Abstract
In this paper, we propose a tiny haptic knob that creates torque feedback in consumer electronic devices. To develop the proposed haptic knob, we use a magnetorheological (MR) fluid. When an input current is applied to a solenoid coil, a magnetic field causes a change in the MR fluid’s viscosity. This change allows the proposed haptic knob to generate a resistive torque. We optimize the structure of the haptic knob, in which two operating modes of MR fluids contribute to the actuation simultaneously. We conduct magnetic path simulation and resistive torque simulation using the finite element method and perform experiments to measure the resistive torque and its torque rate according to the rotational speed and applied current. The results show that the proposed haptic knob generates sufficient torque feedback to stimulate users and creates a variety of haptic sensations.
1. Introduction
Currently, in many consumer electronic devices, a knob is commonly used to handle and manipulate several functions. Because a knob interface does not have start and end positions (it has only a direction of rotation), users can relatively identify the values or items listed in order. For this reason, knob interfaces facilitate a more accurate control compared with other input interfaces, such as buttons or switches, which are often used to perform “on/off” functions. One of the most important factors in designing input devices is delivering a timely and useful response to users through haptic sensation. Let us consider the case where a driver manipulates a navigation menu consisting of 10 submenus using a haptic knob during driving. If the haptic knob creates a haptic pulse every time the cursor meets a new submenu in the navigation menu, the driver can control the menu more intuitively, with less reliance on sight. Furthermore, if the proposed knob provides different resistive torque depending on the targets, the knob can be a better input interface.
Several studies regarding haptic knobs have been conducted. Badescu et al. proposed a rotary haptic knob using a DC motor and brake [1]. Kim et al. suggested a haptic dial system for multimodal prototyping using a DC motor [2]. They also developed a remote controller based on the haptic knob to intuitively interact with a target device [3]. Chapuis et al. presented a haptic knob using an ultrasonic motor and a power clutch [4]. MacLean et al. established a design principle for handheld haptic devices, developed a haptic knob, and implemented a portable handheld device based on the haptic knob [5]. Hua et al. proposed a low-cost one-degree-of-freedom (1-DOF) haptic knob that can be used for rehabilitation or virtual training [6]. Although the devices in these studies were designed to provide a variety of torque feedback, they were too large to be inserted into tiny consumer electronic devices.
One possible approach to construct a tiny haptic knob (or rotary-type haptic actuator) is using magnetorheological (MR) fluids. MR fluid-based haptic actuators have several advantages. One advantage is that the actuators based on MR fluids are operated passively; hence, there is no instability problem in the actuators [7]. Another advantage is that MR fluid-based actuators can be developed not only in free form but can also generate high resistive force/torque under low input voltage in real time [8,9,10]. For these reasons, many researchers have focused on the development of rotary-type haptic actuators using MR fluids.
Qin et al. developed a hybrid rotary-type haptic actuator consisting of a DC motor and MR fluid to achieve a high torque density [11]. Furthermore, they designed a powerful MR actuator with a relatively high dynamic range to develop a multifinger interface [12]. Tri et al. proposed the design of an MR fluid-based bidirectional haptic actuator with two coils placed directly on each side of the housing [13]. Karabulut et al. designed an MR fluid-based haptic actuator that can solve the stiction problem [14]. Nguyen et al. developed linear and rotary actuators and applied them to a 3-DOF spherical force feedback system [15]. Although these modules showed the feasibility of MR fluids for tiny rotary-type haptic knobs, they are still too large to be embedded into small consumer electronic devices.
MR fluids have three operating modes: flow mode, shear mode, and squeeze mode [16]. In the flow mode, MR fluids flow between two stationary plates. In the shear mode, MR fluids flow between two plates moving relative to one another. In the squeeze mode, MR fluids resist the normal directional displacement of the pole owing to a perpendicular external normal force. To maximize the resistive torque generated by MR fluids in a tiny-size device, we must consider a new structure in which multiple operating modes of MR fluids contribute to the actuation simultaneously. In this paper, we propose a haptic knob where two modes (flow and shear) of MR fluids contribute to the generation of haptic sensation simultaneously, resulting in the creation of a sufficiently large resistive torque to stimulate the user. Experiments are conducted to evaluate the haptic performance of the proposed module. The results show that the generated resistive torque can be controlled by the applied current, and the proposed haptic knob can create a variety of haptic sensations.
2. Design of Proposed Haptic Knob
2.1. Structure of Proposed Haptic Knob
The proposed haptic knob consists of a dial plate, a housing cover, a rotary shaft, a solenoid coil, and a housing, as shown in Figure 1a. The solenoid coil was inserted into the housing, MR fluids were poured into the housing, and the rotary shaft was inserted into the housing. Next, we injected the MR fluids into the housing using a syringe to fill in the gap between the rotary shaft and the housing (Figure 1b). The rotary shaft has an overhang to connect the housing cover. We fitted the housing cover to the housing through the overhang and bonded them (Figure 1c) and then tightly bonded the dial plate to the overhang of the rotary shaft while maintaining a small gap between the dial plate and the housing cover (Figure 1d). Figure 1e shows the cross-sectional view of Figure 1d. With this structure, the rotary shaft rotates whenever a user rotates the dial plate (Figure 1f).
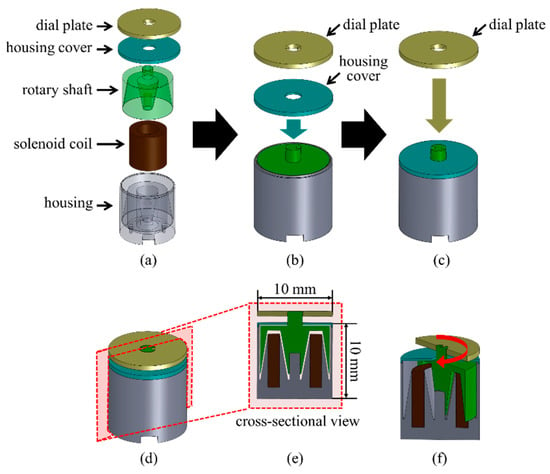
Figure 1.
Schematic and cross-sectional illustrations of the proposed haptic knob: (a–c) assembling procedure of the proposed haptic knob; (d) assembled haptic knob; (e) its cross-sectional view, and (f) schematic illustration of the proposed haptic knob when it rotates
2.2. Design of Rotary Shaft and Housing
The housing has a hollowed groove for the solenoid coil to fit in, as shown in Figure 2a. It has long and thin grooves on its surface and a pivot for aligning the rotational axis and guiding the rotation of the shaft, as shown in Figure 2b. The rotary shaft was designed to be tightly inserted into the housing; a constant gap was also maintained between the housing and rotary shaft. The MR fluid completely filled the gap to generate resistive torque feedback. Figure 2c shows the cross-sectional view of the housing equipped with the solenoid coil, rotary shaft, and housing cover. We drilled a hole in the rotary shaft to place it into the pivot of the housing (Figure 2d). The rotation of the shaft causes the MR fluids in the gap to move. We included long and slender bumps on the inner surfaces of the rotary shaft to accelerate the flow of MR fluids (Figure 2e).
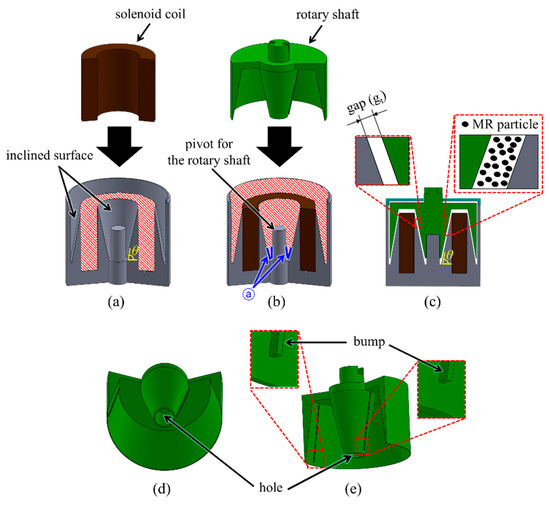
Figure 2.
Detailed structure of the housing and the rotary shaft, and the combined process with the solenoid coil: (a) Process for combining the housing and the solenoid coil; (b) process for combining the rotary shaft and the housing; (c) cross-sectional view of the housing equipped with the solenoid coil, rotary shaft, and housing cover; (d) bottom view of the rotary shaft; (e) long and slender bumps on the surface of the rotary shaft.
There are inclined surfaces in the housing, with oblique angles defined as ϴ. The larger the oblique angle (ϴ) of the inclined surface, the larger the total area of the gaps. Therefore, the oblique angle affects the haptic performance (torque feedback) of the proposed haptic knob. To find the optimal oblique angle, we simulated the resistive torque with changes to the oblique angle. Figure 3a shows the simulation result of the resistive torque generated from the proposed haptic knob. It can be seen that the resistive torque increased as the angle of the inclined surface increased. Although an oblique angle of about 90° increases the haptic performance of the proposed haptic knob, it is difficult to make a sharply carved shape (ⓐ in Figure 2b). The result also shows that the resistive torque does not significantly increase when the oblique angle of the housing exceeds 80°. Therefore, we selected an oblique angle of 80°.
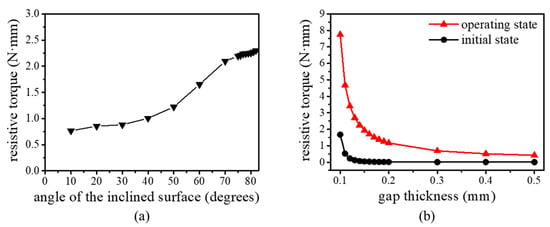
Figure 3.
Simulated resistive torques as a function of the (a) oblique angle of the inclined surface and (b) gap thickness.
The gap thickness (gt) (Figure 2c) between the housing and the rotary shaft is an important factor for maximizing the performance of the proposed haptic knob. For this reason, it is necessary to investigate the resistive torque of the haptic knob as a function of the gap thickness at a fixed oblique angle of 80°. Figure 3b shows the simulated resistive torque of the haptic knob according to the gap thickness without (black line, initial state) and with applied current (red line, operating state). As the gap thickness decreased, the resistive torque of the proposed haptic knob became stronger. The results show that the resistive torque decreased sharply with increasing gap thickness. The ideal haptic knob should have no resistive torque when there is no input current. When the gap thickness exceeds 0.12 mm, the resistive torque in its initial state (without current) is small enough and is almost unchanged, and the operating resistive torque in its operating state (with a current of 250 mA) is sufficient to create a variety of haptic sensations. Therefore, we set the gap thickness to 0.12 mm.
2.3. Design of Solenoid Coil
To increase the resistive torque of the proposed haptic knob, we need to optimize the solenoid coil. The magnetomotive force () can be expressed as a product of the number of turns () of the coil and the current () flowing through the coil (Equation (1)).
where is the input voltage, is the area of the pure conductor, is the resistivity of the coil, and is the total length of the coil wire. The resistivity and total length of the solenoid coil are determined by the wire diameter of the solenoid coil with a constant volume. The optimal wire diameter of the solenoid coil for obtaining the maximum magnetomotive force was simulated by Equation (1). As the wire diameter of the coil increased, the current () flowing through the coil also increased, which increased the generated magnetomotive force. In contrast, under constant power consumption, as the wire diameter of the coil increased, the magnetomotive force decreased. Therefore, the magnetomotive force created from the solenoid coil is maximized at the point of intersection between the rising and falling lines. The wire diameter of the coil was selected as 0.11 mm because the power consumption of the proposed haptic knob was set to 1.25 W (Figure 4).
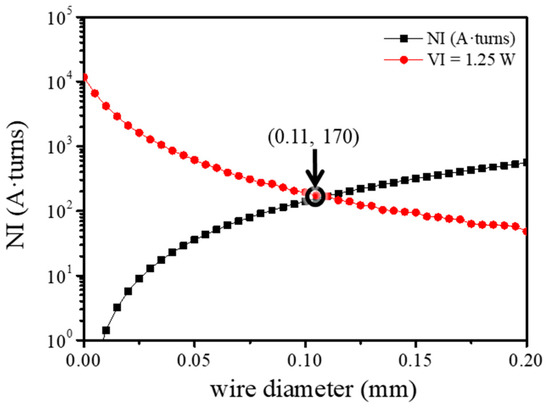
Figure 4.
Magnetomotive force according to the wire diameter of the solenoid coil and limited power consumption.
2.4. Operating Principle of Proposed Haptic Knob and Its Magnetic Flux Path Simulation
Figure 5a shows the design of the proposed haptic knob. We filled the gap between the housing and rotary shaft with MR fluid. Before a magnetic field was applied to the MR fluid in the gap, the MR fluid was in a fluid state (initial state). Because the MR fluid serves as a lubricant in the initial state, the rotary shaft rotates smoothly (Figure 5b). If we apply a magnetic field to the MR fluid through the solenoid coil, magnetic particles in the MR fluid form chain structures in the direction of the applied magnetic field (Figure 5c). The most important aspect in designing haptic knobs based on MR fluids is that multiple operating modes of MR fluids contribute to the actuation. We designed a haptic knob whose structure supports the two operating modes of MR fluids simultaneously. The magnetic chain disturbs the rotation of the rotary shaft, creating a resistive torque when the user rotates the dial plate (shear mode) (Figure 5d). As previously mentioned, there are bumps on the surface of the rotary shaft. The rotation of the bumps accelerates the flow of MR fluids. This accelerated MR fluid flow produces yield stress (flow mode) (Figure 5e) in the gap. Because the total resistive torque is determined by summing up all the torque feedback obtained from the two modes, we can maximize the resistive torque in a small-sized haptic knob. A finite element method simulation using commercial software (Ansys Maxwell) was conducted to investigate the magnetic flux path (Figure 5f). The result shows that there is little magnetic flux leakage in the haptic knob; hence, almost all the magnetic flux can contribute toward the formation of a magnetic chain.
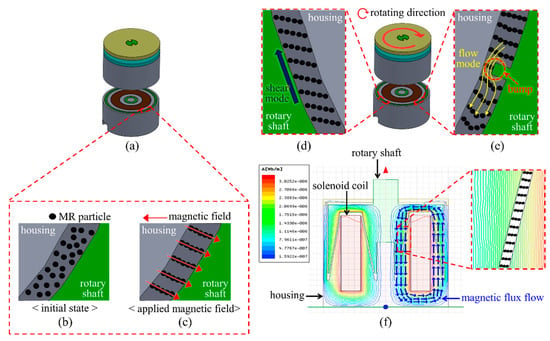
Figure 5.
Operating principle of the proposed haptic knob and its finite element method simulation: (a) Design of the proposed haptic knob; (b) magnetorheological (MR) fluids before magnetic field; (c) MR fluids after magnetic field; (d) shear mode of MR fluids; (e) flow mode of MR fluids; (f) finite element method simulation of the proposed haptic knob.
As we mentioned before, MR fluid is filled in the gap between the rotary shaft and the housing in the proposed haptic knob. Therefore, the resistive torque occurs in four regions (I, II, III, and IV), as shown in Figure 6a. In regions I and II (Figure 6b,c), only shear mode contributes to the actuation, and in regions III and IV (Figure 6d,e), two modes (shear and flow modes) contribute to the actuation at the same time. The resistive torque () generated by the shear mode is calculated by Equations (2) and (3) [17,18,19,20].
where is the viscosity (0.28) of MR fluid, is the circumference of the shaft, is the length of the cross-sectional area of the shaft through which magnetic flux passes (see Figure 6b–e), is the angular velocity of the rotary shaft, is the gap thickness between the shaft and the housing (or between the shaft and the cover), and is the yield stress generated by the MR fluid. This yield stress () is calculated by Equation (3)
where is the carrier fluid constant ( in the case of hydrocarbon oil), is the particle volume percent () in MR fluid, and is the magnetic field intensity (H = At/m, ampere-turns per meter). Moreover, the resistive torque () generated by the flow mode is expressed by Equation (4) [17,18,19,20].
where is the average cross-sectional area of the cone-shaped shaft. The total resistive torque () becomes the sum of the torques created in the four regions (I, II, III, and IV) (Equation (5)). Based on this equation, we conducted a simulation using electromagnetic field simulation software (Ansys Maxwell) to compute the resistive torque as a function of applied input current. Figure 7 shows the output resistive torque variation with respect to the applied current. Through fitting this graph, we composed a mathematical model that relates applied input current and the resistive torque (Equation (6)). In Equations (5) and (6), τshear_I, τshear_II, τshear_III, and τshear_IV are torques by the shear mode in four regions (I, II, III, and IV, respectively), τflow_III and τflow_IV are torques by the flow mode in two regions (III and IV, respectively), and I is the applied current. We found that the output torque exponentially increases as we increase input current.
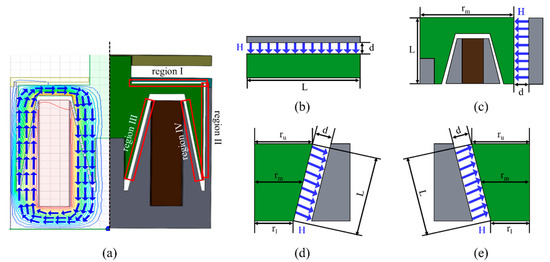
Figure 6.
Parametric setup of the proposed haptic knob: (a) Cross-sectional view of the proposed haptic knob (left: the magnetic simulation result, right: four activation regions in the knob); (b) enlarged picture of region I; (c) enlarged picture of region II; (d) enlarged picture of region III; and (e) enlarged picture of region IV.
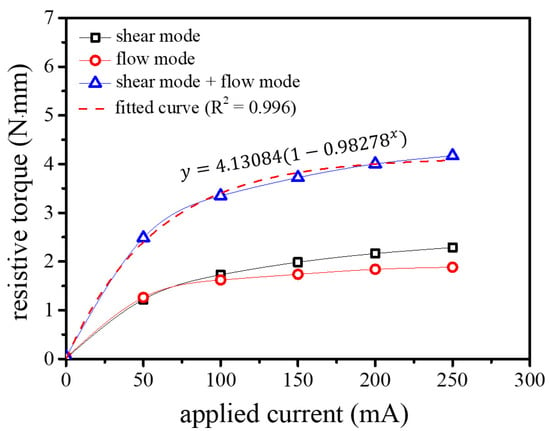
Figure 7.
Calculated resistive torque by the applied current and its fitted curve.
As shown in the simulation result, in our design, because two operating modes of MR fluids contribute to the actuation at the same time, we could increase the resistive torque.
2.5. Fabrication of Proposed Haptic Knob
Figure 8 shows the components of the proposed haptic knob and its fabricated prototype. The haptic knob consists of a dial plate, a housing cover, a rotary shaft, a solenoid coil, and a housing. The housing cover, rotary shaft, and housing are made of a magnetic material (KSC 2504), while the dial plate is made of a nonmagnetic material (stainless steel). The solenoid coil was placed inside the housing with MR fluids, then the rotary shaft was inserted into the housing. Subsequently, the housing cover was sealed and bonded. The assembly of the haptic knob was completed by coupling the dial plate to the rotary shaft.

Figure 8.
Components and prototype of the proposed actuator.
3. Results and Evaluation
To measure the torque feedback from the proposed haptic knob, we constructed an experimental setup consisting of a personal computer (PC), a DC motor driver, a power supply, a control circuit, a load cell, a shaft arm, the proposed haptic knob, a coupler, and a DC motor, as shown in Figure 9. The dial plate of the proposed haptic knob was tightly connected to the DC motor using the coupler, and the shaft arm was connected to the proposed knob. As the DC motor started to rotate, the dial plate and rotary shaft also rotated together. The applied current caused MR fluids in the haptic knob to solidify and stop the DC motor. Torque feedback in the haptic knob was conveyed to the load cell through a shaft arm. The measured data by the load cell were multiplied by the length of the shaft arm (r) to compute the resistive torque. Finally, the computed resistive torque was saved to the PC.
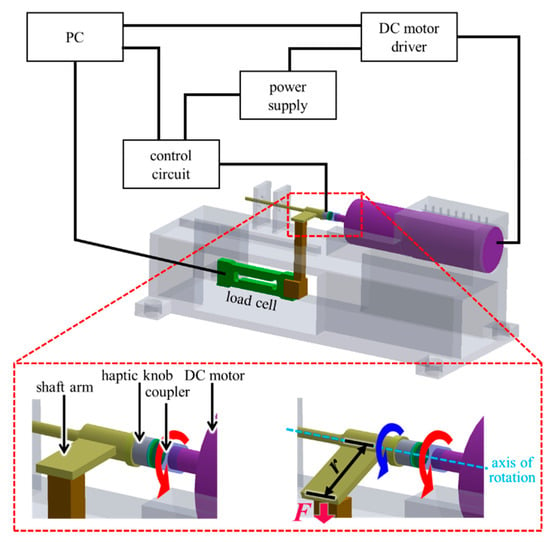
Figure 9.
Experimental setup of the proposed actuator.
We measured the resistive torque of the proposed haptic knob as a function of the applied current and its rotational speed. The result (Figure 10) shows that its resistive torque increased as the applied current and rotational speed increased. The maximum resistive torque ranged from 0.74 N∙mm (with no applied current) to 5.61 N∙mm (with maximum current (250 mA)) in the case with an angular velocity of 90 °/s. The bandwidth of the proposed haptic knob was investigated by measuring the resistive torque of the proposed haptic knob as a function of input frequency. Figure 11 shows the result of its bandwidth.
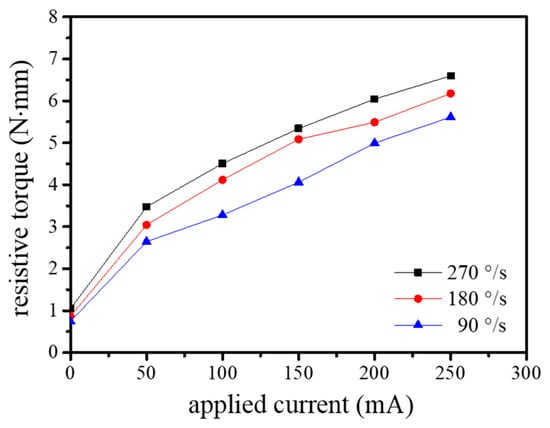
Figure 10.
Experimental result of the proposed actuator.
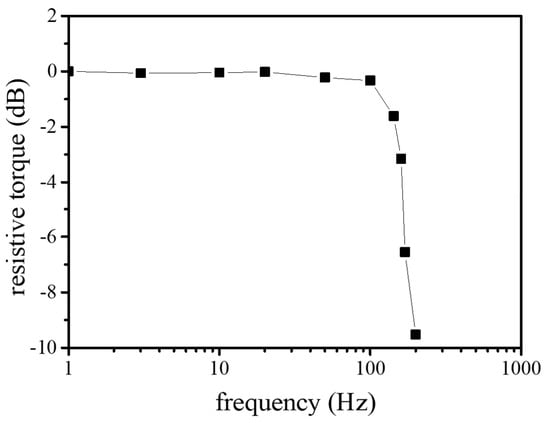
Figure 11.
Measured bandwidth of the proposed haptic knob.
To investigate the haptic performance of the proposed haptic knob, we defined the measured resistive torque rate (Tr) as the ratio of the difference between the maximum and minimum resistive torque (Td) to the maximum resistive torque (Tm) at a given angular velocity. We also defined Tr, Td, and Tm at n degree/s (n °/s) as Trn, Tdn, and Tmn, respectively; for example, Tr90 is the measured resistive torque rate at 90 °/s. Figure 12a,b show the measured resistive torques and torque rates (Tr90, Tr180, and Tr270) at 90 °/s, 180 °/s, and 270 °/s, respectively. The measured resistive torque rates are approximately 87% at 90 °/s, 86% at 180 °/s, and 84% at 270 °/s. It is known that the differential threshold of the resistive torque rate (or torque “just noticeable difference” (JND)) that humans can reliably distinguish is approximately 13% [21,22,23]. Considering this result, the proposed haptic knob can create a variety of haptic sensations.
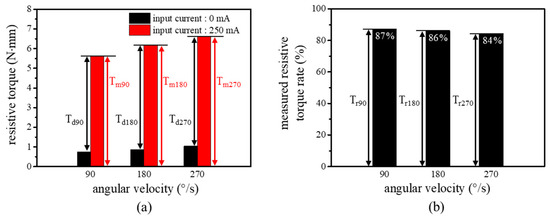
Figure 12.
(a) Resistive torque and (b) measured resistive torque rate at three angular velocities (90 °/s, 180 °/s, and 270 °/s).
4. Conclusions
In this paper, a rotary-type miniature kinesthetic actuator (haptic knob) based on an MR fluid was proposed. To maximize torque feedback, we designed a haptic knob in which two operating modes of the MR fluids contributed to haptic actuation. Experiments were conducted to evaluate the performance of the proposed haptic knob. The results indicate that the measured resistive torque is proportional to the applied current and its rotational speed. Furthermore, its haptic performance covers the torque differential threshold (or torque JND) that humans can reliably distinguish. This means that we can control the resistive torque of the proposed haptic knob with the applied current and use it as a haptic interface for interacting with virtual objects in many consumer electronic devices. For further improvements, it is desirable to suggest a new structure where three operating modes of MR fluids contribute to the actuation of a haptic knob at the same time. It is also desirable to develop a haptic rendering method which provides a realistic haptic/torque sensation to users. We expect that the proposed haptic knob can be used for various applications, such as a dial knob in a smart car or an adjustable wheel for a mouse.
Author Contributions
Y.H.H. designed the research problems; D.-S.C. suggested the idea and configuration of the structure of the paper; I.-H.Y. conducted the experiments and analyzed the results; S.-Y.K. supervised the research. All the authors discussed the results and wrote the paper. Authors 1 (Y.H.H.) and 2 (D.-S.C.) contributed equally. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Priority Research Centers Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2018R1A6A1A03025526). This work also was supported by the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No.2020-0-00594, Morphable Haptic Controller for Manipulating VR·AR Contents). We thank the Cooperative Equipment Center at Koreatech for assistance with fabricating parts.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Badescu, M.; Wampler, C.; Mavroidis, C. Rotary haptic knob for vehicular instrument controls. In Proceedings of the 10th Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Orlando, FL, USA, 24–25 March 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.; Han, M.; Shin, S.; Park, S. A haptic dial system for multimodal prototyping. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence, Yokohama, Japan, 1–3 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, L.; Park, W.; Cho, H.; Park, S. An universal remote controller with haptic interface for home devices. In Proceedings of the 2010 Digest of Technical Papers International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9–13 January 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuis, D.; Michel, X.; Gassert, R.; Chew, C.-M.; Burdet, E.; Bleuler, H. A haptic knob with a hybrid ultrasonic motor and powder clutch actuator. In Proceedings of the Second Joint Eurohaptics Conference and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Tsukaba, Japan, 22–24 March 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, K.E.; Shaver, M.J.; Pai, D.K. Handheld haptics: A USB media controller with force sensing. In Proceedings of the 10th Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Orlando, FL, USA, 24–25 March 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.P.; Fai, Y.C.; Yap, R.; Ming, E.S.L. Development of a low cost haptic knob. Int. J. Mech. Aerosp. Ind. Mechatron. Manuf. Eng. 2011, 5, 2034–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Kwon, D.-S. Stability and performance of haptic interfaces with active/passive actuators—Theory and experiments. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2006, 25, 1121–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, W.H.; Kosasih, P.B.; Zhang, X.Z. Development of an MR-brake-based haptic device. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 1960–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabi, A.G.; Grunwald, A. Design and application of magneto-rheological fluid. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 2658–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.T.; Liao, W.H. A novel multifunctional rotary actuator with magnetorheological fluid. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 065012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Song, A.; Mo, Y. A hybrid actuator with hollowed multi-drum magnetorheological brake and direct-current micromotor for hysteresis compensation. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2019, 30, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Song, A.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, G. A multi-finger interface with MR actuators for haptic applications. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2017, 11, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tri, D.B.; Cuong, V.V.; Quoc, H.N. Development of a new magnetorheological actuator for force feedback application. Int. J. Electron. Electr. Eng. 2017, 5, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, M.G.; Dede, M.I.C. Design and experimental validation of an MR-fluid based brake for use in haptics. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on New Actuators, Bermen, Germany, 25–27 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Le, T.D.; Nguyen, D.N.; Le, T.D.; Lang, T.V.; Ngo, T.V. Development of 3-DOF force feedback system using spherical arm mechanism and MR brakes. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Robot. Res. 2020, 9, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Guo, S.; Song, Y. Magnetorheological fluids actuated haptic-based teleoperated catheter operating system. Micromachines 2018, 9, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, F.D. Characterizing the Behavior of Magnetorheological Fluids at High Velocities and High Shear Rates. Ph.D. Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wereley, N.M.; Pang, L. Nondimensional analysis of semi-active electrorheological and magnetorheological dampers using approximate parallel plate models. Smart Mater. Struct. 1998, 7, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-B.; Choi, Y.-T. Sliding mode control of a shear-mode type ER engine mount. KSME Int. J. 1999, 13, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, M.R.; Carlson, J.D. Controllable squeeze damping using magnetorheological fluid. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on New Actuators, Bremen, Germany, 26–28 June 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, B.; Helson, H. Torque: A new dimension in tactile-kinesthetic sensitivity. Am. J. Psychol. 1965, 78, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodruff, B.; Helson, H. Torque sensitivity as a function of knob radius and load. Am. J. Psychol. 1967, 80, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandura, L.; Srinivasan, M.A. Experiments on human performance in torque discrimination and control. In Proceedings of the ASME Winter Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 13–18 November 1994; Available online: http://www.rle.mit.edu/touchlab/publications/1994_002.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2020).
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).