A Prognostic Framework for Wheel Treads Integrating Parameter Correlation and Multiple Uncertainties
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel parameter-related Wiener process model with consideration of multiple uncertainties is proposed for accurately characterizing the real degradation process of wheel treads.
- (2)
- A recursive algorithm, which integrates KF and EM algorithm, is established to update model parameters and RUL distribution with the updating of online monitoring data.
- (3)
- An investigation of real-world wheel tread signals is used to demonstrate the superiority of the proposed prognostic framework in accuracy improvement.
- (4)
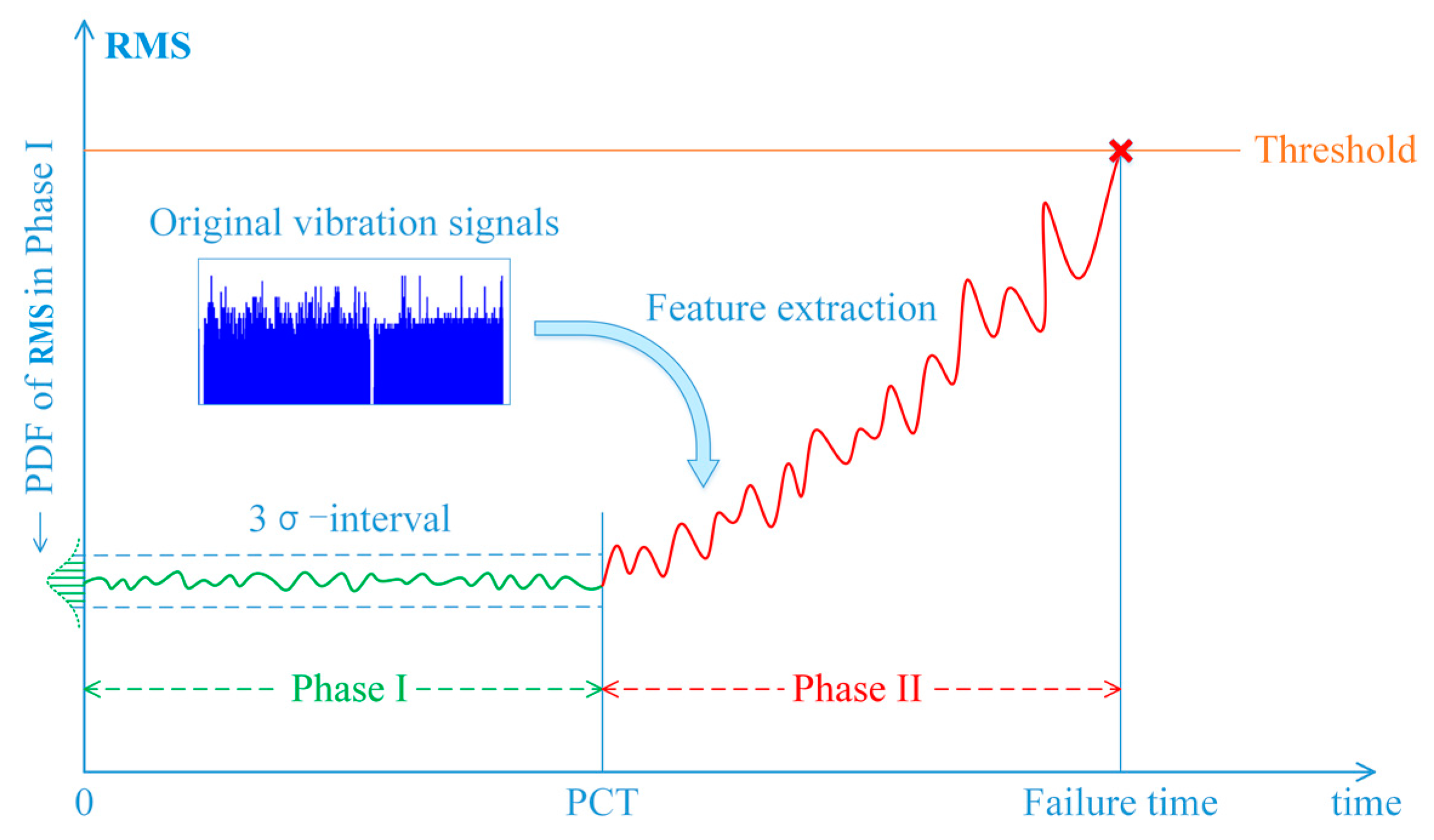
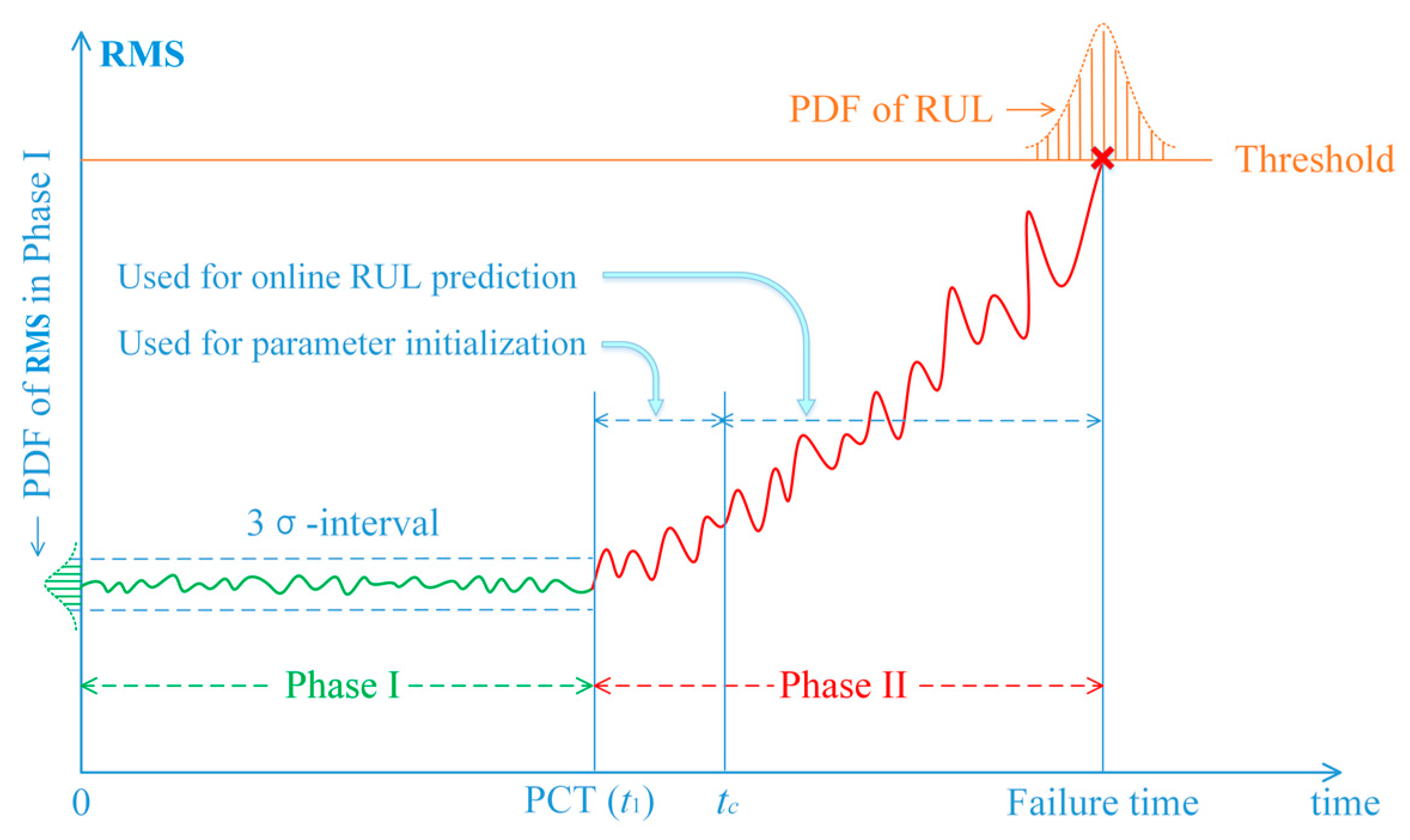
2. Methodology
| Algorithm 1. PCT detection procedure |
|
2.1. RUL Prediction Model
- (1)
- The basic degradation rate is determined by material properties. Due to the heterogeneity among different units, is a random variable instead of deterministic. Here Gaussian distribution is chosen to describe such uncertainty, i.e., [31];
- (2)
- The function of time is determined by specific failure mode;
- (3)
- Standard Brownian motion represents temporal uncertainty of the degradation process.
2.2. Parameter Initialization and Updating Algorithm
| Algorithm 2. KF-step |
|
| Algorithm 3. EM-step |
|
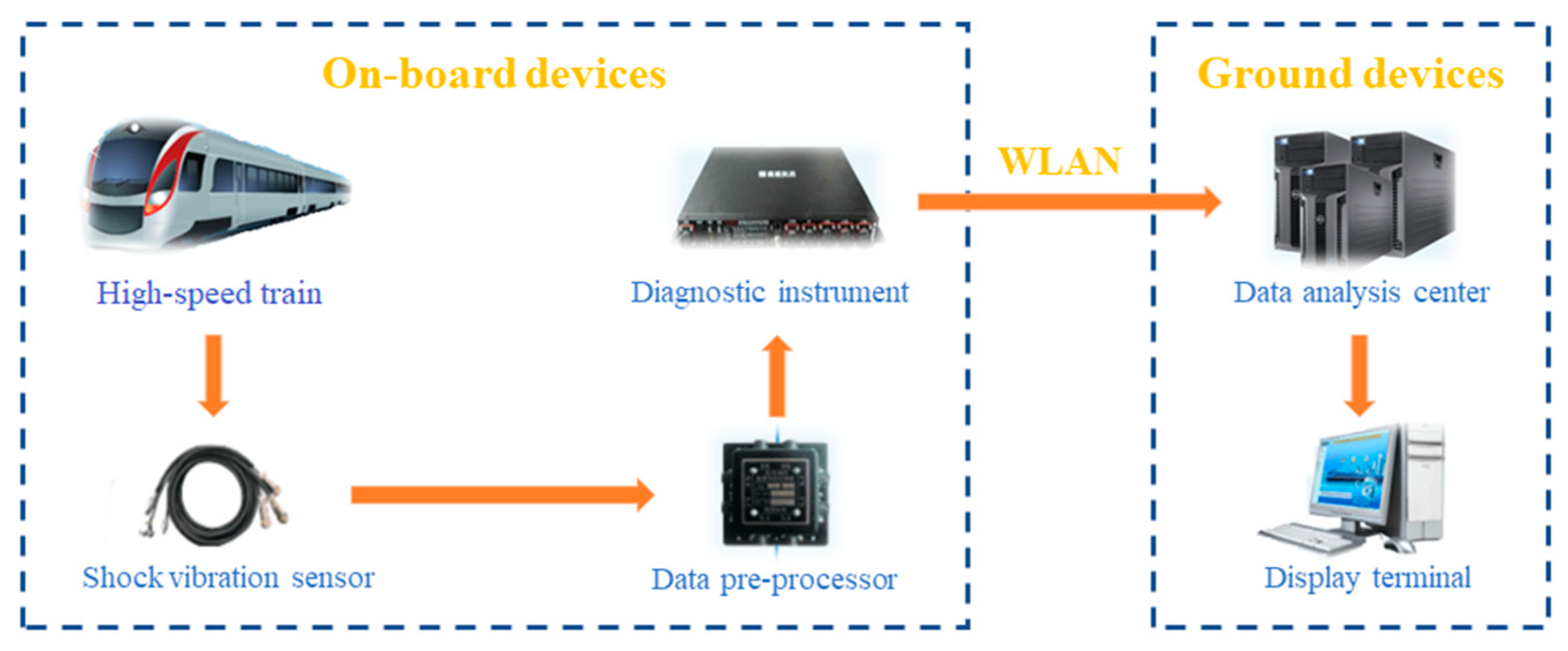
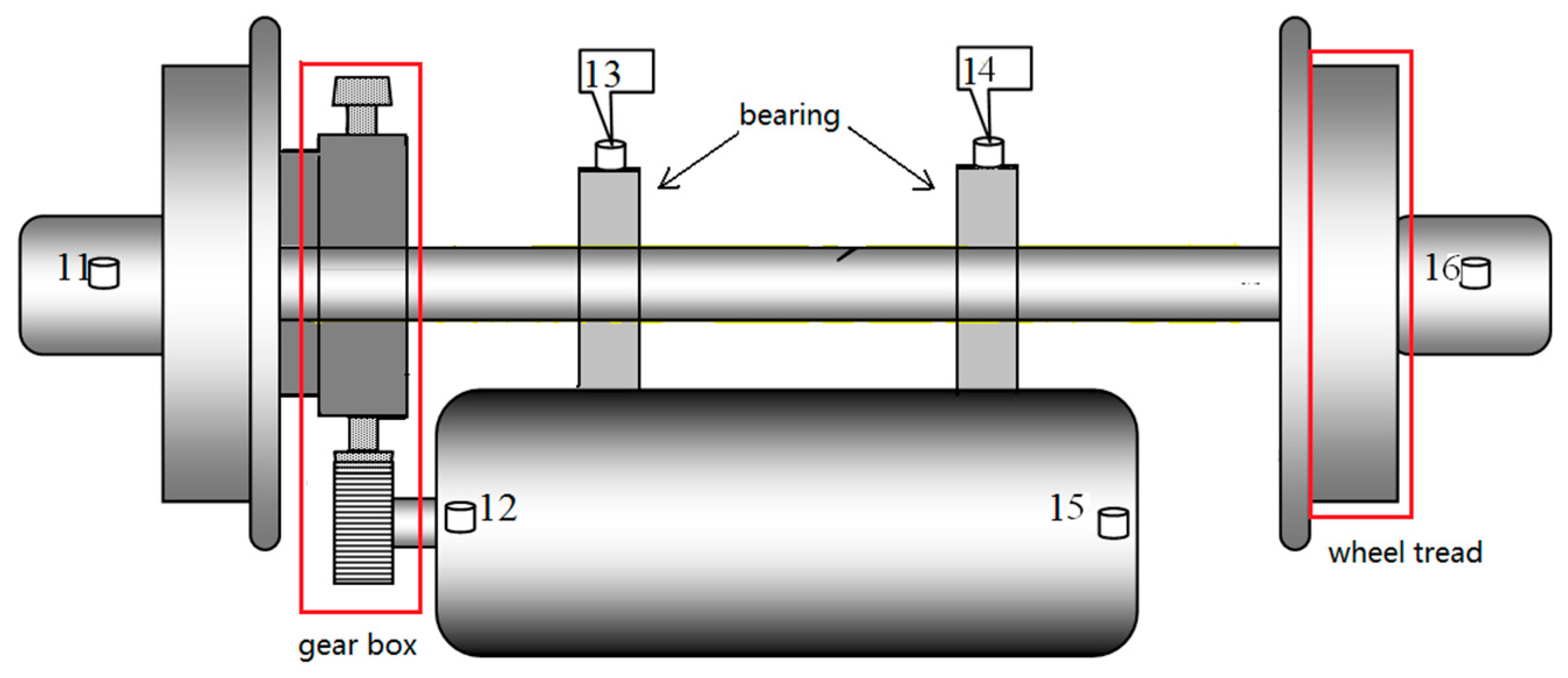
3. Case Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Jin, X.; Xiao, X.; Ling, L.; Zhou, L.; Xiong, J. Study on safety boundary for high-speed train running in severe environments. Int. J. Rail Transit. 2013, 1, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Tang, B.; Gong, X.; Wei, W.; Wang, H. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of the High-Speed Train with Big Data Based on Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 2106–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tan, A.C.C.; Lin, J.H. Gearbox fault diagnosis of high-speed railway train. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 66, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Jin, W.D.; Huang, J. Fault Diagnosis of High Speed Train Bogie Based on Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. Comput. Eng. 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- An, D.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, J.H. Practical options for selecting data-driven or physics-based prognostics algorithms with reviews. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 133, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.S.; Wang, W.; Hu, C.H.; Zhou, D.H. Remaining useful life estimation-A review on the statistical data driven approaches. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 213, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, K.L.; Chen, N.; Zhou, Q.; Hai, Y.; Wang, W. Prognostics and Health Management: A review on data driven approaches. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebraeel, N.; Lawley, M.; Liu, R. Residual life predictions from vibration-based degradation signals: A neural network approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2004, 51, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, N.; Jia, F.; Lei, Y.; Lin, J. A recurrent neural network based health indicator for remaining useful life prediction of bearings. Neurocomputing 2017, 240, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigamonti, M.; Baraldi, P.; Zio, E.; Roychoudhury, I.; Goebel, K.; Poll, S. Ensemble of optimized echo state networks for remaining useful life prediction. Neurocomputing 2018, 281, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.; Yacout, S.; Ouali, M.S. Bidirectional Handshaking LSTM for Remaining Useful Life Prediction. Neurocomputing 2019, 323, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, F.D.; Tsui, K.L.; Zio, E. Combining Relevance Vector Machines and exponential regression for bearing residual life estimation. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2012, 31, 405–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.T.; Hong, T.P.; Yang, B.S.; Nguyen, T.T. Machine Performance Degradation Assessment and Remaining Useful Life Prediction Using Proportional Hazard Model and SVM. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2012, 32, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soualhi, A.; Razik, H.; Clerc, G.; Doan, D.D. Prognosis of Bearing Failures using Hidden Markov Models and the Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Golnaraghi, F. A multi-step predictor with a variable input pattern for system state forecasting. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2009, 23, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, P.; Yu, Y.; Long, Y. A method for remaining useful life prediction of crystal oscillators using the Bayesian approach and extreme learning machine under uncertainty. Neurocomputing 2018, 305, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.B.; Chebel-Morello, B.; Saidi, L.; Malinowski, S.; Fnaiech, F. Accurate bearing remaining useful life prediction based on Weibull distribution and artificial neural network. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2015, 56, 150–172. [Google Scholar]
- Caesarendra, W.; Widodo, A.; Yang, B.S. Application of relevance vector machine and logistic regression for machine degradation assessment. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2010, 24, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.T.; Tian, Z.G. A framework for predicting the remaining useful life of a single unit under time varying operating conditions. Lie Trans. 2013, 45, 964–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Ye, Z.S. RUL Prediction of Deteriorating Products Using an Adaptive Wiener Process Model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 2911–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.; Gebraeel, N. Computing and updating the first-passage time distribution for randomly evolving degradation signals. Lie Trans. 2012, 44, 974–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.L.; Fouladirad, M.; Barros, A. Remaining useful lifetime estimation and noisy gamma deterioration process. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2016, 149, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Si, X.; Hu, C.; Lei, Y. Degradation Data Analysis and Remaining Useful Life Estimation, A Review on Wiener-Process-Based Methods. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 271, 775–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lei, Y.; Lin, J.; Ding, S.X. An improved exponential model for predicting remaining useful life of rolling element bearings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 7762–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X.B. Remaining Useful Life Prediction Using a Novel Two-stage Wiener Process with Stage correlation. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 65227–65238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.S.; Wang, Y.; Tsui, K.L.; Pecht, M. Degradation data analysis using wiener processes with measurement errors. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2013, 62, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.; Gebraeel, N.; Kharoufeh, J.P. Degradation modeling for real-time estimation of residual lifetimes in dynamic environments. IIE Trans. 2015, 47, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Chen, P.; Hong, L.; Shen, L. A random-effects Wiener degradation model based on accelerated failure time. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2018, 180, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.G.; Golchinfar, B.; Donskoy, D.; Hassiotis, S.; Venkiteela, G. Steel Material Degradation Assessment Via Vibro-Acoustic Modulation Technique. Transp. Res. Record. 2019, 2673, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donskoy, D.; Golchinfar, B.; Ramezani, M.; Rutner, M.; Hassiotis, S. Vibro-acoustic amplitude and frequency modulations during fatigue damage evolution. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2102, 040004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.P.; Lei, Y.G.; Yan, T.; Li, N.; Han, T. A Wiener Process Model-based Method for Remaining Useful Life Prediction Considering Unit-to-Unit Variability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.S.; Wang, W.; Hu, C.H.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhou, D.H. A Wiener-process-based degradation model with a recursive filter algorithm for remaining useful life estimation. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2013, 35, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X.B. Group maintenance scheduling for two-component systems with failure interaction. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 71, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

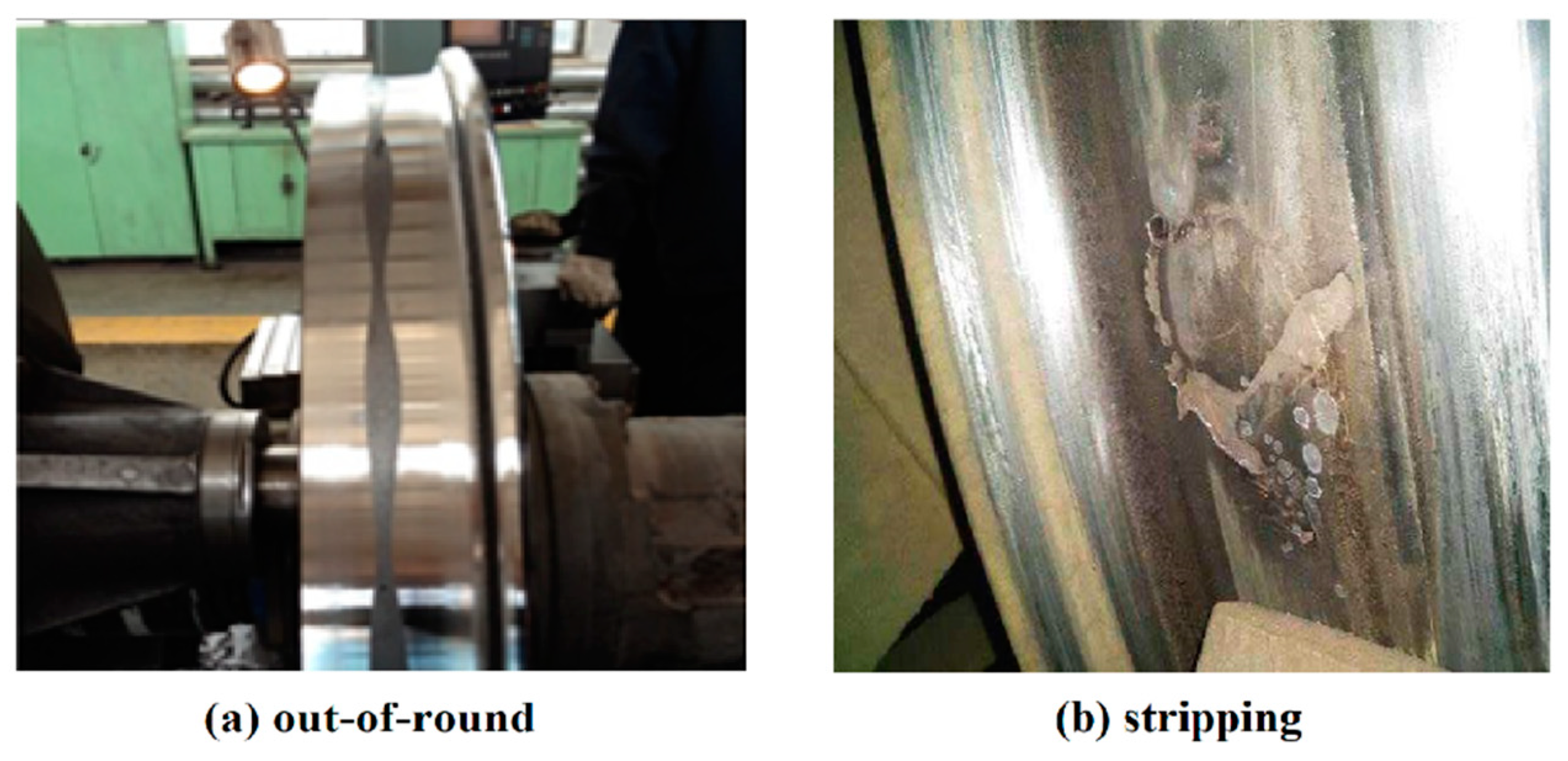
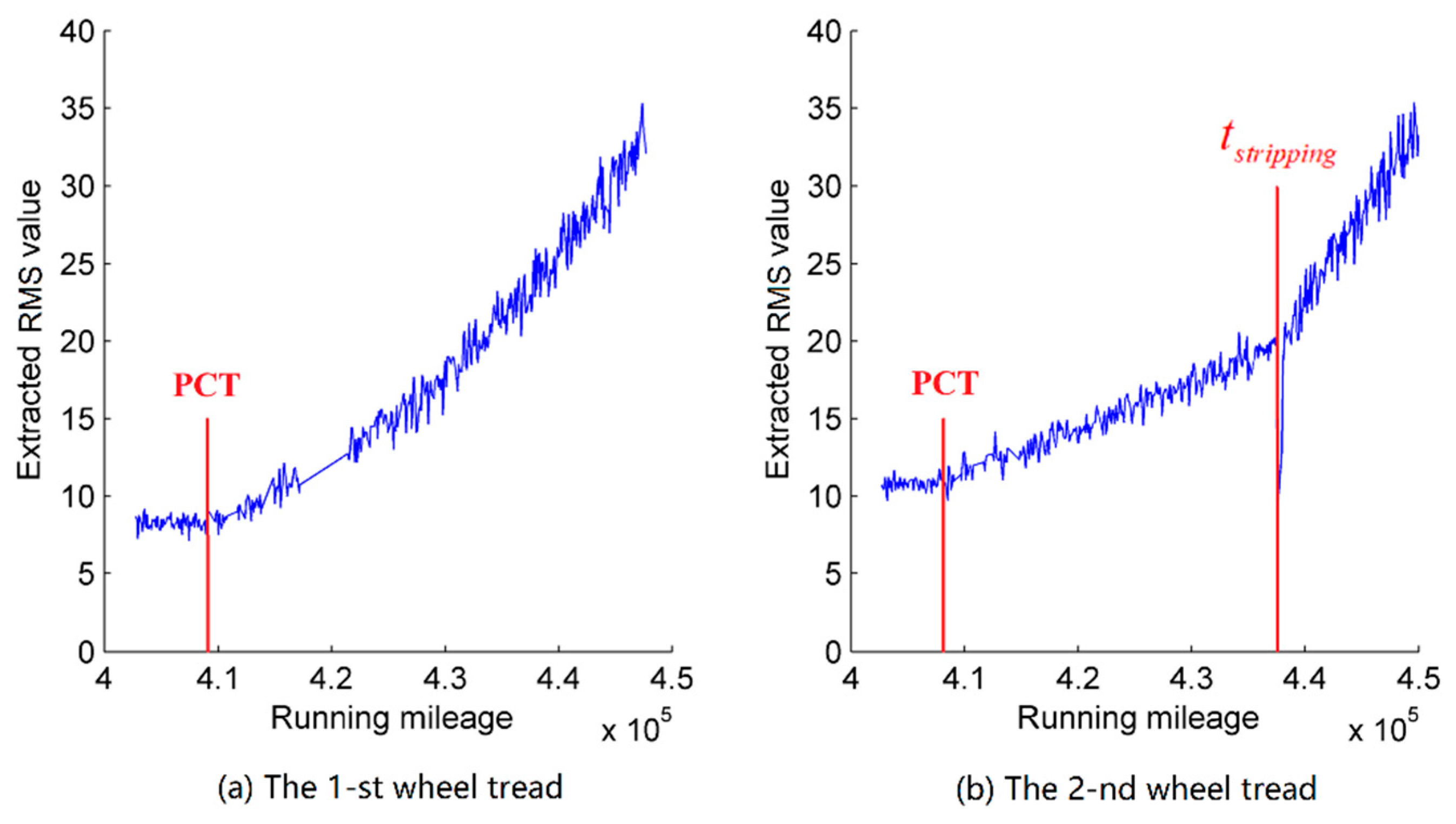

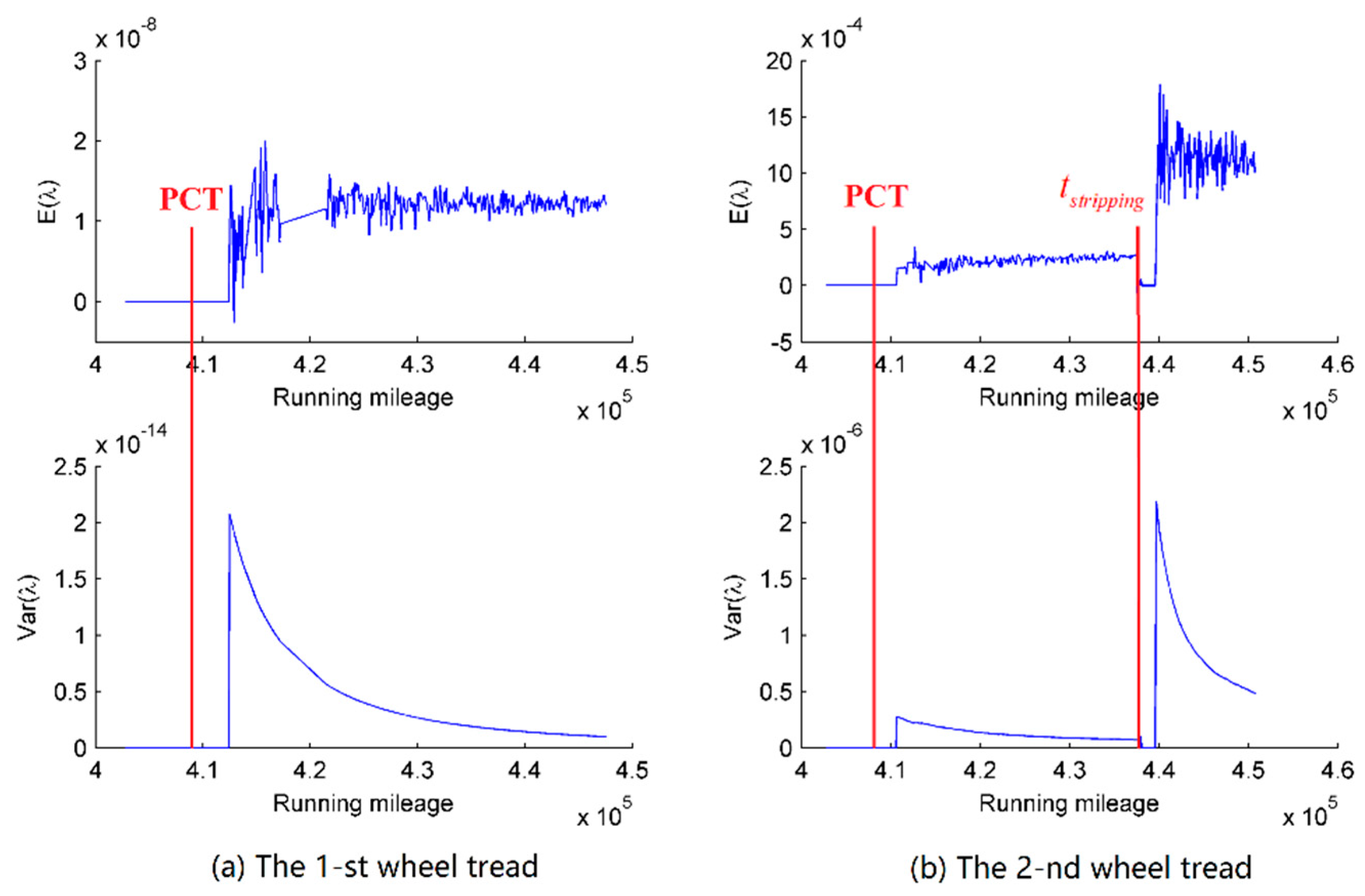


| Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCT of the 1-st wheel tread | 1.13 × 10−8 | 6.40 × 10−10 | 15.62 | 176.11 | 1.44 × 10−2 |
| PCT of the 2-nd wheel tread | 1.07 × 10−4 | 3.40 × 10−3 | 2.80 | 44.12 | 9.60 × 10−3 |
| of the 2-nd wheel tread | 1.80 × 10−3 | 2.70 × 10−3 | 0.61 | 6.56 | 1.07 × 10−2 |
| The 1-st Wheel Tread | The 2-nd Wheel Tread | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monitoring point/km × 105 | 4.30 | 4.35 | 4.40 | 4.45 | 4.30 | 4.35 | 4.40 | 4.45 |
| Actual RUL/km × 104 | 1.79 | 1.29 | 0.79 | 0.29 | 2.00 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 0.50 |
| REs of Model 1 | 11.08% | 7.32% | 4.91% | 2.44% | 93.90% | 130.77% | 13.63% | 3.54% |
| REs of Model 2 | 16.95% | 11.01% | 6.54% | 3.19% | 91.68% | 142.53% | 14.13% | 5.27% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Tang, D. A Prognostic Framework for Wheel Treads Integrating Parameter Correlation and Multiple Uncertainties. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020467
Huang G, Zhao Y, Wang H, Ma X, Tang D. A Prognostic Framework for Wheel Treads Integrating Parameter Correlation and Multiple Uncertainties. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(2):467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020467
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Guifa, Yu Zhao, Han Wang, Xiaobing Ma, and Deyao Tang. 2020. "A Prognostic Framework for Wheel Treads Integrating Parameter Correlation and Multiple Uncertainties" Applied Sciences 10, no. 2: 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020467
APA StyleHuang, G., Zhao, Y., Wang, H., Ma, X., & Tang, D. (2020). A Prognostic Framework for Wheel Treads Integrating Parameter Correlation and Multiple Uncertainties. Applied Sciences, 10(2), 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020467





