Comparative Study on the Corrosion Inhibitive Effect of 2-Mecraptobenzothiazole and Na2HPO4 on Industrial Conveying API 5L X42 Pipeline Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Preparation of Substrates
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
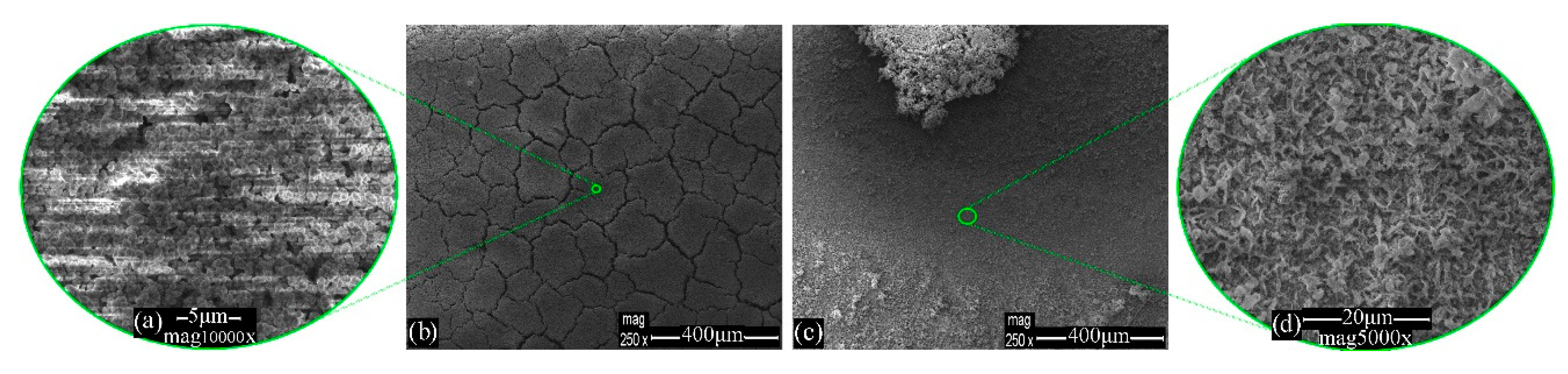
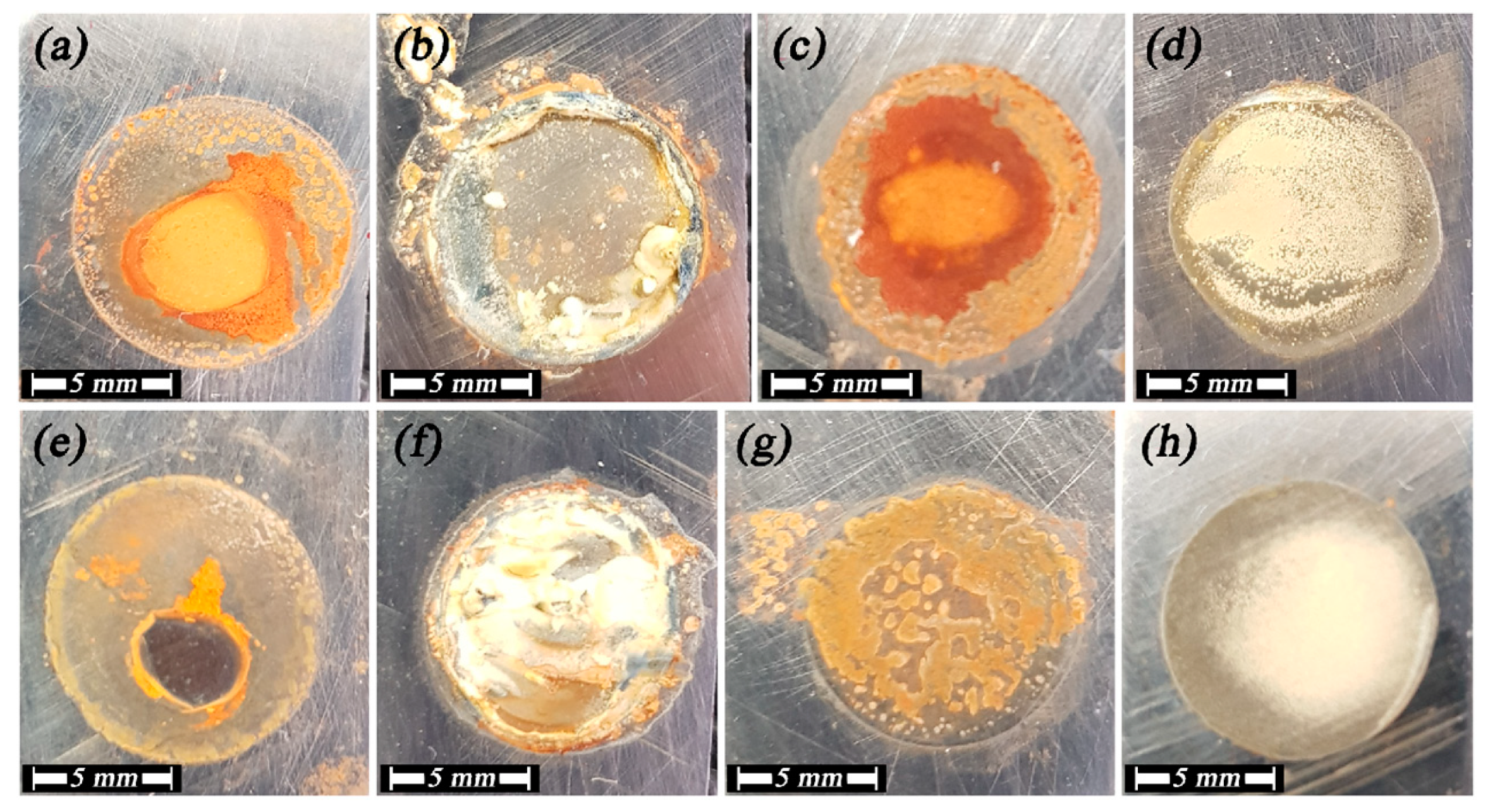
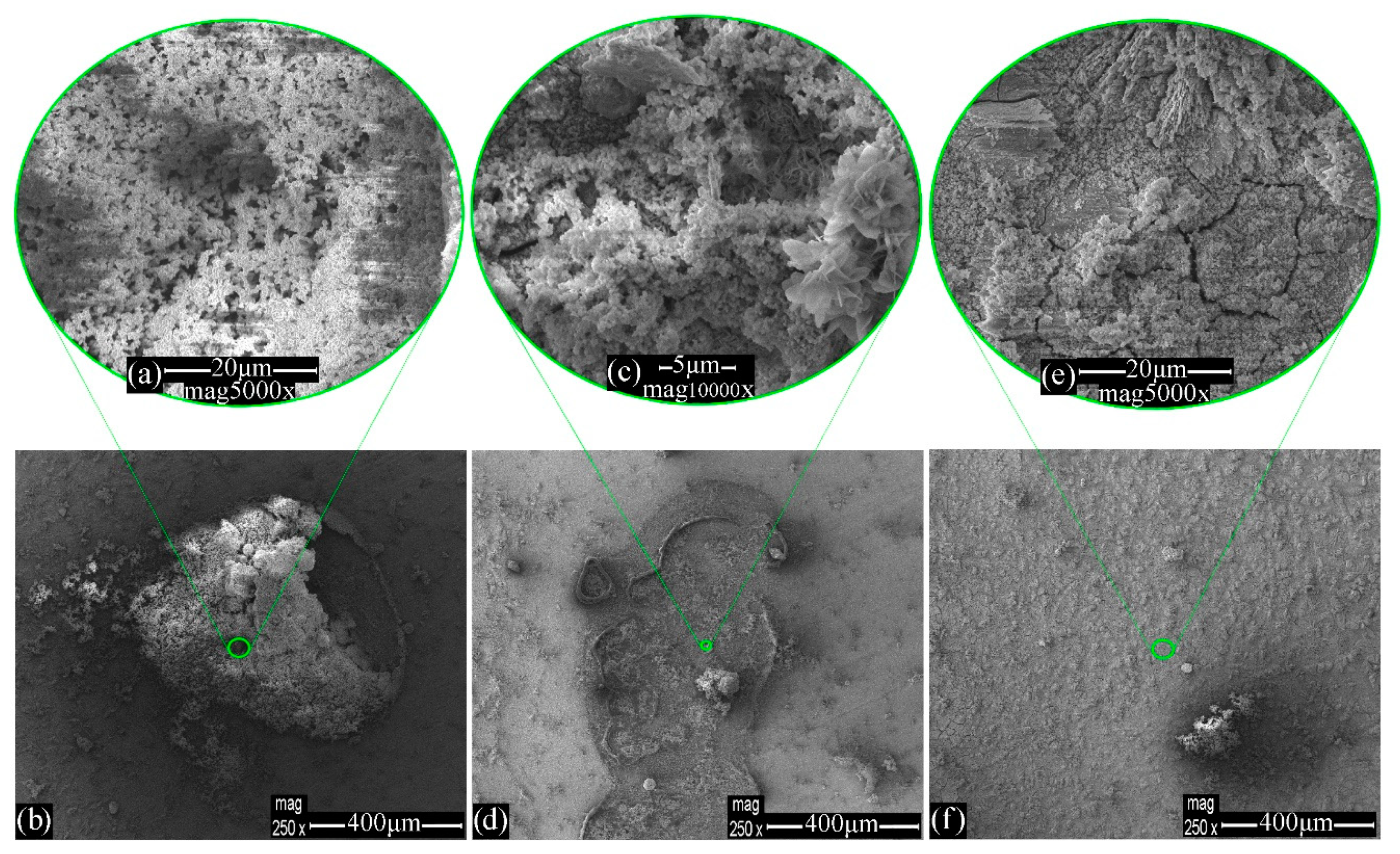
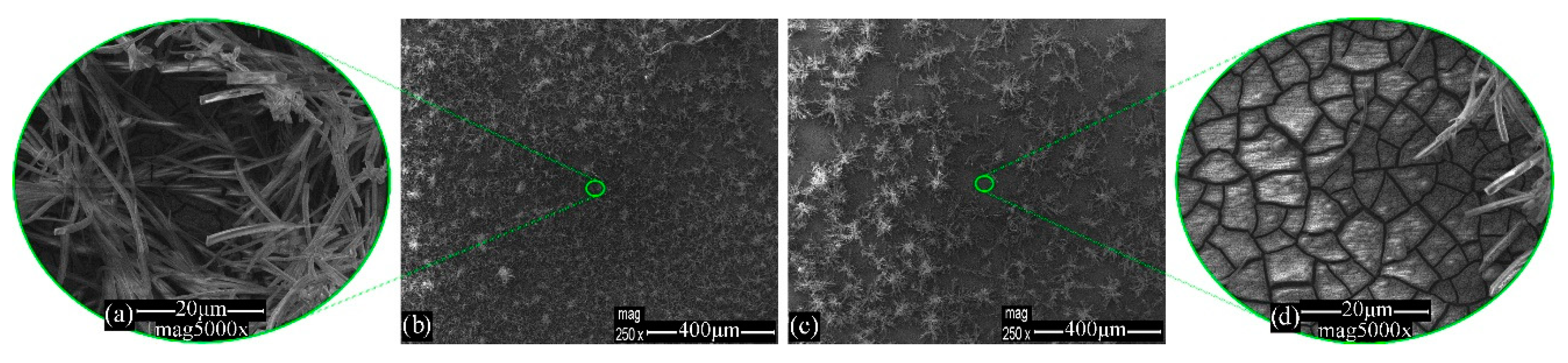
3.1. Morphology Evaluation
3.2. Raman Spectroscopy Analysis
3.3. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
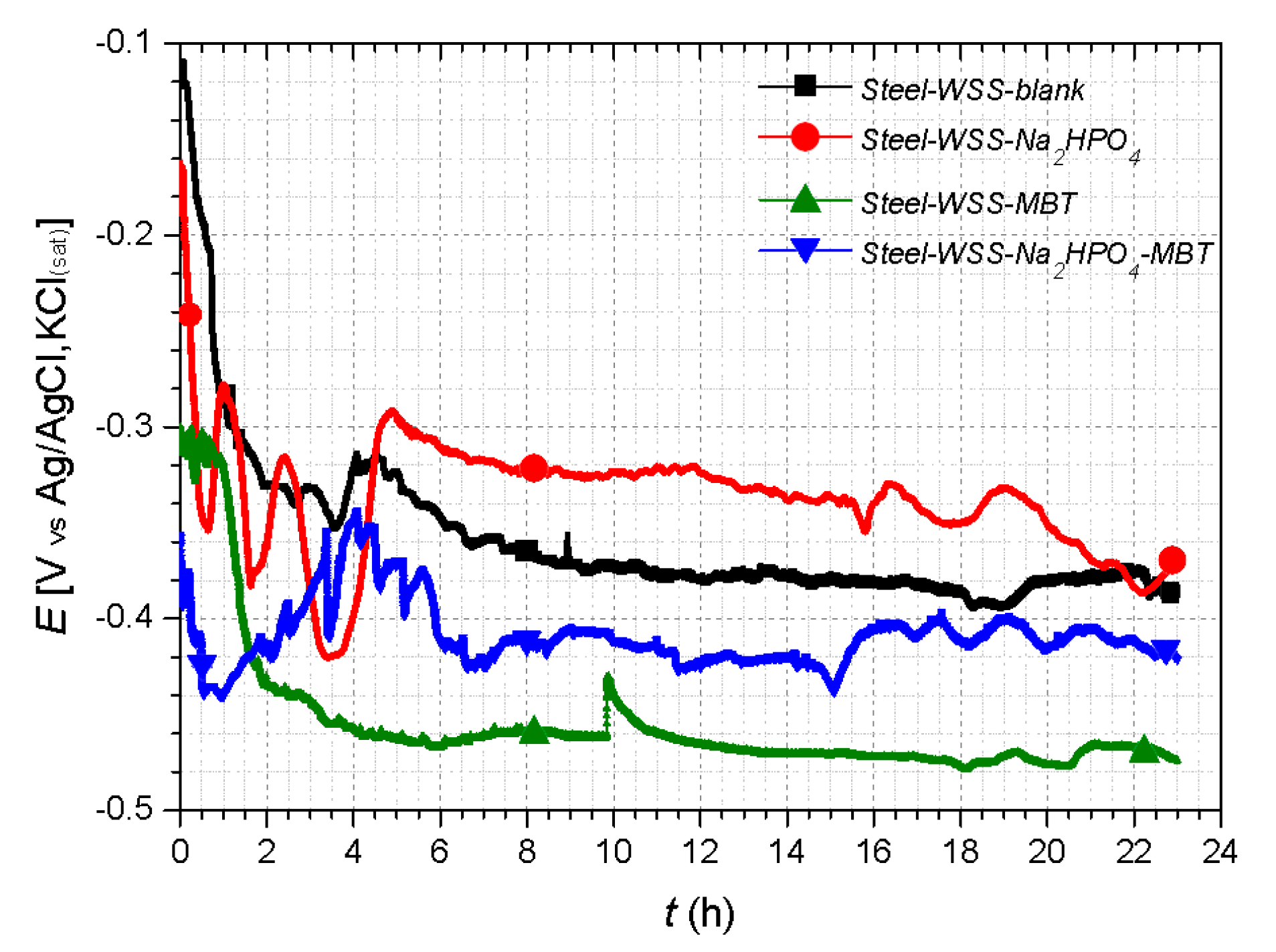
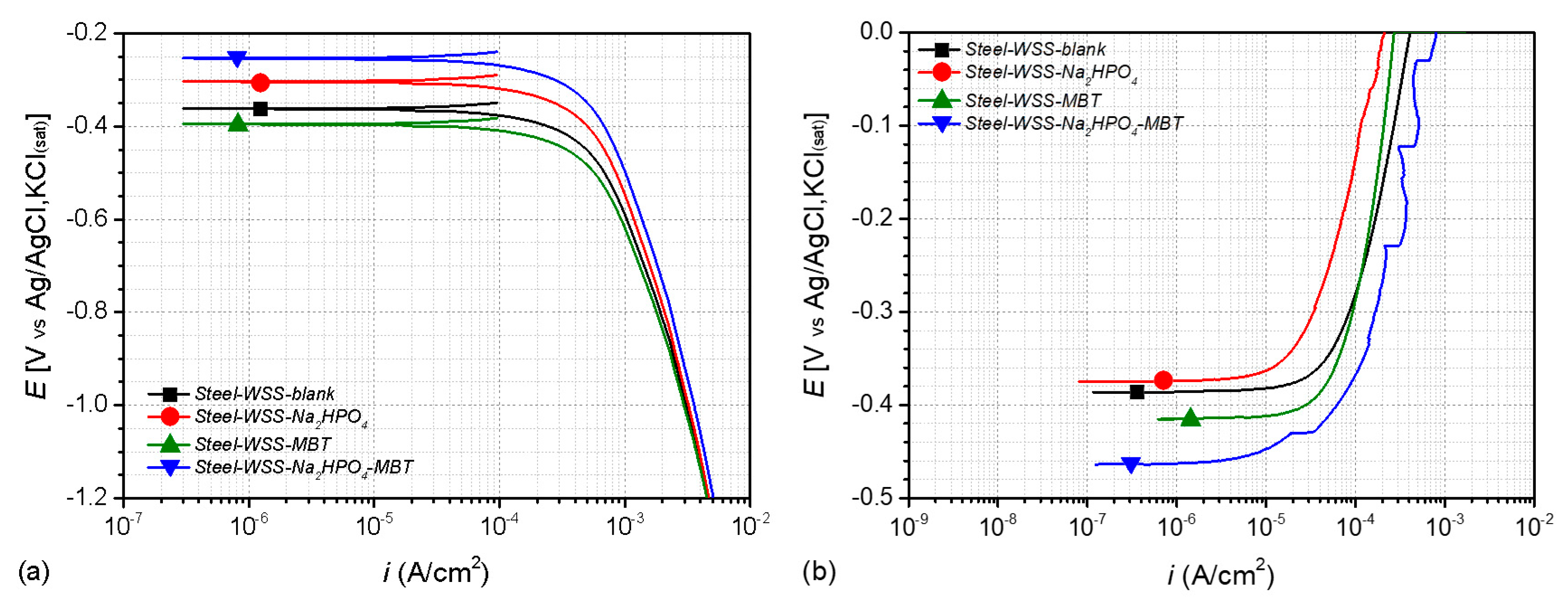
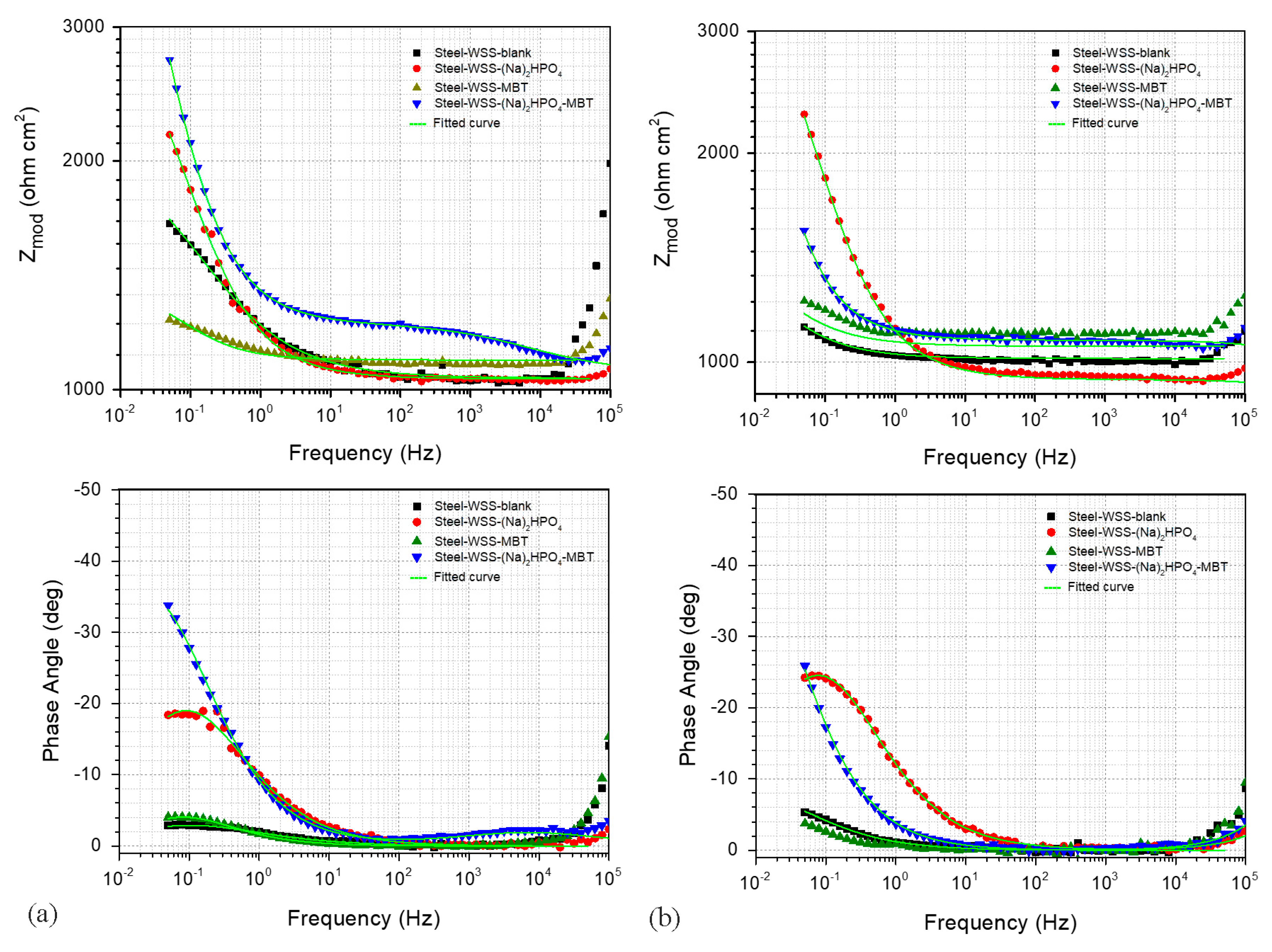
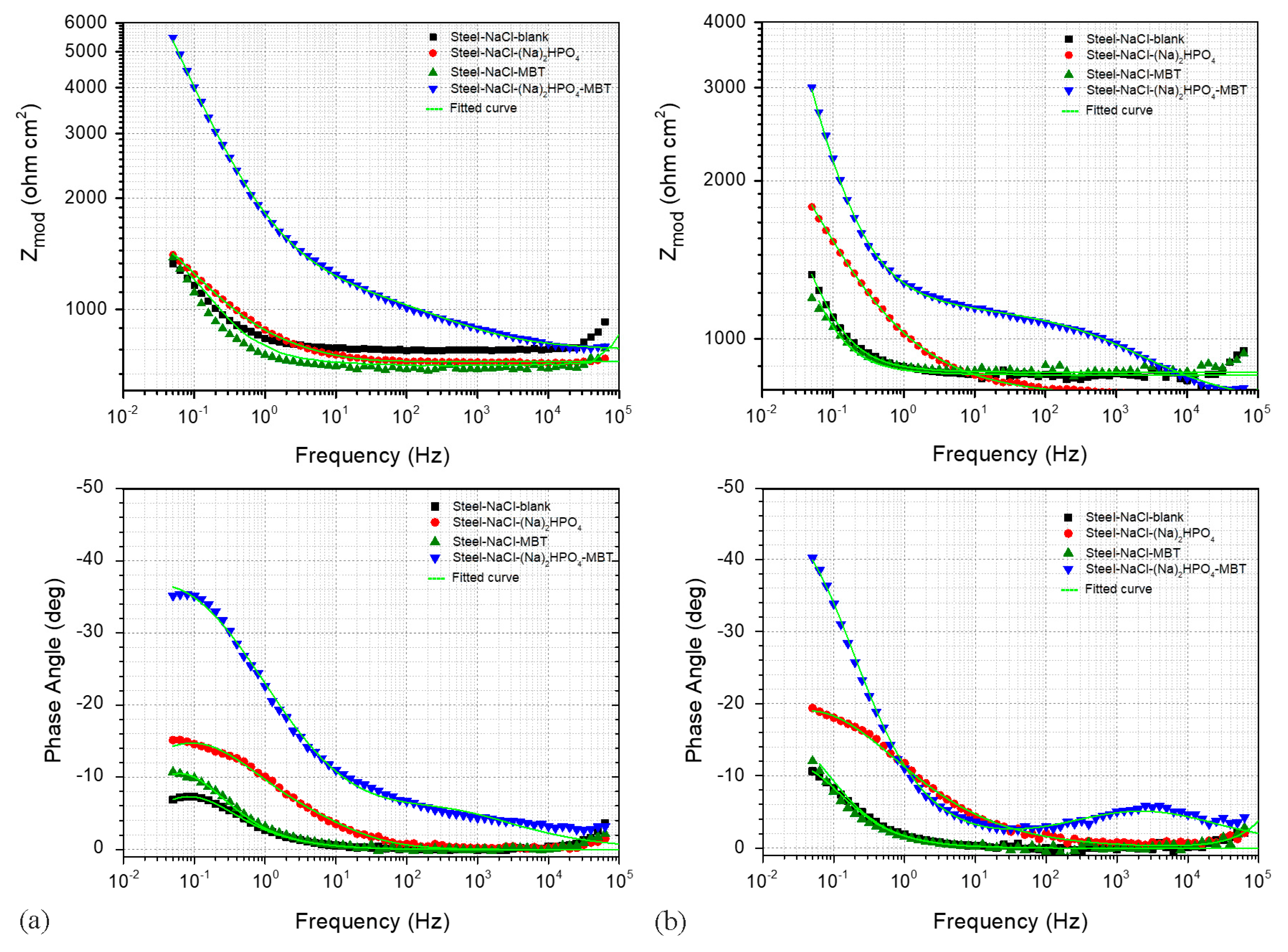
3.4. Electrochemical Studies
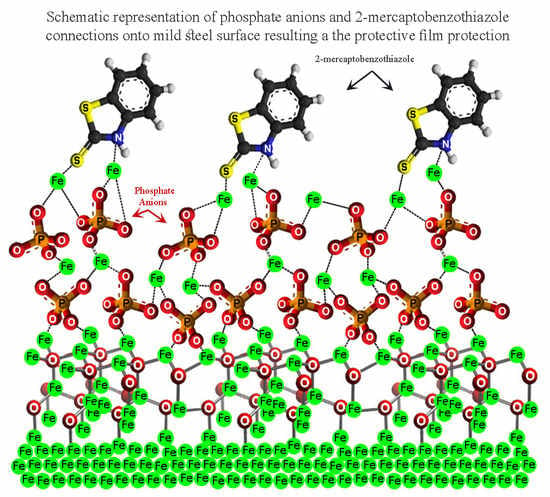
3.5. Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism
3.5.1. The Main Pathway of Corrosion Process in an Fe–C/NaCl (aq) System
3.5.2. Corrosion Inhibitors
3.5.3. The Synergistic Effect
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, U.R.; Taylor, C.A.J. Mechanism of atmospheric rusting. Corros. Sci. 1972, 12, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith William, F.; Hashemi, J.; Wang, S.-H. Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering, 4th ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Raman, A.; Nasrazadani, S.; Sharma, L. Morphology of rust phases formed on weathering steels in various laboratory corrosion tests. Metallography 1989, 22, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Tzeng, H.J.; Wei, L.I.; Wang, L.H.; Oung, J.C.; Shih, H.C. Corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of low-alloy steels under atmospheric conditions. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 1001–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaibari, Z.; Kahraman, R.; Saricimen, H.; Quddus, A. Investigation of atmospheric corrosion of mild steel after treatment by several inhibitor solutions. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2013, 42, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, D.; Díaz, I.; Simancas, J.; Chico, B.; Morcillo, M. Long-term atmospheric corrosion of mild steel. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, I.M.; Arlow, J.S.; Saricimen, H. Initial stages of atmospheric corrosion of steel in the Arabian Gulf. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, T.; Hara, S.; Miyuki, H.; Yamashita, M.; Uchida, H. Composition and protective ability of rust layer formed on weathering steel exposed to various environments. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 2799–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, M.; Chico, B.; Díaz, I.; Cano, H.; de la Fuente, D. Atmospheric corrosion data of weathering steels. A review. Corros. Sci. 2013, 77, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolotyrkin, Y.M. Third International Congress on Metallic Corrosion. Br. Corros. J. 2013, 1, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.; Anwar-ul-Islam, M.; Butt, N.M.; Hussain, N.; Rehman, S.; Arshed, M. Mössbauer study of corrosion of mild steel induced by acid rain. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1999, 241, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migneault, S.; Koubaa, A.; Perré, P.; Riedl, B. Effects of wood fiber surface chemistry on strength of wood–plastic composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 343, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCafferty, E. Surface Chemistry of Aqueous Corrosion Processes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W. Steels: From Materials Science to Structural Engineering; Springer: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Génin, J.M.R. The transformation of chloride-containing green rust one into sulphated green rust two by oxidation in mixed Cl− and SO42− aqueous media. Corros. Sci. 1994, 36, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkins, R.N. The intergranular corrosion and stress corrosion cracking of mild steel in clarke’s solution. Corros. Sci. 1994, 36, 2097–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobin, M.; Malik, A.U.; Andijani, I.N. The effect of heavy metal ions on the localized corrosion behavior of steels. Desalination 2007, 217, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinis, H.; Samar, M.E.H. A method for inhibiting scale formation and corrosion in a cooling water system. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 52, 2609–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.M. Predicting the mechanisms and crack growth rates of pipelines undergoing stress corrosion cracking at high pH. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2657–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliyan, F.F.; Kish, J.R.; Alfantazi, A. Corrosion of New-Generation Steel in Outer Oil Pipeline Environments. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 26, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, N.J.; Mann, S. Influence of inorganic and organic additives on the tailored synthesis of iron oxides. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1991, 87, 3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockris, J.O.M.; Conway, B.E. Hydrogen Overpotential and the Partial Inhibition of the Corrosion of Iron. J. Phys. Colloid Chem. 1949, 53, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ibrahimi, B.; Jmiai, A.; Bazzi, L.; El Issami, S. Amino acids and their derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for metals and alloys. Arab. J. Chem. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCafferty, E. Introduction to Corrosion Science; Springer Science: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, B. Organic compounds as corrosion inhibitors in different environments—A review. Prog. Org. Coat. 1981, 9, 165–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaey, S.A.M.; Abd El-Rehim, S.S.; Taha, F.; Saleh, M.B.; Ahmed, R.A. Inhibition of chloride localized corrosion of mild steel by PO43−, CrO42−, MoO42−, and NO2− anions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2000, 158, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczewska-Boczkowska, K.; Kosmulski, M. 2-Mercaptobenzothiazole as a Corrosion Inhibitor in Low Temperature Ionic Liquids. In Trends in Colloid and Interface Science XXIV; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, N.; Farahani, H. Investigation on 2-mercaptobenzothiazole behavior as corrosion inhibitor for 316-stainless steel in acidic media. Anti Corros. Methods Mater. 2013, 61, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, P.; Wu, L.; Guo, W. Characterization of iron surface modified by 2-mercaptobenzothiazole self-assembled monolayers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 2812–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finšgar, M.; Jackson, J. Application of corrosion inhibitors for steels in acidic media for the oil and gas industry: A review. Corros. Sci. 2014, 86, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, G.; Natarajan, R.; Muralidharan, V.S.; Palaniswamy, N.; Appa Rao, B.V. Inhibition by phosphonic acids—An overview. Anti Corros. Methods Mater. 1997, 44, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multicylinder Test Sequences for Evaluating Automotive Engine Oils: Sequence IID; Sponsored by ASTM Committee B.01 on Automotive Lubricants and D-2 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1993.
- Heit, A.H.; Calvin, C. Corrusion Inhibition Compositions. U.S. Patent C 3, 291 C, 11 September 1962. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM A568/A568M-09. Standard Specification for Sheet, Carbon, Structural, and High-Strength, Low-Alloy, Hot-Rolled and Cold-Rolled, General Requirements for; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D6386-99. Standard Practice for Preparation of Zinc (Hot-Dip Galvanized) Coated Iron and Steel Product and Hardware Surfaces for Painting; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, I. Carbon Steel—Atmospheric Corrosion. In Corrosion Handbook; Revie, R.W., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Etobicoke, ON, Canada, 2008; pp. 515–528. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, R.G.; Scully, J.R.; Shoesmith, D.W.; Buchheit, R.G. The Polarization Resistance Method for Determination of Instantaneous Corrosion Rates. In Electrochemical Techniques in Corrosion Science and Engineering; Schweitzer, P.A., Ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 125–150. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Ci, C.; Li, J.; Lin, K.; Du, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zang, J.; Liu, Y. 4-aminoazobenzene modified natural glucomannan as a green eco-friendly inhibitor for the mild steel in 0.5 M HCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2019, 151, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.M.; Ferreira Fagundes, T.D.S.; Escarpini dos Santos, N.; Shewry de, M.; Rocha, T.; Garrett, R.; Borges, R.M.; Muricy, G.; Valverde, A.L.; Ponzio, E.A. Ircinia strobilina crude extract as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acid medium. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 312, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G44-99. Standard Practice for Exposure of Metals and Alloys by Alternate Immersion in Neutral 3.5% Sodium Chloride Solution; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migahed, M.A.; Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Khamis, E.A.; Zaki, E.G. Quantum chemical calculations, synthesis and corrosion inhibition efficiency of ethoxylated-[2-(2-{2-[2-(2-benzenesulfonylamino-ethylamino)-ethylamino]-ethylamino}-ethylamino)-ethyl]-4-alkyl-benzenesulfonamide on API X65 steel surface under H2S environment. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 212, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Free, M.L.; Yi, G. Electrochemical measurement, modeling, and prediction of corrosion inhibition efficiency of ternary mixtures of homologous surfactants in salt solution. Corros. Sci. 2015, 98, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramaki, K.; Hackerman, N. Inhibition Mechanism of Medium-Sized Polymethyleneimine. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1969, 116, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H. The role of rusts in corrosion and corrosion protection of iron and steel. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1872–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revie, R.W. (Ed.) Uhlig’s Corrosion Handbook; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara, J.; Chico, B.; Simancas, J.; Díaz, I.; de la Fuente, D.; Morcillo, M. An attempt to classify the morphologies presented by different rust phases formed during the exposure of carbon steel to marine atmospheres. Mater. Charact. 2016, 118, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, F. The effect of β-FeOOH on the corrosion behavior of low carbon steel exposed in tropic marine environment. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 112, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Shimodaira, S. The mechanism of formation of iron oxide and oxyhydroxides in aqueous solutions at room temperature. Corros. Sci. 1974, 14, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, D.; Díaz, I.; Alcántara, J.; Chico, B.; Simancas, J.; Llorente, I.; García-Delgado, A.; Jiménez, J.A.; Adeva, P.; Morcillo, M. Corrosion mechanisms of mild steel in chloride-rich atmospheres. Mater. Corros. 2016, 67, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, U.R. Mechanism of rusting. Corros. Sci. 1969, 9, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratmann, M.; Bohnenkamp, K.; Engell, H.J. An electrochemical study of phase-transitions in rust layers. Corros. Sci. 1983, 23, 969–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, V.; Kim, S.; Kang, J.; Gim, J.; Song, J.; Baboo, J.P.; Park, W.; Ahn, D.; Han, J.; Gu, L.; et al. Amorphous iron phosphate: Potential host for various charge carrier ions. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Hihara, L.; Rawlins, J. (Eds.) Intelligent Coatings for Corrosion Control; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Farzanian, K.; Pimenta Teixeira, K.; Perdigão Rocha, I.; De Sa Carneiro, L.; Ghahremaninezhad, A. The mechanical strength, degree of hydration, and electrical resistivity of cement pastes modified with superabsorbent polymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 109, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, N. Effect of Phosphate on the Crystallization of Hematite, Goethite, and Lepidocrocite from Ferrihydrite. Clays Clay Miner. 1999, 47, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertmann, U. Effect of pH on the Formation of Goethite and Hematite from Ferrihydrite. Clays Clay Miner. 1983, 31, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, R.A.; Costa, I.; Faria, D.L.A.D. Characterization of corrosion products formed on steels in the first months of atmospheric exposure. Mater. Res. 2003, 6, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labinger, J.A. Bond-stretch isomerism: A case study of a quiet controversy. C. R. Chim. 2002, 5, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamilselvi, M.; Kamaraj, P.; Arthanareeswari, M.; Devikala, S.; Selvi, J.A. Development of nano SiO2 incorporated nano zinc phosphate coatings on mild steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 332, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, D.; Lepková, K.; Becker, T. Carbon steel corrosion: A review of key surface properties and characterization methods. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 4580–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, D.; Alcántara, J.; Chico, B.; Díaz, I.; Jiménez, J.A.; Morcillo, M. Characterisation of rust surfaces formed on mild steel exposed to marine atmospheres using XRD and SEM/Micro-Raman techniques. Corros. Sci. 2016, 110, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, S.; Odziemkowski, M.; Irish, D.E.; Brossard, L.; Ménard, H. In situ micro-Raman spectroscopy to investigate pitting corrosion product of 1024 mild steel in phosphate and bicarbonate solutions containing chloride and sulfate ions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2001, 31, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaiveegan, P.; Elangovan, N.; Nishimura, T.; Rajendran, N. Weathering Steel in Industrial-Marine-Urban Environment: Field Study. Mater. Trans. 2016, 57, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhyarani, N.; Skanth, G.; Berchmans, S.; Yegnaraman, V.V.; Pradeep, T. A Combined Surface-Enhanced Raman-X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopic Study of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole Monolayers on Polycrystalline Au and Ag Films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 209, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2001; pp. 283–327. [Google Scholar]
- De Faria, D.L.A.; Venâncio Silva, S.; de Oliveira, M.T. Raman microspectroscopy of some iron oxides and oxyhydroxides. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1997, 28, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolitsch, U.; Bernhardt, H.-J.; Lengauer, C.L.; Blass, G.; Tillmanns, E. Allanpringite, Fe3(PO4)2(OH)35H2O, a new ferric iron phosphate from Germany, and its close relation to wavellite. Eur. J. Mineral. 2006, 18, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Brow, R.K. A Raman Study of Iron-Phosphate Crystalline Compounds and Glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 3123–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, M.; Zheng, K.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, H. In Situ Electrochemical Investigation of Pyrite Assisted Leaching of Chalcopyrite. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, H813–H819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, I.; Böttger, U.; Pavlov, S.G.; Hübers, H.W.; Hiesinger, H.; Jessberger, E.K. Laser alteration on iron sulfides under various environmental conditions. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2017, 48, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramanan, M.; Skanth, G.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Vijayamohanan, K.; Pradeep, T. Self-assembled Monolayers of Two Aromatic Disulfides and a Diselenide on Polycrystalline Silver Films: An Investigation by SERS and XPS. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 212, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ali Asaad, M.; Sarbini, N.N.; Sulaiman, A.; Ismail, M.; Huseien, G.F.; Abdul Majid, Z.; Bothi Raja, P. Improved corrosion resistance of mild steel against acid activation: Impact of novel Elaeis guineensis and silver nanoparticles. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 63, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, G.; Prangnell, J. The significance of vivianite in archaeological settings. Geoarchaeology 2006, 21, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, Y.; Calado, L.M.; Shakoor, R.A.; Raj, R.; Kahraman, R.; Taryba, M.G.; Montemor, M.F. Epoxy coatings modified with a new cerium phosphate inhibitor for smart corrosion protection of steel. Corros. Sci. 2019, 159, 108128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Banerjee, T. Effect of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole on aciddissolution and hydrogen absorption of steel. Corros. Sci. 1972, 12, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.G.; Scully, J.R.; Shoesmith, D.W.; Buchheit, R.G. Passivity and localised corrosion. In Electrochemical Techniques in Corrosion Science and Engineering; Schweitzer, P.A., Ed.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 55–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Akbarzade, K.; Danaee, I. Corrosion inhibition of carbon steel immersed in a 1M HCl solution using benzothiazole derivatives. Arab. J. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, N.; Utatsu, K.; Park, S.; Kitsukawa, S.; Sekine, K. Correlation between corrosion rate and AE signal in an acidic environment for mild steel. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.G. Electrochemical thermodynamics and kinetics of relevance to corrosion. In Electrochemical Techniques in Corrosion Science and Engineering; Schweitzer, P.A., Ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 9–54. [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima, I. Carbon Steel—Corrosion in Fresh Waters. In Corrosion Handbook; Revie, R.W., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Etobicoke, ON, Canada, 2008; pp. 529–544. [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima, I. Carbon Steel—Corrosion by Seawater. In Corrosion Handbook; Revie, R.W., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Etobicoke, ON, Canada, 2008; pp. 545–553. [Google Scholar]
- Shifler, D.A.; Aylor, D.M. Testing in environments-seawater. In Corrosion Tests and Standards Application and Interpretation; Baboian, R., Ed.; ASTM International: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005; pp. 362–379. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.H.; Mansfeld, F. Technical Note:Concerning the Conversion of the Constant Phase Element Parameter Y0into a Capacitance. Corrosion 2001, 57, 747–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Lingyan, L.; Lu, J.; Che, C.; Zhong, Z. Corrosion behavior of lanthanum-based conversion coating modified with citric acid on hot dip galvanized steel in aerated 1M NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.S.; Cole, R.H. Dispersion and Absorption in Dielectrics II. Direct Current Characteristics. J. Chem. Phys. 1942, 10, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zuo, Y.; Zhao, X. The effects of 8-hydroxyquinoline on corrosion performance of a Mg-rich coating on AZ91D magnesium alloy. Corros. Sci. 2013, 76, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaesche, H. Corrosion of Metals: Physicochemical Principles and Current Problems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K. Ferrites and Ferrates: Chemistry and Applications in Sustainable Energy and Environmental Remediation; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 489–491. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D.G.; Slade, R.C.T. Structural Aspects of Layered Double Hydroxides. In Layered Double Hydroxides; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. Karaxi, E.; Kartsonakis, I.A.; Charitidis, C.A. Chloride ion entrapment by calcined layered double hydroxides. Int. J. Struct. Integr. 2016, 7, 788–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolard, F.; Bourrié, G. Chapter 5 Geochemistry of Green Rusts and Fougerite. Adv. Agron. 2008, 99, 227–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davesne, E.; Dideriksen, K.; Christiansen, B.C.; Sonne, M.; Ayala-Luis, K.B.; Koch, C.B.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Stipp, S.L.S. Free energy of formation for green rust sodium sulphate (NaFeII6FeIII3(OH)18(SO4)2(s)). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 6451–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Evans, D.G. Layered Double Hydroxides; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Tsui, T.-F. The solubility of CO2 in water and sea water. J. Geophys. Res. 1971, 76, 4203–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Drissi, S.H.; Pytkiewicz, J.; Génin, J.M.R. The anionic species competition in iron aqueous corrosion: Role of various green rust compounds. Corros. Sci. 1997, 39, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Génin, J.M.R.; Refait, P.; Olowe, A.A.; Abdelmoula, M.; Fall, I.; Drissi, S.H. Identification of Green Rust Compounds in the Aqueous Corrosion Processes of Steels; the Case of Microbially Induced Corrosion and Use of 78 K CEMS. Hyperfine Interact. 1998, 112, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, H.; Tounsi, A.; Makayssi, A.; Derja, A.; Benzakour, J.; Outzourhit, A. Corrosion inhibition of Armco iron by 2-mercaptobenzimidazole in sodium chloride 3% media. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 2936–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavian, M.; Ashhari, S. Corrosion inhibition performance of 2-mercaptobenzimidazole and 2-mercaptobenzoxazole compounds for protection of mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1720–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gece, G.; Bilgiç, S. Quantum chemical study of some cyclic nitrogen compounds as corrosion inhibitors of steel in NaCl media. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1876–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrakaty, R.H.; Wazzan, N.A.; Obot, I.B. Theoretical Study of the Mechanism of Corrosion Inhibition of Carbon Steel in Acidic Solution by 2-aminobenzothaizole and 2- Mercatobenzothiazole. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 3535–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Harrison, A.; Li, X.; Whittaker, G.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Cao, P.; Zhang, Z. Study of the adsorption of benzimidazole and 2-mercaptobenzothiazole on an iron surface by confocal micro-Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2004, 35, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, M.; Danaee, I.; Maddahy, M.H.; RashvandAvei, M. Correlated ab Initio and Electroanalytical Study on Inhibition Behavior of 2-Mercaptobenzothiazole and Its Thiole–Thione Tautomerism Effect for the Corrosion of Steel (API 5L X52) in Sulphuric Acid Solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 14875–14889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.T.; Chen, S.-H.; Qi, C.-S. Protection of copper corrosion by carbazole and N-vinylcarbazole self-assembled films in NaCl solution. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2003, 33, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, M.; Bilgiç, S.; Yılmaz, H. The inhibition effects of some cyclic nitrogen compounds on the corrosion of the steel in NaCl mediums. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 195, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.P.; Liu, Z.Y.; Qiu, Y.Q.; Wang, G.D. The improvement of weathering resistance by increasing P contents in cast strips of low carbon steels. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 4342–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, G.; Fujieda, S.; Shinoda, K.; Suzuki, S. Influence of phosphate species on green rust I transformation and local structure and morphology of γ-FeOOH. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2446–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankara, T.S.N. Surface pretreatment by phosphate conversion coatings—A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2005, 9, 130–177. [Google Scholar]
- Nespolo, M. Iron Metabolism. From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Consequences. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Struct. Biol. 2017, 73, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, H.C.W. Phosphates Geochemical, Geobiological and Materials Importance.: Edited by Matthew, J.; Kohn, John Rakovan and John, M. Hughes. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, Vol. 48 (2002). Mineralogical Society of America, 1015 Eighteenth Street, Washington, D.C. 20036, U.S.A. US $40, $30 to MSA, GS, CMS members (ISBN 0 939950 60 X). Can. Mineral. 2003, 41, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbaud, R.; White, M.L.; Poulton, S.W. Surface charge and growth of sulphate and carbonate green rust in aqueous media. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 108, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttner, G.; Strittmatter, J.; Sandhöfner, S. Phosphorus Tripodal Ligands. In Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry II; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keeffe, M. The Bond Valence Method in Crystal Chemistry. In Modern Perspectives in Inorganic Crystal Chemistry; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, J.-P.; Tronc, E.; Chanéac, C. Iron oxides: From molecular clusters to solid. A nice example of chemical versatility. C. R. Geosci. 2006, 338, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twigg, M.V.; Burgess, J. Iron. In Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry II; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 403–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, J.H.; Smith, M.B. Phosphorus Ligands. In Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry II; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 253–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Hendry, M.J.; Essilfie-Dughan, J. Transformation of two-line ferrihydrite to goethite and hematite as a function of pH and temperature. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitrakar, R.; Tezuka, S.; Sonoda, A.; Sakane, K.; Ooi, K.; Hirotsu, T. Phosphate adsorption on synthetic goethite and akaganeite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, C.M. Hydrolysis of inorganic iron (III) salts. Chem. Rev. 1984, 84, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.M.; Botella, M.A.; Cerdá, A.; Martinez, V. Phosphorus uptake and translocation in salt-stressed melon plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 158, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongshao, Z.; Stanforth, R. Competitive adsorption of phosphate and arsenate on goethite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4753–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ler, A.; Stanforth, R. Evidence for surface precipitation of phosphate on goethite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 2694–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Génin, J.-M.R.; Bourrié, G.; Trolard, F.; Abdelmoula, M.; Jaffrezic, A.; Refait, P.; Maitre, V.; Humbert, B.; Herbillon, A. Thermodynamic Equilibria in Aqueous Suspensions of Synthetic and Natural Fe(II)−Fe(III) Green Rusts: Occurrences of the Mineral in Hydromorphic Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorovich, V.I.; Beznosikov, B.O. Morphological and functional study of the thrombocytes in essential polycythemia and thrombocytopenia (Werlhof’s disease). Lab. Anal. Clin. Bacteriol. Inmunol. Parasitol. Hematol. Anat. Patol. Quim. Clin. 1961, 39, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nriagu, J.O. Stability of vivianite and ion-pair formation in the system Fe3(PO4)2-H3PO4H3PO4-H2O. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1972, 36, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Chun, D.-M. α-Fe2O3 as a photocatalytic material: A review. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 498, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCafferty, E. Acid-Base Properties of Surface Oxide Films. In Surface Chemistry of Aqueous Corrosion Processes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



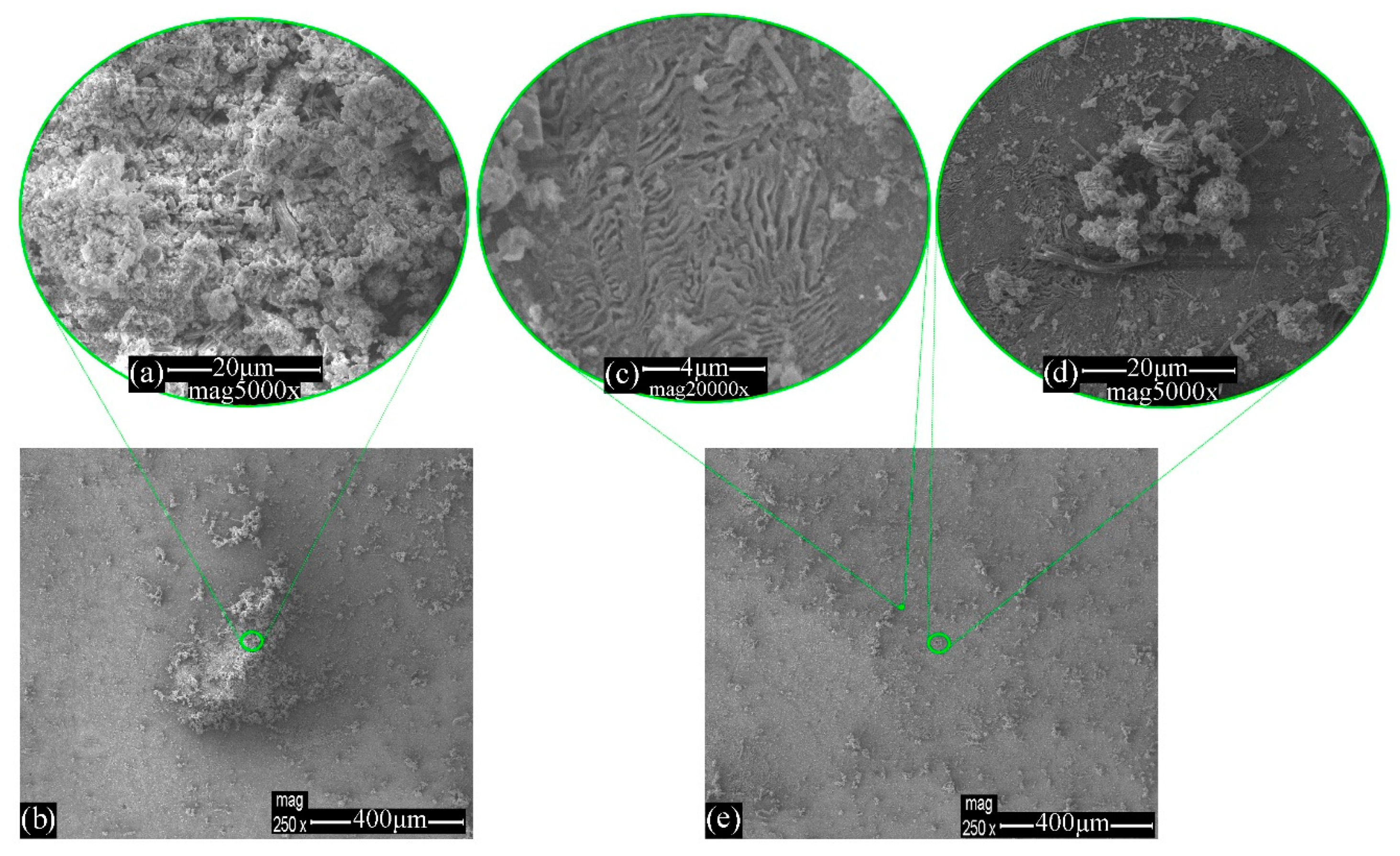

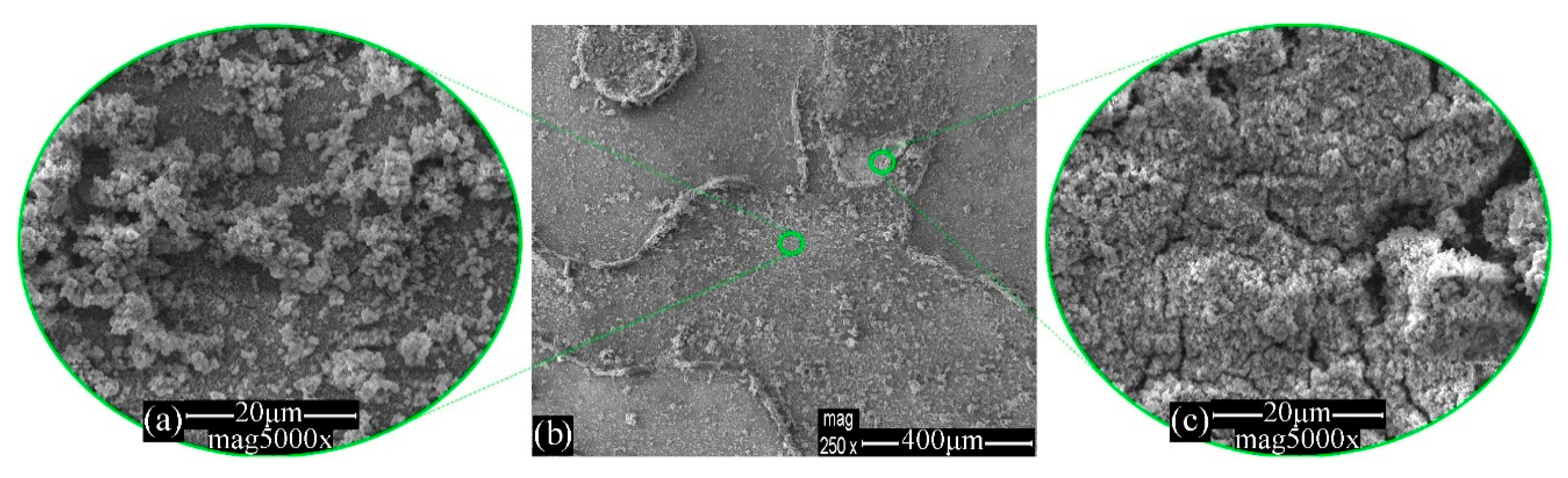

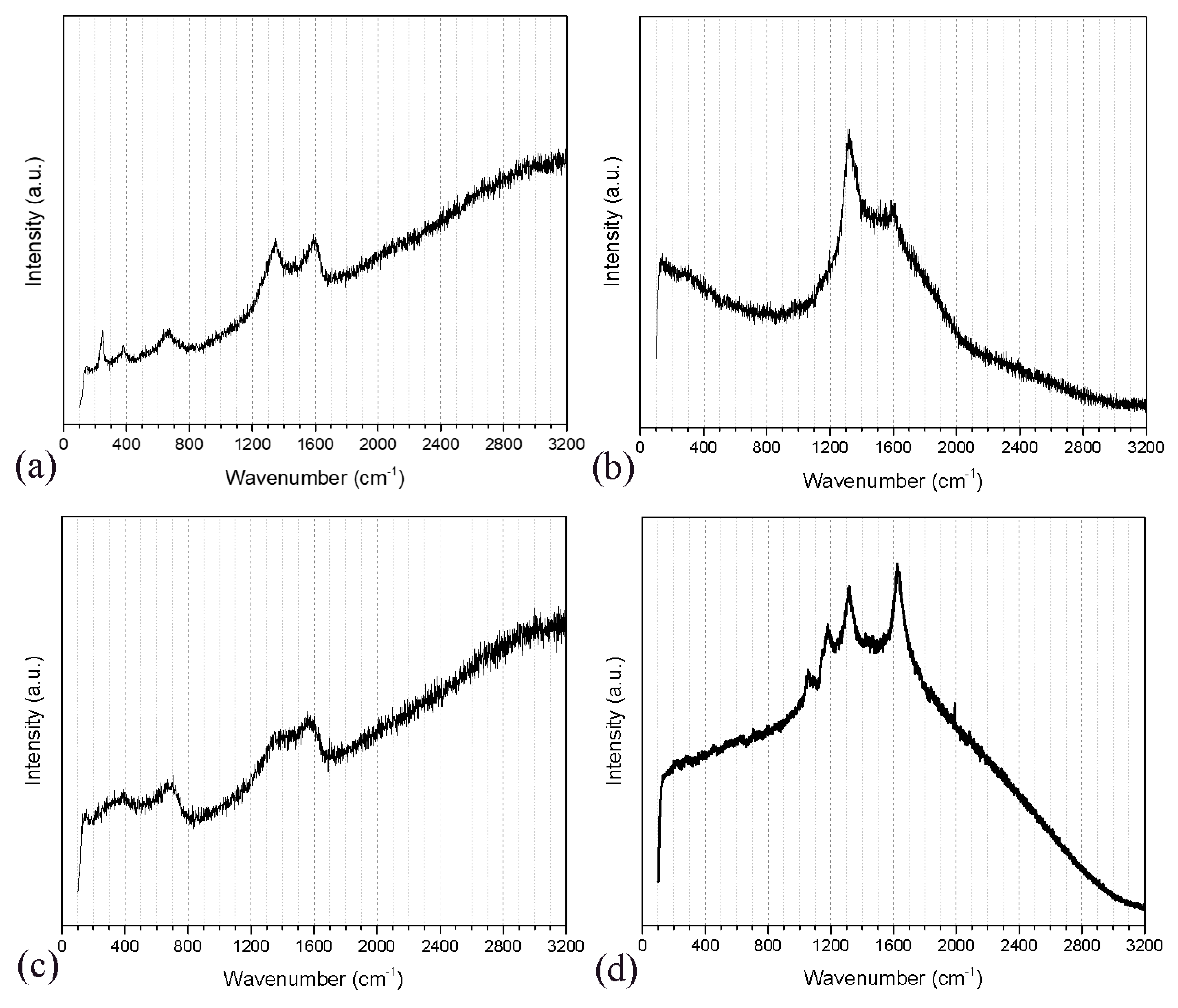
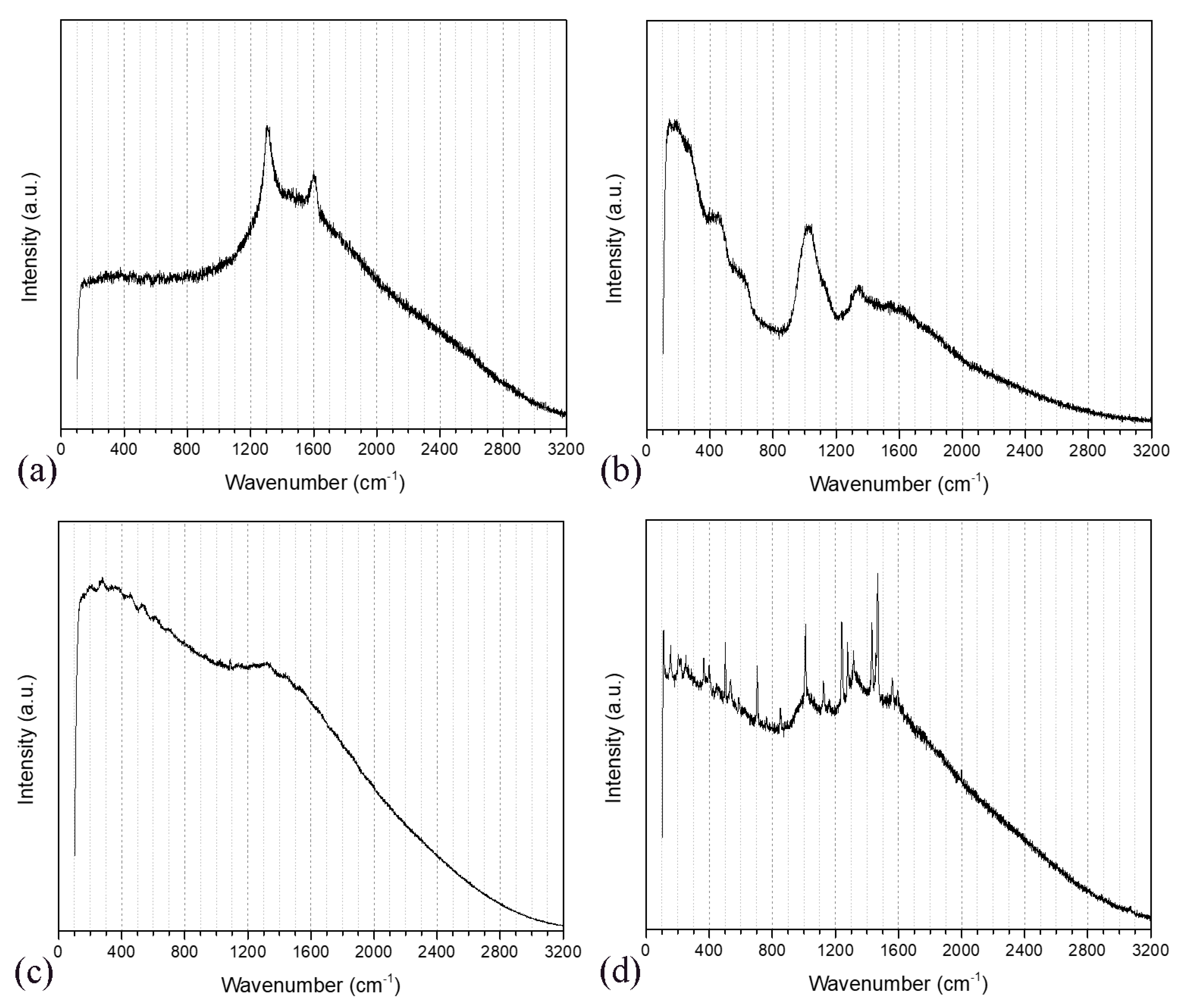




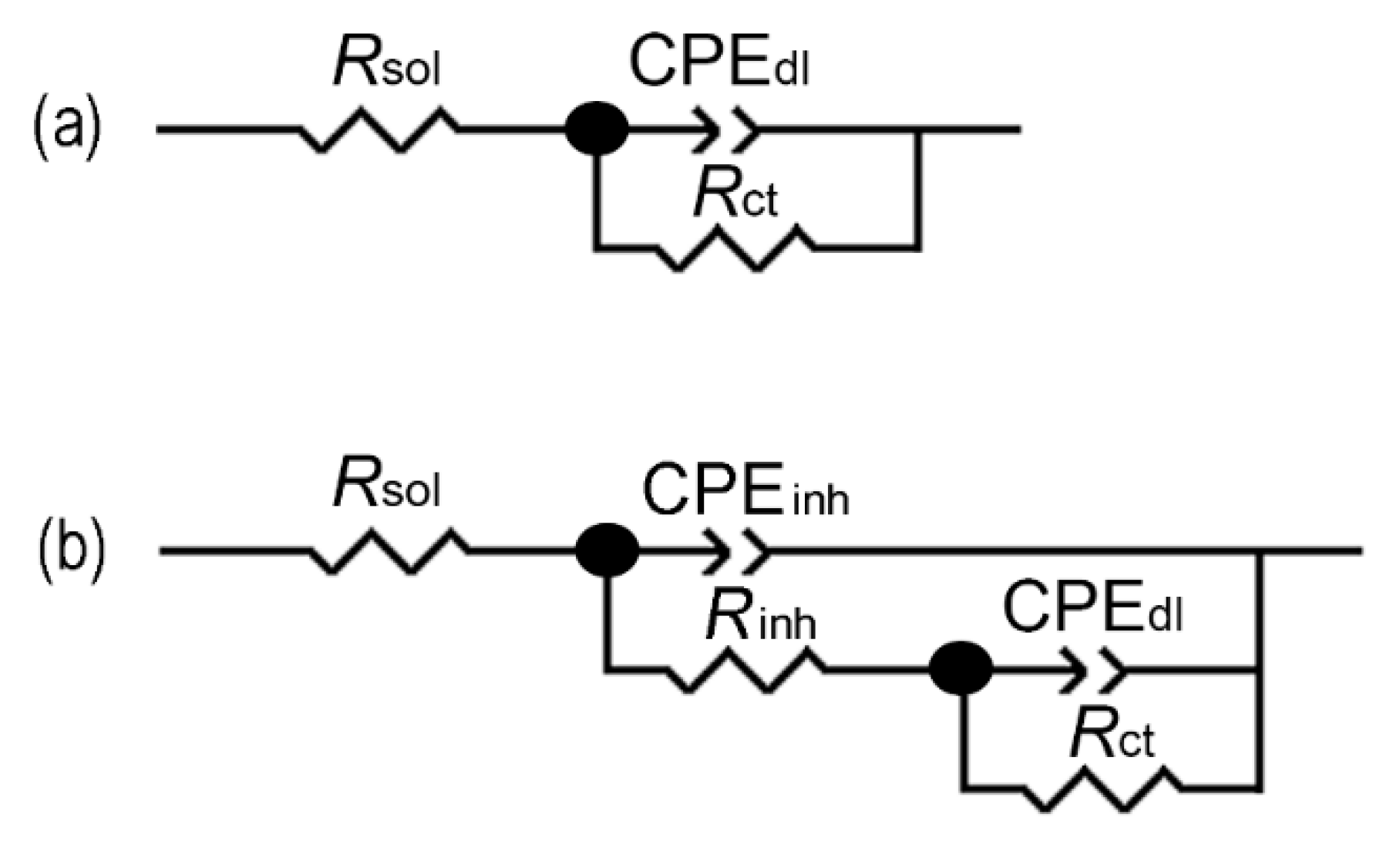
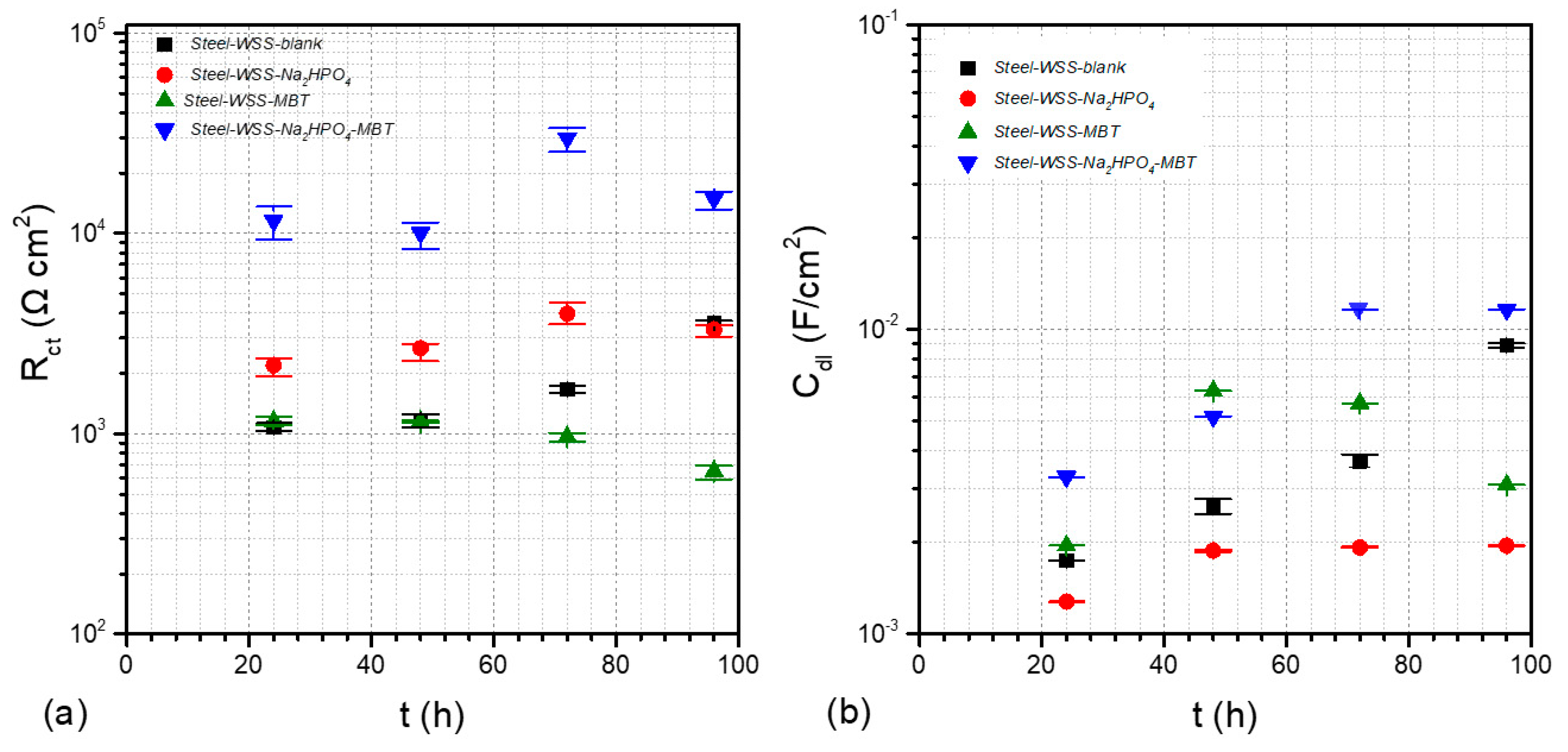
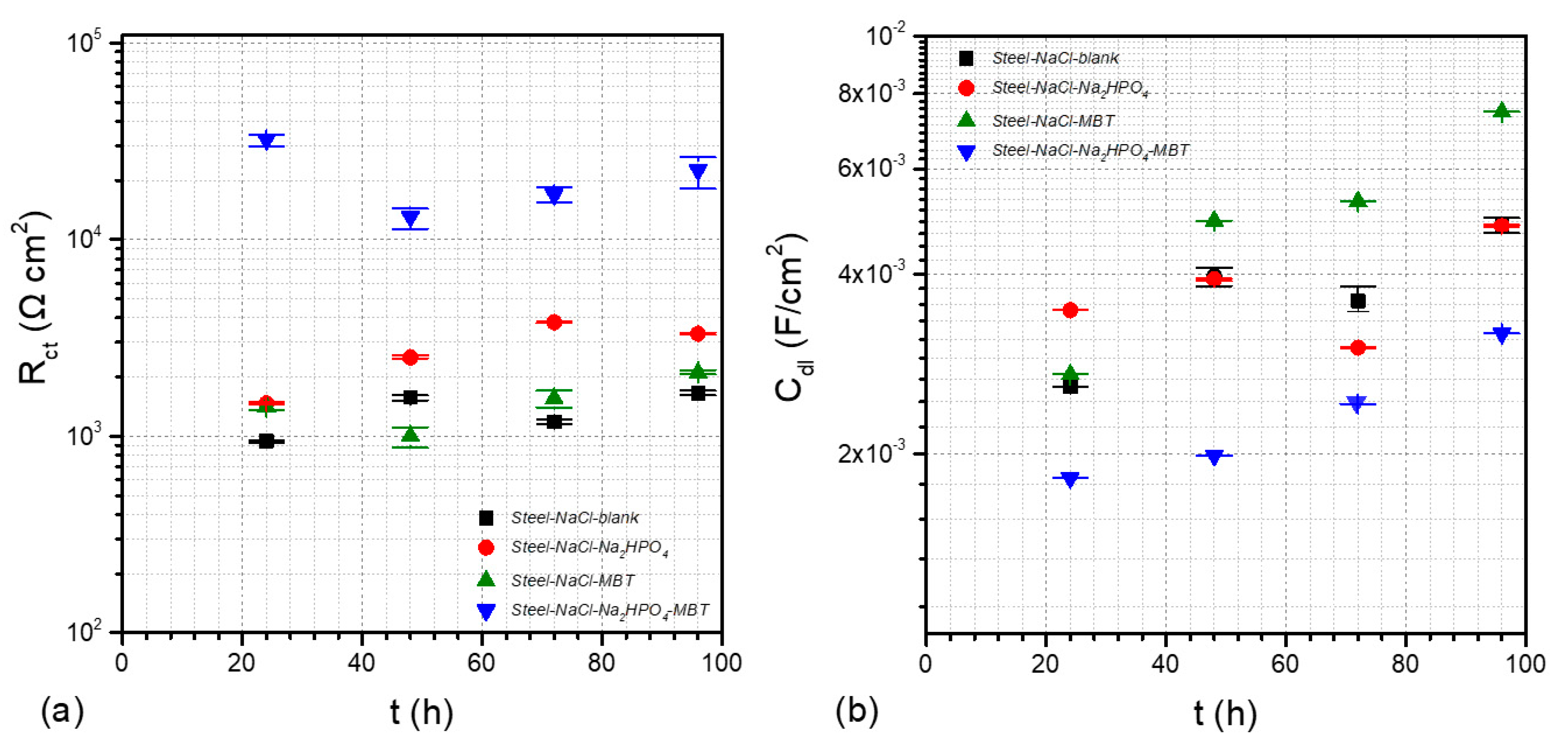
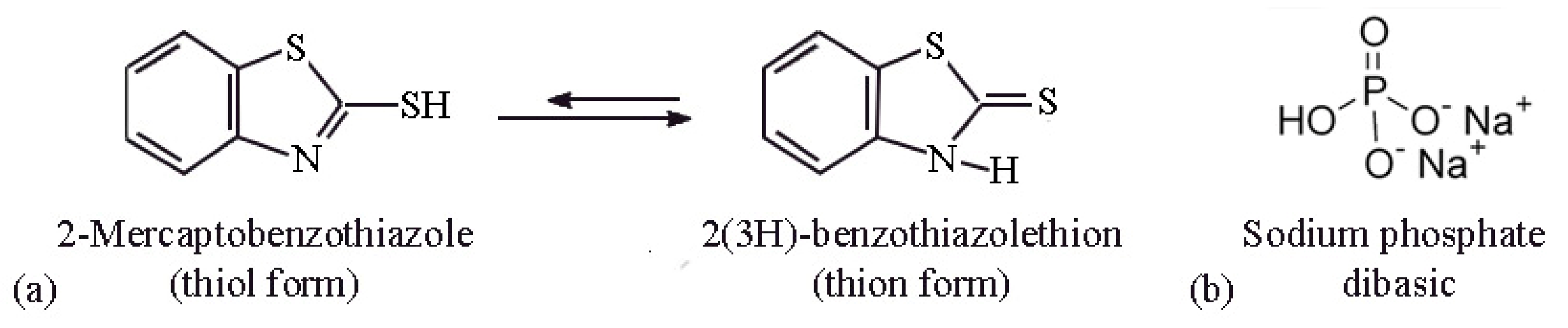

| Κ | Ca | Mg | Fe | Mn | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.7733 | 0.346 | 0.09755 | 1.36 | 0.005 | 0.0052 |
| Composition | pH | Sample |
|---|---|---|
| - | - | Steel–blank |
| WSS | 7.41–7.52 | Steel–WSS–blank |
| WSS + 0.849 g/L Na2HPO4 | 7.78–7.97 | Steel–WSS–Na2HPO4 |
| WSS + 1.014 g/L MBT | 7.33–7.52 | Steel–WSS–MBT |
| WSS + 0.849 g/L Na2HPO4 + 1.014 g/L MBT | 7.38–7.82 | Steel–WSS–Na2HPO4–MBT |
| NaCl 3.5 wt % | 7.71–7.72 | Steel–NaCl–blank |
| NaCl 3.5 wt % + 0.849 g/L Na2HPO4 | 7.78–7.97 | Steel–NaCl–Na2HPO4 |
| NaCl 3.5 wt % + 1.014 g/L MBT | 7.33–7.52 | Steel–NaCl–MBT |
| NaCl 3.5 wt % + 0.849 g/L Na2HPO4 + 1.014 g/L MBT | 7.38–7.82 | Steel–NaCl–Na2HPO4–MBT |
| Sample | Spectrum at | wt % Element Concentration | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | Fe | C | Si | P | S | Na | ||
| Steel–blank | Figure 2a | 0.1 | 92.9 | 3.7 | 2.0 | - | - | - |
| Steel–WSS–blank | Figure 3b | 52.3 | 44.0 | 1.5 | 2.3 | - | - | - |
| Steel–WSS–Na2HPO4 | Figure 4b | 39.9 | 39.5 | 2.6 | 0.2 | 14.2 | - | 2.4 |
| Figure 4f | 16.9 | 72.4 | 3.0 | 1.7 | 2.7 | - | 2.3 | |
| Steel–WSS–MBT | Figure 5e | 44.6 | 46.1 | 4.2 | 1.2 | - | 3.6 | - |
| Figure 5f | 44.4 | 46.9 | 4.3 | 1.5 | - | 2.9 | - | |
| Steel–WSS–Na2HPO4–MBT | Figure 6c | 31.2 | 40.0 | 7.8 | 0.4 | 11.3 | 3.6 | 2.6 |
| Steel–NaCl–Blank | Figure 7e | 61.3 | 38.7 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Steel–NaCl–Na2HPO4 | Figure 8b | 39.3 | 39.0 | 3.0 | 0.3 | 14.9 | - | - |
| Figure 8d | 35.5 | 49.9 | 3.3 | 0.1 | 6.5 | - | 3.0 | |
| Steel–NaCl–MBT | Figure 9b | 23.0 | 67.4 | 4.7 | 1.5 | - | 2.2 | - |
| Steel–NaCl–Na2HPO4–MBT | Figure 10b | 47.1 | 26.8 | 4.5 | - | 16.0 | 5.2 | 0.4 |
| Sample | EOC (V) (Cathodic Branch) (24 h Exposure) | EOC (V) (Anodic Branch) (24 h Exposure) | Rp (Kohm cm2) (96 h Exposure) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel–WSS–blank | −0.361 | −0.386 | 6.279 |
| Steel–WSS–Na2HPO4 | −0.303 | −0.374 | 2.852 |
| Steel–WSS–MBT | −0.394 | −0.415 | 4.731 |
| Steel–WSS–Na2HPO4–MBT | −0.253 | −0.463 | 6.730 |
| Steel–NaCl–blank | −0.435 | −0.462 | 2.822 |
| Steel–NaCl–Na2HPO4 | −0.586 | −0.406 | 1.800 |
| Steel–NaCl–MBT | −0.282 | −0.412 | 3.132 |
| Steel–NaCl–Na2HPO4–MBT | −0.536 | −0.408 | 4.054 |
| Time of Exposure (h) | Synergistic Parameter (Si) | |
|---|---|---|
| Steel–WSS–Na2HPO4–MBT | 24 | 4.76 |
| Steel–NaCl–Na2HPO4–MBT | 24 | 22.6 |
| Steel–WSS–Na2HPO4–MBT | 96 | 1.99 |
| Steel–NaCl–Na2HPO4–MBT | 96 | 4.22 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kartsonakis, I.A.; Stamatogianni, P.; Karaxi, E.K.; Charitidis, C.A. Comparative Study on the Corrosion Inhibitive Effect of 2-Mecraptobenzothiazole and Na2HPO4 on Industrial Conveying API 5L X42 Pipeline Steel. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010290
Kartsonakis IA, Stamatogianni P, Karaxi EK, Charitidis CA. Comparative Study on the Corrosion Inhibitive Effect of 2-Mecraptobenzothiazole and Na2HPO4 on Industrial Conveying API 5L X42 Pipeline Steel. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(1):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010290
Chicago/Turabian StyleKartsonakis, Ioannis A., Panagiota Stamatogianni, Evangelia K. Karaxi, and Costas A. Charitidis. 2020. "Comparative Study on the Corrosion Inhibitive Effect of 2-Mecraptobenzothiazole and Na2HPO4 on Industrial Conveying API 5L X42 Pipeline Steel" Applied Sciences 10, no. 1: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010290
APA StyleKartsonakis, I. A., Stamatogianni, P., Karaxi, E. K., & Charitidis, C. A. (2020). Comparative Study on the Corrosion Inhibitive Effect of 2-Mecraptobenzothiazole and Na2HPO4 on Industrial Conveying API 5L X42 Pipeline Steel. Applied Sciences, 10(1), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010290