2019-07-02 | Landsat-8 | OLI&TIRS | 11 | 30 | 0.01 | 7.644 |
| Area Covered by Buildings. (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAU | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2013 | 2016 | 2019 | 2019–2000 |
| FLORESTI | 1.28 | 3.63 | 5.73 | 6.85 | 8.44 | 9.59 | 8.30 |
| BACIU | 0.43 | 0.80 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 2.39 | 3.01 | 2.58 |
| CHINTENI | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.27 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.78 |
| APAHIDA | 2.55 | 2.85 | 3.33 | 3.38 | 6.30 | 7.91 | 5.36 |
| FELEACU | 0.02 | 0.49 | 1.92 | 2.05 | 2.46 | 2.90 | 2.88 |
| CLUJ-NAPOCA | 11.13 | 13.93 | 14.54 | 14.35 | 18.88 | 20.70 | 9.57 |
| Year | Overall Acc. (%) | Kappa Coefficient | Producer Accuracy (%) | User Accuracy (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Built-Up | Other | Built-Up | Other | |||
| 2000 | 88.40 | 61.15 | 94.42 | 63.15 | 82.76 | 85.42 |
| 2005 | 88.00 | 72.80 | 96.86 | 72.53 | 92.96 | 86.03 |
| 2010 | 85.20 | 70.40 | 98.80 | 71.60 | 98.35 | 77.67 |
| 2013 | 84.60 | 67.63 | 94.43 | 71.36 | 90.48 | 81.63 |
| 2016 | 87.60 | 72.23 | 93.77 | 76.54 | 87.26 | 87.76 |
| 2019 | 86.00 | 70.67 | 94.77 | 74.18 | 91.33 | 83.18 |
| Average | 86.63 | 69.15 | 95.51 | 71.56 | 90.52 | 83.62 |
| FIG. | YEAR | NUMBER OF SAMPLE POINTS | CORRECT PREDICTED | OVERALL ACCURACY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 2000 | 1000 | 889 | 88.90% |
| b | 2005 | 1000 | 875 | 87.50% |
| c | 2010 | 1000 | 954 | 95.40% |
| d | 2013 | 1000 | 914 | 91.40% |
| e | 2016 | 1000 | 932 | 93.20% |
| f | 2019 | 1000 | 926 | 92.60% |
| No. | Source of Data | Built-Up Area (ha.) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2005–2006 | 2010 | 2012–2013 | 2015–2016 | 2018–2019 | ||
| 1 | I.N.S.S.E. | NO DATA | NO DATA | 5165 | 5177 | NO DATA | NO DATA |
| 2 | E.E.A. Urban Atlas | NO DATA | 5378.3 | NO DATA | 6253.44 | NO DATA | 6809.90 |
| 3 | Copernicus Urban Databases (ESM, Imperviousness) | NO DATA | 4705.92 | 5501.44 | 5597.32 | 5724.36 | NO DATA |
| 4 | Image classification | 4857.43 | 5593.38 | 6301 | 6363.93 | 6491.38 | 6731.22 |
| 5 | Mean value | 4857.43 | 5221.9 | 5655.81 | 5847.92 | 6107.87 | 6153.81 |
| 6 | Study method | 4482.13 | 5211.63 | 6246.61 | 6392.52 | 6562.35 | 6836.84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dolean, B.-E.; Bilașco, Ș.; Petrea, D.; Moldovan, C.; Vescan, I.; Roșca, S.; Fodorean, I. Evaluation of the Built-Up Area Dynamics in the First Ring of Cluj-Napoca Metropolitan Area, Romania by Semi-Automatic GIS Analysis of Landsat Satellite Images. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7722. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217722
Dolean B-E, Bilașco Ș, Petrea D, Moldovan C, Vescan I, Roșca S, Fodorean I. Evaluation of the Built-Up Area Dynamics in the First Ring of Cluj-Napoca Metropolitan Area, Romania by Semi-Automatic GIS Analysis of Landsat Satellite Images. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(21):7722. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217722
Chicago/Turabian StyleDolean, Bogdan-Eugen, Ștefan Bilașco, Dănuț Petrea, Ciprian Moldovan, Iuliu Vescan, Sanda Roșca, and Ioan Fodorean. 2020. "Evaluation of the Built-Up Area Dynamics in the First Ring of Cluj-Napoca Metropolitan Area, Romania by Semi-Automatic GIS Analysis of Landsat Satellite Images" Applied Sciences 10, no. 21: 7722. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217722
APA StyleDolean, B.-E., Bilașco, Ș., Petrea, D., Moldovan, C., Vescan, I., Roșca, S., & Fodorean, I. (2020). Evaluation of the Built-Up Area Dynamics in the First Ring of Cluj-Napoca Metropolitan Area, Romania by Semi-Automatic GIS Analysis of Landsat Satellite Images. Applied Sciences, 10(21), 7722. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217722








