Public Sector Transformation in Emerging Economies: Factors Affecting Change Adoption in Pakistan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Approaches to Change Management
2.2. Organizational Change in the Public Sector
2.3. Factors Affecting Change Adoption in the Public Sector
2.4. Theoretical Framework
3. Methodology
3.1. Questionnaire Design
3.2. Questionnaire Distribution and Respondents
3.3. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. The Measurement Model
4.2. Structural Model and Hypothesis Testing
5. Discussion and Concluding Remarks
6. Theoretical Significance and Practical Implication
6.1. Theoretical Contributions
6.2. Methodological Contributions
6.3. Practical Contributions
7. Limitations and Indications for Further Research
- Institutional Theory to better understand how formal structures and normative pressures influence reform;
- Public Value Theory to assess how reforms contribute to citizen-centered service improvements;
- Change Readiness Models to evaluate emotional and psychological dimensions of reform adoption among employees.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdallah, S., & Fan, I. S. (2012). Framework for e-government assessment in developing countries: Case study from Sudan. Electronic Government, an International Journal, 9(2), 158–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulraheem, I., Mordi, C., Oja, Y., & Ajonbadi, H. (2013). Outcomes of planned organisational change in the Nigerian public sector: Insights from the Nigerian higher education institutions. Economic Insights–Trends and Challenges, 2(1), 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Aiyetan, A. O., & Das, D. K. (2021). Evaluation of the factors and strategies for water infrastructure project delivery in South Africa. Infrastructures, 6(5), 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeel, A., & Subramaniam, I. D. (2013). The role of transformation leadership style in motivating public sector employees in Libya. Australian Journal of Basic and A Lied Sciences, 7(2), 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ali, A. A., Singh, S. K., Al-Nahyan, M., & Sohal, A. S. (2017). Change management through leadership: The mediating role of organizational culture. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 25(4), 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alas, R., & Elenurm, T. (2018). Transformation in society and changes in Estonian management and business thinking. In R. A. Crane (Ed.), The Influence of Business Cultures in Europe: An Exploration of Central, Eastern, and Northern Economies (pp. 41–67). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, B. J., & Anwar, G. (2021). An empirical study of employees’ motivation and its influence job satisfaction. International Journal of Engineering, Business and Management, 5(2), 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Al Jawali, H., Darwish, T. K., Scullion, H., & Haak-Saheem, W. (2022). Talent management in the public sector: Empirical evidence from the Emerging Economy of Dubai. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 33(11), 2256–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljumah, A. (2023). The impact of extrinsic and intrinsic motivation on job satisfaction: The mediating role of transactional leadership. Cogent Business & Management, 10(3), 2270813. [Google Scholar]
- Alshahrani, A., Dennehy, D., & Mäntymäki, M. (2022). An attention-based view of AI assimilation in public sector organizations: The case of Saudi Arabia. Government Information Quarterly, 39(4), 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zoubi, M. (2013). Predicting E-business adoption through integrating the constructs of the Rogers’s diffusion of innovation theory combined with technology organization environment model. International Journal of Advanced Computer Research, 3(4), 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, M., Pritchett, L., & Woolcock, M. (2017). Building state capability: Evidence, analysis, action (p. 288). Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Angel-Sveda, A. (2013). Organizational change and development in Romanian public institutions. Annals of University of Oradea, Fascicle Sociology—Philosophy and Social Work, 12(1), 23–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ashok, M., Al Badi Al Dhaheri, M. S. M., Madan, R., & Dzandu, M. D. (2021). How to counter organisational inertia to enable knowledge management practices adoption in public sector organisations. Journal of Knowledge Management, 25(9), 2245–2273. [Google Scholar]
- Assaker, G., Vinzi, V. E., & O’Connor, P. (2010). Structural equation modeling in tourism demand forecasting: A critical review. Journal of Travel & Tourism Research, 10, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Azhar, Z., Alfan, E., Kishan, K., & Assanah, N. H. (2022). Accrual accounting at different levels of the public sector: A systematic literature review. Australian Accounting Review, 32(1), 36–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzaz, F. E., & Salahddine, M. (2022). The digital transformation of the Moroccan public sector: Results of an exploratory study. Change Management: An International Journal, 23(1), 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzone, G., & Palermo, T. (2011). Adopting performance appraisal and reward systems. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 24(1), 90–111. [Google Scholar]
- Basloom, R. S., Mohamad, M. H. S., & Auzair, S. M. (2022). Applicability of public sector reform initiatives of the Yemeni government from the integrated TOE-DOI framework. International Journal of Innovation Studies, 6(4), 286–302. [Google Scholar]
- Battaglio, R. P., Jr., Belardinelli, P., Bellé, N., & Cantarelli, P. (2019). Behavioral Public Administration ad fontes: A Synthesis of Research on Bounded Rationality, Cognitive Biases, and Nudging in Public Organizations. Public Administration Review, 79(3), 304–320. [Google Scholar]
- Bentzen, T. Ø. (2021). Breaking the vicious circle of escalating control: Connecting politicians and public employees through stewardship. Administrative Sciences, 11(3), 63. [Google Scholar]
- Bernroider, E. W. N., & Schmöllerl, P. (2013). A technological, organisational, and environmental analysis of decision-making methodologies and satisfaction in the context of IT induced business transformations. European Journal of Operational Research, 224(1), 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bhattacharya, M., & Wamba, S. (2015). A conceptual framework of RFID adoption in retail using TOE framework. International Journal of Technology Diffusion (IJTD), 6(1), 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhul, B. (2023). New public management reform: Implementation experiences of developing countries and Nepal. Prashasan: The Nepalese Journal of Public Administration, 55(1), 52–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bisogno, M., & Donatella, P. (2022). Earnings management in public-sector organizations: A structured literature review. Journal of Public Budgeting, Accounting & Financial Management, 34(6), 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn, G. (2014). Elements of successful change: The service tasmania experience to public sector reform. Australian Journal of Public Administration, 73(1), 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Brandsen, T., & Kim, S. (2010). Contextualizing the meaning of public management reforms: A comparison of the Netherlands and South Korea. International Review of Administrative Sciences, 76(2), 367–386. [Google Scholar]
- Brinkerhoff, D., & Brinkerhoff, J. (2015). public sector management reform in developing countries: Perspectives beyond NPM orthodoxy. Public Administration and Development, 35(4), 222–237. [Google Scholar]
- Bryson, J. M., Barberg, B., Crosby, B. C., & Patton, M. Q. (2021). Leading social transformations: Creating public value and advancing the common good. Journal of Change Management, 21(2), 180–202. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, W. (2010). Organization changes: Theory and practice. SAGE Publications Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- Burnes, B., & By, R. (2012). Leadership and change: The case for greater ethical clarity. Journal of Business Ethics, 108(2), 239–252. [Google Scholar]
- Burnes, B., & Jackson, P. (2011). Success and failure in organizational change: An exploration of the role of values. Journal of Change Management, 11(2), 133–162. [Google Scholar]
- Busari, A. H., Khan, S. N., Abdullah, S. M., & Mughal, Y. H. (2019). Transformational leadership style, followership, and factors of employees’ reactions towards organizational change. Journal of Asia Business Studies, 14(2), 181–209. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, F., Rafique, T., Nawab, S., Khan, N., & Raza, A. (2013). Organizational transformation in public sector organizations of Pakistan in the quest of change management. Research journal of a lied sciences. Engineering and Technology, 6(16), 3086–3093. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, B. M. (2013). Structural equation modeling with AMOS: Basic concepts, applications, and programming. Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Callanan, M., Houlberg, K., Raudla, R., & Teles, F. (2024). “Top-down” local government mergers: Political and institutional factors facilitating radical amalgamation reforms. Journal of Urban Affairs, 46(10), 2040–2063. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J. W. (2021). Evolution and change in public organizations: Efficiency, legitimacy and the resilience of core organizational elements. In T. A. Bryer (Ed.), Handbook of Theories of Public Administration and Management (pp. 220–233). Edward Elgar Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Canning, J., & Found, P. A. (2015). The effect of resistance in organizational change programmes: A study of a lean transformation. International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences, 7(2/3), 274–295. [Google Scholar]
- Capriotti, M. R., & Donaldson, J. M. (2022). “Why don’t behavior analysts do something?” 1 Behavior analysts’ historical, present, and potential future actions on sexual and gender minority issues. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 55(1), 19–39. [Google Scholar]
- Câmpeanu-Sonea, E., & Sonea, A. (2010). human resource’s development for organizational change. Managerial Challenges of the Contemporary Society, 1, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. L., Lin, Y. C., Chen, W. H., Chao, C. F., & Pandia, H. (2021). Role of government to enhance digital transformation in small service business. Sustainability, 13(3), 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciganek, A. P., Haseman, W., & Ramamurthy, K. (2014). Time to decision: The drivers of innovation adoption decisions. Enterprise Information Systems, 8(2), 279–308. [Google Scholar]
- Collington, R. (2022). Disrupting the welfare state? Digitalisation and the retrenchment of public sector capacity. New Political Economy, 27(2), 312–328. [Google Scholar]
- Cordella, A., & Bonina, C. (2012). A public value perspective for ICT enabled public sector reforms: A theoretical reflection. Government Information Quarterly, 29(4), 512–520. [Google Scholar]
- Cordella, A., & Tempini, N. (2015). E-government and organizational change: Rea raising the role of ICT and bureaucracy in public service delivery. Government Information Quarterly, 32(3), 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordery, C. J., & Hay, D. (2024). Public sector audit: New public management influences and eco-system driven reforms. Journal of Public Budgeting, Accounting & Financial Management. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costan, E., Gonzales, G., Gonzales, R., Enriquez, L., Costan, F., Suladay, D., Atibing, N. M., Aro, J. L., Evangelista, S. S., Maturan, F., & Selerio, E., Jr. (2021). Education 4.0 in developing economies: A systematic literature review of implementation barriers and future research agenda. Sustainability, 13(22), 12763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, T. G., & Huse, E. F. (1989). Organizational Development and Change. West Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, M. P. E., Neves, P., Clegg, S. R., Costa, S., & Rego, A. (2019). Paradoxes of organizational change in a merger context. Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal, 14(3), 217–240. [Google Scholar]
- Dafe, F., Hager, S. B., Naqvi, N., & Wansleben, L. (2022). Introduction: The structural power of finance meets financialization. Politics & Society, 50(4), 523–542. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, F. D. (1989). Technology acceptance model: TAM. Al-Suqri, MN, Al-Aufi, AS: Information Seeking Behavior and Technology Adoption, 205(219), 5. [Google Scholar]
- Decker, P., Durand, R., Mayfield, C. O., McCormack, C., Skinner, D., & Perdue, G. (2012). Predicting implementation failure in organization change. Journal of Organizational Culture, Communications and Conflict, 16(2), 39–59. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez, L., Nchez, I., & Álvarez, I. (2011). Determining factors of e-government development: A worldwide national a roach. International Public Management Journal, 14(2), 218–248. [Google Scholar]
- Dzimińska, M. (2024). A call for innovation culture in Polish academics’ vision of an ideal-type university. Studies in Higher Education, 49(6), 1000–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Easterby-Smith, M., Thorpe, R., & Lowe, A. (2008). Management research: An introduction (3rd ed.). SAGE Publications Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, W., Klein, G., Jiang, J., & Khan, R. M. (2022). Integration networks in IT-enabled transformation programs. International Journal of Managing Projects in Business, 15(6), 913–937. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A. (2013). Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics. Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Fielder, E. E. (1967). A theory of leader effectiveness. McGraw-Hill. [Google Scholar]
- Fullan, M. (2015). The new meaning of educational change. Teachers College Press. [Google Scholar]
- Gangwar, H., Date, H., & Ramaswamy, R. (2015). Understanding determinants of cloud computing adoption using an integrated TAM-TOE model. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 28(1), 107–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gelaidan, H., & Ahmad, H. (2013). The Factors effecting employee commitment to change in public sector: Evidence from Yemen. International Business Research, 6(3), 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Getha-Taylor, H., Grayer, M. J., Kempf, R. J., & O’Leary, R. (2019). Collaborating in the absence of trust? What collaborative governance theory and practice can learn from the literatures of conflict resolution, psychology, and law. The American Review of Public Administration, 49(1), 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, R., Singh, N., Agrawal, P., Espinosa, K., & Bamufleh, D. (2021). Information technology/systems adoption in the public sector. Journal of Global Information Management, 29(4), 172–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giermindl, L. M., Strich, F., Christ, O., Leicht-Deobald, U., & Redzepi, A. (2022). The dark sides of people analytics: Reviewing the perils for organisations and employees. European Journal of Information Systems, 31(3), 410–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goniewicz, K., Burkle, F. M., & Khorram-Manesh, A. (2024). Transforming global public health: Climate collaboration, political challenges, and systemic change. Journal of Infection and Public Health, 18(1), 102615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotsch, M., Gandenberger, C., Serafimov, L., & Miemiec, M. (2023). Top-down and bottom-up strategies for the implementation of corporate social responsibility: A qualitative survey of an international IT services company. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 30(4), 1645–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero, E., & Kim, A. (2013). Organizational structure, leadership and readiness for change and the implementation of organizational cultural competence in Addiction Health Services. Evaluation and Program Planning, 40(1), 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Gultekin, S. (2011). New public management: Is it really new? International Journal of Human Sciences, 8(2), 343–358. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis: A global perspective (7th ed.). Pearson Education. [Google Scholar]
- Halimah, L., Hidayah, Y., Heryani, H., Trihastuti, M., & Arpannudin, I. (2023). The meaning of maintaining a life philosophy of simplicity for life pleasure: A study in Kampung Naga, Tasikmalaya. Journal of Human Behavior in the Social Environment, 33(8), 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, I., Khan, A. K., Sabharwal, M., Arain, G. A., & Hameed, I. (2019). Managing successful change efforts in the public sector: An employee’s readiness for change perspective. Review of Public Personnel Administration, 39(3), 398–421. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, M. D., TitiAmayah, A., & Liu, L. (2016). The role of vision in organizational readiness for change and growth. Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 37(7), 983–999. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstede, G. H. (2005). Cultures in organizations. Mc Graw-Hill. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, G., Witteloostuijn, A., & Christe-Zeyse, J. (2013). A theoretical framework of organizational change. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 26(5), 772–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabalan, J., Dorasamy, M., & Raman, M. (2021). Reshaping higher educational institutions through frugal open innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 7(2), 145. [Google Scholar]
- Jayousi, S., Barchielli, C., Alaimo, M., Caputo, S., Paffetti, M., Zoppi, P., & Mucchi, L. (2024). ICT in nursing and patient healthcare management: Scoping review and case studies. Sensors, 24(10), 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D. S. (2013). Procurement reform in the Philippines: The impact of elite capture and informal bureaucracy. International Journal of Public Sector Management, 26(5), 375–400. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, P., & Ashwin, A. (2013). The business environment (1st ed.). Cengage. [Google Scholar]
- Khanh, N. (2014). The critical factors affecting E-Government adoption: A Conceptual Framework in Vietnam. arXiv, arXiv:1401.4876. [Google Scholar]
- Khaw, K. W., Alnoor, A., Al-Abrrow, H., Tiberius, V., Ganesan, Y., & Atshan, N. A. (2023). Reactions towards organizational change: A systematic literature review. Current Psychology, 42(22), 19137–19160. [Google Scholar]
- Kickert, W. J. M. (2010). Managing emergent and complex change: The case of the Dutch agencification. International Review of Administrative Sciences, 76(3), 489–515. [Google Scholar]
- Kickert, W. J. M. (2014). Specificity of Change Management in Public Organizations: Conditions for Successful Organizational Change in Dutch Ministerial Departments. American Review of Public Administration, 44(6), 693–717. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D. G., & Lee, C. W. (2021). Exploring the roles of self-efficacy and technical support in the relationship between techno-stress and counter-productivity. Sustainability, 13(8), 4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsios, F., & Kamariotou, M. (2017, September 5–7). Strategic change management in public sector transformation: The case of middle manager leadership in Greece. The 31st Annual Conference of the British Academy of Management—BAM 2017, Coventry, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Kotter, J. P. (2010). Leading change: Why transformation efforts fail. Harvard Business School Press. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, B., Krishnan, S., & Sebastian, M. P. (2023). Examining the relationship between national cybersecurity commitment, culture, and digital payment usage: An institutional trust theory perspective. Information Systems Frontiers, 25(5), 1713–1741. [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers, B. S., Higgs, M. J., Kickert, W. J. M., Tummers, L. G., Grandia, J., & Van der Voet, J. (2014). The management of change in public organizations: A literature review. Public Administration, 92(1), 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumasari, B., Sajida, S., Santoso, A. D., & Fauzi, F. Z. (2024). The Reinventing of public administration in the new hybrid world. Teaching Public Administration, 42(2), 206–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J., Vähäsantanen, K., & Collin, K. (2024). Teachers’ professional agency in a centralisation-decentralisation system and a hierarchical cultural context: The case of Hong Kong. Pedagogy, Culture & Society, 32(3), 699–719. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S., Oh, S., & Nam, K. (2016). Transformational and transactional factors for the successful implementation of enterprise architecture in public sector. Sustainability, 8(5), 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, A. (1988). Effective change. Institute of Personnel Management. [Google Scholar]
- Liguori, M. (2012). The supremacy of the sequence: Key elements and dimensions in the process of change. Organization Studies, 33(4), 507–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C. Y., & Ho, Y. H. (2011). Determinants of green practice adoption for logistics companies in China. Journal of Business Ethics, 98, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippitt, R., Watson, J., & Westley, B. (1958). The dynamics of planned change. Brace and World. [Google Scholar]
- Low, C., Chen, Y., & Wu, M. (2011). Understanding the determinants of cloud computing adoption. Industrial Management and Data Systems, 111(7), 1006–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, P. B., & Gaskin, J. (2014). Partial least squares (PLS) structural equation modeling (SEM) for building and testing behavioral causal theory: When to choose it and how to use it. IEEE Transactions on Professional Communication, 57(2), 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfi, A. (2022). Factors influencing the continuance intention to use accounting information system in Jordanian SMEs from the perspectives of UTAUT: Top management support and self-efficacy as predictor factors. Economies, 10(4), 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malodia, S., Dhir, A., Mishra, M., & Bhatti, Z. A. (2021). Future of e-Government: An integrated conceptual framework. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 173, 121102. [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt, J., Oliveira, M. C., & Lederer, M. (2022). Same, same but different? How democratically elected right-wing populists shape climate change policymaking. Environmental Politics, 31(5), 777–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsueda, R. L. (2023). A brief history of structural equation modeling. In Handbook of structural equation modeling (2nd ed., pp. 17–48). Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Mensah, I. K. (2020). Impact of government capacity and E-government performance on the adoption of E-government services. International Journal of Public Administration, 43(4), 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, U., & Sharma, M. (2013). Human factors affecting the adaptability of e-governance. The Indian Public Sector Journal of E-Governance, 36, 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, G. (2013). Selecting the best theory to implement planned change. Nursing Management, 20(1), 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Mongkol, K. (2011). The critical review of new public management model and its criticisms. Research Journal of Business Management, 5(1), 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Montreuil, V. L. (2023). Organizational change capability: A scoping literature review and agenda for future research. Management Decision, 61(5), 1183–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Mowbray, P. K., Wilkinson, A., & Tse, H. H. (2022). Strategic or silencing? Line managers’ repurposing of employee voice mechanisms for high performance. British Journal of Management, 33(2), 1054–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Nawafleh, S., Obeidat, R., & Harfoushi, O. (2012). E-government between developed and developing countries. International Journal of Advanced Corporate Learning, 51, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, O., Guirguis, K., & Steiner, R. (2024). Exploring artificial intelligence adoption in public organizations: A comparative case study. Public Management Review, 26(1), 114–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T. H., Le, X. C., & Vu, T. H. L. (2022). An extended technology-organization-environment (TOE) framework for online retailing utilization in digital transformation: Empirical evidence from Vietnam. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 8, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeidat, R., & Abu-Shanab, E. (2010). Drivers of E-government and E-business in Jordan. Journal of Emerging Technologies in Web Intelligence, 2(3), 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- O’Leary, R., & Vij, N. (2012). Collaborative public management. The American Review of Public Administration, 42(5), 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G., Grenha Teixeira, J., Torres, A., & Morais, C. (2021). An exploratory study on the emergency remote education experience of higher education students and teachers during the COVID-19 pandemic. British Journal of Educational Technology, 52(4), 1357–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otusanya, O. (2011). Corruption as an obstacle to development in developing countries: A review of literature. Journal of Money Laundering Control, 14(4), 387–422. [Google Scholar]
- Page, S. B., Stone, M. M., Bryson, J. M., & Crosby, B. C. (2015). Public value creation by cross-sector collaborations: A framework and challenges of assessment. Public Administration, 93(3), 715–732. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S., Lee, D. S., & Son, J. (2021). Regulatory reform in the era of new technological development: The role of organizational factors in the public sector. Regulation & Governance, 15(3), 894–908. [Google Scholar]
- Peráček, T., & Kaššaj, M. (2023). A critical analysis of the rights and obligations of the manager of a limited liability company: Managerial legislative basis. Laws, 12(3), 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piercy, N., Phillips, W., & Lewis, M. (2013). Change management in the public sector: The use of cross-functional teams. Production Planning and Control, 24(10), 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, C., & Cater-Steel, A. (2009). Justifications, strategies, and critical success factors in successful ITIL implementations in U.S., & Australian companies: An exploratory study. Information Systems Management, 26(2), 164–175. [Google Scholar]
- Popara, M. (2012). Recent A roaches in International Public Management and the need to apply them on Romanian public administration. Review of International Comparative Management, 13(2), 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad Agrawal, K. (2024). Towards adoption of generative AI in organizational settings. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 64(5), 636–651. [Google Scholar]
- Pudjianto, B., Hangjung, Z., Ciganek, A., & Rho, J. J. (2011). Determinants of e-government assimilation in Indonesia: An empirical investigation using a TOE framework. Asia Pacific Journal of Information Systems, 21(1), 50–80. [Google Scholar]
- Raavi, T. S., Radhika, R., & Charan, C. S. (2025). Innovative intelligence ai tools transforming public service excellence. in ai driven tools for sustainable public administration (pp. 189–226). IGI Global Scientific Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, A., Ishaq, M. I., Jamali, D. R., Zia, H., & Haj-Salem, N. (2024). Testing workplace hazing, moral disengagement and deviant behaviors in hospitality industry. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 36(3), 743–768. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, G., & French, R. (2016). Leading, managing and developing people (5th ed.). CIPD. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, E. (2003). Diffusion of innovations (1st ed.). Free Press. [Google Scholar]
- Rowold, J., & Abrell-Vogel, C. (2014). The influence of leaders’ commitment to change on the effectiveness of transformational leadership in change situations—A multilevel investigation. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 27(1), 900–921. [Google Scholar]
- Safdar, R. (2012). Performance measurement and civil services reforms in Pakistan: A study of public sector organizations. Far East Journal of Psychology and Business, 6(5), 56–68. [Google Scholar]
- Samier, E. A., & Tok, M. E. (2021). Women’s Entrepreneurial Leadership Education for the public sector in the Gulf: Curricular values for diversity and inclusion. In Women, entrepreneurship and development in the middle east (pp. 212–230). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Sarja, M., Onkila, T., & Mäkelä, M. (2021). A systematic literature review of the transition to the circular economy in business organizations: Obstacles, catalysts and ambivalences. Journal of Cleaner Production, 286, 125492. [Google Scholar]
- Schein, E. H. (1996). Culture: The missing concept in organization studies. Administrative Science Quarterly, 41(2), 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Shaar, E., Khattab, S., Alkaied, R., & Manna, A. (2015). The Effect of Top Management Su ort on Innovation: The Mediating Role of Synergy between Organizational Structure and Information Technology. International Review of Management and Business Research, 4(2), 499–517. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, N., & Mansoor, A. (2022). Pakistan post and the creation of an innovative business model to enhance financial inclusion. In Public sector reforms in pakistan: Hierarchies, markets and networks (pp. 251–273). Springer International Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Shirey, M. R. (2013). Strategic leadership for organizational change. Lewin’s theory of planned change as a strategic resource. Journal of Nursing Administration, 43(2), 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg, R. J., & Karami, S. (2022). An 8P theoretical framework for understanding creativity and theories of creativity. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 56(1), 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strokosch, K., & Osborne, S. P. (2021). Co-production from a public service logic perspective. In E. Loeffler, & T. Bovaird (Eds.), The Palgrave Handbook of Co-Production of Public Services and Outcomes (pp. 117–131). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Ştefan, E. E. (2024). Integrity and transparency in the work of public authorities. Aspects of comparative public law. Juridical Tribune-Review of Comparative and International Law, 14, 564–583. [Google Scholar]
- Teo, T., Srivastava, S., & Jiang, L. (2008). Trust and electronic government success: An empirical study. Journal of Management Information Systems, 253, 99–132. [Google Scholar]
- Thi, L., Lim, H., & Al-Zoubi, M. (2014). Estimating influence of toe factors on E-government usage: Evidence of Jordanian Companies. International Journal of Business and Society, 153, 413–436. [Google Scholar]
- Tien, N. H., Ngoc, N. M., & Anh, D. B. H. (2021). The situation of high quality human resource in FDI enterprises in Vietnam: Exploitation and development solutions. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Growth Evaluation, 2(1), 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Tornatzky, L. G., & Fleischer, M. (1990). The processes of technological innovation. Lexington Books. [Google Scholar]
- Troshani, I., Jerram, C., & Hill, S. (2011). Exploring the public sector adoption of HRIS. Industrial Management and Data Systems, 111(3), 470–488. [Google Scholar]
- Utouh, H. M., & Kitole, F. A. (2024). Forecasting effects of foreign direct investment on industrialization towards realization of the Tanzania development vision 2025. Cogent Economics & Finance, 12(1), 2376947. [Google Scholar]
- Vander Elst, S., & De Rynck, F. (2014). Alignment processes in public organizations: An interpretive a roach. Information Polity, 19(4), 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Voet, J. (2014). The effectiveness and specificity of change management in a public organization: Transformational leadership and a bureaucratic organizational structure. European Management Journal, 32(3), 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Voet, J. (2016). Change leadership and public sector organizational change: Examining the interactions of transformational leadership style and red tape. The American Review of Public Administration, 46(6), 660–682. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Voet, J., Kuipers, B., & Groeneveld, S. (2013, June 20–22). Implementing change in public organizations: The relationship between leadership and affective commitment to change in a public sector context (Conference session). 11th Public Management Research Conference, Madison, WI, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, 27(3), 425–478. [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen, P., Jalonen, H., & Tammeaid, M. (2022). Public sector leadership: A human-centred approach. Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Vorwerk Marren, I., Davis, A., & Williamson, C. M. (2024). Strategizing for survival–enablers of South African not-for-profit organization sustainability. Cogent Business & Management, 11(1), 2323775. [Google Scholar]
- Vries, M. D., & Nemec, J. (2013). Public sector reform: An overview of recent literature and research on NPM and alternative paths. International Journal of Public Sector Management, 26(1), 4–16. [Google Scholar]
- Waller, L., & Genius, A. (2015). Barriers to transforming government in Jamaica. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy, 9(4), 480–497. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y., Wang, Y., & Yang, Y. (2010). Understanding the determinants of RFID adoption in the manufacturing industry. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 77(5), 803–815. [Google Scholar]
- Weerakkody, V., El-Haddadeh, R., Sabol, T., Ghoneim, A., & Dzupka, P. (2012). E-government implementation strategies in developed and transition economies: A comparative study. International Journal of Information Management, 32(1), 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wetherly, P., & Otter, D. (2011). The business environment themes and issues (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Widodo, W. (2015). The implementation of knowledge strategy-based entrepreneurial capacity to achieve sustainable competitive advantage. International Research Journal of Business Studies, 6(2), 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- World Bank. (2022). Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/532121636474869984/pdf/Disclosable-Version-of-the-ISR-Governance-and-Policy-Program-for-Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa-KP-P156410-Sequence-No-08.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2025).
- Wu, Y., & Tham, J. (2023). The impact of executive green incentives and top management team characteristics on corporate value in China: The mediating role of environment, social and government performance. Sustainability, 15(16), 12518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, S., & Hartley, J. (2021). Learning to lead with political astuteness. International Public Management Journal, 24(4), 562–583. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J., & Chae, M. (2009). Varying criticality of key critical success factors national e-strategy along the status of economic development of nations. Government Information Quarterly, 26, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, T., & George, J. (2013). Why aren’t organizations adopting virtual worlds? Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 772–790. [Google Scholar]
- Younus, M., Pribadi, U., Nurmandi, A., & Rahmawati, I. Z. (2023). Comparative analysis of E-Government development index: A case study of South Asian countries. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy, 17(4), 552–574. [Google Scholar]
- Yuksel, Y. (2017). Organizational resistance and receptivity. The Journal of International Social Research, 10(52), 1219–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y., Xu, S., Zhang, L., & Yang, M. (2021). Big data and human resource management research: An integrative review and new directions for future research. Journal of Business Research, 133, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoukoua, E. A. (2024). The role of public actors in the governance of French non-profit organisations: Proposing an integrated governance analysis framework. In Non-profit Governance (pp. 48–64). Routledge. [Google Scholar]

| Steps | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Establish a sense of urgency | The need to change. |
| 2. Create a guiding coalition | With authority and credibility. |
| 3. Develop a vision and strategy | A clear aim and way forward. |
| 4. Communicate the change vision | Promote understanding and commitment. |
| 5. Empower broad-based action | Enable people to act and overcome barriers. |
| 6. Generate short-term wins | To motivate and ensure further support. |
| 7. Consolidate gains and produce more change | Maintain change momentum. |
| 8. Anchor new approaches in the culture | New values, attitudes, and behaviors. |
| TOE Factors | Constructs and Abbreviations | No of Items | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical context | IT infrastructure (IT) | 4 Items | Teo et al. (2008); J. Yoon and Chae (2009); Pudjianto et al. (2011); Gangwar et al. (2015) |
| Collaboration (COL) | 3 Items | ||
| Organizational context | Top management (TM) | 4 Items | Teo et al. (2008); Wang et al. (2010); Pudjianto et al. (2011); Low et al. (2011); Gangwar et al. (2015); Shaar et al. (2015); Lee et al. (2016) |
| Human resources (HR) | 3 Items | ||
| Technical competence (TEC) | 4 Items | ||
| Reward system (RS) | 3 Items | ||
| Environmental context | Political (POL) | 3 Items | J. Yoon and Chae (2009); Pollard and Cater-Steel (2009); Pudjianto et al. (2011); Gangwar et al. (2015); Lee et al. (2016) |
| Economy (ECO) | 4 Items | ||
| Socio-cultural (CUL) | 4 Items | ||
| Legal (LEG) | 3 Items |
| Demographic | Category | Frequencies | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 225 | 75 |
| Female | 75 | 25 | |
| Age | 20 or Less | 18 | 6 |
| 21–30 | 71 | 23.7 | |
| 31–40 | 99 | 33 | |
| 41–50 | 75 | 25 | |
| 51–60 | 37 | 12.3 | |
| Education | High School | 34 | 11.3 |
| Diploma | 49 | 16.3 | |
| Bachelor | 78 | 26 | |
| Masters | 119 | 39.7 | |
| PhD | 20 | 6.7 | |
| Pay Grade | 1–4 | 27 | 9 |
| 5–9 | 62 | 20.7 | |
| 10–15 | 57 | 19 | |
| 16–22 | 152 | 50.7 | |
| Prefer not to say | 2 | 0.7 | |
| Years of Experience | 5 or Less | 68 | 22.7 |
| 6–10 | 76 | 25.3 | |
| 11–15 | 54 | 18 | |
| 16–22 | 76 | 25.3 | |
| Prefer not to say | 26 | 8.7 | |
| Department/Organisation | Excise and Taxation | 31 | 10.3 |
| Health | 56 | 18.7 | |
| Education | 61 | 20.3 | |
| Planning | 11 | 3.7 | |
| Finance | 17 | 5.7 | |
| Agriculture | 5 | 1.7 | |
| Environment | 17 | 5.7 | |
| Communication | 18 | 6 | |
| Energy and Power | 21 | 7 | |
| Transport | 4 | 1.3 | |
| Law | 53 | 17.7 | |
| Tourism | 3 | 1 | |
| Others | 3 | 1 |
| Constructs | Items | Factor | C-α | CR | AVE | MSV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loadings | ||||||
| Reward system (RS) | RS1: There are clear reward systems in the organisation. | 0.971 | 0.825 | 0.931 | 0.818 | 0.103 |
| RS2: Incentives are in place at all levels to motivate employees. | 0.983 | |||||
| RS3: Employees are aware of the existence of the reward system | 0.961 | |||||
| Economy (ECO) | ECO1: There is great donor’s support to implement change. | 0.963 | 0.894 | 0.992 | 0.97 | 0.123 |
| ECO2: There are enough funds available to implement change. | 0.891 | |||||
| ECO3: Economic growth in the region is satisfactory | 0.881 | |||||
| Socio-cultural (CUL) | Cul1: There is general acceptance for change within our organisation. | 0.872 | 0.791 | 0.914 | 0.731 | 0.038 |
| Cul2: Our organisation has innovative culture. | 0.861 | |||||
| Cul3: Local tradition and beliefs support the change. | 0.852 | |||||
| Cul4: There is readiness for change within the organisation | 0.771 | |||||
| Legal (LEG) | Leg1: Adequate legal/regulatory framework in Place | 0.871 | 0.824 | 0.957 | 0.881 | 0.123 |
| Leg2: Introduction of new legislations supports the change. | 0.842 | |||||
| Leg3: Government has authority to enforce decisions | 0.781 | |||||
| Human resources (HR) | HR1: There is enough human resource to implement change. | 0.961 | 0.813 | 0.864 | 0.68 | 0.041 |
| HR2: Our organisation provides regular training programmes for employees to cope with change. | 0.879 | |||||
| HR3: Sufficient skilled workforce available to implement change | 0.761 | |||||
| Political (POL) | POL1: There is political stability. | 0.861 | 0.795 | 0.922 | 0.798 | 0.099 |
| POL2: There are consistent government policies. | 0.852 | |||||
| POL3: There is government support for change. | 0.843 | |||||
| POL4: Public reform is a priority for the political leadership | 0.731 | |||||
| Top management (TM) | TM1: Top management is committed to change. | 0.789 | 0.874 | 0.929 | 0.814 | 0.264 |
| TM2: Top management supports the change. | 0.767 | |||||
| TM3: Top management is capable of implementing change | 0.734 | |||||
| IT infrastructure (IT) | IT1: IT infrastructure is ready for the change Initiatives. | 0.91 | 0.885 | 0.863 | 0.686 | 0.264 |
| IT2: There is ample availability of internet connection. | 0.86 | |||||
| IT3: There is acceptable reliability of internet connection. | 0.746 | |||||
| IT4: Network is regularly monitored to avoid internet crash | 0.741 | |||||
| Technical competence (TEC) | TEC1: There is an adequate technological infrastructure. | 0.971 | 0.926 | 0.911 | 0.773 | 0.06 |
| TEC2: Government provides adequate technical support. | 0.874 | |||||
| TEC3: Our organisation provides all needed hardware and equipment | 0.851 | |||||
| Collaboration (CM) | CM1: Staff members were consulted about the reasons for change. | 0.86 | 0.936 | 0.909 | 0.769 | 0.069 |
| CM2: Front line staff and office workers can raise topics for discussion. | 0.74 | |||||
| CM3: Our department provide sufficient time for consultation. | 0.71 |
| Construct | RS | ECO | CUL | LEG | HR | POL | TM | IT | TEC | COL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reward system | 0.904 | |||||||||
| Economy | −0.011 | 0.985 | ||||||||
| Socio-cultural | 0.195 | 0.013 | 0.855 | |||||||
| Legal | 0.100 | 0.351 | 0.148 | 0.939 | ||||||
| Human resource | 0.025 | −0.148 | 0.034 | 0.153 | 0.825 | |||||
| Political | 0.188 | −0.168 | 0.036 | −0.042 | 0.202 | 0.893 | ||||
| Top management | 0.321 | 0.069 | 0.088 | 0.211 | 0.195 | 0.314 | 0.902 | |||
| IT infrastructure | 0.299 | −0.048 | 0.064 | 0.090 | 0.058 | 0.234 | 0.514 | 0.828 | ||
| Technical competence | −0.014 | 0.186 | 0.085 | 0.245 | −0.105 | 0.059 | 0.117 | 0.099 | 0.879 | |
| Collaboration | 0.026 | 0.207 | 0.030 | 0.262 | −0.036 | −0.024 | 0.176 | 0.078 | 0.145 | 0.877 |
| Fit Index | Recommended Criteria | Results of CFA (First Run) | Results of CFA (Final Model) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /d.f. | <3 | 1.790 | 1.547 | Hair et al. (2010); Field (2013) |
| CFI | >0.9 | 0.965 | 0.978 | Field (2013) |
| GFI | >0.8 | 0.874 | 0.901 | Field (2013) |
| AGFI | >0.8 | 0.841 | 0.881 | Field (2013) |
| RMSEA | <0.08 | 0.051 | 0.043 | Hair et al. (2010) |
| TLI | >0.9 | 0.959 | 0.971 | Hair et al. (2010) |
| NFI | >0.9 | 0.925 | 0.936 | Field (2013) |
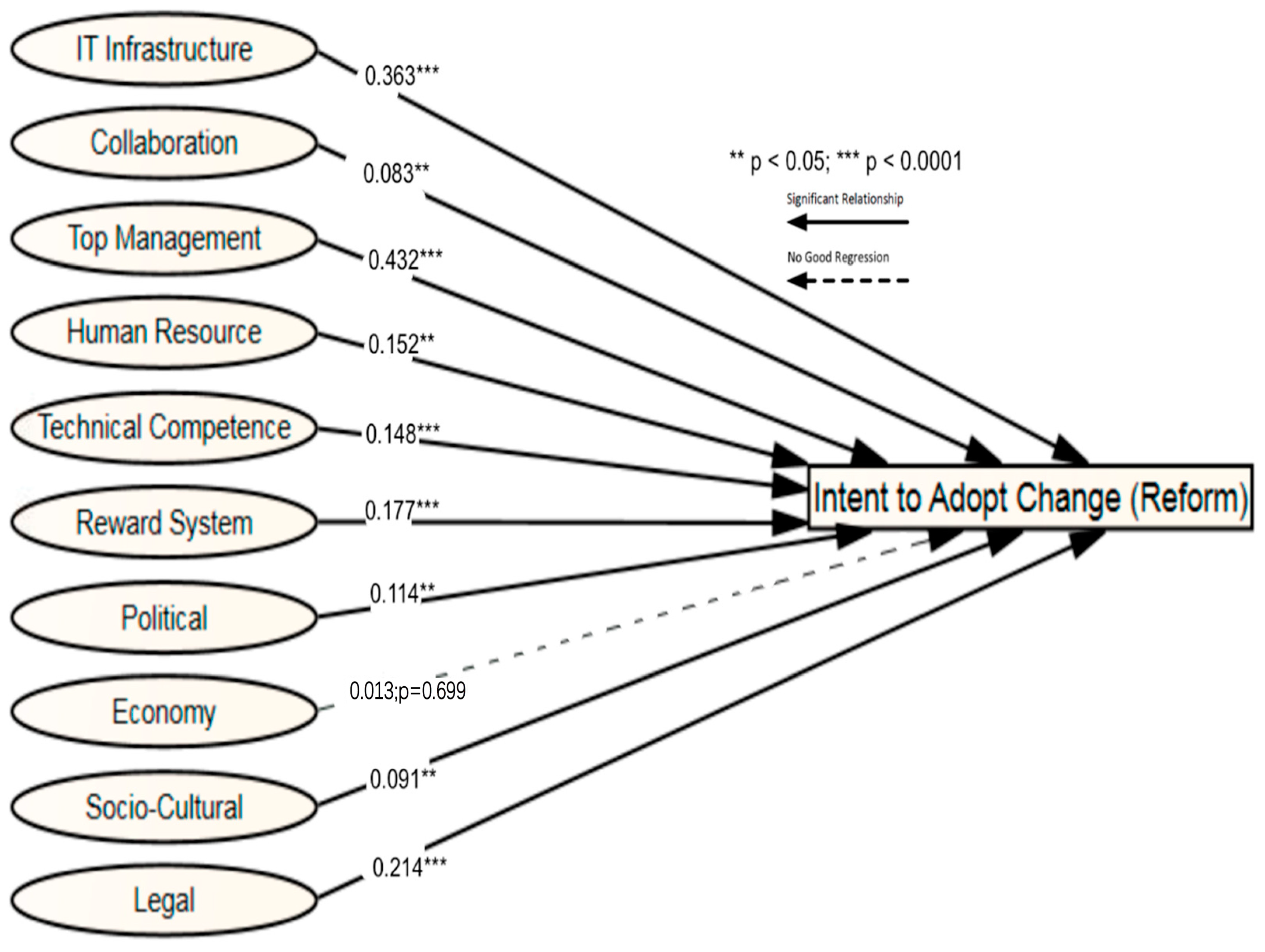
| Hypothesis | Path | Estimate | p | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1a | IT -----> Intent to adopt change (reform) | 0.363 | *** | Supported |
| H1b | COL -----> Intent to adopt change (reform) | 0.083 | 0.016 | Supported |
| H2a | TM -----> Intent to adopt change (reform) | 0.432 | *** | Supported |
| H2b | HR -----> Intent to adopt change (reform) | 0.152 | 0.002 | Supported |
| H2c | TEC -----> Intent to adopt change (reform) | 0.148 | *** | Supported |
| H2d | RS -----> Intent to adopt change (reform) | 0.177 | *** | Supported |
| H3a | POL -----> Intent to adopt change (reform) | 0.114 | 0.003 | Supported |
| H3b | ECO -----> Intent to adopt change (reform) | 0.013 | 0.699 | Not Supported |
| H3c | CUL -----> Intent to adopt change (reform) | 0.091 | 0.001 | Supported |
| H3d | LEG -----> Intent to adopt change (reform) | 0.214 | *** | Supported |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nawaz, M.K.; Eltweri, A.; Abbas, K.; Al-Karaki, W.; Edghiem, F.; Foster, S.; Adali, M. Public Sector Transformation in Emerging Economies: Factors Affecting Change Adoption in Pakistan. Adm. Sci. 2025, 15, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15040126
Nawaz MK, Eltweri A, Abbas K, Al-Karaki W, Edghiem F, Foster S, Adali M. Public Sector Transformation in Emerging Economies: Factors Affecting Change Adoption in Pakistan. Administrative Sciences. 2025; 15(4):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15040126
Chicago/Turabian StyleNawaz, Muhammad Kamran, Ahmed Eltweri, Khalid Abbas, Wa’el Al-Karaki, Farag Edghiem, Scott Foster, and Munir Adali. 2025. "Public Sector Transformation in Emerging Economies: Factors Affecting Change Adoption in Pakistan" Administrative Sciences 15, no. 4: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15040126
APA StyleNawaz, M. K., Eltweri, A., Abbas, K., Al-Karaki, W., Edghiem, F., Foster, S., & Adali, M. (2025). Public Sector Transformation in Emerging Economies: Factors Affecting Change Adoption in Pakistan. Administrative Sciences, 15(4), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15040126





