Rapid Sonochemically-Assisted Synthesis of Highly Stable Gold Nanoparticles as Computed Tomography Contrast Agents
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of AuNPs
2.2. Materials
2.3. AuNPs Synthesis Using a Sonochemical Approach
2.4. Cytocompatibility Experiment
2.5. In Vitro CT Samples Preparation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
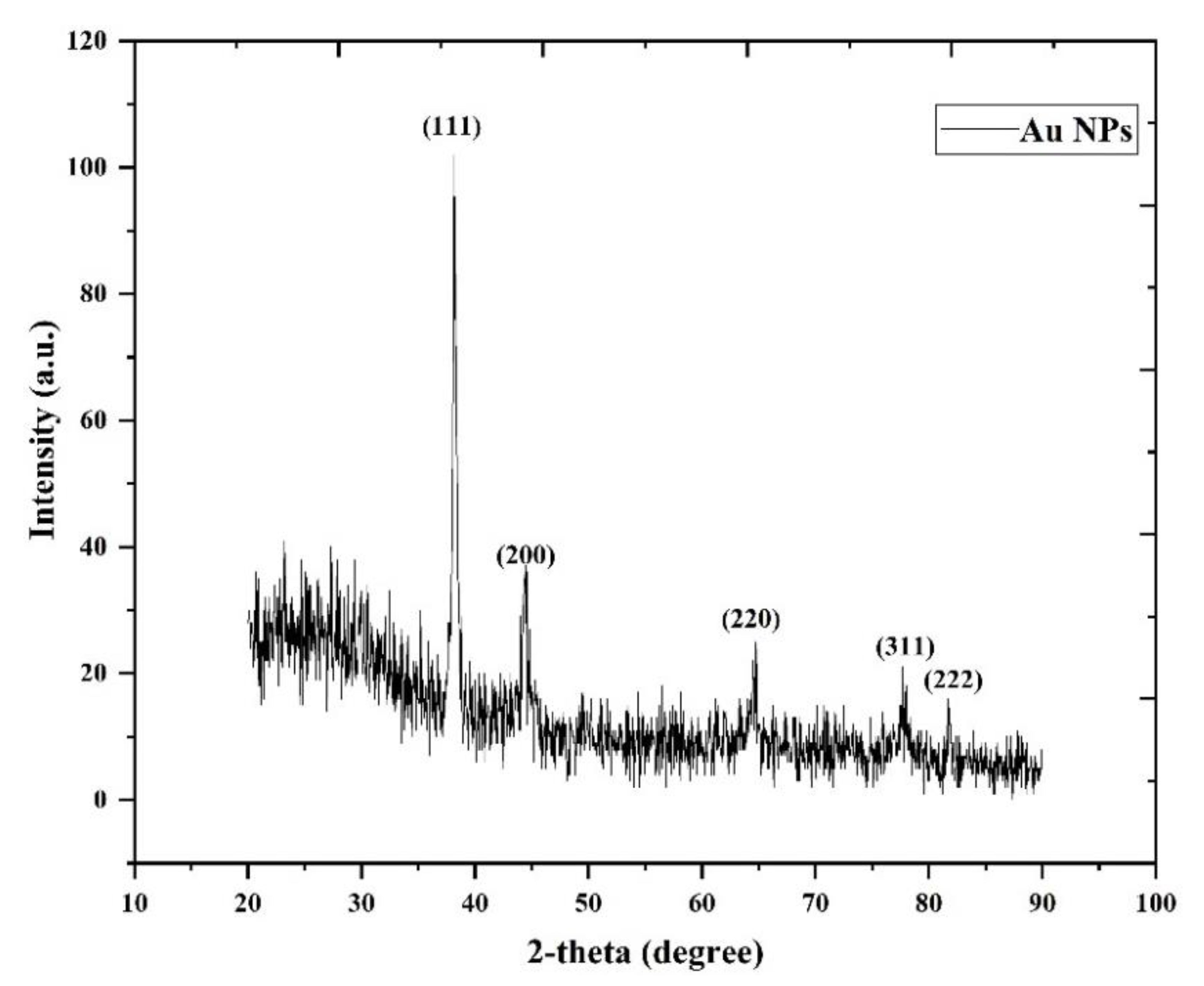
3.1. XRD Analysis
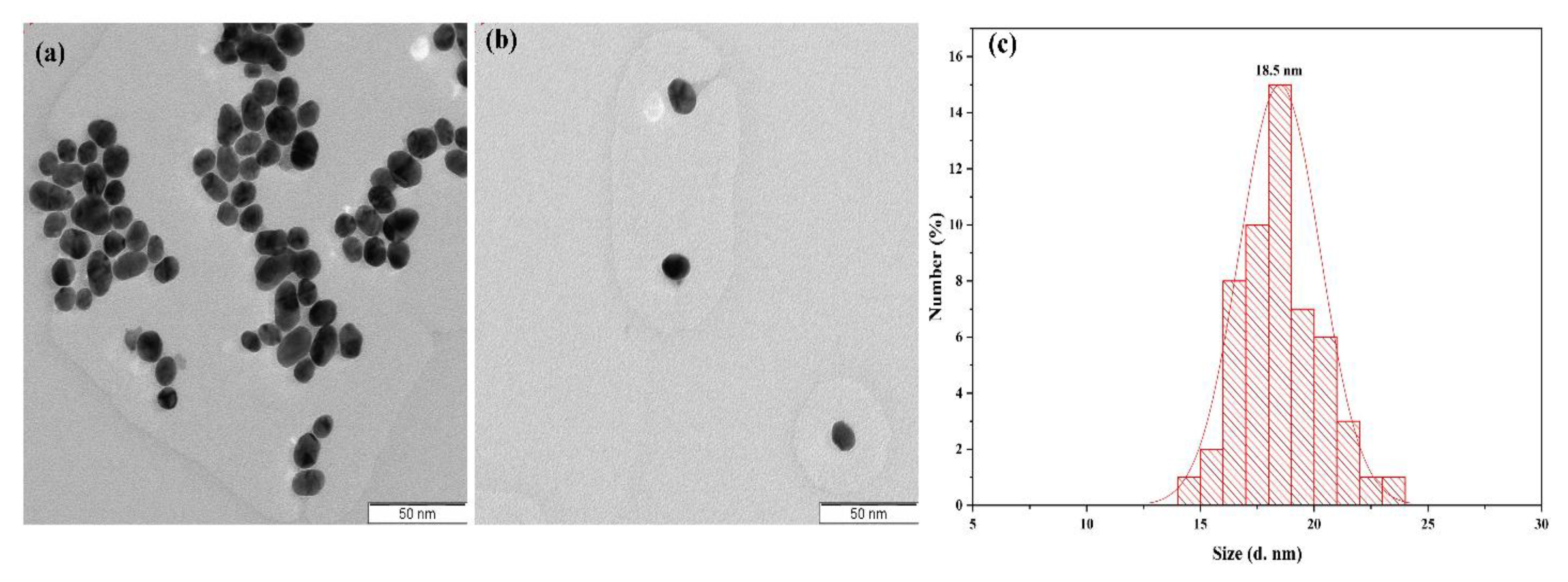
3.2. TEM and Size Distribution
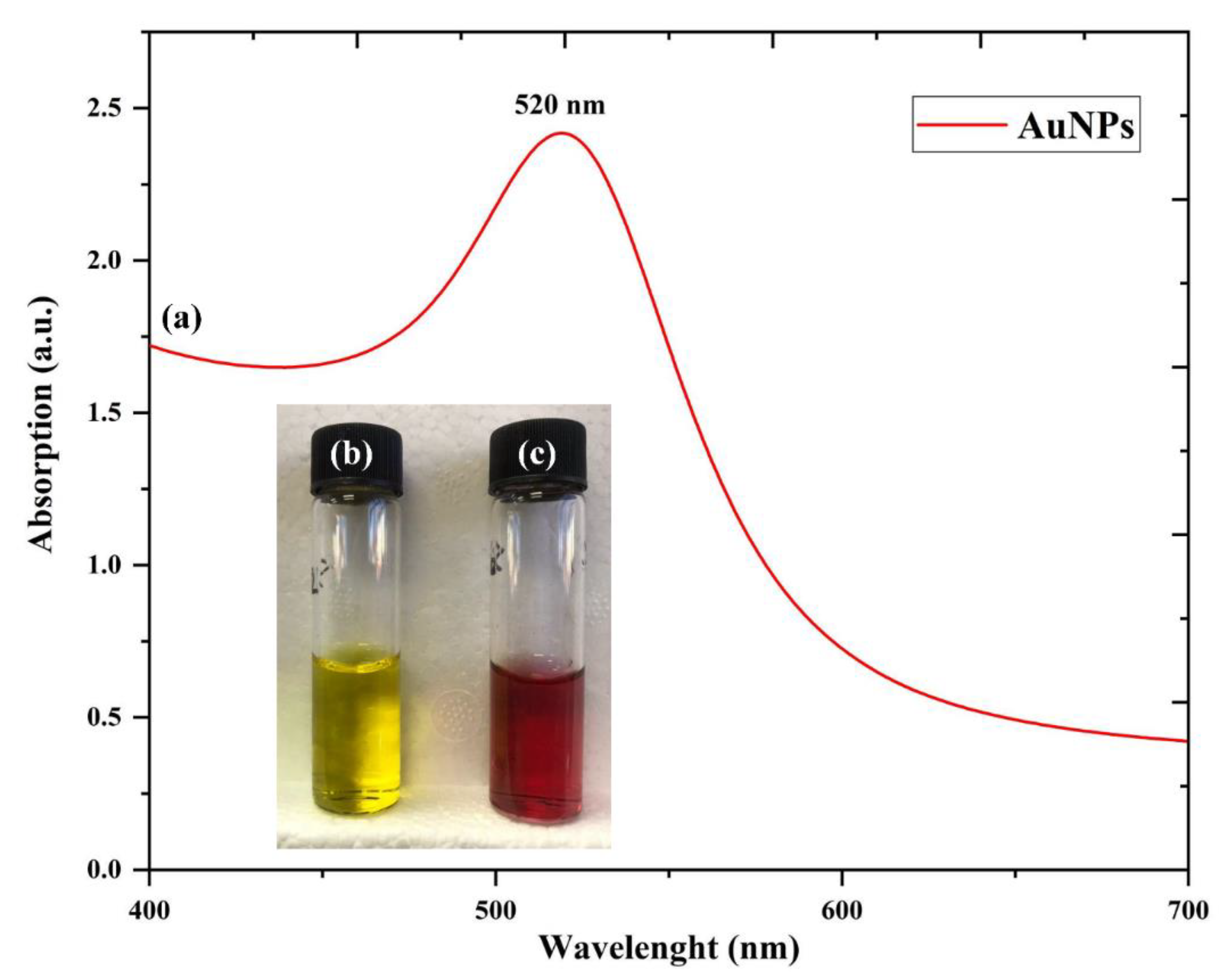
3.3. UV-Visible Analysis
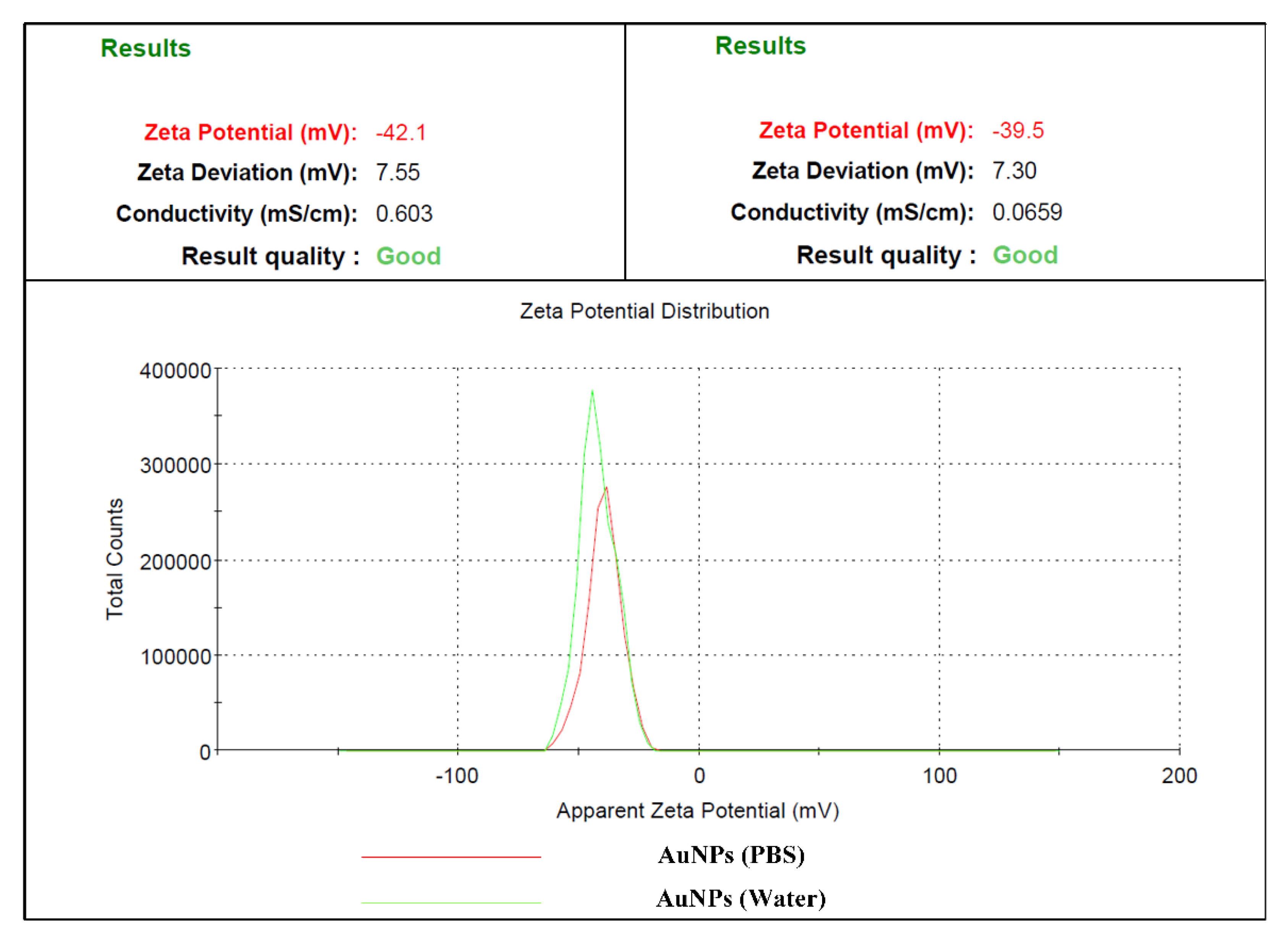
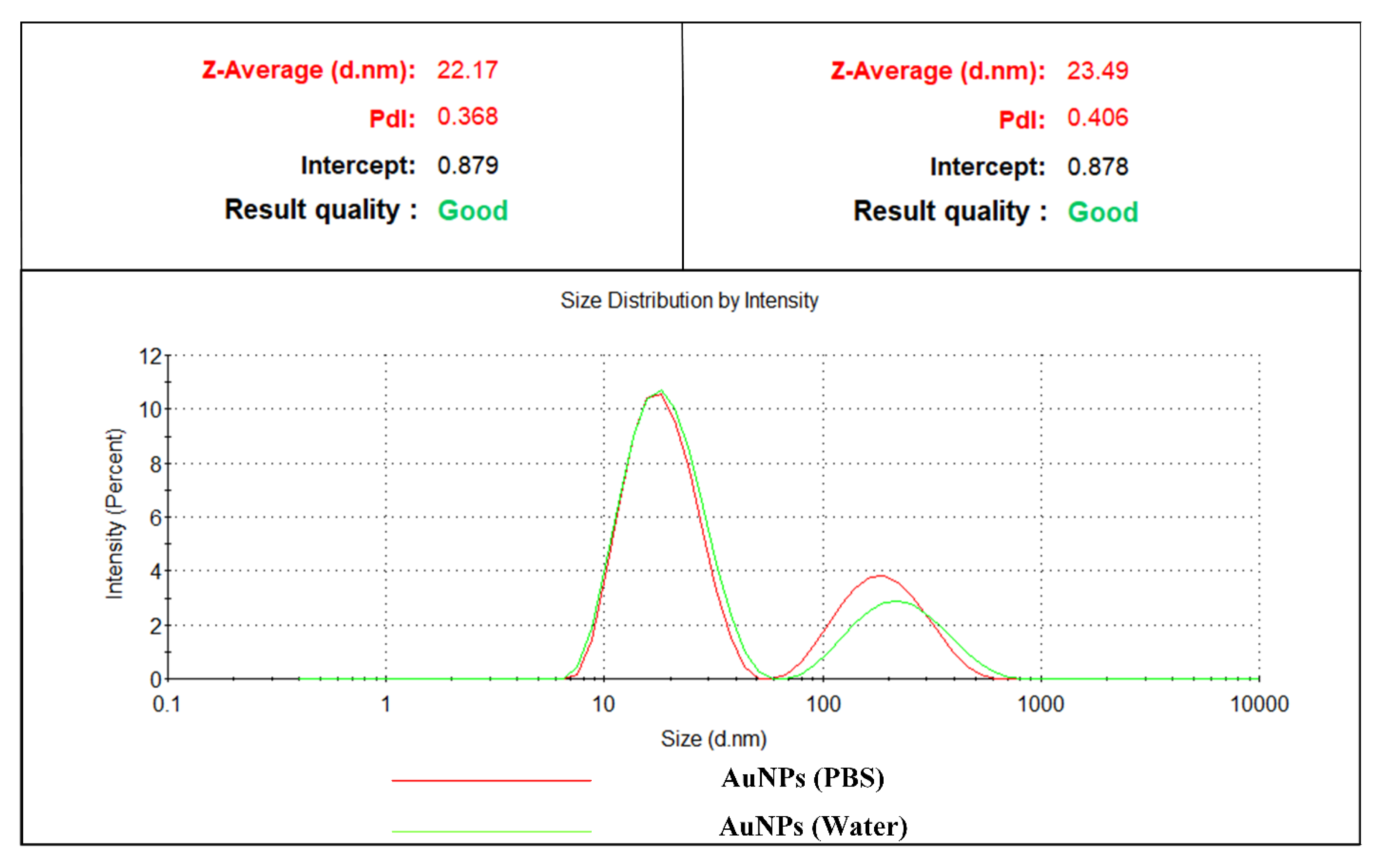
3.4. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
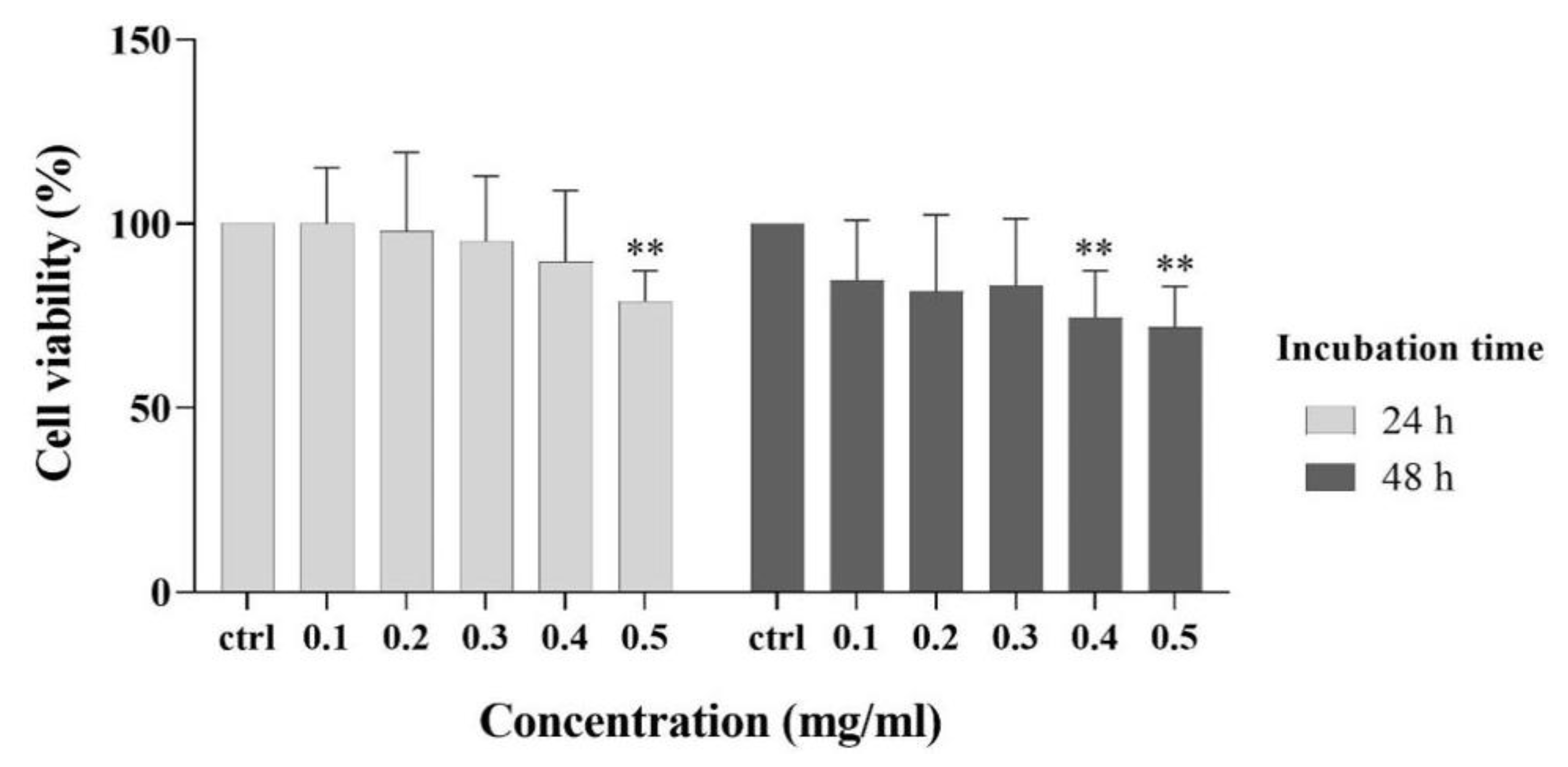
3.5. Cytocompatibility Experiment
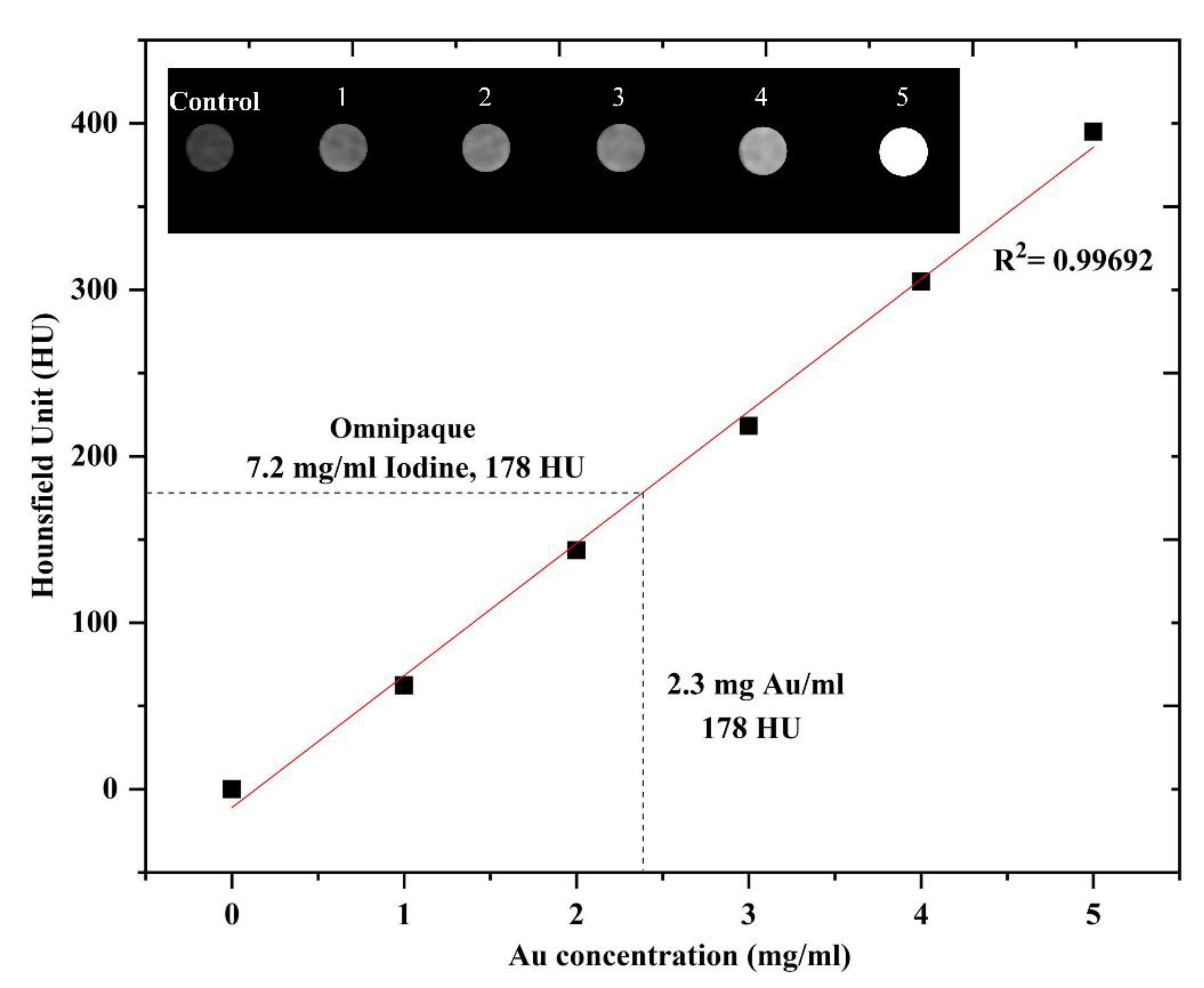
3.6. In Vitro CT Imaging
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsieh, J. Computed Tomography: Principles, Design, Artifacts, and Recent Advances; SPIE Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chhour, P.; Naha, P.C.; O’Neill, S.M.; Litt, H.I.; Reilly, M.P.; Ferrari, V.A.; Cormode, D.P. Labeling monocytes with gold nanoparticles to track their recruitment in atherosclerosis with computed tomography. Biomaterials 2016, 87, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Ghazani, A.A.; Chan, W.C. Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircher, M.F.; Willmann, J.K. Molecular body imaging: MR imaging, CT, and US. part I. principles. Radiology 2012, 263, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, A.L.; Dhanantwari, A.; Jurcova, M.; Cheheltani, R.; Naha, P.C.; Ivanc, T.; Shefer, E.; Cormode, D.P. Improved sensitivity of computed tomography towards iodine and gold nanoparticle contrast agents via iterative reconstruction methods. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalishwaralal, K.; Luboshits, G.; Firer, M. Synthesis of gold nanoparticle: Peptide–drug conjugates for targeted drug delivery. In Drug Delivery Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Rabeea, M.A.; Owaid, M.N.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Dheyab, M.A. Mycosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using the extract of Flammulina velutipes, Physalacriaceae, and their efficacy for decolorization of methylene blue. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Mehrdel, B.; Khaniabadi, B.M. Gold-coated iron oxide nanoparticles as a potential photothermal therapy agent to enhance eradication of breast cancer cells. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1497, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Owaid, M.N.; Rabeea, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S. Mycosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by the Portabello mushroom extract, Agaricaceae, and their efficacy for decolorization of Azo dye. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100312. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, N.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Jameel, M.S.; Dheyab, M.A.; Amiri, I. Identifying metal nanoparticle size effect on sensing common human plasma protein by counting the sensitivity of optical absorption spectra damping. Plasmonics 2019, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, L.; Yin, M. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Fritillaria cirrhosa and its anti-diabetic activity on Streptozotocin induced rats. Arab. J. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naharuddin, N.Z.A.; Sadrolhosseini, A.R.; Bakar, M.H.A.; Tamchek, N.; Mahdi, M.A. Laser ablation synthesis of gold nanoparticles in tetrahydrofuran. Opt. Mater. Express 2020, 10, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, M.E.; van Raap, M.B.F.; Rivas, P.C.; Zelis, P.M.; Girardin, P.; Pasquevich, G.A.; Alessandrini, J.L.; Muraca, D.; Sánchez, F.H. Stability and relaxation mechanisms of citric acid coated magnetite nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 5436–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo, I.R.; Tufenkji, N. Influence of solution chemistry on the deposition and detachment kinetics of a CdTe quantum dot examined using a quartz crystal microbalance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3176–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, M.R.; Lowry, G.V.; Jones, K.L.; Hochella, J.; F, M.; di Giulio, R.T.; Casman, E.; Bernhardt, E.S. Decreasing uncertainties in assessing environmental exposure, risk, and ecological implications of nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojea-Jiménez, I.; Puntes, V. Instability of cationic gold nanoparticle bioconjugates: The role of citrate ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13320–13327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Aruguete, D.M.; Murayama, M.; Hochella, M.F., Jr. Influence of size and aggregation on the reactivity of an environmentally and industrially relevant nanomaterial (PbS). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8178–8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.K.; Lyon, D.Y.; Alvarez, P.J. Comparative eco-toxicity of nanoscale TiO2, SiO2, and ZnO water suspensions. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3527–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dederichs, T.; Moöller, M.; Weichold, O. Temperature-dependent colloidal stability of hydrophobic nanoparticles caused by surfactant adsorption/desorption and depletion flocculation. Langmuir 2009, 25, 10501–10506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziuk, D.; Grigoriev, D.; Zhang, W.; Su, D.; Moöhwald, H.; Shchukin, D. Ultrasound-assisted fusion of preformed gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. 2010, 114, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basarir, F.; Yoon, T.-H. Sonication-assisted layer-by-layer deposition of gold nanoparticles for highly conductive gold patterns. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belova, V.; Moöhwald, H.; Shchukin, D.G. Sonochemical intercalation of preformed gold nanoparticles into multilayered clays. Langmuir 2008, 24, 9747–9753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okitsu, K.; Ashokkumar, M.; Grieser, F. Sonochemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles: Effects of ultrasound frequency. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 20673–20675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, F.; Yamamoto, N.; Todoriki, M.; Jin, J. Sonochemical preparation of gold nanoparticles for sensitive colorimetric determination of nereistoxin insecticides in environmental samples. Talanta 2018, 188, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrani, S.; Razmi, Z.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Javadian, H. Ultrasound-accelerated synthesis of gold nanoparticles modified choline chloride functionalized graphene oxide as a novel sensitive bioelectrochemical sensor: Optimized meloxicam detection using CCD-RSM design and application for human plasma sample. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 42, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Choi, S.U.; Jang, S.P.; Lee, S.Y. Production of aqueous spherical gold nanoparticles using conventional ultrasonic bath. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Du, J.; Han, B.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, Z. Sonochemical formation of single-crystalline gold nanobelts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1116–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, A.I.; Aziz, A.A.; Noqta, O.A. Green sonochemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles using palm oil leaves extracts. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 7, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.I.; Aziz, A.A.; Sodipo, B.K. Application of central composite design for optimization of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles via sonochemical method. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobaradaran, S.; Nodehi, R.N.; Yaghmaeian, K.; Jaafari, J.; Niari, M.H.; Bharti, A.K.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Azari, A.; Shariatifar, N. Catalytic decomposition of 2-chlorophenol using an ultrasonic-assisted Fe3O4–TiO2@ MWCNT system: Influence factors, pathway and mechanism study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 512, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, M.S.; Aziz, A.A.; Dheyab, M.A. Comparative analysis of platinum nanoparticles synthesized using sonochemical-assisted and conventional green methods. Nano Struct. Nano Objects 2020, 23, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S. Synthesis and Optimization of the Sonochemical Method for Functionalizing Gold Shell on Fe3O4 Core Nanoparticles using Response Surface Methodology. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 21, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Noqta, O.A.; Mehrdel, B. Synthesis and coating methods of biocompatible iron oxide/gold nanoparticle and nanocomposite for biomedical applications. Chin. J. Phys. 2020, 64, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.P.d.S.; Carvalho, B.S.; Luchez, C.V.; Politi, M.J.; Brandt, C.A. Optimization of the ultrasound-assisted synthesis of allyl 1-naphthyl ether using response surface methodology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-García, J.; Santoyo-Salzar, J.; Rangel-Cortes, E.; Goya, G.; Cardozo-Mata, V.; Pescador-Rojas, J. Effect of ultrasonic irradiation power on sonochemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 70, 105274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameel, M.S.; Aziz, A.A.; Dheyab, M.A.; Mehrdel, B.; Khaniabadi, P.M. Rapid sonochemically-assisted green synthesis of highly stable and biocompatible platinum nanoparticles. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 20, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-M.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, B. Sonochemical synthesis of silica particles and their size control. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 380, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Choi, B.G.; Yang, S.H.; Shin, W.H.; Kang, J.K.; Jung, D.; Hong, W.H. Ionic-Liquid-Assisted Sonochemical Synthesis of Carbon-Nanotube-Based Nanohybrids: Control in the Structures and Interfacial Characteristics. Small 2009, 5, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okitsu, K.; Nishimura, R. Sonochemical reduction method for controlled synthesis of metal nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. In Proceedings of the 20th International Congress on Acoustics, ICA, Sydney, Australia, 23–27 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Ng, H.P.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, J.; Han, F.; Peng, F.; Fu, L. Gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, stability test, and application for the rice growth. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piella, J.; Bastús, N.G.; Puntes, V. Size-Controlled Synthesis of Sub-10-nanometer Citrate-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles and Related Optical Properties. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.C.; Hajfathalian, M.; Maidment, P.S.; Hsu, J.C.; Naha, P.C.; Si-Mohamed, S.; Breuilly, M.; Kim, J.; Chhour, P.; Douek, P. Effect of gold nanoparticle size on their properties as contrast agents for computed tomography. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Li, K.; Cao, X.; Xiao, T.; Hou, W.; Zheng, L.; Guo, R.; Shen, M.; Zhang, G.; Shi, X. Facile formation of dendrimer-stabilized gold nanoparticles modified with diatrizoic acid for enhanced computed tomography imaging applications. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 6768–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodipo, B.K.; Aziz, A.A. One minute synthesis of amino-silane functionalized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by sonochemical method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayathulhan, R.; Sodipo, B.K.; Aziz, A.A. Nucleation and growth of zinc oxide nanorods directly on metal wire by sonochemical method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.G.; Muthoosamy, K.; Zhou, M.; Ashokkumar, M.; Huang, N.M.; Manickam, S. Sonochemical and sustainable synthesis of graphene-gold (G-Au) nanocomposites for enzymeless and selective electrochemical detection of nitric oxide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 622–629. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, R.; Dalvi, S.V. Sonocrystallization: Monitoring and controlling crystallization using ultrasound. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 115911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, I.; Tung, L.D.; Maenosono, S.; Wälti, C.; Thanh, N.T. Synthesis of core-shell gold coated magnetic nanoparticles and their interaction with thiolated DNA. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 2624–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilgin, P.; Ozay, O.; Ozay, H. A novel hydrogel containing thioether group as selective support material for preparation of gold nanoparticles: Synthesis and catalytic applications. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 241, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Wang, D.; Schaaf, P. Tunable plasmon resonance of semi-spherical nanoporous gold nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 2014, 1, 035018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Lee, J.; Park, T.J.; Lee, S.J.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, J. Ultrasensitive DNA monitoring by Au–Fe3O4 nanocomplex. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 163, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamipour, S.; Sadjadi, M.; Farhadyar, N. Fabrication and spectroscopic studies of folic acid-conjugated Fe3O4@ Au core–shell for targeted drug delivery application. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2015, 148, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Suslick, K.S. The effects of ultrasound on crystals: Sonocrystallization and sonofragmentation. Crystals 2018, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.-C.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles: Assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 293–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Size and temperature dependence of the plasmon absorption of colloidal gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 4212–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, K.G.; Frigo, T.B.; Groman, J.Y.; Groman, E.V. Synthesis of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxides using reduced polysaccharides. Bioconjugate Chem. 2004, 15, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Noqta, O.A.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Mehrdel, B. Simple rapid stabilization method through citric acid modification for magnetite nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dixit, C.K. Methods for characterization of nanoparticles. In Advances in Nanomedicine for the Delivery of Therapeutic Nucleic Acids; Elsevier: Potsdam, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, S.; Aghaei, H.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Monajemi, M.; Bazrafshan, A.A. Synthesis of nanocomposites of iron oxide/gold (Fe3O4/Au) loaded on activated carbon and their application in water treatment by using sonochemistry: Optimization study. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sana, S.; Boodhoo, K.; Zivkovic, V. Production of starch nanoparticles through solvent-antisolvent precipitation in a spinning disc reactor. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.G.; Ciminelli, V.S.; Mohallem, N.D.S. A comparison of TEM and DLS methods to characterize size distribution of ceramic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 733, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagendorfer, H.; Kaegi, R.; Parlinska, M.; Sinnet, B.; Ludwig, C.; Ulrich, A. Characterization of silver nanoparticle products using asymmetric flow field flow fractionation with a multidetector approach—A comparison to transmission electron microscopy and batch dynamic light scattering. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2678–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Kuang, H.; Zhang, W.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Wei, H.; Xu, H. Comparisons of the biodistribution and toxicological examinations after repeated intravenous administration of silver and gold nanoparticles in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labouta, H.I.; Sarsons, C.; Kennard, J.; Gomez-Garcia, M.J.; Villar, K.; Lee, H.; Cramb, D.T.; Rinker, K.D. Understanding and improving assays for cytotoxicity of nanoparticles: What really matters? RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 23027–23039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Simchi, A.; Milani, A.; Stroeve, P. Cell toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 336, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Liu, S.; He, J.; Pan, C.C.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Ding, Y.; Huo, D.; Hu, Y. Synthesis and application of strawberry-like Fe3O4-Au nanoparticles as CT-MR dual-modality contrast agents in accurate detection of the progressive liver disease. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Hao, R.; Liu, F.; Su, X.; Hou, Y. Single-crystalline α-Fe2O3 nanostructures: Controlled synthesis and high-index plane-enhanced photodegradation by visible light. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 6888–6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, J.-C.; Shen, M.-W.; Shi, X.-Y. Formation of multifunctional Fe3O4/Au composite nanoparticles for dual-mode MR/CT imaging applications. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23, 078704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovtzer, R.; Agrawal, A.; Kotov, N.A.; Popovtzer, A.; Balter, J.; Carey, T.E.; Kopelman, R. Targeted gold nanoparticles enable molecular CT imaging of cancer. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4593–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajeesh, M.; Francis, B.; Annie, J.; Varma, P.H. Nano iron oxide–hydroxyapatite composite ceramics with enhanced radiopacity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, L.; Cai, H.; Sun, W.; Shen, M.; Zhang, G.; Shi, X. Facile one-pot synthesis of Fe3O4@ Au composite nanoparticles for dual-mode MR/CT imaging applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10357–10366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Tung, G.A.; Sun, S. Size and concentration effect of gold nanoparticles on X-ray attenuation as measured on computed tomography. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4167–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali Dheyab, M.; Abdul Aziz, A.; Jameel, M.S.; Moradi Khaniabadi, P.; Oglat, A.A. Rapid Sonochemically-Assisted Synthesis of Highly Stable Gold Nanoparticles as Computed Tomography Contrast Agents. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207020
Ali Dheyab M, Abdul Aziz A, Jameel MS, Moradi Khaniabadi P, Oglat AA. Rapid Sonochemically-Assisted Synthesis of Highly Stable Gold Nanoparticles as Computed Tomography Contrast Agents. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(20):7020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207020
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli Dheyab, Mohammed, Azlan Abdul Aziz, Mahmood S. Jameel, Pegah Moradi Khaniabadi, and Ammar A. Oglat. 2020. "Rapid Sonochemically-Assisted Synthesis of Highly Stable Gold Nanoparticles as Computed Tomography Contrast Agents" Applied Sciences 10, no. 20: 7020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207020
APA StyleAli Dheyab, M., Abdul Aziz, A., Jameel, M. S., Moradi Khaniabadi, P., & Oglat, A. A. (2020). Rapid Sonochemically-Assisted Synthesis of Highly Stable Gold Nanoparticles as Computed Tomography Contrast Agents. Applied Sciences, 10(20), 7020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207020






