Quantifying the Rate, Degree, and Heterogeneity of Morphological Change during an Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Using Digital Holographic Cytometry
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culturing
2.2. Treatment
2.3. Digital Holographic Imaging and Analysis
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
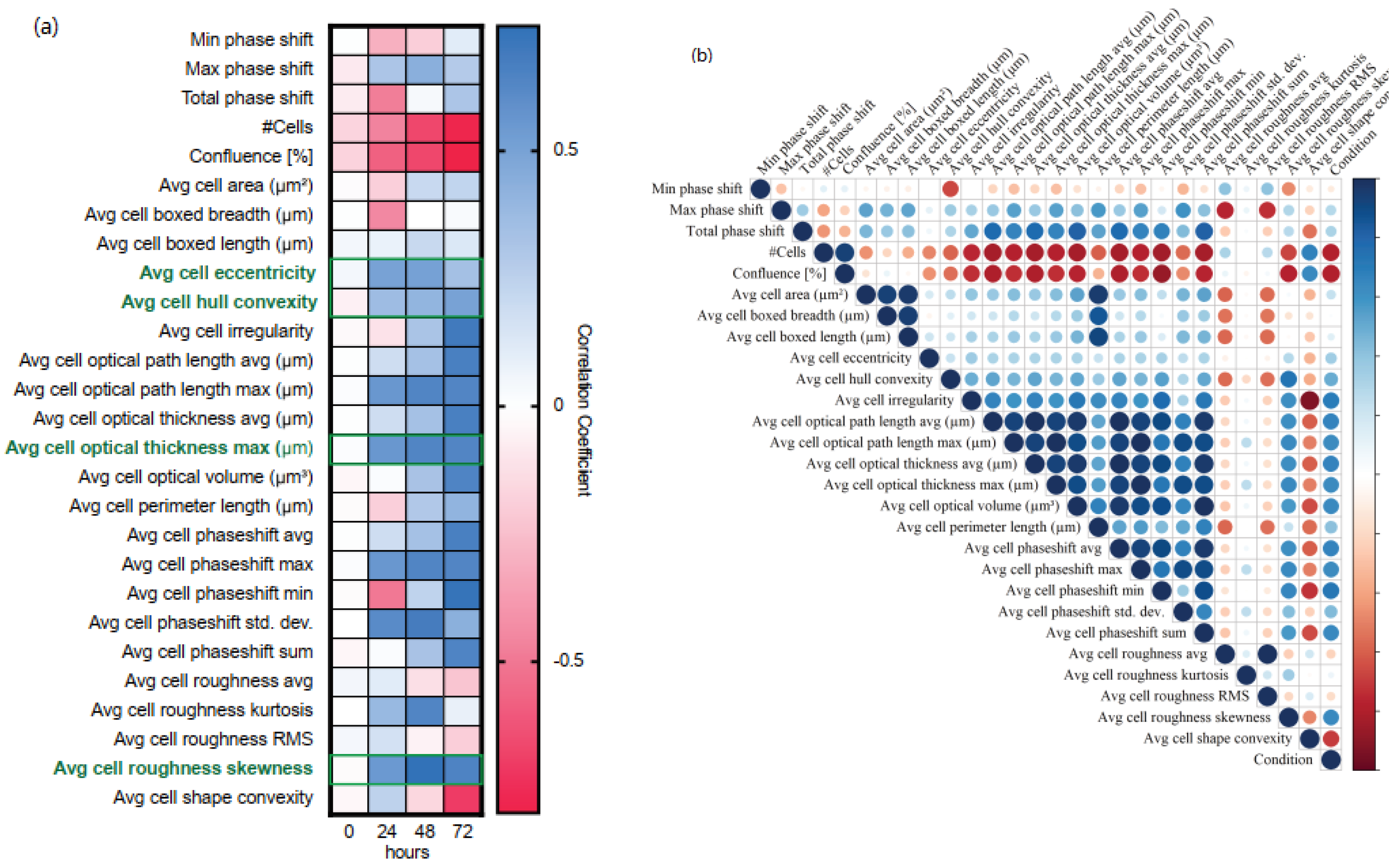
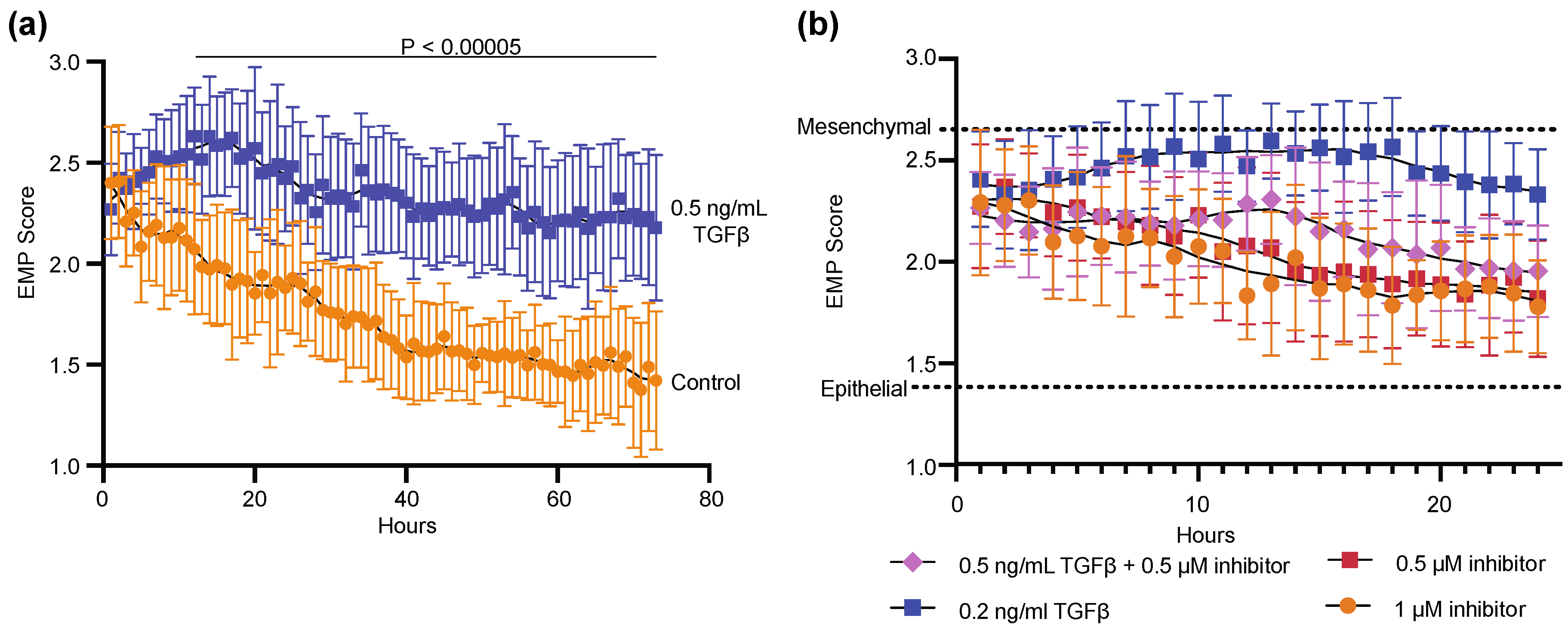
3.1. Monitoring of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Using DHC
3.2. Generation of an EMP Classifer for NMuMG Cells
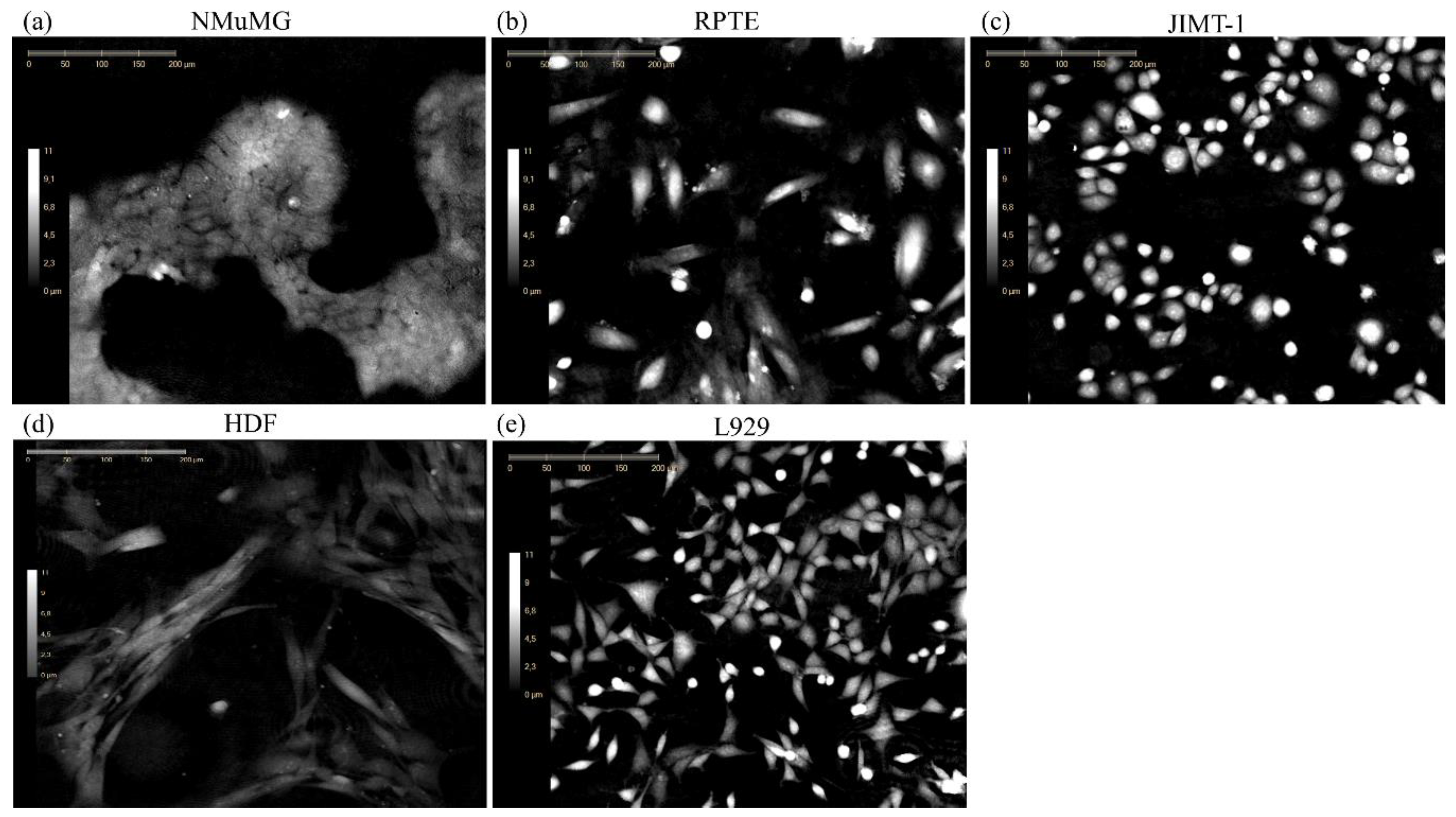
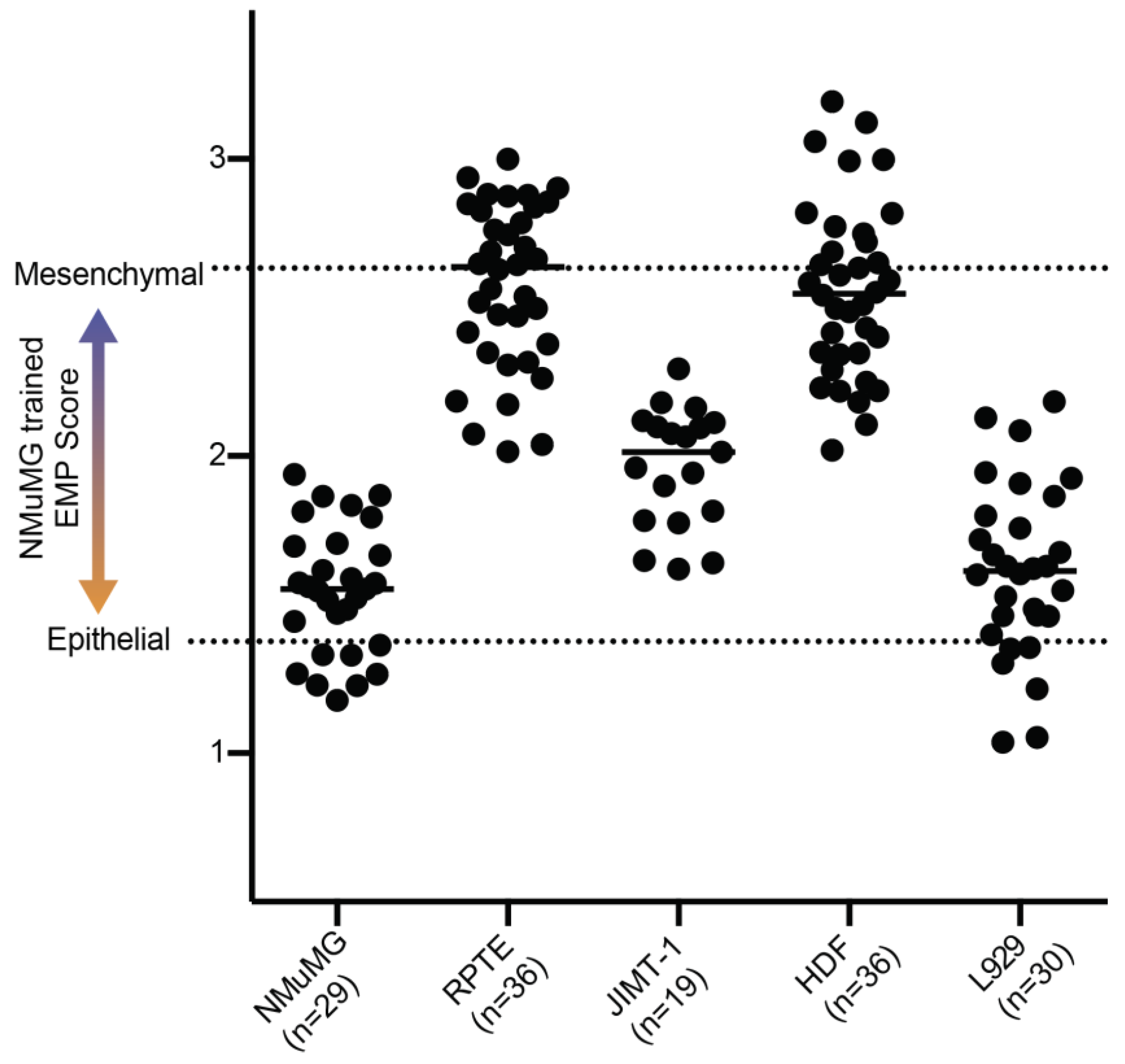
3.3. Application of NMuMG EMP Classifer to Other Lines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nieto, M.A.; Huang, R.Y.Y.J.; Jackson, R.A.A.; Thiery, J.P.P. Emt: 2016. Cell 2016, 166, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: At the Crossroads of Development and Tumor Metastasis. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocaña, O.; Córcoles, H.R.; Fabra, A.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Acloque, H.; Vega, S.; Barrallo-Gimeno, A.; Cano, A.; Nieto, M.A. Metastatic Colonization Requires the Repression of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Inducer Prrx1. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.; Donaher, J.; Murphy, D.; Chau, S.; Yang, J. Spatiotemporal regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition is essential for squamous cell carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Complexity and opportunities. Front. Med. 2018, 12, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodorogea, A.; Calinescu, A.; Antohe, M.; Balaban, M.; Nedelcu, R.I.; Turcu, G.; Ion, D.A.; Badarau, I.A.; Popescu, C.M.; Popescu, R.; et al. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Skin Cancers: A Review. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M.; et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Lièvre, M.; Thomas, C.; Hinkal, G.; Ansieau, S.A.; Puisieux, A. Generation of breast cancer stem cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.X.; Bos, P.D.; Massagué, J. Metastasis: From dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2009, 9, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, F.M.; Stewart, T.A.; Thompson, E.W.; Monteith, G.R. Targeting EMT in cancer: Opportunities for pharmacological intervention. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elaskalani, O.; Razak, N.B.A.; Falasca, M.; Metharom, P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition as a therapeutic target for overcoming chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2017, 9, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.; Traenkle, B.; Rothbauer, U. Real-time analysis of epithelial-mesenchymal transition using fluorescent single-domain antibodies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, J.; Traenkle, B.; Rothbauer, U. Visualizing epithelial-mesenchymal transition using the chromobody technology. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5592–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Yeganeh, O.; Levin, Y.; Hooker, J.C.; Hamilton, G.C.; Wolfson, T.; Gamst, A.; Zand, A.K.; Heba, E.; Loomba, R.; et al. In vivo visualization and characterization of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast tumors. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2094–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaked, T.N.; Satterwhite, L.L.; Rinehart, T.M.; Wax, A. Quantitative analysis of biological cells using digital holographic microscopy. In Holography, Research and Technologies; Rosen, J., Ed.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, K.; El-Schich, Z.; Miniotis, M.F.; Wingren, A.G.; Janicke, B.; Oredsson, S. Cells and holograms—holograms and digital holographic microscopy as a tool to study the morphology of living cells. In Holography—Basic Principles and Contemporary Applications; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hejna, M.; Jorapur, A.; Song, J.S.; Judson, R.L. High accuracy label-free classification of kinetic cell states from holographic cytometry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.; Pohl, L.; Ketelhut, S.; Kastl, L.; Gorzelanny, C.; Götte, M.; Schnekenburger, J.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Kemper, B. Nanoencapsulated capsaicin changes migration behavior and morphology of madin darby canine kidney cell monolayers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, B.; Bauwens, A.; Vollmer, A.; Ketelhut, S.; Lengehanenberg, P.; Müthig, J.; Karch, H.; Von Bally, G. Label-free quantitative cell division monitoring of endothelial cells by digital holographic microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luther, E.; Mendes, L.P.; Pan, J.; Costa, D.F.; Torchilin, V.P. Applications of label-free, quantitative phase holographic imaging cytometry to the development of multi-specific nanoscale pharmaceutical formulations. Cytom. Part A 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavillon, N.; Kühn, J.; Moratal, C.; Jourdain, P.; Depeursinge, C.; Magistretti, P.J.; Marquet, P. Early cell death detection with digital holographic microscopy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriraman, S.K.; Pan, J.; Sarisozen, C.; Luther, E.; Torchilin, V. Enhanced Cytotoxicity of Folic Acid-Targeted Liposomes Co-Loaded with C6 Ceramide and Doxorubicin: In Vitro Evaluation on HeLa, A2780-ADR, and H69-AR Cells. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappaz, B.; Breton, B.; Shaffer, E.; Turcatti, G. Digital holographic microscopy: A quantitative label-free microscopy technique for phenotypic screening. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2014, 17, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamlund, S.; Strand, D.; Janicke, B.; Alm, K.; Oredsson, S. Influence of salinomycin treatment on division and movement of individual cancer cells cultured in normoxia or hypoxia evaluated with time-lapse digital holographic microscopy. Cell Cycle 2017, 4101, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, V.; Nguyen, T.; Bui, V.; Chung, B.M.; Chang, L.-C.; Nehmetallah, G.; Raub, C. Quantitative scoring of epithelial and mesenchymal qualities of cancer cells using machine learning and quantitative phase imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2020, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuche, E.; Bevilacqua, F.; Depeursinge, C. Digital holography for quantitative phase-contrast imaging. Opt. Lett. 1999, 24, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, A.D.; Heldin, C.; Heldin, P. Efficient TGF b-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition depends on hyaluronan synthase HAS2. Oncogene 2013, 4355–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.K.; Beauchamp, R.D.; Datta, P.K. A Specific Inhibitor of TGF-β Receptor Kinase, SB-431542, as a Potent Antitumor Agent for Human Cancers. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Law, B.K.; Aakre, M.E.; Edgerton, M.; Shyr, Y.; Bhowmick, N.A.; Moses, H.L. Transforming growth factor beta-regulated gene expression in a mouse mammary gland epithelial cell line. Breast Cancer Res. 2003, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roitshtain, D.; Wolbromsky, L.; Bal, E.; Greenspan, H.; Satterwhite, L.L.; Shaked, N.T. Quantitative phase microscopy spatial signatures of cancer cells. Cytom. Part A 2017, 91, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makdasi, E.; Laskar, O.; Milrot, E.; Schuster, O.; Shmaya, S.; Yitzhaki, S. Whole-Cell Multiparameter Assay for Ricin and Abrin Activity-Based Digital Holographic Microscopy. Toxins 2019, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.; Tarantola, M.; Janshoff, A. Dynamics of TGF-β induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition monitored by Electric Cell-Substrate Impedance Sensing, BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Judson, R.; Hejna, M.; Jorapur, A.; Song, J.S.; Zhang, Y. Quantification of mammalian tumor cell state plasticity with digital holographic cytometry. Quant. Phase Imaging IV 2018, 1050312, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, V.K.; Nguyen, T.C.; Chung, B.M.; Nehmetallah, G.; Raub, C.B. Quantitative assessment of cancer cell morphology and motility using telecentric digital holographic microscopy and machine learning. Cytom. Part A 2018, 93, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, R.; Judson-Torres, R.L. Research Techniques Made Simple: Feature Selection for Biomarker Discovery. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamlund, S.; Janicke, B.; Alm, K.; Judson-Torres, R.L.; Oredsson, S. Quantifying the Rate, Degree, and Heterogeneity of Morphological Change during an Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Using Digital Holographic Cytometry. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4726. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144726
Kamlund S, Janicke B, Alm K, Judson-Torres RL, Oredsson S. Quantifying the Rate, Degree, and Heterogeneity of Morphological Change during an Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Using Digital Holographic Cytometry. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(14):4726. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144726
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamlund, Sofia, Birgit Janicke, Kersti Alm, Robert L. Judson-Torres, and Stina Oredsson. 2020. "Quantifying the Rate, Degree, and Heterogeneity of Morphological Change during an Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Using Digital Holographic Cytometry" Applied Sciences 10, no. 14: 4726. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144726
APA StyleKamlund, S., Janicke, B., Alm, K., Judson-Torres, R. L., & Oredsson, S. (2020). Quantifying the Rate, Degree, and Heterogeneity of Morphological Change during an Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Using Digital Holographic Cytometry. Applied Sciences, 10(14), 4726. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144726





