Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Machinery Using Hierarchical Lempel-Ziv Complexity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Proposed Hierarchical Lempel-Ziv Complexity
2.1. Lempel-Ziv Complexity
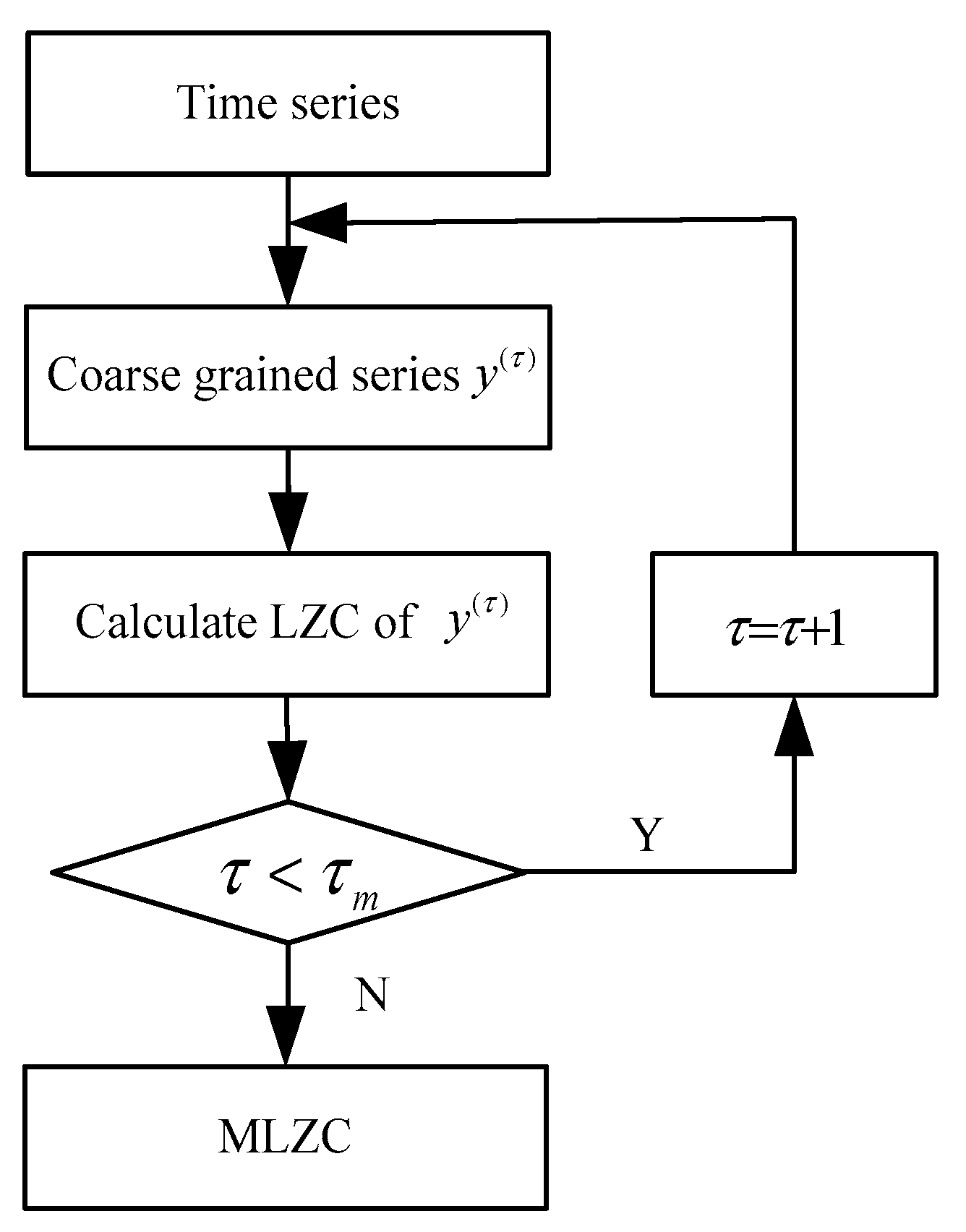
2.2. Multi-Scale Lempel-Ziv Complexity
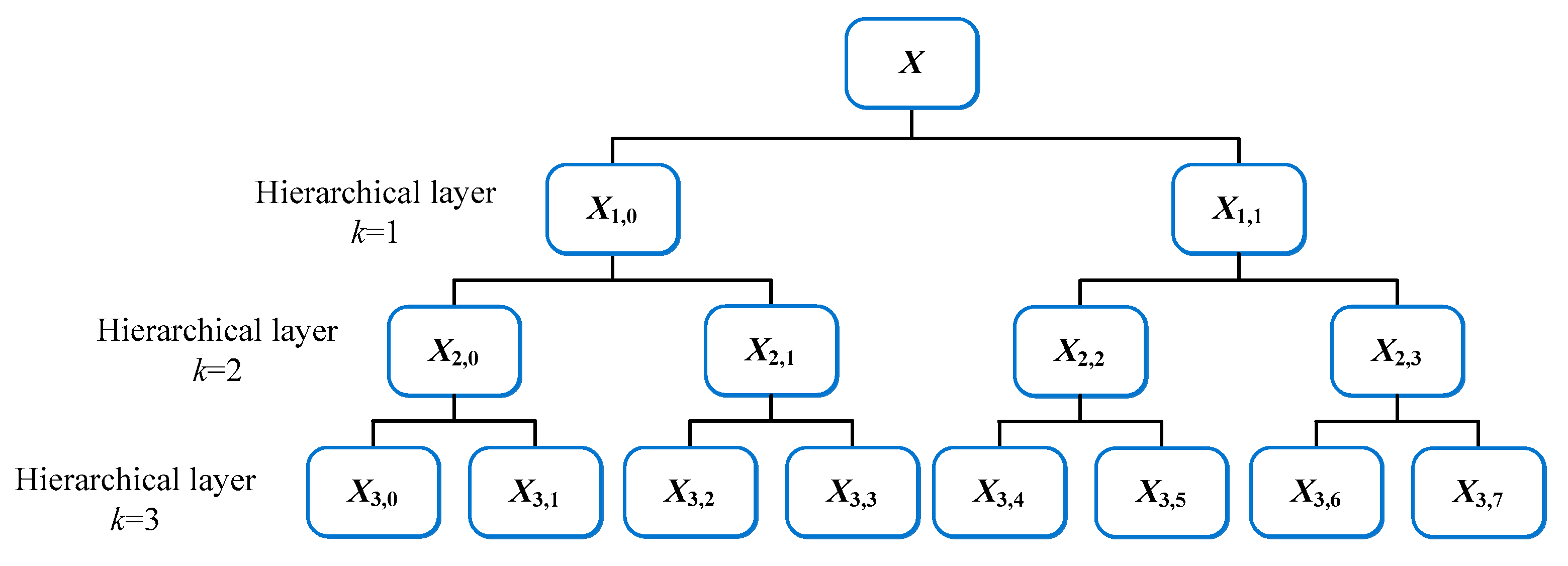
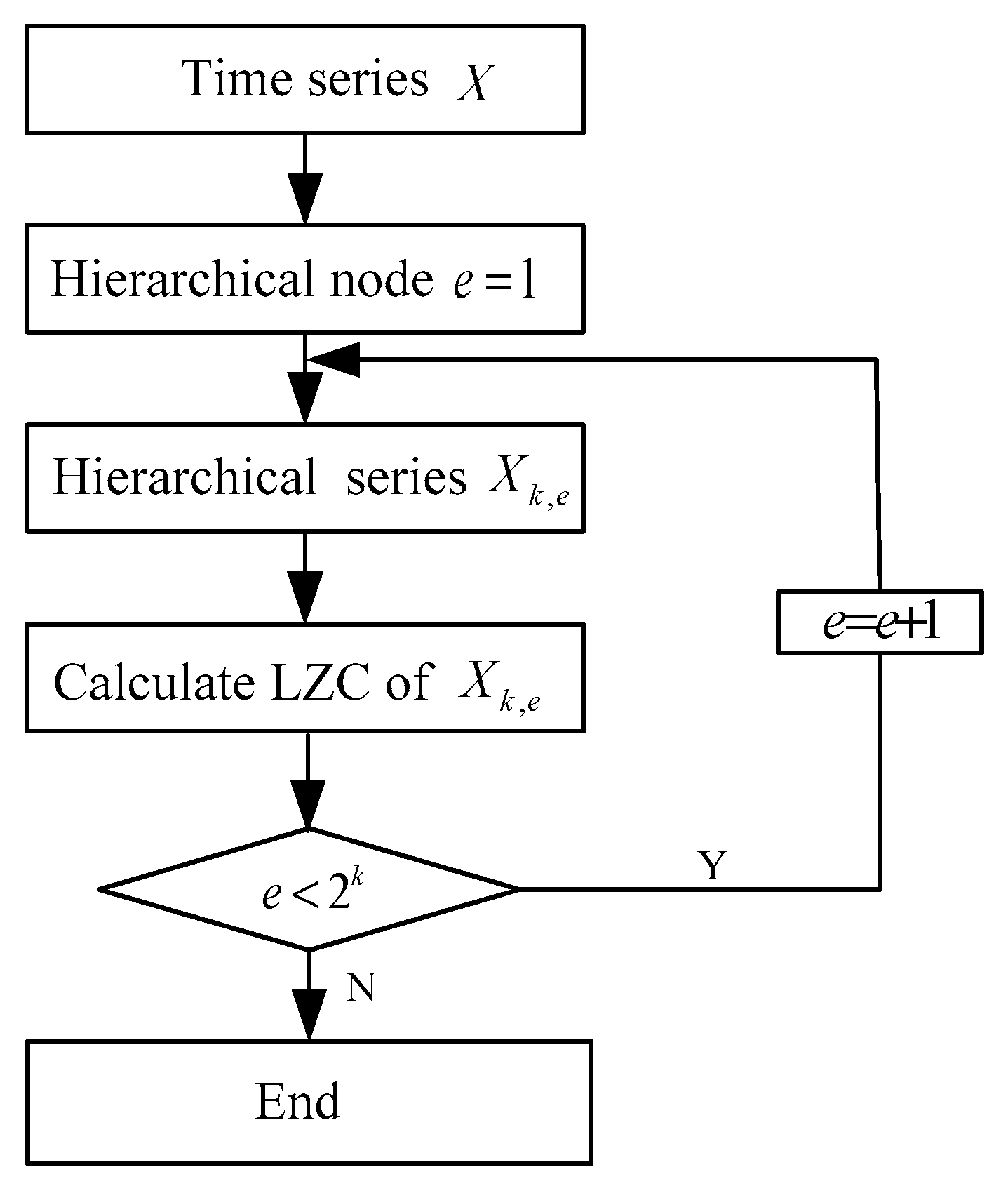
2.3. Hierarchical Lempel-Ziv Complexity
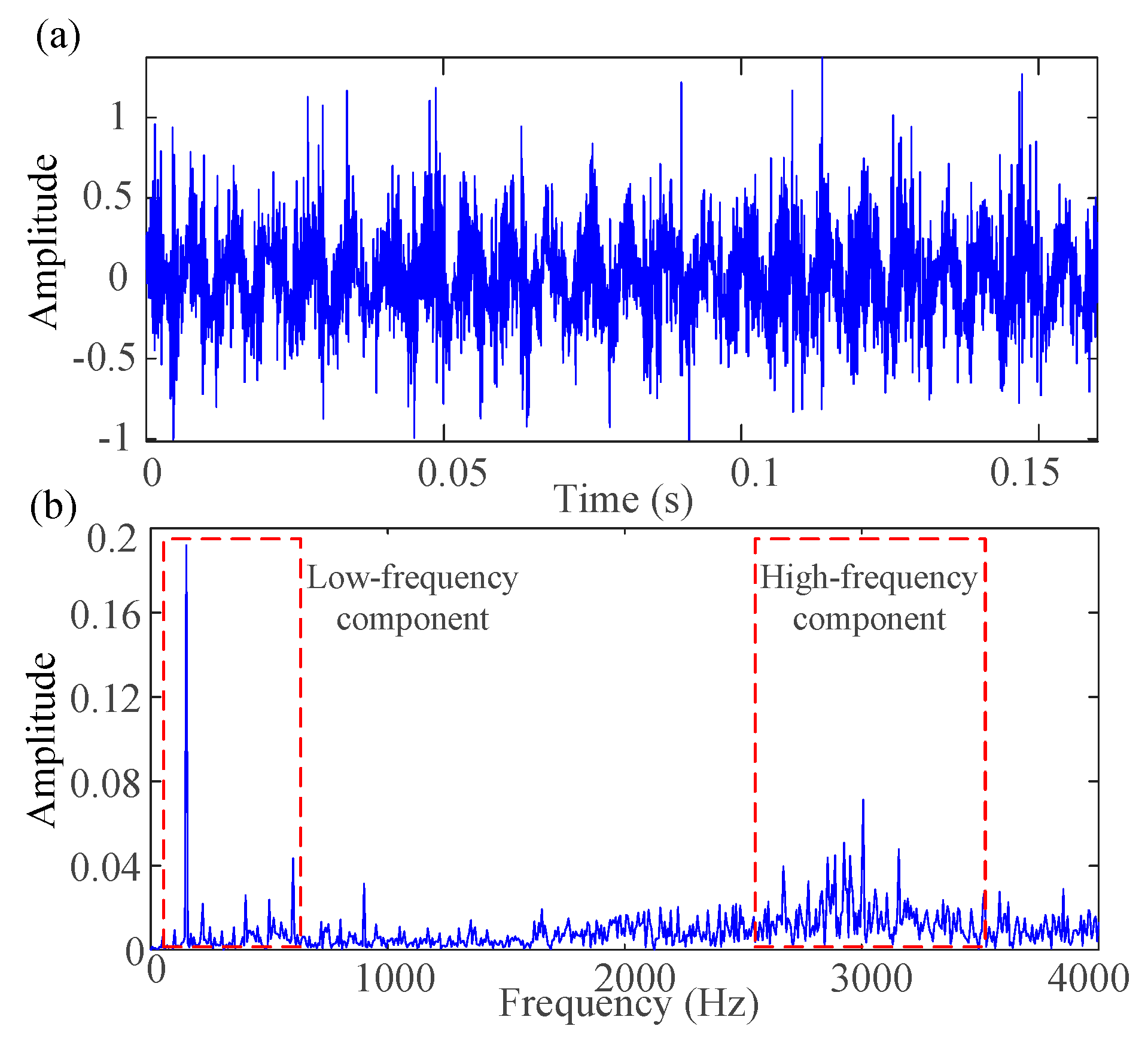
2.4. Simulated Impulsive Signal
3. Proposed Fault Diagnosis Framework
3.1. Support Vector Machine
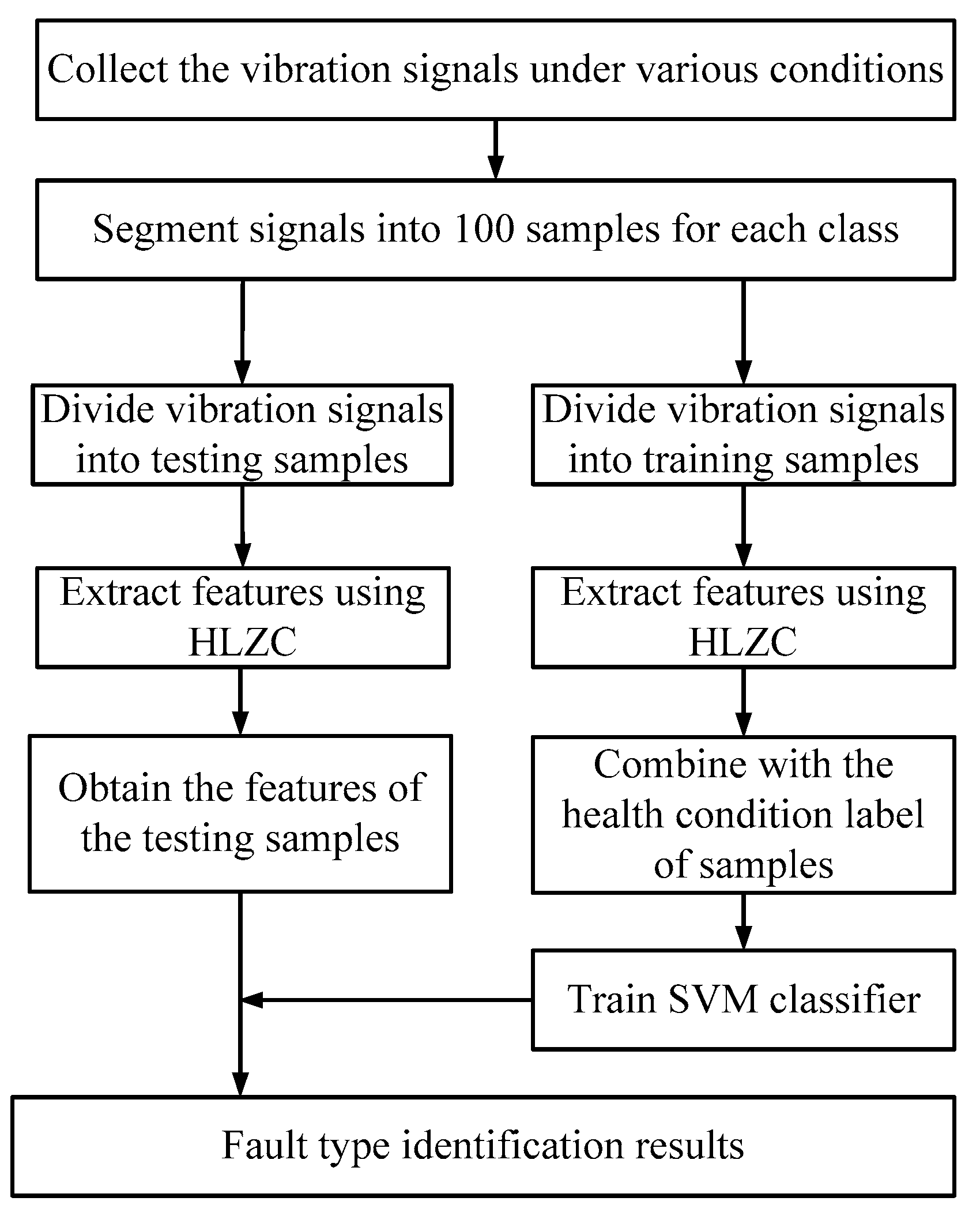
3.2. Proposed Method
- (1)
- Measure the vibration data for various conditions of rotating machinery;
- (2)
- Partition the measured vibration data into training datasets and testing datasets;
- (3)
- Utilize HLZC to extract fault features from the vibration signals. Note that the hierarchical decomposition layers of HLZC is set as , and thus 31 features will be obtained;
- (4)
- Train SVM classifier using the training features;
- (5)
- Test the trained SVM classifier, wherein the output of SVM can be used to recognize the different fault types of rotating machinery.
4. Experimental Validations
4.1. Experiment 1
4.2. Experiment 2
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- LZC was extended to hierarchical decomposition analysis, namely, HLZC;
- (2)
- HLZC considered the fault information hidden in both low-frequency and high-frequency components through conducting the averaging and differencing operations;
- (3)
- A novel fault diagnosis scheme was proposed by combining HLZC and SVM;
- (4)
- The proposed method was verified using both simulated and experimental signals.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, R.; Yang, B.; Zio, E.; Chen, X. Artificial intelligence for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery: A review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 108, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Yin, J. Multi-scale Symbolic Lempel-Ziv: An Effective Feature Extraction Approach for Fault Diagnosis of Railway Vehicle Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, X.; Liang, M. Iterative generalized synchrosqueezing transform for fault diagnosis of wind turbine planetary gearbox under nonstationary conditions. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 52, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeljaber, O.; Avci, O.; Kiranyaz, S.; Gabbouj, M.; Inman, D.J. Real-time vibration-based structural damage detection using one-dimensional convolutional neural networks. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 388, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elasha, F.; Greaves, M.; Mba, D.; Fang, D. A comparative study of the effectiveness of vibration and acoustic emission in diagnosing a defective bearing in a planetry gearbox. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 115, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.B.; Parey, A. Modelling of acoustic emission generated due to pitting on spur gear. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 86, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Lin, J. Health Assessment of Rotating Machinery Using a Rotary Encoder. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Tse, P.W.; Chu, F. An improved Hilbert–Huang transform and its application in vibration signal analysis. J. Sound Vib. 2005, 286, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Tang, G.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Blind source separation of composite bearing vibration signals with low-rank and sparse decomposition. Measurement 2019, 145, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y. A New Family of Model-Based Impulsive Wavelets and Their Sparse Representation for Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 2716–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yao, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J. Periodic impulses extraction based on improved adaptive VMD and sparse code shrinkage denoising and its application in rotating machinery fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 126, 568–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Pan, H.; Cheng, J. Rolling bearing fault detection and diagnosis based on composite multiscale fuzzy entropy and ensemble support vector machines. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 85, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Gao, R. Complexity as a Measure for Machine Health Evaluation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2004, 53, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Gao, R.X. Approximate Entropy as a diagnostic tool for machine health monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 824–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Y.; Luo, S. A rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on multi-scale fuzzy entropy and variable predictive model-based class discrimination. Mech. Mach. Theory 2014, 78, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Liu, Y.; Gao, R.X. Permutation entropy: A nonlinear statistical measure for status characterization of rotary machines. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2012, 29, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Pan, H.; Yang, S.; Cheng, J. Generalized composite multiscale permutation entropy and Laplacian score based rolling bearing fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 99, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Xu, M.; Huang, W. A fault diagnosis scheme for planetary gearboxes using modified multi-scale symbolic dynamic entropy and mRMR feature selection. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 91, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-D.; Wu, C.-W.; Lin, S.-G.; Lee, K.-Y.; Peng, C.-K. Analysis of complex time series using refined composite multiscale entropy. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 378, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Liang, M. Fault severity assessment for rolling element bearings using the Lempel–Ziv complexity and continuous wavelet transform. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 320, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Gong, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H. Double-dictionary matching pursuit for fault extent evaluation of rolling bearing based on the Lempel-Ziv complexity. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 385, 372–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, B.; Ma, J.; Jin, Z. Quantitative trend fault diagnosis of a rolling bearing based on Sparsogram and Lempel-Ziv. Measurement 2018, 128, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liang, Z.; Li, X. A permutation Lempel-Ziv complexity measure for EEG analysis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2015, 19, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Xu, M.; Zheng, H. Fault diagnosis of bearing based on Symbolic Aggregate approXimation and Lempel-Ziv. Measurement 2019, 138, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, M.; Wei, Y.; Huang, W. A new rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on multiscale permutation entropy and improved support vector machine based binary tree. Measurement 2016, 77, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.-K. Multiscale Entropy Analysis of Complex Physiologic Time Series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 068102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Deng, Z. Intelligent fault identification of rotary machinery using refined composite multi-scale Lempel–Ziv complexity. J. Manuf. Syst. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, R.; Huang, W. A fault diagnosis scheme for rolling bearing based on local mean decomposition and improved multiscale fuzzy entropy. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 360, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Peng, C.-K.; Xu, Y. Hierarchical entropy analysis for biological signals. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2011, 236, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elton, R.J.; Vasuki, P.; Mohanalin, J. Voice Activity Detection Using Fuzzy Entropy and Support Vector Machine. Entropy 2016, 18, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Si, S.; Huang, S. Entropy Based Fault Classification Using the Case Western Reserve University Data: A Benchmark Study. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2020, 69, 754–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Morales, J.D.; Palacios-Hernández, E.R.; Campos-Delgado, D.U. Multiple-fault diagnosis in induction motors through support vector machine classification at variable operating conditions. Electr. Eng. 2016, 100, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, K.J.; Kimes, R.V. Empirical characterization of random forest variable importance measures. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008, 52, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
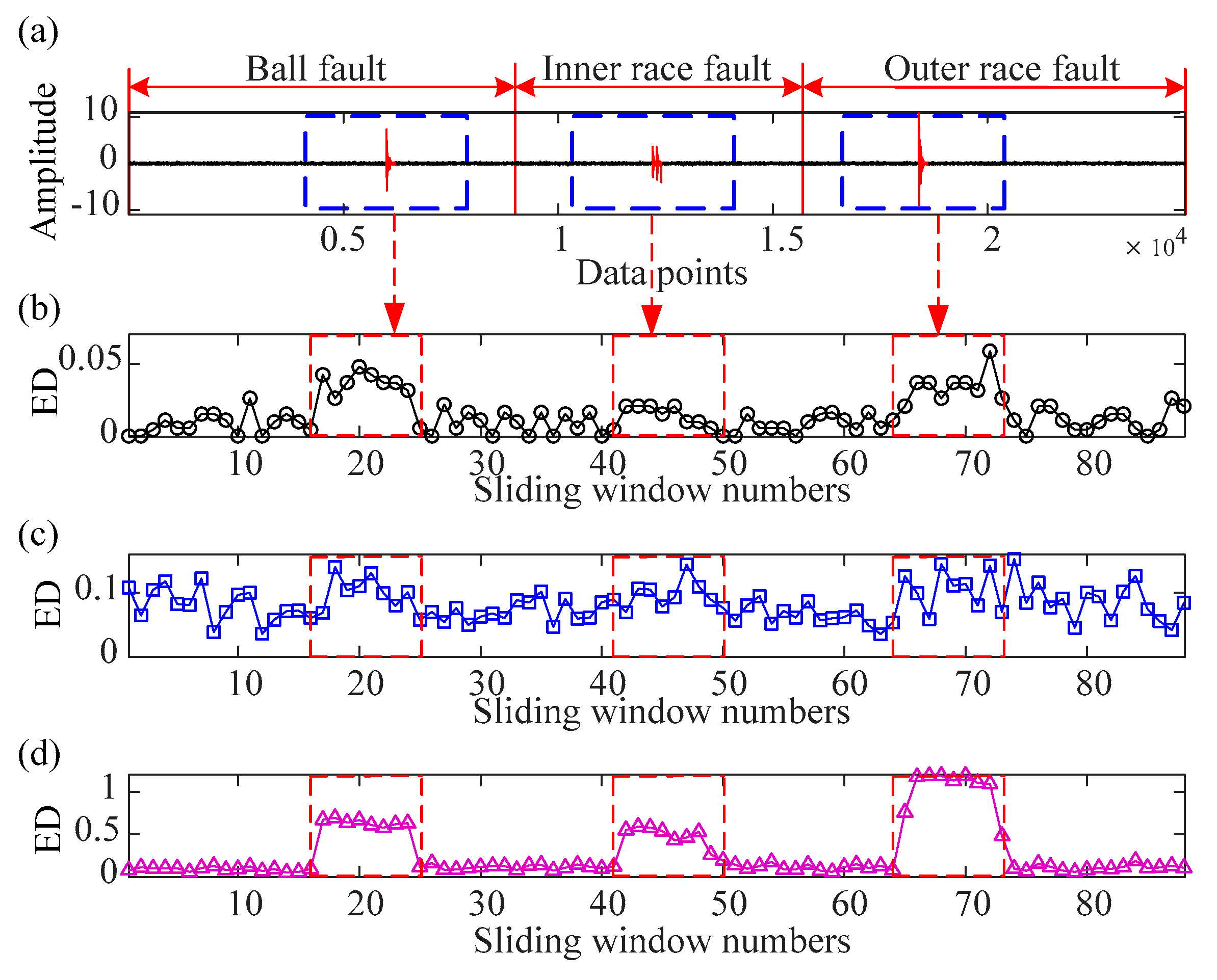
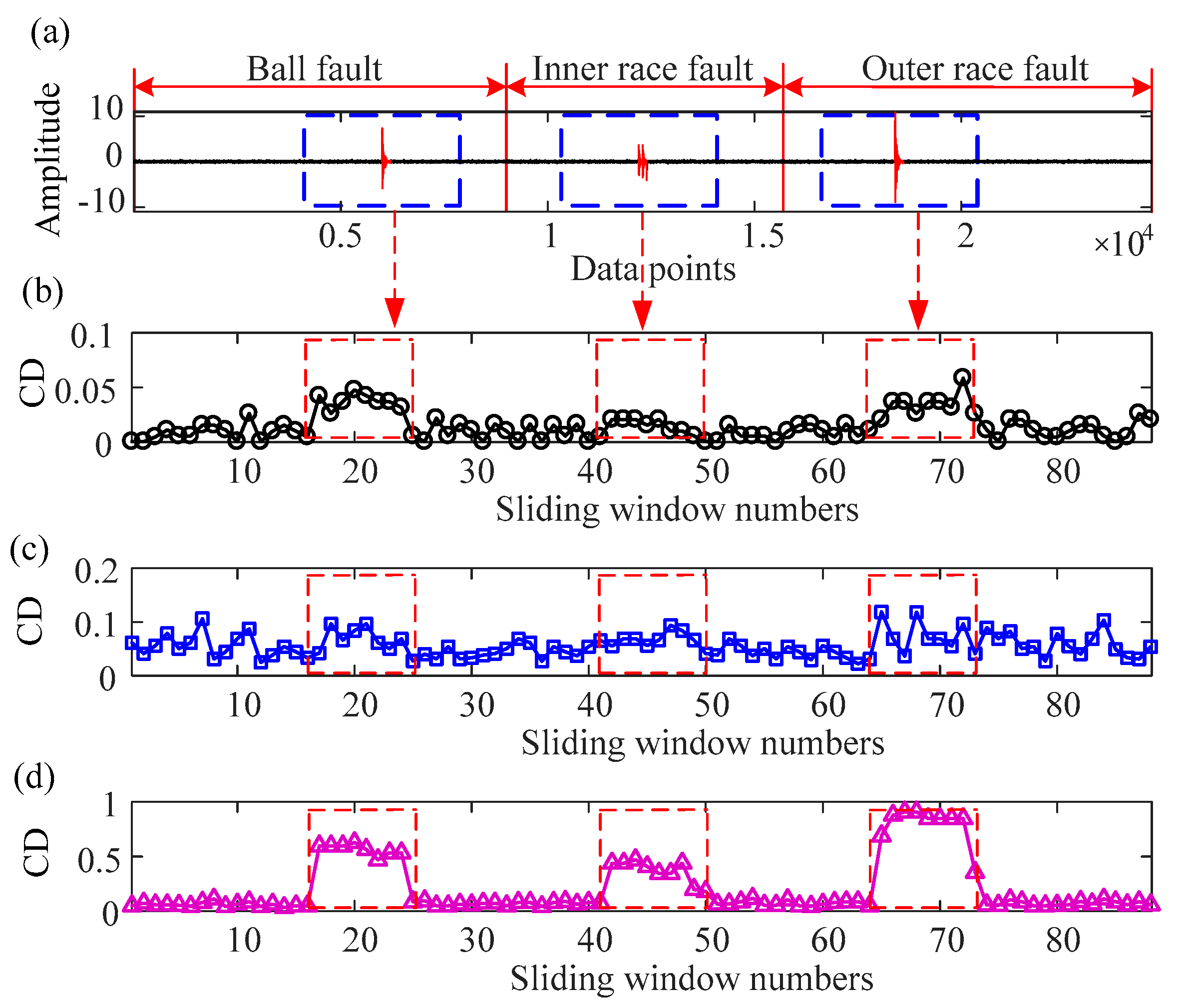
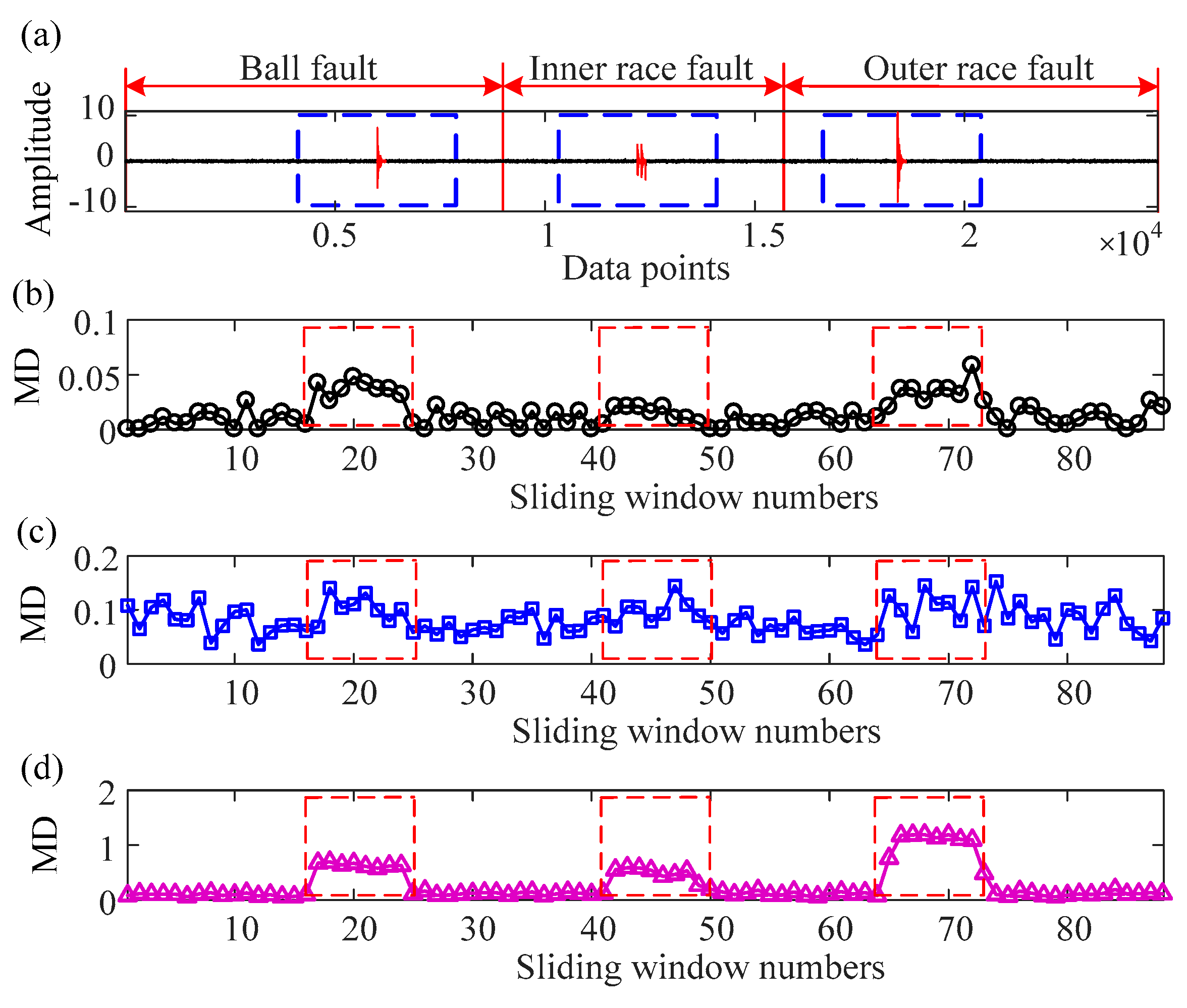

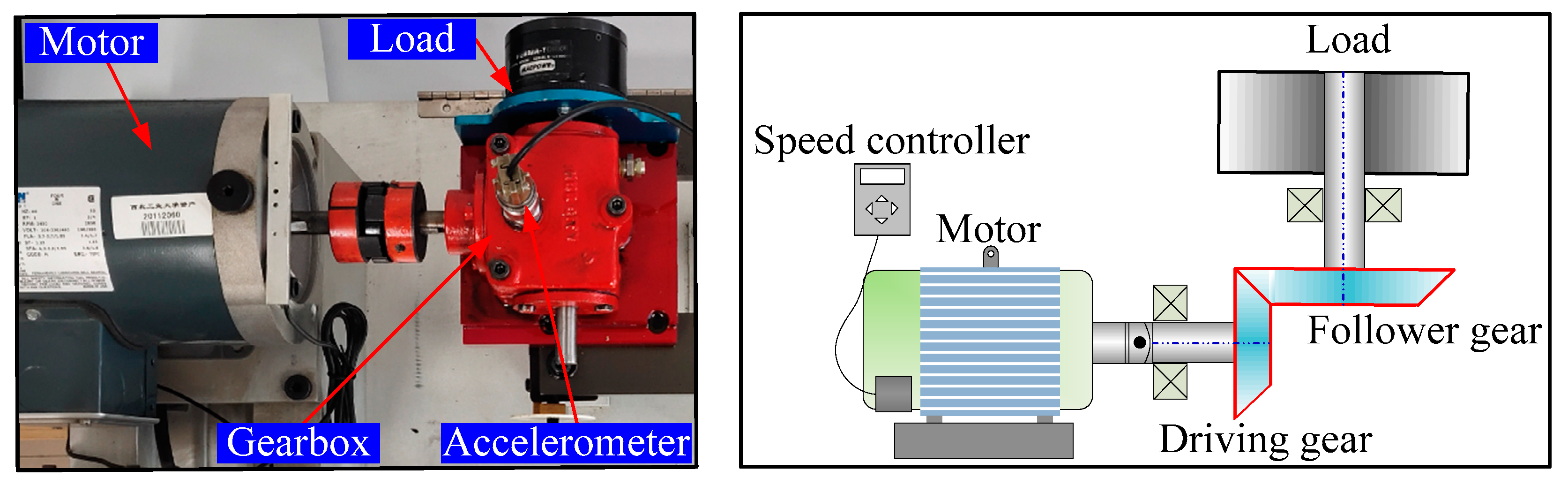
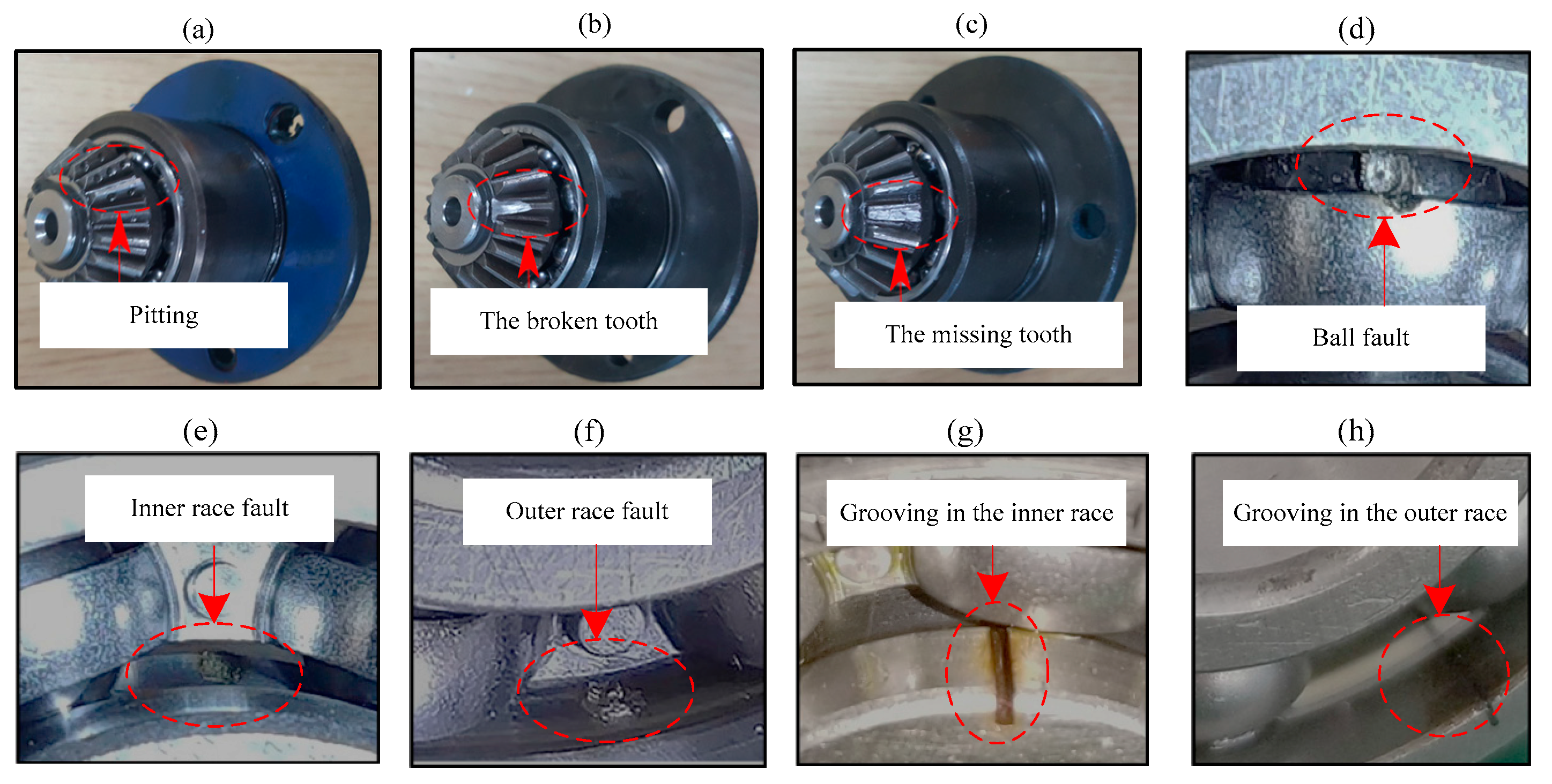
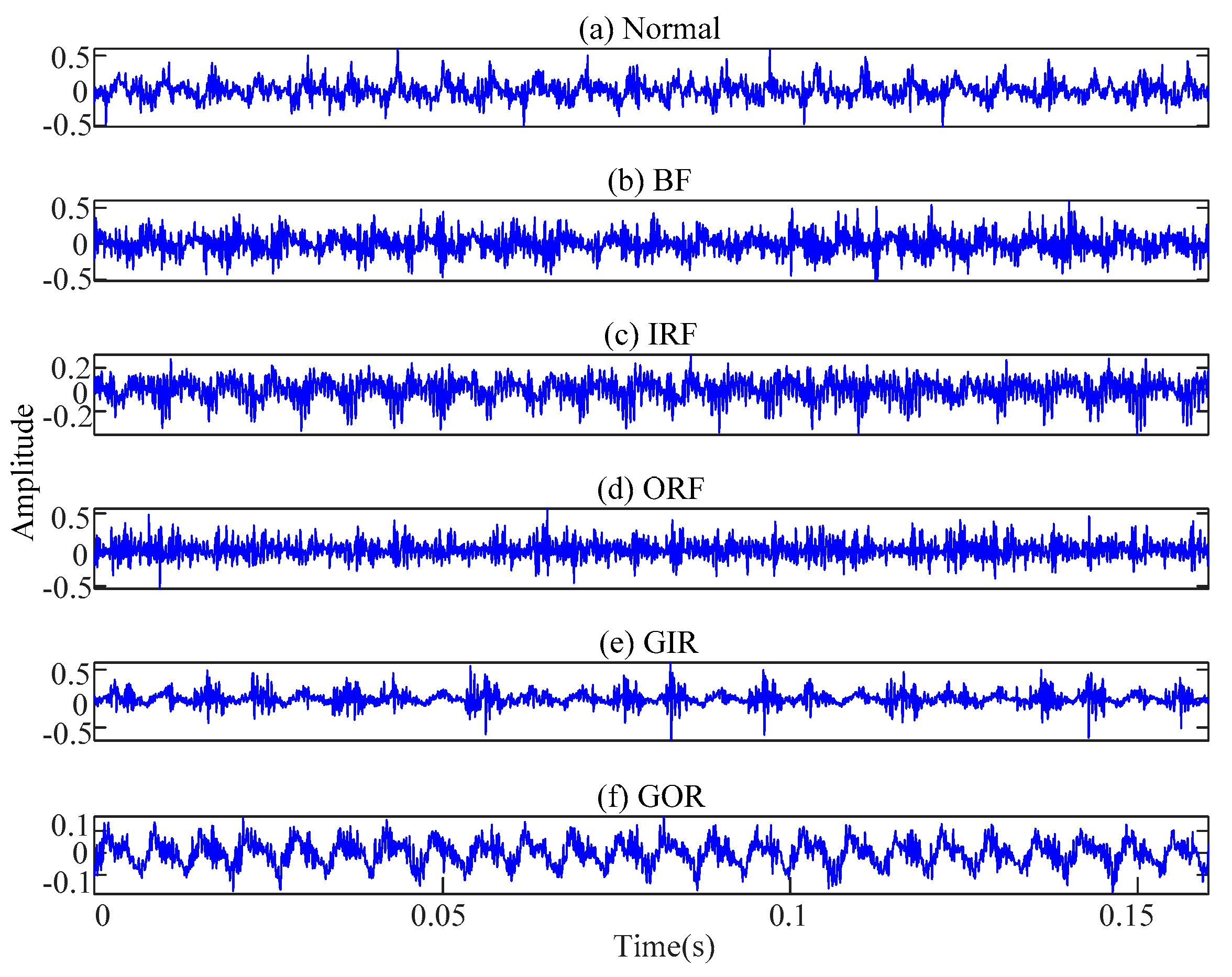
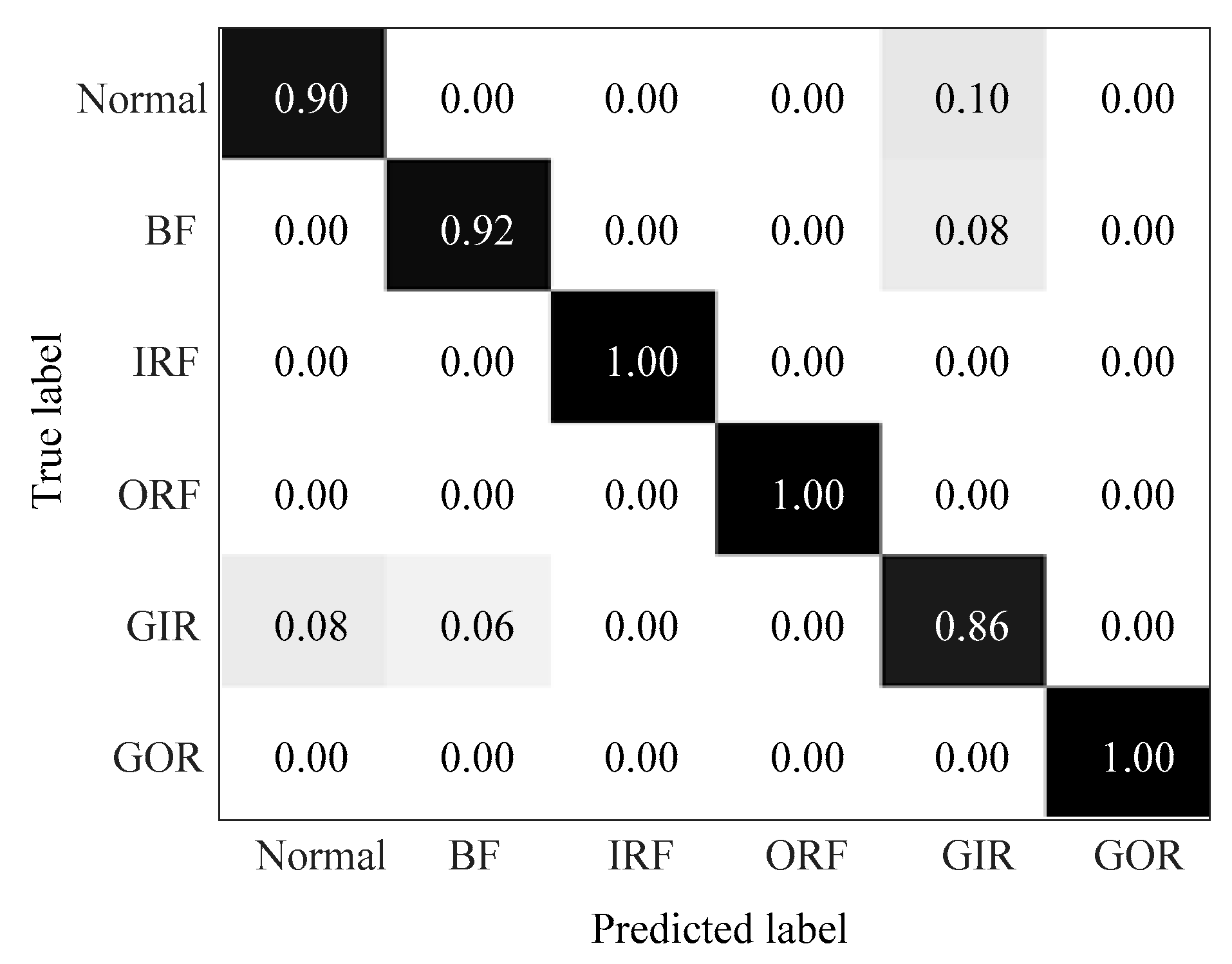
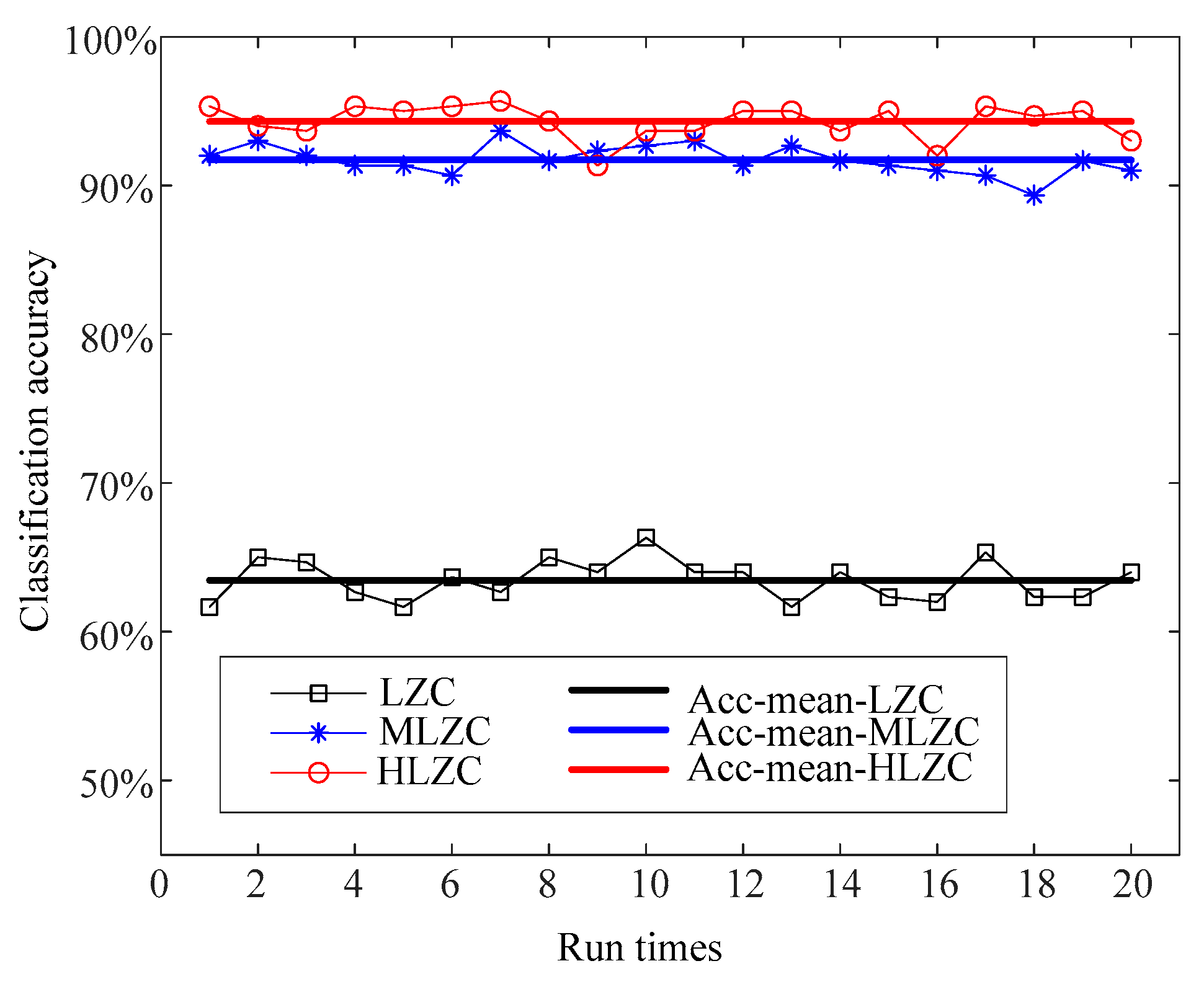
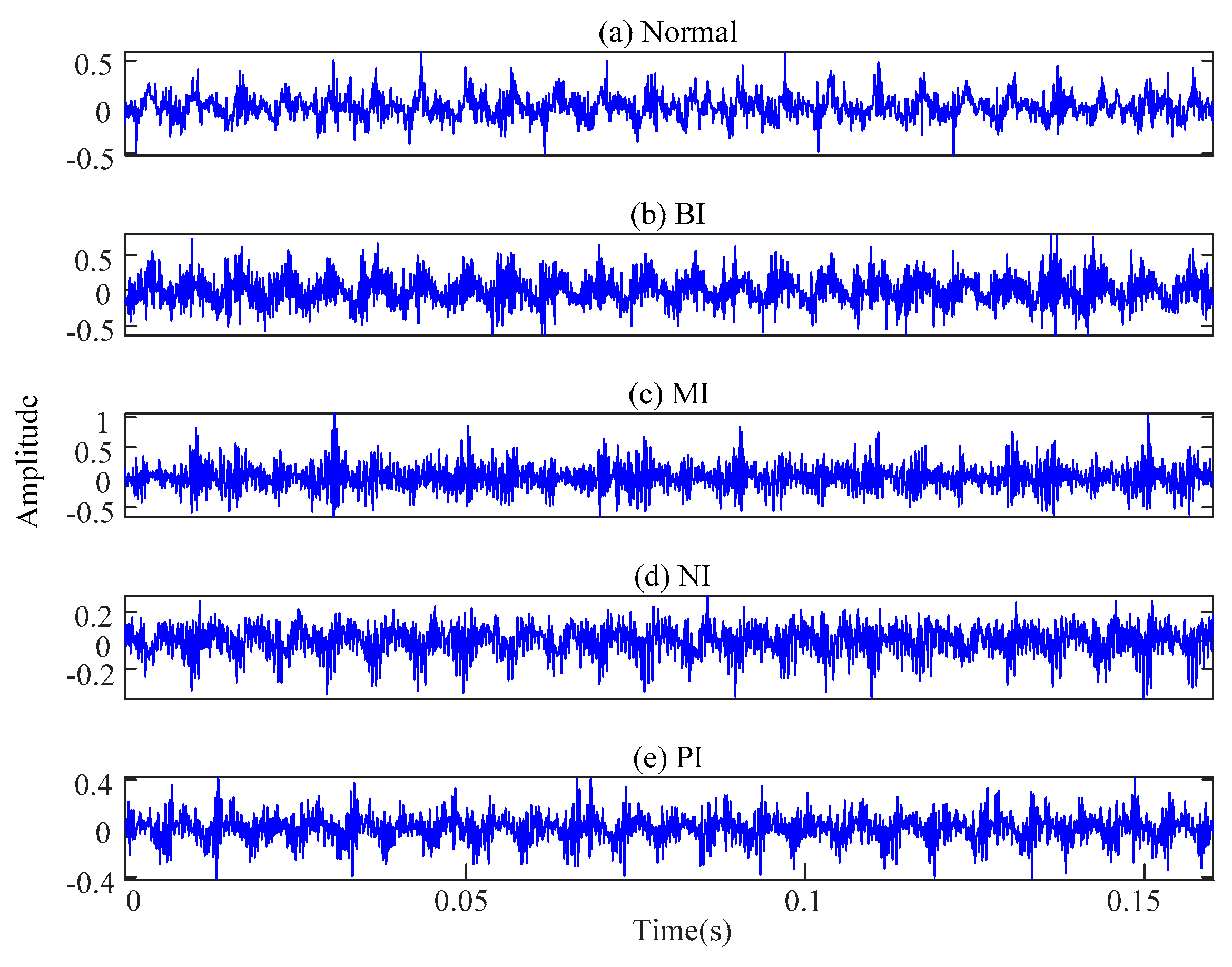


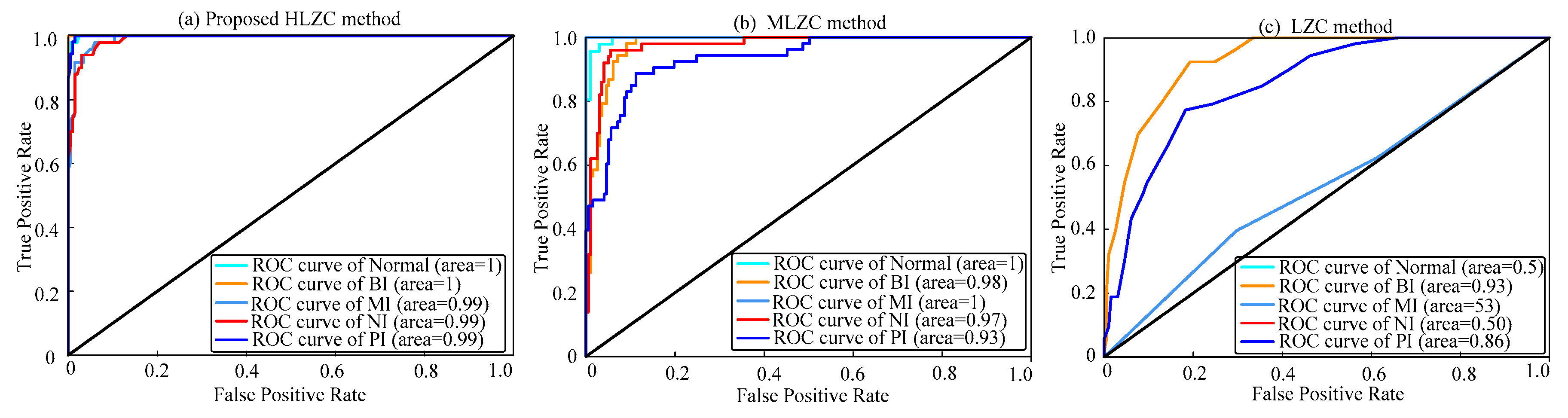
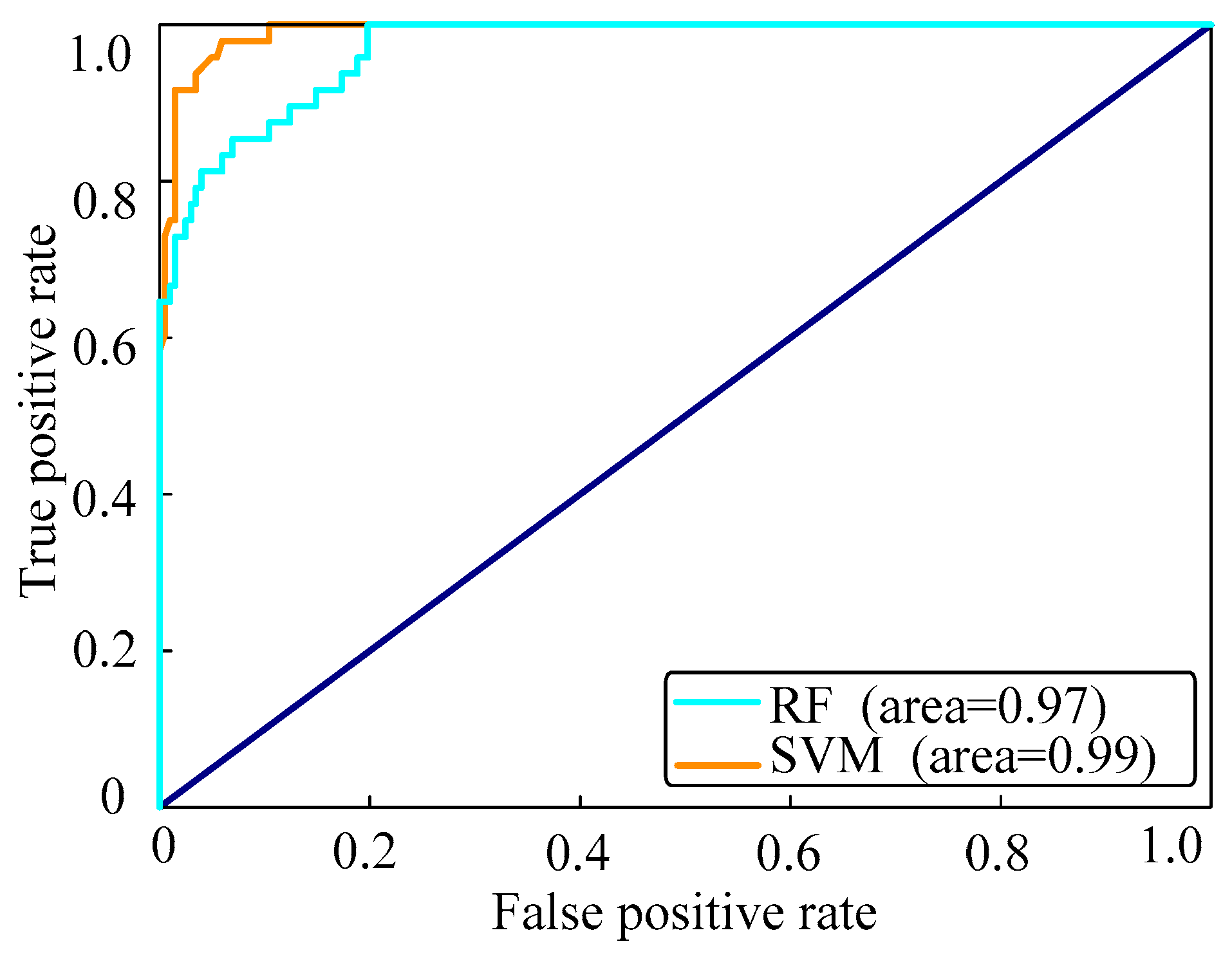
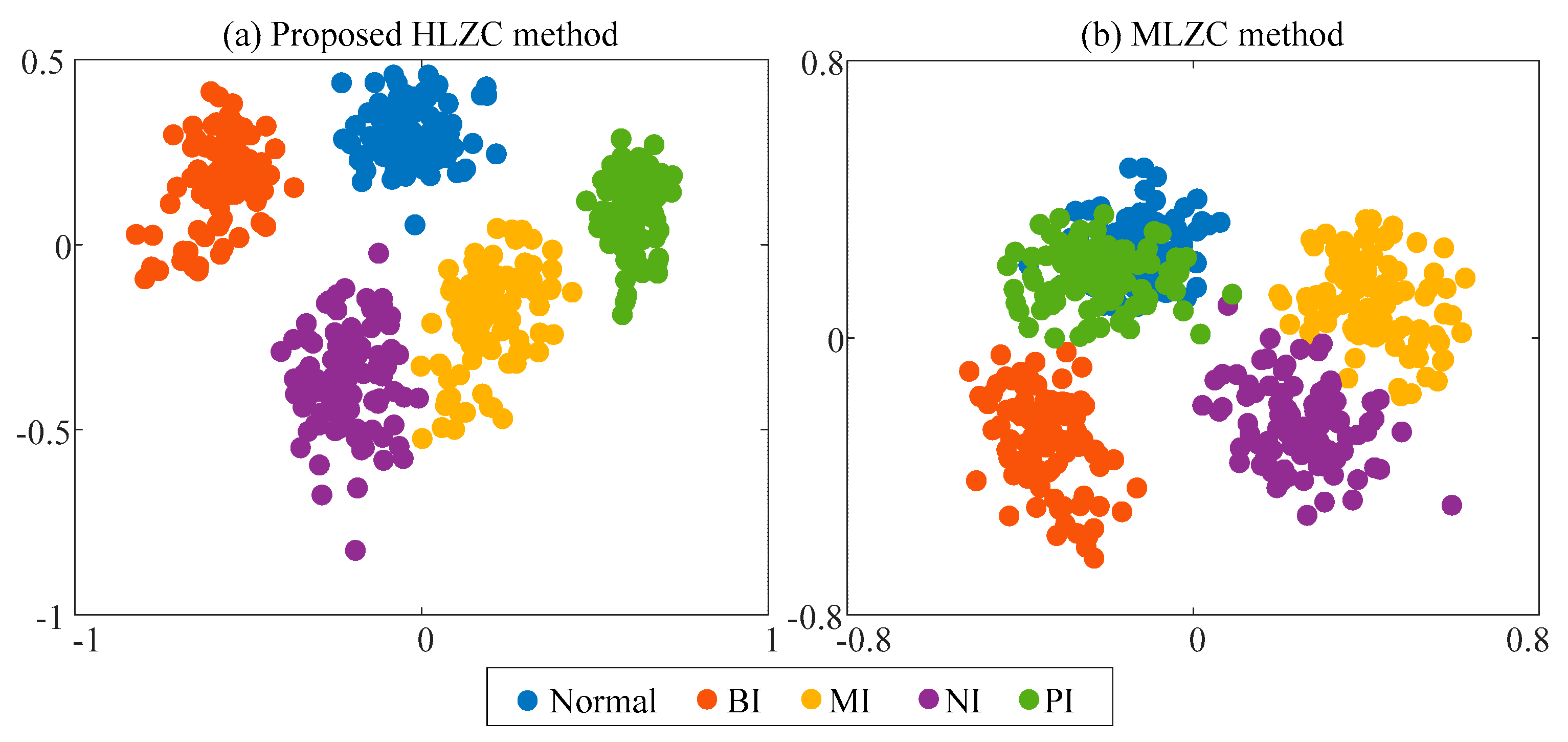
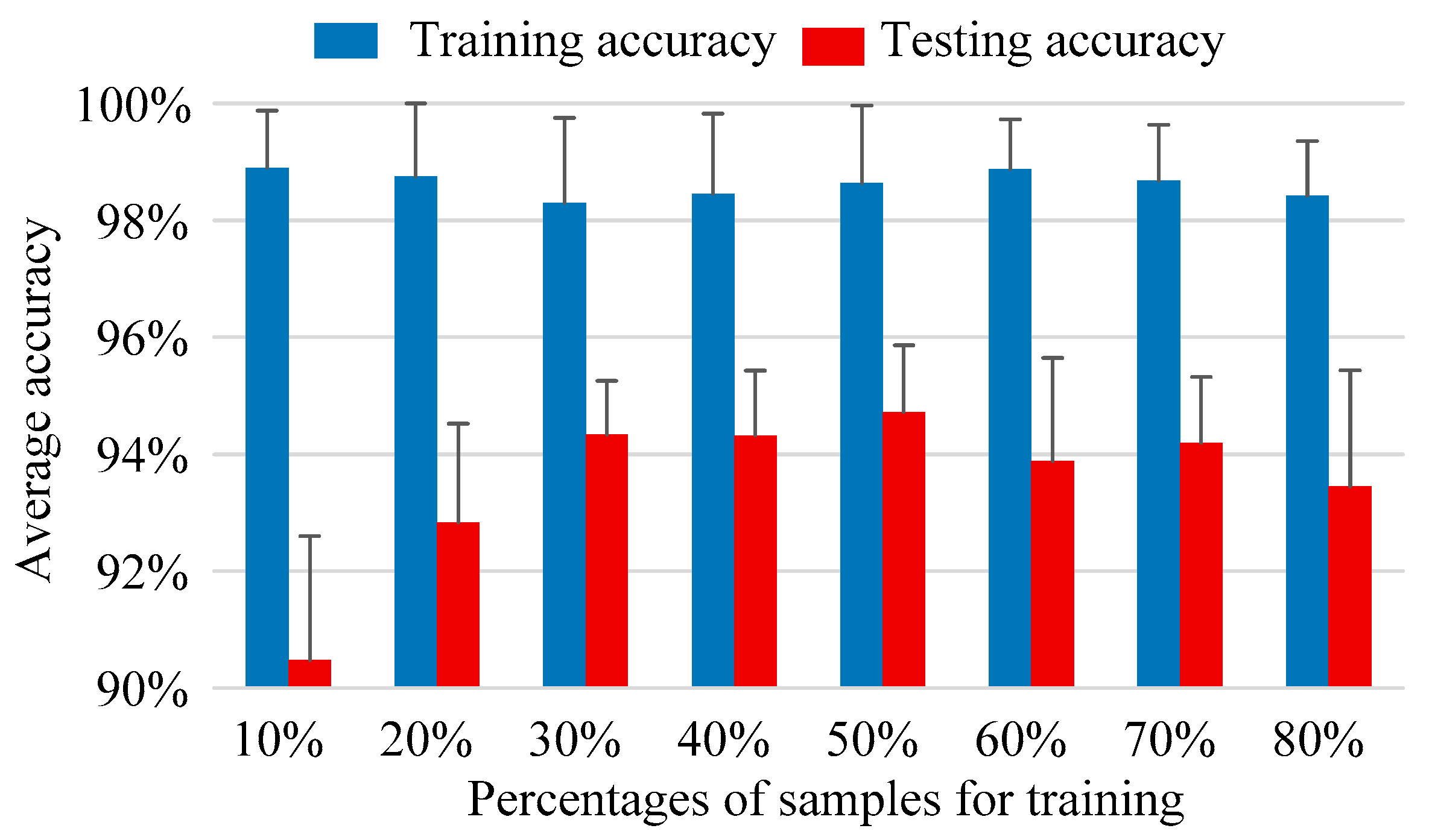
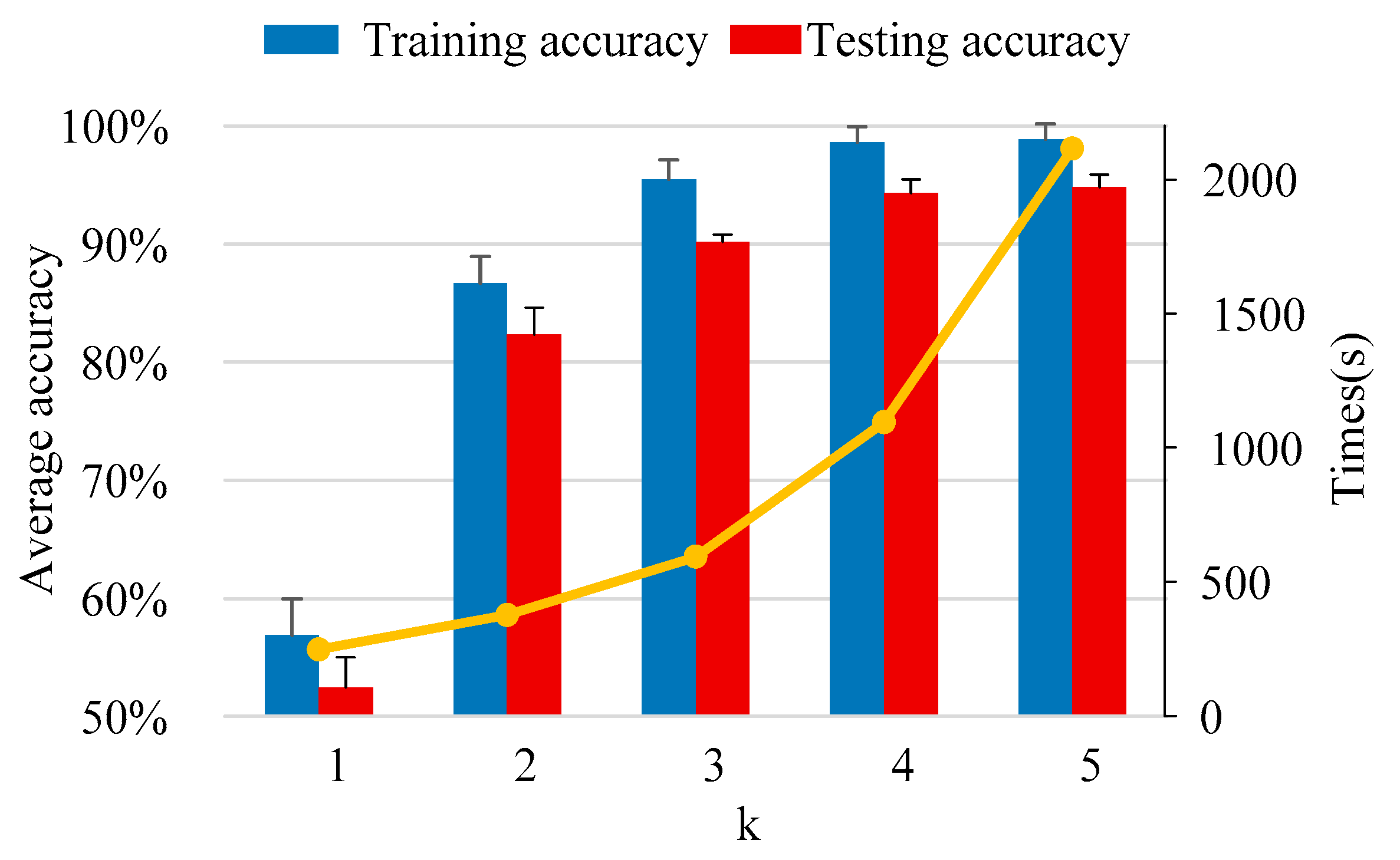

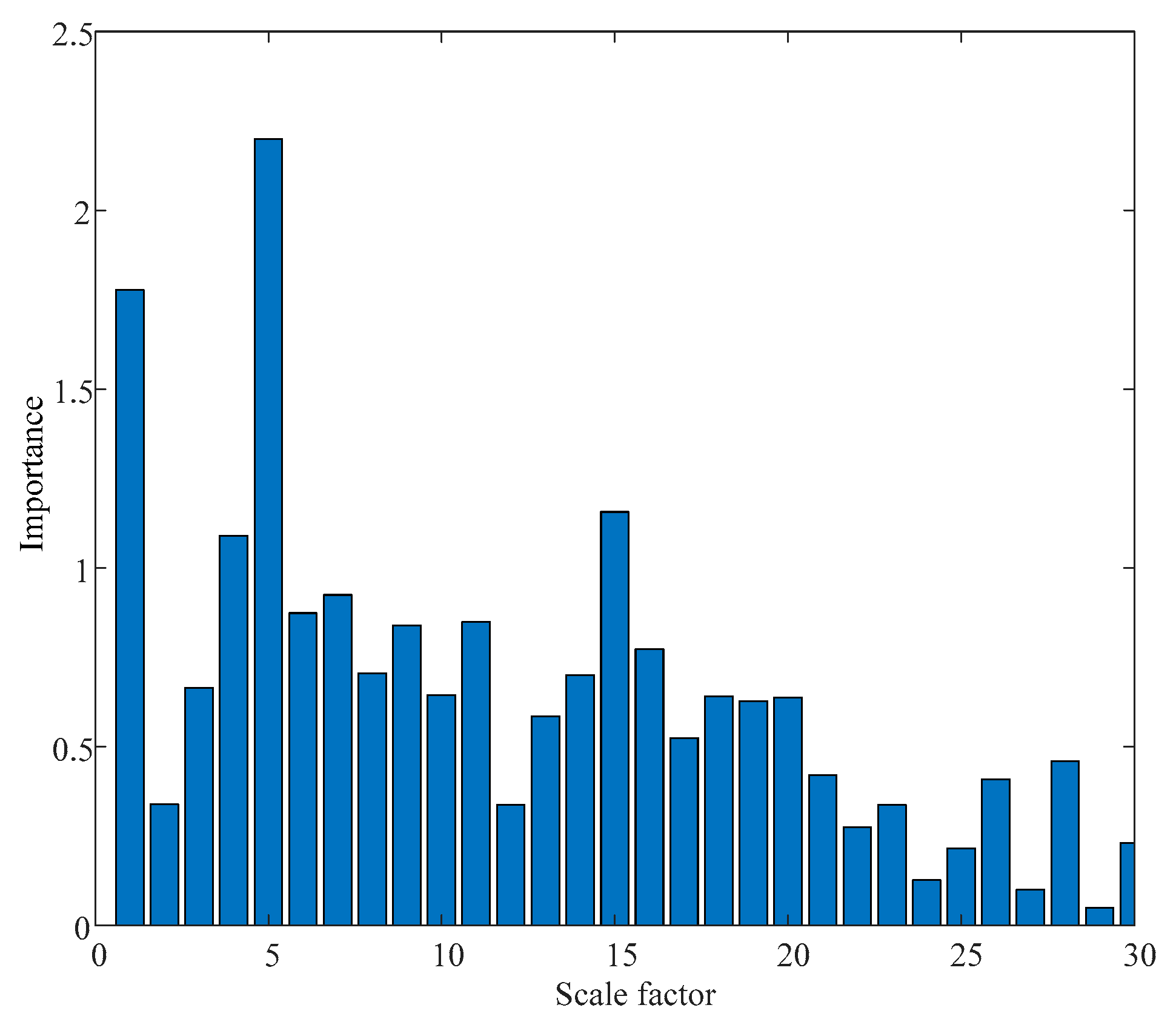
| Fault Class | Class Label | Damage Diameter (mm) | Number of Training Samples | Number of Testing Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 1 | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| Ball fault | 2 | 0.01 | 50 | 50 |
| Inner race fault | 3 | 0.01 | 50 | 50 |
| Outer race fault | 4 | 0.01 | 50 | 50 |
| Grooving in the inner race | 5 | 0.2 | 50 | 50 |
| Grooving in the outer race | 6 | 0.2 | 50 | 50 |
| Experiments | HLZC | MLZC | LZC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) | Accuracy (%) | Accuracy (%) | |||||||
| Max | Min | Mean | Max | Min | Mean | Max | Min | Mean | |
| 1 | 95.67 | 91.33 | 94.30 | 93.67 | 89.33 | 91.72 | 66.33 | 61.67 | 63.47 |
| 2 | 97.20 | 92 | 94.72 | 90 | 84.80 | 87.82 | 45.20 | 36 | 41.22 |
| Fault Class | Class Label | Damage Diameter (mm) | Number of Training Samples | Number of Testing Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 1 | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| BI | 2 | 0.01 | 50 | 50 |
| MI | 3 | 0.01 | 50 | 50 |
| NI | 4 | 0.01 | 50 | 50 |
| PI | 5 | 0.01 | 50 | 50 |
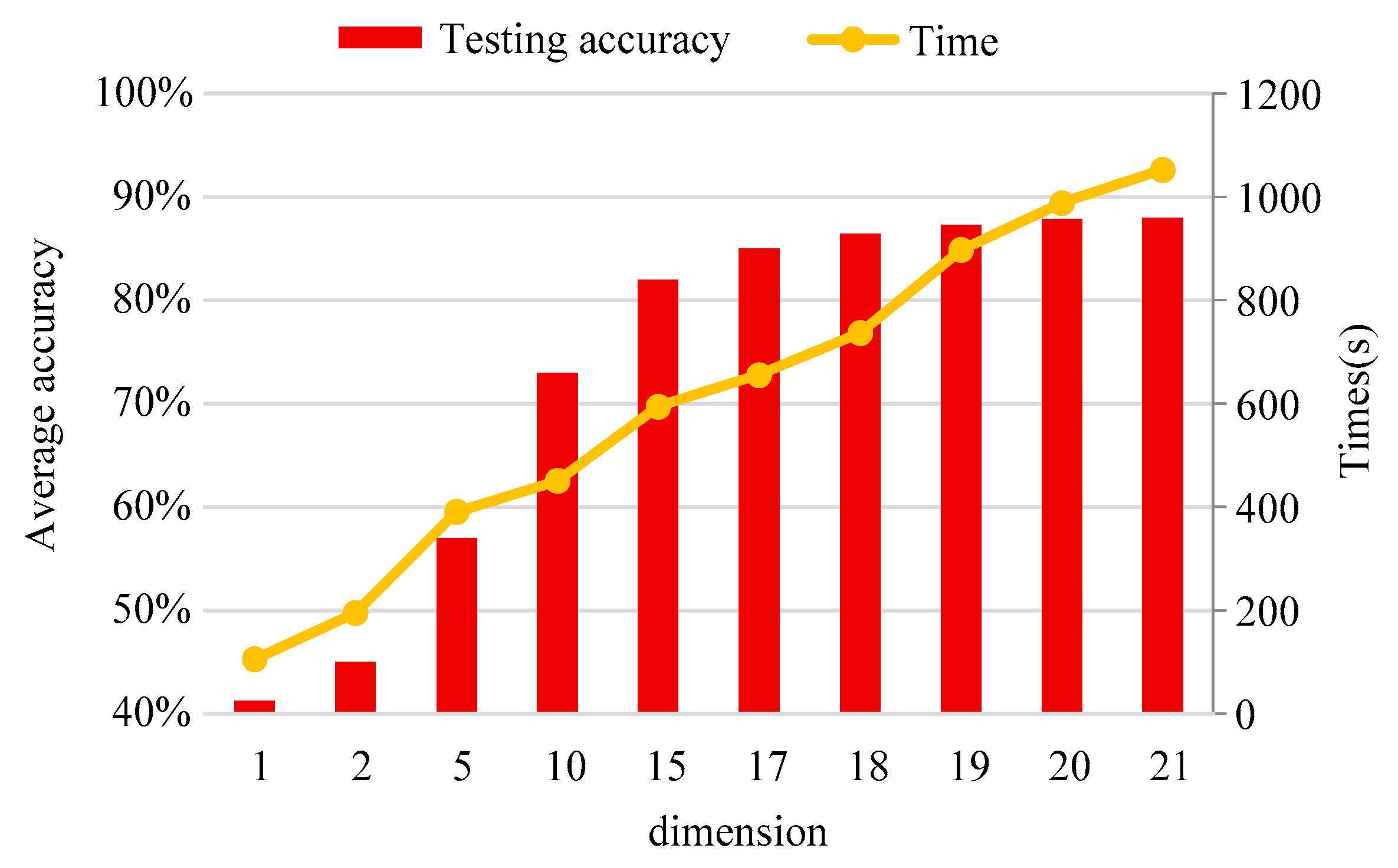
| Scale Factor τ | 1 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max (%) | 45.2 | 52 | 60 | 75 | 85 | 88 | 89 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| Min (%) | 36 | 43 | 52 | 70 | 78 | 82 | 84 | 83 | 85 | 85 |
| Mean (%) | 41.22 | 45 | 57 | 73 | 82 | 85 | 86.4 | 87.2 | 87.82 | 87.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, B.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, X.; Li, Y. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Machinery Using Hierarchical Lempel-Ziv Complexity. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124221
Han B, Wang S, Zhu Q, Yang X, Li Y. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Machinery Using Hierarchical Lempel-Ziv Complexity. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(12):4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124221
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Bing, Shun Wang, Qingqi Zhu, Xiaohui Yang, and Yongbo Li. 2020. "Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Machinery Using Hierarchical Lempel-Ziv Complexity" Applied Sciences 10, no. 12: 4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124221
APA StyleHan, B., Wang, S., Zhu, Q., Yang, X., & Li, Y. (2020). Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Machinery Using Hierarchical Lempel-Ziv Complexity. Applied Sciences, 10(12), 4221. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124221






