Olive Oils Classification via Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Olive Oil Samples
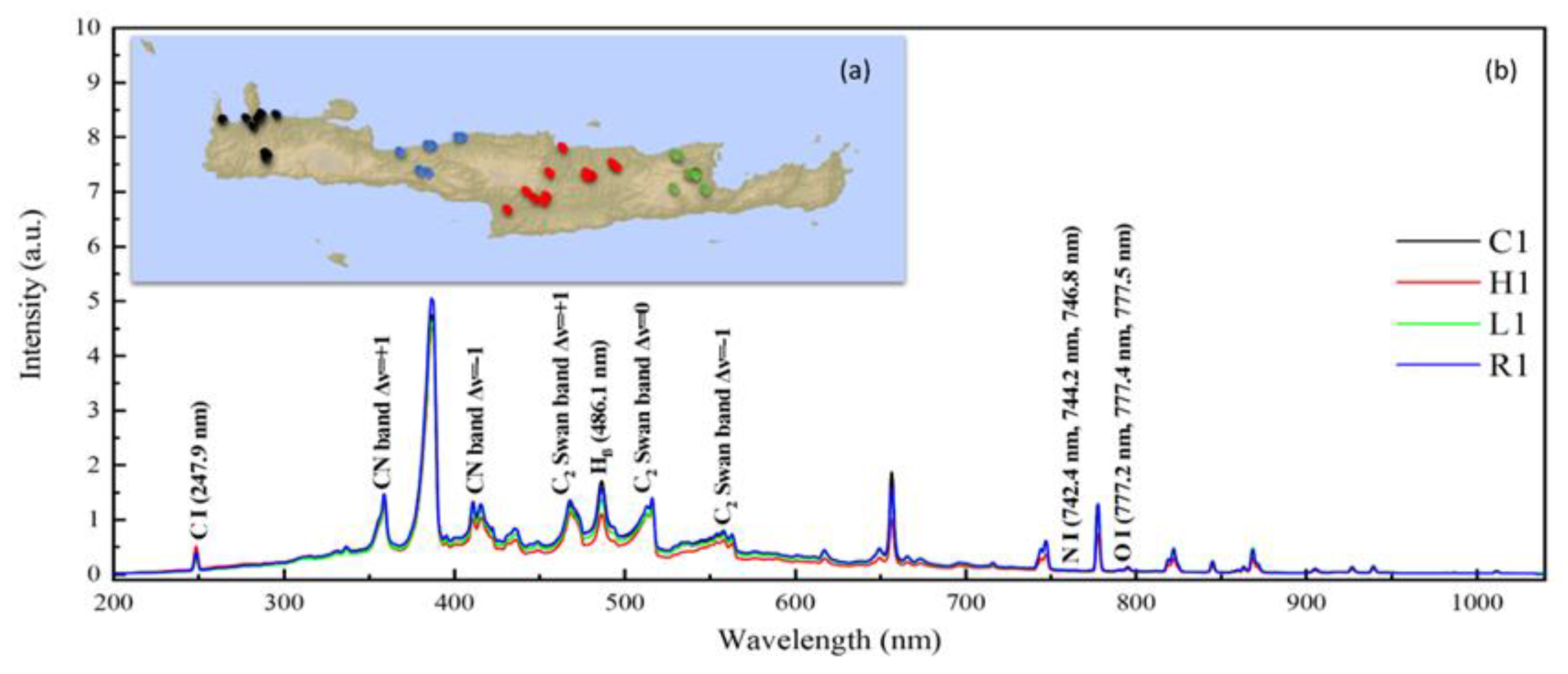
2.2. LIBS Setup
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
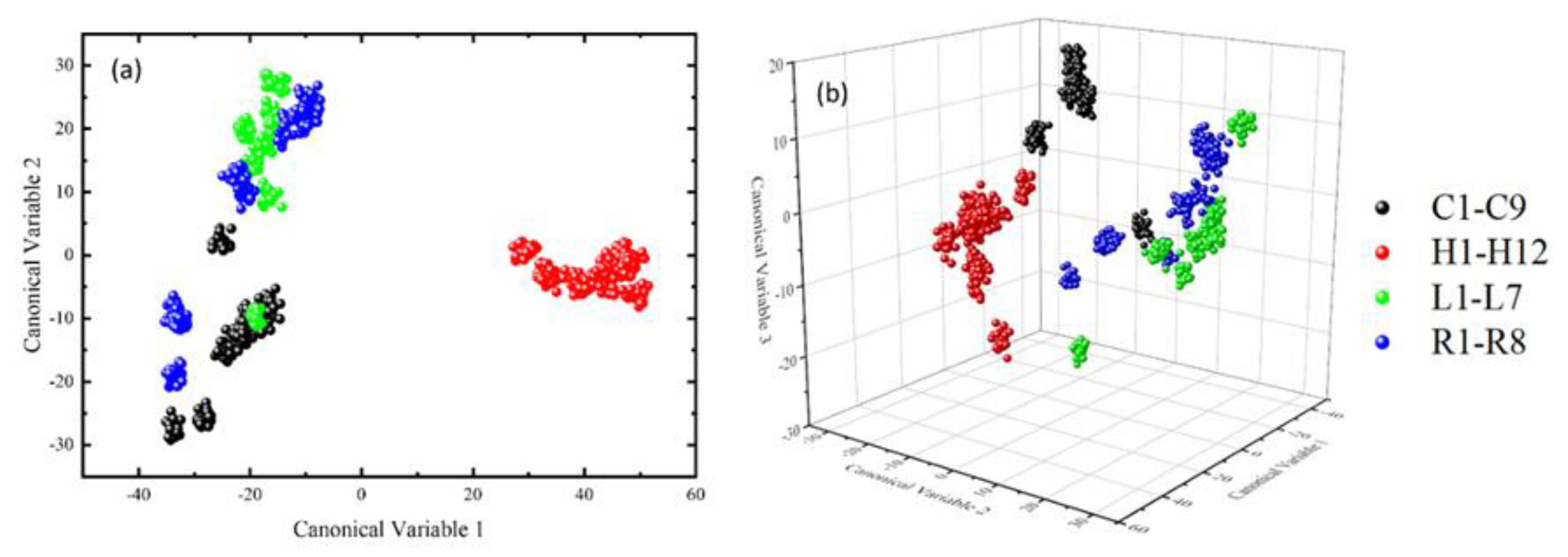
3.1. Classification Using the Raw LIBS Spectroscopic Data
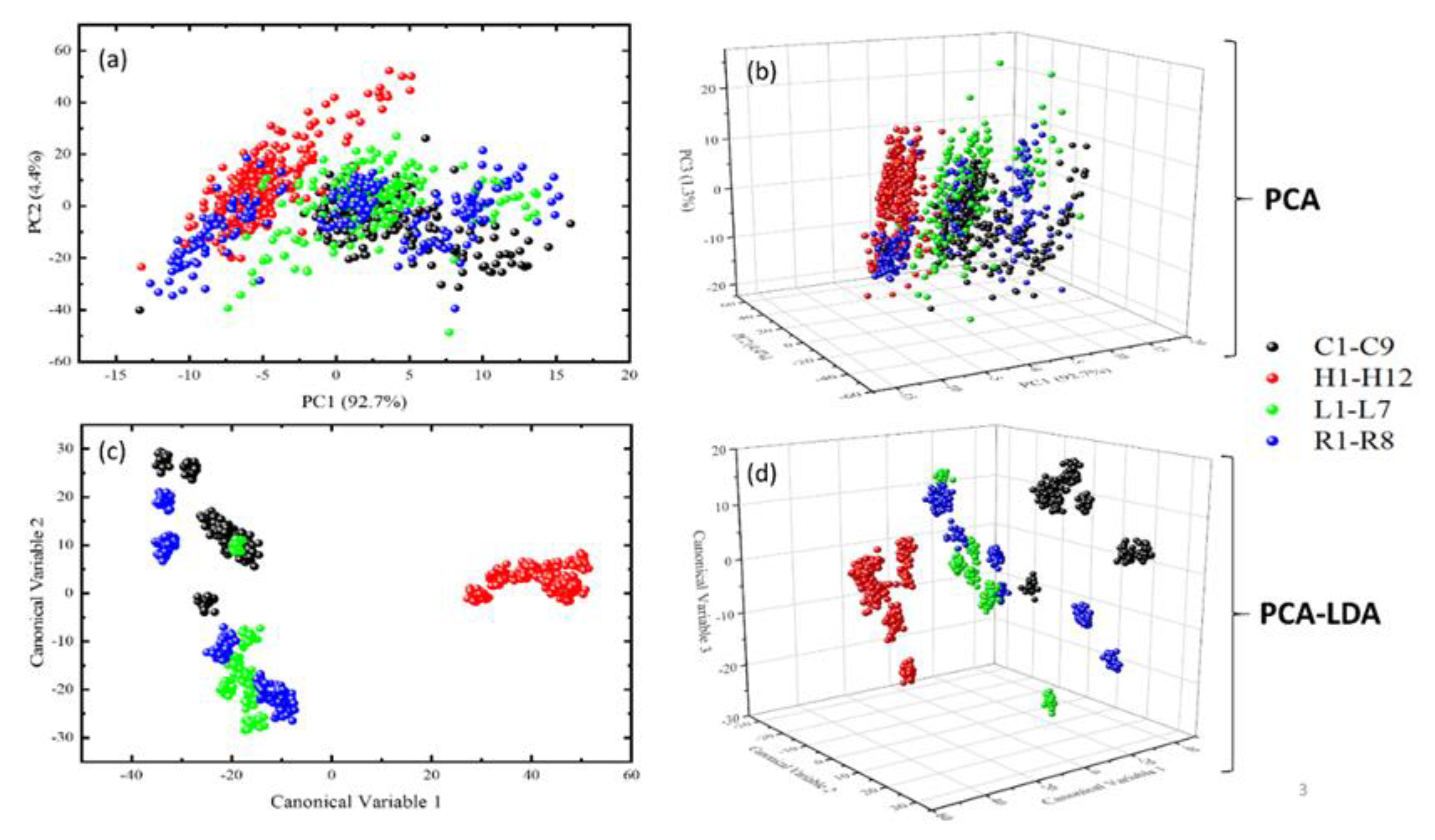
3.2. Classification Results Using the PCA Pre-Processed LIBS Spectroscopic Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Union. Regulation (EU) No 1151/2012 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 November 2012 on quality schemes for agricultural products and foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2012, L343, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Boskou, D. Olive Oil: Chemistry and Technology, 2nd ed.; AOCS Publishing: Champaign, IL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Likudis, Z. Olive Oils with Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) and Protected Geographical Indication (PGI). In Products from Olive Tree; Boskou, D., Clodoveo, M.L., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markiewicz-Keszycka, M.; Cama-Moncunill, R.; Casado-Gavalda, M.P.; Sullivan, C.; Cullen, P.J. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for food authentication. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 28, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standards and Methods. Available online: http://www.internationaloliveoil.org/estaticos/view/224-testing-methods (accessed on 18 December 2019).
- Longobardi, F.; Ventrella, A.; Napoli, C.; Humpfer, E.; Schütz, B.; Schäfer, H.; Kontominas, M.G.; Sacco, A. Classification of olive oils according to geographical origin by using 1H NMR fingerprinting combined with multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, P.V.; Agiomyrgianaki, A.; Christophoridou, S.; Spyros, A.; Dais, P. Geographical Characterization of Greek Virgin Olive Oils (Cv. Koroneiki) Using1H and31P NMR Fingerprinting with Canonical Discriminant Analysis and Classification Binary Trees. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3200–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapp, H.S.; Defernez, M.; Kemsley, E.K. FTIR Spectroscopy and Multivariate Analysis Can Distinguish the Geographic Origin of Extra Virgin Olive Oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6110–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendini, A.; Cerretani, L.; Di Virgilio, F.; Belloni, P.; Bonoli-Carbognim, M.; Lercker, G. Preliminary Evaluation of the Application of the FTIR Spectroscopy to Control the Geographic Origin and Quality of Virgin Olive Oils. J. Food Qual. 2007, 30, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korifi, R.; Le Dréau, Y.; Molinet, J.; Artaud, J.; Dupuy, N. Composition and authentication of virgin olive oil from French PDO regions by chemometric treatment of Raman spectra. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2011, 42, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, M.I.; Marinas, A.; Marinas, J.M.; Urbano, F.J.; Caridad, J.M.; Moalem, M. Chemometric study of Andalusian extra virgin olive oils Raman spectra: Qualitative and quantitative information. Talanta 2016, 156–157, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.P.; Franca, A.S.; Irudayaraj, J. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Applied to Food Safety. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, J.O.; Moncayo, S.; Rosales, J.D.; de Villena, F.J.M.; Alvira, F.C.; Bilmes, G.M. Application of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) and Neural Networks to Olive Oils Analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. 2013, 67, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbesse Kongbonga, Y.G.; Ghalila, H.; Onana, M.B.; Ben Lakhdar, Z. Classification of vegetable oils based on their concentration of saturated fatty acids using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Food Chem. 2014, 147, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazeli, O.; Bellou, E.; Stefas, D.; Couris, S. Laser-based classification of olive oils assisted by machine learning. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremers, D.A.; Radziemski, L.J. Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- De Giacomo, A.; Hermann, J. Laser-induced plasma emission: From atomic to molecular spectra. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 183002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tang, H.; Li, H. Chemometrics in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. J. Chemom. 2018, 32, e2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Gao, L.; Yue, Z.; Shabbir, S.; Xu, W.; Wu, M.; Yu, J. Determination of minor metal elements in steel using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with machine learning algorithms. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2020, 166, 105802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattmann, R.; Monch, I.; Krause, H.; Noll, R.; Couris, S.; Hatziapostolou, A.; Mavromanolakis, A.; Fotakis, C.; Larrauri, E.; Miguel, R. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy for Polymer Identification. Appl. Spectrosc. 1998, 52, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefas, D.; Gyftokostas, N.; Bellou, E.; Couris, S. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Assisted by Machine Learning for Plastics/Polymers Identification. Atoms 2019, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.K.; Sharma, J.; Pathak, A.K.; Ghany, C.T.; Gondal, M.A. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS): A novel technology for identifying microbes causing infectious diseases. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 1221–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudiuso, R.; Melikechi, N.; Abdel-Salam, Z.A.; Harith, M.A.; Palleschi, V.; Motto-Ros, V.; Busser, B. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for human and animal health: A review. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2019, 152, 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ye, L.; Peng, J.; Song, K.; Shen, T.; Zhang, T.; He, Y. Fast Detection of copper content in rice by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with uni- and multivariate analysis. Sensors 2018, 18, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.-T.; Banaru, D.; Sarnet, T.; Hermann, J. Two-step procedure for trace element analysis in food via calibration-free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2018, 150, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zivkovic, S.; Savovic, J.; Kuzmanovic, M.; Petrovic, J.; Momcilovic, M. Alternative analytical method for direct determination of Mn and Ba in peppermint tea based on laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Microchem. J. 2018, 137, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union Commission. Commission Delegated Regulation No 2016/2095 of 26 September 2016 amending Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91 on the characteristics of olive oil and olive-residue oil and on the relevant methods of analysis. Off. J. Eur. Union 2016, L326, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe, I.T. Principal Component Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tharwat, A.; Gaber, T.; Ibrahim, A.; Hassanien, A.E. Linear discriminant analysis: A detailed tutorial. AIC 2017, 30, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cover, T.; Hart, P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1967, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M.W. Evaluation: From Precision, Recall and F-Factor to ROC, Informedness, Markedness & Correlation; Technical Report SIE-07-001; School of Informatics and Engineering, Flinders University: Adelaide, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]

| Sample | k-NN | SVC | LDA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f1-Score | Support | f1-Score | Support | f1-Score | Support | |
| C1 | 0.9 | 11 | 1 | 11 | 0.9 | 11 |
| C2 | 0.9 | 7 | 0.9 | 7 | 1 | 7 |
| C3 | 0.4 | 3 | 0.7 | 3 | 0.9 | 3 |
| C4 | 0.7 | 6 | 0.8 | 6 | 0.5 | 6 |
| C5 | 0.5 | 6 | 0.9 | 6 | 0.4 | 6 |
| C6 | 0.2 | 5 | 0.7 | 5 | 0.2 | 5 |
| C7 | 0.9 | 6 | 0.8 | 6 | 0.9 | 6 |
| C8 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.8 | 4 | 0.4 | 4 |
| C9 | 0.5 | 9 | 0.8 | 9 | 0.5 | 9 |
| H1 | 0.3 | 5 | 0.7 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 |
| H2 | 0.7 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 |
| H3 | 0.3 | 2 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| H4 | 0.3 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| H5 | 0.6 | 7 | 1 | 7 | 0.6 | 7 |
| H6 | 0.2 | 8 | 0.9 | 8 | 0.9 | 8 |
| H7 | 0.4 | 7 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 7 |
| H8 | 0.8 | 10 | 0.9 | 10 | 0.9 | 10 |
| H9 | 0.4 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 | 0.7 | 5 |
| H10 | 0.6 | 10 | 0.9 | 10 | 0.7 | 10 |
| H11 | 0.6 | 6 | 0.7 | 6 | 0.5 | 6 |
| H12 | 0.6 | 5 | 0.8 | 5 | 0.4 | 5 |
| L1 | 0 | 5 | 0.7 | 5 | 0.7 | 5 |
| L2 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| L3 | 0.6 | 9 | 0.8 | 9 | 0.8 | 9 |
| L4 | 0.3 | 8 | 0.8 | 8 | 0.5 | 8 |
| L5 | 0.7 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 5 |
| L6 | 0.4 | 6 | 0.9 | 6 | 0.3 | 6 |
| L7 | 0.8 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| R1 | 0.7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 0.4 | 3 |
| R2 | 0.4 | 5 | 0.8 | 5 | 0.7 | 5 |
| R3 | 0.2 | 8 | 0.9 | 8 | 0.8 | 8 |
| R4 | 0.8 | 8 | 1 | 8 | 0.8 | 8 |
| R5 | 0.8 | 5 | 0.8 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| R6 | 0.8 | 2 | 0.8 | 2 | 0.8 | 2 |
| R7 | 0.7 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 | 0.2 | 5 |
| R8 | 0.8 | 6 | 0.8 | 6 | 0.8 | 6 |
| macro avg | 0.6 | 216 | 0.9 | 216 | 0.7 | 216 |
| k-NN | SVC | LDA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | f1-Score | Support | f1-Score | Support | f1-Score | Support |
| C1 | 0.9 | 11 | 1 | 11 | 1 | 11 |
| C2 | 0.9 | 7 | 0.9 | 7 | 1 | 7 |
| C3 | 0.4 | 3 | 0.7 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| C4 | 0.7 | 6 | 0.8 | 6 | 0.9 | 6 |
| C5 | 0.5 | 6 | 0.9 | 6 | 1 | 6 |
| C6 | 0.2 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 |
| C7 | 0.9 | 6 | 0.8 | 6 | 1 | 6 |
| C8 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.8 | 4 | 0.9 | 4 |
| C9 | 0.5 | 9 | 0.9 | 9 | 0.9 | 9 |
| H1 | 0.3 | 5 | 0.7 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| H2 | 0.7 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 |
| H3 | 0.3 | 2 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| H4 | 0.3 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| H5 | 0.6 | 7 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 7 |
| H6 | 0.2 | 8 | 0.9 | 8 | 1 | 8 |
| H7 | 0.4 | 7 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 7 |
| H8 | 0.8 | 10 | 0.9 | 10 | 1 | 10 |
| H9 | 0.4 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| H10 | 0.6 | 10 | 0.8 | 10 | 0.9 | 10 |
| H11 | 0.6 | 6 | 0.7 | 6 | 0.8 | 6 |
| H12 | 0.6 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 | 0.6 | 5 |
| L1 | 0 | 5 | 0.8 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 |
| L2 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| L3 | 0.6 | 9 | 0.8 | 9 | 0.9 | 9 |
| L4 | 0.3 | 8 | 0.8 | 8 | 0.9 | 8 |
| L5 | 0.7 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| L6 | 0.4 | 6 | 0.9 | 6 | 0.9 | 6 |
| L7 | 0.8 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| R1 | 0.7 | 3 | 0.9 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| R2 | 0.4 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 |
| R3 | 0.2 | 8 | 0.9 | 8 | 0.9 | 8 |
| R4 | 0.8 | 8 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 8 |
| R5 | 0.8 | 5 | 0.8 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| R6 | 0.8 | 2 | 0.8 | 2 | 0.8 | 2 |
| R7 | 0.7 | 5 | 0.9 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| R8 | 0.8 | 6 | 0.8 | 6 | 0.9 | 6 |
| macro avg | 0.6 | 216 | 0.9 | 216 | 0.9 | 216 |
| Sample | f1-Score | Support | Sample | f1-Score | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1 | 5 | H10 | 1 | 5 |
| C2 | 1 | 5 | H11 | 1 | 5 |
| C3 | 1 | 5 | H12 | 1 | 5 |
| C4 | 0.9 | 5 | L1 | 0.7 | 5 |
| C5 | 0.7 | 5 | L2 | 0.9 | 5 |
| C6 | 0.9 | 5 | L3 | 1 | 5 |
| C7 | 1 | 5 | L4 | 1 | 5 |
| C8 | 1 | 5 | L5 | 0.9 | 5 |
| C9 | 1 | 5 | L6 | 1 | 5 |
| H1 | 0.9 | 5 | L7 | 1 | 5 |
| H2 | 0.9 | 5 | R1 | 1 | 5 |
| H3 | 0.7 | 5 | R2 | 0.9 | 5 |
| H4 | 0.6 | 5 | R3 | 0.9 | 5 |
| H5 | 1 | 5 | R4 | 1 | 5 |
| H6 | 0.9 | 5 | R5 | 1 | 5 |
| H7 | 1 | 5 | R6 | 0.9 | 5 |
| H8 | 1 | 5 | R7 | 1 | 5 |
| H9 | 1 | 5 | R8 | 0.9 | 5 |
| macro avg | 0.9 | 180 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gyftokostas, N.; Stefas, D.; Couris, S. Olive Oils Classification via Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103462
Gyftokostas N, Stefas D, Couris S. Olive Oils Classification via Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(10):3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103462
Chicago/Turabian StyleGyftokostas, Nikolaos, Dimitrios Stefas, and Stelios Couris. 2020. "Olive Oils Classification via Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy" Applied Sciences 10, no. 10: 3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103462
APA StyleGyftokostas, N., Stefas, D., & Couris, S. (2020). Olive Oils Classification via Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103462








