Featured Application
Flow features on the roof region of an isolated high-rise building for urban wind energy harvesting; wind loading over high-rise building roof.
Abstract
The human migration from rural to urban areas has triggered a chain reaction causing the spiking energy demand of cities worldwide. High-rise buildings filling the urban skyline could potentially provide a means to improve the penetration of renewable wind energy by installing wind turbines at their rooftop. However, the above roof flow region has not received much attention and most results deal with low-rise buildings. This study investigates the flow pattern above the roof of a high-rise building by analysing velocity and pressure measurements performed in an atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel, including four wind directions and two different roof shapes. Comparison of the surface pressure patterns on the flat roof with available low-rise building studies shows that the surface pressure contours are consistent for a given wind direction. At 0° wind direction, a separation bubble is detected, while cone vortices dominate at 30° and 45°. The determining factor for the installation of small wind turbines is the vicinity to the roof. Thus, 45° wind direction shows to be the most desirable angle by bringing the substantial amplification of wind and keeping the turbulence intensity low. Decking the roof creates favourable characteristics by overcoming the sensitivity to the wind direction while preserving the speed-up effect.
1. Introduction
The world has been rapidly urbanising for the past five decades, with ~54% of the population currently living in urban areas, expected to reach ~66% by 2050 [1]. As a result, cities are transforming with more high-rise buildings being planned to cope with the increasing dwelling demand, living standards and sustainability [2]. This unprecedented societal change goes in parallel with a meteoric rise in the energy demand, estimated to increase by 56% before 2040 [3].
Renewable energy needs to play a crucial role to meet the demand without affecting urban resilience and sustainability. Wind energy represents the most successful source of renewable energy, due to its steadily increasing reliability, ever-reducing costs and economical and environmental feasibility [4]. While the predominant wind energy production comes from large wind farms, having received enormous resources to optimise their output [5], an opportunity may arise from distributed generation [6], with small wind turbines installed in optimal locations close to consumers. A recent study showed that, in a hypothetical scenario, having small wind turbines installed on 1500 high-rise buildings in major cities in the Netherlands, urban wind energy has the potential to annually yield 150 GWh of electricity, i.e., enough to power up ~60,000 typical Dutch households [7]. Advocates of urban wind energy harvesting support it due to the perspective of having ready-to-use energy at the consumption place, eliminating a significant cost contribution in wind farms [8,9].
Some authors have attempted to estimate the potential of generating wind energy in cities, using the annual wind speed variability and the typical installation height as reference [10,11]. Although results suggest that small-scale wind turbines are only to be installed on the outskirts of cities, the local flow conditions are normally not considered for such evaluations, hence these studies have a limited scope. The ideal method to assess the local wind flow pattern above buildings would require to directly perform measurements on site, as done for wind farms. This is a rather expensive solution, which is not yet justified in terms of the expected yield of urban wind energy [12,13]. However, other approaches can be used for the assessment of the wind resource in urban areas, including atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel testing or computational fluid dynamics (CFD). In recent years, CFD has successfully provided a way for the determination of mean flow conditions and it has contributed to the understanding of the wind flow above buildings. However, the accuracy and reliability of the CFD solutions remain a concern that requires further validation efforts [13,14]. Thus, wind tunnel experimentation is still considered to be the most effective approach [13].
The main constraint to the performance of small wind turbines installed on buildings comes essentially from the lack of information on the urban wind resource at the installation site [13,15]. In fact, the urban flow is very complex and strongly influenced by the building features, spacing or relative height between them, or their orientation with respect to the main wind direction [16]. As the performance of a wind turbine in the built environment is only significant when there is an adequate wind supply, buildings minimising the disturbance to the wind resource or, even better, enhancing the wind flow would be expected to augment greatly their wind energy potential [12]. Campos-Arriaga [17] confirmed that among buildings in a given location, the tallest ones show to improve the wind energy resource, and hence are to be preferred as suitable locations to install wind turbines.
Besides the importance of the local wind speed acceleration, turbulence is another important factor, which affects the design, the operability and service life of wind turbines. Moreover, the assessment of the wind energy potential should also account for different approaching wind directions.
Most of the literature about the flow pattern above buildings is related to isolated low-rise buildings. The majority of works report on wind tunnel studies focusing on the relationship between flow pattern and surface pressure. Ginger and Letchford [18] studied the flow mechanism above a low-rise building under different wind angles. They identified a 2D separation bubble forming when the flow is perpendicular to the building side, and 3D conical vortices for oblique angles. Kawai and Nishimura [19] also detected conical vortices from surface pressure under smooth and turbulent boundary layer inflows under oblique wind. The study revealed that fluctuations in the surface pressure are correlated to the movement of conical vortices forming above the roof. Subsequently, Kawai [20] used hot-wire anemometry to reconstruct the structure of conical vortices above the roof. The strength of the conical vortices is larger in the smooth flow than in the turbulent flow. The presence of 3D conical vortices has also been confirmed using the quasi-steady theory [21], laser Doppler anemometry [22,23] and numerical large eddy simulation [24]. Further investigations on the formation mechanism, size and fluctuation of conical vortices have been provided investigating the effect of incident winds [25,26] and the shape of the building [27,28], leading to the development of analytical models for conical vortices on low-rise buildings [29,30,31].
More specific works related to urban wind harvesting are mostly related to idealised parametric studies considering simple configurations, for example, standalone cubes, prismatic buildings or groups of simple buildings [13]. Besides the flat roof type, many studies also investigated other types of roofs aiming at finding more favourable shapes for wind energy potential. These studies are dominantly using CFD as a methodology. For example, Toja-Silva et al. [32] considered a flat-roof building with a 2:1 height-to-width ratio. Different turbulence models were tested and results were compared with experimental data to identify the regions of the roof that perform best. Ledo et al. [33] investigated the flow above low-rise buildings using CFD with regards to the shape of the roof, either flat, pitched or pyramidal. Based on the turbulence intensity and the velocity above the roof, the flat roof presented the most favourable shape. Moreover, it was found that the power density above the flat roof is greater and more consistent than above the other roof types. Abohela et al. [34] performed CFD simulations further focusing on the effect of roof shape and expanded the analysis covering the flow above spherical and vaulted roofs with lower turbulence characteristics. Additionally, Toja-Silva et al. [35] investigated the roof–wall transition geometry by testing different variations of a spherical roof using CFD and showed that a soft transition (curved edge) between the wall and the roof leads to a desired speed-up. Lu and Ip [11] carried out CFD tests investigating the wind flow over three configurations of two tall buildings by considering parameters such as building height, type of roof (flat and cater-corner flat roof) and distance using meteorological data. Balduzzi et al. [36] characterised the flow field in the rooftop area of two buildings using CFD and assessed general criteria as the height and the width of its upwind building and the distance between the buildings themselves, to evaluate the convenience of a microeolic turbine installation on the roof.
In contrast, there are very few wind tunnel tests focusing specifically on wind velocity measurements of the flow above the roof of high-rise buildings. An example of a well-documented wind tunnel database was published by the Architectural Institute of Japan (AIJ) [37]. The database aims to provide benchmark validation test cases to validate CFD studies and, eventually, it was used to set best practice guidelines for the prediction and the assessment of the pedestrian wind environment around buildings [38]. Along with low-rise test cases, the AIJ also reports on high-rise buildings. Another similar database is the CEDVAL database [39], which was designed to validate numerical dispersion models. CEDVAL provides flow measurements of cubic and prismatic building shapes either isolated or in a regular array. Both AIJ and CEDVAL datasets have in common the fact that they mostly report pedestrian level winds. Although some measurement points above the roof are provided, they are limited in scope and extension.
Therefore, the flow above the roof of high-rise buildings remains a rather unexplored topic of building aerodynamics. Moreover, the effect of the wind direction is also largely disregarded in investigations.
Incidentally, CFD studies in the literature do present some sort of validation using experimental data, however more appropriate test cases are needed, including measurements of the velocity field at more specific locations above the roof [35,40]. This study aims to provide an adequate database with test cases specifically targeting the wind energy potential over high-rise buildings. An experimental campaign was performed at the “Building Aerodynamics Laboratory” of Ruhr University Bochum (WIST). Within this campaign, the presented study is contributing to the identification of the flow pattern above an isolated high-rise building with a height-to-width ratio of 3:1 under different incident wind directions. Besides considering a flat roof benchmark case, the study also treats a deck roof case, presumably more favourable for improving wind energy harvesting. The present dataset is available at Mendeley Data [41]. The flow above the same high-rise building model was also analysed in [42] with reference to building clusters, and that dataset is also available at Mendeley Data [43]. Both experimental studies were part of the activities of the EU COST Action TU1304 [44,45]. In addition, the presented work brings more insight into the flow-specific characteristics, particularly important for urban wind exploitation. It also provides a comparison to the flow pattern observed above flat-roof low-rise buildings, in terms of flow structures and augmented wind speed.
2. Experimental Methodology
2.1. High-Rise Building Models
A 1:300 scale model of a high-rise building, square in plan, has been used in this investigation. Two roof shapes are considered: a flat roof and a deck-type roof as shown in Figure 1a,b, respectively. As shown in Figure 1a, the height of the building is denoted by H (400 mm) and the width by D (133.3 mm).
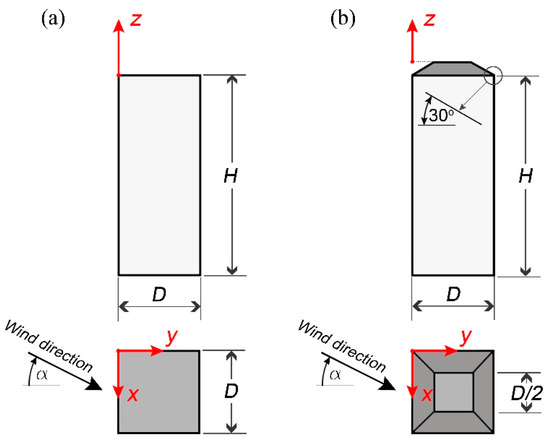
Figure 1.
High-rise building model used in the investigation, (a) with a flat roof, (b) with a deck roof.
In the context of the atmospheric boundary layer winds, low-rise buildings are defined as those having two heights smaller than the width (2H < D) and H < 30 m [46]. This matches the definition of squat buildings given by Cook [47], whereas the building is considered tall when 2H > D. This distinction is made based on the behaviour of the wind and its path to overcome the building as an obstacle. When the building is tall, the wind finds it easier to flow around the sides than over the top of the building, except for an area very close to the top, as opposed to squat buildings [47]. In recent literature, related to the flow around buildings, the term high-rise building is used for buildings having a height-to-width ratio of H/D ≥ 2:1, as in [48,49]. Thus, the ratio of H/D = 3:1 is chosen as an example for the geometry of a high-rise building.
The inclination of the deck roof in Figure 1b is 30°. The dimensions of the deck roof are the same as those of the flat-roof building with the added cap to the flat roof. The hypothesis here is that the deck-type roof helps to reduce both the separated flow and its turbulence intensity in the above roof flow and hence enhance the quality and mean speed of the wind above the roof for wind energy harvesting. The flow pattern around the two buildings was investigated under four different wind angles, namely 0°, 15°, 30° and 45°.
2.2. Wind Tunnel Setup and Incoming Flow
The experiments have been conducted in the atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel of the Ruhr-University Bochum, Germany. The wind tunnel has a cross-section of 1.6 × 1.8 m2 and a test section length of 9.4 m. Figure 2 shows the wooden models mounted on a rotating table in the wind tunnel. The reference velocity Uref used to normalise the data was measured using a Prandtl tube mounted at the height of the high-rise building model and placed 1 m upstream of the model. Reynolds number related to all measurements based on the mean velocity at the height of high-rise building and the side of the roof is Re ~ 1.4 × 105. Horizontal buoyancy is found to be absent in the wind tunnel, as very low decay of the static pressure is measured throughout the measurement section [50].
Figure 2.
The two building models mounted in the wind tunnel, (a) flat roof and (b) deck roof.
The boundary layer flow is generated in the wind tunnel using both spires at the tunnel inlet and roughness elements as shown in Figure 2a. The mean wind profile matches that of a power law with the exponent of 0.2 as shown in Figure 3a. This wind profile is found to be consistent in the lateral direction of the wind tunnel, covering the central portion of the test section. This spans over approximately 0.9 m at least (±0.45 m from the central position), which is outside of the influence of the walls [51]. This is representative of the terrain category II [52] simulating realistic conditions of the flow around isolated high-rise buildings. Further, measured data can be used as an approximation for the flow pattern in case of an urban area with a dominant high-rise building surrounded by low-rise buildings. This arrangement is common on the outskirts of large cities, university campuses displaced from city centres, etc., all representing potential locations for efficient urban wind energy harvesting. The mean stream-wise wind speed (Uref), the stream-wise turbulence intensity (IU) and the vertical turbulence intensity (IW) at the height of the model are 16 m/s, 13% and 11%, respectively.
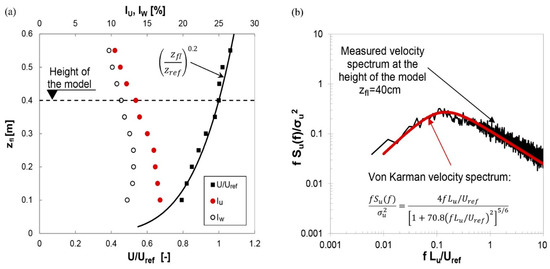
Figure 3.
(a) Mean stream-wise wind speed (U/Uref), stream-wise turbulence intensity (IU) and vertical turbulence intensity (IW) profiles, measured from the floor of the wind tunnel (Uref is the mean wind speed at the model height), (b) longitudinal velocity spectrum at the height of the model.
2.3. Experimental Procedure
In addition to the velocity measurements, the surface pressure has also been obtained at different locations to present a comprehensive database where pressure and wind speed results can be used as a validation test case.
The surface pressure on the roofs of the models was measured using 64 pressure taps, distributed as shown in Figure 4. The pressure sensors are four active element piezoresistive bridges. Two different pressures sensors were used: Honeywell 170 PC (measurement range: ±35 mbar) and AMSYS 5812-0001-D-B (measurement range: ±10.34 mbar). Due to the narrow spaces in the model, the pressure sensors were placed outside of the model and connected to the bores in the wooden deck by brass connectors (inner diameter 1 mm) and plastic pressure tubes (inner diameter 1.5 mm), that are freed from burrs and debris. The length of plastic pressure tubes was about 0.9 m. The calibration of the pressure measurement system included two phases: static and dynamic. The static calibration was performed to establish the pressure–voltage relation for each pressure sensor, while dynamic calibration was performed to correct the dynamic effects of tubes [53]. Surface pressures were acquired with a sampling frequency of 1000 Hz and were scanned in a sample-and-hold modus, enabling the simultaneous sampling of signals. For each measurement, 28 samples of 4.7 s length were collected, where each sample corresponds to a 10 min long sample in full scale. The maximum uncertainty of surface pressures based on five repeated measurements was estimated to be ~2.5%. More details about the pressure measurement equipment that consisted of pressure sensors, a tubing system, amplifiers and analog/digital (A/D) converters can be found in [54].
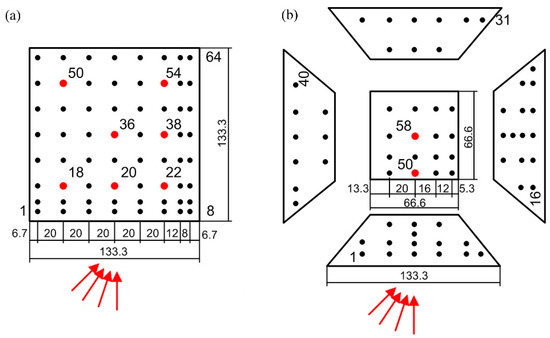
Figure 4.
Distribution of pressure taps on the surface of the high-rise buildings: (a) at the flat roof and (b) at the deck roof, for 0°, 15°, 30° and 45° wind angles.
The velocities above the roof were mainly measured at three different heights (z/D = 0.075, 0.3 and 0.45) above the points marked in red in Figure 4. In addition, above points 36 of the flat roof and 58 of the deck roof, at the centre of the roof, ten heights are considered with the spacing of z/D = 0.075. The hot-wire anemometer consisted of two cross wires allowing to measure both stream-wise and vertical velocity components. All velocity data, including hot-wire anemometer and Prandtl tube, are sampled with the frequency of 2000 Hz. The hot-wire anemometer was calibrated in laminar flow conditions in a calibration tunnel by exposing a probe to the set of known velocities, while corresponding voltages were recorded. The adopted fitting curve is a fourth order polynomial curve with coefficients calculated by fitting the data in the least-squares sense. Uncertainties related to the velocity measurements were calculated following the procedure presented by [55,56]. The total uncertainty of the velocity consisted of calibration, linearisation, positioning of the probe, digitalisation and uncertainty due to variation in the experimental conditions (such as temperature or ambient pressure). The maximum uncertainty of the time-averaged stream-wise velocity was 5.6%. The maximum uncertainties of the stream-wise and vertical turbulence intensities were estimated to be 9.6% and 9.4%, respectively. These uncertainty estimates correspond to the 95% confidence interval. The manual positioning of the hot-wire anemometer was detected as one of the main contributions to uncertainty, as established based on three repeated measurements at ten different heights above the middle point of the flat roof.
The flow in the roof region is expectably inherently 3D. Some degree of cross-flow is expected in those regions of the flow where vorticity occurs, i.e., closer to the surface. Eventual three-dimensionality in the flow is estimated looking at the performance of the signal measurements and the level of turbulence intensity. In regions where IU > 30%, the flow is likely to be affected by a reversed direction or strong cross-component. It is worth noting that even using 3D probes, reversed flow conditions cannot be detected either. Furthermore, those regions of highly skewed flow are not suitable for urban wind energy. Therefore, the degree of precision given by hot-wire anemometry is considered sufficient for the scope of the study: to understand the evolution of vortex structures and compare them to the surface pressure distribution for the sake of wind energy applications.
No blockage corrections of the measured results were considered, as even in the worst case, the normal-to-wind areas of the testing models were smaller than 1.8% of the wind tunnel cross-section.
3. Results
3.1. Flat-roof Building
3.1.1. Wind Velocity
In this subsection, the velocity measurements above the flat-roof building are discussed for the four wind angles of attack, 0°, 15°, 30° and 45°. The velocity profiles over two alignments, x/D = 0.2 and x/D = 0.8, are plotted in Figure 5, considering points 18–50 and 22–38–54 (Figure 4a). Depending on different wind angles, the positions of these points are changing. For example, at small angles, point 18 lies in the upstream half of the roof, while point 50 lies downstream. However, in the case of large wind angles, both points 18–50 are in the upstream half of the roof. In addition to velocity profiles, Figure 5 shows the longitudinal (IU) and vertical (IW) turbulence intensities, obtained by
where σU and σW are the standard deviations of stream-wise and vertical wind velocity components and U is the mean stream-wise wind speed. Figure 5 also illustrates the acceleration of the stream-wise wind speed as calculated with (U − Uref)/Uref, where Uref is the mean reference velocity measured with a Prandtl tube placed upstream of the model.
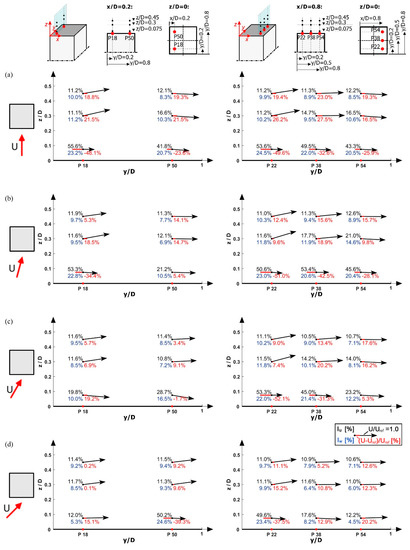
Figure 5.
Velocity vectors profiles, based on the stream-wise and vertical velocity components, showing the stream-wise turbulence intensity IU, the vertical turbulence intensity IW and the percentage increase in the stream-wise wind speed. Each numerical value reported at every measurement point in the figure shows the following statistics: IU [%] above on the left; IW [%] below on the left; (U − Uref)/Uref [%] below on the right. Profiles over the flat-roof high-rise building are measured above points 18 and 50 (belonging to the marked line x/D = 0.2, left) and above the points 22, 38 and 54 (belonging to the marked line x/D = 0.8, right) for wind directions: (a) 0°, (b) 15°, (c) 30° and (d) 45°. The arrows indicate the velocity magnitude normalised with the reference velocity (Uref), as referred to the unity vector represented in the legend.
Figure 5a shows the velocity profiles above points 18 and 22 for the wind angle of 0°. A strong separation develops at the upstream edge, as velocity vectors above the height of z/D = 0.3 point upwards. In the vicinity of the roof, a high stream-wise turbulence intensity zone can be detected, reaching up to a value of 55%. In regions of turbulence intensities >30%, hot-wire measurements are expected to be affected by some inaccuracy and, therefore, results cannot be treated as reliable [55]. Nevertheless, these high values of turbulence intensity confirm the existence of separated flow. The separation bubble from the windward edge reattaches in the vicinity of points 50 and 54, as velocity vectors point downwards.
At 15°, the velocity profiles above the upstream points 18 and 22 are similar to those found at 0°. However, profiles above points 38 and 50 show some differences. The velocity vectors above point 38 are no longer parallel to the roof, pointing slightly upwards, suggesting a downwind shift of the average moving vertex core. Besides, vectors above point 50 at heights z/D ≥ 0.3 are nearly parallel to the roof, seemingly out of the separation region, as the flow behaves analogously to points upstream of the separation bubble.
As the wind angle increases to 30°, a small separation cone generates along the upstream edge of the building, starting at its upstream corner. The down-pointing velocity vectors at the lower measuring points suggest that both points 18 and 50 are located at the tail of the separation cone where the flow tends to attach to the roof. The profiles above the line x/D = 0.8 indicate a slightly smaller separation compared to the 15° wind angle. This is followed by the reduction in turbulence intensities of the flow above points 38 and 54.
At 45°, the wind flow is highly turbulent close to the roof above point 50 and less turbulent above point 18. This suggests that a large separation cone occurs at the upstream edge and increases in size along the length of the building side. In this particular case, the lower measurement position above point 50 lies entirely in the separation zone as IU is larger than 50%. In addition, another separation cone formed along the other upstream side of the building is affecting the flow above points 22 and, to a lesser extent, 38. In fact, the lower measurement position above point 38 is pointing slightly downwards, suggesting that it is located at the tail of the separation cone. However, the flow at higher positions above points 38 and 54 seems to lie out of the influence of the separation cone.
One possible way to verify inferences related to the flow patterns is the use of flow visualisation techniques, such as smoke injection. Another way would be to perform and analyse CFD simulations that are validated with the presented experimental results. Thus, future work will focus on justifying and exploring in-depth recognised flow patterns.
Figure 5 also shows that the pair of points 18–22 and 50–54 at 0° and 22–50 at 45° have a similar configuration, confirming that the flow is symmetric at those angles.
3.1.2. Surface Pressure
The flow pattern above the roof can also be analysed based on surface pressure. In addition, surface pressure can provide more reliable validation as it usually has lower uncertainty levels compared to velocity measurements. Figure 6 shows the contours of the mean surface pressure coefficient of the flat-roof building, at the four wind angles. The pressure coefficient (Cp) is defined as
where p∞, ρ and Uref are the free-stream pressure, the air density and the reference velocity, respectively.
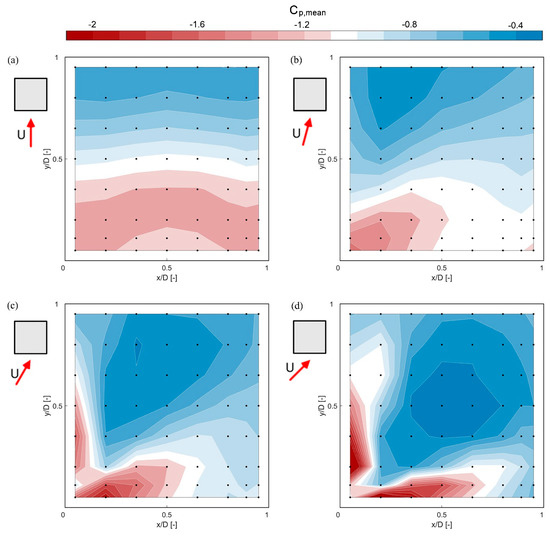
Figure 6.
Mean surface pressure coefficient (Cp,mean) distributions on the flat roof for different approaching flow angles: (a) 0°, (b) 15°, (c) 30° and (d) 45°. Black dots on the surface plot represent the measurement taps.
Figure 6a shows a significant reduction in the surface pressure at 0° close to the upstream edge due to the flow separation, followed by a subsequent increase downstream. A similar distribution of the surface pressure is found at 15° with a slightly higher reduction in the pressure close to the upstream corner. At higher wind angles of 30° and 45°, the contour maps are similar to each other, with a high reduction in surface pressure located at a limited area along both upstream edges. This pattern of pressure contours indicates the existence of two intense conical structures, as observed from the velocity measurements presented in Figure 5. As expected, for the 45° wind angle, the surface pressure distribution is symmetrical around the diagonal line of the roof. The non-uniform arrangement of the measuring taps might be responsible for the slightly asymmetric pattern in Figure 6d.
To provide an improved understanding of the effect of the wind direction on the surface pressure, Figure 7 shows the mean pressure coefficient and its standard deviation along two alignments on the roof, at x/D = 0.35 and x/D = 0.8. For all wind angles in Figure 7a, a characteristic upstream hump shape is observed, which is typical for a flow with a separated region followed by a reattachment [57]. The hump shape is related to the high negative pressure values in the separation region. The largest suction lies directly below the average moving vortex core [23]. The length of the mean recirculation region is related to the peak location of the standard deviation value, considering that the peak occurs just upstream of the mean reattachment position [57]. For wind angles of 0° and 15°, the hump shape is wider than in the case of 30° and 45°. This is the consequence of the large separation bubble generating at the upstream edge, which entails a long recirculation region. Comparing Figure 7a,b, the growth in the size of the conical vortices along the side of the building can be noticed for the 30° and 45° wind angles.
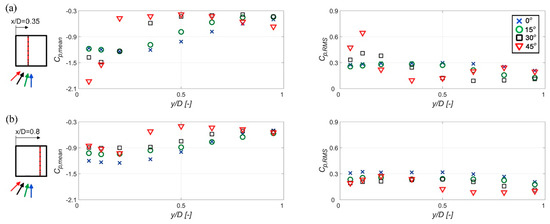
Figure 7.
Mean (Cp mean) and standard deviation (Cp RMS) distributions of the surface pressure coefficient for different wind angles, 0°, 15°, 30° and 45°, along different alignments on the roof: (a) x/D = 0.35, (b) x/D = 0.8.
3.1.3. Turbulence Intensity and Flow Acceleration
Figure 8 gives further insight on the turbulence intensity in the stream-wise (IU) and vertical (IW) directions above all measuring points for the four wind angles. Along with local wind profiles, the inflow turbulence intensity at the same height is also shown as a reference (taken from Figure 3), using a black-filled circle mark.
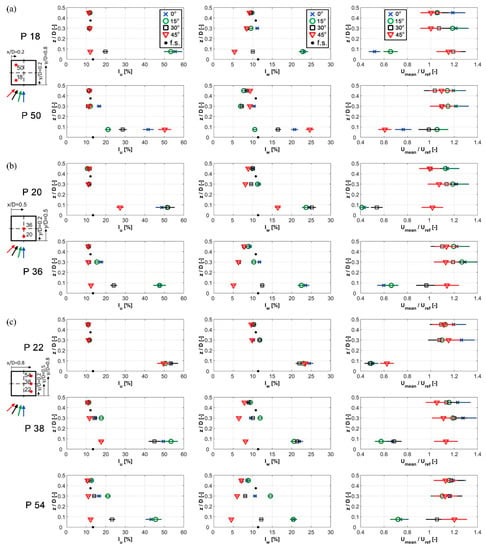
Figure 8.
Stream-wise (IU) and vertical (IW) turbulence intensity, and normalised stream-wise velocity U/Uref with uncertainty limits, as measured above the flat roof at 0°, 15°, 30° and 45°. Measurement points include: (a) 18–50 (marked line x/D = 0.2), (b) 20–36 (marked line x/D = 0.5) and (c) 22–38–54 (x/D = 0.8). Free-stream reference values (at the inlet profile shown in Figure 3) are also marked for the turbulence intensity (•).
At 0°, the stream-wise turbulence intensity for all measurement points in the vicinity of the roof is >30%, indicating the presence of a large separation bubble. This is followed by turbulence intensities of ~20–25% in the vertical direction. At z/D = 0.3, the turbulence intensity in the stream-wise direction is still higher than the reference profile value, within the limits 15–21%. This is not the case for upstream points (18, 20 and 22), where values are comparable to the reference ones. Turbulence intensities in the vertical direction are comparable to the reference profile within the range 10–13%. Measurements above the height of z/D = 0.3 are closer to the free-stream values, suggesting that the height of the separation region is slightly above 0.3D.
Similarly, to the previous case, turbulence intensity profiles at 15° show high turbulence close to the roof. Values at z/D = 0.075 are mostly over 30% for IU and over 20% for IW, followed by a reduction in turbulence with increasing height. At z/D = 0.3, turbulence intensity lies in the ranges of 12–22% and ~10–15% for the stream-wise and vertical directions, respectively. Moreover, Figure 8 reveals that values above the alignment x/D = 0.2 and x/D = 0.5 show a slight shift in turbulence intensities compared to 0° for both the stream-wise and vertical directions. In contrast, an increase in turbulence intensity is noticeable above the alignment x/D = 0.8. This suggests that the separation bubble moves to the right while maintaining the height of ~0.3D.
Considering the 30° wind angle case, most of the points in the vicinity of the roof, at z/D = 0.075, show IU > 30% and IW > 15%. Exceptions are points above the main diagonal over the roof (36 and 54) with lower values, ~23% for IU and ~13% for IW. It leads to the conclusion that these points are near the border of the cone vortex formed at the upstream edge. Measurements from height z/D = 0.3 are analogous to the reference profile values.
For a wind angle of 45°, higher values of turbulence intensities, reaching up to 50% in stream-wise and 25% in the vertical direction, are observed at the lowest measured heights, in regions affected by the two separation cones. Turbulence levels are increasing as the cone is increasing in size (e.g., above points 20 and 22). Above the main diagonal on the roof (points 18, 36 and 54), measurements at all heights are characterised by relatively low turbulence intensities. These turbulence levels are comparable or even lower, as in the case of vertical turbulence, than the reference inflow. Namely, the wind separates from the two upstream sides of the building, forming two cone vortices, while the flow at the centre of the roof might be fully attached. Again, as at 30°, turbulence intensities from height z/D = 0.3 for all points match free-stream values.
Thus, it can be concluded that for wind angles of 30° and 45°, turbulence assumes characteristics similar to the free-stream values above the height z/D = 0.3 at all positions on the roof. Arguably, the wind direction of 45° provides a suitable flow pattern for wind energy, as the turbulence intensities above the main diagonal of the roof are low, even at positions closer to the roof.
To compare the speed-up effect above the roof, Figure 8 additionally illustrates the normalised velocity profiles above the measuring points for the different wind angles. These profiles are normalised using the reference velocity (Uref). A similar normalisation is also shown in Figure 5.
At 0°, the zones of high turbulence intensity close to the roof are characterised by low values of normalised wind speed. Above, at heights z/D = 0.3 and z/D = 0.45, an increase in wind speed in the range of 20–30% can be observed. The highest value of ~30% occurs above point 36 at z/D = 0.3, suggesting this is the upper limit of the separation zone.
Similar to the previous case, at 15°, a decrease in wind speed occurs due to the separation in the vicinity of the roof. In this case, an increase in the normalised velocity of ~15–20% is identified above several measuring points from the height z/D = 0.3.
At 30°, normalised velocities at the lowest measurement height are mostly <1. At height z/D = 0.3, they are increased by the range of 10–20%, reaching 20% in the zone above the cone vortex development.
For a wind angle of 45°, even at the vicinity of the roof, all points at the main diagonal are experiencing an increase in wind speed of more than 15%. Yet, the maximum velocity increase of 20% occurs above the downstream point 54. These positions close to the roof are good candidates for wind harvesting due to their location and the fact that turbulence intensity levels are rather low for this wind direction. When all the cases are considered, the most favourable result regarding flow acceleration is detected above point 36 at a height of z/D = 0.3 at 0°. Still, this region seems to be affected by slightly higher turbulence intensity levels, implying that for the adequate positioning of the wind turbine, an even higher location, just by a bit, should be considered.
3.1.4. Flow Pattern Comparison with Other Flat-Roof Buildings
In order to compare the flow above high-rise buildings with available results for low-rise buildings, a comparison with the databases AIJ and CEDVAL is proposed. The CEDVAL database reports flow measurements around a cube (H/D = 1:1) obtained through laser Doppler anemometry (LDA two-component system) for various wind directions. At 0°, a large separation over the top of the roof is detected. However, the actual size of the separation length is not available due to the lack of measurement data near the roof, as the closest measurement positions are located at z/D = 0.2. The maximum velocity increase of 21% occurs above the central point of the cube at z/D = 0.6. This is followed by slightly higher turbulence intensity levels than the reference ones [39].
The CEDVAL database also considers an incident angle of 45°. Close to the roof, i.e., at a height of z/D = 0.2, the normalised velocity increase is in the range 12–15%. The maximum value is reached at a similar location as in the present study, i.e., close to the downstream point 54. As also found in the present study, at 45°, turbulence intensities IU and IW are comparable to or even lower than the reference inflow values.
A significantly smaller separation bubble, as compared to the current case, is instead reported in the AIJ dataset [37], which considers a square isolated flat-roof building, at 0°, with a ratio of H/D = 2:1. Based on the reversed flow detected, the reattachment length can be estimated at ~1/4D, which is lower than in the present case. This can be attributed to the higher turbulence intensity in the inflow. In addition, a slightly lower flow acceleration ~24% is found above the location at 1/4D at height z/D = 0.375, compared to the current high-rise case, where similar turbulence intensities to the reference one are recorded.
Comparing the surface pressure patterns on the flat roof from the low-rise buildings [37,39] and the current high-rise building, it can be concluded that the surface pressure contours are consistent for a given wind direction. These patterns reveal the existence of analogous flow structures, i.e., separation bubble at α = 0° and conical vortices for the oblique wind direction, as observed in Figure 6. The Architectural Institute of Japan published two databases on pressure measurement on low-rise and high-rise buildings. Those experimental campaigns were mainly focused on the sides of the buildings and only measurements on the low-rise buildings included measurement positions at the flat roof. Figure 9 compares the mean pressure coefficient over the centre line of two cubes having respectively H/D = 1:2 and H/D = 1:1, taken from the AIJ database, for the two wind directions 0° and 45°. As mentioned above, the size of the hump shape of the pressure coefficient curve, which is related to the high negative pressure in the separation region, can be used as an estimate of the size of the separation bubble. Figure 9 shows a possible trend for the hump shape, which is increasing alongside the height of the building. A smaller increase in size seems to occur for 45°, yet more windward measurement points would be required for a more detailed analysis.
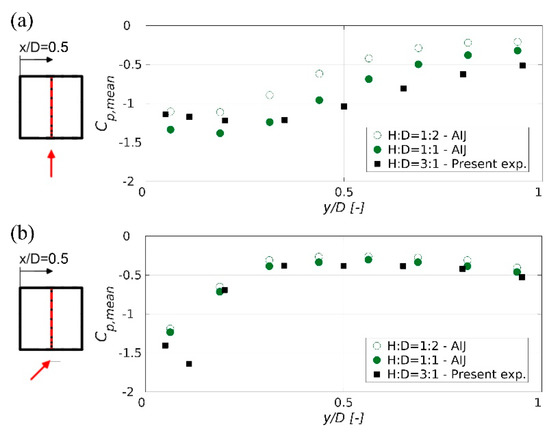
Figure 9.
Mean distributions of the surface pressure coefficient (Cp,mean) along alignment x/D = 0.5 for different building configurations, a half cube H/D = 1:2 and a cube H/D = 1:1 from the Architectural Institute of Japan (AIJ) database and high-rise H/D = 3:1 from the present experiment for two wind angles: (a) 0° and (b) 45°.
The increase in the size of the separation bubble is combined with an increase in the acceleration effect above the roof. The velocity measurements over buildings with different aspect ratios, namely H/D = 1:1 from the CEDVAL database; H/D = 2:1 from the AIJ database; and H/D = 3:1 from the current study, reveal that the wind acceleration increases together with the building height. Further, the CFD study by Abohela et al. [34] shows the same conclusion regarding the acceleration effect over the barrel-vaulted roof of a high-rise building with three different heights.
A comprehensive study considering the same inflow conditions and measurement locations above the flat roof would provide more general conclusions on the effect of building height to identify favourable locations suitable for wind energy exploitation.
3.2. Deck-roof Building
3.2.1. Wind Velocity
The following subsection presents the results of the velocity measurements above the deck-roof building, obtained for wind angles of 0° and 45°. The mean velocity and turbulence intensity have been measured above two points on the roof top, i.e., points 50 and 58, marked in red in Figure 4b. The velocity has been measured at ten heights above the roof centre point (point 58 in Figure 4b) and five heights above point 50 at 0°, and four heights above both points at 45°. The normalised velocity profiles, based on the stream-wise and vertical velocity components above these points, are shown in Figure 10, together with the longitudinal (IU) and vertical (IW) turbulence intensities calculated using Equation (1). Figure 10 also shows the percentage increase in the mean value of the stream-wise velocity component as in the previous section. In order to compare the behaviour of the deck-roof to that of the flat-roof building, Figure 10 also shows the wind profiles above x/D = 0.5 (points 20 and 36) for the same wind angles.
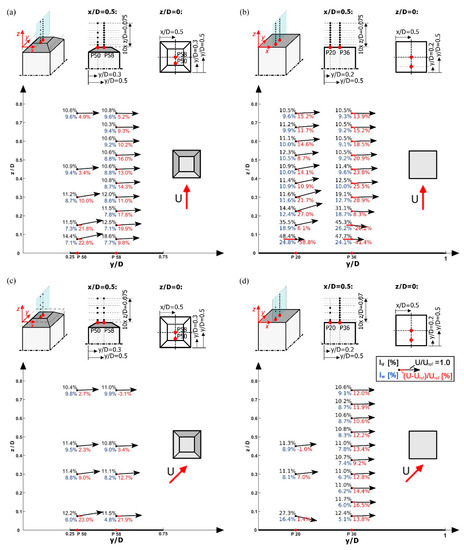
Figure 10.
Velocity vectors profiles, based on the stream-wise and vertical velocity components, showing the stream-wise turbulence intensity IU, the vertical turbulence intensity IW and the percentage increase in the stream-wise wind speed. Each numerical value reported at every measurement point in the figure shows the following statistics: IU [%] above on the left; IW [%] below on the left; (U-Uref)/Uref [%] below on the right. Profiles over the deck-roof high-rise building are measured above points 18 and 50 (alignment x/D = 0.2, left-hand-side), for wind directions of: (a) 0° and (c) 45°; and over the flat-roof high-rise building above the points 20 and 36 (x/D = 0.5), for wind directions of: (b) 0° and (d) 45°. The arrows indicate the velocity magnitude normalised with reference velocity (Uref), as referred to the unity vector represented in the legend.
At 0°, results in Figure 10a show that velocity vectors above point 50 point upwards, which suggests that the flow separates at the windward edge of the deck-roof building. However, the velocity vectors above point 58 are almost parallel to the roof, indicating that the size of the separation bubble is much smaller than that above the flat-roof building presented in Figure 10b. It is interesting to note that turbulence intensities are lower close to the top of the deck-roof building, in contrast to high-turbulence intensity zones detected in the same zone in Figure 10b. This may be explained by the effect of the shape of the deck roof. As the incoming air overcomes the obstacle provided by the high-rise building, lifting over the roof of the building, the streamlines of the velocity vectors follow the shape of the roof, thus preventing the development of the large separation bubble at the upstream edge. This fact is supported by the flow acceleration noticeable in the vicinity of the roof.
At 45°, a similar flow pattern can be observed above the central points (point 58 in Figure 10c and point 36 in Figure 10d) for both roof shapes. The lack of a vertical velocity component at the lowest measurement positions as well as low turbulence levels indicate that the flow is attached to the roof. The difference is noticeable in the flow above point 50 for the deck-roof building case and point 20 for the flat roof case. While point 20 is in the separation zone at flat-height z/D = 0.075, point 50 seems to be above the separation zone due to the low turbulence intensities and the increase in the mean value of the wind speed.
3.2.2. Surface Pressure
The plot of the distribution of the mean surface pressure coefficient on the deck roof is shown in Figure 11 for wind angles of 0°, 15°, 30° and 45°.
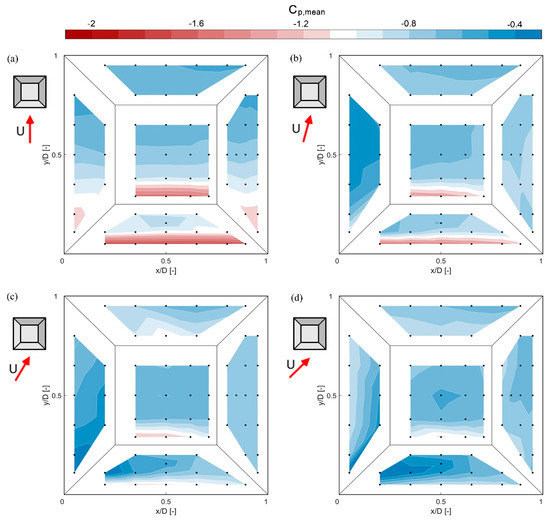
Figure 11.
Mean surface pressure coefficient (Cp,mean) distributions on the deck roof for different approaching flow angles: (a) 0°, (b) 15°, (c) 30° and (d) 45°. Black dots on the surface plot represent the measurement taps.
At 0°, at the central flat portion of the deck roof, a reduction in the surface pressure close to the leading edge is limited to a more confined area compared to the flat roof case (Figure 6). As the approaching wind angle increases, the separated area linked to the leading edge decreases. At 30° and 45°, the shape of the pressure contours still shows slight similarities to the flat roof case (Figure 6), as the contours become denser close to the windward corner. Nevertheless, the number of measurement points in this confined area is limited and it is not clear from the pressure plots if small conical vortices exist. However, the results presented in Figure 10c confirm the existence. Thus, for all wind angles, the shape of the deck roof suppresses considerably the separation area. In addition, at all plots, it can be observed that downstream of this confined high-suction area the surface pressure distribution is rather uniform. This uniform pressure indicates that the flow is generally attached to the roof. Looking at the distribution over the decks of the roof, a similar pattern can be observed. The windward sides have a high-suction zone close to the upwind edges, while on the leeward sides the pressure distribution is mostly uniform.
3.2.3. Turbulence Intensity and Flow Acceleration
The measurements of turbulence intensities in the stream-wise (IU) and vertical (IW) directions over the deck roof are shown in Figure 12 for two wind angles of 0° and 45°, at four heights above the measurement points on the alignment x/D = 0.5, together with the free-stream values marked with black circles. The figure also includes the normalised velocity profiles of the mean value of the stream-wise component in order to examine the speed-up effect above the roof.
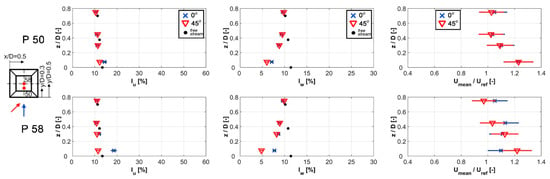
Figure 12.
Profiles of stream-wise (IU) and vertical (IW) turbulence intensities (with the reference profile from the free-stream, values marked with black circles), and normalised stream-wise velocity Umean/Uref, with uncertainty limits, measured over the deck roof for two different wind angles of 0° and 45°, above points 50 and 58 (x/D = 0.5).
Considering the results for both wind angles, the turbulence intensity profiles present favourable conditions for the installation of wind turbines over the deck roof. Namely, measurements of the stream-wise turbulence intensity at the majority of heights are comparable to the free-stream ones, not exceeding 13%. The only exception is the value at height z/D = 0.075 above point 58 at 0°, which reaches 19%, indicating that it is affected by upstream separation. Vertical turbulence intensity values are even lower than the reference ones for all cases, particularly close to the roof, as they are in the range of 5–10%.
In the vicinity of the roof, for both wind angles, the wind speed accelerates with a rate of more than 20%. Moreover, a larger area seems to be affected at 45° with this favourable flow condition. As the height increases, the speed-up effect gradually decreases.
Presented results for the deck-roof building show that the wind direction has a small effect on both the mean wind velocity and turbulence intensity above the roof. In addition, although the deck roof generates a velocity amplification of similar magnitude compared to the flat roof at 0°, this occurs at notably lower positions (closer to the roof surface). Moreover, the turbulence intensity in that zone is equal or even lower compared to the free-stream at most measurement points. Similar flow conditions are observed over the deck roof at 45° compared to the flat roof case.
4. Conclusions
A series of experimental tests has been carried out in a boundary layer wind tunnel to measure both the velocity field and the surface pressure above the roof of a high-rise building. Besides providing validation test cases of future numerical investigations, the study aims at improving the understanding of the flow pattern of the roof region for wind energy harvesting. The effects of wind direction and roof shape have been investigated in terms of flow pattern, turbulence intensity and accelerated wind velocity.
For all wind angles, the flow separates at the leading edge of the flat roof. Nevertheless, different separation patterns take place, depending on the angle of the wind, which are visible in both the surface pressure and wind speed profiles. At 0°, the separation bubble extends to about 2/3 of the building width, with a height of about 0.3D. In contrast to the separation bubble, cone vortices dominate the flow pattern at 30° and 45°. The cone vortices grow in size as they evolve along the side of the building. The largest size for cone vortices is found at 30°.
As a broad region is affected by the separation, the 0° configuration is the most turbulent one. In general, as the wind angle increases, the region of high turbulence intensity reduces gradually, and 45° is found to be the most preferable wind direction, minimising turbulence. As regards the flow acceleration, the 0° configuration provides the highest increase in wind speed, up to U~1.3Uref at z~0.3H at the centre of the roof. However, this position is still influenced by relatively high turbulence intensities. On the other hand, the 45° wind direction provides a substantial amplification of wind speed up to 20%, at significantly lower positions close to the roof with a lower turbulence intensity. This vicinity to the roof is the determining factor for the installation of small wind turbines.
A similar behaviour is observed in comparison with the flow over low-rise buildings. Namely, similar flow patterns are recognised for different flow angles and besides, similar areas are detected as the most favourable locations for the possible installation of wind turbines. In addition, an increase in building height seems to be followed by an increase in wind acceleration. Yet, more detailed studies are needed to provide more definitive conclusions on the relation between building features and wind resource.
Decking the roof significantly improves the flow for wind energy purposes. Among the most important observations is the insensitivity of the flow above the deck roof to changes in wind direction, unlike in the flat roof case. Results also show a far smaller separation zone for all wind directions, which is beneficial as wind turbines can be installed closer to the surface. Turbulence intensities are equal to or lower than the reference value of the free-stream wind profile for all configurations, highlighting the advantage of this shape. Besides the favourable effect on turbulence intensities at lower heights, the deck-roof shape performs well in terms of enhanced wind acceleration, reaching a maximum increase in wind speed of around 20%.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, H.H., A.Š.G. and G.V.; methodology, validation, resources H.H. and A.Š.G.; formal analysis, H.H., A.Š.G. and K.K.V.; investigation, H.H., A.Š.G. and R.H.; data curation, A.Š.G. and K.K.V.; writing—original draft preparation, H.H. and A.Š.G.; writing—review and editing, A.Š.G., K.K.V. and G.V.; supervision, R.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the COST Action TU1804 WINERCOST—“Wind Energy to enhance the concept of Smart cities” through a Short Term Scientific Mission to conduct the experiments. Further, this work was supported by the Luxembourg National Research Fund (FNR) under project reference C19/SR/13639741.
Acknowledgments
The support of the European Commission’s Framework Program “Horizon 2020” through the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Innovative Training Networks (ITN) “AEOLUS4FUTURE—Efficient harvesting of the wind energy” (H2020-MSCA-ITN-2014: Grant agreement no. 643167) is also acknowledged. The time and support received at the Ruhr-University Bochum by the Christian Neuhaus, Cornelia Kalender, Ulf Winkelmann are also acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviation
| Cp | pressure coefficient |
| Cp,mean | mean surface pressure coefficient |
| Cp RMS | standard deviation of the surface pressure coefficient |
| D | width of building model |
| f | frequency |
| H | height of building model |
| IU | stream-wise turbulence intensity |
| IW | vertical turbulence intensity |
| LU | longitudinal integral length-scale |
| p | surface pressure |
| p∞ | free-stream pressure |
| Re | Reynolds number |
| SU(f) | spectral density function for wind velocity |
| U | mean stream-wise wind speed |
| Uref | mean stream-wise wind speed at model height (H) |
| x, y, z | coordinates |
| zfl | height above wind tunnel floor |
| zref | reference height equal to height of building model (H) |
| ρ | air density |
| σU | standard deviation of stream-wise wind velocity component |
| σW | standard deviation of vertical wind velocity component |
References
- United Nations—Department of Economic and Social Affairs—Population Division. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019.
- Cheng, V. Understanding density and high density. In Designing High-Density Cities for Social and Environmental Sustainability; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Energy Information Administration—EIA. EIA Projects World Energy Consumption Will Increase 56% by 2040—Today in Energy. 2013. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=12251# (accessed on 6 December 2019).
- Walsh, C.; Pineda, I. Wind Energy in Europe in 2018. Trends and Statistics; Wind Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- van Kuik, G.; Ummels, B.; Hendriks, R. Perspectives of Wind Energy. In Sustainable Energy Technologies; Hanjalić, K., Van de Krol, R., Lekić, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieros, G.; Chaviaropoulos, P.; Sørensen, J.D.; Bulder, B.H.; Jamieson, P. Upscaling wind turbines: Theoretical and practical aspects and their impact on the cost of energy. Wind Energy 2012, 15, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeiha, A.; Montazeri, H.; Blocken, B. A framework for preliminary large-scale urban wind energy potential assessment: Roof-mounted wind turbines. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahaj, A.S.; Myers, L.; James, P.A.B. Urban energy generation: Influence of micro-wind turbine output on electricity consumption in buildings. Energy Build. 2007, 39, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummala, A.; Velamati, R.K.; Sinha, D.K.; Indraja, V.; Krishna, V.H. A review on small scale wind turbines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 1351–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, D.R.; Barlow, J.F.; Cockerill, T.T. Estimating the potential yield of small wind turbines in urban areas: A case study for Greater London, UK. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2013, 115, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Ip, K.Y. Investigation on the feasibility and enhancement methods of wind power utilization in high-rise buildings of Hong Kong. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Quraan, A.; Stathopoulos, T.; Pillay, P. Comparison of wind tunnel and on site measurements for urban wind energy estimation of potential yield. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2016, 158, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulos, T.; Alrawashdeh, H.; Al-Quraan, A.; Blocken, B.; Dilimulati, A.; Paraschivoiu, M.; Pila, P. Urban wind energy: Some views on potential and challenges. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 179, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocken, B. 50 years of Computational Wind Engineering: Past, present and future. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2014, 129, 69–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, T.; Estanqueiro, A. A new methodology for urban wind resource assessment. Renew. Energy 2016, 89, 598–605. [Google Scholar]
- Stankovic, S.; Campbell, N.; Harries, A. Urban Wind Energy; Earthscan Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Arriaga, L. Wind Energy in the Built Environment: A Design Analysis Using CFD and Wind Tunnel Modelling Approach; University of Nottingham: Nottingham, UK, 2009; Available online: http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/10806/1/CamposArriagaPhDThesis.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- Ginger, J.D.; Letchford, C.W. Characteristics of large pressures in regions of flow separation. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1993, 49, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, H.; Nishimura, G. Characteristics of fluctuating suction and conical vortices on a flat roof in oblique flow. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1996, 60, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, H. Structure of conical vortices related with suction fluctuation on a flat roof in oblique smooth and turbulent flows. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1997, 69–71, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, D.; Meroney, R.N. A model of roof-top surface pressures produced by conical vortices: Model development. Wind Struct. An Int. J. 2001, 4, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwood, R.; Wood, C.J. Conical vortex movement and its effect on roof pressures. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1997, 69–71, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, D.; Meroney, R.N.; Sarkar, P.P.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, F. Flow visualization of conical vortices on flat roofs with simultaneous surface pressure measurement. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2000, 84, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tamura, T. Large-eddy simulations of flow past a square cylinder using structured and unstructured grids. Comput. Fluids 2016, 137, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Sarkar, P.P.; Mehta, K.C.; Zhao, Z. Influence of incident wind turbulence on pressure fluctuations near flat-roof corners. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2001, 89, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, H. Local peak pressure and conical vortex on building. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2002, 90, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Kumar, K. Effect of geometry on wind pressures on low-rise hip roof buildings. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2002, 90, 755–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, S.; Pindado, S.; Meseguer, J.; Sanz-Andrés, A. A parametric, experimental analysis of conical vortices on curved roofs of low-rise buildings. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2005, 93, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryggeson, H.; Lyberg, M.D. Stationary vortices attached to flat roofs. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2010, 98, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, Y.; Tamura, T.; Kataoka, H. LES analysis of unsteady characteristics of conical vortex on a flat roof. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 2007–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Suganuma, S.; Kikuchi, H.; Hibi, K. Proper orthogonal decomposition of random wind pressure field. J. Fluids Struct. 1999, 13, 1069–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toja-Silva, F.; Peralta, C.; Lopez-Garcia, O.; Navarro, J.; Cruz, I. On Roof Geometry for Urban Wind Energy Exploitation in High-Rise Buildings. Computation 2015, 3, 299–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledo, L.; Kosasih, P.B.; Cooper, P. Roof mounting site analysis for micro-wind turbines. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abohela, I.; Hamza, N.; Dudek, S. Effect of roof shape, wind direction, building height and urban configuration on the energy yield and positioning of roof mounted wind turbines. Renew. Energy 2013, 50, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toja-Silva, F.; Lopez-Garcia, O.; Peralta, C.; Navarro, J.; Cruz, I. An empirical-heuristic optimization of the building-roof geometry for urban wind energy exploitation on high-rise buildings. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 769–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balduzzi, F.; Bianchini, A.; Ferrari, L. Microeolic turbines in the built environment: Influence of the installation site on the potential energy yield. Renew. Energy 2012, 45, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Architectural Institute of Japan. Guidebook for Practical Applications of CFD to Pedestrian Wind Environment around Buildings. 2007. Available online: https://www.aij.or.jp/jpn/publish/cfdguide/index_e.htm (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- Tominaga, Y.; Mochida, A.; Yoshie, R.; Kataoka, H.; Nozu, T.; Yoshikawa, M.; Shirasawa, T. AIJ guidelines for practical applications of CFD to pedestrian wind environment around buildings. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEDVAL. Compilation of Experimental Data for Validation of Microscale Dispersion Models; Hamburg University: Hamburg, Germany, 2006; Available online: https://mi-pub.cen.uni-hamburg.de/index.php?id=628 (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- Toja-Silva, F.; Peralta, C.; Lopez-Garcia, O.; Navarro, J.; Cruz, I. Roof region dependent wind potential assessment with different RANS turbulence models. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2015, 142, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glumac, A.Š.; Hemida, H.; Vita, G.; Vranešević, K.K.; Höffer, R. Wind tunnel experimental data for flow characteristics above the roof of isolated high-rise building for wind energy harvesting considering two shapes of the roof, flat roof and deck roof. Mendeley Data 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glumac, A.Š.; Hemida, H.; Höffer, R. Wind energy potential above a high-rise building influenced by neighboring buildings: An experimental investigation. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 175, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glumac, A.Š.; Hemida, H.; Höffer, R. Wind tunnel experimental data for flow characteristics above the roof of high-rise buildings in group arrangement for wind energy harvesting. Mendeley Data 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniotopoulos, C.; Borri, C. Wind Energy Technology reconsideration to enhance the concept of smart cities. In WORKSHOP Trends and Challenges for Wind Energy Harvesting; Eindhoven University of Technology: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- COST Action TU1304. WINERCOST—Wind energy Technology Reconsideration to Enhance the Concept of Smart Cities. 2018. Available online: http://winercost.com/ (accessed on 6 December 2019).
- Uematsu, Y.; Isyumov, N. Wind pressures acting on low-rise buildings. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1999, 82, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J. The Designer’s Guide to Wind Loading of Building Structures: Static Structures Pt. 2; Butterworth-Heinemann Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga, Y. Flow around a high-rise building using steady and unsteady RANS CFD: Effect of large-scale fluctuations on the velocity statistics. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2015, 142, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toja-Silva, F.; Peralta, C.; Lopez-Garcia, O.; Navarro, J.; Cruz, I. Effect of roof-mounted solar panels on the wind energy exploitation on high-rise buildings. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2015, 145, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipps, A. Experimentelle Untersuchung der Vertailung des Statishen Druckes in der Messstrecke des Grenzschichtwindkanals; Ruhr University Bochum: Bochum, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Arunchalam, S. Hot Wire Velocity Measurements in Boundary Layer Wind Tunnel; Internal Report; Building Aerodynamics Laboratory, Ruhr University Bochum: Bochum, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- EN 1991-1-4. Eurocode 1: Actions on Structures—Part 1–4: General Actions—Wind Actions; The European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus, C. Numerische Frequenzabhängige Kalibrierung Langer Druckmessschlauchsysteme; Technical report; Building Aerodynamics Laboratory, Ruhr University Bochum: Bochum, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hemida, H.; Šarkić, A. Wind Tunnel Tests—Air flow around Buildings—Final Report of a Short Term Scientific Mission—COST Action TU1304. WINERCOST, COST Action TU1304. 2014. Available online: http://winercost.com/cost_files/STSM_report-Sarkic_Hemida.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- Jørgensen, F.E. How to Measure Turbulence with Hot-Wire Anemometers—A Practical Guide; Dantec Dynamics: Skovlunde, Denmark, 2002; pp. 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Yavuzkurt, S. A guide to uncertainty analysis of hot-wire data. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 1984, 106, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haan, F.L. The Effects of Turbulence on the Aerodynamics of Long-Span Bridges; University of Notre Dame: Notre Dame, Indiana, 2000. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).