Abstract
High concentrations of negative air ions (NAIs) and low concentrations of positive air ions (PAI), along with a low monopole coefficient (PAI/NAI), are likely to provide physiological and psychological benefits to the humans. A water body produces NAIs through the Lenard effect. This concept can be applied in designing garden waterscapes in residential buildings to provide fresh and healthy air for urban residents. In this study, we conducted several experiments to assess the effectiveness of different waterscape designs in producing air ions. The results revealed that increasing waterfall tiers, slopes, impact points, widths, and heights increased the NAI concentrations and reduced the values of monopole coefficients, thus providing health benefits to humans. In particular, increasing waterfall tiers and slopes increased the NAI concentrations most substantially. Moreover, we established a composite waterscape and determined that it produced fewer NAIs along with a less favorable monopole coefficient compared with the data observed at the experimentally adjusted tiers and slopes. Therefore, we suggest that simple waterscapes with multiple waterfall tiers or steep waterfall slopes should be favored over complex waterscapes. Such simple designs can help construct a garden that provides health benefits.
1. Introduction
An excessive concentration of positive ions in an environment may cause diseases in humans. For example, people who stay in an air-conditioned space for prolonged periods are susceptible to Legionnaires’ disease. This disease can damage the immune system, and might even lead to death in severe cases [1,2,3]. Kosenko et al. [4] discovered that high concentrations of positive air ions (PAI) lead to a symptom called “sharaf” or “hamsin” in people living in the deserts of the Middle East. Conversely, high concentrations of negative air ions (NAIs) boost metabolism, strengthen interactions between the muscular and immune systems, increase energy levels, and produce health benefits for emotions, memory, and human development. NAIs also help improve the functions of the central nervous system, respiratory system, and cardiovascular system, in addition to promoting hematopoiesis and enzyme activities [3,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. Wu et al. [2] demonstrated that negatively charged air ions are effective in preventing and alleviating more than 30 diseases.
Dr. Philipp Lenard [12], a Nobel laureate in physics, proposed in 1892 that when water drops from a high altitude, the droplets collide with one another and break up, resulting in charge separation and ionization. The phenomenon in which the breakup of water droplets generate NAIs is called the Lenard effect. Several factors could affect generation and concentration of NAIs including water drop, dissolved impurities, temperature, speed of the impinging air blast, and foreign impinging surfaces of droplets. Kosenko et al. [4] suggested that water shearing produces superoxide ions (O2−), then superoxide ions combine with water molecule clusters to form the structure O2− (H2O)n. Iwama [13] further indicated that was essentially regarded as a natural source of NAIs. These NAIs generated by the “Lenard effect” might improve erythrocyte deformability, and thus aerobic metabolism.
Artificial corona discharge is an efficient way to generate radioactive NAIs [14]. When a high negative voltage is applied to a conductor/electrode and generated electric field is high enough, corona discharge occurs [15,16]. If a charged conductor/electrode has a sharp, needle-type point, the electric field around the tip will be significantly higher than for other parts, and the air near the electrode can become ionized, generating NAIs [17]. Intensity of corona discharge depends on the shape and size of the conductors as well as the applied voltage [14]. However, previous studies have also shown that artificially generated NAIs present an obvious disadvantage, the emission of ozone [14,18], which is a powerful oxidant and could be seriously harmful to health if in long-term and/or high-dose exposure. Furthermore, many NAI generators release ozone, including well-known brand ionizers [19,20,21,22,23]. Lin et al. [24] found out that artificial NAIs also generated byproducts of noxious gas such as ozone and nitric oxide, and discovered that PAIs act on certain activities such as exciting sympathetic nerves, leading to a harmful impact on human health.
Yen [25] simulated the generation of NAIs from the breakup of water droplets by using three types of nozzles in an indoor spray chamber. The author observed that combining different nozzles produced a higher concentration of NAIs than did using a single nozzle; moreover, combining three nozzles generated the highest ion concentration. Weng [26] studied the relationship between NAI concentration and the distance from urban landscaping fountains. The author identified an exponential relationship between the observed NAI concentrations and the distance from the fountains. NAI concentration was higher in areas close to the fountains than in those farther from the fountains. Atomization of water droplets was also analyzed, and the results showed that the atomization pressure was proportional to the NAI concentration, indicating that the NAI concentration was higher under high atomization pressures. Li et al. [27] measured the concentrations of NAIs among fountains from two regions in Shanghai. They determined that NAI concentration was proportional to the fountain size; however, the concentration was negatively correlated with the distance from the fountains (i.e., the concentration of NAIs decreased as the distance between the measurement location and fountains increased). Tan et al. [28] measured the concentration and distribution of NAIs among three waterscapes at a coastal resort in Yangjiang, Guangdong, China. The results also demonstrated a negative correlation between NAI concentration and the distance from the waterscapes. Therefore, they suggested that the distance between a waterscape and activity area should be shortened to improve visitors’ health. Wang et al. [29] discovered that fountains and other dynamic waterscapes can be added appropriately in design to compensate for the negative impact of excessive urban cement pavement and pedestrian and vehicle traffic on air anion concentration.
In nature, waterfalls, forests, rivers, valleys, lakes, and ponds have abundant NAIs but few PAIs, resulting in a low monopole coefficient, namely the PAI–NAI ratio [30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]. However, people living in urban areas cannot frequently visit natural environments and enjoy fresh air. Hence, in urban areas, designing home gardens that can generate high concentrations of NAIs has become a common approach to constructing healthy environments [39]. Wu et al. [3,40] indicated that the concentration of NAIs produced by waterscapes in residential gardens is close to that produced in parks. Additionally, they reported that the NAIs produced by such waterscapes had the benefits of improving spatial quality and health. Such waterscapes fulfilled urban residents’ needs for visiting natural waterscapes and pursuing great health. Further research should be conducted on the design of waterscapes that produce optimal NAI concentrations and health benefits. Wang [41] stated that NAIs can effectively improve the original appearance of a city and constantly strengthen the physical and mental health of residents, so that the urban residents can enjoy a better life. Sun [42] observed that living along the waterside and being closer to nature promotes a healthy lifestyle. Zhu [43] suggested that water is a bridge between humans and nature, and that waterscapes are a charming element in landscape art. Water makes the environment alive and lovely, and shortens the distance between the environment and the humans.
A residential garden is considered an extension of the house [44]. Studies have demonstrated that residential gardens have multiple advantages such as enhancing scenic beauty [45], creating recreational and psychological benefits, providing a venue for family- or friend-oriented events [46], and providing economic returns [47]. Furthermore, Andrews and Coppola [48] discovered that different home gardens evoke different perceptions, preferences, and responses among people [49], which can be helpful for physiological and psychological recovery [50]. Sun et al. [51] have suggested that residential waterscapes can improve the living environment effectively and stimulate health, and therefore designing waterscapes that meet the demand of citizens from a user’s perspective require the active exploration of waterscape designers. However, previous studies have often been limited to measuring NAIs generated by the Leonard effect on existing natural water features (such as waterfalls), forests, or artificial waterscapes. Knowledge of the guidelines and specification of waterscape design is relatively unknown, and lacks practical evidence regarding how waterscapes could produce optimal NAI concentrations. Therefore, this study conducted several experiments to verify the optimal design of waterscapes and performed trials to examine different design parameters. The findings can be applied to establish design guidelines and even standardize measurement of water landscape development.
2. Material and Methods
We conducted experiments in an experimental box in an enclosed space. The box comprised a set of acrylic devices, a water cycle system, and upper and lower reservoirs. The waterfall height, width, slope, tiers, and impact points could be adjusted by using the acrylic devices. Figure 1 and Figure 2 present the details of the experimental setup. Experiments for observing NAI and PAI concentrations were conducted by adjusting the following variables: waterfall brink height, waterfall flow width, waterfall channel slope, number of tiers, and number of impact points. After referring to common waterscape designs in residential gardens in Taiwan, we set the variables as follows: maximum waterfall height = 150 cm; maximum waterfall width = 80 cm; maximum waterfall slope = 75°; maximum number of tiers = 5; and maximum number of impact points = 4.
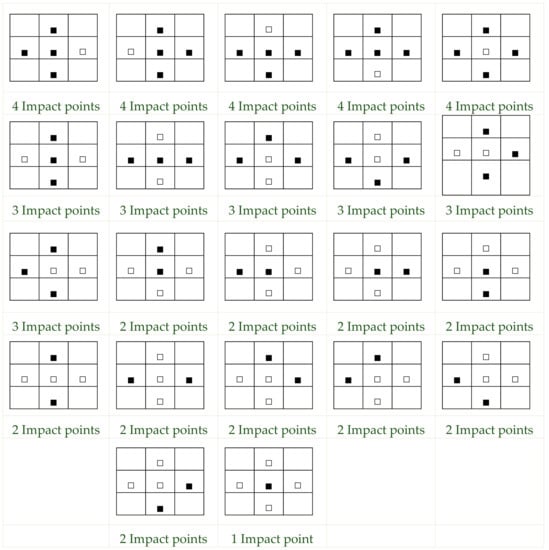
Figure 1.
Different patterns of impact point combinations.
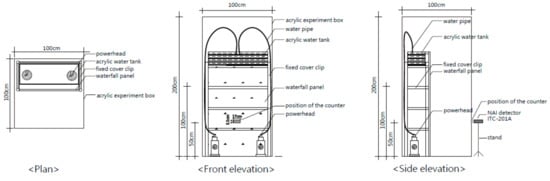
Figure 2.
Installation drawing of devices for the waterscape design and air ion generation experiments.
(1) Waterfall height in waterscape
We defined the waterfall height as the distance between the brink of the waterfall and the bottom of the lower reservoir. The height was divided into five experimental groups: 50, 75, 100, 125, and 150 cm. The control variables were the width of the brink (80 cm), slope of the waterfall (90°), number of waterfall tiers (0 tier), and number of impact points (0 point).
(2) Waterfall width in waterscape
We defined the waterfall width as the width of the flow section. The width was divided into five experimental groups: 30, 40, 50, 60, and 70 cm. The control variables were the height of the waterfall (150 cm), slope of the waterfall (90°), number of waterfall tiers (0 tier), and number of impact points (0 point).
(3) Waterfall slope in waterscape
We defined the waterfall slope as the angle between the waterfall panel and the ground plane. The slope was divided into four experimental groups: 30°, 45°, 60°, and 75°. The control variables were the height of the waterfall (150 cm), width of the waterfall (80 cm), number of tiers (0 tier), and number of impact points (0 point).
(4) Waterfall tier in waterscape
We defined the waterfall tier as the vertical tier from which the water dropped. The waterfall tier was divided into five experimental groups: 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 tiers. The control variables were the height of the waterfall (150 cm), width of the waterfall (80 cm), slope of the waterfall (90°), and number of impact points (0 point).
(5) Waterfall impact points in waterscape
We defined the number of impact points as the number of objects hit by the water. The impact point was defined as a cube with a 10-cm length on each side, arrayed as Figure 1. The number of impact points was divided into four experimental groups: 1, 2, 3, and 4 points. The control variables were the height of the waterfall (150 cm), width of the waterfall (80 cm), slope of the waterfall (90°), and number of tiers (0 tier).
We used ITC-201A (ANDES Electric Co., Ltd., Hachinohe, Japan) as the PAI and NAI detector. The horizontal distance between the detector and waterscape was 70 cm, and the vertical distance was 50 cm above ground (Figure 2). The detector can detect the concentrations of PAIs and NAIs with electron mobility values greater than 0.5 cm2 V−1 s−1 per unit air volume. The detector has a measurement range of 10–1,236,000 pcs/cm3 and a detection interval of 0.5 s; the detector also measures air temperature and humidity. We calibrated the detector for 30 s for the height, width, slope, tiers, and impact points in the experimental device in order to ensure steady detector operation. Subsequently, we used the detector to conduct the measurements.
In general, the detector can detect PAI and NAI concentrations effectively for temperatures ranging from 5 to 35 °C and humidity under 85%. In this study, a few experiments also measured PAIs and NAIs effectively while humidity was up to 90%. Before recording data, the machine needs 10 to 20 seconds to calibrate and then generate stabilized monitoring values. In each experiment, the detection duration was 180 s, and the PAI and NAI concentrations were measured every 0.5 s; thus, 360 data items were collected. The same process was repeated three times for each experiment, and the resulting values were averaged. Next, the monopole coefficients were calculated. Finally, regression analysis was conducted using various experimental groups in Microsoft Excel.
3. Results
3.1. NAI and PAI Concentrations Measured at Different Waterfall Heights
We set five waterfall height values (i.e., 50, 75, 100, 125, and 150 cm) and compared the PAI and NAI concentrations generated when these heights were applied. The results revealed that the NAI concentrations ranged from 21 to 172 pcs/cm3, whereas the PAI concentrations ranged from 221 to 304 pcs/cm3 (Table 1). The regression analysis results demonstrated that the waterfall height was positively correlated with the PAI and NAI concentrations. Specifically, in the polynomial regression, the regression coefficient (R2) was 0.97 for the NAI–waterfall height correlation and 0.64 for the PAI–waterfall height correlation (Figure 3). In addition, the lowest monopole coefficient (q) was 1.8, which was observed at the heights of 125 and 150 cm. Height was thus negatively correlated with the monopole coefficient.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of positive air ions (PAI) and native air ions (NAI) concentrations at different waterfall heights.
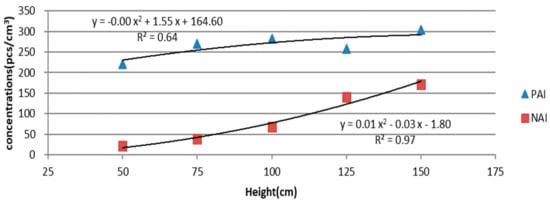
Figure 3.
Regression models for correlations between PAI and NAI concentrations and waterfall heights.
3.2. PAI and NAI Concentrations Measured at Different Waterfall Widths
We set five experiments based on waterfall width values (i.e., 30, 40, 50, 60, and 70 cm) and compared generated PAI and NAI concentrations. The NAI concentrations ranged from 55 to 210 pcs/cm3, whereas the PAI concentrations ranged from 227 to 268 pcs/cm3 (Table 2). PAI concentrations were higher than NAI. Regression analysis results showed that the correlation between the waterscape width and ion concentration could be expressed by a quadratic polynomial. In particular, the R2 value for the NAI–waterfall width and correlations was 0.89, while the correlation coefficient of the PAI–waterfall width was 0.49 (Figure 4). Furthermore, the lowest monopole coefficient (q) was 1.2, which was observed for a width of 60 cm.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics of PAI and NAI concentrations at different waterfall widths.
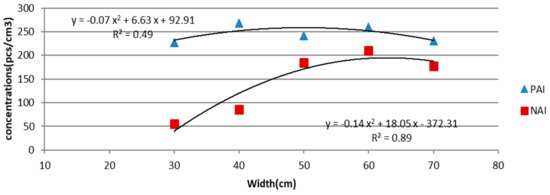
Figure 4.
Regression models for correlations between PAI and NAI concentrations and waterfall width.
3.3. PAI and NAI Concentrations at Different Waterfall Tiers
We set five waterfall tiers (i.e., 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 tiers) and compared the PAI and NAI concentrations at these tiers. The NAI concentrations ranged from 1686 to 3940 pcs/cm3, whereas the PAI concentrations ranged from 868 to 1648 pcs/cm3 (Table 3). In contrast to the results in the preceding experiments, the NAI concentrations were greater than the PAI concentrations in this experiment. The regression analysis results also revealed that the correlation between the waterfall tier and ion concentration could be expressed by a quadratic polynomial. Specifically, the R2 values for the PAI–waterfall tier and NAI–waterfall tier correlations were the same (0.92; Figure 5). Additionally, all monopole coefficients (q) determined at the five tiers were less than 1; the lowest coefficient was 0.3, which was detected when the number of tiers was 5. According to Kong et al. [33], a low monopole coefficient (q) indicates comfort for people. Thus, the experimental results indicate that waterfall tier can be a parameter that leads to ion concentrations providing comfort to people.

Table 3.
Descriptive statistics of PAI and NAI concentrations at different waterfall tiers.
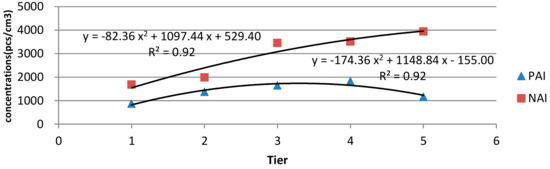
Figure 5.
Regression models for correlations between PAI and NAI concentrations and waterfall tiers.
3.4. NAI and PAI Concentrations at Different Waterfall Slopes
We set four slope levels (i.e., 30°, 45°, 60°, and 75°) and compared the ion concentrations at these slopes. The NAI concentrations ranged from 1837 to 3619 pcs/cm3, and the PAI concentrations ranged from 1248 to 2699 pcs/cm3 (Table 4). The NAIs were more than the PAIs at all four slopes. The regression analysis results showed that the correlation between the waterfall slope and ion concentration could be expressed by a quadratic polynomial. Specifically, the R2 values for the NAI–waterfall slope and PAI–waterfall slope correlations were 0.99 and 0.97, respectively (Figure 6). The monopole coefficients (q) of four slope types did not exceed 1; the lowest coefficient was 0.6, which was observed at the 60 degree slope.

Table 4.
Descriptive statistics of PAI and NAI concentrations at different waterfall slopes.
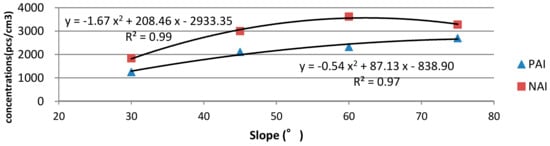
Figure 6.
Regression models for correlations between PAI and NAI concentrations and waterfall slopes.
3.5. PAI and NAI Concentrations at Different Waterfall Impact Points
We set four waterfall impact points (i.e., 1, 2, 3, and 4 points) and compared the PAI and NAI concentrations generated when these impact points were applied. The NAI concentrations ranged from 348 to 637 pcs/cm3, and the PAI concentrations ranged from 254 to 356 pcs/cm3 (Table 5). The NAI concentrations were slightly higher than the PAI concentrations at all four points. The regression analysis results demonstrated that the correlation between the impact points and ion concentrations could be expressed by a quadratic polynomial. Specifically, the R2 values for the NAI–impact point and PAI–impact point correlations were 0.99 and 0.85, respectively (Figure 7). The monopole coefficients (q) were less than 1 at all four points; the lowest coefficient was 0.6 and was observed when the number of impact points was set to 2 and 4. These results indicate that the number of impact points could serve a parameter of comfort among people.

Table 5.
Descriptive statistics of PAI and NAI concentrations at different impact points.
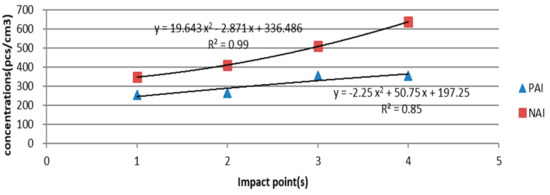
Figure 7.
Regression models for correlations between PAI and NAI concentrations and waterfall impact points.
4. Discussion
4.1. NAI Concentrations Observed for Different Waterscape Designs
In our experiments, polynomial regression is applied to fit trends of the number of produced negative air ions with each experiment. Results show that R2 values with waterfall heights, widths, tiers, slopes, and impact points were 0.97, 0.89, 0.92, 0.99, and 0.99 (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7), respectively. This means that increasing height, width, tier, slope, and impact points could enhance production of NAIs for waterfalls.
These results demonstrate that the various waterfall tiers and slopes led to the highest PAI and NAI concentrations, followed by the impact points and widths; the corresponding monopole coefficients were relatively low. By contrast, adjusting the waterfall height resulted in the lowest PAI and NAI concentrations, and the monopole coefficients were relatively high (Table 6 and Table 7). The highest NAI concentration (3940 pcs/cm3) was achieved when the number of waterfall tiers was set to 5 (Table 6), with the corresponding monopole coefficient (0.3) being the lowest. This NAI concentration is between the NAI concentration produced in forests and that produced in waterfalls, indicating its favorable healing and recovery effects [52]. Zhou et al. [53] have demonstrated that NAIs also have great potential for enhancing indoor air quality by reducing airborne microorganisms in ventilation systems.

Table 6.
Summary of experimental results.

Table 7.
Descriptive statistics of PAIs and NAIs produced by a composite waterscape.
Wu [2] also demonstrated that NAIs can eradicate particulate matter. Yan et al. [54] discovered that NAI concentrations ranged from 2000 to 5000 pcs/cm3 in the forest areas of Gansu Province, China. They determined that areas with high NAI concentrations had low levels of pollution. Accordingly, the experimental results of the current study demonstrate that adjusting waterfall tiers and slopes could be effective in reducing pollution.
4.2. PAI Concentrations Observed for Different Waterscape Designs
Wu [2] observed that an environment with an excessive concentration of PAI is associated with diseases in humans. Therefore, people should avoid staying in enclosed and air-conditioned rooms for prolonged periods. Excessive PAI concentrations lead to pollution in the pipes of air conditioners, causing harm to human health. Most air pollutants, such as exhaust gases and waste from construction sites and equipment, electrical equipment, and transportation, carry positive ions in the atmosphere. Compared with positive ions, negative ions have a shorter half-life and hence are more likely to react and form bonds with positive ions and other pollutants such as particulate matter, leading to a reduction of NAI concentrations.
Here, polynomial regression was also used to examine relations generating positive air ions with waterfall heights, widths, tiers, slopes and impact points, resulting in R2 values of 0.64, 0.49, 0.92, 0.97, and 0.85 (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7). This is evidence of a positive correlation between increase of height, width tier, slope, and impact points and the amount of PAIs produced by waterfalls.
More PAIs were produced at the different waterfall tiers and slopes than at the other settings (Table 6). The waterfall slope of 75° produced the highest PAI concentration (2699 pcs/cm3). However, this slope also produced the highest NAI concentration (3273 pcs/cm3), and the corresponding monopole coefficient was low (0.8). These results imply that a waterscape involving a waterfall slope of 75° could provide comfort to people [33].
4.3. Monopole Coefficients Observed for Different Waterscape Designs
While water drops from a high altitude, droplets collide with one another and break up, resulting in charge separation and ionization. In this study, results showed the produced amount of PAIs was more in both experimental groups of water depth and width (Table 1 and Table 2). However, in experimental groups of slope, stratum number, and impact point, concentrations of NAI were found to be higher (Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5). This suggests that boosting the collision probability of water molecules (e.g., increasing the number of strata) could contribute to the generation of air negative ions when designing waterscapes. On the other hand, water landscapes with pure, vertical waterfalls tend to produce more PAIs than NAIs.
Monopole coefficient can be a suitable measurement of the air quality regarding air ions [3]. Wu [3] found that NAI/PAI value is higher when near to waterfalls and green spaces; however, it is low at road entrances. Thus, landscape elements such as waterfall and green spaces could be considered as driving factors in the quality of air ions. Wu also demonstrated that the Lenard effect occurs near waterfalls and produces both high negative and positive air ions. Ma [55] stated that the average monopole coefficient was in the range of 1.1–1.2. In this study, the monopole coefficients observed at the different waterfall tiers, slopes, and impact points were between 0.3 and 0.8 (Table 6). These results indicate that waterfall tiers, slopes, and impact points are effective in realizing an environment that has more desirable NAI concentrations and monopole coefficients than common outdoor environments. Conversely, the coefficients observed at the different waterfall heights and widths mostly exceeded 1.2. Specifically, the highest coefficient (10.5) was observed at the waterfall height of 50 cm, which was considerably higher than those observed at other settings. Therefore, we suggest that waterscapes with considerable heights and widths should be avoided.
4.4. Analysis of Ion Production and Monopole Coefficient of a Composite Waterscape
We designed a composite waterscape by using waterfall tier, slope, and impact point settings that produced the highest NAI concentrations. This composite waterscape comprised five waterfall tiers and four impact points, as well as a waterfall slope of 60°, height of 150 cm, and width of 80 cm. The resulting PAI and NAI concentrations were 1008 and 852 pcs/cm3, respectively, with the corresponding monopole coefficient being 1.2. Compared with the data observed at the different experimentally adjusted waterfall tiers and slopes, the NAI concentration was lower, but the PAI concentration and monopole coefficient were higher for the composite waterscape. These results suggest that a composite waterscape could not necessarily produce high NAI concentrations with a low monopole coefficient. In other words, the design of waterscapes in gardens should not be excessively complex.
According to the 2018 Revision of World Urbanization Prospects, published by the United Nations (UN) in 2018, 78.2% of Taiwan’s population lives in urban areas, comprising 18.6 million people. Projections show that the overall growth of urban population could be oversaturated with a peak of 20 million people by 2041, a proportion that is expected to increase to 87.5% by 2050. This means that the demand for urban parks and residential gardens should go up along with increasing population density. Waterscapes will generate NAI ions that can improve air quality and enhance visual beauty, bringing both physiological and mental health benefits upon users. Design measurements of waterscapes obtained from this study can provide the basic standard to develop water landscapes in Taiwan in the future.
For the Pearson correlation analysis (Table 8), the number of PAIs and humidity showed a significant positive correlation with a correlation coefficient of 0.806, suggesting that the higher the humidity, the more positive ions are generated. It also indicates that NAI amount has a significant positive correlation with humidity (0.856) and PAI amount (0.915). This means that a higher number of NAIs can be produced with the presence of more PAIs. In addition, temperature and humidity present significant negative correlations with the Monopole coefficient, with correlation coefficients of −0.698 and −0.661. This implies that the Monopole coefficient is getting smaller along with increases of humidity. At this moment, lessPAIs would be detected when higher values of NAIs can be found.

Table 8.
Pearson correlations among temperature, humidity, PAIs, and NAIs.
5. Conclusions
This study conducted experiments to verify the production of air ions in different waterscape designs. We discovered that increasing waterfall tiers, slopes, impact points, widths, and heights led to high NAI concentrations with low monopole coefficients, which can provide health benefits. In particular, increasing the waterfall tiers and slopes considerably elevated the NAI concentrations to a tier close to the NAI concentration produced in natural forests. Furthermore, we verified that a composite waterscape resulted in less favorable NAI production with a lower monopole coefficient compared to the data observed at the different experimentally adjusted waterfall tiers and slopes. Accordingly, we suggest that in terms of providing health benefits to people, a simple waterscape with multiple waterfall tiers and a steep slope is preferable to a complex waterscape. The findings can be adopted by establishing garden waterscapes that provide health benefits.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-F.W.; Funding acquisition, C.-F.W.; Investigation, T.-Y.C.; Methodology, S.-H.C.; Software, S.-H.C.; Validation, S.-Y.W.; Visualization, T.-Y.C.; Writing–original draft, S.-Y.W.; Writing–review & editing, C.-F.W.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China, Taiwan, for financially supporting this research under Contract No. 100-2410-H-005-050 and MOST 105-2621-M-005-003-MY3. This work also was supported by the “Innovation and Development Center of Sustainable Agriculture” from the Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Charry, J.M.; Kvet, R. Air Ions: Physical and Biological Aspects; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.C. Control of Volatile Organic Compounds, Particulates, and Bioaerosols with the Aid of Negative Air Ions in Indoor Environment. PhD Thesis, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, 30 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.F.; Lai, C.H.; Chu, H.J.; Lin, W.H. Evaluating and mapping of spatial air ion quality patterns in a residential garden using a geostatistic method. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 2304–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosenko, E.A.; Kaminsky, Y.G.; Stavrovskaya, I.G.; Sirota, T.V.; Kondrashova, M.N. The stimulatory effect of negative air ions and hydrogen peroxide on the activity of superoxide dismutase. FEBS Letters 1997, 410, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.F. The health benefit of forest recreation. Master’s Thesis, National Taipei University of Nursing and Health Science, Taipei, Taiwan, 30 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.N.; Ding, X.D. The effect of minus ion in the air on sports ability and its application in exercise. China. J. Hubei Sports Sci. 2006, 25, 534–536. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.W.; Li, C.Y.; Ge, J.R.; Yang, J.M.; Liu, X.Q. Progress of aero-anion in forest environment. J. Northwest Forestry University 2007, 22, 57–61. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, W.; Lin, X.Y. Air anion level and valuation in major tourist areas of acheng district. Agric. Technol. Informa. Mod. Landsc. Archit. 2007, 10, 45–50. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.P.; Wang, C. Urban green space and human health. World Forestry Res. 2007, 20, 32–37. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.M.; Rao, S.T.; Wang, L.L. Study on improving effects of negative ion technique on environment in an underground railway station. J. Heat. Vent. Air Cond. 2008, 39, 122–128. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.X.; Xiao, L.H.; Huang, Y.Y.; Lin, X.D. Study on concentrations of air anion in Nanao island. Guangzhou Chemical Industry 2009, 37, 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Lenard, P. Über die Electrizität derWasserfälle. Ann. Phys. 1892, 46, 584–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, H. Negative air ions created by water shearing improve erythrocyte deformability and aerobic metabolism. Indoor Air 2004, 14, 293–297. (in Japanese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Y.; Ali, M.; Ramachandran, S. Negative air ions and their effects on human health and air quality improvement. Singapore. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altamimi, G.; Illias, H.A.; Mokhtar, N.; Mokhlis, H.; Bakar, A.H.A. Corona discharges under various types of electrodes. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Power and Energy (PECon), Kuching Sarawak, Malaysia, 1–3 December 2014; pp. 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ogar, V.N.; Bendor, S.A.; James, A.E. Analysis of corona effect on transmission line. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2017, 6, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Berendt, A.; Budnarowska, M.; Mizeraczyk, J. DC negative corona discharge characteristics in air flowing transversely and longitudinally through a needle-plate electrode gap. J. Electrostat. 2018, 92, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutto, H.C. Superoxide and ozone production by corona discharge. J. Chem. Soc. 1984, 80, 2301–2311. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, D.; Mainelis, G.; Fennell, D. Effect of an ionic air cleaner on indoor/outdoor particle ratios in a residential environment. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.L.; Tung, T.C.W.; Burnett, J. Quantication of dust removal and ozone emission of ionizer air-cleaners by chamber testing. J. Electrostatics 2001, 51, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Lee, G.W.M. Oxidation of volatile organic compounds by negative air ions. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6287–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, M.S.; Siegel, J.A.; Corsi, R.L. Ultrafine particle removal and generation by portable air cleaners. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5003–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.P. Enhancement of the deposition of ultrafine secondary organic aerosols by the negative air ion and the effect of relative humidity. J. Air Waste Manag. 2012, 62, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.F.; Lin, J.M. Generation and determination of negative air ions. J. Anal. Test 2017, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, L.H. The Study of Negative Air Ion Produced by Water Droplet Breakup. Master’s Thesis, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, 30 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, C.L. The study on generation method of environmental negative air ions. Master’s Thesis, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, 30 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.G.; Liu, Q.; Li, J. Study on air negative ions produced by fountain and its effecting factors. J. Environ. Health 2000, 17, 205–207. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, G.W.; Guo, S.H.; Zeng, F.F. Distribution characteristic of air negative ion concentration in three landscape dropping waterscape environment. Landsc. Theory Study Guangdong Landsc. Archi. 2014, 3, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Shi, F. Study of air anion concentration in various water statuses. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 518–523, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Wang, F.; Guo, J.G.; Zhang, M.R.; Yu, Y.W. A review: Negative air ions and its main influence factors in forest areas. China. J. Inner Mongolia Agricultural University 2008, 2, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, D.Y.; Guo, N.W.; Wu, S.Y. Study on negative ions characteristics in forest recreation area. Leisure Recreation Health Benefits Symposium JinWen University Science Technology 2004, 299–315. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.S.; Liu, J.; Di, Y.B.; Xiang, H.; Liu, J.; Li, B.F. Observing air anion concentration in Beidaihe and anion’s evaluation standard. J. Environ. Manag. College China 2008, 18, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, J.J.; Lin, J.M.; Zhang, J.S. Construction and application of attribute assessment model of air Anion. Environ. Sci. Survey 2008, 27, 84–86. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, D.; Liang, Y.H. Effect of urban greenbelt structure on air negative ions concentration. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 988–991. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.C.; Yao, C.S.; Guo, J.P.; Xu, C.X. Distribution of negative air ions and its relation to air quality of the Yuelu Mountain. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 2006, 26, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.P.; Wu, F.C.; Xie, Y.H.; Xiong, J.A.; Feng, F.L. The study of negative air ions in scenic of guiding county. J. Natural Sci. Hunan Normal University 2007, 30, 110–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.W.; Li, C.Y.; Ge, J.R.; Liu, F.; Li, D.H.; Chen, D.H.; Yang, J.M. Aero-anion concentration in silver chain forest. J. Northwest Forestry University 2007, 35, 29–31. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.X.; Xiang, H.; Huang, C.S.; Wang, Y.J. Experimental research on the concentration of negative air ions. J. Xi’an University Eng. Sci. Technol. 2007, 21, 803–806. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.F.; Lin, W.H.; Lai, C.H. Relationship between residual garden landscape and air ions distribution. J. Archit. 2010, 71, 213–232. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.F.; Lin, W.H. Development and perspective on negative air ions in Taiwan and China. JORS 2009, 22, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Landscape planning and design of large city square musical fountain based on the recognition of music features. Open House Int. Gateshead 2018, 43, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y. Study on the waterscape design of modern residential districts. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 438–439, 1730–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Y.; Li, Y.K. A preliminary analysis of the waterscape in face of the shortage of water. Procedia Eng. 2011, 21, 693–699. [Google Scholar]
- Sigmon, S.T.; Whitcomb, S.R.; Snyder, C.R. Psychological home. In Psychological Sense of Community: Research, Applications, and Implications; Fisher, A.T., Sonn, C.C., Bishop, B.J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Sime, J. What makes a house a home: The garden? In Housing: Design, Research, Education; Bulos, M., Teymur, N., Eds.; Aldershot, Avebury: Farnham, UK, 1993; pp. 239–254. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, M.; Church, A. I never promised you a rose garden: Gender, leisure and home-making. Leisure Stud. 2000, 19, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syme, G.J.; Kantola, S.J.; Thomas, J.F. Water resources and the quarter acre block. In People and the Man Made Environment; Thorne, R., Arden, S., Eds.; University of Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 1980; pp. 192–201. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, T.J.; Coppola, D.M. Idiosyncreatic characteristics of saccadic eye movements when viewing different visual environments. Vision Res. 1999, 39, 2947–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T.C.; Vining, J. Methodological issues in the assessment of landscape quality. In Human Behavior and Environment: Advances in Theory and Research; Altman, I., Wohlwill, J., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 39–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, R.; Kaplan, S. The Experience of Nature: A Psychological Perspective; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.H.; Bo, S.; Guo, T.H. Residential waterscape design based on traditional healing garden theory. J. Simulation Systems Sci. Technol. 2016, 17, 4.1–4.6. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, H.R.; He, Q.T. Forest and air anion. World For. Res. 2000, 13, 19–23. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, Y.; Huang, G.S.; Lai, A.C.K. Numerical and experimental study on airborne disinfection by negative ions in air duct flow. Build. Environ. 2018, 127, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.J.; Wang, H.R.; Hou, Z.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Xu, Q.; Tokola, T. Spatial analysis of the ecological effects of negative air ions in urban vegetated areas: A case study in Maiji. Urban Forestry Urban Greening 2015, 14, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.J. Anion principle and application. J. Sci. Development 2007, 413, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).