Osseointegration of Maxillary Dental Implants in Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial Human Histomorphometric Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
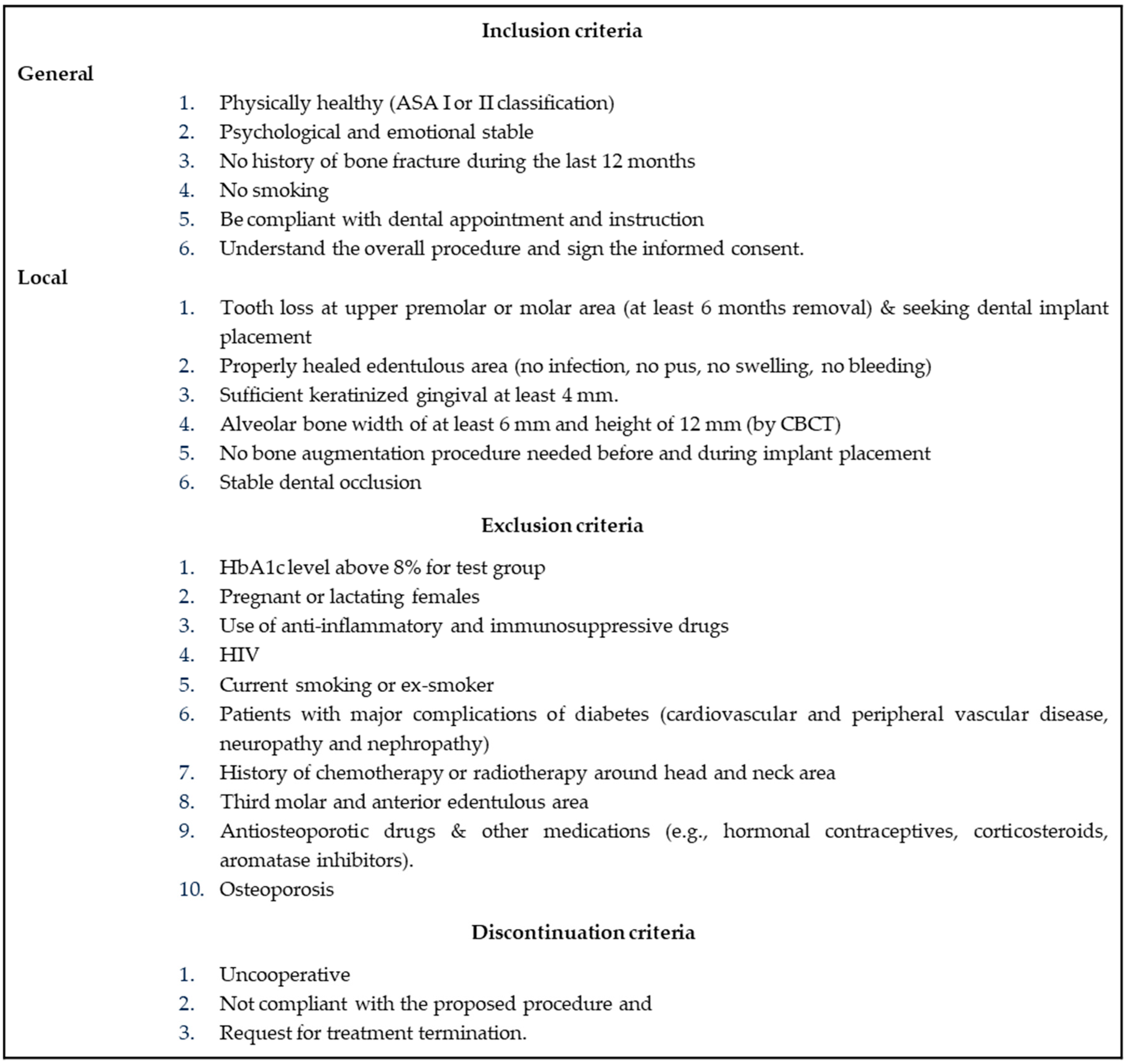
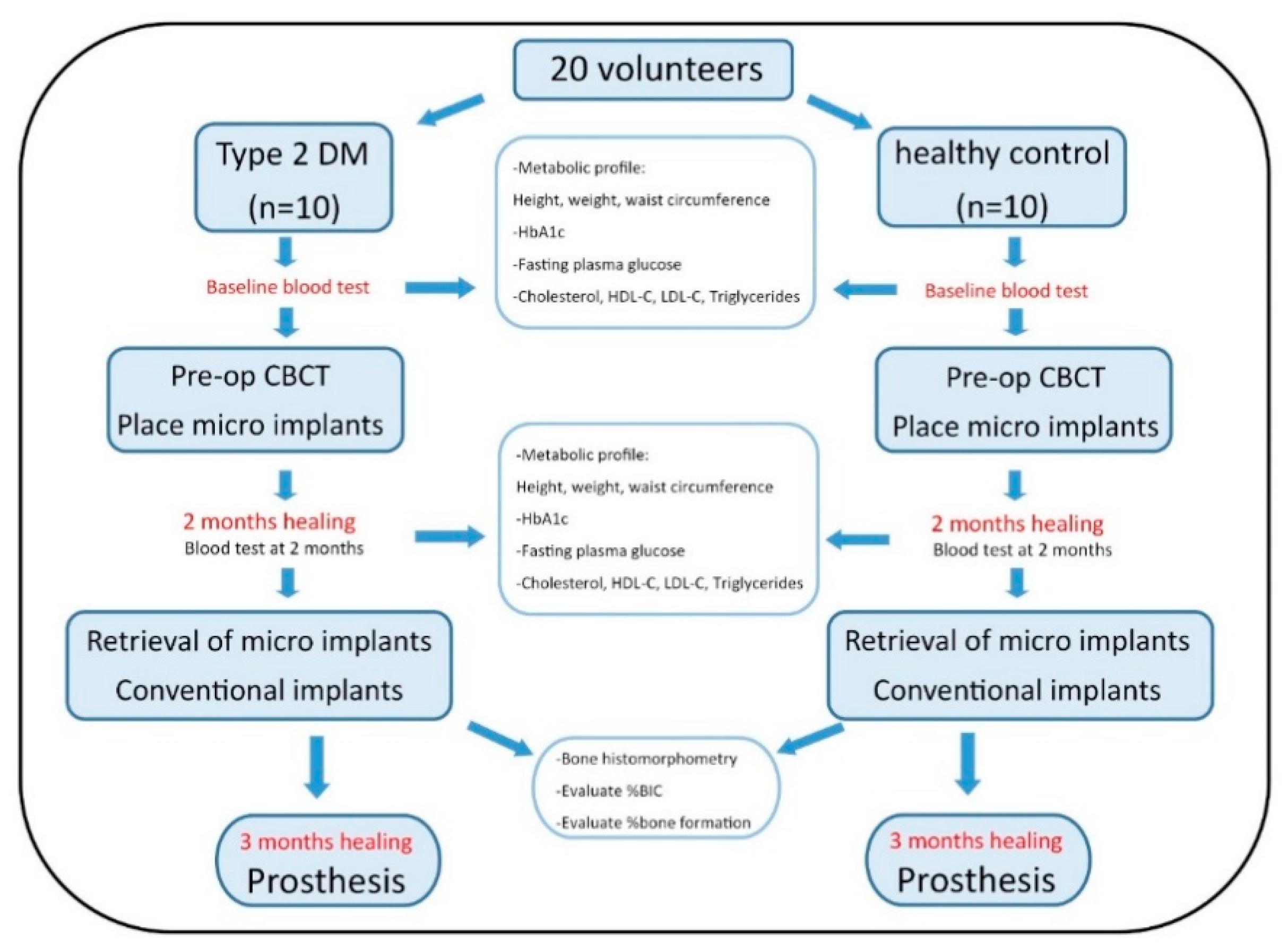
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Micro-Implant Design and Characteristics
2.1.1. Surgical Procedure
Micro-Implant Placement
Conventional Implant Placement
2.2. Blood Test
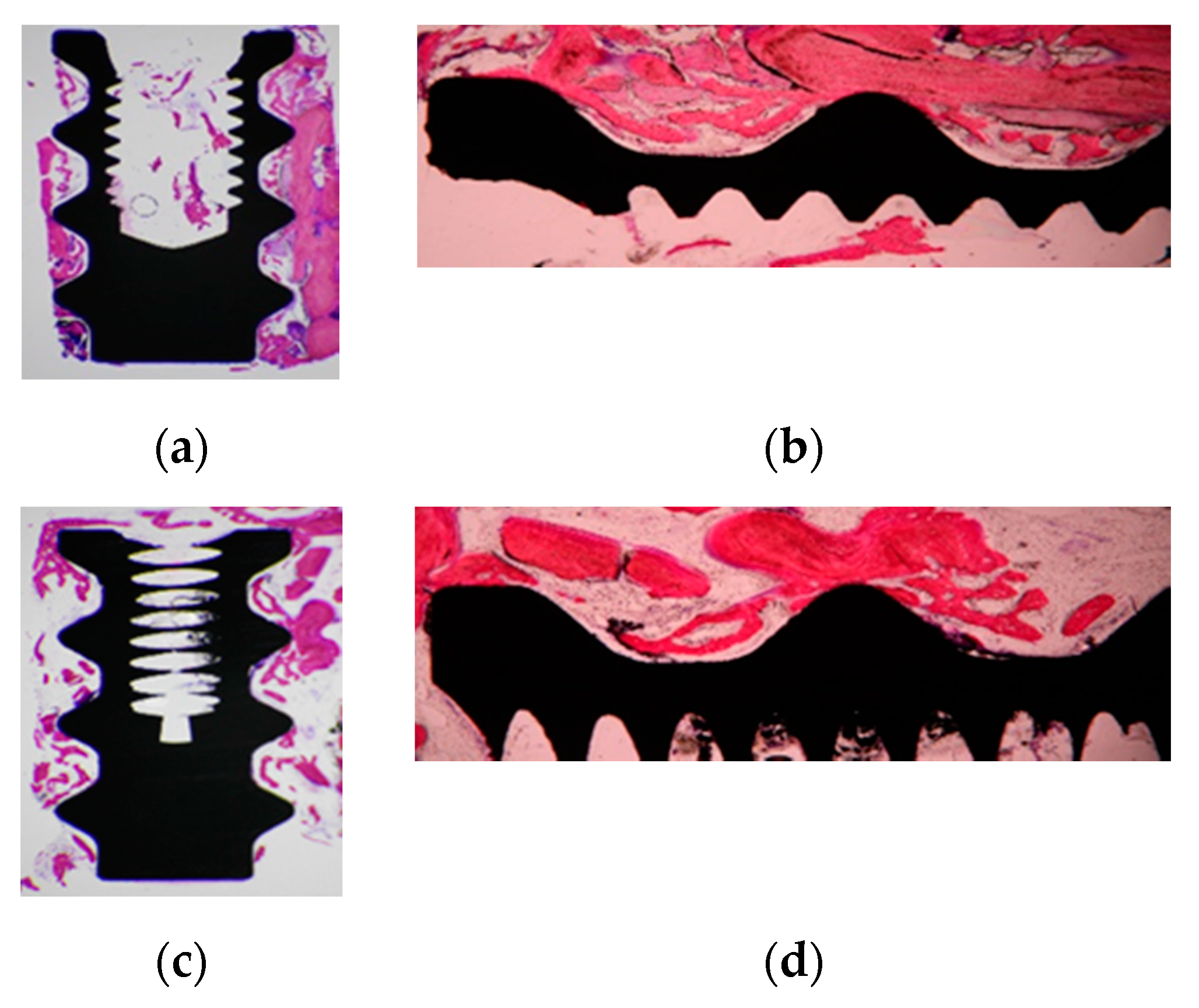
2.3. Histological Preparation and Histomorphometric Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
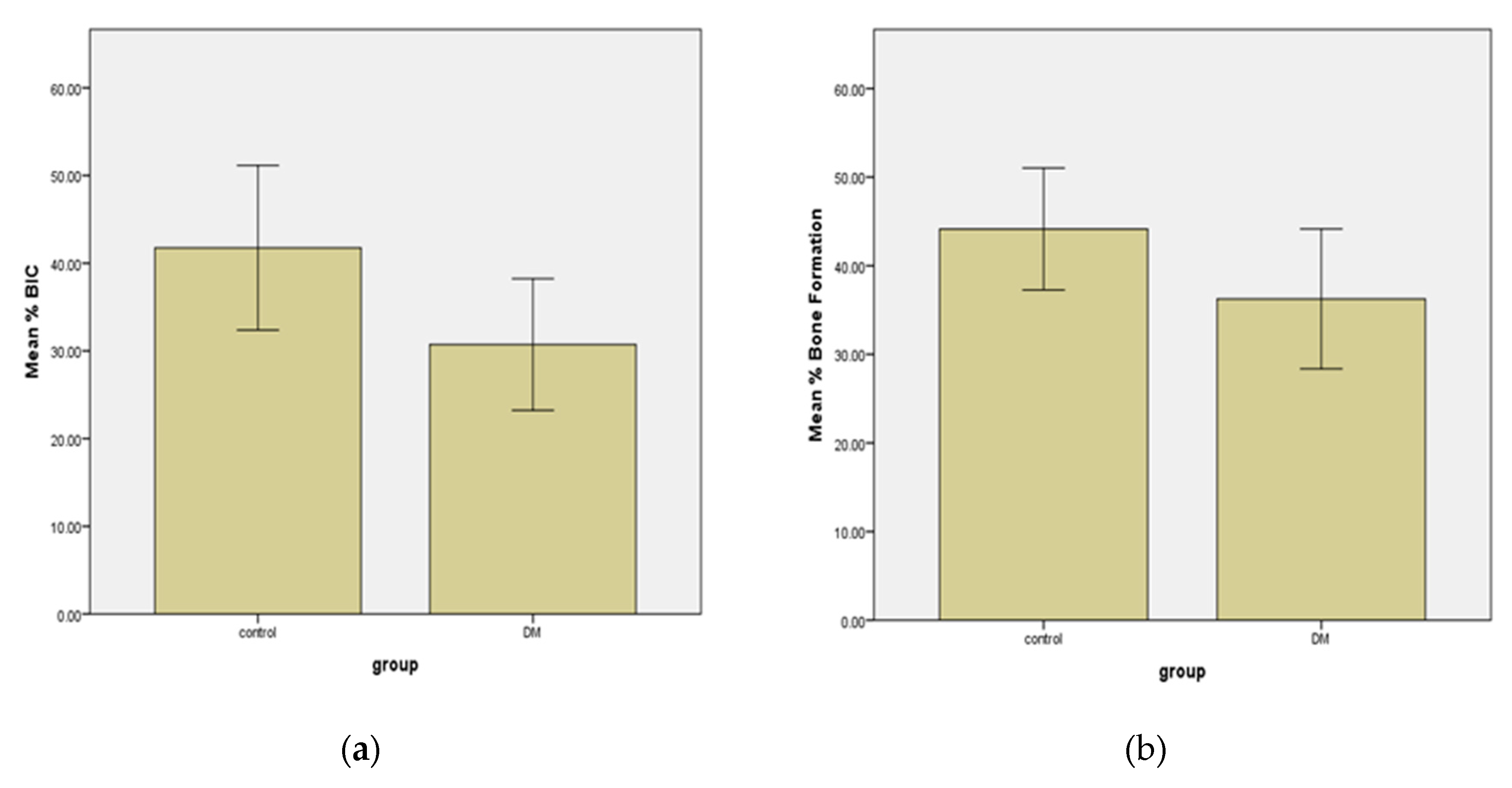
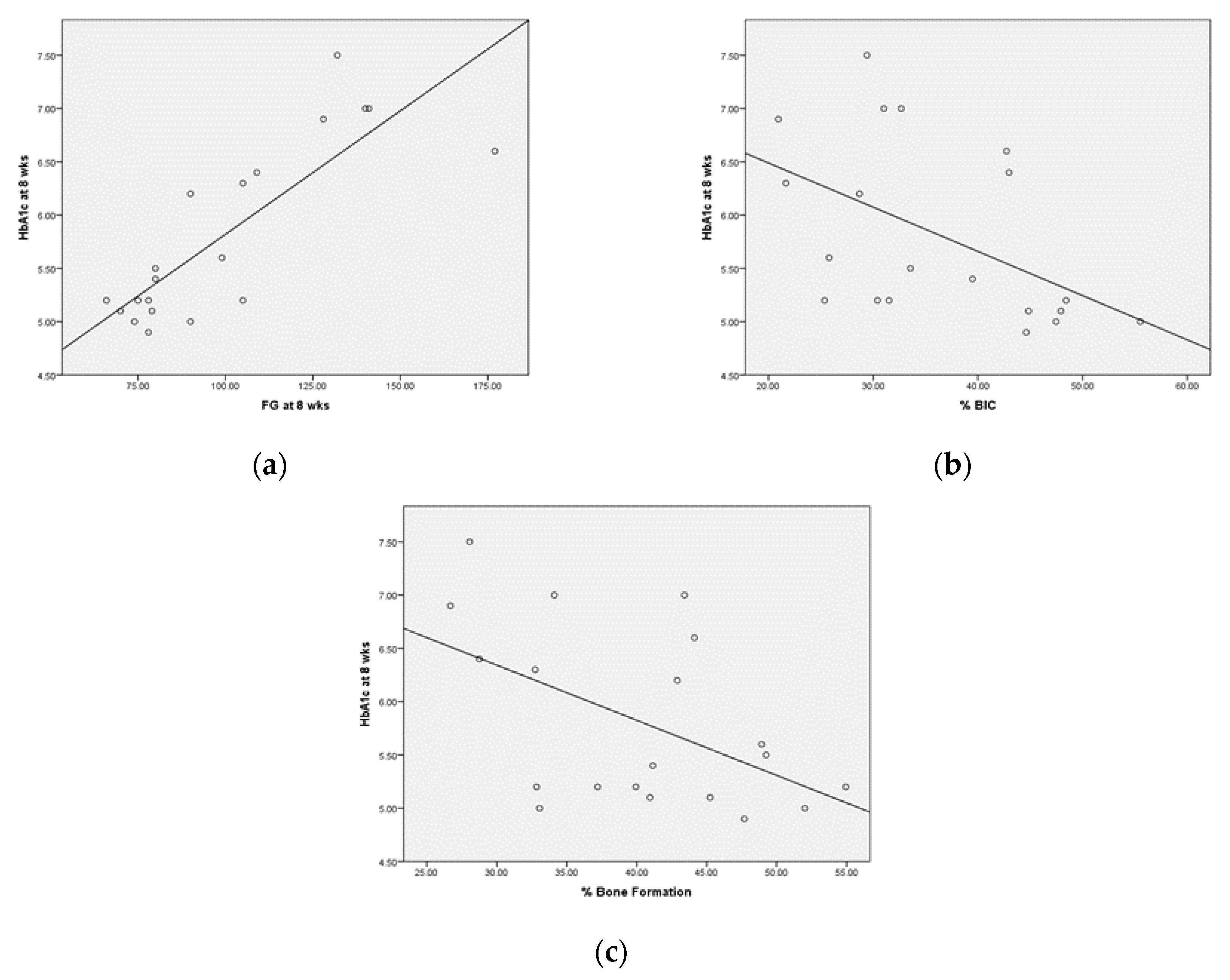
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alsaadi, G.; Quirynen, M.; Komarek, A.; van Steenberghe, D. Impact of local and systemic factors on the incidence of oral implant failures, up to abutment connection. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2007, 34, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombelli, A.; Cionca, N. Systemic diseases affecting osseointegration therapy. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2006, 17, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diz, P.; Scully, C.; Sanz, M. Dental implants in the medically compromised patient. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, R.E.; Garg, A.K. Bone structure, metabolism, and physiology: Its impact on dental implantology. Implant. Dent. 1998, 7, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Diabetes 2016. Available online: http://www.who.int/diabetes/global-report/en/ (accessed on 15 April 2019).
- Mokdad, A.H.; Ford, E.S.; Bowman, B.A.; Dietz, W.H.; Vinicor, F.; Bales, V.S.; Marks, J.S. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 2003, 289, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmet, P.; Alberti, K.; Shaw, J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 2001, 414, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.B.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Stampfer, M.J.; Colditz, G.A.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B. Physical activity and television watching in relation to risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus in men. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Americal Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 88, 787–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Després, J.P.; Lemieux, I. Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 2006, 444, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade, W.T. Diabetes-related microvascular and macrovascular diseases in the physical therapy setting. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khader, Y.S.; Dauod, A.S.; El-Qaderi, S.S.; Alkafajei, A.; Batayha, W.Q. Periodontal status of diabetics compared with nondiabetics: A meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2006, 20, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiko, Y.; Selimovic, D. The mechanism of protracted wound healing on oral mucosa in diabetes. review. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2010, 10, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.A. Glycemic Control in Diabetes. Oman Med. J. 2010, 25, 232–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonora, E.; Tuomilehto, J. The pros and cons of diagnosing diabetes with A1C. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oates, T.W.; Dowell, S.; Robinson, M.; McMahan, C.A. Glycemic control and implant stabilization in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Salvatierra, A.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; Gonzalez-Jaranay, M.; Moreu, G.; Delgado-Ruiz, R.A.; Gomez-Moreno, G. Peri-implant evaluation of immediately loaded implants placed in esthetic zone in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2: A two-year study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Moreno, G.; Aguilar-Salvatierra, A.; Roldan, J.R.; Guardia, J.; Gargallo, J.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L. Peri-implant evaluation in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A 3-year study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiraldini, B.; Conte, A.; Casarin, R.C.; Casati, M.Z.; Pimentel, S.P.; Cirano, F.R.; Ribeiro, F.V. Influence of Glycemic Control on Peri-Implant Bone Healing: 12-Month Outcomes of Local Release of Bone-Related Factors and Implant Stabilization in Type 2 Diabetics. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, T.W.; Galloway, P.; Alexander, P.; Green, A.V.; Huynh-Ba, G.; Feine, J.; McMahan, C.A. The effects of elevated hemoglobin A1c in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on dental implants. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2014, 145, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowell, S.; Oates, T.W.; Robinson, M. Implant success in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus with varying glycemic control: A pilot study. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2007, 138, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawil, G.; Younan, R.; Azar, P.; Sleilati, G. Conventional and advanced implant treatment in the type II diabetic patient: Surgical protocol and long-term clinical results. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2008, 23, 744–752. [Google Scholar]
- Americal Diabetes Association. The absence of a glycemic threshold for the development of long-term complications: The perspective of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes 1996, 45, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busenlechner, D.; Fürhauser, R.; Haas, R.; Watzek, G.; Mailath, G.; Pommer, B. Long-term implant success at the Academy for Oral Implantology: 8-year follow-up and risk factor analysis. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2014, 44, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, H.F.; Ochi, S.; Winkler, S. Implant survival in patients with type 2 diabetes: Placement to 36 months. Ann. Periodontol. 2000, 5, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubert, D.M.; Weinstein, B.F.; Bordin, S.; Leroux, B.G.; Flemmig, T.F. Prevalence and predictive factors for peri-implant disease and implant failure: A cross-sectional analysis. J. Periodontol. 2015, 86, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Silva, G.; Cortelli, J.; Costa, J.; Costa, F. Prevalence and risk variables for peri-implant disease in Brazilian subjects. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2006, 33, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naujokat, H.; Kunzendorf, B.; Wiltfang, J. Dental implants and diabetes mellitus—A systematic review. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2016, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajami, E.; Bell, S.; Liddell, R.S.; Davies, J.E. Early bone anchorage to micro- and nano-topographically complex implant surfaces in hyperglycemia. Acta Biomater. 2016, 39, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Tangl, S.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.; Rausch-Fan, X. Potential mechanism for osseointegration of dental implants in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 53, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Molon, R.S.; Morais-Camilo, J.A.; Verzola, M.H.; Faeda, R.S.; Pepato, M.T.; Marcantonio, E., Jr. Impact of diabetes mellitus and metabolic control on bone healing around osseointegrated implants: Removal torque and histomorphometric analysis in rats. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Wilmowsky, C.; Stockmann, P.; Harsch, I.; Amann, K.; Metzler, P.; Lutz, R.; Moest, T.; Neukam, F.W.; Schlegel, K.A. Diabetes mellitus negatively affects peri-implant bone formation in the diabetic domestic pig. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, A.; Richards, R.; Milz, S.; Schneider, E.; Pearce, S. Animal models for implant biomaterial research in bone: A review. Eur. Cell Mater. 2007, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, S.; Piattelli, A.; De Figueiredo, L.C.; Feres, M.; De Melo, L.; Iezzi, G.; Alba, R.C.; Shibli, J.A. Histologic evaluation of early human bone response to different implant surfaces. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, N.; Bin, S.; Jing, Z.; Wei, S.; Yingqiong, Z. Influence of implant surface topography on bone-regenerative potential and mechanical retention in the human maxilla and mandible. Am. J. Dent. 2014, 27, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shibli, J.A.; Mangano, C.; Mangano, F.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Cassoni, A.; Bechara, K.; Ferreia, J.D.B.; Dottore, A.M.; Iezzi, G.; Piattelli, A. Bone-to-Implant Contact Around Immediately Loaded Direct Laser Metal-Forming Transitional Implants in Human Posterior Maxilla. J. Periodontol. 2013, 84, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degidi, M.; Perrotti, V.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G. Mineralized bone-implant contact and implant stability quotient in 16 human implants retrieved after early healing periods: A histologic and histomorphometric evaluation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2010, 25, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mangano, C.; Shibli, J.A.; Pires, J.T.; Luongo, G.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G. Early bone formation around immediately loaded transitional implants inserted in the human posterior maxilla: The effects of fixture design and surface. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4152506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Broggini, N.; Wieland, M.; Schenk, R.; Denzer, A.; Cochran, D.; Hoffmann, B.; Lussi, A.; Steinemann, S. Enhanced bone apposition to a chemically modified SLA titanium surface. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, K.; Breuner, G. A method for the study of undecalcified bones and teeth with attached soft tissues* The Säge-Schliff (sawing and grinding) Technique. J. Oral. Patho. Med. 1982, 11, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Xu, J.; Huo, N.; Cai, C.; Liu, H. Does a higher glycemic level lead to a higher rate of dental implant failure?: A meta-analysis. JADA 2016, 147, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.E. Understanding peri-implant endosseous healing. J. Dent. Educ. 2003, 67, 932–949. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anner, R.; Grossmann, Y.; Anner, Y.; Levin, L. Smoking, diabetes mellitus, periodontitis, and supportive periodontal treatment as factors associated with dental implant survival: A long-term retrospective evaluation of patients followed for up to 10 years. Implant. Dent. 2010, 19, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oates, T.W.; Huynh-Ba, G.; Vargas, A.; Alexander, P.; Feine, J. A critical review of diabetes, glycemic control, and dental implant therapy. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 117–127. [Google Scholar]


| Participant | Gender | Age | BMI | Waist Circumference (WC) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Male | Female | Mean ± SE | Mean ± SE | Mean ± SE | ||
| Group | Control | 10 | 3 | 7 | 50.3 ± 3.1 (years) | 24.6 ± 1.2 | 33.6 ± 1.2 (inches) |
| T2DM | 10 | 5 | 5 | 60.5 ± 1.2 (years) | 24.1 ± 1.0 | 33.4 ± 1.3 (inches) | |
| Total number | 20 | ||||||
| Significance | p = 0.01 | p = 0.844 | p = 0.796 | ||||
| Control (n = 10) | T2DM (n = 10) | |
|---|---|---|
| FPG at baseline | 80.4 ± 8.9 (mg/dL) | 117.1 ± 20.5 (mg/dL) * |
| FPG at 8 weeks | 77 ± 6.4 (mg/dL) | 122.6 ± 26.1 (mg/dL) * |
| HbA1c at baseline | 5.3 ± 0.2 (%) | 6.43 ± 0.6 (%) |
| HbA1c at 8 weeks | 5.1 ± 0.1 (%) | 6.47 ± 0.6 (%) * |
| Cholesterol at baseline | 222.1 ± 43.7 (mg/dL) | 164.3 ± 48.9 (mg/dL) |
| Cholesterol at 8 weeks | 213.1 ± 51.8 (mg/dL) | 164.9 ± 44.6 (mg/dL) |
| HDL-C at baseline | 61 ± 16.1 (mg/dL) | 53.7 ±17 (mg/dL) |
| HDL-C at 8 weeks | 60.7 ± 17.8 (mg/dL) | 55.2 ± 17.3 (mg/dL) |
| LDL-C at baseline | 136.3 ± 42 (mg/dL) | 90.5 ± 35.1 (mg/dL) |
| LDL-C at 8 weeks | 134.2 ± 46.8 (mg/dL) | 87.1 ± 37.3 (mg/dL) |
| Triglycerides at baseline | 124 ± 96.6 (mg/dL) | 101 ± 49.9 (mg/dL) |
| Triglycerides at 8 weeks | 91.4 ± 40.5 (mg/dL) | 112.8 ± 80.7 (mg/dL) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sam, L.; Chattipakorn, S.; Khongkhunthian, P. Osseointegration of Maxillary Dental Implants in Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial Human Histomorphometric Study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6762. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196762
Sam L, Chattipakorn S, Khongkhunthian P. Osseointegration of Maxillary Dental Implants in Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial Human Histomorphometric Study. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(19):6762. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196762
Chicago/Turabian StyleSam, Lyly, Siriporn Chattipakorn, and Pathawee Khongkhunthian. 2020. "Osseointegration of Maxillary Dental Implants in Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial Human Histomorphometric Study" Applied Sciences 10, no. 19: 6762. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196762
APA StyleSam, L., Chattipakorn, S., & Khongkhunthian, P. (2020). Osseointegration of Maxillary Dental Implants in Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial Human Histomorphometric Study. Applied Sciences, 10(19), 6762. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196762




