Soil Loss Analysis of an Eastern Kentucky Watershed Utilizing the Universal Soil Loss Equation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE)
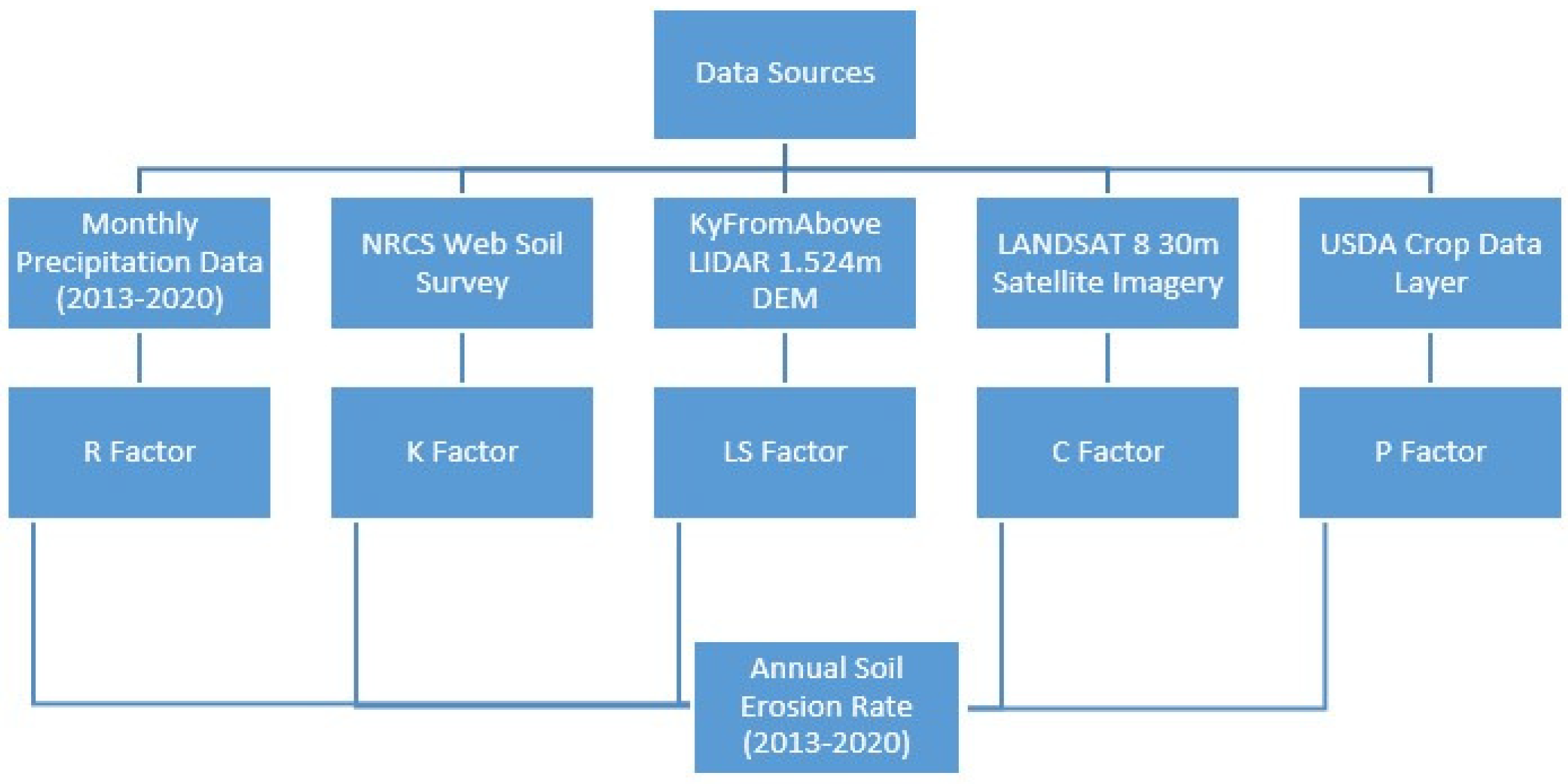
2.3. Data Collection and Processing
3. Results
Descriptive Statistics
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parveen, R.; Uday, K. Integrated Approach of Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) and Geographic Information System (GIS) for Soil Loss Risk Assessment in Upper South Koel Basin, Jharkhand. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2012, 4, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GSP. Global Soil Partnership Endorses Guidelines on Sustainable Soil Management. 2016. Available online: http://www.fao.org/global-soil-partnership/resources/highlights/detail/en/c/416516/ (accessed on 22 July 2021).
- Lal, R. Soil Carbon Sequestration Impacts on Global Climate Change and Food Security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration to mitigate climate change. Geoderma 2004, 123, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, S.A.J.; Rebecca, L.-K. Saving Soil—A ‘Landholder’s Guide to Preventing and Repairing Soil Erosion; Northern Rivers Catchment Management Authority: Huntly, New South Wales, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Dwight, D.S. Predicting Rainfall-Erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountains: Guide for Selection of Practices for Soil and Water Conservation; Agricultural Research Service, U.S. Dept. of Agriculture in Cooperation with Purdue Agricultural Experiment Station: Washington, MD, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Science and Education Administration, U.S. Dept. of Agriculture: Beltsville, MD, USA, 1978.
- Alewell, C.; Pasquale, B.; Katrin, M.; Panos, P. Using the USLE: Chances, challenges and limitations of soil erosion modeling. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedela, N.H.; Steven, C.M.; Todd, C.R.; Richard, H.H.; Wayne, T.S.; John, L.C.; Mary, B.A.; Jackson, C.R.; Ernest, W.T. Runoff Curve Numbers for 10 Small Forested Watersheds in the Mountains of the Eastern United States. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion By Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning With The Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); US Government Printing Office: Springfield, VA, USA, 1997.
- Renard, K.G.; Jeremy, R.F. Using monthly precipitation data to estimate the R-factor in the revised USLE. J. Hydrol. 1994, 157, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoldus, H.M.J. Methodology used to determine the maximum potential average annual soil loss due to sheet and rill erosion in Morocco. FAO Soils Bull. 1977, 34, 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ateshian, J.K.H. Estimation of rainfall erosion index. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1974, 100, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H. New developments in estimating water erosion. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 1974, 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Cooley, K.R. Erosivity Values for Individual Design Storms. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1980, 106, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanton, J.R.; Renard, K.G. USLE rainfall factor for southwestern U.S. rangelands. Agric. Rev. Man. 1982, 50–62. [Google Scholar]
- Naqvi, H.R.; Laishram, M.; Javed, M.; Masood, A.S. Multi-temporal annual soil loss risk mapping employing Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model in Nun Nadi Watershed, Uttrakhand (India). Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 4045–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R. Revised Universal Sil Loss Equation Version 2 (RUSLE2) Handbook; USDA National Soil Erosion Research Lab: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; pp. 18–20.
- Gardiner, E.P.; Judy, L.M. Sensitivity of Rusle to Data Resolution: Modeling Sediment Delivery in the Upper Little Tennessee River Basin. In Proceedings of the 2001 Georgia Water Resources Conference, Athens, GA, USA, 26–27 March 2001; pp. 561–565. [Google Scholar]
- Dissmeyer, G.E.; George, R.F. A Guide for Predicting Sheet and Rill Erosion on Forest Land; Forgotten Books: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Desmet, P.J.; Govers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, R. Module 3: Erosion Mechanisms and the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266468156_Module_3_Erosion_Mechanisms_and_the_Revised_Universal_Soil_Loss_Equation_RUSLE?enrichId=rgreq-899b7ecd11b8b514caaf794fd47570f8-XXX&enrichSource=Y292ZXJQYWdlOzI2NjQ2ODE1NjtBUzoxODUyNDcwMTg3OTA5MTJAMTQyMTE3 (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Selmy, S.A.H.; Al-Aziz, S.H.A.; Jiménez-Ballesta, R.; García-Navarro, F.J.; Fadl, M.E. Modeling and assessing potential soil erosion hazards using usle and wind erosion models in integration with gis techniques: Dakhla oasis, egypt. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.J.; Hong, Z.; Yiqing, G. Applications of Erosion Hotspots for Watershed Investigation in the Appalachian Hills of the United States. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Knijff, J.M.F.; Jones, R.F.A.; Montanarella, L. Soil Erosion Risk Assessment in Italy; European Soil Bureau, European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 1999; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Karaburun, A. Estimation of C factor for soil erosion modeling using NDVI in Buyukcekmece watershed. Ozean J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 3, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durigon, V.L.; Carvalho, D.F.; Antunes, M.A.H.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Fernandes, M. NDVI time series for monitoring RUSLE cover management factor in a tropical watershed. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro, A.; Thais, C.T.; Carina, B.C.; Rodrigo, B.P.; Jose, M.J.; Dulce, B.B.R.; Paulo, T.S.O. Improving cover and management factor (C-factor) estimation using remote sensing approaches for tropical regions. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, D.A.; Detlef, D.; Bořivoj, Š.; Daniel, D. Quantifying the Sensitivity of NDVI-Based C Factor Estimation and Potential Soil Erosion Prediction using Spaceborne Earth Observation Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korose, C.P.; Andrew, G.L.; Scott, D.E. The Proximity of Underground Mines to Urban and Developed Lands in Illinois; Technical Report; University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign: Champaign, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, D.I. Catalog of Hydrologic Units in Kentucky; Kentucky Geological Survey: Lexington, KY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA. Climate at a Glance: County Time Series. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/cag/county/time-series/KY-195/tavg/ann/6/1895-2021?base_prd=true&begbaseyear=1901&endbaseyear=2020 (accessed on 26 July 2021).
- Monger, C. Web Soil Survey. Available online: https://websoilsurvey.sc.egov.usda.gov/App/HomePage.htm (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- USGS. EarthExplorer. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Han, W.; Yang, Z.; Di, L.; Mueller, R. CropScape: A Web service based application for exploring and disseminating U.S. conterminous geospatial cropland data products for decision support. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 84, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R.; McCool, D.K.; Renard, K.G.; Moldenhauer, W.C. Conversion of the universal soil loss equation to S.I. metric units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1981, 36, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg, J.; Fabrice, A.M. Quantification of Erosion in Selected Catchment Areas of the Ruzizi River (DRC) Using the (R)USLE Model. Land 2020, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, C.; Wu, J.Q.; McCool, D.K.; Stockle, C.O. Estimating water erosion and sediment yield with G.I.s, RUSLE, and SEDD. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2003, 58, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Prasannakumar, V.; Vijith, H.; Abinod, S.; Geetha, N. Estimation of soil erosion risk within a small mountainous sub-watershed in Kerala, India, using Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) and geo-information technology. Geosci. Front. 2012, 3, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahleb, A.; Hadji, R.; Zahri, F.; Boudjellal, R.; Chibani, A.; Hamed, Y. Water-Borne Erosion Estimation Using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) Model over a Semiarid Watershed: Case Study of Meskiana Catchment, Algerian-Tunisian Border. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2022, 40, 4217–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Bai, Z.; Rong, L.; Li, Y.; Ding, J.; Tao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Wang, W. Investigation method for regional soil erosion based on the Chinese Soil Loss Equation and high-resolution spatial data: Case study on the mountainous Yunnan Province, China. Catena 2020, 184, 104237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Organization | City (Location) | Station ID | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kentucky Mesonet | Pikeville 13 S | DORT | 37.28 | −82.52 |
| NCDC (NOAA) | Fedscreek 1 SE | USC00152812 | 37.39 | −82.26 |
| NCDC (NOAA) | Clintwood 1 W | USC00441825 | 37.15 | −82.49 |
| NCDC (NOAA) | Huntington Tri State Airport | USW00003860 | 38.37 | −82.55 |
| Kentucky Mesonet | Whitesburg 2 NW | WTBG | 37.13 | −82.84 |
| Parameters | Definition | Source | Original Spatial Resolution | Date of Acquisition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R (MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1) | Rainfall/Runoff Erosivity Index | 5 Stations: 2 Kentucky Mesonet stations; 3 NOAA stations | N/A | 15 March 2021 |
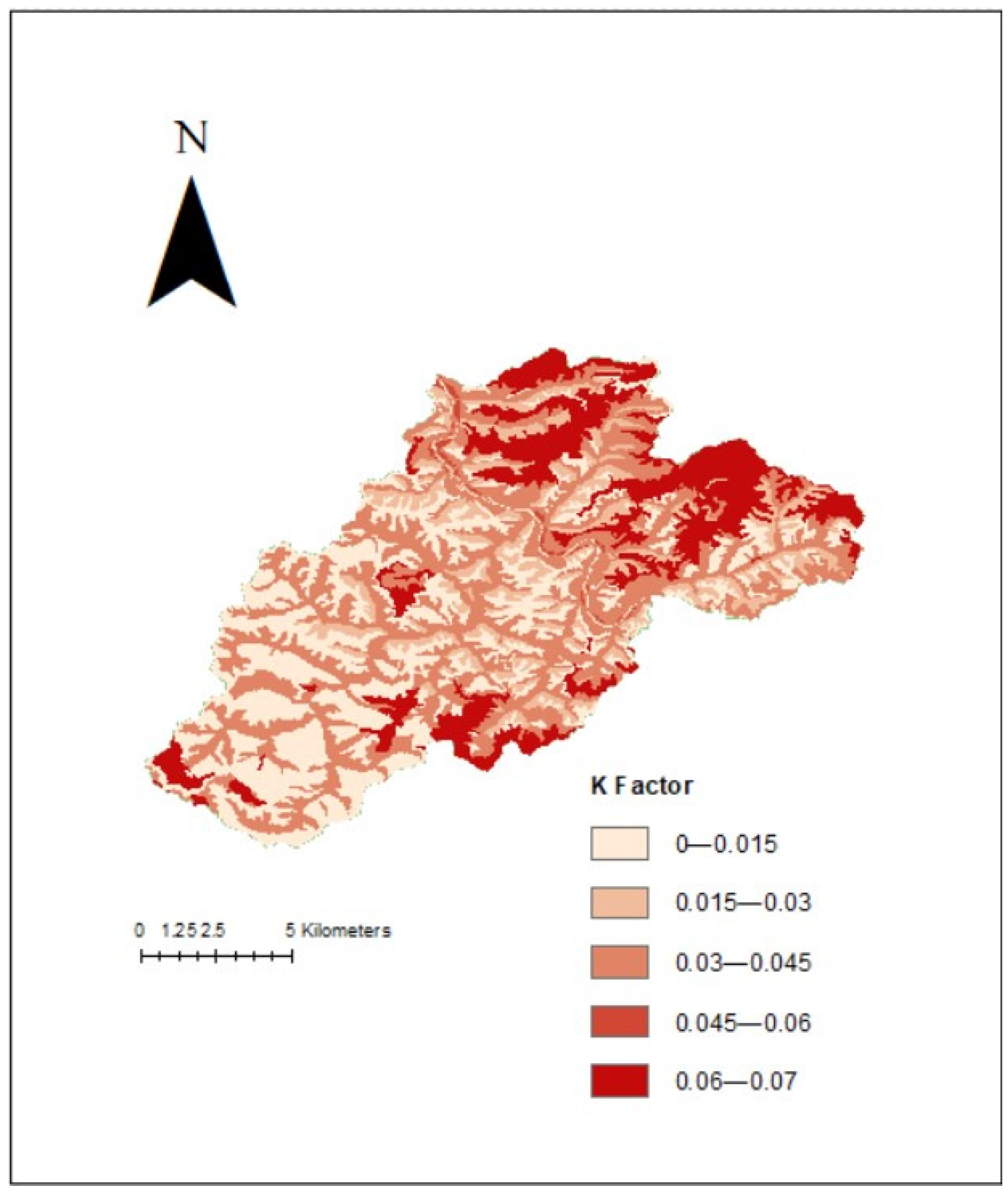
| K (Mg h MJ−1 mm−1) | Soil Erosivity Factor | NRCS web soil survey | N/A | 11 November 2020 |
| LS | Slope and length of Slope Factor | KyFromAbove LIDAR DEM 5 ft (1.524 m) | 1.524 m | 24 March 2021 |
| C | Cover Management Factor | Landsat 8 Data | 30 m | 19 June 2021 |
| P | Supporting Conservation practices | USDA Crop Data Layer, USDA RUSLE Guide | 30 m | 14 April 2021 |
| Land Cover Classes | P Factor Values |
|---|---|
| Dense Vegetation | 1 |
| Sparse Vegetation | 0.8 |
| Built-up (Developed) | 1 |
| Water Bodies | 1 |
| Scrub Land | 1 |
| Agricultural cropland | 0.5 |
| Fallow Land | 0.9 |
| Bare Soil/Barren Land | 1 |
| Year | Yearly Precipitation (mm) | MFI (mm) | R Factor (MJ mm ha−1 h−1 yr−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 1375.4 | 137.9 | 661.9 |
| 2014 | 1209.4 | 114.7 | 471.7 |
| 2015 | 1331.3 | 134.8 | 635.0 |
| 2016 | 1203.0 | 127.5 | 573.0 |
| 2017 | 1317.9 | 138.1 | 667.6 |
| 2018 | 1638.0 | 150.1 | 775.1 |
| 2019 | 1364.2 | 137.3 | 657.7 |
| 2020 | 1452.2 | 137.3 | 658.1 |
| Year | NDVI | C Factor |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 0.244 | 0.038 |
| 2014 | 0.215 | 0.039 |
| 2015 | 0.256 | 0.037 |
| 2016 | 0.225 | 0.038 |
| 2017 | 0.311 | 0.034 |
| 2018 | 0.227 | 0.039 |
| 2019 | 0.299 | 0.035 |
| 2020 | 0.269 | 0.037 |
| % of Watershed | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Cover Classes | P Factor | Average % of Watershed | Area of Watershed (sq. km) | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Corn | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other Hay/Non Alfalfa | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Open Water | 1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Developed/Open Space | 1 | 2.3 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| Developed/Low Intensity | 1 | 1.8 | 2.7 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Developed/Med intensity | 1 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Developed/High Intensity | 1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Barren | 1 | 3.2 | 4.9 | 1.2 | 2.3 | 4.5 | 3.1 | 4.6 | 3.3 | 3.6 | 3.2 |
| Deciduous Forest | 1 | 78.7 | 120.6 | 71.3 | 70.2 | 79.5 | 79.9 | 79.6 | 78.7 | 85.1 | 85.3 |
| Evergreen Forest | 1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 0.5 |
| Mixed Forest | 1 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Shrubland | 1 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.9 | 2.8 |
| Grassland/Pasture | 0.9 | 11.6 | 17.8 | 21.6 | 22.2 | 10.7 | 11.4 | 10.4 | 12.1 | 2.2 | 2.3 |
| Woody Wetlands | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Soybeans | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Herbaceous Wetlands | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Land Use | % of Watershed | Mean C Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Urban | 4.9 | 0.039 |
| Forest | 79.3 | 0.037 |
| Grassland | 11.6 | 0.037 |
| Rate of Soil Loss (Mg ha−1 yr−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Mean Annual Soil Loss Estimate (A) | Low (A < 1.5) | Moderate (1.5 < A < 5) | High (A > 5) |
| 2013 | 2.4 | 63.4% | 25.4% | 11.2% |
| 2014 | 1.8 | 70.2% | 23.0% | 6.8% |
| 2015 | 2.3 | 64.5% | 25.2% | 10.3% |
| 2016 | 2.2 | 65.7% | 24.6% | 9.7% |
| 2017 | 2.2 | 65.5% | 25.0% | 9.5% |
| 2018 | 2.9 | 59.4% | 26.2% | 14.4% |
| 2019 | 2.3 | 64.7% | 24.8% | 10.5% |
| 2020 | 2.4 | 64.1% | 25.4% | 10.5% |
| Land Cover Class | A | K | LS | C | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Water | 3.8 | 0.019 | 7.5 | 0.041 | 1.0 |
| Developed/Open Space | 3.4 | 0.032 | 4.4 | 0.038 | 1.0 |
| Developed/Low Intensity | 3.8 | 0.037 | 4.1 | 0.039 | 1.0 |
| Developed/Med intensity | 2.5 | 0.041 | 2.4 | 0.040 | 1.0 |
| Developed/High Intensity | 1.0 | 0.045 | 0.9 | 0.042 | 1.0 |
| Barren | 2.5 | 0.056 | 1.8 | 0.039 | 1.0 |
| Deciduous Forest | 2.5 | 0.027 | 3.8 | 0.037 | 1.0 |
| Evergreen Forest | 2.2 | 0.034 | 2.6 | 0.039 | 1.0 |
| Mixed Forest | 8.2 | 0.028 | 11.8 | 0.039 | 1.0 |
| Shrubland | 1.4 | 0.050 | 1.2 | 0.037 | 1.0 |
| Grassland/Pasture | 2.2 | 0.050 | 2.1 | 0.037 | 0.9 |
| Land Cover Type | Mean % of Watershed Area | Estimated Mean Soil Loss Rate (Mg ha−1 yr−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Developed Land | 4.9 | 3.4 |
| Undeveloped Land | 94.9 | 2.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, B.G.; Gyawali, B.R.; Zourarakis, D.; Gebremedhin, M.; Antonious, G. Soil Loss Analysis of an Eastern Kentucky Watershed Utilizing the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Environments 2022, 9, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9100126
Jones BG, Gyawali BR, Zourarakis D, Gebremedhin M, Antonious G. Soil Loss Analysis of an Eastern Kentucky Watershed Utilizing the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Environments. 2022; 9(10):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9100126
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Bilal G., Buddhi R. Gyawali, Demetrio Zourarakis, Maheteme Gebremedhin, and George Antonious. 2022. "Soil Loss Analysis of an Eastern Kentucky Watershed Utilizing the Universal Soil Loss Equation" Environments 9, no. 10: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9100126
APA StyleJones, B. G., Gyawali, B. R., Zourarakis, D., Gebremedhin, M., & Antonious, G. (2022). Soil Loss Analysis of an Eastern Kentucky Watershed Utilizing the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Environments, 9(10), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9100126







