Novel Electronic Device to Quantify the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Endodontic Reciprocating Files after Using and Sterilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
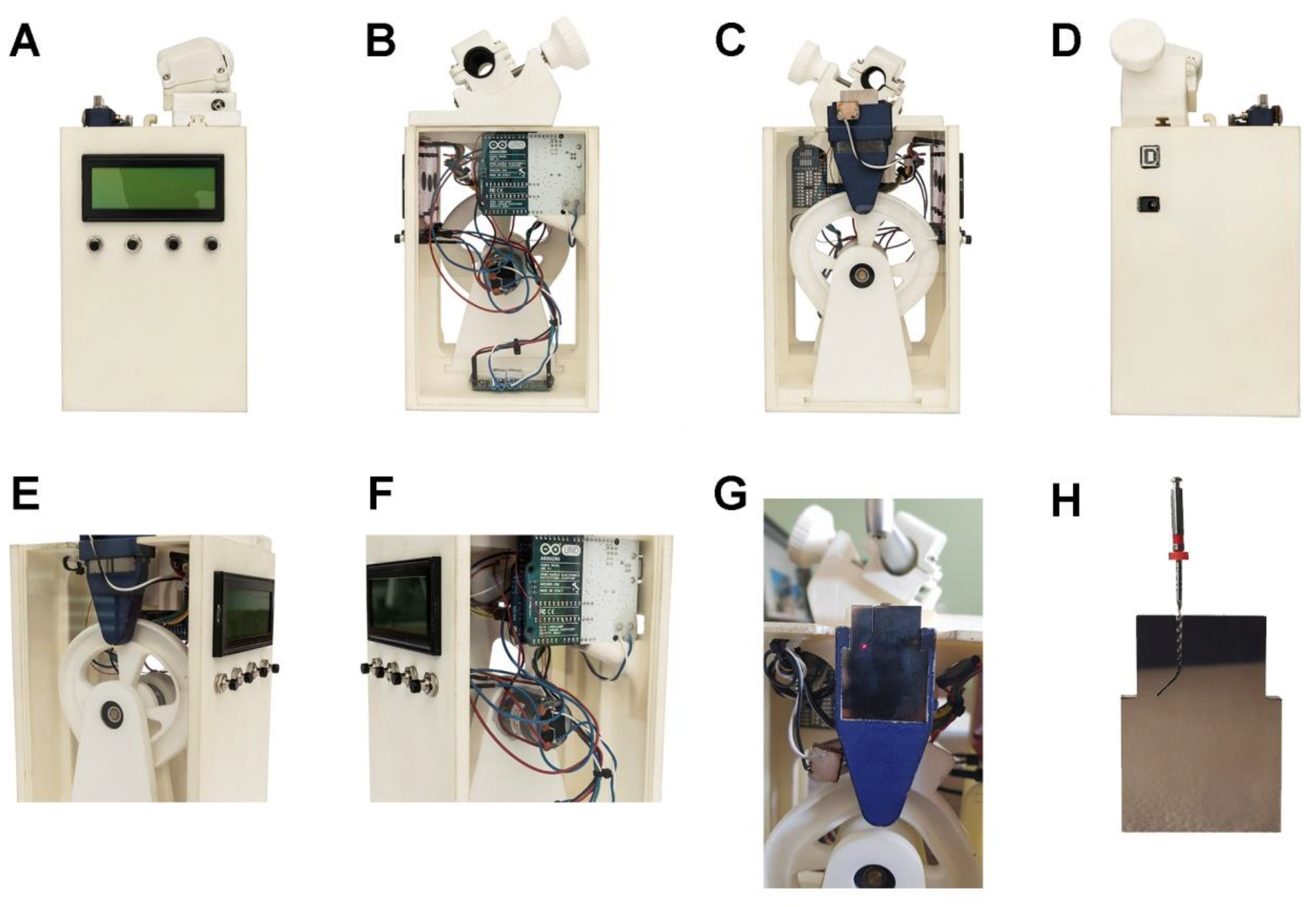
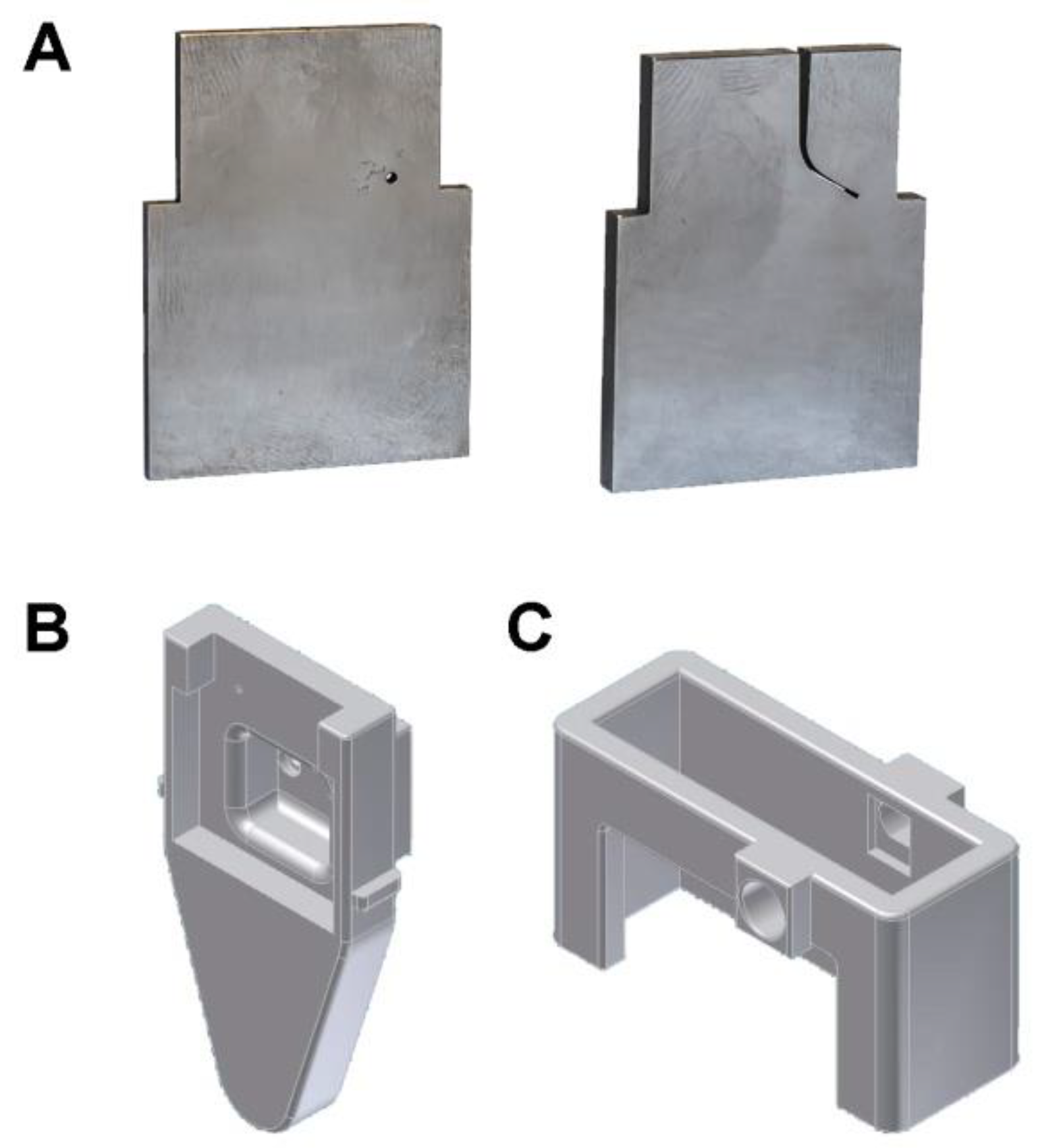
2.2. Experimental Cycling Fatigue Procedure
2.3. Statistical Tests
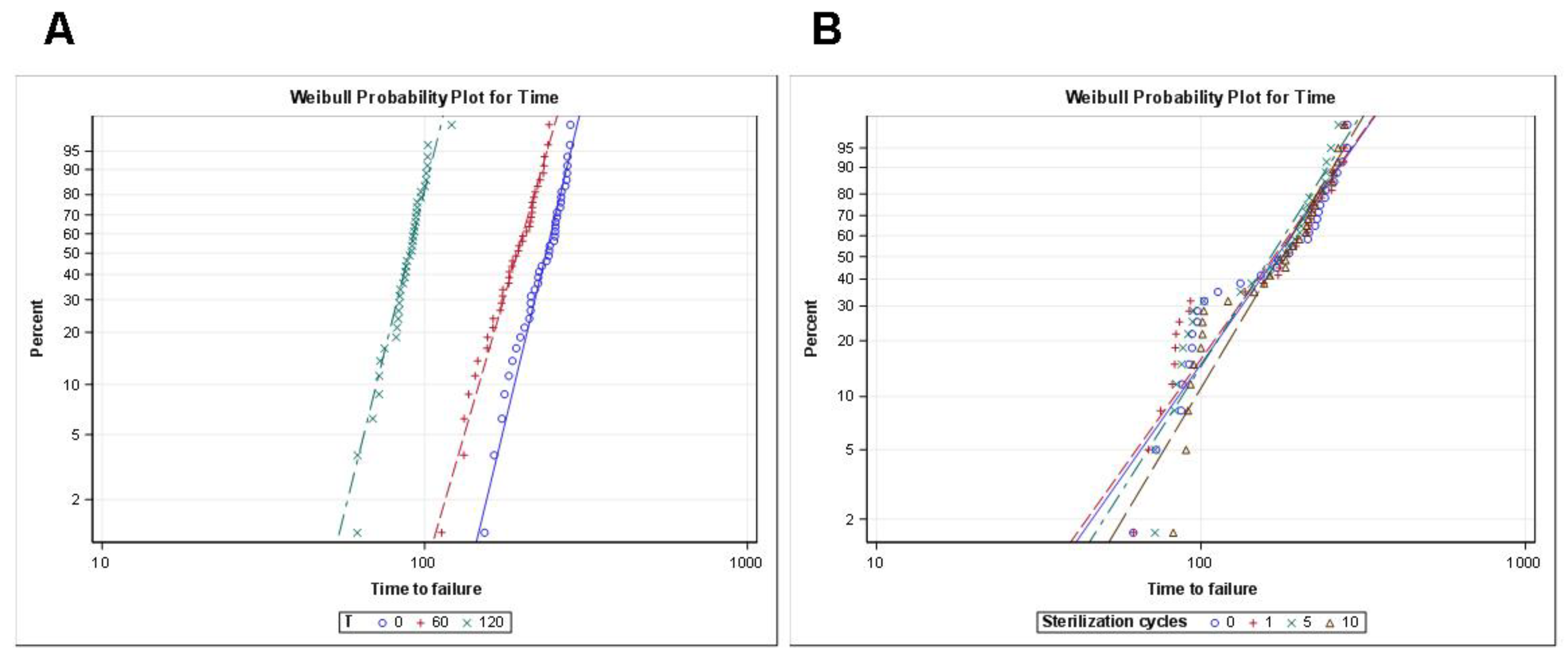
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gavini, G.; Santos, M.D.; Caldeira, C.L.; Machado, M.; Freire, L.G.; Iglecias, E.F.; Peters, O.A.; Candeiro, G. Nickel-titanium instruments in endodontics: A concise review of the state of the art. Braz. Oral. Res. 2018, 32, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhou, H.M.; Zheng, Y.F.; Campbell, L.; Peng, B.; Haapasalo, M. Metallurgical characterization of controlled memory wire nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testarelli, L.; Plotino, G.; Al-Sudani, D.; Vincenzi, V.; Giansiracusa, A.; Grande, N.M.; Gambarini, G. Bending properties of a new nickel-titanium alloy with a lower percent by weight of nickel. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1293–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotino, G.; Costanzo, A.; Grande, N.M.; Petrovic, R.; Testarelli, L.; Gambarini, G. Experimental evaluation on the influence of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue of new nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laneve, E.; Raddato, B.; Dioguardi, M.; Di Gioia, G.; Troiano, G.; Lo Muzio, L. Sterilisation in Dentistry: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Dent. 2019, 2019, 650728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, N.C.; Rathod, Y.V.; Shenoi, P.R.; Shori, D.D.; Khode, R.T.; Khadse, A.P. Evaluation of new technique of sterilization using biological indicator. J. Conserv. Dent. 2017, 20, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, T.B.V.G.; Garapati, S.; Agrawal, R.; Reddy, S.; Razdan, A.; Kumar, S.K. Sterilizing Endodontic Files by four different sterilization methods to prevent cross-infection. An In-vitro Study. J. Int. Oral. Health 2013, 5, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Spagnuolo, G.; Ametrano, G.; D’antò, V.; Rengo, C.; Simeone, M.; Riccitiello, F.; Amato, M. Effect of autoclaving on the surfaces of TiN-coated and conventional nickel–titanium rotary instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2012, 45, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casper, R.B.; Roberts, H.W.; Roberts, M.D.; Himel, V.T.; Bergeron, B.E. Comparison of autoclaving effects on torsional deformation and fracture resistance of three innovative endodontic file systems. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1572–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valois, C.R.; Silva, L.P.; Azevedo, R.B. Multiple autoclave cycles affect the surface of rotary nickel-titanium files: An atomic force microscopy study. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alapati, S.B.; Brantley, W.A.; Svec, T.A.; Powers, J.M.; Nusstein, J.M.; Daehn, G.S. SEM observations of nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments that fractured during clinical use. J. Endod. 2005, 31, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, F.R.; Pappalettere, C.; Di Comite, M.; Corsalini, M.; Mori, G.; Ballini, A.; Crincoli, V.; Pettini, F.; Rapone, B.; Boccaccio, A. Effect of different irrigating solutions and endodontic sealers on bond strength of the dentin-post interface with and without defects. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 9, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seago, S.T.; Bergeron, B.E.; Kirkpatrick, T.C.; Roberts, M.D.; Roberts, H.W.; Himel, V.T.; Sabey, K.A. Effect of Repeated Simulated Clinical Use and Sterilization on the Cutting Efficiency and Flexibility of Hyflex CM Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilfer, P.B.; Bergeron, B.E.; Mayerchak, M.J.; Roberts, H.W.; Jeansonne, B.G. Multiple autoclave cycle effects on cyclic fatigue of nickel-titanium rotary files produced by new manufacturing methods. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfoqom Alazemi, M.; Bryant, S.T.; Dummer, P.M. Deformation of HyFlex CM instruments and their shape recovery following heat sterilization. Int. Endod. J. 2015, 48, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, F.; Adeodato, C.; Barbosa, I.; Aboud, L.; Scelza, P.; Zaccaro Scelza, M. Movement kinematics and cyclic fatigue of NiTi rotary instruments: A systematic review. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubizarreta-Macho, A.; Mena Álvarez, J.; Albadalejo Martínez, A.; Segura-Egea, J.J.; Caviedes Brucheli, J.; Agustín-Panadero, R.; López Píriz, R.; Alonso-Ezpeleta, O. Influence of the pecking motion on the cyclic fatigue resistance of endodontic rotary files. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S.W. A comparison of canal preparations in straight and curved root canals. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. 1971, 32, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, J.; Zarzosa, J.I.; Pallarés, A. A Comparative Study of Cyclic Fatigue of 10 Different Types of Endodontic Instruments: An in Vitro Study. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 2019, 53, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Deus, G.; Vieira VT, L.; da Silva EJ, N.; Lopes, H.; Elias, C.N.; Moreira, E.J. Bending resistance and dynamic and static cyclic fatigue life of Reciproc and WaveOne large instruments. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keleş, A.; Eymirli, A.; Uyanık, O.; Nagas, E. Influence of static and dynamic cyclic fatigue tests on the lifespan of four reciprocating systems at different temperatures. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruett, J.P.; Clement, D.J.; Carnes, D.L., Jr. Cyclic fatigue testing of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 1997, 23, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsmann, M.; Donnermeyer, D.; Schäfer, E. A critical appraisal of studies on cyclic fatigue resistance of engine-driven endodontic instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 1427–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olcay, K.; Eyuboglu, T.F.; Erkan, E. Cyclic fatigue resistance of wave one gold, protaper next and 2shape nickel titanium rotary instruments using a reliable method for measuring temperature. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2019, 22, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.; Arias, A.; Macorra, J.C.; Govindjee, S.; Peters, O.A. Resistance to cyclic fatigue of reciprocating instruments determined at body temperature and phase transformation analysis. Aust. Endod. J. 2019, 45, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, D.; Galli, M.; Morese, A.; Seracchiani, M.; Ferri, V.; Miccoli, G.; Gambarini, G.; Testarelli, L. A comparative study of mechanical resistance of two reciprocating files. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2019, 11, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topçuoğlu, H.S.; Topçuoğlu, G.; Kafdağ, Ö.; Arslan, H. Cyclic fatigue resistance of new reciprocating glide path files in 45- and 60-degree curved canals. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Ha, J.H.; Cheung, G.S.P.; Versluis, A.; Kwak, S.W.; Kim, H.C. Safety of the factory preset rotation angle of reciprocating instruments. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 1671–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generali, L.; Puddu, P.; Borghi, A.; Brancolini, S.; Lusvarghi, L.; Bolelli, G.; Consolo, U.; Pedullà, E. Mechanical properties and metallurgical features of new and ex vivo used Reciproc Blue and Reciproc. Int. Endod. J. 2020, 53, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.; Macorra, J.C.; Govindjee, S.; Peters, O.A. Effect of gamma-ray sterilization on phase transformation behavior and fatigue resistance of contemporary nickel-titanium instruments. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Sovereto, D.; Aiuto, R.; Laino, L.; Illuzzi, G.; Laneve, E.; Raddato, B.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Dioguardi, A.; Zhurakivska, K.; et al. Effects of Hot Sterilization on Torsional Properties of Endodontic Instruments: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.J.; Hou, B.X.; Hou, X.M. Effect of autoclave on surface microstructure and cyclic fatigue resistance of R-phase rotary instruments. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2018, 50, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pedullà, E.; Benites, A.; La Rosa, G.M.; Plotino, G.; Grande, N.M.; Rapisarda, E.; Generali, L. Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Instruments after Immersion in Sodium Hypochlorite and/or Sterilization. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champa, C.; Divya, V.; Srirekha, A.; Karale, R.; Shetty, A.; Sadashiva, P. An analysis of cyclic fatigue resistance of reciprocating instruments in different canal curvatures after immersion in sodium hypochlorite and autoclaving: An in vitro study. J. Conserv. Dent. 2017, 20, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Özyürek, T.; Yılmaz, K.; Uslu, G. The effects of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Gold nickel-titanium instruments. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2017, 42, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Shen, Y.; Peng, B.; Haapasalo, M. Effect of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of thermally treated Nickel-Titanium instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2016, 49, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

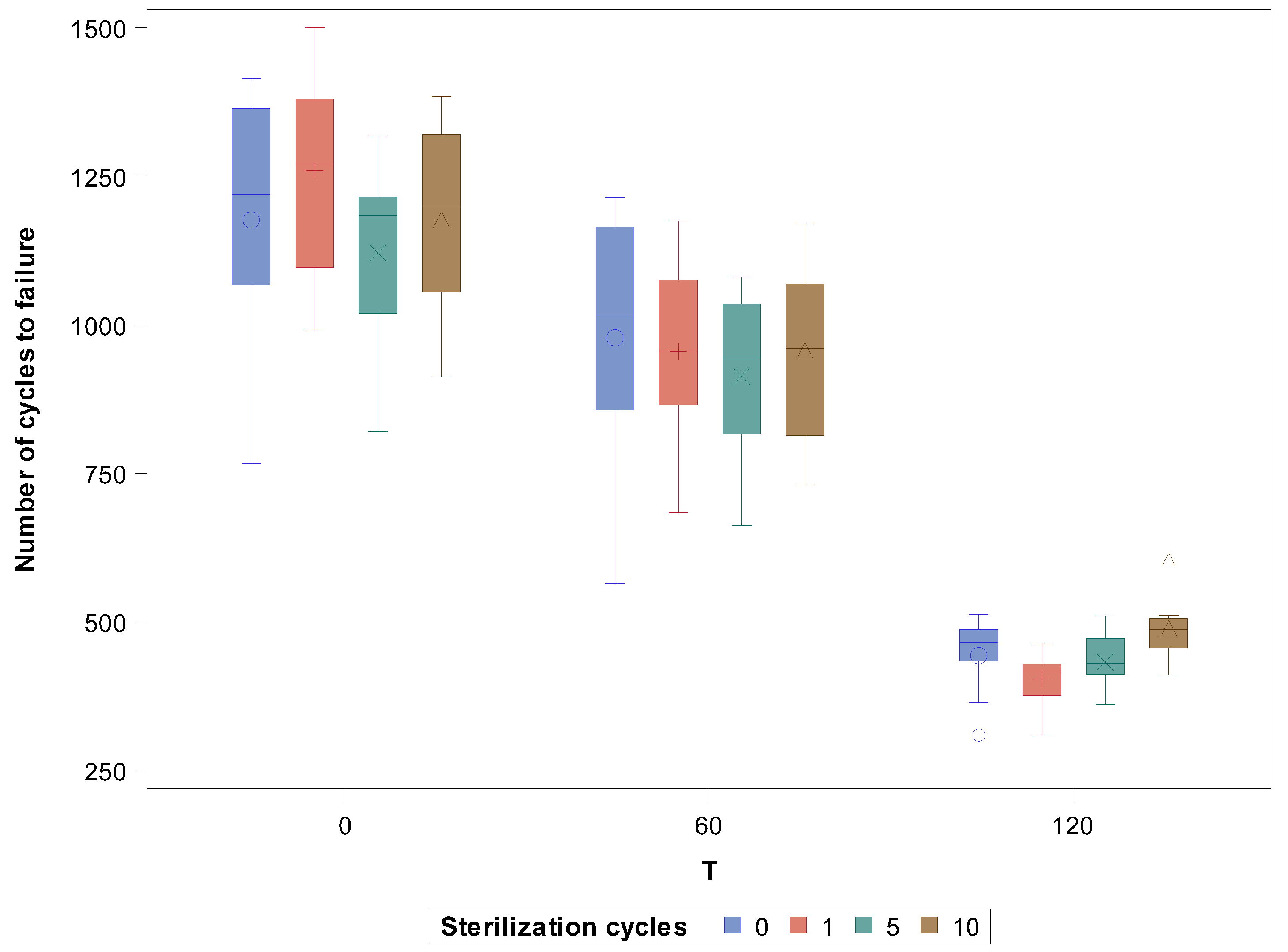
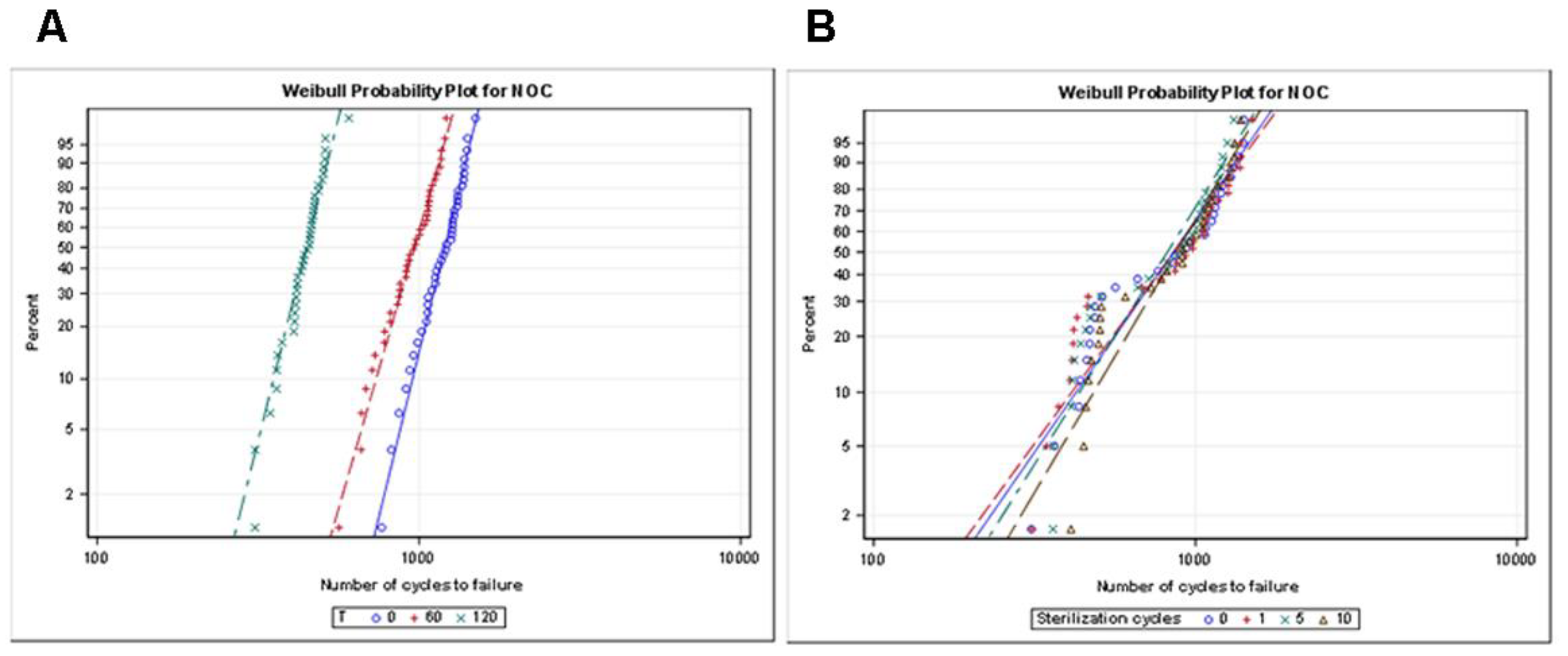
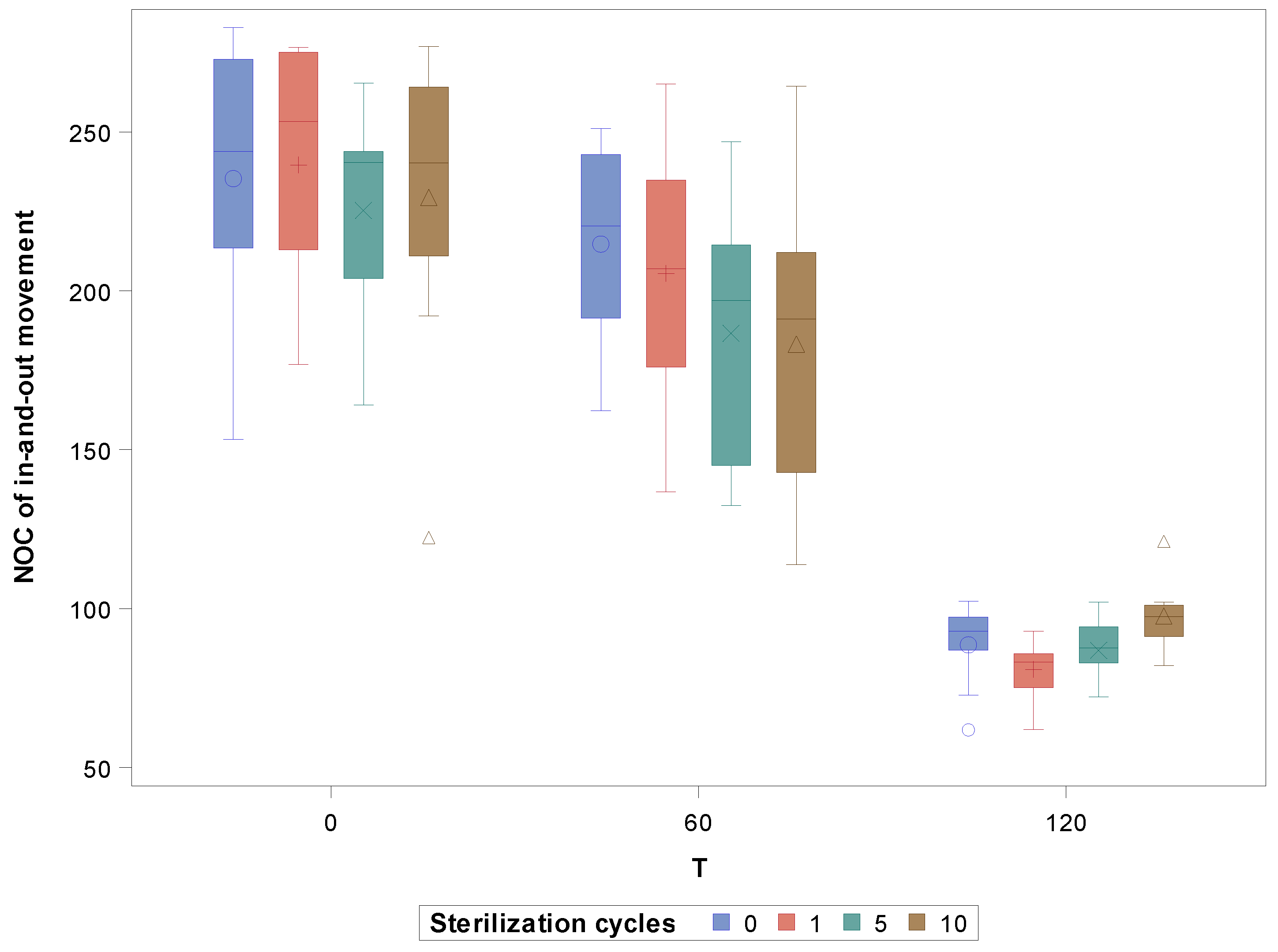

| Time of Use | Sterilization Cycles | n | Mean | SD | Minimum | Maximum | Fracture Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 s | 0 a | 10 | 235.29 | 45.07 | 153.20 | 282.83 | 3.06 |
| 1 a | 10 | 239.55 | 35.54 | 176.75 | 276.66 | 3.10 | |
| 5 a | 10 | 225.26 | 32.04 | 164.10 | 265.31 | 3.17 | |
| 10 a | 10 | 235.30 | 32.83 | 182.28 | 276.91 | 3.04 | |
| 60 s | 0 b | 10 | 195.59 | 45.56 | 112.84 | 242.92 | 3.13 |
| 1 b | 10 | 191.45 | 31.82 | 136.77 | 234.89 | 3.06 | |
| 5 b | 10 | 182.64 | 28.97 | 132.47 | 216.00 | 3.01 | |
| 10 b | 10 | 191.18 | 29.71 | 145.94 | 234.33 | 3.04 | |
| 120 | 0 c | 10 | 88.58 | 12.39 | 61.82 | 102.35 | 3.11 |
| 1 c | 10 | 80.85 | 9.70 | 61.91 | 92.87 | 3.08 | |
| 5 c | 10 | 86.90 | 9.56 | 72.16 | 102.01 | 2.99 | |
| 10 c | 10 | 97.62 | 10.40 | 82.09 | 121.11 | 3.02 |
| Study Group | Weibull Shape (β) | Weibull Scale (η) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | St Error | Lower | Upper | Estimate | St Error | Lower | Upper | |
| 0 s | 8.3142 | 1.0833 | 6.4404 | 10.7332 | 248.5615 | 4.9655 | 239.0173 | 258.4868 |
| 60 s | 6.8989 | 0.8808 | 5.3716 | 8.8603 | 203.9091 | 4.9179 | 194.4944 | 213.7794 |
| 120 s | 8.0777 | 0.9119 | 6.4743 | 10.0782 | 93.5190 | 1.9349 | 89.8025 | 97.3892 |
| 0 cycles | 2.7040 | 0.4074 | 2.0127 | 3.6328 | 195.6014 | 13.9108 | 170.1516 | 224.8576 |
| 1cycle | 2.6640 | 0.4060 | 1.9761 | 3.5913 | 192.7207 | 13.8859 | 167.3392 | 221.9521 |
| 5 cycles | 2.9873 | 0.4529 | 2.2195 | 4.0208 | 185.5872 | 11.9333 | 163.6121 | 210.5138 |
| 10 cycles | 3.1770 | 0.4761 | 2.3685 | 4.2617 | 195.9868 | 11.8612 | 174.0652 | 220.6693 |
| Time of Use | Sterilization Cycles | n | Mean | SD | Minimum | Maximum | Fracture Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 s | 0 a | 10 | 1176.35 | 225.32 | 766.00 | 1414.00 | 3.06 |
| 1 a | 10 | 1259.40 | 162.90 | 989.50 | 1500.00 | 3.10 | |
| 5 a | 10 | 1120.85 | 156.52 | 820.50 | 1316.50 | 3.17 | |
| 10 a | 10 | 1176.44 | 164.09 | 911.35 | 1384.50 | 3.04 | |
| 60 s | 0 b | 10 | 977.90 | 227.76 | 564.00 | 1214.50 | 3.13 |
| 1 b | 10 | 954.80 | 157.00 | 684.00 | 1174.50 | 3.06 | |
| 5 b | 10 | 913.30 | 144.78 | 662.50 | 1080.00 | 3.01 | |
| 10 b | 10 | 955.80 | 148.54 | 729.50 | 1171.50 | 3.04 | |
| 120 | 0 c | 10 | 442.96 | 61.98 | 309.10 | 512.00 | 3.11 |
| 1 c | 10 | 404.26 | 48.51 | 309.55 | 464.35 | 3.08 | |
| 5 c | 10 | 431.98 | 48.33 | 360.80 | 510.00 | 2.99 | |
| 10 c | 10 | 488.12 | 51.96 | 410.45 | 605.50 | 3.02 |
| Study Group | Weibull Shape (β) | Weibull Scale (η) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | St Error | Lower | Upper | Estimate | St Error | Lower | Upper | |
| 0 s | 8.1790 | 1.0424 | 6.3712 | 10.4999 | 1257.379 | 25.5617 | 1208.264 | 1308.4906 |
| 60 s | 6.9078 | 0.8808 | 5.3803 | 8.8690 | 1018.7335 | 24.5392 | 971.7553 | 1067.9829 |
| 120 s | 8.0244 | 0.9069 | 6.4301 | 10.0141 | 467.0982 | 9.7300 | 448.4118 | 486.5633 |
| 0 cycles | 2.7040 | 0.4074 | 2.0127 | 3.6328 | 195.6014 | 13.9108 | 170.1516 | 224.8576 |
| 1cycle | 2.6640 | 0.4060 | 1.9761 | 3.5913 | 192.7207 | 13.8859 | 167.3392 | 221.9521 |
| 5 cycles | 2.9873 | 0.4529 | 2.2195 | 4.0208 | 185.5872 | 11.9333 | 163.6121 | 210.5138 |
| 10 cycles | 3.1770 | 0.4761 | 2.3685 | 4.2617 | 195.9868 | 11.8612 | 174.0652 | 220.6693 |
| Time of Use | Sterilization Cycles | n | Mean | SD | Minimum | Maximum | Fracture Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0s | 0 a | 10 | 235.29 | 45.07 | 153.20 | 282.83 | 3.06 |
| 1 a | 10 | 239.55 | 35.54 | 176.75 | 276.66 | 3.10 | |
| 5 a | 10 | 225.26 | 32.04 | 164.10 | 265.31 | 3.17 | |
| 10 a | 10 | 229.30 | 46.31 | 122.28 | 276.91 | 3.04 | |
| 60s | 0 b | 10 | 214.69 | 30.30 | 162.27 | 251.10 | 3.13 |
| 1 b | 10 | 205.45 | 38.46 | 136.77 | 265.01 | 3.06 | |
| 5 b | 10 | 186.64 | 38.88 | 132.47 | 246.87 | 3.01 | |
| 10 b | 10 | 183.18 | 48.23 | 113.82 | 264.33 | 3.04 | |
| 120 | 0 c | 10 | 88.58 | 12.39 | 61.82 | 102.35 | 3.11 |
| 1 c | 10 | 80.85 | 9.70 | 61.91 | 92.87 | 3.08 | |
| 5 c | 10 | 86.90 | 9.56 | 72.16 | 102.01 | 2.99 | |
| 10 c | 10 | 97.62 | 10.40 | 82.09 | 121.11 | 3.02 |
| Study Group | Weibull Shape (β) | Weibull Scale (η) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | St Error | Lower | Upper | Estimate | St Error | Lower | Upper | |
| 0 s | 7.8371 | 1.0332 | 6.0526 | 10.1478 | 247.8093 | 5.2331 | 237.7620 | 258.2813 |
| 60 s | 5.9056 | 0.7502 | 4.6039 | 7.5752 | 213.5034 | 6.0177 | 202.0287 | 225.6298 |
| 120 s | 8.0777 | 0.9119 | 6.4743 | 10.0782 | 93.5190 | 1.9349 | 89.8025 | 97.3892 |
| 0 cycles | 2.8397 | 0.4369 | 2.1004 | 3.8391 | 202.3470 | 13.6633 | 177.2639 | 230.9795 |
| 1cycle | 2.6486 | 0.4087 | 1.9573 | 3.5841 | 198.0170 | 14.3348 | 171.8235 | 228.2036 |
| 5 cycles | 2.9091 | 0.4413 | 2.1610 | 3.9163 | 187.3384 | 12.3756 | 164.5872 | 213.2345 |
| 10 cycles | 2.8747 | 0.4233 | 2.1540 | 3.8366 | 191.7153 | 12.8646 | 168.0889 | 218.6626 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zubizarreta-Macho, Á.; Alonso-Ezpeleta, Ó.; Albaladejo Martínez, A.; Faus Matoses, V.; Caviedes Brucheli, J.; Agustín-Panadero, R.; Mena Álvarez, J.; Vizmanos Martínez-Berganza, F. Novel Electronic Device to Quantify the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Endodontic Reciprocating Files after Using and Sterilization. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4962. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144962
Zubizarreta-Macho Á, Alonso-Ezpeleta Ó, Albaladejo Martínez A, Faus Matoses V, Caviedes Brucheli J, Agustín-Panadero R, Mena Álvarez J, Vizmanos Martínez-Berganza F. Novel Electronic Device to Quantify the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Endodontic Reciprocating Files after Using and Sterilization. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(14):4962. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144962
Chicago/Turabian StyleZubizarreta-Macho, Álvaro, Óscar Alonso-Ezpeleta, Alberto Albaladejo Martínez, Vicente Faus Matoses, Javier Caviedes Brucheli, Rubén Agustín-Panadero, Jesús Mena Álvarez, and Fernando Vizmanos Martínez-Berganza. 2020. "Novel Electronic Device to Quantify the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Endodontic Reciprocating Files after Using and Sterilization" Applied Sciences 10, no. 14: 4962. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144962
APA StyleZubizarreta-Macho, Á., Alonso-Ezpeleta, Ó., Albaladejo Martínez, A., Faus Matoses, V., Caviedes Brucheli, J., Agustín-Panadero, R., Mena Álvarez, J., & Vizmanos Martínez-Berganza, F. (2020). Novel Electronic Device to Quantify the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Endodontic Reciprocating Files after Using and Sterilization. Applied Sciences, 10(14), 4962. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144962







