Mechanism and Investment Analysis of Recycling Gasoline Solvent with Mineral Powder for Asphalt Cleaning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
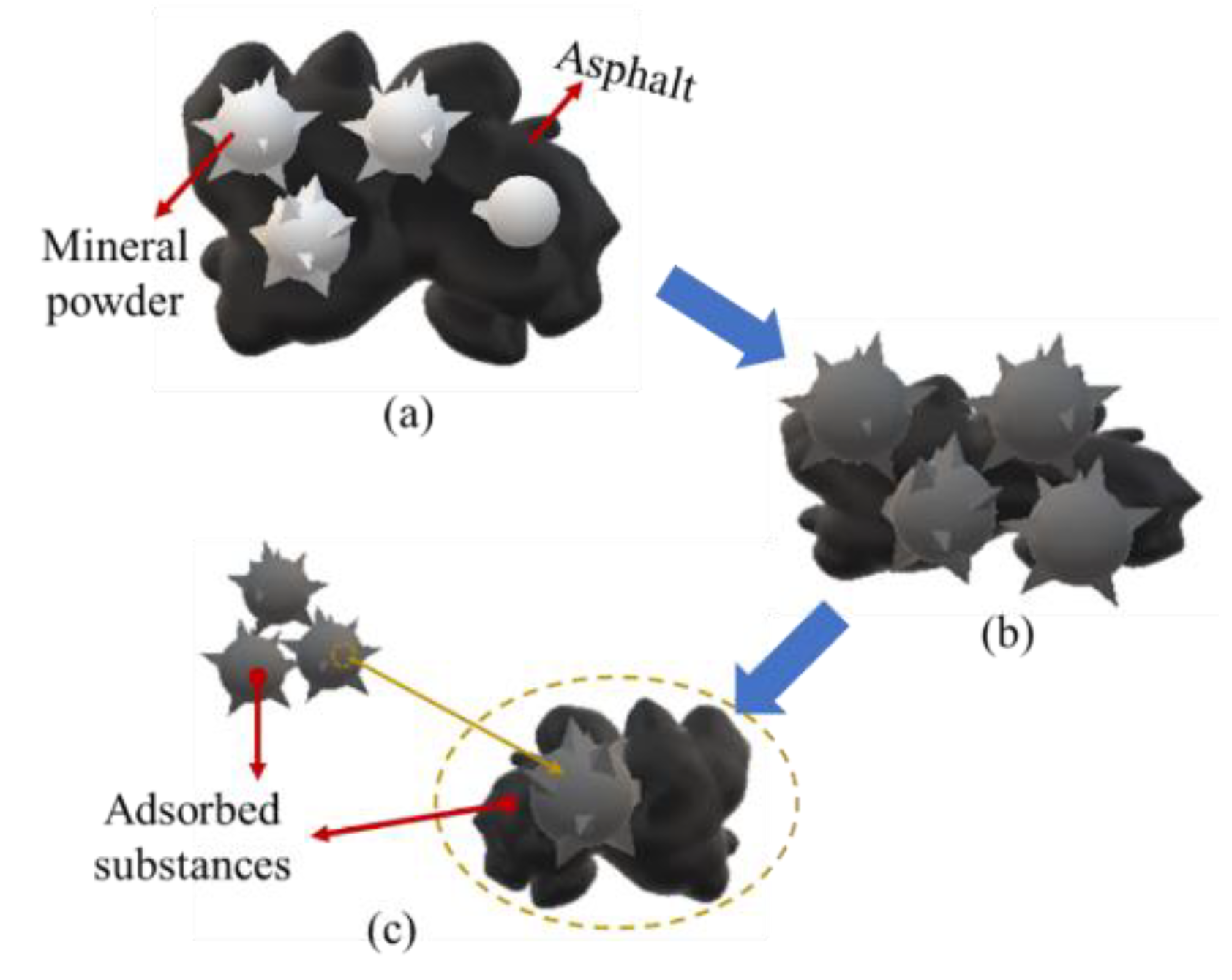
3.1. Mechanism Performance
3.1.1. Crystal Phase of Absorbed Mineral Powder
3.1.2. Chemical Compositions of Absorbed Mineral Powder
3.1.3. Qualitative Analysis by Functional Groups of Mineral Powder
3.1.4. Adsorption Efficiency of Mineral Powder
3.2. Cost and Environmental Impact Analyses
3.2.1. Economic Evaluations
3.2.2. Environmental Impacts
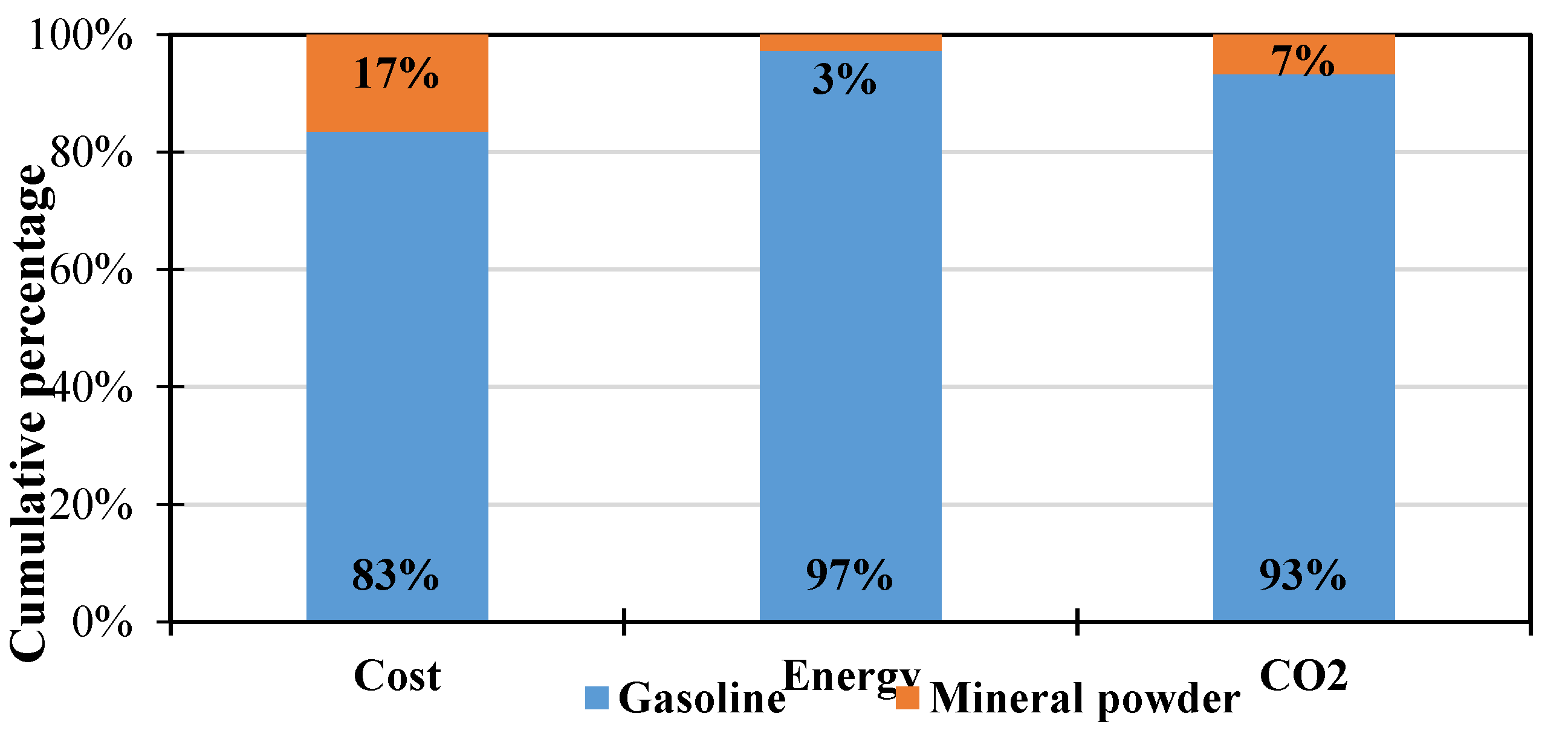
3.2.3. Comparative Interpretations
4. Conclusions
- Mineral powder mixed with gasoline is an effective solution to remove bituminous binder commonly found in experimental devices in asphalt laboratories. The mechanism can be explained as a physical interaction between the mineral powder and asphalt binder.
- Almost 4% of the binder can be adsorbed by the gasoline solution, thus proving the beneficial effect generated by the use of mineral powder.
- The investigated case suggests that removing 1 kg asphalt binder with pure gasoline costs CNY 71.20, consumes 362.90 MJ energy and emits 25.80 kg equivalent CO2., and that adding a mineral powder can reduce these quantities by 80%, 97% and 93%, respectively.
- Although the rough surface of the mineral powder determines the physical adsorption strength, the low adsorption rate limits the benefits in practical application. Future research should focus on the improvement of the adsorption rate.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
References
- Strano, E.; Giometto, A.; Shai, S.; Bertuzzo, E.; Mucha, P.J.; Rinaldo, A. The scaling structure of the global road network. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurance, S.G.W.; Clements, G.R.; Sloan, S.; O’Connell, C.S.; Mueller, N.D.; Goosem, M.; Venter, O.; Edwards, D.P.; Phalan, B.; Balmford, A.; et al. A global strategy for road building. Nature 2014, 513, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulac, J. Global Land Transport Infrastructure Requirements. Paris Int. Energy Agency 2013, 20, 2014. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&as_vis=1&q=Dulac%2C+J.%2C+Global+land+transport+infrastructure+requirements.+Paris%3A+International+Energy+Agency%2C+2013.+20%3A+p.+2014&btnG= (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Steger, S.; Bleischwitz, R. Drivers for the use of materials across countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Shu, X.; Huang, B. Sustainability innovations in transportation infrastructure: An overview of the special volume on sustainable road paving. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, R.; Cui, Z. Quantitative Analysis of Risk in Safety Engineering Laboratory. Res. Explor. Lab. 2019, 2, 64. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&as_vis=1&q=Quantitative+analysis+of+risk+in+safety+engineering+laboratory.+&btnG= (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Gao, L.; Jiang, B.; Lin, M.-Q. Research on Management and Construction Strategy of Engineering Laboratory in the Context of New Engineering Education. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual International Conference on Management, Economics and Social Development (ICMESD 2019), Suzhou, China, 21–22 June 2019; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Hoeven, M. World Energy Outlook 2012; International Energy Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 2013; Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&as_vis=1&q=Van+der+Hoeven%2C+M.%2C+World+energy+outlook+2012.+International+Energy+Agency%3A+Tokyo&btnG= (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Shafiee, S.; Topal, E. When will fossil fuel reserves be diminished? Energy Policy 2009, 37, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeper, S.A.; Wankat, P.C. Gasohol production by extraction of ethanol from water using gasoline as solvent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1982, 21, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H. Building Decorative Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 342–358. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.L. Selective solubility: “Like dissolves like”. J. Chem. Educ. 1977, 54, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBee, W.C.; Sullivan, T.A. Improved Resistance of Sulfur-Asphalt Paving Formulations to Attack by Fuels. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1977, 16, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, L.A. Asphalt Paint. U.S. Patent 2,542,608, 20 February 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer, E.; Byron, D. Alternative Fuels in Fire Debris Analysis: Biodiesel Basics. J. Forensic Sci. 2007, 52, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contributors of Wikipedia. Gasoline. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Gasoline&oldid=934730337 (accessed on 8 January 2020).
- Vulimiri, S.V.; Pratt, M.M.; Kulkarni, S.; Beedanagari, S.; Mahadevan, B. Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity of Solvents and Gases. In Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 379–396. [Google Scholar]
- Smallwood, I.M. Handbook of Organic Solvent Properties; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hayden, J.W.; Comstock, E.G.; Comstock, B.S. The Clinical Toxicology of Solvent Abuse. Clin. Toxicol. 1976, 9, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadin, H.; Liccione, J.J. Disulfide Toxicological Profile for Carbon. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Abadin%2C+H.+and+J.J.+Liccione%2C+Toxicological+profile+for+carbon+disulfide.+1996&btnG= (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Zabrodskii, P.F.; Germanchuk, V.G.; Kirichuk, V.F.; Karpenko, N.I. Effect of tetrachloromethane on the immune system. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2004, 137, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattey, D. PART 8—Chemical-Induced Ocular Side Effects. In Clinical Ocular Toxicology; Fraunfelder, F.T., Fraunfelder, F.W., Chambers, W.A., Eds.; Saunders: Edinburgh, UK, 2008; pp. 289–306. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/books/drug-induced-ocular-side-effects/fraunfelder/978-0-323-31984-3 (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Chen, M.-Z.; Lin, J.-T.; Wu, S.-P.; Liu, C.-H. Utilization of recycled brick powder as alternative filler in asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1532–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remisova, E. Study of mineral filler effect on asphalt mixtures properties. Bitum. Mix. Pavements VI 2015, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, L.; Chuanfeng, Z.; Yong, Q.; Heng, B.; Keyao, L.; Junfei, H. Analysing the effects of the mesoscopic characteristics of mineral powder fillers on the cohesive strength of asphalt mortars at low temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 65, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.; Fan, W.; Zhuang, C.; Qian, C.; Lv, X. Effects of the morphological characteristics of mineral powder fillers on the rheological properties of asphalt mastics at high and medium temperatures. Powder Technol. 2019, 348, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöström, J.; Bindler, R.; Granberg, T.; Kylander, M.E. Procedure for Organic Matter Removal from Peat Samples for XRD Mineral Analysis. Wetlands 2018, 39, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, H.W.P.; De Almeida, E.; Tomazello-Filho, M.; De Carvalho, H.W.P. Space-resolved determination of the mineral nutrient content in tree-rings by X-ray fluorescence. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Wu, S. Aging Mechanism and Rejuvenating Possibility of SBS Copolymers in Asphalt Binders. Polymers 2020, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.P.S. Mineral Analysis of Pantja Goat Milk through Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy. IJCS 2019, 7, 3510–3512. Available online: http://www.chemijournal.com/archives/?year=2019&vol=7&issue=3&ArticleId=6056&si=false (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Press, C.S. China Energy Statistical Yearbook 2013; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2013. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2013/indexeh.htm (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Kayser, H.A. Gasoline demand and car choice: Estimating gasoline demand using household information. Energy Econ. 2000, 22, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullien, A.; Proust, C.; Martaud, T.; Rayssac, E.; Ropert, C. Variability in the environmental impacts of aggregate production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuholt, E. Life cycle assessment of gasoline and diesel. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 1995, 14, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Le Saoût, G.; Gallucci, E.; Scrivener, K. Influence of limestone on the hydration of Portland cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielinski, J.; Kriech, A.; Huber, G.; Horton, A.; Osborn, L. Analysis of vacuum tower asphalt extender and effect on bitumen and asphalt properties. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2015, 16, 90–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, B.D. Analysis of limestones and dolomites by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. In Masonry: Materials, Testing, and Applications; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Van Loon, J.A. Analytical Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy: Selected Methods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/books/analytical-atomic-absorption-spectroscopy/van-loon/978-0-12-714050-6 (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Xiang, K.; Wang, X.; Huang, G.; Zheng, J.; Huang, J.; Li, G. Thermal ageing behavior of styrene–butadiene random copolymer: A study on the ageing mechanism and relaxation properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1704–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Al-Degs, Y.S.; Amer, M. Determination of motor gasoline adulteration using FTIR spectroscopy and multivariate calibration. Talanta 2008, 76, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejová, J. FTIR techniques in clay mineral studies. Vib. Spectrosc. 2003, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Wu, S.; Cai, J.; Zhou, M.; Zha, J. Effects of two biomass ashes on asphalt binder: Dynamic shear rheological characteristic analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 56, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Matsui, I.; Feng, N. Effect of compound mineral powders on workability and rheological property of HPC. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.J.; Hukins, D.W. Morphology of Mineral Deposits on Encrusted Urinary Catheters Investigated by Scanning Electron Microscopy. J. Urol. 1989, 142, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miadonye, A.; Evans, L. The Solubility of Asphaltenes in Different Hydrocarbon Liquids. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2010, 28, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NUMBEO. Gasoline, Petrol Prices, in Gas Prices; NUMBEO: Belgrade, Serbia, 2020; Available online: https://www.numbeo.com/gas-prices/country_result.jsp?country=Norway (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Hao, H.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, F. Compression ignition of low-octane gasoline: Life cycle energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Appl. Energy 2016, 181, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lepech, M.D.; Keoleian, G.A.; Qian, S.; Li, V.C. Dynamic Life-Cycle Modeling of Pavement Overlay Systems: Capturing the Impacts of Users, Construction, and Roadway Deterioration. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2010, 16, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norgate, T.; Haque, N. Energy and greenhouse gas impacts of mining and mineral processing operations. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
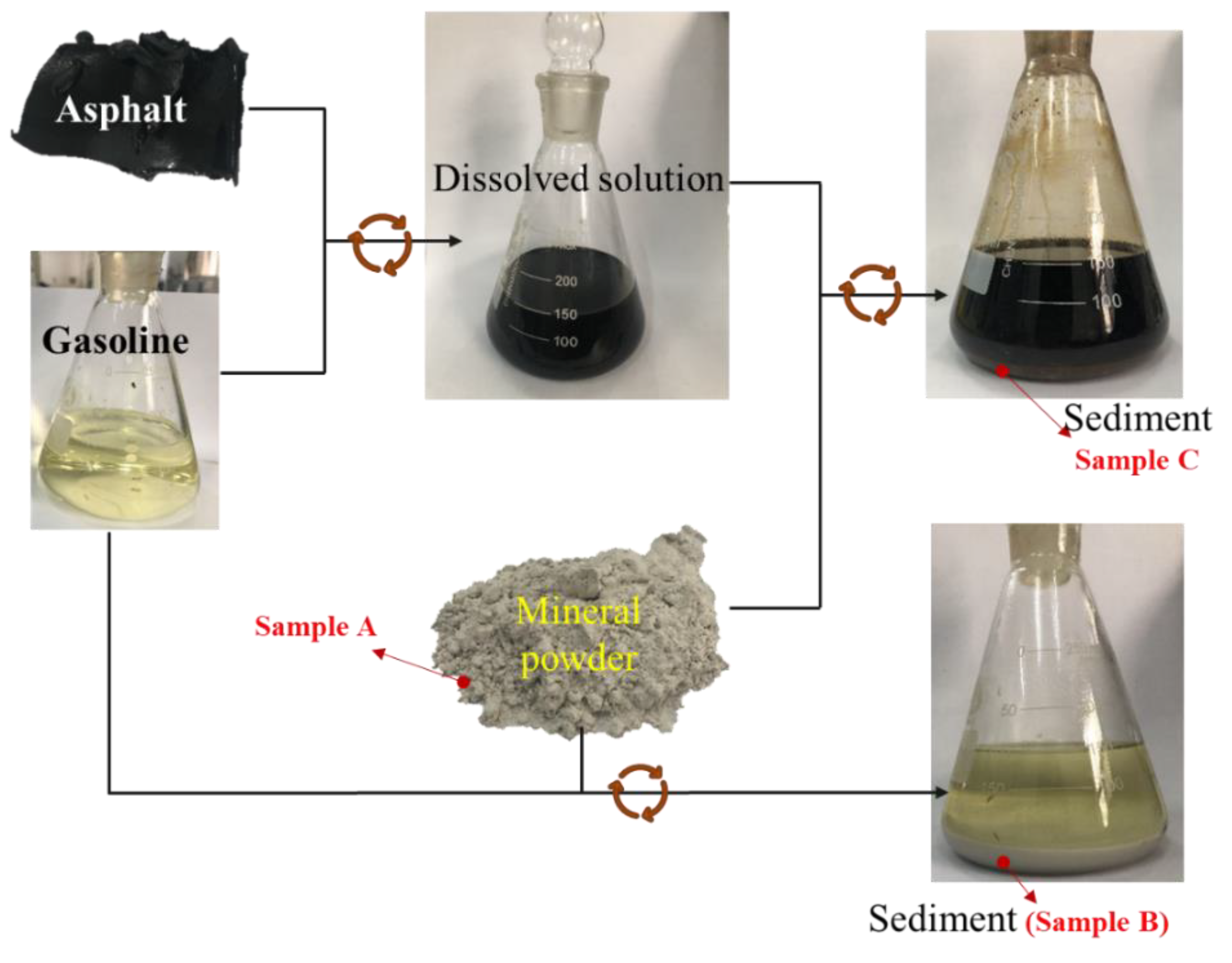
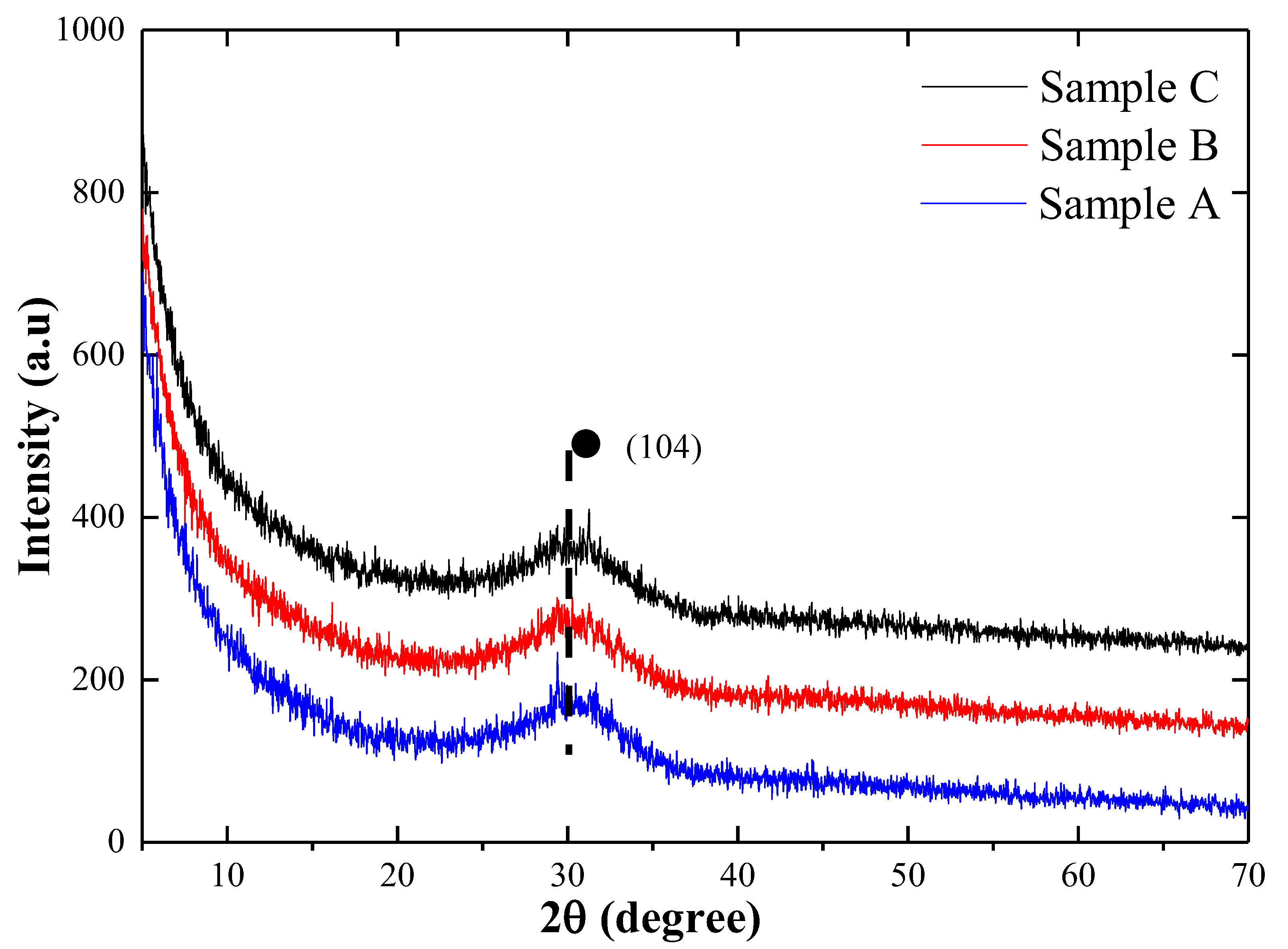
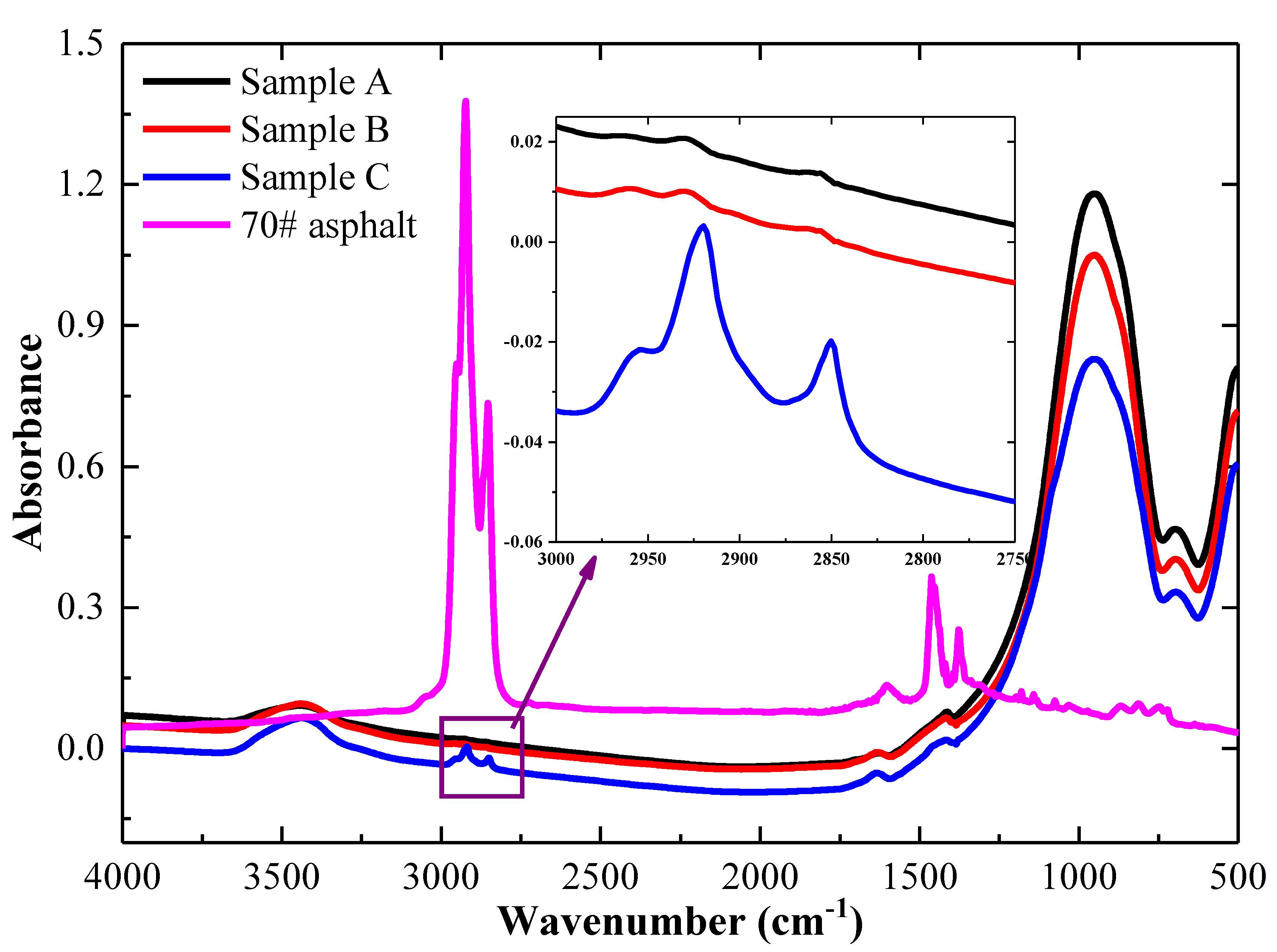
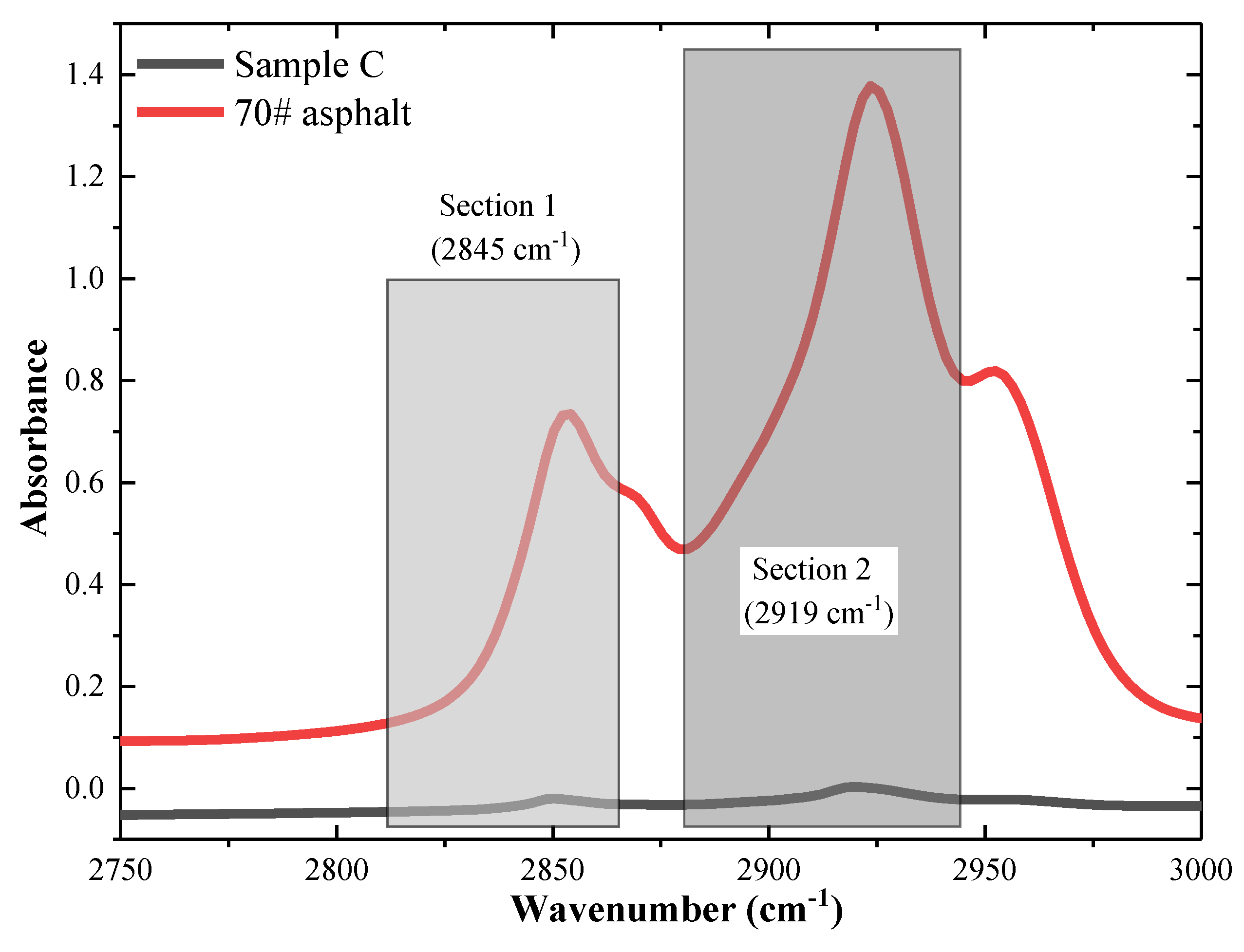
| Property | Result | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Specific gravity | 1.034 | ASTM D70 |
| Penetration at 25 °C (0.1 mm) | 63 | ASTM D5 |
| Ductility, 5 cm/min, 5 °C (mm) | 37 | ASTM D113 |
| Softening point (°C) | 48 | ASTM D36 |
| Apparent viscosity, 135 °C (Pa·s) | 0.46 | ASTM D4402 |
| Loss on heating (wt.%) | +0.09 | ASTM D6 |
| Property | Result | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Apparent density (t/m3) | >2.701 | T 0352-2000 |
| Moisture content (%) | <0.1 | T 0103-1993 |
| Hydrophilic coefficient | 0.8 | T 0353-2000 |
| Plasticity index (%) | 3.4 | T 0354-2000 |
| Passing rate (0.075 mm sieve, %) | 86.7 | T 0351-2000 |
| Composition | Content (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample A | Sample B | Sample C | |
| Na2O | 0.325 | 0.357 | 0.392 |
| MgO | 7.835 | 8.488 | 8.413 |
| Al2O3 | 15.749 | 16.755 | 16.218 |
| SiO2 | 32.612 | 33.651 | 32.987 |
| SO3 | 2.373 | 2.315 | 2.674 |
| K2O | 0.445 | 0.423 | 0.442 |
| CaO | 39.237 | 36.788 | 37.600 |
| TiO2 | 0.758 | 0.615 | 0.638 |
| MnO | 0.133 | 0.141 | 0.155 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.241 | 0.218 | 0.194 |
| SrO | 0.102 | 0.085 | 0.094 |
| Y2O3 | 0.012 | 0.010 | 0.012 |
| ZrO2 | 0.049 | 0.041 | 0.044 |
| BaO | 0.103 | 0.114 | 0.133 |
| ZnO | 0 | 0 | 0.005 |
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Assignment | Origin of the Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|
| 2919 | Methylene C–H anti-symmetry stretching | Methylene units |
| 2845 | Methyl C–H symmetry stretching | Methylene units |
| Peak Wavenumber (cm−1) and Areas | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Section 1 (2919 cm−1) | Section 2 (2845 cm−1) | 2750–3000 cm−1 | |
| 70# asphalt | 17.385 | 7.845 | 62.362 |
| Sample C | 0.710 | 0.295 | 2.369 |
| Percentage (%) | 4.084 | 3.760 | 3.799 |
| Cost (CNY) | Energy Consumption (MJ) | Equivalent CO2 EMISSION (kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gasoline | 71.20 | 362.90 | 25.80 |
| Mineral powder | 14.10 | 10.02 | 1.85 |
| Reducing percentage | 80% | 97% | 93% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Li, H.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, S. Mechanism and Investment Analysis of Recycling Gasoline Solvent with Mineral Powder for Asphalt Cleaning. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5761. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175761
Wang F, Li H, Jiang Q, Yang C, Li Y, Wu S. Mechanism and Investment Analysis of Recycling Gasoline Solvent with Mineral Powder for Asphalt Cleaning. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(17):5761. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175761
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fusong, Hechuan Li, Qi Jiang, Chao Yang, Yuanyuan Li, and Shaopeng Wu. 2020. "Mechanism and Investment Analysis of Recycling Gasoline Solvent with Mineral Powder for Asphalt Cleaning" Applied Sciences 10, no. 17: 5761. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175761
APA StyleWang, F., Li, H., Jiang, Q., Yang, C., Li, Y., & Wu, S. (2020). Mechanism and Investment Analysis of Recycling Gasoline Solvent with Mineral Powder for Asphalt Cleaning. Applied Sciences, 10(17), 5761. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175761










