Levels and Changes of Physical Activity in Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Contextualizing Urban vs. Rural Living Environment
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
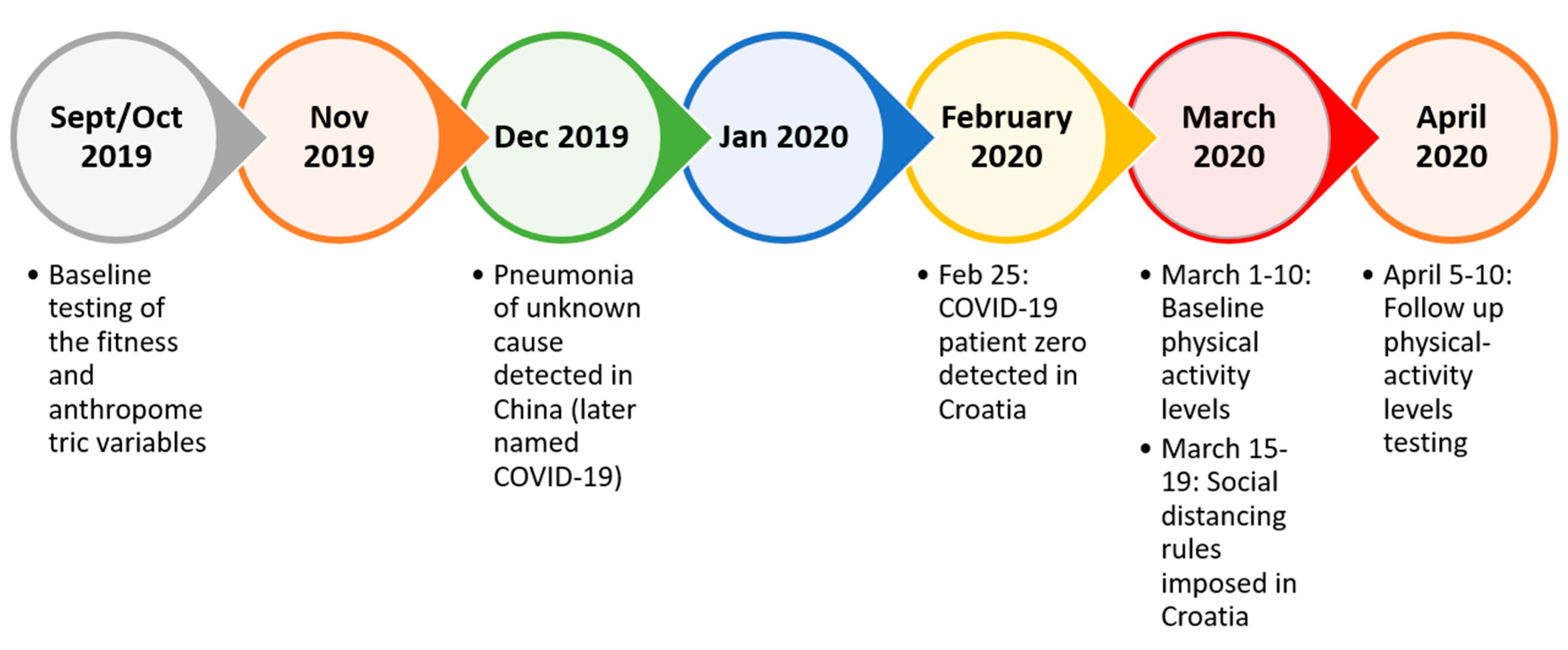
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Variables and Testing
2.3. Statistics
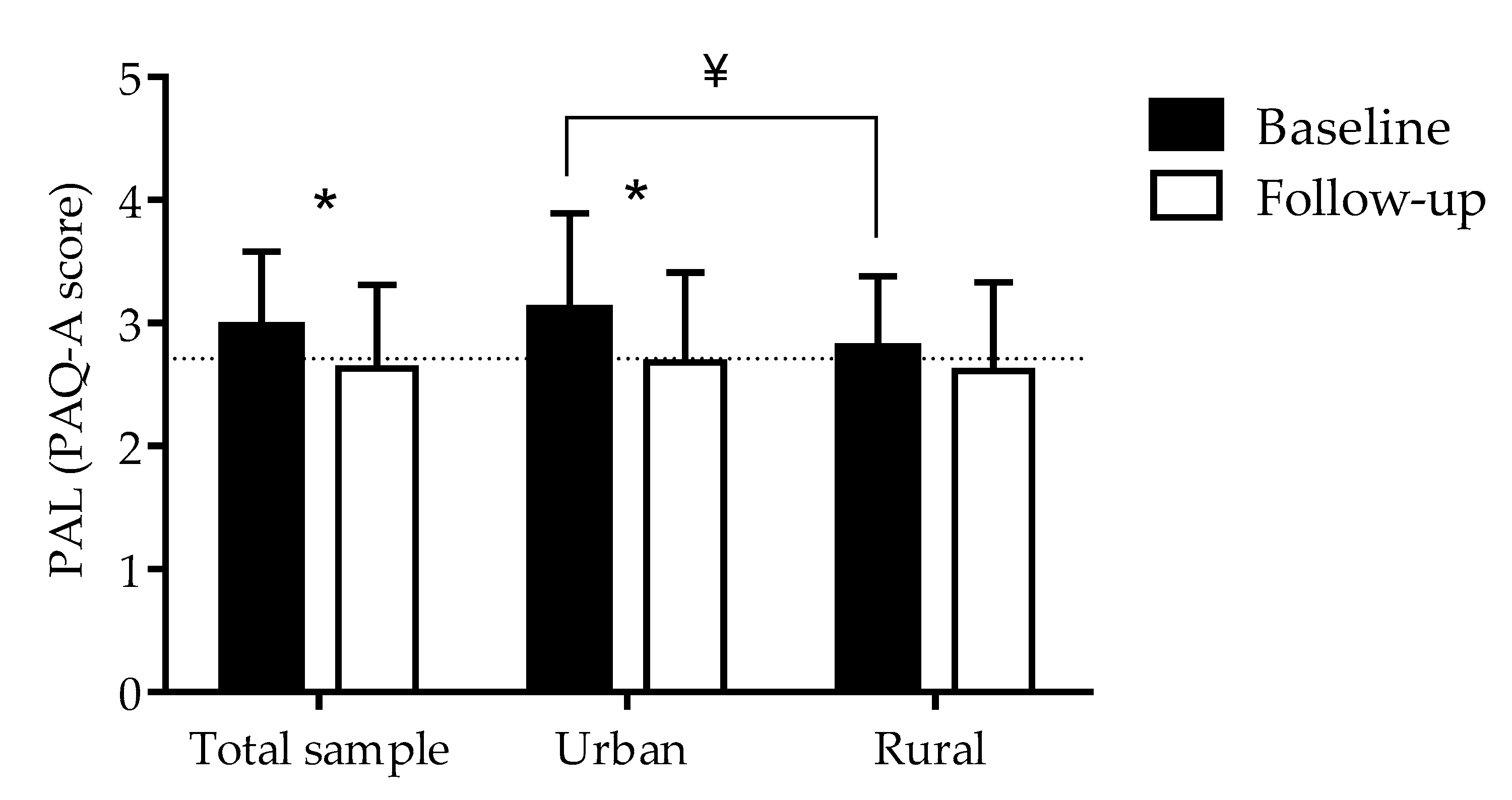
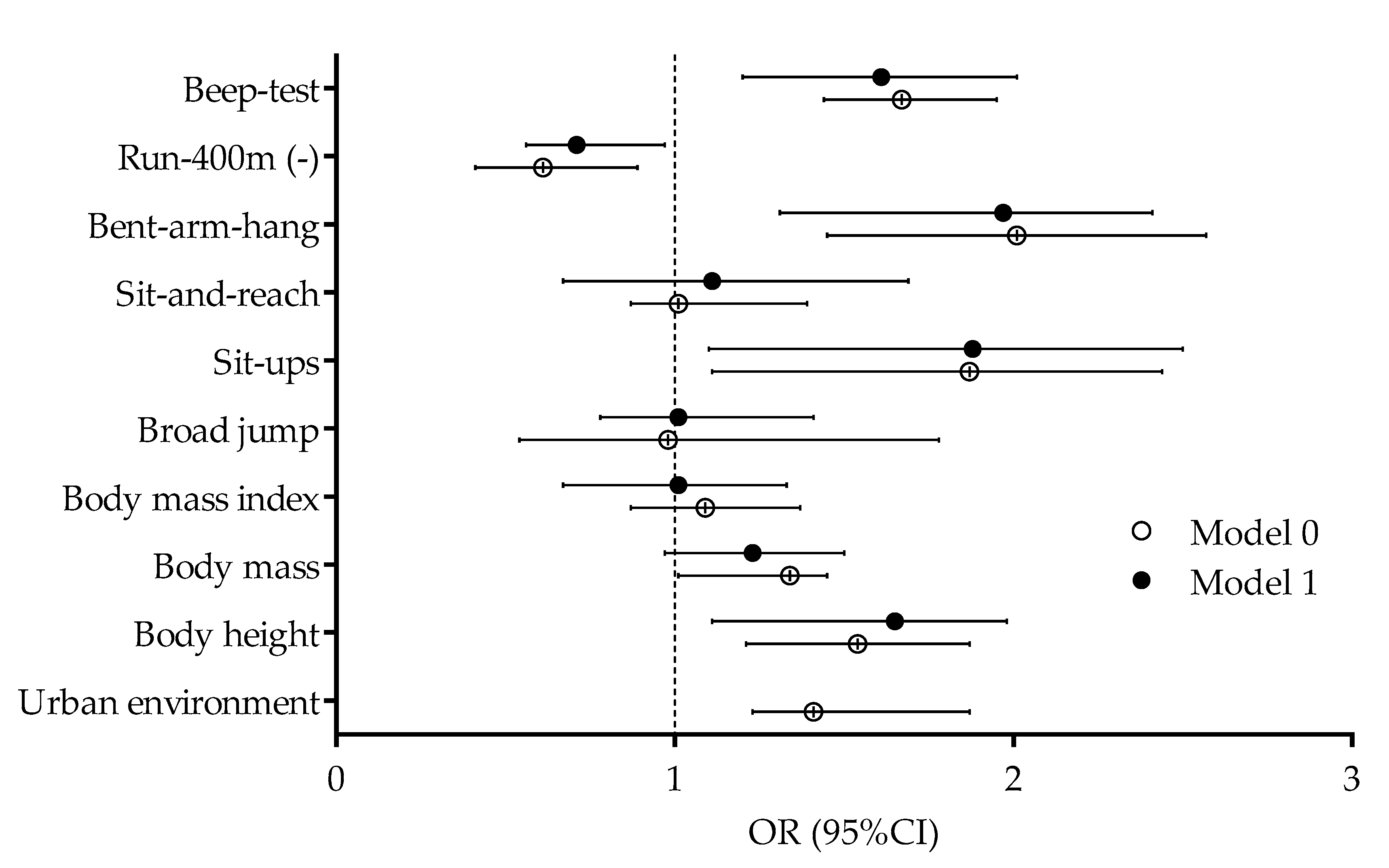
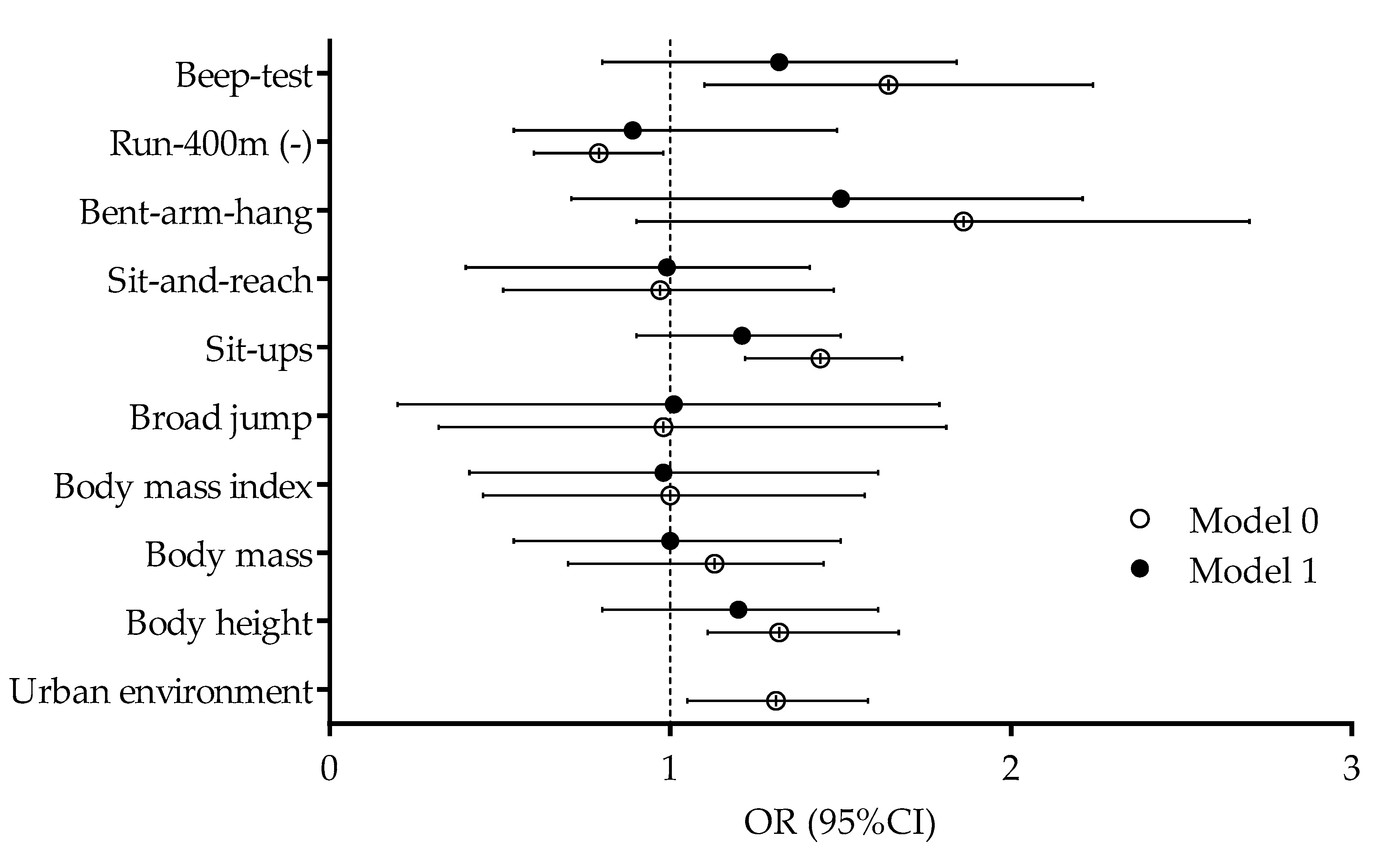
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in Physical Activity Levels among Rural and Urban Adolescents as a Result of the COVID-19 Pandemic
4.2. Correlates of Physical Activity Levels before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Urban and Rural Adolescents
4.3. Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howley, E.T. Type of activity: Resistance, aerobic and leisure versus occupational physical activity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, S364–S369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann-Sloutskis, D.; Wanner, M.; Zimmermann, E.; Martin, B.W. Physical activity levels and determinants of change in young adults: A longitudinal panel study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavill, N.; Kahlmeier, S.; Racioppi, F. Physical Activity and Health in Europe: Evidence for Action; WHO Regional Office Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Micucci, D.; Mobilio, M.; Napoletano, P. Unimib shar: A dataset for human activity recognition using acceleration data from smartphones. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, W.B.; Malina, R.M.; Blimkie, C.J.; Daniels, S.R.; Dishman, R.K.; Gutin, B.; Hergenroeder, A.C.; Must, A.; Nixon, P.A.; Pivarnik, J.M. Evidence based physical activity for school-age youth. J. Pediatrics 2005, 146, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Bull, F.C. Global trends in insufficient physical activity among adolescents: A pooled analysis of 298 population-based surveys with 1· 6 million participants. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/global-PA-recs-2010.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Dumith, S.C.; Gigante, D.P.; Domingues, M.R.; Kohl, H.W., III. Physical activity change during adolescence: A systematic review and a pooled analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefan, L.; Mišigoj-Duraković, M.; Devrnja, A.; Podnar, H.; Petrić, V.; Sorić, M. Tracking of physical activity, sport participation, and sedentary behaviors over four years of high school. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telama, R.; Yang, X.; Leskinen, E.; Kankaanpää, A.; Hirvensalo, M.; Tammelin, T.; Viikari, J.S.; Raitakari, O.T. Tracking of physical activity from early childhood through youth into adulthood. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Horst, K.; Paw, M.J.C.A.; Twisk, J.W.; Van Mechelen, W. A brief review on correlates of physical activity and sedentariness in youth. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, A.E.; Hoelscher, D.M.; Kelder, S.H. Prevalence of physical activity and sedentary behaviors in US high school students by metropolitan status and geographic region. J. Phys. Act. Health 2006, 3, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, S.G.H.; Schroeder, K.; Lee, J.; Fulkerson, J.A.; Kubik, M.Y. The Association between Parents and Children Meeting Physical Activity Guidelines. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2020, 52, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donatiello, E.; Russo, M.D.; Formisano, A.; Lauria, F.; Nappo, A.; Reineke, A.; Sparano, S.; Barba, G.; Russo, P.; Siani, A. Physical activity, adiposity and urbanization level in children: Results for the Italian cohort of the IDEFICS study. Public Health 2013, 127, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regis, M.F.; Oliveira, L.M.F.T.D.; Santos, A.R.M.D.; Leonidio, A.D.C.R.; Diniz, P.R.B.; Freitas, C.M.S.M.D. Urban versus rural lifestyle in adolescents: Associations between environment, physical activity levels and sedentary behavior. Einstein (São Paulo) 2016, 14, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallis, J.F.; Cerin, E.; Conway, T.L.; Adams, M.A.; Frank, L.D.; Pratt, M.; Salvo, D.; Schipperijn, J.; Smith, G.; Cain, K.L. Physical activity in relation to urban environments in 14 cities worldwide: A cross-sectional study. Lancet 2016, 387, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sygit, K.M.; Sygit, M.; Wojtyła-Buciora, P.; Lubiniec, O.; Stelmach, W.; Krakowiak, J. Physical activity as an important element in organizing and managing the lifestyle of populations in urban and rural environments. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. AAEM 2019, 26, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenowatz, C.; Hinterkorner, F.; Greier, K. Physical Fitness in Upper Austrian Children Living in Urban and Rural Areas: A Cross-Sectional Analysis with More Than 18,000 Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathrellou, E.; Lazarou, C.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Sidossis, L.S. Physical activity patterns and sedentary behaviors of children from urban and rural areas of Cyprus. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2007, 15, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Machado-Rodrigues, A.M.; Coelho-e-Silva, M.J.; Mota, J.; Cumming, S.P.; Riddoch, C.; Malina, R.M. Correlates of aerobic fitness in urban and rural Portuguese adolescents. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2011, 38, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillón, P.; Ortega, F.B.; Ferrando, J.A.; Casajus, J.A. Physical fitness in rural and urban children and adolescents from Spain. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2011, 14, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopcakova, J.; Veselska, Z.D.; Geckova, A.M.; Klein, D.; van Dijk, J.P.; Reijneveld, S.A. Are school factors and urbanization supportive for being physically active and engaging in less screen-based activities? Int. J. Public Health 2018, 63, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-Rodrigues, A.M.; Coelho-e-Silva, M.J.; Mota, J.; Padez, C.; Ronque, E.; Cumming, S.P.; Malina, R.M. Cardiorespiratory fitness, weight status and objectively measured sedentary behaviour and physical activity in rural and urban Portuguese adolescents. J. Child. Health Care 2012, 16, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loucaides, C.A.; Chedzoy, S.M.; Bennett, N. Differences in physical activity levels between urban and rural school children in Cyprus. Health Educ. Res. 2004, 19, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucksch, J.; Kopcakova, J.; Inchley, J.; Troped, P.; Sudeck, G.; Sigmundova, D.; Nalecz, H.; Borraccino, A.; Salonna, F.; Veselska, Z.D. Associations between perceived social and physical environmental variables and physical activity and screen time among adolescents in four European countries. Int. J. Public Health 2019, 64, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjolie, A.N.; Thuen, F. School journeys and leisure activities in rural and urban adolescents in Norway. Health Promot. Int. 2002, 17, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-C.; Shih, T.-P.; Ko, W.-C.; Tang, H.-J.; Hsueh, P.-R. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and corona virus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, J.; Enria, D.; Giesecke, J.; Heymann, D.L.; Ihekweazu, C.; Kobinger, G.; Lane, H.C.; Memish, Z.; Oh, M.-d.; Schuchat, A. COVID-19: Towards controlling of a pandemic. Lancet 2020, 395, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Situation Report, 72. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200401-sitrep-72-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=3dd8971b_2 (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Hall, G.; Laddu, D.R.; Phillips, S.A.; Lavie, C.J.; Arena, R. A tale of two pandemics: How will COVID-19 and global trends in physical inactivity and sedentary behavior affect one another? Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitbit. The Impact of Coronavirus on Global Activity. Available online: https://blog.fitbit.com/covid-19-global-activity/ (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Rundle, A.G.; Park, Y.; Herbstman, J.B.; Kinsey, E.W.; Wang, Y.C. COVID-19 Related School Closings and Risk of Weight Gain among Children. Obesity 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekulic, D.; Blazevic, M.; Gilic, B.; Kvesic, I.; Zenic, N. Prospective Analysis of Levels and Correlates of Physical Activity During COVID-19 Pandemic and Imposed Rules of Social Distancing; Gender Specific Study Among Adolescents from Southern Croatia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljanovic Damjanovic, V.; Obradovic Salcin, L.; Zenic, N.; Foretic, N.; Liposek, S. Identifying Predictors of Changes in Physical Activity Level in Adolescence: A Prospective Analysis in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Int J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojskic, H.; Eslami, B. Relationship between Obesity, Physical Activity, and Cardiorespiratory Fitness Levels in Children and Adolescents in Bosnia and Herzegovina: An Analysis of Gender Differences. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez-Porres, J.; Alvero-Cruz, J.R.; Sardinha, L.B.; López-Fernández, I.; Carnero, E.A. Cut-off values for classifying active children and adolescents using the Physical Activity Questionnaire: PAQ-C and PAQ-A. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mraković, M.; Findak, V.; Metikoš, D.; Neljak, B. Developmental characteristics of motor and functional abilities in primary and secondary school pupils. Kineziol. Međunarodni Znan. Časopis Iz Područja Kineziol. I Sporta 1996, 28, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Leger, L.A.; Mercier, D.; Gadoury, C.; Lambert, J. The multistage 20 metre shuttle run test for aerobic fitness. J. Sports Sci. 1988, 6, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgić, I.; Žimbrek, T.; Tratnik, M.; Markovina, J.; Juračak, J. Quality of life in rural areas of Croatia: To stay or to leave? Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 5, 653–660. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman Markovic, B.; Vrdoljak, D.; Kranjcevic, K.; Vucak, J.; Kern, J.; Bielen, I.; Ivezic Lalic, D.; Katic, M.; Reiner, Z. Continental-Mediterranean and rural-urban differences in cardiovascular risk factors in Croatian population. Croat. Med. J. 2011, 52, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujevic, T.; Sporis, G.; Milanovic, Z.; Pantelic, S.; Neljak, B. Differences between health-related physical fitness profiles of Croatian children in urban and rural areas. Coll. Antropol. 2013, 37, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Machado-Rodrigues, A.M.; Coelho, E.S.M.J.; Mota, J.; Padez, C.; Martins, R.A.; Cumming, S.P.; Riddoch, C.; Malina, R.M. Urban-rural contrasts in fitness, physical activity, and sedentary behaviour in adolescents. Health Promot. Int. 2014, 29, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.L.; Kirkner, G.J.; Mayo, K.; Matthews, C.E.; Durstine, J.L.; Hebert, J.R. Urban, rural, and regional variations in physical activity. J. Rural Health 2005, 21, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandercock, G.; Angus, C.; Barton, J. Physical activity levels of children living in different built environments. Prev. Med. 2010, 50, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.F.; Prochaska, J.J.; Taylor, W.C. A review of correlates of physical activity of children and adolescents. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago-Peñas, C.; Rey, E.; Casáis, L.; Gómez-López, M. Relationship between performance characteristics and the selection process in youth soccer players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2014, 40, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, S.L.; McWhannell, N.; Michalsik, L.B.; Twist, C. Anthropometric and physical performance characteristics of top-elite, elite and non-elite youth female team handball players. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malina, R.M.; Bouchard, C.; Bar-Or, O. Growth, Maturation, and Physical Activity; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Drenowatz, C.; Greier, K.; Ruedl, G.; Kopp, M. Association between Club Sports Participation and Physical Fitness across 6-to 14-Year-Old Austrian Youth. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Government of the Republic of Croatia. Coronavirus Protection Measures. Available online: https://vlada.gov.hr/coronavirus-protection-measures/28950 (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Croatian Institute of Public Health. Živjeti Zdravo Kod Kuće [Living Healthy at Home]. Available online: https://www.hzjz.hr/sluzba-promicanje-zdravlja/zivjeti-zdravo-kod-kuce-preporucene-dnevne-razine-tjelesne-aktivnosti-za-sve-dobne-skupine/ (accessed on 14 April 2020).
| Variables | Main Effects | Interaction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environment | Measurement | Environment x Measurement | ||||
| PAL | F-test | p | F-test | p | F-test | p |
| 4.11 | 0.01 | 4.29 | 0.04 | 2.98 | 0.05 | |
| Total (n = 823) | Rural (n = 381) | Urban (n = 442) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical activity at baseline | |||
| Body height | 0.21 * | 0.28 * | 0.19 * |
| Body mass | 0.17 * | 0.19 * | 0.21 * |
| Body mass index | 0.13 * | 0.05 | 0.14 * |
| Broad jump | 0.23 * | 0.35 * | 0.26 * |
| Sit-ups | 0.21 * | 0.28 * | 0.25 * |
| Sit-and-reach | 0.01 | −0.03 | 0.06 |
| Bent-arm-hang | 0.28 * | 0.27 * | 0.35 * |
| Run-400 m | 0.02 | −0.31 * | 0.07 |
| Multi-level-test | 0.39 * | 0.32 * | 0.38 * |
| Physical activity at follow-up | |||
| Body height | 0.07 * | 0.13 * | 0.01 |
| Body mass | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| Body mass index | −0.04 | −0.04 | −0.01 |
| Broad jump | 0.16 * | 0.05 | 0.16 * |
| Sit-ups | 0.19 * | 0.08 | 0.19 * |
| Sit-and-reach | 0.11 * | 0.09 | 0.05 |
| Bent-arm-hang | 0.11 * | 0.05 | 0.18 * |
| Run-400 m | 0.09 | −0.05 | 0.08 |
| Multi-level-test | 0.11 * | 0.04 | 0.17 * |
| Physical activity difference between baseline and follow-up | |||
| Body height | 0.04 | 0.13 * | 0.20 * |
| Body mass | 0.05 | 0.13 * | 0.23 * |
| Body mass index | 0.10 * | 0.09 | 0.18 * |
| Broad jump | 0.10 * | 0.17 * | 0.07 |
| Sit-ups | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.03 |
| Sit-and-reach | −0.05 | −0.11 * | 0.00 |
| Bent-arm-hang | 0.16 * | 0.11 * | 0.12 * |
| Run-400 m | −0.04 | −0.10 * | −0.04 |
| Multi-level-test | 0.28 * | 0.25 * | 0.20 * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zenic, N.; Taiar, R.; Gilic, B.; Blazevic, M.; Maric, D.; Pojskic, H.; Sekulic, D. Levels and Changes of Physical Activity in Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Contextualizing Urban vs. Rural Living Environment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113997
Zenic N, Taiar R, Gilic B, Blazevic M, Maric D, Pojskic H, Sekulic D. Levels and Changes of Physical Activity in Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Contextualizing Urban vs. Rural Living Environment. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(11):3997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113997
Chicago/Turabian StyleZenic, Natasa, Redha Taiar, Barbara Gilic, Mateo Blazevic, Dora Maric, Haris Pojskic, and Damir Sekulic. 2020. "Levels and Changes of Physical Activity in Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Contextualizing Urban vs. Rural Living Environment" Applied Sciences 10, no. 11: 3997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113997
APA StyleZenic, N., Taiar, R., Gilic, B., Blazevic, M., Maric, D., Pojskic, H., & Sekulic, D. (2020). Levels and Changes of Physical Activity in Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Contextualizing Urban vs. Rural Living Environment. Applied Sciences, 10(11), 3997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113997








