Global Trends in Air Pollution Modeling over Cities Under the Influence of Climate Variability: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scientific Databases
2.2. Review Methodology
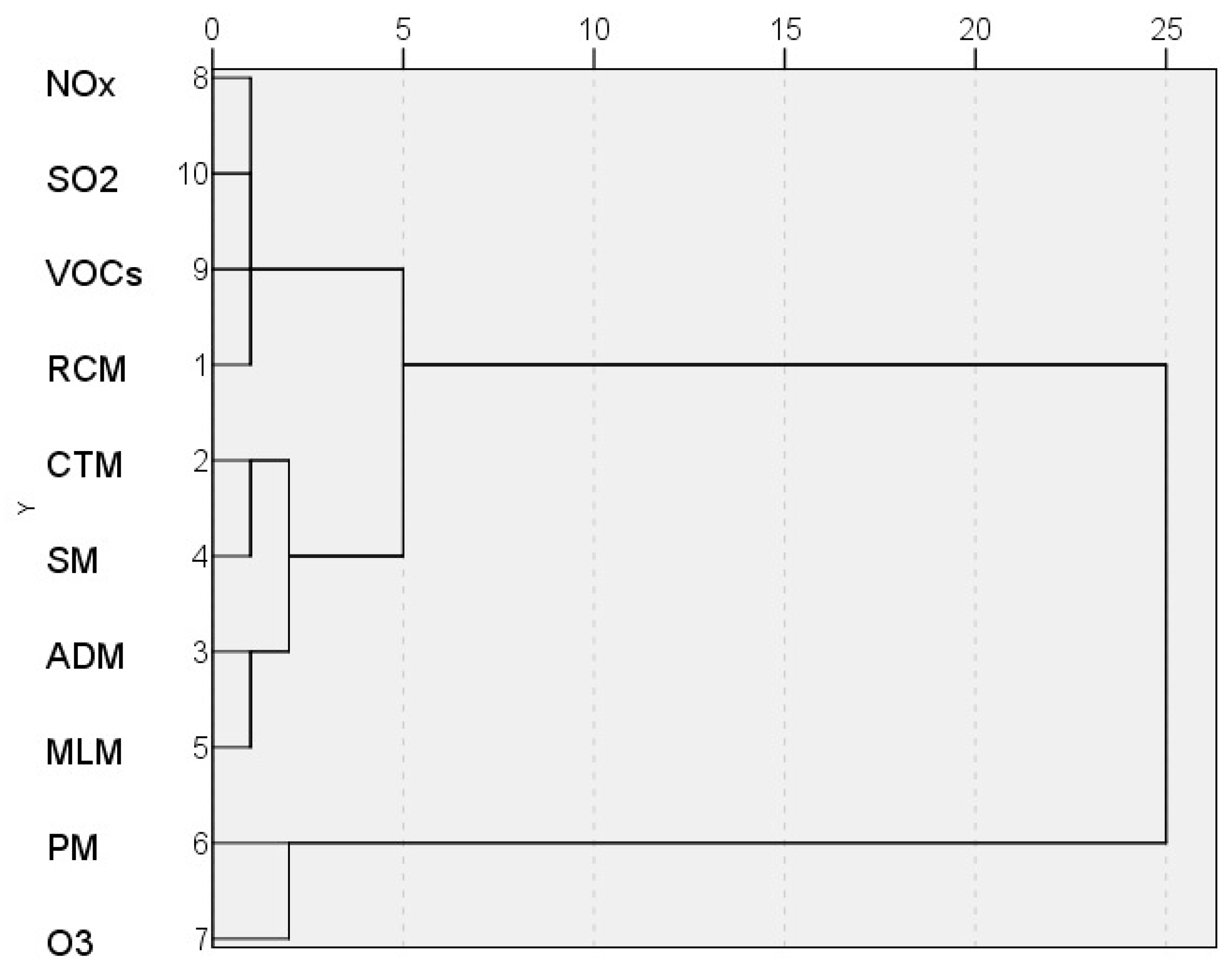
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Types of Models Detected
3.1.1. Temporal Aspects
3.1.2. Monetary Aspects
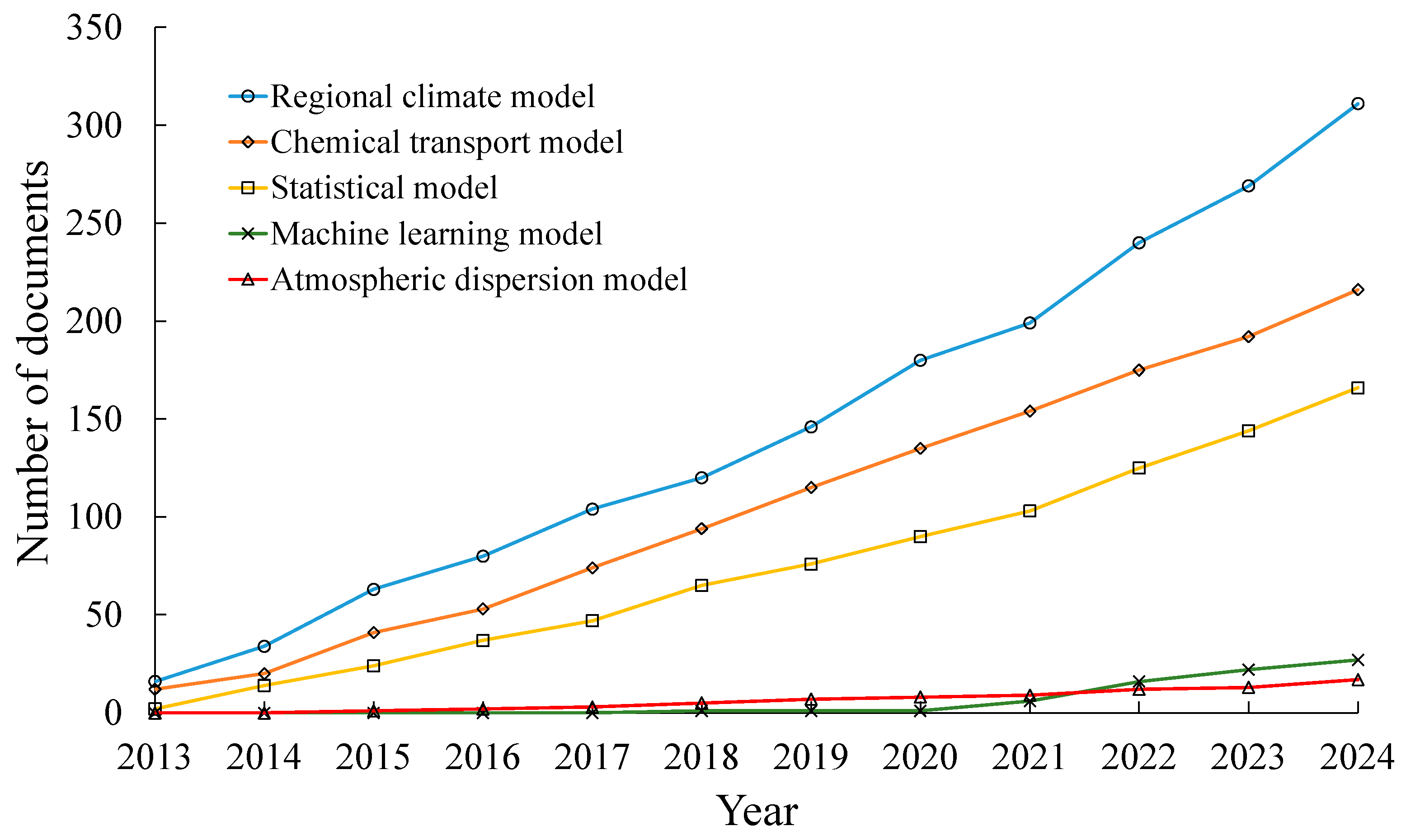
3.2. Detected Models
3.3. Climate Parameters: Temporal Aspects
3.4. Air Pollutants: Temporal Aspects
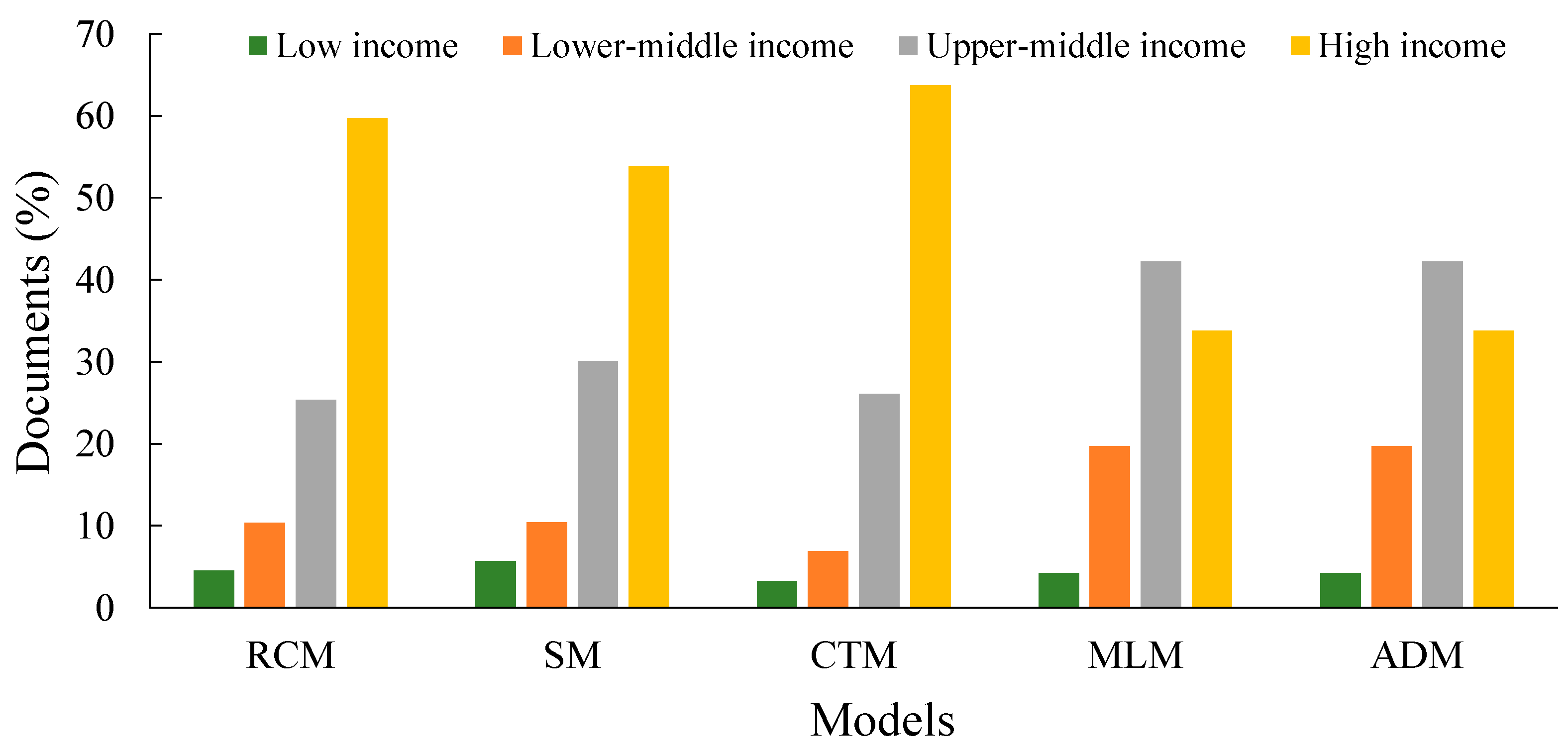
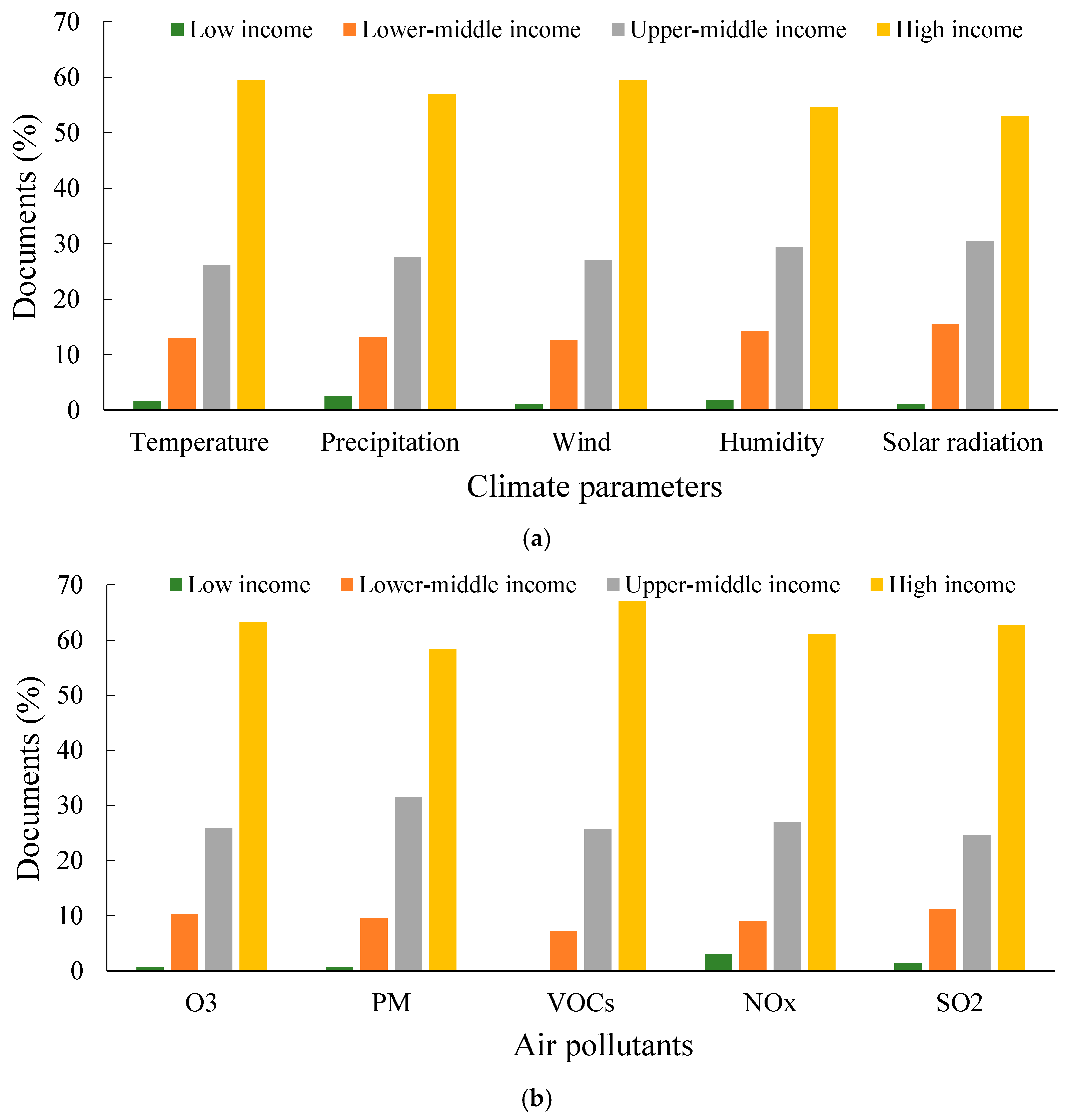
3.5. Climate Parameters and Air Pollutants: Monetary Aspects
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADM | atmospheric dispersion model |
| ADMS | Atmospheric Dispersion Modeling System |
| AERMOD | Steady-State Gaussian Plume Model |
| ANNs | Artificial Neural Networks |
| ARIMA | Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average Model |
| BHM | Bayesian Hierarchical Model |
| CALPUFF | Non-Steady-State Meteorological and Air Quality Modeling System |
| CAMx | Comprehensive Air Quality Model with Extensions |
| CHIMERE | Multi-Scale Chemistry-Transport Model |
| CMAQ | Community Multiscale Air Quality |
| COSMO-CLM | Consortium for Small-Scale Modeling-Climate Limited-Area Modeling |
| CTM | chemical transport model |
| CV | climate variability |
| GAM | Generalized Additive Model |
| GBMs | Gradient Boosting Machines |
| GEOS-Chem | Goddard Earth Observing System-Global 3-D Model of Atmospheric Chemistry |
| GLM | Generalized Linear Model |
| HIRLAM | High-Resolution Limited Area Model |
| HYSPLIT | Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory Model |
| KNNs | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| LOTOS-EUROS | Open-Source Chemical Transport Model |
| MLM | machine learning model |
| MOZART | Model for Ozone and Related Chemical Tracers |
| RCM | regional climate model |
| RegCM | Regional Climate Model |
| RFs | Random Forests |
| SM | statistical model |
| SVMs | Support Vector Machines |
| WRF | Weather Research and Forecasting Model |
| WRF-Chem | Weather Research and Forecasting Model Coupled with Chemistry |
References
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human Health Effects of Air Pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trail, M.; Tsimpidi, A.P.; Liu, P.; Tsigaridis, K.; Rudokas, J.; Miller, P.; Nenes, A.; Hu, Y.; Russell, A.G. Sensitivity of Air Quality to Potential Future Climate Change and Emissions in the United States and Major Cities. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.J.; Winner, D.A. Effect of Climate Change on Air Quality. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, A.M.; Naik, V.; Leibensperger, E.M. Air Quality and Climate Connections. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 65, 645–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.; Wang, X.-J.; Harun, S.B.; Shamsudin, S.B.; Ismail, T.; Minhans, A. Climate Variability and Changes in the Major Cities of Bangladesh: Observations, Possible Impacts and Adaptation. Reg. Environ. Change 2016, 16, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasper, R.; Blohm, A.; Ruth, M. Social and Economic Impacts of Climate Change on the Urban Environment. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Menendez, F.; Monier, E.; Selin, N.E. The Role of Natural Variability in Projections of Climate Change Impacts on U.S. Ozone Pollution. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2911–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacressonnière, G.; Foret, G.; Beekmann, M.; Siour, G.; Engardt, M.; Gauss, M.; Watson, L.; Andersson, C.; Colette, A.; Josse, B.; et al. Impacts of Regional Climate Change on Air Quality Projections and Associated Uncertainties. Clim. Change 2016, 136, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pienkosz, B.D.; Saari, R.K.; Monier, E.; Garcia-Menendez, F. Natural Variability in Projections of Climate Change Impacts on Fine Particulate Matter Pollution. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippertz, P.; Evans, M.J.; Field, P.R.; Fink, A.H.; Liousse, C.; Marsham, J.H. The Possible Role of Local Air Pollution in Climate Change in West Africa. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odubo, T.C.; Kosoe, E.A. Sources of Air Pollutants: Impacts and Solutions. In Air Pollutants in the Context of One Health: Fundamentals, Sources, and Impacts; Izah, S.C., Ogwu, M.C., Shahsavani, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 75–121. ISBN 978-3-031-74165-4. [Google Scholar]
- Etim, N.G.; Imarhiagbe, O. Unraveling the Fundamentals of Air Pollutants. In Air Pollutants in the Context of One Health: Fundamentals, Sources, and Impacts; Izah, S.C., Ogwu, M.C., Shahsavani, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 33–73. ISBN 978-3-031-74165-4. [Google Scholar]
- Pleijel, H.; Grundström, M.; Karlsson, G.P.; Karlsson, P.E.; Chen, D. A Method to Assess the Inter-Annual Weather-Dependent Variability in Air Pollution Concentration and Deposition Based on Weather Typing. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 126, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, H. Integrating Climate Change Adaptation Strategies in Urban Planning and Landscape Design of Addis Ababa City, Ethiopia. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2017, 27, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Pandey, P. Air Pollution, Climate Change, and Human Health in Indian Cities: A Brief Review. Front. Sustain. Cities 2021, 3, 705131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massad, R.S.; Lathière, J.; Strada, S.; Perrin, M.; Personne, E.; Stéfanon, M.; Stella, P.; Szopa, S.; de Noblet-Ducoudré, N. Reviews and Syntheses: Influences of Landscape Structure and Land Uses on Local to Regional Climate and Air Quality. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 2369–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, A.-L.; Tella, A.; Baloo, L.; Adebisi, N. A Review of the Inter-Correlation of Climate Change, Air Pollution and Urban Sustainability Using Novel Machine Learning Algorithms and Spatial Information Science. Urban Clim. 2021, 40, 100989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallos, G.; Mitsakou, C.; Alastuey, A.; van Aardenne, J.; Astitha, M.; Cusack, M.; Doering, U.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Kanakidou, M.; et al. Mechanisms of Climate Variability, Air Quality and Impacts of Atmospheric Constituents in the Mediterranean Region. In Regional Assessment of Climate Change in the Mediterranean: Volume 1: Air, Sea and Precipitation and Water; Navarra, A., Tubiana, L., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 119–156. ISBN 978-94-007-5781-3. [Google Scholar]
- Castelhano, F.J.; Pedroso, A.C.N.; Cobelo, I.; Borge, R.; Roig, H.L.; Adams, M.; Amini, H.; Koutrakis, P.; Réquia, W.J. The Impact of Long-Term Weather Changes on Air Quality in Brazil. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 283, 119182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.-C.; Dai, Y.-T.; Mkasimongwa, S.W.; Hsiao, M.-C.; Lai, L.-W. The Impact of Atmospheric Synoptic Weather Condition and Long-Range Transportation of Air Mass on Extreme PM10 Concentration Events. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, O.L.Q.; Niño-Ruiz, E.D.; Pinel, N. On the Mathematical Modelling and Data Assimilation for Air Pollution Assessment in the Tropical Andes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 35993–36012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Azizi, T. Urban Climate Dynamics: Analyzing the Impact of Green Cover and Air Pollution on Land Surface Temperature—A Comparative Study Across Chicago, San Francisco, and Phoenix, USA. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garuma, G.F. Review of Urban Surface Parameterizations for Numerical Climate Models. Urban Clim. 2018, 24, 830–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbehadji, I.E.; Obagbuwa, I.C. Systematic Review of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for Spatiotemporal Air Quality Prediction. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karroum, K.; Lin, Y.; Chiang, Y.-Y.; Ben Maissa, Y.; El Haziti, M.; Sokolov, A.; Delbarre, H. A Review of Air Quality Modeling. MAPAN 2020, 35, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Harbawi, M. Air Quality Modelling, Simulation, and Computational Methods: A Review. Environ. Rev. 2013, 21, 149–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri Shahraiyni, H.; Sodoudi, S. Statistical Modeling Approaches for PM10 Prediction in Urban Areas; A Review of 21st-Century Studies. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, G.; Beelen, R.; de Hoogh, K.; Vienneau, D.; Gulliver, J.; Fischer, P.; Briggs, D. A Review of Land-Use Regression Models to Assess Spatial Variation of Outdoor Air Pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7561–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Lu, H. Air Pollution Forecasts: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybarczyk, Y.; Zalakeviciute, R. Machine Learning Approaches for Outdoor Air Quality Modelling: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, B.; Rafael, S.; Coelho, M.C.; Ferreira, J. Connecting the Dots between Urban Morphology and the Air Quality of Cities under a Changing Climate: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhunushalieva, G.; Teuber, R. Roles of Innovation in Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals: A Bibliometric Analysis. J. Innov. Knowl. 2024, 9, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Santamaría, K.; Zafra-Mejía, C.A.; Rondón-Quintana, H.A. Macro-Morphological Traits of Leaves for Urban Tree Selection for Air Pollution Biomonitoring: A Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafra, C.; Temprano, J.; Tejero, I. The Physical Factors Affecting Heavy Metals Accumulated in the Sediment Deposited on Road Surfaces in Dry Weather: A Review. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Lankao, P.; Qin, H.; Borbor-Cordova, M. Exploration of Health Risks Related to Air Pollution and Temperature in Three Latin American Cities. Soc. Sci. Med. 2013, 83, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-118-94740-1. [Google Scholar]
- Tahir Bahadur, F.; Rasool Shah, S.; Rao Nidamanuri, R. Air Pollution Monitoring, and Modelling: An Overview. Environ. Forensics 2024, 25, 309–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNider, R.T.; Pour-Biazar, A. Meteorological Modeling Relevant to Mesoscale and Regional Air Quality Applications: A Review. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2020, 70, 2–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menut, L.; Tripathi, O.P.; Colette, A.; Vautard, R.; Flaounas, E.; Bessagnet, B. Evaluation of Regional Climate Simulations for Air Quality Modelling Purposes. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 2515–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baklanov, A.; Zhang, Y. Advances in Air Quality Modeling and Forecasting. Glob. Transit. 2020, 2, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y. A Comprehensive Analysis of the Spatio-Temporal Variation of Urban Air Pollution in China during 2014–2018. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 220, 117066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, P.; Sivakumar, V. Application of k-Means and Hierarchical Clustering Techniques for Analysis of Air Pollution: A Review (1980–2019). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleke, T.T.; Giorgi, F.; Diro, G.T.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Giuliani, G.; Ayal, D.; Kassahun, T.; Sintayehu, W.D.; Demissie, T. Effect of Urbanization on East African Climate as Simulated by Coupled Urban-Climate Model. Clim. Serv. 2023, 31, 100398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, V.; Lemonsu, A.; Hidalgo, J.; Voogt, J. Urban Climates and Climate Change. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2020, 45, 411–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engardt, M.; Langner, J. Simulations of Future Sulphur and Nitrogen Deposition over Europe Using Meteorological Data from Three Regional Climate Projections. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2013, 65, 20348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Oleson, K.; Bou-Zeid, E.; Krayenhoff, E.S.; Bray, A.; Zhu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, C.; Oppenheimer, M. Global Multi-Model Projections of Local Urban Climates. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.A.; Kahnert, M.; Andersson, C.; Kokkola, H.; Hansson, U.; Jones, C.; Langner, J.; Devasthale, A. Integration of Prognostic Aerosol–Cloud Interactions in a Chemistry Transport Model Coupled Offline to a Regional Climate Model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Coupled Chemistry-Meteorology/Climate Modelling (CCMM): Status and Relevance for Numerical Weather Prediction, Atmospheric Pollution and Climate Research. Available online: https://library.wmo.int/records/item/55161-coupled-chemistry-meteorology-climate-modelling-ccmm-status-and-relevance-for-numerical-weather-prediction-atmospheric-pollution-and-climate-research?offset=7 (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Langner, J.; Engardt, M.; Baklanov, A.; Christensen, J.H.; Gauss, M.; Geels, C.; Hedegaard, G.B.; Nuterman, R.; Simpson, D.; Soares, J.; et al. A Multi-Model Study of Impacts of Climate Change on Surface Ozone in Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 10423–10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Rattan, P.; Mor, S.; Aggarwal, A.N. Generalized Additive Models: Building Evidence of Air Pollution, Climate Change and Human Health. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 104987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, F. Singular Value Decomposition Analysis of Spatial Relationships between Monthly Weather and Air Pollution Index in China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.J.; Shiu, H.-Y.; Chang, J.H.-H.; Ooi, M.C.G.; Li, H.-H.; Homma, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Chiueh, P.-T.; Maneechot, L.; Nik Sulaiman, N.M. Spatiotemporal Impact of COVID-19 on Taiwan Air Quality in the Absence of a Lockdown: Influence of Urban Public Transportation Use and Meteorological Conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautela, K.S.; Goyal, M.K. Transforming Air Pollution Management in India with AI and Machine Learning Technologies. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarian, N.; Lipson, M.; Norford, L.K. Chapter 4—Multiscale Modeling Techniques to Document Urban Climate Change. In Urban Climate Change and Heat Islands; Paolini, R., Santamouris, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 123–164. ISBN 978-0-12-818977-1. [Google Scholar]
- Gündoğdu, S.; Elbir, T. Elevating Hourly PM2.5 Forecasting in Istanbul, Türkiye: Leveraging ERA5 Reanalysis and Genetic Algorithms in a Comparative Machine Learning Model Analysis. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebi, K.L.; Hondula, D.; Kinney, P.; Monaghan, A.; Morin, C.W.; Ogden, N.; Springmann, M. Health Risks of Climate Variability and Change. In Handbook of Environmental and Ecological Statistics; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-315-15250-9. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, A.; Soares, A.O. Hybrid Model for Urban Air Pollution Forecasting: A Stochastic Spatio-Temporal Approach. Math. Geosci. 2014, 46, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohn, L.M.; Geels, C.; Andersen, C.; Andersson, C.; Bennet, C.; Christensen, J.H.; Im, U.; Karvosenoja, N.; Kindler, P.A.; Kukkonen, J.; et al. Evaluation of Multidecadal High-Resolution Atmospheric Chemistry-Transport Modelling for Exposure Assessments in the Continental Nordic Countries. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 290, 119334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, H.; Tai, A.P.K.; Val Martin, M.; Yung, D.H.Y. Responses of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Air Quality to Future Climate, Land Use, and Emission Changes: Insights from Modeling across Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monks, P.S.; Archibald, A.T.; Colette, A.; Cooper, O.; Coyle, M.; Derwent, R.; Fowler, D.; Granier, C.; Law, K.S.; Mills, G.E.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone and Its Precursors from the Urban to the Global Scale from Air Quality to Short-Lived Climate Forcer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8889–8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Dang, R.; Xue, D.; Li, B.; Tang, J.; Leung, L.R.; Liao, H. North China Plain as a Hot Spot of Ozone Pollution Exacerbated by Extreme High Temperatures. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 4705–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, S.; Lakhani, A. Tropospheric Ozone and Its Natural Precursors Impacted by Climatic Changes in Emission and Dynamics. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1007942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dingenen, R.; Dentener, F.; Crippa, M.; Leitao, J.; Marmer, E.; Rao, S.; Solazzo, E.; Valentini, L. TM5-FASST: A Global Atmospheric Source–Receptor Model for Rapid Impact Analysis of Emission Changes on Air Quality and Short-Lived Climate Pollutants. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16173–16211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Gu, Y.; Yim, S.H.L. Assessing Local and Transboundary Fine Particulate Matter Pollution and Sectoral Contributions in Southeast Asia during Haze Months of 2015–2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.J.; Girach, I.A.; Harithasree, S.; Bhuyan, K.; Ojha, N.; Kumar, M. Urban Ozone Variability Using Automated Machine Learning: Inference from Different Feature Importance Schemes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Maity, R. Assessing the Potential of AI–ML in Urban Climate Change Adaptation and Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munandar, D.; Ruchjana, B.N.; Abdullah, A.S.; Pardede, H.F. Integration GSTARIMA with Deep Neural Network to Enhance Prediction Accuracy on Rainfall Data. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2024, 12, 2409106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, S.H.M.; Griffiths, P.T.; Nowack, P.J.; Archibald, A.T. Short-Term Forecasting of Ozone Air Pollution across Europe with Transformers. Environ. Data Sci. 2023, 2, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, G.; Chen, C.; Huang, X.; Che, H.; Zhang, X.; He, K.; Zhang, Q. Separating Emission and Meteorological Contributions to Long-Term PM2.5 Trends over Eastern China during 2000–2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9475–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Popoola, O.A.M.; Hood, C.; Carruthers, D.; Jones, R.L.; Liu, H.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Archibald, A.T. Constraining Emission Estimates of Carbon Monoxide Using a Perturbed Emissions Ensemble with Observations: A Focus on Beijing. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 1587–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Fernandes Duarte, E.; Costa, M.J.; Salgueiro, V.C.; Lucio, P.S.; Potes, M.; Bortoli, D.; Salgado, R. Fire-Pollutant-Atmosphere Interaction and Its Impact on Mortality in Portugal During Wildfire Seasons. ESS Open Arch. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emetere, M.E.; Akinlabi, E.T. Introduction to Environmental Modeling. In Introduction to Environmental Data Analysis and Modeling; Emetere, M.E., Akinlabi, E.T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–27. ISBN 978-3-030-36207-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pourkiaei, M.; Rahif, R.; Falzone, C.; Elnagar, E.; Doutreloup, S.; Martin, J.; Fettweis, X.; Lemort, V.; Attia, S.; Romain, A.-C. Systematic Framework for Quantitative Assessment of Indoor Air Quality under Future Climate Scenarios; 2100s Projection of a Belgian Case Study. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 93, 109611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfold, M.J.; Latif, M.T.; Samah, A.A.; Mead, M.I.; Harris, N.R.P. Influence of Northeast Monsoon Cold Surges on Air Quality in Southeast Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ashfold, M.J.; Pyle, J.A.; Robinson, A.D.; Meneguz, E.; Nadzir, M.S.M.; Phang, S.M.; Samah, A.A.; Ong, S.; Ung, H.E.; Peng, L.K.; et al. Rapid Transport of East Asian Pollution to the Deep Tropics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3565–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppas, S.C.; Papadogiannaki, S.; Parliari, D.; Kontos, S.; Poupkou, A.; Tzoumaka, P.; Kelessis, A.; Zanis, P.; Casasanta, G.; de’Donato, F.; et al. Future Climate Change Impact on Urban Heat Island in Two Mediterranean Cities Based on High-Resolution Regional Climate Simulations. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabat, P.; Somot, S.; Cassou, C.; Mallet, M.; Michou, M.; Bouniol, D.; Decharme, B.; Drugé, T.; Roehrig, R.; Saint-Martin, D. Modulation of Radiative Aerosols Effects by Atmospheric Circulation over the Euro-Mediterranean Region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 8315–8349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colette, A.; Bessagnet, B.; Vautard, R.; Szopa, S.; Rao, S.; Schucht, S.; Klimont, Z.; Menut, L.; Clain, G.; Meleux, F.; et al. European Atmosphere in 2050, a Regional Air Quality and Climate Perspective under CMIP5 Scenarios. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7451–7471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, N.; Sillmann, J.; Mar, K.A.; Rust, H.W.; Solberg, S.; Andersson, C.; Engardt, M.; Bergström, R.; Bessagnet, B.; Colette, A.; et al. A Multi-Model Comparison of Meteorological Drivers of Surface Ozone over Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 12269–12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, H.M.; Kala, J.; Ng, A.W.M.; Muthukumaran, S. An Evaluation of the Performance of a WRF Multi-Physics Ensemble for Heatwave Events over the City of Melbourne in Southeast Australia. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 50, 2553–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauwaet, D.; Viaene, P.; Brisson, E.; van Lipzig, N.P.M.; van Noije, T.; Strunk, A.; Van Looy, S.; Veldeman, N.; Blyth, L.; De Ridder, K.; et al. The Effect of Climate Change and Emission Scenarios on Ozone Concentrations over Belgium: A High-Resolution Model Study for Policy Support. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5893–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahura, A.; Baklanov, A.; Makkonen, R.; Boy, M.; Petäjä, T.; Lappalainen, H.K.; Nuterman, R.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Arnold, S.R.; Jochum, M.; et al. Towards Seamless Environmental Prediction—Development of Pan-Eurasian EXperiment (PEEX) Modelling Platform. Big Earth Data 2024, 8, 189–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komkoua Mbienda, A.J.; Tchawoua, C.; Vondou, D.A.; Choumbou, P.; Kenfack Sadem, C.; Dey, S. Impact of Anthropogenic Aerosols on Climate Variability over Central Africa by Using a Regional Climate Model. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Ivey, C.E.; Blanchard, C.L.; Do, K.; Lee, S.-M.; Russell, A.G. Separating Emissions and Meteorological Impacts on Peak Ozone Concentrations in Southern California Using Generalized Additive Modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhani, F.; Ehsani, A.H.; McGuirk, S.L.; Shafiepour Motlagh, M.; Mousavi, S.M.; Rashidi, Y.; Mirmazloumi, S.M. Examining and Predicting the Influence of Climatic and Terrestrial Factors on the Seasonal Distribution of Ozone Column Depth over Tehran Province Using Satellite Observations. Acta Geophys. 2024, 72, 1191–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Medina, D.S.; Zafra-Mejía, C.A.; Rondón-Quintana, H.A. ARIMA Analysis of PM Concentrations during the COVID-19 Isolation in a High-Altitude Latin American Megacity. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafra, C.; Ángel, Y.; Torres, E. ARIMA Analysis of the Effect of Land Surface Coverage on PM10 Concentrations in a High-Altitude Megacity. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Cai, J.; Feng, Y.; Gu, L.; Guan, X.; Liu, N.; Gu, H.; Li, X. Association between Air Pollution, Meteorological Factors and Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Incidence in Zhejiang Province: A Bayesian Spatio-Temporal Modelling Study. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 336, 120745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, M.; Holloway, T.; Choi, S.; O’Neill, S.M.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Jin, X.; Fiore, A.M.; Henze, D.K.; et al. Methods, Availability, and Applications of PM2.5 Exposure Estimates Derived from Ground Measurements, Satellite, and Atmospheric Models. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 1391–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Wei, W.; Cheng, S.; Han, X.; Wang, X. Meteorological Characteristics within Boundary Layer and Its Influence on PM2.5 Pollution in Six Cities of North China Based on WRF-Chem. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 228, 117417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, G.; Sahu, S.K.; Rathod, A.; Tikle, S.; Singh, V.; Sandeepan, B.S. Role of Meteorological Regime in Mitigating Biomass Induced Extreme Air Pollution Events. Urban Clim. 2021, 35, 100756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Fang, T.; Yim, S.H.L. Source Emission Contributions to Particulate Matter and Ozone, and Their Health Impacts in Southeast Asia. Environ. Int. 2024, 186, 108578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payami, M.; Choi, Y.; Salman, A.K.; Mousavinezhad, S.; Park, J.; Pouyaei, A. A 1D CNN-Based Emulator of CMAQ: Predicting NO2 Concentration over the Most Populated Urban Regions in Texas. Artif. Intell. Earth Syst. 2024, 3, e230055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tong, D.; He, K. Multi-Year Downscaling Application of Two-Way Coupled WRF v3.4 and CMAQ v5.0.2 over East Asia for Regional Climate and Air Quality Modeling: Model Evaluation and Aerosol Direct Effects. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 2447–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.; He, T.-L.; Jones, D.; Liu, J.; Shen, Y. Meteorological and Anthropogenic Drivers of Surface Ozone Change in the North China Plain in 2015–2021. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Evident PM2.5 Drops in the East of China Due to the COVID-19 Quarantine Measures in February. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Emmons, L.K.; Worden, H.M.; Kumar, R.; He, C.; Gaubert, B.; Zheng, Z.; Tilmes, S.; Buchholz, R.R.; Martinez-Alonso, S.-E.; et al. Application of the Multi-Scale Infrastructure for Chemistry and Aerosols Version 0 (MUSICAv0) for Air Quality Research in Africa. Geosci. Model Dev. 2023, 16, 6001–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgianto, R.H.; Rivaniputra, R.; Kinanti, N.P.; Saputra, A.H.; Khoir, A.N. A Numerical Simulation of PM2.5 Concentration Using the WRF-Chem Model during a High Air Pollution Episode in 2019 in Jakarta, Indonesia. IJAAS 2022, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Li, Y. An Atmospheric Vulnerability Assessment Framework for Environment Management and Protection Based on CAMx. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Qu, Y.; Li, M.; Xie, M. Elucidating Drivers of Severe Wintertime Fine Particulate Matter Pollution Episodes in the Yangtze River Delta Region of Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacressonnière, G.; Watson, L.; Gauss, M.; Engardt, M.; Andersson, C.; Beekmann, M.; Colette, A.; Foret, G.; Josse, B.; Marécal, V.; et al. Particulate Matter Air Pollution in Europe in a + 2 °C Warming World. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 154, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhvar, V.N.; Pascal, M.; Markakis, K.; Colette, A.; Hauglustaine, D.; Valari, M.; Klimont, Z.; Medina, S.; Kinney, P. A Multi-Scale Health Impact Assessment of Air Pollution over the 21st Century. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, C.; Forsell, N.; Kiesewetter, G.; Schaap, M.; Schöpp, W. Ozone Concentrations and Damage for Realistic Future European Climate and Air Quality Scenarios. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pseftogkas, A.; Koukouli, M.-E.; Segers, A.; Manders, A.; van Geffen, J.; Balis, D.; Meleti, C.; Stavrakou, T.; Eskes, H. Comparison of S5P/TROPOMI Inferred NO2 Surface Concentrations with In Situ Measurements over Central Europe. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwokolo, S.C.; Proutsos, N.; Meyer, E.L.; Ahia, C.C. Machine Learning and Physics-Based Hybridization Models for Evaluation of the Effects of Climate Change and Urban Expansion on Photosynthetically Active Radiation. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku Yusof, K.M.K.; Azid, A.; Abdullah Sani, M.S.; Samsudin, M.S.; Muhammad Amin, S.N.S.; Abd Rani, N.L.; Jamalani, M.A. The Evaluation on Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) and Multiple Linear Regressions (MLR) Models over Particulate Matter (PM10) Variability during Haze and Non-Haze Episodes: A Decade Case Study. Mal. J. Fund. Appl. Sci. 2019, 15, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, K. Spatiotemporally Mapping of the Relationship between NO2 Pollution and Urbanization for a Megacity in Southwest China during 2005–2016. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehie, O.; Jamal, M.H.B.; Shahid, S. Characterization and Prediction of PM2.5 Levels in Afghanistan Using Machine Learning Techniques. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2024, 155, 9081–9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.; Franklin, M.; Lee, H.; Garay, M.; Kalashnikova, O. Temporal and Spatial Autocorrelation as Determinants of Regional AOD-PM2.5 Model Performance in the Middle East. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhathloul, S.H.; Mishra, A.K.; Khan, A.A. Low Visibility Event Prediction Using Random Forest and K-Nearest Neighbor Methods. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2024, 155, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masroor, M.; Avtar, R.; Sajjad, H.; Choudhari, P.; Kulimushi, L.C.; Khedher, K.M.; Komolafe, A.A.; Yunus, A.P.; Sahu, N. Assessing the Influence of Land Use/Land Cover Alteration on Climate Variability: An Analysis in the Aurangabad District of Maharashtra State, India. Sustainability 2022, 14, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-del-Valle, C. Searching Through Smart Design Methods for Architecture. In The Routledge Companion to Smart Design Thinking in Architecture & Urbanism for a Sustainable, Living Planet; Routledge: London, UK, 2024; ISBN 978-1-003-38411-3. [Google Scholar]
- Vuolo, M.R.; Acutis, M.; Tyagi, B.; Boccasile, G.; Perego, A.; Pelissetti, S. Odour Emissions and Dispersion from Digestate Spreading. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, M.; Tahir, Z.; Mahmood, S.A.; Batool, S.; Tariq, A.; Lu, L.; Soufan, W. Spatio-Temporal Assessment of Aerosol and Cloud Properties Using MODIS Satellite Data and a HYSPLIT Model: Implications for Climate and Agricultural Systems. Atmos. Environ. X 2024, 21, 100242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yicun, G.; Mohammad Khorshiddoust, A.; Mohammadi, G.H.; Hoseini Sadr, A.; Aghlmand, F. The Relationship between PM2.5 Concentrations and Atmospheric Conditions in Severe and Persistent Urban Pollution in Tabriz, Northwest of Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridzuan, N.; Ujang, U.; Azri, S.; Choon, T.L. Visualising urban air quality using AERMOD, CALPUFF and CFD models: A critical review. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 44, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzu, S.L.; Cetinkaya, A.Y. Climatological Evaluation in a Central Anatolian City and Indirect Effects of Climatological Variation on Air Quality. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez-Huerta, M.; Sosa Echeverría, R.; Fuentes García, G.; Antonio Durán, R.; Sánchez Álvarez, P.; Magaña, V.; Retama, A. Influence of Particulate Matter on Air Quality Due to “Nortes” Events in the Gulf of Mexico. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, D.; Coburn, M.; Cox, S.; Bulot, F.M.J.; Xie, Z.-T.; Vanderwel, C. Comparing Large-Eddy Simulation and Gaussian Plume Model to Sensor Measurements of an Urban Smoke Plume. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadaverugu, R.; Dhyani, S.; Dasgupta, R.; Kumar, P.; Matli, C. Urban Sustainability and Resilience Building: Blue-Green Infrastructure for Air Pollution Abatement and Realizing Multiple Co-Benefits. In Blue-Green Infrastructure Across Asian Countries: Improving Urban Resilience and Sustainability; Dhyani, S., Basu, M., Santhanam, H., Dasgupta, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 397–417. ISBN 978-981-16-7128-9. [Google Scholar]
- Aktas, Y.D.; Stocker, J.; Carruthers, D.; Hunt, J. A Sensitivity Study Relating to Neighbourhood-Scale Fast Local Urban Climate Modelling within the Built Environment. Procedia Eng. 2017, 198, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoun, H.; Bellakhal, G.; Kanfoudi, H.; Zhang, X.; Chahed, J. One-Way Coupling of WRF with a Gaussian Dispersion Model: A Focused Fine-Scale Air Pollution Assessment on Southern Mediterranean. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 22892–22906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Tong, D.; Lee, P.; Tang, Y.; Huang, J.; Campbell, P.C.; Mcqueen, J.; Pye, H.O.T.; et al. Evaluation of the Offline-Coupled GFSv15–FV3–CMAQv5.0.2 in Support of the next-Generation National Air Quality Forecast Capability over the Contiguous United States. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 3969–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Ngan, F. Coupling of Important Physical Processes in the Planetary Boundary Layer between Meteorological and Chemistry Models for Regional to Continental Scale Air Quality Forecasting: An Overview. Atmosphere 2011, 2, 464–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.; Baklanov, A. Integrated Modeling for Forecasting Weather and Air Quality: A Call for Fully Coupled Approaches. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6845–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baklanov, A.; Smith Korsholm, U.; Nuterman, R.; Mahura, A.; Nielsen, K.P.; Sass, B.H.; Rasmussen, A.; Zakey, A.; Kaas, E.; Kurganskiy, A.; et al. Enviro-HIRLAM Online Integrated Meteorology–Chemistry Modelling System: Strategy, Methodology, Developments and Applications (v7.2). Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 2971–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsholm, U.; Baklanov, A.; Sørensen, J.H. Status and Evaluation of Enviro-HIRLAM: Differences Between Online and Offline Models. In Integrated Systems of Meso-Meteorological and Chemical Transport Models; Baklanov, A., Alexander, M., Sokhi, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 61–74. ISBN 978-3-642-13980-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, D.; Gao, W.; Zhang, J.; Morino, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yu, P.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Ge, B.; Tang, G.; et al. Investigating the Evolution of Summertime Secondary Atmospheric Pollutants in Urban Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafra, C.; Suárez, J.; Pachón, J.E. Public Health Considerations for Pm10 in a High-Pollution Megacity: Influences of Atmospheric Condition and Land Coverage. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Singh, S.; Mall, R.K. Chapter 17—Urban Ecology and Human Health: Implications of Urban Heat Island, Air Pollution and Climate Change Nexus. In Urban Ecology; Verma, P., Singh, P., Singh, R., Raghubanshi, A.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 317–334. ISBN 978-0-12-820730-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lorelei de Jesus, A.; Thompson, H.; Knibbs, L.D.; Kowalski, M.; Cyrys, J.; Niemi, J.V.; Kousa, A.; Timonen, H.; Luoma, K.; Petäjä, T.; et al. Long-Term Trends in PM2.5 Mass and Particle Number Concentrations in Urban Air: The Impacts of Mitigation Measures and Extreme Events Due to Changing Climates. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, M.T.; Ghalehteimouri, K.J.; Talkhabi, H.; Dolatshahi, Z. The Relationship between Atmospheric Temperature Inversion and Urban Air Pollution Characteristics: A Case Study of Tehran, Iran. Discov. Environ. 2023, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelani, A.B.; Rao, P.S. Temporal Variations in Surface Air Temperature Anomaly in Urban Cities of India. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2013, 121, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mote, P.W.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Kunkel, K.E. Climate. In Climate Change in the Northwest: Implications for Our Landscapes, Waters, and Communities; Dalton, M.M., Mote, P.W., Snover, A.K., Eds.; Island Press/Center for Resource Economics: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 25–40. ISBN 978-1-61091-512-0. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Liang, X.-Z.; Lei, H.; Wuebbles, D.J. Future U.S. Ozone Projections Dependence on Regional Emissions, Climate Change, Long-Range Transport and Differences in Modeling Design. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 128, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Pedreros, J.G.; Lagüela López, S.; Rodríguez Martín, M. Spatial Models of Solar and Terrestrial Radiation Budgets and Machine Learning: A Review. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberschelp, C.; Pfister, S.; Hellweg, S. Globally Regionalized Monthly Life Cycle Impact Assessment of Particulate Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 16028–16038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Raffaele, F. The Climate of the Mediterranean Region and Future Projections in Relation to Air Quality Issues. In Atmospheric Chemistry in the Mediterranean Region: Volume 1—Background Information and Pollutant Distribution; Dulac, F., Sauvage, S., Hamonou, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 61–76. ISBN 978-3-031-12741-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhao, C.; Lolli, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y. Diurnal Variation of Summer Precipitation Modulated by Air Pollution: Observational Evidences in the Beijing Metropolitan Area. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 094053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Shen, L. Meteorology and Climate Influences on Tropospheric Ozone: A Review of Natural Sources, Chemistry, and Transport Patterns. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2019, 5, 238–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, P.; Feng, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. Influence of Topography and Synoptic Weather Patterns on Air Quality in a Valley Basin City of Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 934, 173362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayr, D.; Plaza, M.P.; Gilles, S.; Kolek, F.; Leier-Wirtz, V.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Damialis, A. Pollen Long-Distance Transport Associated with Symptoms in Pollen Allergics on the German Alps: An Old Story with a New Ending? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Jin, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Du, S.; Li, Y.; He, C. Surface Ozone in Global Cities: A Synthesis of Basic Features, Exposure Risk, and Leading Meteorological Driving Factors. Geogr. Sustain. 2024, 5, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markakis, K.; Valari, M.; Engardt, M.; Lacressonniere, G.; Vautard, R.; Andersson, C. Mid-21st Century Air Quality at the Urban Scale under the Influence of Changed Climate and Emissions—Case Studies for Paris and Stockholm. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1877–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, S.; Yadav, R.; Beig, G.; Gunthe, S.S.; Ojha, N. On the Processes Governing the Variability of PTR-MS Based VOCs and OVOCs in Different Seasons of a Year over Hillocky Mega City of India. Atmos. Res. 2021, 261, 105736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menut, L. Modeling of Regional Atmospheric Pollution; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024; ISBN 978-1-78945-102-3. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Carlton, A.; Cohen, R.C.; Brune, W.H.; Brown, S.S.; Wolfe, G.M.; Jimenez, J.L.; Pye, H.O.T.; Lee Ng, N.; Xu, L.; et al. Southeast Atmosphere Studies: Learning from Model-Observation Syntheses. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 2615–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, L.V.; Miranda, A.G.B. Short Term Forecasting of Persistent Air Quality Deterioration Events in the Metropolis of Sao Paulo. Urban Clim. 2024, 55, 101876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, R.V.; Andenna, C. A Machine Learning Approach to Investigate the Surface Ozone Behavior. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Kostopoulou, E.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Pozzer, A.; Tanarhte, M.; Tyrlis, E. Model Projected Heat Extremes and Air Pollution in the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East in the Twenty-First Century. Reg. Environ. Change 2014, 14, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Hu, J.; Wan, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Xiang, S.; et al. A Combined Arctic-Tropical Climate Pattern Controlling the Inter-Annual Climate Variability of Wintertime PM2.5 over the North China Plain. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, H.C.; Abbas, S.; Yang, J.; Zhu, R.; Wong, M.S. Spatiotemporal Prediction of Increasing Winter Perceived Temperature across a Sub-Tropical City for Sustainable Planning and Climate Change Mitigation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcins, D.; Christofferson, R.C.; Yoon, J.-H.; Nazli, S.N.; Sly, P.D.; Cormier, S.A.; Shen, G. Updates in Air Pollution: Current Research and Future Challenges. Ann. Glob. Health 2024, 90, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, O.; Crawford, J.; Murphy, J.; Rojas, N.Y.; Huneeus, N.; Dawidowski, L.; Hoelzemann, J. Regional and Urban Air Quality in the Americas. In Handbook of Air Quality and Climate Change; Akimoto, H., Tanimoto, H., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–43. ISBN 978-981-15-2527-8. [Google Scholar]
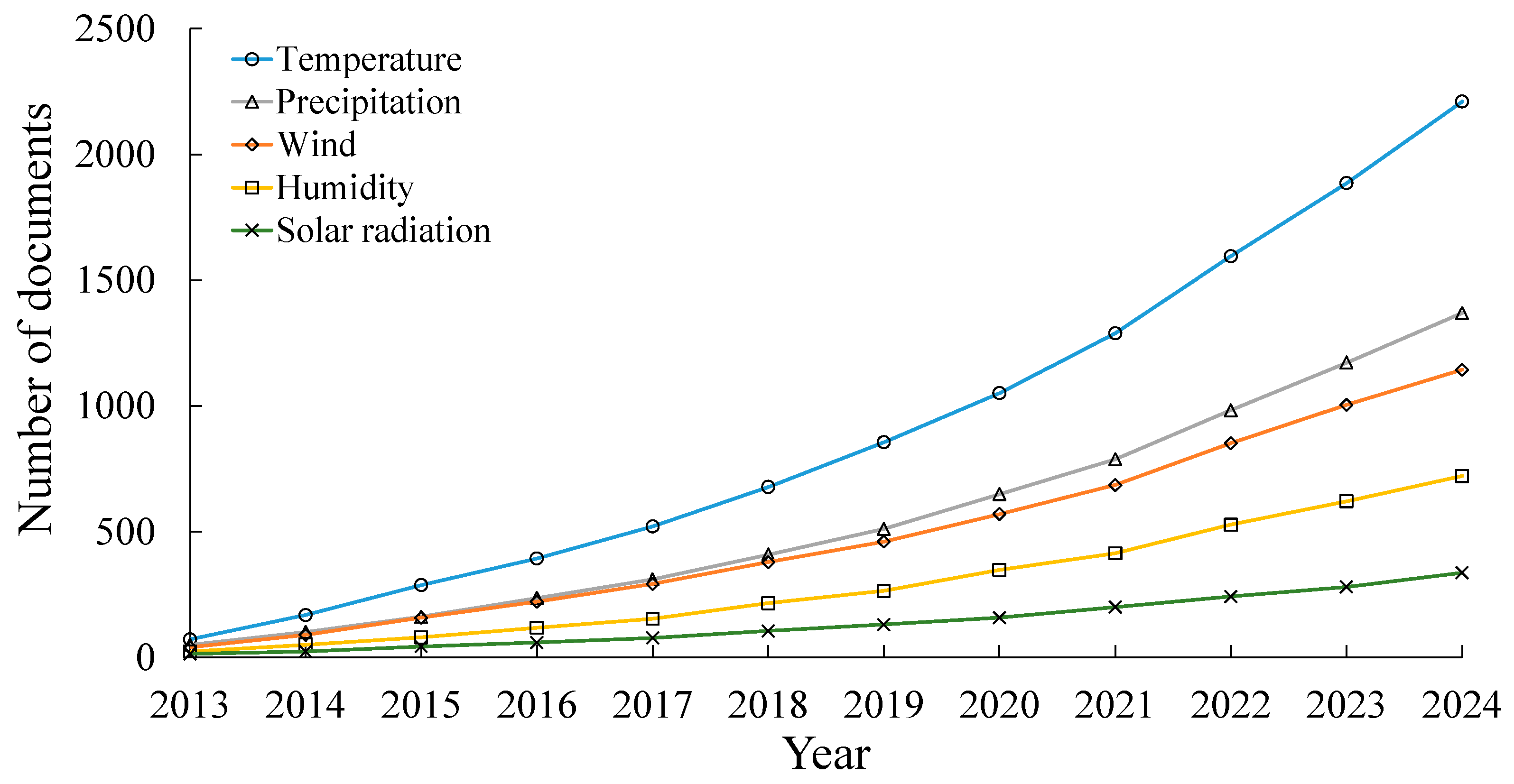


| Stage | Keywords | Scopus | Science Direct | Springer Link | WoS | Google Scholar | Average QI | Average Quartile | Quartile Variation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD | QI | DD | QI | DD | QI | DD | QI | DD | QI | |||||
| Stage 1: General search | Model, urban, air pollution, climate variability | 2965 | 1 | 624 | 1 | 672 | 1 | 405 | 1 | 13,200 | ||||
| Stage 2: Types of models | Regional climate model (RCM) | 310 | 0.401 | 51 | 0.295 | 30 | 0.357 | 134 | 0.435 | 970 | 0.389 | 0.375 | Q3 | Q3 |
| Statistical model (SM) | 163 | 0.211 | 58 | 0.335 | 29 | 0.345 | 60 | 0.195 | 756 | 0.303 | 0.278 | Q3 | Q3–Q4 | |
| Chemical transport model (CTM) | 212 | 0.274 | 35 | 0.202 | 14 | 0.167 | 55 | 0.179 | 572 | 0.229 | 0.210 | Q4 | Q3–Q4 | |
| Machine learning model (MLM) | 72 | 0.093 | 25 | 0.145 | 8 | 0.095 | 26 | 0.084 | 161 | 0.065 | 0.096 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Atmospheric dispersion model (ADM) | 17 | 0.022 | 4 | 0.023 | 3 | 0.036 | 33 | 0.107 | 34 | 0.014 | 0.040 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Total | 774 | 173 | 84 | 308 | 2493 | |||||||||
| Stage | Keywords | Scopus | Science Direct | Springer Link | WoS | Google Scholar | Average QI | Average Quartile | Quartile Variation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD | QI | DD | QI | DD | Index | DD | DD | QI | DD | |||||
| Stage 3: Models | Regional climate models (RCMs) | |||||||||||||
| WRF | 390 | 0.874 | 52 | 0.486 | 45 | 0.882 | 29 | 0.906 | 1150 | 0.837 | 0.797 | Q1 | Q1–Q3 | |
| RegCM | 18 | 0.040 | 51 | 0.477 | 4 | 0.078 | 1 | 0.031 | 82 | 0.060 | 0.137 | Q4 | Q3–Q4 | |
| COSMO-CLM | 17 | 0.038 | 3 | 0.028 | 1 | 0.020 | 1 | 0.031 | 85 | 0.062 | 0.036 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| HIRLAM | 21 | 0.047 | 1 | 0.009 | 1 | 0.020 | 1 | 0.031 | 57 | 0.041 | 0.030 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Total | 446 | 107 | 51 | 32 | 1374 | |||||||||
| Statistical models (SMs) | ||||||||||||||
| GAM | 47 | 0.296 | 19 | 0.317 | 5 | 0.313 | 13 | 0.565 | 215 | 0.319 | 0.362 | Q3 | Q3–Q4 | |
| ARIMA | 59 | 0.371 | 18 | 0.300 | 7 | 0.438 | 1 | 0.043 | 269 | 0.399 | 0.310 | Q3 | Q3–Q4 | |
| GLM | 46 | 0.289 | 19 | 0.317 | 4 | 0.250 | 6 | 0.261 | 165 | 0.245 | 0.272 | Q3 | Q4 | |
| BHM | 7 | 0.044 | 4 | 0.067 | 0 | 0.000 | 3 | 0.130 | 25 | 0.037 | 0.056 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Total | 159 | 60 | 16 | 23 | 674 | |||||||||
| Chemical transport models (CTMs) | ||||||||||||||
| WRF-Chem | 184 | 0.307 | 23 | 0.299 | 13 | 0.302 | 19 | 0.373 | 425 | 0.277 | 0.311 | Q3 | Q3–Q4 | |
| CMAQ | 150 | 0.250 | 17 | 0.221 | 13 | 0.302 | 8 | 0.157 | 372 | 0.243 | 0.235 | Q4 | Q3–Q4 | |
| GEOS-Chem | 97 | 0.162 | 21 | 0.273 | 9 | 0.209 | 12 | 0.235 | 362 | 0.236 | 0.223 | Q4 | Q3–Q4 | |
| MOZART | 89 | 0.148 | 4 | 0.052 | 2 | 0.047 | 5 | 0.098 | 166 | 0.108 | 0.091 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| CAMx | 32 | 0.053 | 7 | 0.091 | 2 | 0.047 | 2 | 0.039 | 94 | 0.061 | 0.058 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| CHIMERE | 30 | 0.050 | 3 | 0.039 | 3 | 0.070 | 1 | 0.020 | 77 | 0.050 | 0.046 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| LOTOS-EUROS | 18 | 0.030 | 2 | 0.026 | 1 | 0.023 | 4 | 0.078 | 37 | 0.024 | 0.036 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Total | 600 | 77 | 43 | 51 | 1533 | |||||||||
| Machine learning models (MLMs) | ||||||||||||||
| ANNs | 101 | 0.616 | 38 | 1.652 | 9 | 0.125 | 4 | 0.108 | 402 | 0.754 | 0.651 | Q2 | Q3–Q4 | |
| RFs | 80 | 0.488 | 33 | 1.435 | 5 | 0.069 | 14 | 0.378 | 272 | 0.510 | 0.576 | Q2 | Q2–Q4 | |
| SVMs | 35 | 0.213 | 17 | 0.739 | 8 | 0.111 | 2 | 0.054 | 168 | 0.315 | 0.287 | Q3 | Q3–Q4 | |
| KNNs | 14 | 0.085 | 6 | 0.261 | 1 | 0.014 | 0 | 0.000 | 56 | 0.105 | 0.093 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| GBMs | 4 | 0.024 | 4 | 0.174 | 0 | 0.000 | 5 | 0.135 | 13 | 0.024 | 0.072 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Total | 234 | 98 | 23 | 25 | 911 | |||||||||
| Atmospheric dispersion models (ADMs) | ||||||||||||||
| HYSPLIT | 146 | 0.890 | 19 | 0.826 | 18 | 0.250 | 35 | 0.946 | 423 | 0.794 | 0.741 | Q2 | Q1 | |
| AERMOD | 8 | 0.049 | 2 | 0.087 | 18 | 0.250 | 0 | 0.000 | 45 | 0.084 | 0.094 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| CALPUFF | 8 | 0.049 | 1 | 0.043 | 18 | 0.250 | 2 | 0.054 | 29 | 0.054 | 0.090 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| ADMS | 2 | 0.012 | 1 | 0.043 | 18 | 0.250 | 0 | 0.000 | 36 | 0.068 | 0.075 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Total | 164 | 23 | 72 | 37 | 533 | |||||||||
| Stage | Keywords | Scopus | Science Direct | Springer Link | WoS | Google Scholar | Average QI | Average Quartile | Quartile Variation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD | QI | DD | QI | DD | QI | DD | DD | QI | DD | |||||
| Stage 4: Climate parameters | Temperature | 1595 | 0.380 | 563 | 0.294 | 586 | 0.296 | 126 | 0.406 | 11,500 | 0.300 | 0.335 | Q3 | Q3 |
| Wind | 852 | 0.203 | 416 | 0.218 | 423 | 0.214 | 83 | 0.268 | 8110 | 0.212 | 0.223 | Q4 | Q3–Q4 | |
| Precipitation | 983 | 0.234 | 409 | 0.214 | 477 | 0.241 | 35 | 0.113 | 9170 | 0.239 | 0.208 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Humidity | 528 | 0.126 | 309 | 0.162 | 295 | 0.149 | 44 | 0.142 | 5860 | 0.153 | 0.146 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Solar radiation | 242 | 0.058 | 215 | 0.112 | 197 | 0.100 | 22 | 0.071 | 3650 | 0.095 | 0.087 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Total | 4200 | 1912 | 1978 | 310 | 38,290 | |||||||||
| Stage 4: Air pollutants | Ozone | 1029 | 0.390 | 236 | 0.316 | 268 | 0.391 | 124 | 0.369 | 5340 | 0.383 | 0.370 | Q3 | Q3 |
| Particulate matter | 833 | 0.316 | 216 | 0.290 | 175 | 0.255 | 147 | 0.438 | 3950 | 0.283 | 0.316 | Q3 | Q3 | |
| Volatile organic compounds | 274 | 0.104 | 104 | 0.139 | 85 | 0.124 | 24 | 0.071 | 1630 | 0.117 | 0.111 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Nitrogen oxides | 260 | 0.099 | 94 | 0.126 | 86 | 0.125 | 29 | 0.086 | 1600 | 0.115 | 0.110 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Sulfur dioxide | 240 | 0.091 | 96 | 0.129 | 72 | 0.105 | 12 | 0.036 | 1430 | 0.103 | 0.093 | Q4 | Q4 | |
| Total | 2636 | 746 | 686 | 336 | 13,950 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Enciso-Díaz, W.C.; Zafra-Mejía, C.A.; Hernández-Peña, Y.T. Global Trends in Air Pollution Modeling over Cities Under the Influence of Climate Variability: A Review. Environments 2025, 12, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060177
Enciso-Díaz WC, Zafra-Mejía CA, Hernández-Peña YT. Global Trends in Air Pollution Modeling over Cities Under the Influence of Climate Variability: A Review. Environments. 2025; 12(6):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060177
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnciso-Díaz, William Camilo, Carlos Alfonso Zafra-Mejía, and Yolanda Teresa Hernández-Peña. 2025. "Global Trends in Air Pollution Modeling over Cities Under the Influence of Climate Variability: A Review" Environments 12, no. 6: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060177
APA StyleEnciso-Díaz, W. C., Zafra-Mejía, C. A., & Hernández-Peña, Y. T. (2025). Global Trends in Air Pollution Modeling over Cities Under the Influence of Climate Variability: A Review. Environments, 12(6), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060177








