Is a Land Use Regression Model Capable of Predicting the Cleanest Route to School?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
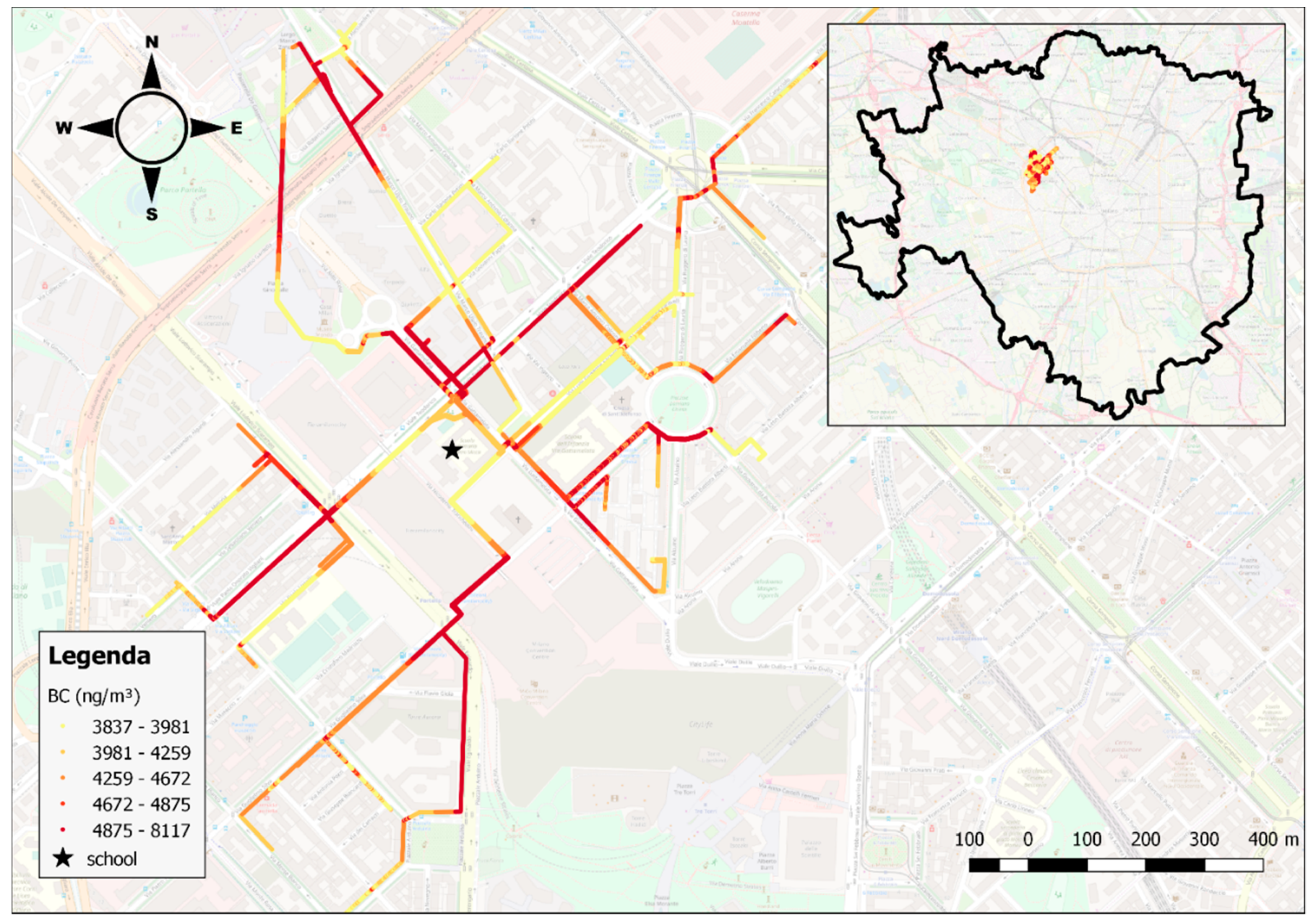
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Analysis
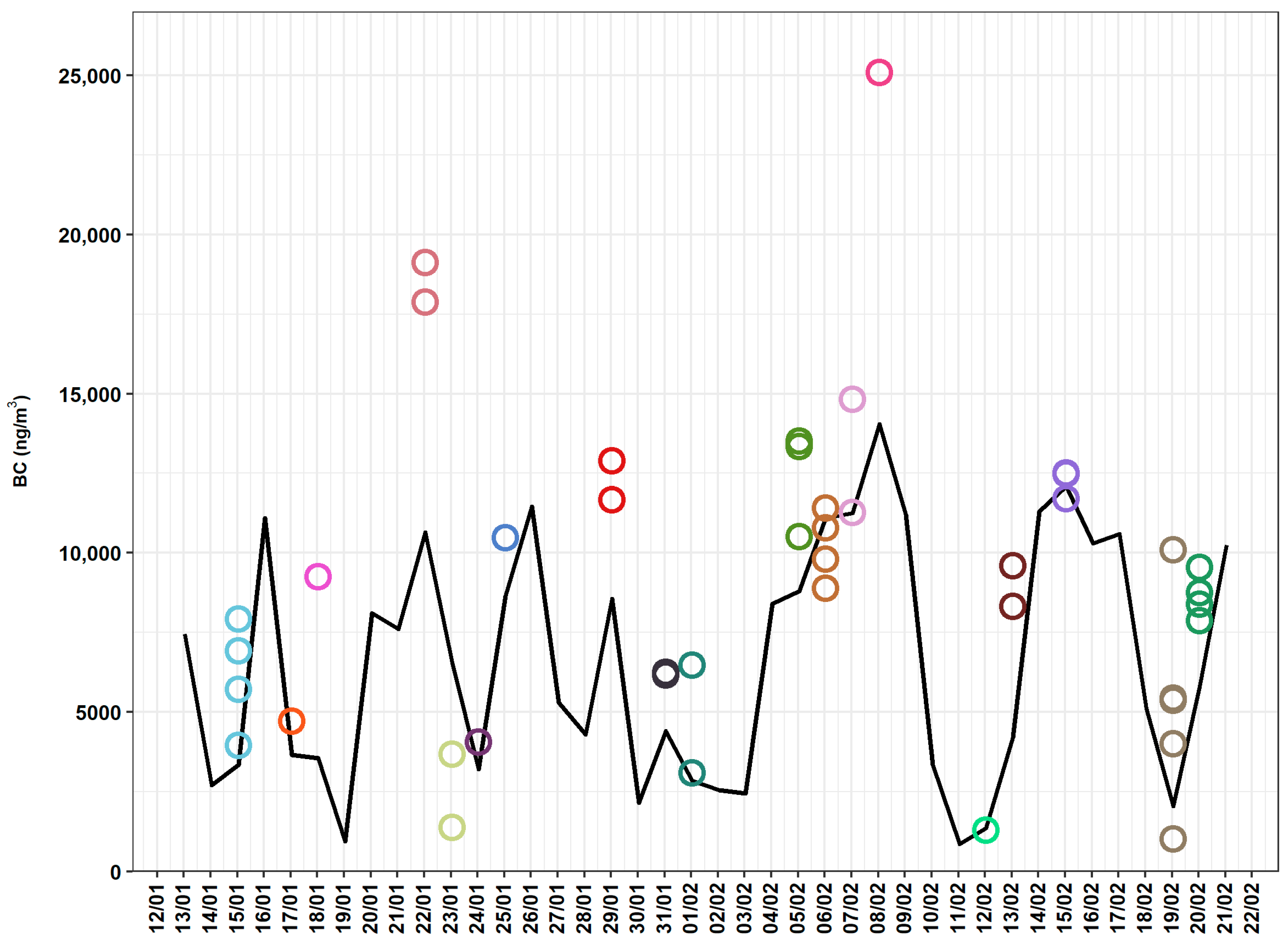
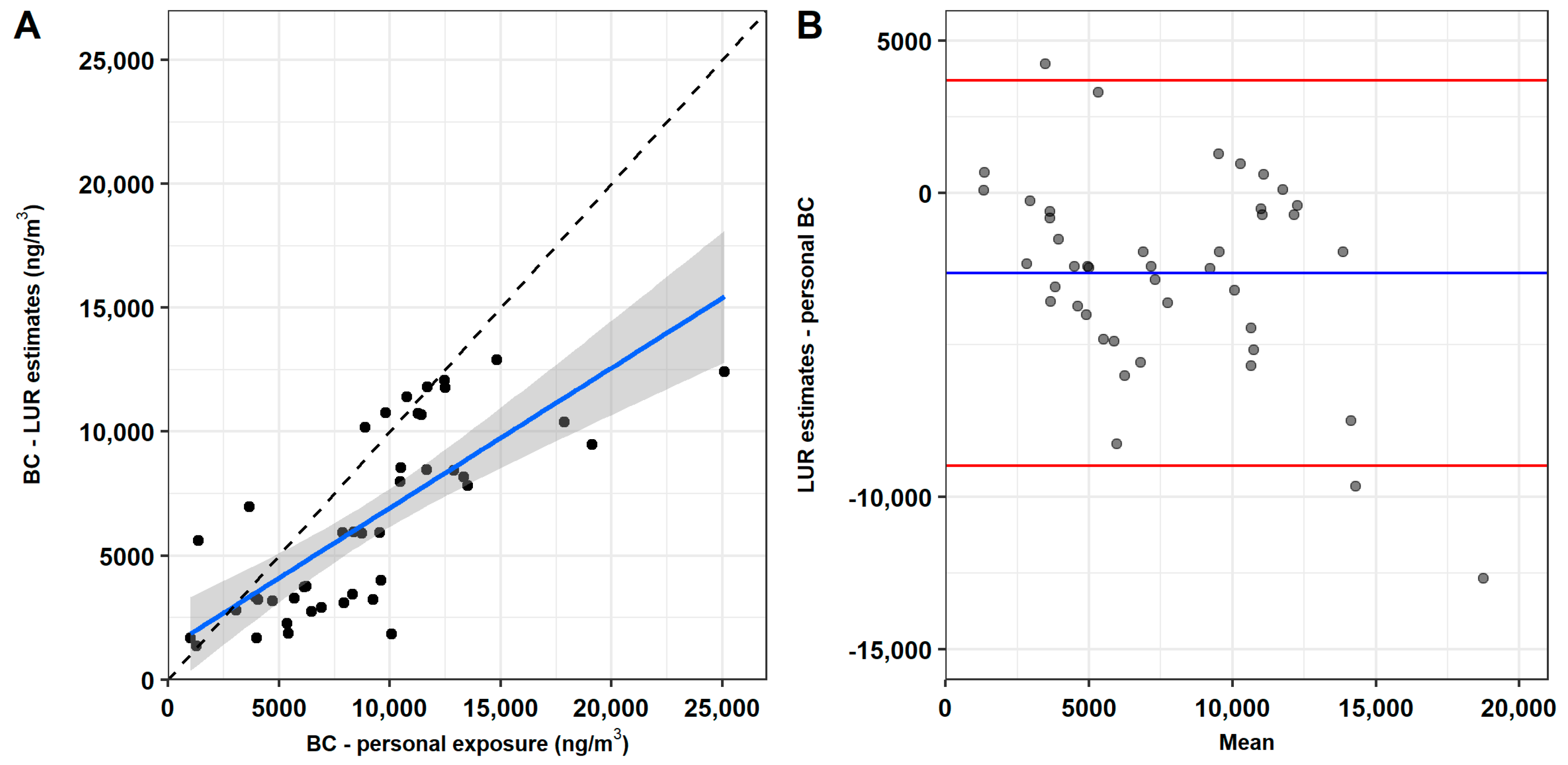
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryan, P.H.; LeMasters, G.K. A review of land-use regression models for characterizing intraurban air pollution exposure. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19 (Suppl. 1), 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoek, G.; Beelen, R.; de Hoogh, K.; Vienneau, D.; Gulliver, J.; Fischer, P.; Briggs, D. A review of land-use regression models to assess spatial variation of outdoor air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7561–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, D.; Tchepel, O. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics in Air Pollution Exposure Assessmen. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dons, E.; Laeremans, M.; Orjuela, J.P.; Palencia, I.A.; de Nazelled, A.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Van Poppel, M.; Carrasco-Turigase, G.; Standaert, A.; De Boever, P.; et al. Transport most likely to cause air pollution peak exposures in everyday life: Evidence from over 2000 days of personal monitoring. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 213, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dons, E.; Int Panis, L.; Van Poppel, M.; Theunis, J.; Wets, G. Personal exposure to Black Carbon in transport microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 55, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonanno, G.; Stabile, L.; Morawska, L.; Russi, A. Children exposure assessment to ultrafine particles and black carbon: The role of transport and cooking activities. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Health and environment: Addressing the health impact of air pollution. 2015. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/253206 (accessed on 27 July 2019).
- Health Effect Institute (HEI). Understanding the Health Effects of Ambient Ultrafine Particles. 2012. Available online: https://www.healtheffects.org/system/files/Perspectives3.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2019).
- Janssen, N.A.; Hoek, G.; Simic-Lawson, M.; Fischer, P.; van Bree, L.; ten Brink, H.; Keuken, M.; Atkinson, R.W.; Anderson, H.R.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Black Carbon as an Additional Indicator of the Adverse Health Effects of Airborne Particles Compared with PM10 and PM2.5. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Health effects of Black Carbon. 2012. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/environment-and-health/air-quality/publications/2012/health-effects-of-black-carbon-2012 (accessed on 27 July 2019).
- Rivas, I.; Donaire-Gonzalez, D.; Bouso, L.; Esnaola, M.; Pandolfi, M.; de Castro, M.; Viana, M.; Alvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Alastuey, A.; et al. Spatiotemporally resolved black carbon concentration, schoolchildren’s exposure and dose in Barcelona. Indoor Air 2016, 26, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boniardi, L.; Dons, E.; Campo, L.; Van Poppel, M.; Int Panis, L.; Fustinoni, S. Annual, seasonal, and morning rush hour Land Use Regression models for black carbon in a school catchment area of Milan, Italy. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provost, E.B.; Int Panis, L.; Saenen, N.D.; Kicinskia, M.; Louwies, T.; Vrijens, K.; De Boever, P.; Nawrot, T.S. Recent versus chronic fine particulate air pollution exposure as determinant of the retinal microvasculature in school children. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.B.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Litonjua, A.A.; Oken, E.; Gillman, M.W.; Kloog, I.; Luttmann-Gibson, H.; Zanobetti, A.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.; et al. Lifetime Exposure to Ambient Pollution and Lung Function in Children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Huang, W.; Zhu, T.; Hu, M.; Brunekreef, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cheng, H.; Gehring, U.; Li, C.; et al. Acute respiratory inflammation in children and black carbon in ambient air before and during the 2008 Beijing Olympics. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.H.; Bellinger, D.C.; Coull, B.A.; Anderson, S.; Barber, R.; Wright, R.O.; Wright, R.J. Associations between traffic-related black carbon exposure and attention in a prospective birth cohort of urban children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guxens, M.; Lubczyńska, M.J.; Muetzel, R.L.; Dalmau-Bueno, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hoek, G.; van der Lugt, A.; Verhulst, F.C.; White, T.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Air Pollution Exposure During Fetal Life, Brain Morphology, and Cognitive Function in School-Age Children. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 84, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunyer, J.; Esnaola, M.; Alvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Forns, J.; Rivas, I.; López-Vicente, M.; Suades-González, E.; Foraster, M.; Garcia-Esteban, R.; Basagaña, X.; et al. Association between traffic-related air pollution in schools and cognitive development in primary school children: A prospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, S.; Romero, K.; Psoter, K.J.; Curriero, F.C.; Chen, C.; Johnson, C.M.; Kaji, D.; Breysse, P.N.; Williams, D.L.; Ramanathan, M.; et al. Association of traffic air pollution and rhinitis quality of life in Peruvian children with asthma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Rivas, I.; López-Vicente, M.; Suades-González, E.; Donaire-Gonzalez, D.; Cirach, M.; de Castro, M.; Esnaola, M.; Basagaña, X.; Dadvand, P.; et al. Impact of commuting exposure to traffic-related air pollution on cognitive development in children walking to school. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231 Pt 1, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankey, S.; Lindsey, G.; Marshall, J.D. Population-Level Exposure to Particulate Air Pollution during Active Travel: Planning for Low-Exposure, Health-Promoting Cities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tainio, M.; de Nazelle, A.J.; Götschi, T.; Kahlmeier, S.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; de Sá, T.H.; Kelly, P.; Woodcock, J. Can air pollution negate the health benefits of cycling and walking? Prev. Med. 2016, 87, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; Basagaña, X.; Cirach, M.; Cole-Hunter, T.; Dadvand, P.; Donaire-Gonzalez, D.; Foraster, M.; Gascon, M.; Martinez, D.; et al. Health impacts related to urban and transport planning: A burden of disease assessment. Environ. Int. 2017, 107, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khreis, H.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Childhood Asthma: Recent Advances and Remaining Gaps in the Exposure Assessment Methods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Statistics Institute (ISTAT). 2018. Available online: http://dati.istat.it/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=DCIS_POPRES1 (accessed on 27 July 2019).
- Weingartner, E.; Saatho, H.; Schnaiterb, M.; Streita, N.; Bitnarc, B.; Baltensperger, U. Absorption of light by soot particles: Determination of the absorption coefficient by means of aethalometers. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2003, 34, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, N.; Molter, A.; Peel, J.L.; Volckens, J. An accurate filter loading correction is essential for assessing personal exposure to black carbon using an Aethalometer. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagler, G.S.W.; Yelverton, T.L.B.; Vedantham, R.; Hansen, A.D.A.; Turner, J.D. Post-processing method to reduce noise while preserving high time resolution in Aethalometer real-time black carbon data. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virkkula, A.; Mäkelä, T.; Hillamo, R.; Yli-Tuomi, T.; Hirsikko, A.; Hämeri, K.; Koponen, I.K. A simple procedure for correcting loading effects of aethalometer data. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eeftens, M.; Beelen, R.; de Hoogh, K.; Bellander, T.; Cesaroni, G.; Cirach, M.; Declercq, C.; Dėdelė, A.; Dons, E.; de Nazelle, A.; et al. Development of Land Use Regression Models for PM2.5, PM2.5 absorbance, PM10 and Pmcoarse in 20 European Study Areas; Results of the Escape Project. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11195–11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QGIS Development Team. QGIS Geographic Information System. Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. 2016. Available online: http://qgis.osgeo.org (accessed on 27 July 2019).
- Henderson, S.B.; Beckerman, B.; Jerrett, M.; Brauer, M. Application of land use regression to estimate long-term concentrations of traffic-related nitrogen oxides and fine particulate matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2422–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 27 July 2019).
- Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Donaire-Gonzalez, D.; Rivas, I.; de Castro, M.; Cirach, M.; Hoek, G.; Seto, E.; Jerrett, M.; Sunyer, J. Variability in and agreement between modeled and personal continuously measured black carbon levels using novel smartphone and sensor technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2977–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paunescu, A.C.; Attoui, M.; Bouallala, S.; Sunyer, J.; Momas, I. Personal measurement of exposure to black carbon and ultrafine particles in schoolchildren from PARIS cohort (Paris, France). Indoor Air 2017, 27, 766–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Lopes, I.; Martins, V.; Faria, T.; Correia, C.; Almeida, S.M. Children’s exposure to sized-fractioned particulate matter and black carbon in an urban environment. Build. Environ. 2019, 155, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minet, L.; Liu, R.; Valois, M.F.; Xu, J.; Weichenthal, S.; Hatzopoulou, M. Development and Comparison of Air Pollution Exposure Surfaces Derived from On-Road Mobile Monitoring and Short-Term Stationary Sidewalk Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3512–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nunen, E.; Vermeulen, R.; Tsai, M.Y.; Probst-Hensch, N.; Ineichen, A.; Davey, M.; Imboden, M.; Ducret-Stich, R.; Naccarati, A.; Raffaele, D.; et al. Land Use Regression Models for Ultrafine Particles in Six European Areas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3336–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunno, B.J. Spatial Patterns in Rush-Hour vs. Work-Week Diesel-Related Pollution across a Downtown CoreInt. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anowar, S.; Eluru, N.; Hatzopoulou, M. Quantifying the value of a clean ride: How far would you bicycle to avoid exposure to traffic-related air pollution? Transp. Res. Part A 2017, 105, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mean ± SD | Min–Max | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 9.1 ± 0.7 | 7–11 |
| Distance (m) | 650 ± 258 | 114–1403 |
| Measured BC (ng/m3) | 9003 ± 4864 | 1014–25,097 |
| MRH LUR BC estimate (ng/m3) | 6365 ± 3676 | 1365–12,886 |
| MRH AQN background BC (ng/m3) | 6635 ± 3730 | 1350–14,050 |
| Route | Day | Distance (m) | Measured BC (Mean ± SD, ng/m3) | MRH LUR BC Estimate (Mean ± SD, ng/m3) | MRH AQN Background BC (Mean, ng/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Route 1 | 13/02/2019 | 482 | 8320 ± 1892 | 5633 ± 761 | 4200 |
| Route 2 | 13/02/2019 | 486 | 9591 ± 2189 | 6576 ± 871 | 4200 |
| Route 3 | 06/02/2019 | 939 | 9798 ± 2217 | 10,753 ± 2510 | 11,100 |
| Route 4 | 06/02/2019 | 492 | 8884 ± 2125 | 10,169 ± 1954 | 11,100 |
| Route 5 | 06/02/2019 | 1403 | 10,779 ± 4594 | 11,390 ± 2490 | 11,100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boniardi, L.; Dons, E.; Campo, L.; Van Poppel, M.; Int Panis, L.; Fustinoni, S. Is a Land Use Regression Model Capable of Predicting the Cleanest Route to School? Environments 2019, 6, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6080090
Boniardi L, Dons E, Campo L, Van Poppel M, Int Panis L, Fustinoni S. Is a Land Use Regression Model Capable of Predicting the Cleanest Route to School? Environments. 2019; 6(8):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6080090
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoniardi, Luca, Evi Dons, Laura Campo, Martine Van Poppel, Luc Int Panis, and Silvia Fustinoni. 2019. "Is a Land Use Regression Model Capable of Predicting the Cleanest Route to School?" Environments 6, no. 8: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6080090
APA StyleBoniardi, L., Dons, E., Campo, L., Van Poppel, M., Int Panis, L., & Fustinoni, S. (2019). Is a Land Use Regression Model Capable of Predicting the Cleanest Route to School? Environments, 6(8), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6080090







