The Sustainable Management of Nitrogen Fertilizers for Environmental Impact Mitigation by Biochar Applications to Soils: A Review from the Past Decade
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Compilation
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
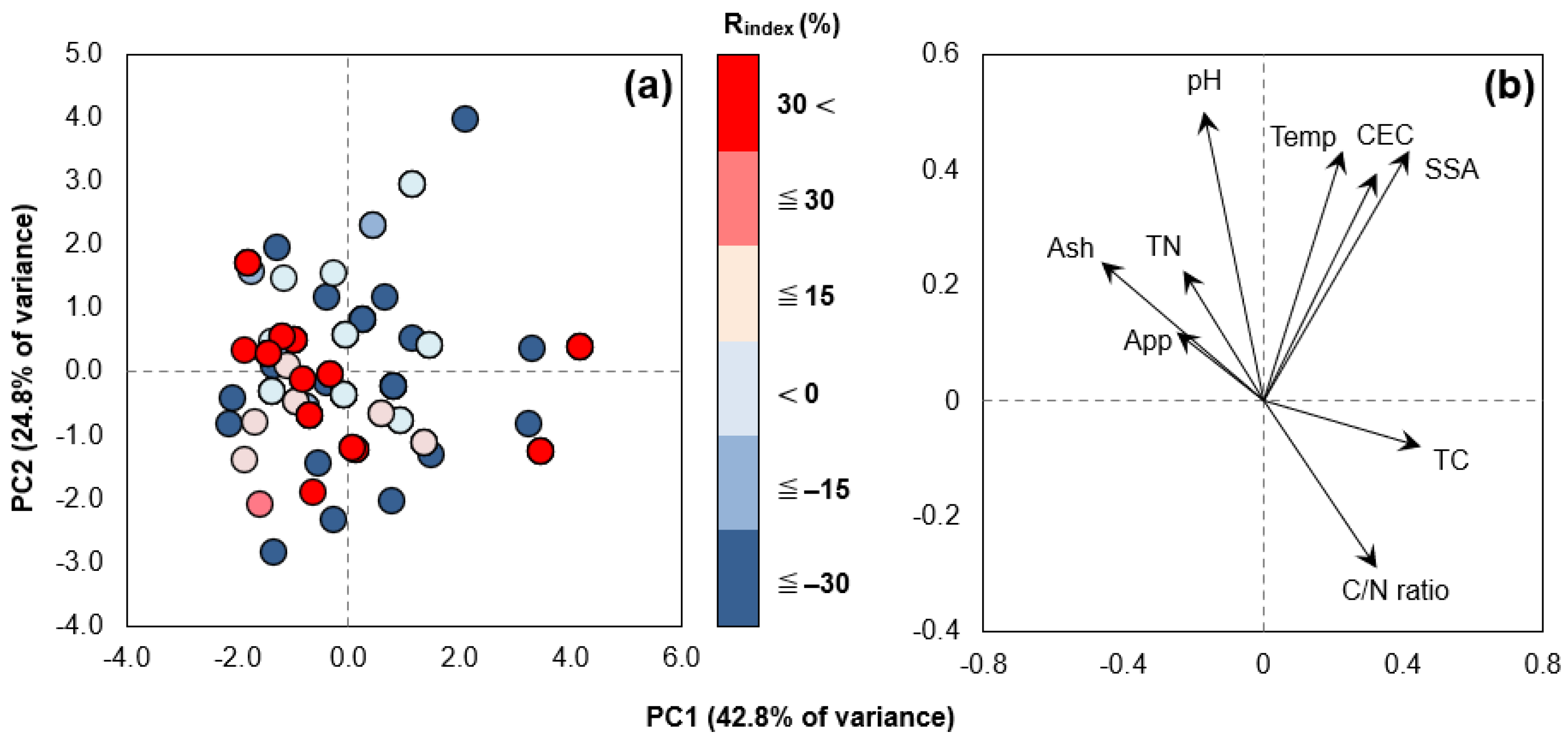
3.1. Biochar Physicochemical Properties
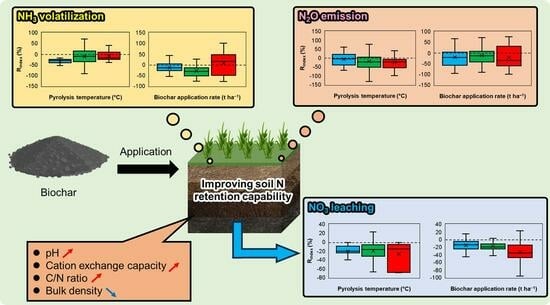
3.2. Mitigation of Ammonia Volatilization
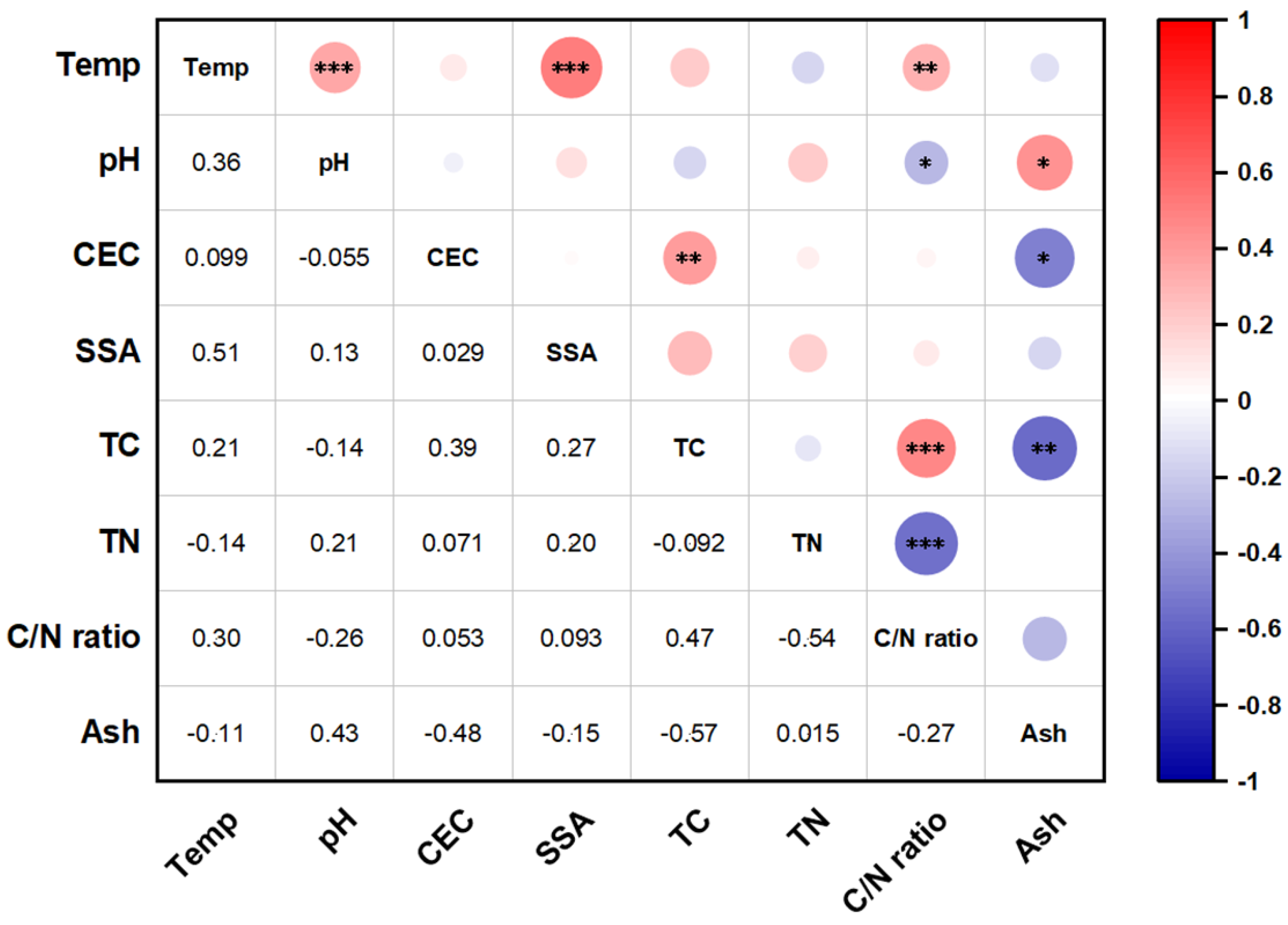
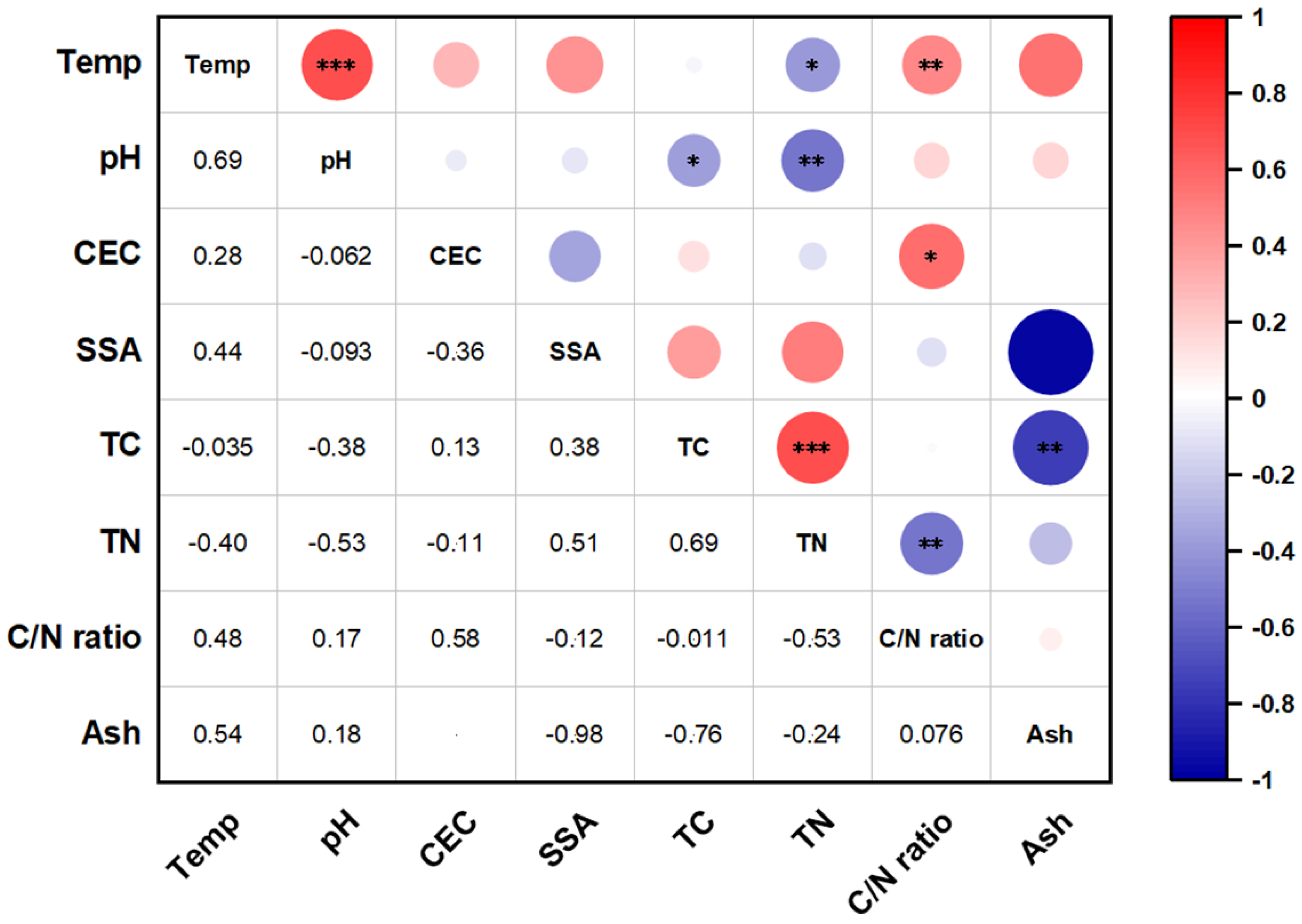
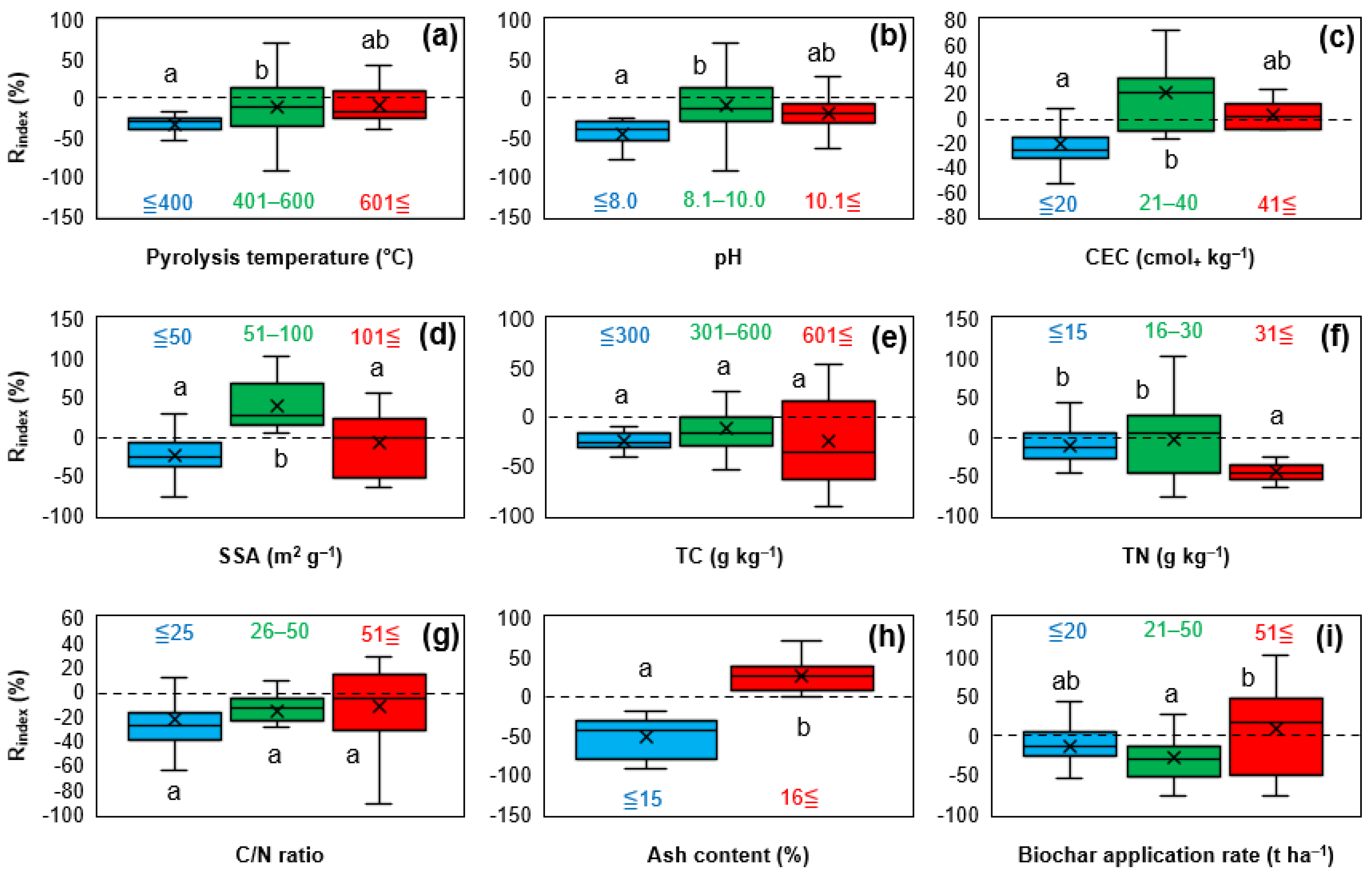
3.2.1. Effect of Biochar Physicochemical Properties
3.2.2. Effect of Various Experimental Conditions
3.3. Mitigation of Nitrate Leaching
3.3.1. Effect of Biochar Physicochemical Properties
3.3.2. Effect of Various Experimental Conditions
3.4. Mitigation of Nitrous Oxide Emission
3.4.1. Effect of Biochar Physicochemical Properties
3.4.2. Effect of Various Experimental Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.; Deng, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, J. Optimizing Nitrogen Application Rates to Maximize Productivity While Reducing Environmental Risk by Regulating Nitrogen and Water Utilization in Mixed Cropping Systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 303, 109053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDESA. Key Messages, World Population Prospects; UNDESA: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, S.; Luo, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Tang, N.; Fei, Y.; Hu, R. Organic Fertilizer Application Reduce Ammonia Volatilization in an Acidic Soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 383, 109510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; She, D.; Ding, J.; Abulaiti, A.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, F.; Shan, J.; Xia, Y. Coping with Groundwater Pollution in High-Nitrate Leaching Areas: The Efficacy of Denitrification. Environ. Res. 2024, 250, 118484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Sheng, X.; Bloszies, S.; et al. Intermediate Soil Acidification Induces Highest Nitrous Oxide Emissions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, S.; Kohira, Y.; Sato, S. Effects of Sugarcane Bagasse Biochar on Ammonium and Nitrate Adsorption and Leaching in a Japanese Tropical Soil Cropped with Japanese Mustard Spinach (Brassica rapa). Asian J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 10, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, H.; Ye, Q.; Zhu, S.; Peng, Z.; Li, Y.; Deng, L.; Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Organic Fertilization Effects on Soil Bacterial Diversity and Community Composition in Agroecosystems. Plants 2023, 12, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Cotton, A.; Wei, Z.; Xia, Y.; Daniell, T.; Yan, X. How Does Partial Substitution of Chemical Fertiliser with Organic Forms Increase Sustainability of Agricultural Production? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Xu, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Divergence in Fungal Abundance and Community Structure between Soils under Long-Term Mineral and Organic Fertilization. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, R.; Heinemann, C.; Schmid, S.M.; Steinhoff-Wagner, J. Survey on Storage, Application and Incorporation Practices for Organic Fertilizers in Germany. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herencia, J.F.; García-Galavís, P.A.; Dorado, J.A.R.; Maqueda, C. Comparison of Nutritional Quality of the Crops Grown in an Organic and Conventional Fertilized Soil. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management: An Introduction. In Biochar for Environmental Management, Science and Technology; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2009; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kohira, Y.; Fentie, D.; Lewoyehu, M.; Wutisirirattanachai, T.; Gezahegn, A.; Addisu, S.; Sato, S. Mitigation of Ammonia Volatilization from Organic and Inorganic Nitrogen Sources Applied to Soil Using Water Hyacinth Biochars. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, L. Insights into CO2 and N2O Emissions Driven by Applying Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizers in Upland Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fentie, D.; Mihretie, F.A.; Kohira, Y.; Legesse, S.A.; Lewoyehu, M.; Sato, S. Enhancing Soil Environments and Wheat Production through Water Hyacinth Biochar under Deficit Irrigation in Ethiopian Acidic Silty Loam Soil. Soil Syst. 2024, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezahegn, A.; Selassie, Y.G.; Agegnehu, G.; Addisu, S.; Mihretie, F.A.; Kohira, Y.; Lewoyehu, M.; Sato, S. Synergistic Effects of Aquatic Weed Biochar and Inorganic Fertilizer on Soil Properties, Maize Yield, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency on Nitisols of Northwestern Ethiopian Highlands. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 21, 101939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.E.-E.A.Z. Carbon Sequestration, Kinetics of Ammonia Volatilization and Nutrient Availability in Alkaline Sandy Soil as a Function on Applying Calotropis Biochar Produced at Different Pyrolysis Temperatures. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egyir, M.; Luyima, D.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, K.S.; Oh, T.-K. Volatilisations of Ammonia from the Soils Amended with Modified and Nitrogen-Enriched Biochars. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, T.; Cao, T.; Yang, T.; Meng, J.; Chen, W. Effects of Biochar Application on Nitrogen Leaching, Ammonia Volatilization and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Two Distinct Soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Thangarajan, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Sarkar, B.; Khan, N.; Ok, Y.S.; Naidu, R. Biochar-Induced Concomitant Decrease in Ammonia Volatilization and Increase in Nitrogen Use Efficiency by Wheat. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Donner, E.; Vasileiadis, S.; Skinner, W.; Smith, E.; Lombi, E. The Effect of Biochar Feedstock, Pyrolysis Temperature, and Application Rate on the Reduction of Ammonia Volatilisation from Biochar-Amended Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, Y.; Sato, S. Effect of Biochar Application on Suppression of Ammonia Volatilization from Anaerobic Digestion Effluent Mixed with Soil as a Nitrogen Source. Wood Carbonization Res. Soc. 2020, 17, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Yang, J.; Yao, R.; Wang, X.; Xie, W.; Zhu, W.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; Tao, J. Interactive Effects of Soil Amendments (Biochar and Gypsum) and Salinity on Ammonia Volatilization in Coastal Saline Soil. CATENA 2020, 190, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Sun, H.; Xue, L.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Q.; Lu, K.; Yang, L. Biochar Applied at an Appropriate Rate Can Avoid Increasing NH3 Volatilization Dramatically in Rice Paddy Soil. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; A, D.; Feng, Y.; Vithanage, M.; Mandal, S.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, H. Floating Duckweed Mitigated Ammonia Volatilization and Increased Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Rice in Biochar Amended Paddy Soils. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Lu, H.; Chu, L.; Shao, H.; Shi, W. Biochar Applied with Appropriate Rates Can Reduce N Leaching, Keep N Retention and Not Increase NH3 Volatilization in a Coastal Saline Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaimart, J.; Acharya, K.; Mrozik, W.; Davenport, R.J.; Vinitnantharat, S.; Werner, D. Coconut Husk Biochar Amendment Enhances Nutrient Retention by Suppressing Nitrification in Agricultural Soil Following Anaerobic Digestate Application. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, H.; Shi, W.; Müller, K.; Van Zwieten, L.; Wang, H. Wheat Straw Biochar Application Increases Ammonia Volatilization from an Urban Compacted Soil Giving a Short-Term Reduction in Fertilizer Nitrogen Use Efficiency. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jeyakumar, P.; Shao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhu, R.; Qian, Q.; et al. Effect of Biofertilizer and Wheat Straw Biochar Application on Nitrous Oxide Emission and Ammonia Volatilization from Paddy Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Donner, E.; Smith, E.; Sarkar, B.; Lombi, E. Biochar with Near-Neutral pH Reduces Ammonia Volatilization and Improves Plant Growth in a Soil-Plant System: A Closed Chamber Experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, R.; Kammann, C.; Pelissetti, S.; Taupe, N.; Bertora, C.; Monaco, S.; Grignani, C. Does Soil Amended with Biochar and Hydrochar Reduce Ammonia Emissions Following the Application of Pig Slurry? Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.I.; Xu, Y.; Shi, D.; Li, J.; Li, H.; El-Sappah, A.H.; Elrys, A.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Zhou, C.; Wang, L.; et al. Nitrogen Transformation Genes and Ammonia Emission from Soil under Biochar and Urease Inhibitor Application. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 223, 105491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Liu, D.; Yuan, J.; Ni, K.; Zaman, M.; Luo, J.; Lindsey, S.; Ding, W. A Two Years Study on the Combined Effects of Biochar and Inhibitors on Ammonia Volatilization in an Intensively Managed Rice Field. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 264, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Ding, J.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y. Impact of Biochar Application on Ammonia Volatilization from Paddy Fields under Controlled Irrigation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhong, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K.; Wu, W. Reducing Ammonia Volatilization from Paddy Field with Rice Straw Derived Biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xia, G.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Chi, D.; Bolan, N.S.; Chang, S.X.; Wang, T.; Ok, Y.S. Mulched Drip Irrigation and Biochar Application Reduce Gaseous Nitrogen Emissions, but Increase Nitrogen Uptake and Peanut Yield. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, G.; Kim, H.; Chen, J.; Kim, Y. Effects of Biochar Addition on Nitrogen Leaching and Soil Structure Following Fertilizer Application to Rice Paddy Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Ning, L.; Xun, M.; Feng, F.; Li, P.; Yue, S.; Song, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, H. Biochar Can Increase Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Malus Hupehensis by Modulating Nitrate Reduction of Soil and Root. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Mo, C.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, J.; Lin, J. Microbial Mechanism of Biochar Addition on Nitrogen Leaching and Retention in Tea Soils from Different Plantation Ages. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Liu, D.; Wu, F.; Chen, Y.; He, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xing, S.; Mao, Y. Nitrogen Retention Potentials of Magnesium Oxide- and Sepiolite-Modified Biochars and Their Impacts on Bacterial Distribution under Nitrogen Fertilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanthle, A.K.; Lenka, N.K.; Lenka, S.; Tedia, K. Biochar Impact on Nitrate Leaching as Influenced by Native Soil Organic Carbon in an Inceptisol of Central India. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 157, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.-L.; Lee, C.-H.; Jien, S.-H. Reduction of Nutrient Leaching Potential in Coarse-Textured Soil by Using Biochar. Water 2020, 12, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, W.; Shangguan, Z. Effect of Biochar Application Method on Nitrogen Leaching and Hydraulic Conductivity in a Silty Clay Soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 183, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, A.; Mattana, S.; Chin-Pampillo, J.; Otero, N.; Carrey, R.; Mondini, C.; Gascó, G.; Martí, E.; Margalef, R.; Alcañiz, J.M.; et al. Fresh Biochar Application Provokes a Reduction of Nitrate Which Is Unexplained by Conventional Mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wen, Y.; Tan, X.; Zeng, Y.; Shang, Q. Adsorption and Leaching Characteristics of Ammonium and Nitrate from Paddy Soil as Affected by Biochar Amendment. Plant Soil Environ. 2021, 67, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, E.P.A.; Hillary, A.K.; Fukuda, T.; Shinogi, Y. The Effects of Rice Husk Char on Ammonium, Nitrate and Phosphate Retention and Leaching in Loamy Soil. Geoderma 2016, 277, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, R.L.; Anderson, T.R.; Ballantine, K.A. Biochar Simultaneously Reduces Nutrient Leaching and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Restored Wetland Soils. Wetlands 2020, 40, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sika, M.P.; Hardie, A.G. Effect of Pine Wood Biochar on Ammonium Nitrate Leaching and Availability in a South African Sandy Soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutscherova, N.; Houška, J.; Navas, M.; Masaguer, A.; Benito, M.; Vazquez, E. Leaching of Ammonium and Nitrate from Acrisol and Calcisol Amended with Holm Oak Biochar: A Column Study. Geoderma 2018, 323, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troy, S.M.; Lawlor, P.G.; O’ Flynn, C.J.; Healy, M.G. The Impact of Biochar Addition on Nutrient Leaching and Soil Properties from Tillage Soil Amended with Pig Manure. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Tan, G.; Wang, H.; Gai, X. Effect of Biochar Additions to Soil on Nitrogen Leaching, Microbial Biomass and Bacterial Community Structure. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Xing, G. Nitrification, Acidification, and Nitrogen Leaching from Subtropical Cropland Soils as Affected by Rice Straw-Based Biochar: Laboratory Incubation and Column Leaching Studies. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Jones, D.L.; Hill, P.; Bastami, M.S.; Tu, C.L. Influence of Biochar Produced from Different Pyrolysis Temperature on Nutrient Retention and Leaching. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 64, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiraj, E.; Libutti, A.; Malltezi, J.; Rroço, E.; Brahushi, F.; Monteleone, M.; Sulçe, S. Effect of Organic Amendments on Nitrate Leaching Mitigation in a Sandy Loam Soil of Shkodra District, Albania. Ital. J. Agron. 2018, 13, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Asadi, H.; Abrishamkesh, S. Effects of Rice Husk Biochar on Selected Soil Properties and Nitrate Leaching in Loamy Sand and Clay Soil. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammann, C.I.; Schmidt, H.-P.; Messerschmidt, N.; Linsel, S.; Steffens, D.; Müller, C.; Koyro, H.-W.; Conte, P.; Joseph, S. Plant Growth Improvement Mediated by Nitrate Capture in Co-Composted Biochar. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, S.S.; Asoodar, M.A.; Moghadam, B.K. Short-Term Impacts of Biochar, Tillage Practices, and Irrigation Systems on Nitrate and Phosphorus Concentrations in Subsurface Drainage Water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, M.A.; Oliver, G.; Clothier, B.E.; Bound, S.A.; Green, S.A.; Close, D.C. Effect of Biochar on Nutrient Leaching in a Young Apple Orchard. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, A.; Rengel, Z. Long-term Biochar Application Promotes Rice Productivity by Regulating Root Dynamic Development and Reducing Nitrogen Leaching. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrenti, G.; Toselli, M. Soil Leaching as Affected by the Amendment with Biochar and Compost. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 226, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, A.; Yang, S.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z. Biochar Amendment Reduces Paddy Soil Nitrogen Leaching but Increases Net Global Warming Potential in Ningxia Irrigation, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Berruti, F.; Greenhalf, C.; Tian, X.; Henry, H.A.L. Increased Retention of Soil Nitrogen over Winter by Biochar Application: Implications of Biochar Pyrolysis Temperature for Plant Nitrogen Availability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 236, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamer, M.; Bilal Chattha, M.; Mahmood, A.; Naqve, M.; Hassan, M.U.; Shaaban, M.; Rasul, F.; Batool, M.; Rasheed, A.; Tang, H.; et al. Rice Residue-Based Biochar Mitigates N2O Emission from Acid Red Soil. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, P.; Godbout, S.; Palacios, J.H.; Jeanne, T.; Hogue, R.; Dubé, P.; Limousy, L.; Raghavan, V. Effect of Six Engineered Biochars on GHG Emissions from Two Agricultural Soils: A Short-Term Incubation Study. Geoderma 2018, 327, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Luo, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Easily Mineralizable Carbon in Manure-based Biochar Added to a Soil Influences N2O Emissions and microbial-N Cycling Genes. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felber, R.; Leifeld, J.; Horák, J.; Neftel, A. Nitrous Oxide Emission Reduction with Greenwaste Biochar: Comparison of Laboratory and Field Experiments. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Neupane, A.; Xu, S.; Abdoulmoumine, N.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Walker, F.; Jagadamma, S. Application Methods Influence Biochar–Fertilizer Interactive Effects on Soil Nitrogen Dynamics. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 1871–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, S.; Neupane, A.; Abdoulmoumine, N.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Walker, F.R.; Jagadamma, S. Co-Application of Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Reduced Nitrogen Losses from Soil. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shen, G.; Sun, M.; Cao, X.; Shang, G.; Chen, P. Effect of Biochar on Nitrous Oxide Emission and Its Potential Mechanisms. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.L.; Clarke, M.L.; Othman, M.; Ramsden, S.J.; West, H.M. Biochar-Mediated Reductions in Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Soil Amended with Anaerobic Digestates. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 79, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelissen, V.; Saha, B.K.; Ruysschaert, G.; Boeckx, P. Effect of Different Biochar and Fertilizer Types on N2O and NO Emissions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chang, Z.-Z.; Xue, X.-M.; Yu, J.-G.; Shi, X.-X.; Ma, L.Q.; Li, H.-B. Biochar Decreases Nitrogen Oxide and Enhances Methane Emissions via Altering Microbial Community Composition of Anaerobic Paddy Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Duan, P.; Yan, X.; Xiong, Z. Biochar-Enriched Soil Mitigated N2O and NO Emissions Similarly as Fresh Biochar for Wheat Production. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Voroney, R.P.; Price, G.W. Effects of Biochar Amendments on Soil Microbial Biomass and Activity. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 2104–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Han, X.; Ping, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K.; Chen, M.; Wu, W. Effect of Rice-Straw Biochar on Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Paddy Soils under Elevated CO2 and Temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameloot, N.; Maenhout, P.; De Neve, S.; Sleutel, S. Biochar-Induced N2O Emission Reductions after Field Incorporation in a Loam Soil. Geoderma 2016, 267, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, T.E.; Six, J.; Reay, D.S.; Sohi, S.P. Impact of Pine Chip Biochar on Trace Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Soil Nutrient Dynamics in an Annual Ryegrass System in California. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kim, H.; Yoo, G. Effects of Biochar Addition on CO2 and N2O Emissions Following Fertilizer Application to a Cultivated Grassland Soil. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Du, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Ejaz, I.; Hu, N.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Trade-off between Soil Carbon Emission and Sequestration for Winter Wheat under Reduced Irrigation: The Role of Soil Amendments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 352, 108535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Duan, P.; Shen, H.; Gunina, A.; Yan, X.; Xiong, Z. Biochar Amendment Mitigated N2O Emissions from Paddy Field during the Wheat Growing Season. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 117026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevon, D.; Fursa, S.R.; Malcolm, A.L. Intercoder Reliability and Validity of WebPlotDigitizer in Extracting Graphed Data. Behav. Modif. 2017, 41, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-I.; Park, H.-J.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Seo, B.-S.; Kwak, J.-H.; Yang, H.I.; Xu, X.; Tang, S.; Cheng, W.; Lim, S.-S.; et al. Biochar-Induced Reduction of N2O Emission from East Asian Soils under Aerobic Conditions: Review and Data Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhai, L.; Liu, S.; Ren, T.; Liu, H. Effects of Feedstock and Pyrolysis Temperature on Biochar Adsorption of Ammonium and Nitrate. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.-H.; Xu, R.-K.; Zhang, H. The Forms of Alkalis in the Biochar Produced from Crop Residues at Different Temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3488–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar Physicochemical Properties: Pyrolysis Temperature and Feedstock Kind Effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chen, J.; Peng, H.; Leng, S.; Li, H.; Qu, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, W.; et al. Effect of Biomass Type and Pyrolysis Temperature on Nitrogen in Biochar, and the Comparison with Hydrochar. Fuel 2021, 291, 120128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, R. Effects of Pyrolysis Temperature and Heating Time on Biochar Obtained from the Pyrolysis of Straw and Lignosulfonate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 176, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzediegwu, C.; Arshad, M.; Ulah, A.; Naeth, M.A.; Chang, S.X. Fuel, Thermal and Surface Properties of Microwave-Pyrolyzed Biochars Depend on Feedstock Type and Pyrolysis Temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, P.; Angers, D.A.; Chantigny, M.H.; Gasser, M.-O.; MacDonald, J.D.; Pelster, D.E.; Bertrand, N. NH3 Volatilization, Soil Concentration and Soil pH Following Subsurface Banding of Urea at Increasing Rates. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 93, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wabel, M.I.; Al-Omran, A.; El-Naggar, A.H.; Nadeem, M.; Usman, A.R.A. Pyrolysis Temperature Induced Changes in Characteristics and Chemical Composition of Biochar Produced from Conocarpus Wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.; Li, Q.; Lv, T.; Misselbrook, T.; Liu, X. Response of Ammonia Volatilization to Biochar Addition: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abujabhah, I.S.; Doyle, R.; Bound, S.A.; Bowman, J.P. The Effect of Biochar Loading Rates on Soil Fertility, Soil Biomass, Potential Nitrification, and Soil Community Metabolic Profiles in Three Different Soils. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2211–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.-J.; Li, H.-Q.; Yang, J.-S.; Wang, X.-P.; Xie, W.-P.; Zhang, X. Biochar Addition Inhibits Nitrification by Shifting Community Structure of Ammonia-Oxidizing Microorganisms in Salt-Affected Irrigation-Silting Soil. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quin, P.R.; Cowie, A.L.; Flavel, R.J.; Keen, B.P.; Macdonald, L.M.; Morris, S.G.; Singh, B.P.; Young, I.M.; Van Zwieten, L. Oil Mallee Biochar Improves Soil Structural Properties—A Study with x-Ray Micro-CT. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.; Yu, X.; Zhang, M.; Jing, X. Fabrication of Layered Double Hydroxide Spheres through Urea Hydrolysis and Mechanisms Involved in the Formation. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; E, Y.; Lan, Y.; He, T.; Chen, W.; Meng, J. Effect of Biochar on Urea Hydrolysis Rate and Soil ureC Gene Copy Numbers. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 3122–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, N.; Saad, J.K.; Van Laethem, C.; Machet, J.M.; Maucorps, J.; Mary, B. Nitrate Leaching in Intensive Agriculture in Northern France: Effect of Farming Practices, Soils and Crop Rotations. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 111, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edeh, I.G.; Mašek, O.; Buss, W. A Meta-Analysis on Biochar’s Effects on Soil Water Properties—New Insights and Future Research Challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, C.; Parikh, S.J.; Scow, K.M. Impact of Biochar on Water Retention of Two Agricultural Soils—A Multi-Scale Analysis. Geoderma 2019, 340, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, N.; Joseph, S.; Schmidt, H.-P.; Kammann, C.I.; Harter, J.; Borch, T.; Young, R.B.; Varga, K.; Taherymoosavi, S.; Elliott, K.W.; et al. Organic Coating on Biochar Explains Its Nutrient Retention and Stimulation of Soil Fertility. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohira, Y.; Fentie, D.; Lewoyehu, M.; Wutisirirattanachai, T.; Gezahegn, A.; Addisu, S.; Sato, S. Elucidation of Ammonium and Nitrate Adsorption Mechanisms by Water Hyacinth Biochar: Effects of Pyrolysis Temperature. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 762–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Qian, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, B.; Ma, H.; Wu, Z. A Potential Mg-Enriched Biochar Fertilizer: Excellent Slow-Release Performance and Release Mechanism of Nutrients. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.G.I.D.; Moldrup, P.; Paradelo, M.; Elsgaard, L.; De Jonge, L.W. Effects of Biochar on Dispersibility of Colloids in Agricultural Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, G.; Steffens, D.; Moser, G.; Müller, C.; Kammann, C.I. Biochar Reduced Nitrate Leaching and Improved Soil Moisture Content without Yield Improvements in a Four-Year Field Study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 237, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; Van Der Velde, M.; Bastos, A.C. A Quantitative Review of the Effects of Biochar Application to Soils on Crop Productivity Using Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaji, H.; Chandran, V.; Mathew, L. Chapter 13—Organic Fertilizers as a Route to Controlled Release of Nutrients. Control. Release Fertil. Sustain. Agric. 2021, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, K.; Duynisveld, W.H.M.; Böttcher, J. Nitrogen Fertilization and Nitrate Leaching into Groundwater on Arable Sandy Soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2006, 169, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, J.; Guzman-Bustamante, I.; Kuehfuss, S.; Ruser, R.; Well, R.; Spott, O.; Kappler, A.; Behrens, S. Gas Entrapment and Microbial N2O Reduction Reduce N2O Emissions from a Biochar-Amended Sandy Clay Loam Soil. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obia, A.; Mulder, J.; Hale, S.E.; Nurida, N.L.; Cornelissen, G. The Potential of Biochar in Improving Drainage, Aeration and Maize Yields in Heavy Clay Soils. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, J.; Krause, H.-M.; Schuettler, S.; Ruser, R.; Fromme, M.; Scholten, T.; Kappler, A.; Behrens, S. Linking N2O Emissions from Biochar-Amended Soil to the Structure and Function of the N-Cycling Microbial Community. ISME J. 2014, 8, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qin, Y.; Zou, J.; Liu, Q. Effects of Water Regime during Rice-Growing Season on Annual Direct N2O Emission in a Paddy Rice–Winter Wheat Rotation System in Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Cui, L.; Pan, G.; Li, L.; Hussain, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Crowley, D. Effect of Biochar Amendment on Yield and Methane and Nitrous Oxide Emissions from a Rice Paddy from Tai Lake Plain, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-J.; Wang, X.-H.; Li, H.; Yao, H.-Y.; Su, J.-Q.; Zhu, Y.-G. Biochar Impacts Soil Microbial Community Composition and Nitrogen Cycling in an Acidic Soil Planted with Rape. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9391–9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. Effects of Combined Biochar and Organic Fertilizer on Nitrous Oxide Fluxes and the Related Nitrifier and Denitrifier Communities in a Saline-Alkali Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herencia, J.F.; García-Galavís, P.A.; Maqueda, C. Long-Term Effect of Organic and Mineral Fertilization on Soil Physical Properties Under Greenhouse and Outdoor Management Practices. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Majou, H.; Muller, F.; Penhoud, P.; Bruand, A. Prediction of Water Retention Properties of Syrian Clayey Soils. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2022, 36, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Deng, X.; Herbert, S.; Xing, B. Impacts of Adding Biochar on Nitrogen Retention and Bioavailability in Agricultural Soil. Geoderma 2013, 206, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Du, L.; Shi, S.; Xing, G. Nitrous Oxide Emission from Wetland Rice Soil as Affected by the Application of Controlled-Availability Fertilizers and Mid-Season Aeration. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 32, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
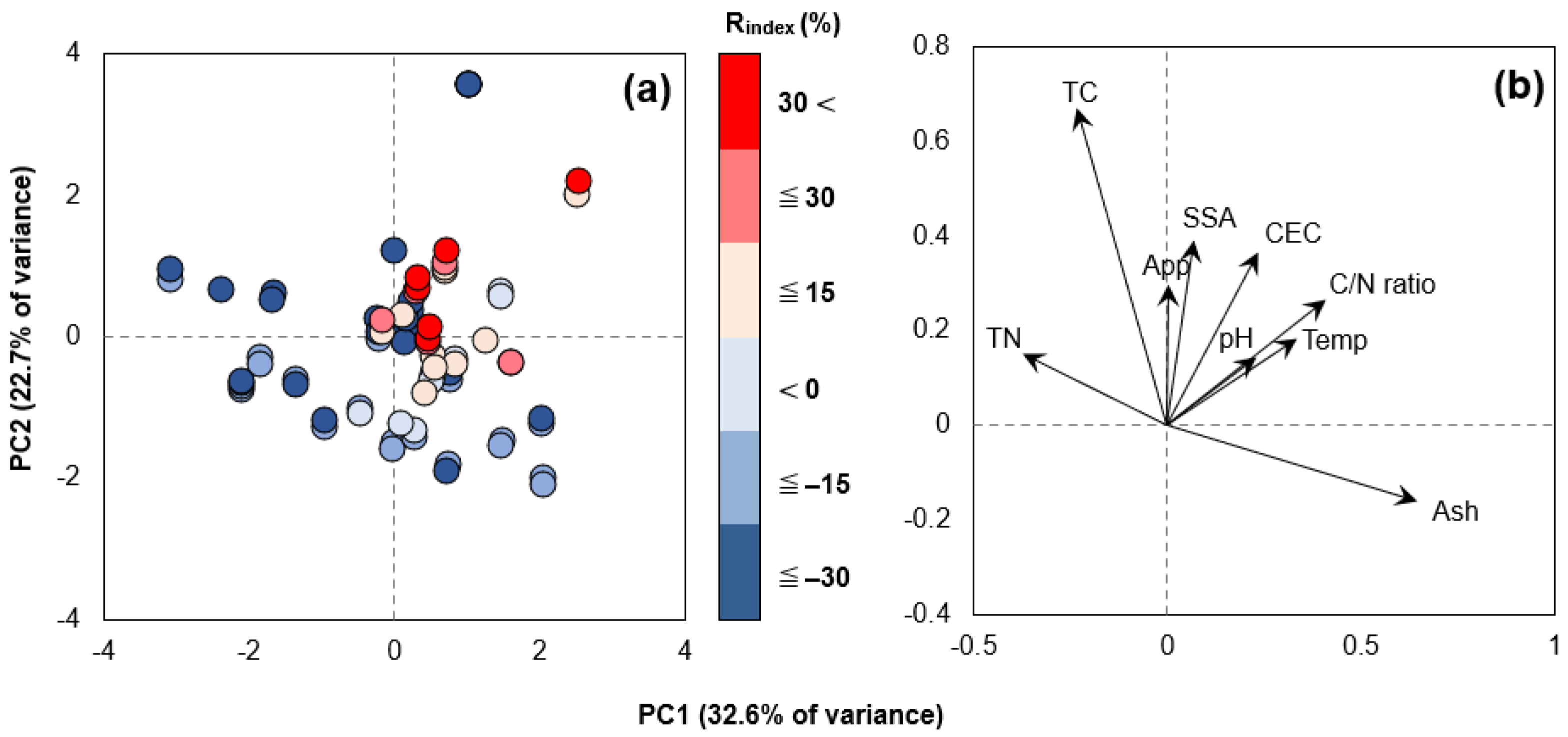
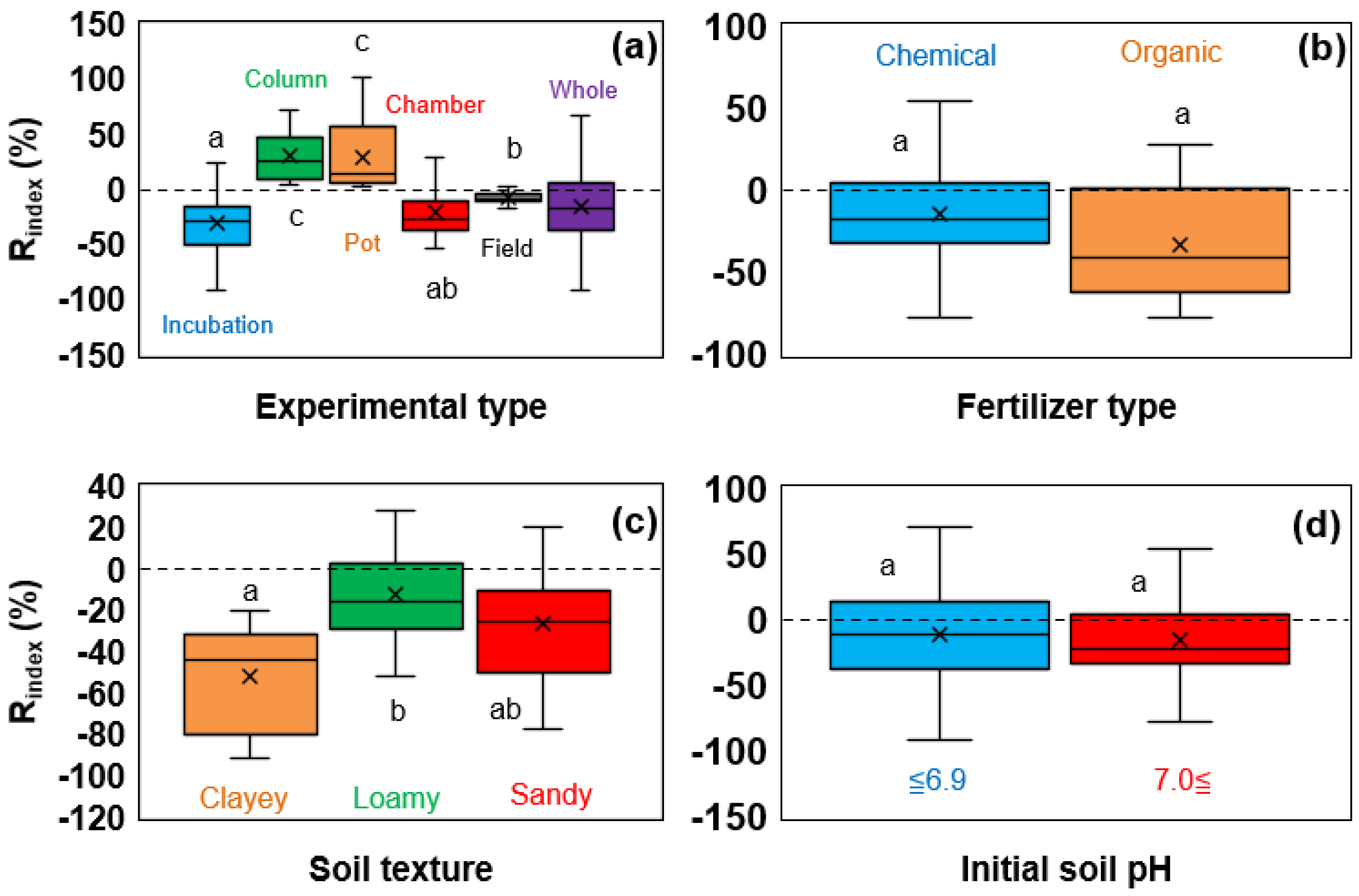

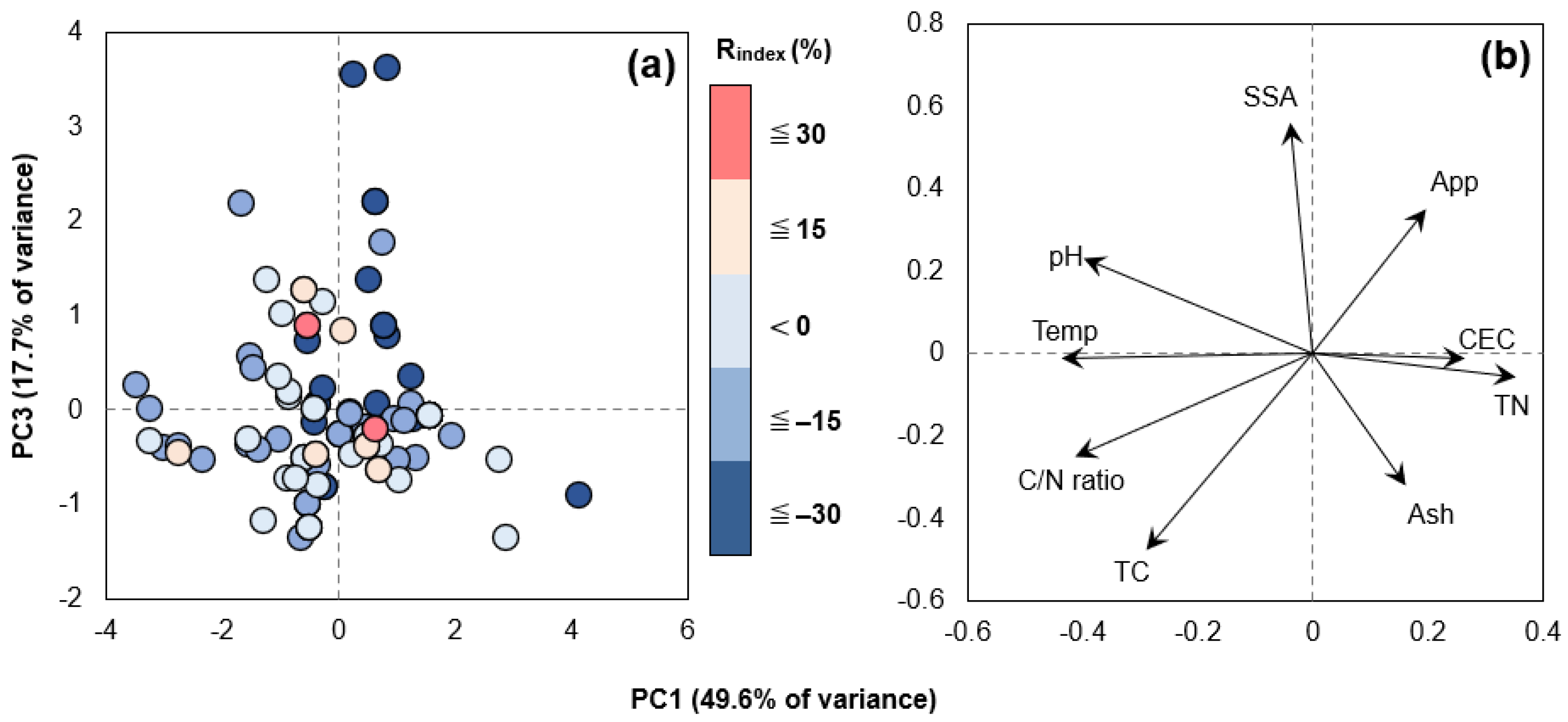
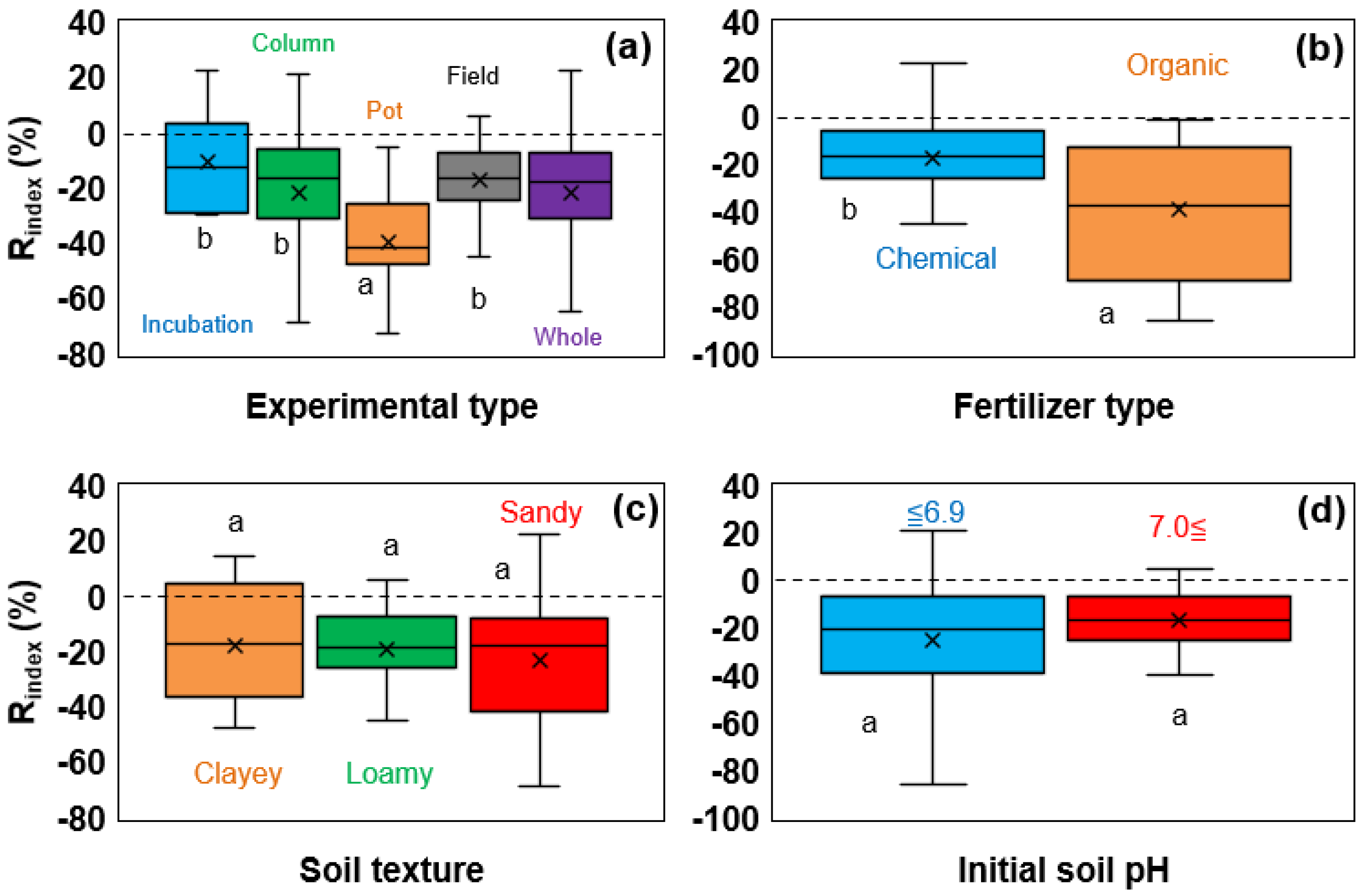


| Index | Experimental Types | References |
|---|---|---|
| NH3 volatilization | Incubation | [17,18,19,20,21,22,23] |
| Column | [24,25,26] | |
| Pot | [27,28,29] | |
| Chamber | [30,31] | |
| Field | [32,33,34,35,36] | |
| NO3−-N leaching | Incubation | [19,37] |
| Column | [26,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52] | |
| Pot | [27,53,54,55,56] | |
| Field | [57,58,59,60,61,62] | |
| N2O emission | Incubation | [63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74] |
| Pot | [29,75] | |
| Column | [25,47] | |
| Field | [61,62,66,76,77,78,79,80] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kohira, Y.; Fentie, D.; Lewoyehu, M.; Wutisirirattanachai, T.; Gezahegn, A.; Ahmed, M.; Akizuki, S.; Addisu, S.; Sato, S. The Sustainable Management of Nitrogen Fertilizers for Environmental Impact Mitigation by Biochar Applications to Soils: A Review from the Past Decade. Environments 2025, 12, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060182
Kohira Y, Fentie D, Lewoyehu M, Wutisirirattanachai T, Gezahegn A, Ahmed M, Akizuki S, Addisu S, Sato S. The Sustainable Management of Nitrogen Fertilizers for Environmental Impact Mitigation by Biochar Applications to Soils: A Review from the Past Decade. Environments. 2025; 12(6):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060182
Chicago/Turabian StyleKohira, Yudai, Desalew Fentie, Mekuanint Lewoyehu, Tassapak Wutisirirattanachai, Ashenafei Gezahegn, Milkiyas Ahmed, Shinichi Akizuki, Solomon Addisu, and Shinjiro Sato. 2025. "The Sustainable Management of Nitrogen Fertilizers for Environmental Impact Mitigation by Biochar Applications to Soils: A Review from the Past Decade" Environments 12, no. 6: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060182
APA StyleKohira, Y., Fentie, D., Lewoyehu, M., Wutisirirattanachai, T., Gezahegn, A., Ahmed, M., Akizuki, S., Addisu, S., & Sato, S. (2025). The Sustainable Management of Nitrogen Fertilizers for Environmental Impact Mitigation by Biochar Applications to Soils: A Review from the Past Decade. Environments, 12(6), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060182