Bioremediation of Polluted Soil Sites with Crude Oil Hydrocarbons Using Carrot Peel Waste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Crude Oil Polluted Soil Origin
2.2. Carrot Peel Waste Medium
2.3. Carob Kibbles Medium
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Characterization of Carrot Peel Waste and Carob Kibbles
2.6. Physico-Chemical Characterization of Crude Oil
2.6.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
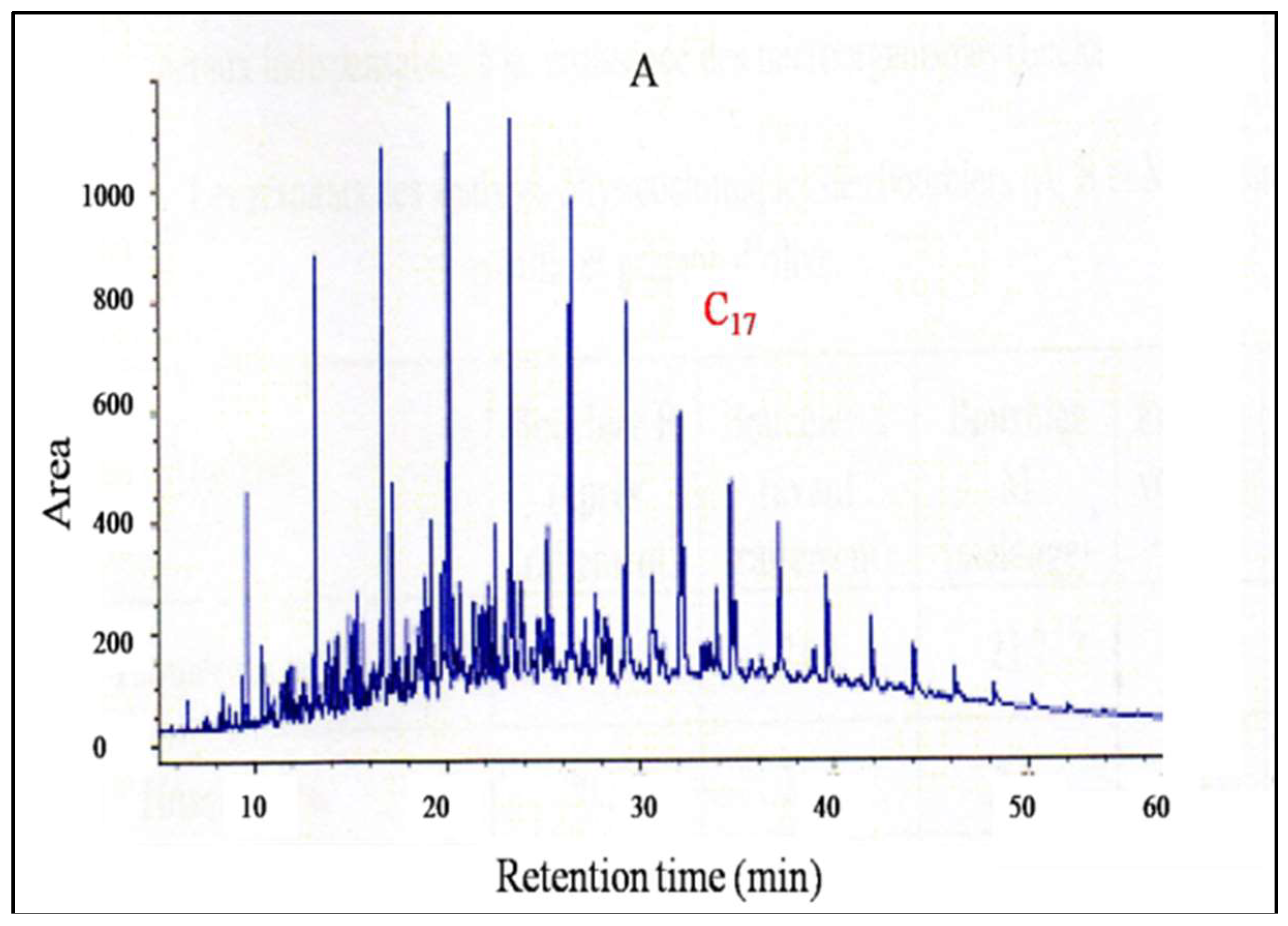
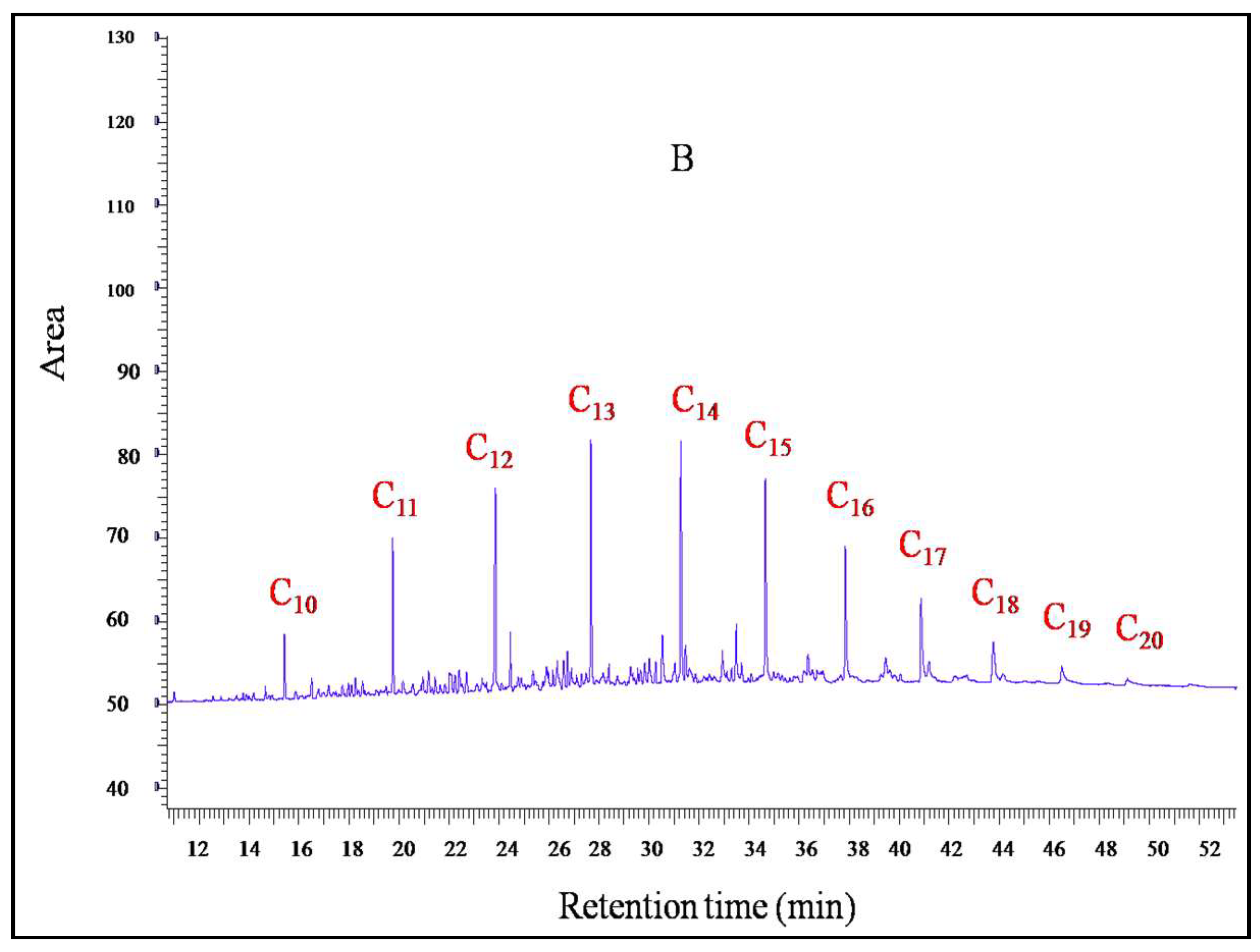
2.6.2. Gas Chromatographic (GC-FID) Analysis
2.6.3. Physicochemical Parameters Measurements of Crude Oil Polluted Soil
2.7. Microbiological Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of Carrot Peel Waste and Carob Kibbles
3.2. Mineral Composition of Crude Oil Polluted Soil
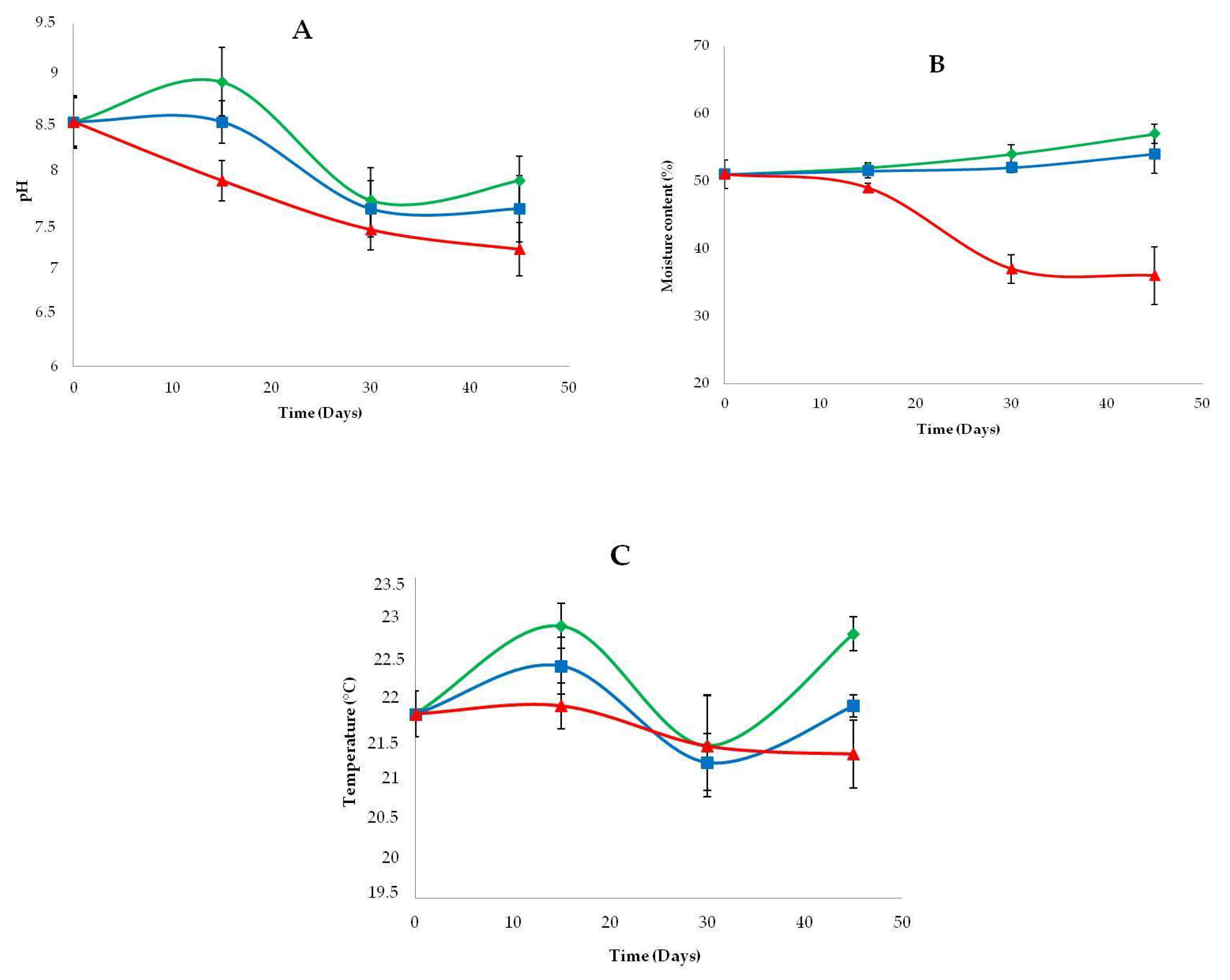
3.3. Physicochemical Properties of Amended and Unamended Samples
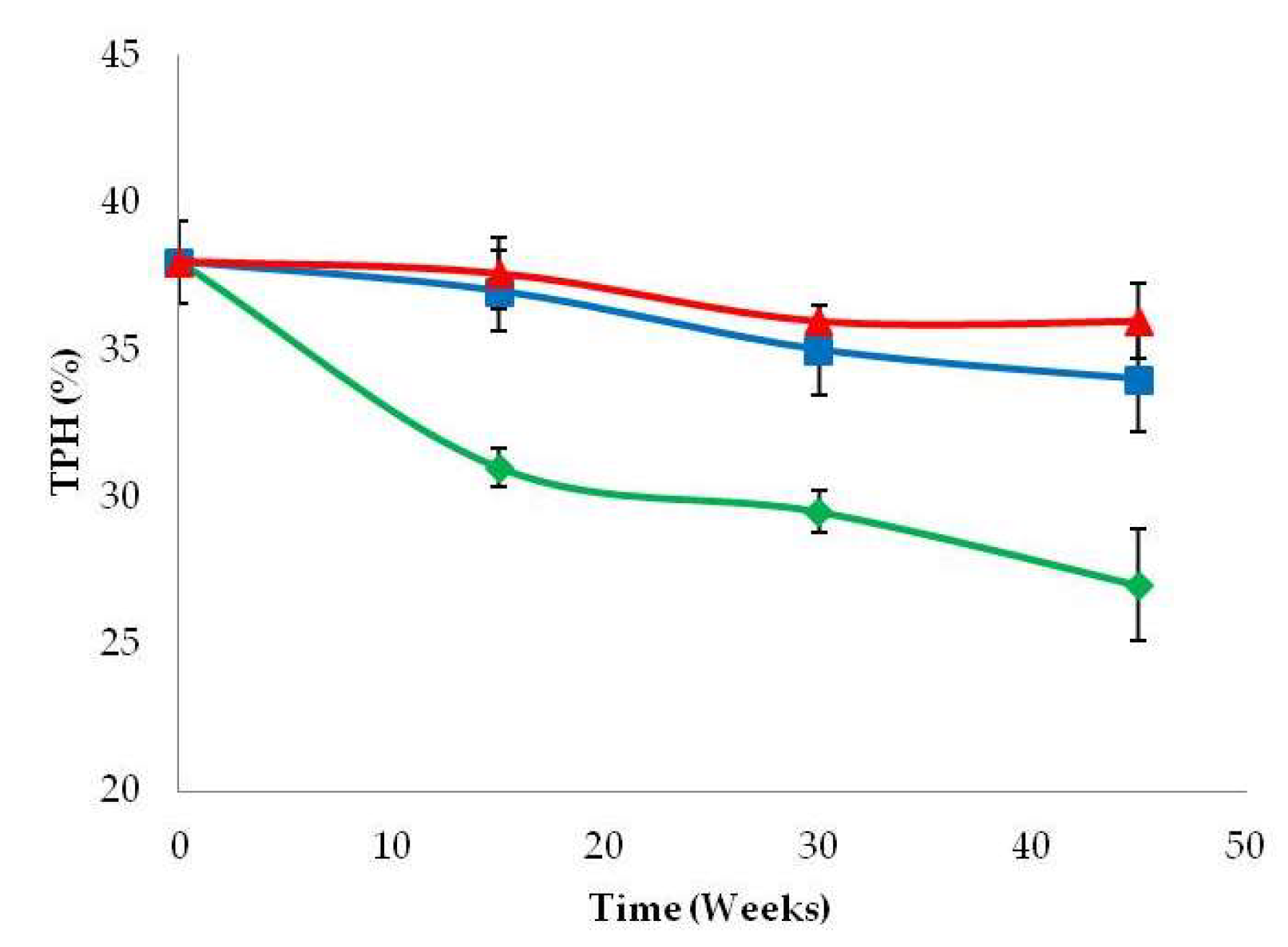
3.4. Crude Oil Polluted Soil Degradation
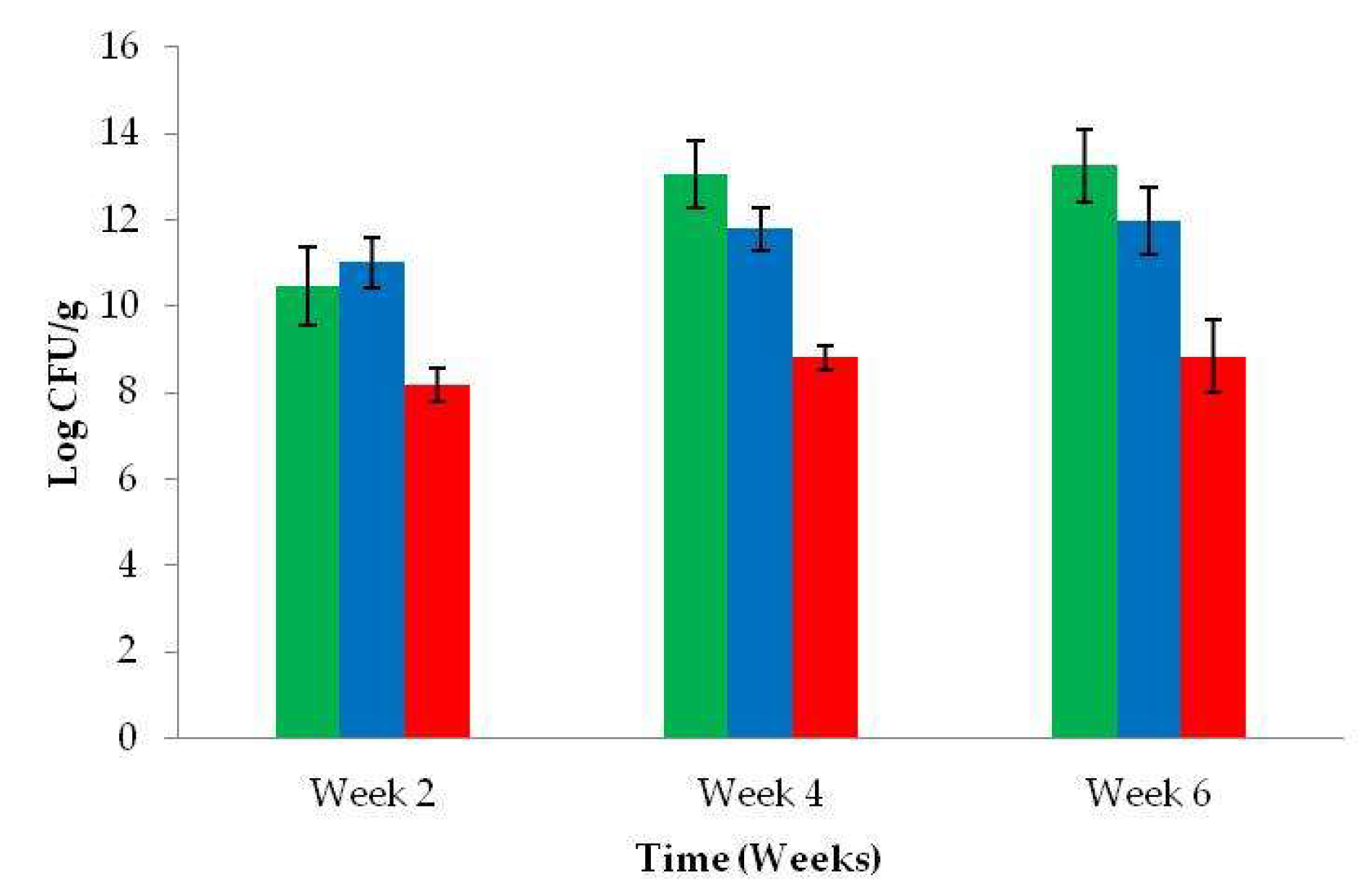
3.5. Microbial Counts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romanus, A.A.; Ikechukwu, E.F.; Patrick, A.S.; Goddey, U.; Helen, O. Efficiency of plantain peel and Guinea corn shaft for bioremediation of crude oil polluted soil. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 5, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez, M.I.; Arevalo, A.P.; Sotomayor, S.; Bailon-Moscoso, N. Contamination by oil crude extraction—Refinement and their effects on human health. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadrasnia, A.; Salmah, I.; Emenike, C.U.; Shahsavari, N. Remediation of oil contaminated media using organic material supplementation. Petrol. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minai-Tehrani, D.; Minoui, S.; Herfatmanesh, A. Effect of salinity on biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) of heavy crude oil in soil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 82, 82–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, M.; Afyuni, M.; Hajabbasi, M.A.; Nourbakhsh, F.; Sabzalian, M.R.; Christensen, J.H. Phytoremediation of an aged petroleum contaminated soil using endophyte infected and non-infected grasses. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graj, W.; Lisiecki, P.; Szulc, A.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Wojtera-Kwiczor, J. Bioaugmentation with petroleum-degrading consortia has a selective growth-promoting impact on crop plants germinated in diesel oil-contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeil, A.S.; Akbar, A. Occurrence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Kuwait soil. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulsalam, S.; Omale, A.B. Comparison of biostimulation and bioaugmentation techniques for the remediation of used motor oil contaminated soil. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2009, 52, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelo, L.W. In situ and bioremediation of organic pollutants in aquatic sediments. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 177, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Castro, G.A.; Uad, I.; Rodríguez-Calvo, A.; González-López, J.; Calvo, C. Response of autochthonous microbiota of diesel polluted soils to land-farming treatments. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwogu, T.P.; Azubuike, C.C.; Ogugbue, C.J. Enhanced bioremediation of soil artificially contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons after amendment with Capra aegagrus hircus (Goat) Manure. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, S.J.; Cammarota, M.C.; Freire, D.D.D.C. Production of CO2 in crude oil bioremediation in clay soil. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2005, 48, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreolli, M.; Lampis, S.; Brignoli, P.; Vallini, G. Bioaugmentation and biostimulation as strategies for the bioremediation of a burned woodland soil contaminated by toxic hydrocarbons: A comparative study. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 153, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, S. Phytoremediation for Oily Desert Soils. In Advances in Applied Bioremediation; Singh, A., Kuhad, R., Ward, O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 279–298. [Google Scholar]
- Nyman, J.A. Effect of crude oil and chemical additives on metabolic activity of mixed microbial populations in fresh marsh soils. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 37, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamoudi-Belarbi, L.; Nouri, L.; Bendifallah, L.; Hamoudi, S.; Belkacemi, K. Biostimulation of microbial community by carob (Ceratonia siliqua) to degrade total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) in contaminated soil. In Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions, EMCEI 2017; Advances in Science, Technology and Innovation IEREK Interdisciplinary Series for Sustainable Development; Kallel, A., Ksibi, M., Ben Dhia, H., Khélifi, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 275–276. [Google Scholar]
- Alotaibi, H.S.; Usman, A.R.; Abduljabbar, A.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Al-Faraj, A.I.; Sallam, A.S.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Carbon mineralization and biochemical effects of short-term wheat straw in crude oil contaminated sandy soil. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 88, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abioye, P.O.; Aziz, A.A.; Agamuthu, P. Enhanced biodegradation of used engine oil in soil amended with organic wastes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 209, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Barahona, L.; Rodrıguez-Vázquez, R.; Hernández-Velasco, M.; Vega-Jarquın, C.; Zapata-Pérez, O.; Mendoza-Cantú, A.; Albores, A. Diesel removal from contaminated soils by biostimulation and supplementation with crop residues. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2004, 27, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, R.K.; Firestone, M.K. Enhanced phenanthrene biodegradation in soil by slender oat root exudates and root debris. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, E.; Crawford, R.L. Effects of oxygen, nitrogen and temperature on gasoline biodegradation in soil. Biodegradation 1995, 6, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, A.; Aydin, S.; Ince, B.; Ince, O. Reconstruction of bacterial community structure and variation for enhanced petroleum hydrocarbons degradation through biostimulation of oil contaminated soil. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beolchini, F.; Rocchetti, L.; Regoli, F.; Dell’Anno, A. Bioremediation of marine sediments contaminated by hydrocarbons: Experimental analysis and kinetic modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binet, P.; Portal, J.M.; Leyval, C. Fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in the rhizosphere and mycorrhizosphere of ryegrass. Plant Soil 2000, 227, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.M.; Raymond, R.L. Stimulated petroleum biodegradation. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 1977, 5, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Kukkadapu, R.K.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Zachara, J.M.; Kennedy, D.W.; Kostandarithes, H.M. Microbial reduction of structural Fe (III) in illite and goethite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Crowley, D.E. Biostimulation of PAH degradation with plants containing high concentrations of linoleic acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4382–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshitomi, K.J.; Shann, J.R. Corn (Zea mays L.) root exudates and their impact on C-14-pyrene mineralization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilley, K.A.; Banks, M.K.; Schwab, A.P. Dissipation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the rhizosphere. J. Environ. Qual. 1996, 25, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokop, Z.; Nečasová, A.; Klánová, J.; Čupr, P. Bioavailability and mobility of organic contaminants in soil: New three-step ecotoxicological evaluation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 4312–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babin, D.; Vogel, C.; Zühlke, S.; Schloter, M.; Pronk, G.J.; Heister, K.; Spiteller, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Smalla, K. Soil mineral composition matters: Response of microbial communities to phenanthrene and plant litter addition in long-term matured artificial soils. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acourene, S.; Tama, M. Utilisation des Dattes de Faible Valeur Marchande (Rebuts de Deglet-Nour, Tinissine et Tantboucht) Comme Substrat pour la Fabrication de la Levure Boulangère. Rev. Energ. Ren. 2001. Available online: https://www.cder.dz/download/bio_1.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- ICDD International Centre for Diffraction Data, Powder Diffraction File 2 database, Pennsylvania, USA. 1999. Available online: http://www.icdd.com (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- API. API RP-45: Recommended Practice for Analysis of Oil-Field Waters, 3rd ed.; API Publishing Services; American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cutright, T.J. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon biodegradation and kinetics using Cunninghamella echinulata var. elegans. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1995, 35, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidali, M. Bioremediation: An overview. Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 73, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, J. Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases; USDA Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. Available online: http://www.ars-grin.gov/duke/ (accessed on 25 October 2017).
- Swindell, C.M.; Aelion, C.M.; Pfaender, F.K. Influence of minerals and organic nutrients anaerobic biodegradation and the adaptation response of surface microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 212–217. [Google Scholar]
- Eissa, H.A.; Salama, M.F. Effect of macerate enzymes on the yield, quality, volatile compounds and rheological property of prickly pear juice. Nahrung/Food 2002, 46, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodja, M. Drilling Fluid: Performance Study and Environmental Considerations. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut National Polytechnique, Toulouse, France, February 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Marchal, R.; Penet, S.; Solano-Serena, F.; Vandecasteele, J.P. Gasoline and diesel oil biodegradation. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2003, 58, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, T.; Ballerini, D. Biorestauration des sols et des aquifères contaminés par des hydrocarbures et des composés halogénés. Bull. Soc. Fr. Microbiol. 2001, 16, 204–209. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, P.; Atlas, R.M. Hydrocarbon biodegradation in soils and methods for soil biotreatment. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 1989, 8, 305–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibble, J.T.; Bartha, R. The effect of environmental parameters on the biodegradation of oil sludge. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1979, 37, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumari, B.; Singh, S.N.; Singh, D.P. Induced degradation of crude oil mediated by microbial augmentation and bulking agents. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.M. Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons: An environmental perspective. Microbiol. Rev. 1981, 45, 180–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prescott, L.M.; Harley, J.P.; Klein, D.A. Microbiology, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill Science: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 154–196. ISBN -13. [Google Scholar]
- Bossert, I.; Kachel, W.M.; Bartha, R. Fate of hydrocarbons during oily sludge disposal in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 47, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aislabie, J.; Saul, D.J.; Foght, J.M. Bioremediation of hydrocarbon-contaminated polar soils. Extremophiles 2006, 10, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muangchinda, C.; Chavanich, S.; Viyakarn, V.; Watanabe, K.; Imura, S.; Vangnai, A.S.; Pinyakong, O. Abundance and diversity of functional genes involved in the degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons in Antarctic soils and sediments around Syowa Station. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4725–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaric, N. Biosurfactants and their application for soil bioremediation. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2001, 39, 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kindi, S.; Abed, R.M. Comparing oil degradation efficiency and bacterial communities in contaminated soils subjected to biostimulation using different organic wastes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.G.; Bartha, R. Effects of jet fuel spills on the microbial community of soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marinescu, M.; Lacatusu, A.; Gament, E.; Plopeanu, G.; Carabulea, V.; Mihai, M. A review of biological methods to remediate crude oil polluted soil. Ann. Univ. Craiova-Agric. Montanol. Cadastre Ser. 2017, 46, 335–340. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Saleh, E.; Hassan, A. Enhanced crude oil biodegradation in soil via biostimulation. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2016, 18, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Elements (mg/L) | Carrot Peel Waste | Carob Kibbles |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 32.06 ± 2.01 a | 26.08 ± 2.30 a |
| Magnesium | 7.29 ± 0.30 | 6.28 ± 0.20 |
| Phosphorus | 25.10 ± 1.20 | 7.1 ± 0.20 |
| Nitrate | 3.01 ± 0.20 | 1.02 ± 0.10 a |
| Nitrite | 0.5 ± 0.02 | 0.4 ± 0.01 |
| Parameters | ||
| Total solid extract (%) | 19.24 ± 2.04 a | 30.45 ± 2.40 a |
| Moisture (%) | 80.76 ± 4.30 | 69.55 ± 3.40 |
| pH | 5.31 ± 0.95 | 5.32 ± 0.90 |
| Minerals | Crude Oil Polluted Soil | Unpolluted Soil [40] | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-clay minerals | Barite | BaSO4 | |
| Quartz | Quartz | SiO2 | |
| Calcite | - | CaCO3 | |
| Dolomite | - | CaMg(CO3)2 | |
| Anhydrite | - | Ca(SO4) | |
| Albite | - | NaAlSi3O8 | |
| Ankerite | - | Ca (Fe, Mg, Mn)(CO3)2 | |
| Barium chloride hydrate | - | BaCl2·2H2O | |
| - | Microcline, ordered | KAlSi3O8 | |
| - | Gypsum | CaSO4·2H2O | |
| Clay in low concentrations | Illite, trioctahedral | - | K0.5 (Al, Fe, Mg)3·(Si, Al)4 O10 (OH)2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamoudi-Belarbi, L.; Hamoudi, S.; Belkacemi, K.; Nouri, L.; Bendifallah, L.; Khodja, M. Bioremediation of Polluted Soil Sites with Crude Oil Hydrocarbons Using Carrot Peel Waste. Environments 2018, 5, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5110124
Hamoudi-Belarbi L, Hamoudi S, Belkacemi K, Nouri L, Bendifallah L, Khodja M. Bioremediation of Polluted Soil Sites with Crude Oil Hydrocarbons Using Carrot Peel Waste. Environments. 2018; 5(11):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5110124
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamoudi-Belarbi, Latifa, Safia Hamoudi, Khaled Belkacemi, L’Hadi Nouri, Leila Bendifallah, and Mohamed Khodja. 2018. "Bioremediation of Polluted Soil Sites with Crude Oil Hydrocarbons Using Carrot Peel Waste" Environments 5, no. 11: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5110124
APA StyleHamoudi-Belarbi, L., Hamoudi, S., Belkacemi, K., Nouri, L., Bendifallah, L., & Khodja, M. (2018). Bioremediation of Polluted Soil Sites with Crude Oil Hydrocarbons Using Carrot Peel Waste. Environments, 5(11), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5110124




