Abstract
Current environmental pollution and degradation are problems of global concern. Environmental assessment indices are commonly applied for managing and diagnosing the health of ecosystems. However, most indices are specific to a type or group of pollutants or environmental characteristics. Therefore, this study focused on the development of a multi-metric index with the potential to integrate the environmental conditions assessed by specific indices. This index was named the Integrated Environmental Conditions Index (IECI). The IECI was applied to assess the environmental condition of rivers (Escanela, Jalpan, Ayutla, and Santa María) in the Sierra Gorda Biosphere Reserve in Mexico during two periods: the rainy and dry seasons. The study of surface water and sediment in riverbeds was addressed. We characterised ten study sites using both environmental indices and pollution indices associated with toxic metals/metalloids and microplastics. The IECI detected spatio-temporal changes. Seasonal variations in the environmental conditions were evident, as well as a reduction in environmental integrity in upstream sites, mainly due to the presence of microplastics and toxic metals/metalloids. The IECI proved effective in assessing environmental integrity and represents a valuable management tool for integrating environmental data and supporting informed decision-making.
1. Introduction
Pollution and environmental degradation are critical issues with consequences for both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, compromising biodiversity and human well-being. Legacy and emerging pollutants, such as persistent organic compounds, pharmaceuticals, toxic metals/metalloids (TMs), and microplastics (MPs), generate cumulative adverse impacts that accelerate the degradation of soil, water, and air [1,2,3]. Environmental degradation diminishes the essential functions of ecosystems and weakens the capacity of natural systems to sustain natural processes. Urgent measures are needed to curb pollution and human impacts [4,5].
On the one hand, TMs are part of the Earth’s crust, but their presence and abundance in aquatic and terrestrial systems may increase because of anthropogenic activities. Naturally, traces of these elements may reach water bodies through soil erosion and runoff; nevertheless, mining, manufacturing, industrial discharges, and agricultural wastes intensify their input to waterbodies [6,7]. The presence of TMs is a growing concern due to their toxic effects on aquatic life and potential risks to human health. Some elements such as iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), or zinc (Zn) are known to be essential for the biological functioning of aquatic biota, and others such as lead (Pb), arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd) or chromium (Cr) are highly toxic even in low concentrations [8,9]. They persist in the environment and bioaccumulate in organisms, causing several physiological damage and subsequently ecological effects [7,10].
On the other hand, plastic waste represents a significant emerging concern due to large amounts present in the environment. The excessive use and inadequate management of these materials have resulted in the accumulation of high quantities of waste [11]. In 2024, the annual world plastics production reached 430.9 million tonnes, which could translate into potential pollution [12]. Approximately 9% of plastics are recycled and more than 50% conceivably end up in landfills, wastewater, and aquatic ecosystems [13]. MPs, particles < 5 mm in size, stem from plastic problems. MPs are created both by synthetic materials like microbeads used in personal care products or pellets to produce several plastic products (primary MPs), and by degradation of larger plastic debris such as bottles, containers, bags, and clothes (secondary MPs) [3,14]. These emerging pollutants are characterised by having diverse shapes, additives, and polymeric composition, which increases the complexity of their study. Furthermore, MPs can transport trace amounts of pollutants such as TMs through adsorption processes, which may lead to synergistic effects [14,15].
Pollution and environmental quality indices are fundamental tools for assessing and diagnosing the state of health of ecosystems, allowing complex information to be synthesized into understandable indicators that can be compared across time and space [16,17]. These indices facilitate the identification of critical areas, the prioritisation of mitigation actions and effective communication with decision-makers and society in general [18]. Among their advantages is the ability to integrate multiple environmental variables into a single value, simplifying the interpretation and monitoring of environmental trends [19]. However, indices generally condense information on a single group of variables or pollutant types, which can result in limited or even underestimated interpretations of the real state of environmental health [20]. Developing replicable methodologies that integrate multiple environmental stressors and factors is a global priority for effective management and conservation [21].
The aim of this research was the formulation of a multi-metric index that could synthesize and reflect the environmental status in a single score. We hypothesise that the IECI can detect spatio-temporal variations more effectively than conventional indices. This index would integrate several environmental diagnoses considered as metrics, such as the environmental integrity of aquatic ecosystems and the risks of emerging/legacy pollutants. This index would be applicable to other types of ecosystems. To test the potential of the index, we used environmental data from rivers in the Sierra Gorda Biosphere Reserve (SGBR) in Mexico, which is a biosphere reserve where previous studies have detected TMs and MPs as the main pollutants [22,23]. The indices considered as metrics were Habitat Quality (HQ) for habitat conditions [24,25], Water Quality Index (WQI) for water resource suitability [26], Pollution Load Index (PLI) for MP pollution [27,28], Heavy Metal Pollution Index (HPI), and Potential Ecological Risk Index (PERI) for TM pollution [29,30]. This study seeks to assess the status of environmental health and consequently identify critical sites or seasons that may require special attention.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area, Sampling and Environmental Variables
The SGBR ranks among the most valuable Natural Protected Areas (NPAs) of Mexico, spanning an area of 3836 km2 in the Central Mexican Plateau. The study area is located between 20°50′–21°45′ N and 98°50′–100°10′ W. The local climate is characterised by a semi-hot to warm temperature range and sub-humid to semi-dry conditions. The average annual temperature is predominantly above 18 °C. Precipitation above 80 mm from June to October. The region supports diverse vegetation, including pine, oak, and deciduous forests, as well as xeric scrub. Four major rivers—Escanela, Jalpan, Ayutla, and Santa María—flow through the reserve as tributaries of the Tamuín River, joining the Pánuco River and ultimately discharging into the Gulf of Mexico [31]. The studied river sections range from 1253 to 480 m a.s.l. The Jalpan Reservoir, located at the confluence of the Escanela and Jalpan Rivers, has been designated as a Ramsar site of international importance (No. 1352) [32]. The SGBR comprises eleven core zones where activities are primarily restricted to conservation and research [33]. Anthropogenic influences include human settlements (notably the towns of Ahuacatlán and Jalpan), tourism, sport fishing, farming, and mining (over 100 mines, mainly artisanal) [34,35,36] (Figure 1).
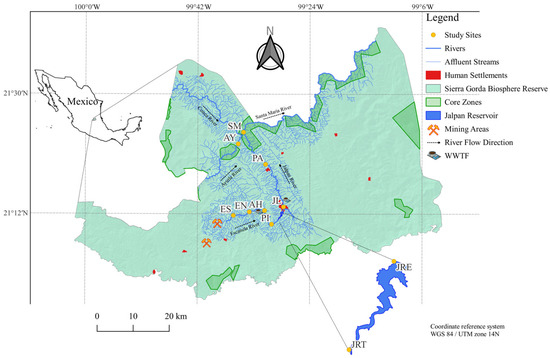
Figure 1.
Sierra Gorda Biosphere Reserve, Querétaro. Escanela River: ES, Escanela; EN, Escanelilla; PI, Pizquintla; AH, Ahuacatlán. Jalpan Reservoir: JRT: Jalpan Reservoir Tributary; JRE: Jalpan Reservoir Effluent. Jalpan River: PA, Purísima; JL, Jalpan. Ayutla River: AY, Ayutla. Santa Maria River: SM, Santa María. WWTF, Wastewater Treatment Facility.
We selected 10 sampling sites across the rivers and reservoir: four on the Escanela River, two on the Jalpan River, one on the Jalpan Reservoir’s tributary and one on its effluent, one on the Ayutla River, and one on the Santa María River (Figure 1). Composite samples of surface water and sediment were collected in duplicate from littoral and central zones. Environmental variables were monitored in October 2022 (rainy season) and April 2023 (dry season). An October 2022 dataset of variables and MP concentrations were recovered from a previous publication [23]. Physicochemical parameters, including dissolved oxygen (mg L−1), oxygen saturation (%), temperature (°C), pH, conductivity (mS cm−1), and salinity (UPS), were measured in situ at each study site using a multiparameter probe (Hydrolab®, Quanta, Austin, TX, USA). Additionally, 500 mL of water were collected in duplicate polyethylene containers for physicochemical analyses and 100 mL in sterile bags (Whirl-Pak®, Pleasant Prairie, WI, USA) for microbiological testing. Water quality parameters analysed included nitrates (NO3, mg L−1) and colour (Pt-Co) via HACH DR3900 spectrophotometer (HACH Company, Loveland, CO, USA) techniques, while hardness (CaCO3, mg L−1), alkalinity (CaCO3, mg L−1), chlorides (Cl, mg L−1), 5-day biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5, mg L−1), and faecal and total coliforms (MPN 100 mL−1) were assessed following the American Public Health Association methods [37].
We developed an index integrating environmental integrity and pollution indices for emerging/legacy pollutants, thereby reflecting the risk in a single value. The index was developed based on an adaptation of the variations in the Integrated Biomarker Response index (IBRv2 [38]) and incorporating several environmental assessment indices. We made adjustments and this version was named the Integrated Environmental Conditions Index (IECI). A series of environmental assessment indices, HQ, WQI, PLI, HPI, and PERI, were evaluated to test the applicability and potential of the index. This analysis addressed the assessment of rivers in the SGBR, Mexico.
2.2. Characterization of Environmental Conditions
The HQ and WQI were calculated for the environmental characterisation of the study sites. We determined HQ in accordance with the Rapid Bioassessment Protocols for Use in Streams and Wadable Rivers, including ten visual-assessment parameters such as channel alterations, riverine area stability, riparian vegetation condition, and sediment deposition. Habitat quality is categorized as poor, marginal, sub-optimum and optimum on a score scale of 0 to 200 [24,25]. The WQI proposed by Dinius [26] was computed using the following Equation (1):
where i denotes a parameter, Ii is the sub-index in parameter i, Wi is the weight assigned to parameter i, and n is the number of parameters. The WQI ranges from 0 to 100, with values approaching 100 indicating higher water quality. The index values are categorized for aquatic life protection as 70 < excellent ≤ 100, 60 < good ≤ 70, 50 < acceptable ≤ 60, 40 < bad ≤ 50, and ≤40 very bad. The parameters used to compute the WQI were dissolved oxygen, BOD5, pH, conductivity, hardness, alkalinity, chlorides, nitrates, colour, air and water temperature, and faecal and total coliforms.
2.3. Determination of Toxic Metals/Metalloids
Composite samples were collected from three sections of the streambed, including the central and both littoral zones. Surface water and sediments were sampled at each study site and stored in 500 mL containers for subsequent laboratory analysis. Polyethylene containers were previously washed with 10% HNO3 solution for 48 h. The surface water samples were adjusted to pH < 2 with concentrated HNO3 (J.T. Baker®, Radnor, PA, USA, 69%). The sediment samples were oven-dried at 65 °C until constant weight. Sample digestion procedures were carried out according to Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) methods: 3051 half-scale for surface water and 3051a for sediments. We used a microwave oven (AntonPaar®, Multiwave GO, Graz, Austria) to digest 22.5 mL of water sample and 0.5 g of dry weight sediment sample with 2.5 mL and 10 mL of concentrated HNO3, respectively [39]. Furthermore, TM levels (Al, Fe, Pb, Cr, Cd, and As) were measured by an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES; PerkinElmer®, OPTIMA 2100DV, Shelton, CT, USA). Calibration standards (Continuing Check Verification Standard 1, CCV1-A-100, High Purity Standards), along with blanks and control samples, were employed to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the extraction process and subsequent elemental determinations. Detection and quantification limits are presented in Supplementary Table S1. The determinations were performed at the Centro Mexicano para la Producción más Limpia (Mexican Centre for Cleaner Production; CMPL, in Spanish) of the Instituto Politécnico Nacional (National Polytechnic Institute; IPN, in Spanish).
2.4. Quantification and Validation of Microplastics
MP samples were collected from the same river sections as those used for TM sampling. At each site, surface water and sediment were sampled and transferred to 500 mL glass containers sealed with metal caps. Extraction of MPs from water samples was conducted through a direct filtration process, employing a glass filtration system (WHEATON®, DWK Life Sciences, Millville, NJ, USA) and nitrocellulose filters 47 mm in diameter with a pore size of 1.2 μm (MF-Millipore™, MilliporeSigma, Burlington, VT, USA). For sediments, MPs were extracted using the density separation method. Samples were oven-dried at 40 ± 1 °C and sieved through a 4.75 mm mesh. Subsequently, four 20 g subsamples were transferred individually to glass flasks. Pre-treatment involved adding 25 mL of 30% H2O2 to facilitate the removal of organic matter. Afterwards, 50 mL of a ZnCl2 solution (ρ ≈ 1.5 g/cm3) was added to each flask, which was then stirred and left to settle for 48 h. The supernatant was filtered following the same procedure as for the water samples. MPs were quantified as the number of items per litre of water and per kilogram of dry sediment, respectively [40,41]. Recovery control and analytical error values averaged 95.55 ± 1.95% for water and 86.66 ± 2.22% for sediment samples.
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR; SHIMADZU®, IRAffinity-1S, Kioto, Japan) was employed to determine the polymeric composition of MPs [41]. A random subsample (≈50%) of the total particles extracted from the filters was selected for analyses, consistent with methodological recommendations for subsampling (>10%) [42,43]. Polymer types were identified by comparing the spectra with the open access “Open Specy” database [44]. MP concentrations were proportionally corrected based on the FTIR results. Microstructure analyses were conducted at the Centro de Desarrollo de Productos Bióticos (Centre for the Development of Biotic Products; CEPROBI, in Spanish) of the Instituto Politécnico Nacional (National Polytechnic Institute). Furthermore, MPs were characterised by shape and colour using a stereo microscope (Leica®, DMS1000, Wetzlar, Germany).
Multiple control measures were employed to minimise external MP contamination throughout sample processing. Only glass and metal materials were allowed, and all containers were covered with aluminium foil. Collection containers and laboratory instruments were pre-cleaned and rinsed with filtered deionised water before use. All solutions employed were pre-filtered. During sample processing, only cotton laboratory coats and polymer-free gloves were worn. To prevent airborne contamination, samples were processed under a laminar flow hood with the windows kept closed. The work areas and stereo microscope were thoroughly cleaned prior to each use; each processing batch comprised the collected samples and two procedural blanks to ensure analytical integrity.
2.5. Pollution and Risk Assessment Indices
2.5.1. Heavy Metal Pollution Index (HPI)
The degree of TM pollution was determined by the HPI [29]. This shows the combined influence of individual TM. We calculated the HPI with the following Equations (2)–(4):
where i indicates a TM and n is the number of integrated TM. The HPI includes the unit weight (Wi), which is the value inversely proportional to the recommended maximum level (Si) of each TM. Qi denotes the sub-index, and Mi the measured concentration of the ith TM. The Si values used for freshwater and sediment were the limits recommended by Mexican guidelines [45] and by international guidelines [46]. HPI values are categorized as low contaminated ≤ 50, 50 < moderate contaminated ≤ 100, and high contaminated > 100 [47].
2.5.2. Potential Ecological Risk Index (PERI)
The PERI was assessed to estimate the ecological risk posed by TMs in river water and sediment [30]. It was calculated with the following Equations (5)–(6):
where i indicates a TM and n represents the total number of TM determined in this study. is the monomial potential ecological risk factor, Ci is the TM concentration detected, Co is the background TM concentration and is the coefficient of relative toxicity for each TM (Pb = 5, Cd = 30, As = 10, Cr = 2, Al = 1 and Fe = 1) [30,48,49]. The minimum TM concentration in sediment was designated as Co due to this is the first study evaluating this environmental matrix in the study area. Risk is characterised in four categories: low < 150; 150 ≤ moderate < 300; 300 ≤ high < 600; significantly high ≥ 600 [48].
2.5.3. Pollution Load Index (PLI)
The PLI was computed to evaluate the degree of MP pollution [27,28,50]. It was determined using the following Equations (7)–(9):
where i denotes a study site and n represents the number of sites located within the river system. The index incorporates a concentration factor (CFi), defined as the ratio between the MP concentration at each site (Cᵢ) and the minimum concentration reported in the literature (Co). This index categorises pollution load and its associated risk into five levels: low ≤ 1; 1 < middle ≤ 2; 2 < high ≤ 3; 3 < very high ≤ 10; 10 < extremely high. In view of the limited data for the study area, Co was set as the lowest MP concentration measured during the sampling seasons, in accordance with previous studies [51,52].
2.6. Data Processing for the Integrated Environmental Conditions Index (IECI)
The previous indices were integrated into the IECI, which was conducted following next steps and mathematical procedures:
- Obtain the absolute value of the respective index (X) for each study site.
- Perform a linear inversion on indices that display higher numerical values indicating better environmental conditions or lower impact levels (e.g., the WQI and HQ). The environmental indices tend to reflect the ecological condition state or the degree of pollution, within a defined and usually categorised range of values. The IECI seeks to reveal detrimental effects or impacts with high values and better ecological health with low values. Therefore, linear inversion is necessary when an index requires it; the inverted values are obtained by subtracting the original index values (Xoriginal) from the maximum index scale value (Xmax).
- Transformation into an intensification/attenuation index (Y) relative to the threshold value of the given index (X0i); i indicates an index and j is the study site.Thresholds represent quantitative limits beyond which pollutant concentrations or environmental changes may adversely affect human health or ecosystem integrity. They delineate the transition from a good to a degraded ecological state and serve as scientific benchmarks for assessing environmental quality [53].For this study, the threshold values were established based on the categorical levels of each index that indicate an adverse impact or detrimental condition. For this study, the threshold values are as follows: PLI = 1, HPI = 50; PERI = 150; WQI′ = 30; HQ′ = 35.
- Equalise negative values (attenuation indices) to 0 because they are below the threshold values (X0i = 0).
- Estimation of an index of deviation (A), which reflects the relative magnitude over the threshold values; σYi is the standard deviation of the Yi,j values.
- Calculation of the final value for the IECI. The index represents the summation of the deviation indices for each study site (Ai,j).
- Representation of results in radar plots, bar plots or both.
- We suggest constructing a categorised scale for the management of the study areas based on the calculated IECI scores. The categories were established based on the statistical distribution of overall data, using quartiles with equal percentiles (0.25) [54]. This would provide a simple strategy for identifying critical concern areas that may require greater attention (Figure 2; Table 1).
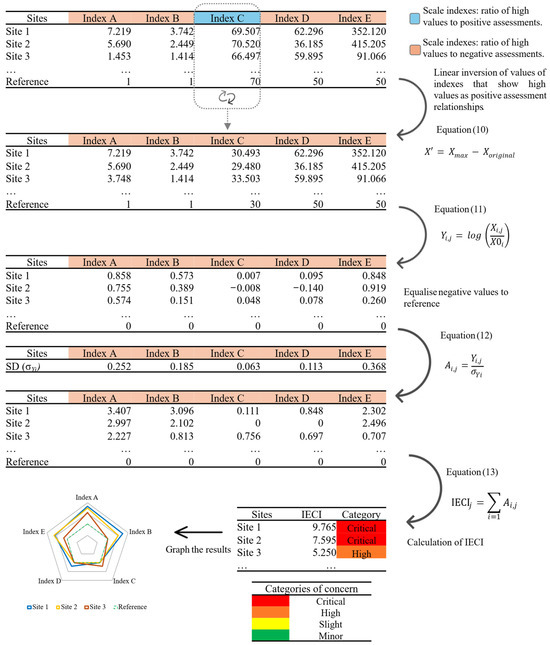 Figure 2. Diagram of the procedure for the IECI calculations.
Figure 2. Diagram of the procedure for the IECI calculations. Table 1. Suggested categories of concern for managing study sites and areas.
Table 1. Suggested categories of concern for managing study sites and areas.
2.7. IECI Validation
The validation process involved testing the fit of the model for the IECIobserved versus the IECIexpected, followed by applying the modified index of agreement by Willmott (1981) [55], which ranges from 0 to 1, with 1 indicating a perfect fit. To obtain the IECIexpected value, a multiple linear regression analysis was performed between the IECI and the results of the Metal Pollution Index (MPI [56]) applied to the data of TMs in surface water and sediments from the study sites. The MPI employs a geometric average to provide a single, summary figure of overall TM pollution in a sample, such as water, sediment, or biological tissue [57], serving as an independent variable for the IECI validation.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Data curation and exploratory statistical analysis were performed. Shapiro–Wilk test was used to assess normality, which is a powerful and widely recommended test for small to medium sample sizes (n < 50) and Levene’s test, which is robust to departures from normality, was applied to evaluate the assumptions of homoscedasticity of the datasets [58]. Based on these results, parametric test was selected for data that met both assumptions (Student’s t test) since it offers greater statistical power and precision for hypothesis testing. In instances where the normality or homogeneity of variances was not met, non-parametric tests were employed (Mann–Whitney U, Kruskal–Wallis’s and Dunn’s post hoc tests) [59,60]. Student’s t and Mann–Whitney U tests were applied to the WQI, HQ, and IECI datasets to detect significant differences between study seasons. Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn’s post hoc tests were applied to the HPI, PERI, and PLI data to identify significant differences between environmental matrices and study seasons. Spearman’s rank correlation analysis was applied to examine the relationships among the range of evaluated indices. The thresholds for significant differences were p < 0.05. The statistical processing and graphical representation of the data were performed using the XLSTAT 2023.1.2 and the R package “ggplot2” version 3.5.1.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Environmental Characterization
Habitat quality (HQ) had average scores of 121 ± 43.25 and 116 ± 46.23 in October 2022 and April 2023, respectively, suggesting an acceptable overall quality and reflecting long-term physical integrity. However, study site JRE reflected “poor quality”, and sites AH, JRT, JL, and PA had “marginal quality” in both seasons; sites ES, EN, PI, AY, and SM showed “sub-optimal” and “optimal” qualities (Figure 3A,B). Water quality (WQI) was similar between study seasons (p = 0.218); nevertheless, the average score in October 2022 was 68 ± 6.24, suggesting an overall “good quality”, and in April 2023 it was 74 ± 8.51, indicating “excellent quality”. Among study sites, the lowest values were obtained at JRT in both seasons (52 in October 2022 and 62 in April 2023); the rest of the sites showed “good to excellent” water quality with scores above 60 (Figure 3C,D).
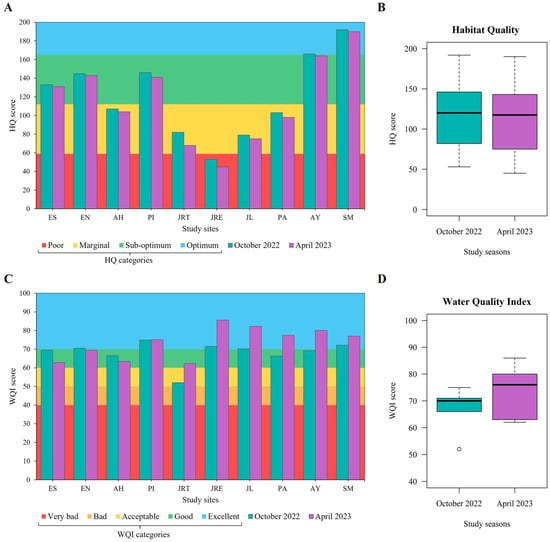
Figure 3.
Habitat Quality (HQ) and Water Quality Index (WQI). (A) HQ values of study sites during each study season; (B) HQ comparation between study seasons (t test, p = 0.859); (C) WQI values of study sites during each study season; (D) WQI comparation between study seasons (Mann–Whitney U test, p = 0.218).
These results indicate an acceptable ecological condition regionally, but highlight significant spatial heterogeneity across sites, consistent with findings in other subtropical basins in Central Mexico [61]. “Poor” or “marginal” habitats feature reduced natural elements, such as sinuosity, bank stability, and riparian vegetation protection [24]. Riverbank degradation from human activities such as agriculture, livestock, or urbanization diminishes aquatic habitat availability and heterogeneity, limiting refuges for aquatic fauna [62,63]. For instance, AH and JL (Escanela–Jalpan River) have historically been associated with poorer habitat quality due to proximity to human settlements and pollution [22,23,64]. In contrast, AY and SM exhibit stable natural elements, providing habitat for aquatic organisms and preserving ecological integrity.
On the other hand, WQI indicates temporal homogeneity in water quality; however, the slightly higher average WQI in April 2023 (dry season) versus October 2022 (rainy season) suggests varying hydrological influences. Rainy seasons can degrade water quality through precipitation and runoff inputs [20], as observed in the Rio Grande sub-basin in the Tehuacán–Cuicatlán Biosphere Reserve, Mexico [65]. The reduced water quality detected at JRT could be attributed to anthropogenic pressure. Observed factors include ecotourism, rural settlements, and land-use changes (pre-dominantly secondary vegetation). Therefore, wastewater discharges and nutrient from the watershed could be some sources of pollution that reduce water quality [66,67].
3.2. Heavy Metal/Metalloid Pollution and Risk
We detected TMs in both study seasons. In October 2022, the descending order of concentration in surface water was Fe > Al > As > Pb > Cd > Cr, and in sediment it was Fe > Al > Pb > As > Cr > Cd. In April 2023, the descending order of concentration was Al > Fe > Pb > Cd > As > Cr in surface water and Fe > Al > Pb > As > Cr > Cd in sediment (Table 2). According to quality guidelines of National Water Commission (CONAGUA, in Spanish) [45] and Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment [46], the concentrations of Cd (April 2023) and Al (both seasons) in surface water and those of Pb and As (both seasons) in sediment exceeded the limits recommended for the development of aquatic life. High Al levels may result from sediment exchange and rock weathering, as Al is the third most abundant element in the Earth’s crust. However, it may generate toxicity at multiple levels, impacting human health and key biological functions in aquatic organisms [68,69,70].

Table 2.
TMs (mg L−1; mg kg−1 dry weight) and MPs (items L−1; items kg−1 dry weight) (concentrations ± standard deviation) determined in environmental matrices during study seasons. Recommended quality guidelines for the protection of freshwater aquatic life in water (W; mg L−1) and sediment (S; mg kg−1 dry weight) are included.
Study sites showing high levels of TMs pollution in surface water were JRT (HPI = 116) in October 2022 and ES and AH (HPI = 501 and 934, respectively) in April 2023. In sediment, these sites were ES (HPI = 352 and 415) and EN (HPI = 256 and 254) for both study seasons (Figure 4A,B). There were no significant temporal differences in HPI scores between surface water and sediment (Kruskal–Wallis’s test, p = 0.636) (Figure 4C). The average contributions of each TM to HPI, from highest to lowest, were: Cr > Al > Cd > As > Pb > Fe in surface water and Fe > Cr > Cd > As > Al > Pb in sediment during October 2022; Cr > Al > Cd > As > Fe > Pb in surface water and Fe > Cr > Cd > Al > As > Pb in sediment during April 2023. In other freshwater systems, values that were considered critical contamination levels (HPI > 100) have been reported. Values in the range of 100–150 have been reported in surface waters of lentic systems in India, some attributed to the proximity of coal mines [71,72], while in the Barnoi River in Bangladesh, HPI values of 122 to 463 were reported [73].
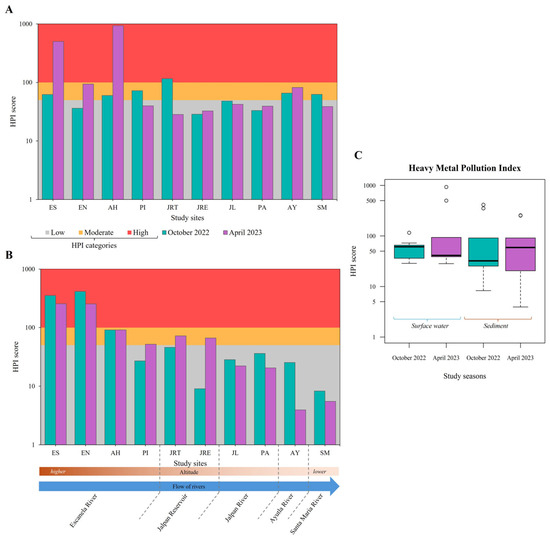
Figure 4.
Heavy Metal Pollution Index (HPI). (A) HPI surface water values of study sites during each study season; (B) HPI sediment values of study sites during each study season; (C) mean HPI comparation between study seasons (Kruskal–Wallis’s test, p = 0.636).
This shows that the sites located in the Escanela–Jalpan system are highly impacted by TMs, possibly due to proximity to mining areas and human settlements. On the one hand, the operation of the water treatment facilities near AH and JL is currently uncertain [36]. On the other hand, the Mexican Geological Service (SGM, in Spanish) has records soil concentrations of As (100–400 mg kg−1), Pb (40–450 mg kg−1) and Cd (1–13 mg kg−1) in the mining zones located within the SGBR [35]. In previous studies, the presence of As, Cd, Cr, Pb and other TMs in similar concentrations has been detected in surface water of rivers, including sites such as ES, EN, AH and JL [22]. Besides anthropogenic inputs from point and diffuse sources, soil geochemistry may naturally contribute to TMs in water bodies [74]. However, the scarcity of long-term geological data requires further research to establish natural background levels and improve environmental assessments.
On the other hand, the concentrations of the TMs analysed in surface water were of “low ecological risk” at all study sites for both seasons. Most sites obtained PERI scores below 15, except for sites JRT (October 2022), and ES and AH (April 2023), which yielded values above 20 (PERI = 22.90, 25.12, and 33.48, respectively) (Figure 5A). In sediment, sites JRE (PERI = 79.13) in October 2022, AY (PERI = 48.02) in April 2023 and SM (PERI = 62.83 and 62.52) in both study seasons showed “low ecological risk”; however, there were sites such as ES, EN, and AH (PERI > 785) which in both study seasons reached the category of “significantly high ecological risk” (Figure 5B). In both study seasons, the ecological risk shown by the PERI was significantly higher in sediment than in surface water (p < 0.0001) (Figure 5C). In mining regions, PERI values averaging 47.4 were reported in water from the Hunhe River Basin, China [75], and ranging values from 83 to 929 in sediments from the Aries River Basin, Romania [76]. In Mexico, very high PERI values in sediments ( = 4276.13) were obtained in the San Juan–Taxco River System in Guerrero State, considering potential toxic elements such as Pb and Cd [77].
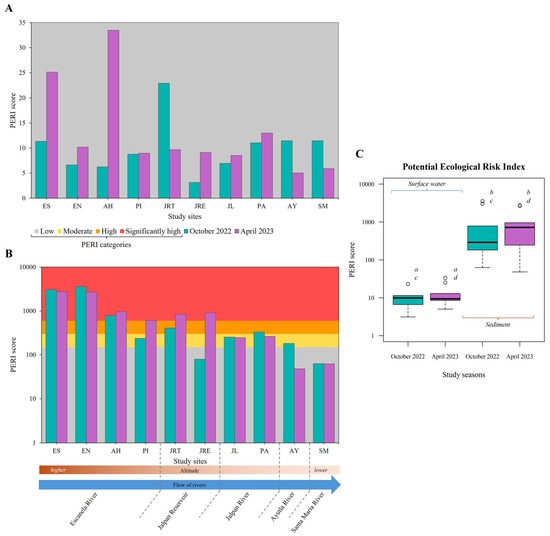
Figure 5.
Potential Ecological Risk Index (PERI). (A) PERI surface water values of study sites during each study season; (B) PERI sediment values of study sites during each study season; (C) PERI comparation between study seasons (Kruskal–Wallis’s test, p < 0.0001); Dunn’s post hoc test: a (p = 0.848), b (p = 0.818), c (p < 0.0001), d (p < 0.0001).
The greatest ecological risk in sediments arises from the tendency of TMs to precipitate. Sediments have been confirmed as the main sink and reservoir for TMs, storing approximately 99% of the TMs that enter the aquatic environment [78,79]. The abundance of Fe and the hardness of the water in the rivers of the SGBR can limit the solubility of TMs and favour their precipitation by interaction with oxides and hydroxides [48,49]. Therefore, the long-term risks are much greater than in the overlying water column. The average contributions of each TM to PERI, from highest to lowest, were: Pb > Cd > Fe > As > Cr > Al in surface water and As > Cd > Pb > Cr > Al and Fe in sediment during October 2022; Cd > Pb > As > Cr > Fe > Al in surface water and Cd > As > Pb > Cr > Al and Fe in sediment during April 2023. The fluctuations suggest seasonal variations in the persistence and mobility of TMs. Temporarily, the TMs of greatest concern were Pb and Cd in surface water and Cd and As in sediment (Supplementary Figure S1).
Nonessential TMs such as Pb, Cd, and As are highly toxic in both water and sediments, even at low concentrations [6,80,81]. Pb ions are insoluble in water, but the formation of salts with nitrates and chlorides can facilitate their leaching from soils and entry into water bodies [82]. Cd and its ions are highly soluble in water, which facilitates their mobility and bioaccumulation [83]. The free ion Cd2+ is the most bioavailable form and can enter aquatic biota via calcium channels due to its structural similarity to Ca2+ [84]. As is found primarily in inorganic forms (As3+ and As5+), with As5+ being the most soluble and bioavailable in oxygen-rich environments, and thus, very toxic [85]. About 10% of surface waters in rivers and lakes contain As-related compounds [86]. Although the concentration of Cr and its contribution to PERI is minimal, its presence may represent a latent danger.
3.3. Microplastic Pollution
According to previous research, in October 2022, the highest number of MPs in surface water was found at site ES (110.87 items L−1), and a lower number was observed at sites JRE, JL, and SM (<5 items L−1). In sediments, up to 175 items kg−1 were found at site ES, while the lowest concentration was 12.5 items kg−1 at sites PI and AY [23]. On the other hand, we detected during April 2023 a maximum MP concentration of 6.90 items L−1 at site AH, followed by ES and PI (4.55 items L−1 and 4.21 items L−1, respectively), and in the rest of the sites, amounts lower than 2.35 items L−1 were recorded, except in PA and SM, where MPs were undetected. In contrast, the highest amounts of MPs in sediments were found at sites AH (162.5 items kg−1) and EN (137.5 items kg−1) and the lowest at PA (12.5 items kg−1). In surface water, concentrations were significantly higher in October 2022 than in April 2023 (Mann–Whitney U test, p < 0.001), while in sediment, the concentrations were similar (Mann–Whitney U test, p = 0.351) (Table 2).
Compared to coastal studies, research on MPs in freshwater environments of Mexico is limited (26% of reported investigations [87]), but the reported concentrations are alarmingly high. Concentrations in water range from 1.6 to 936 items L−1, and in sediments from 12.5 to 1633 items kg−1 in ecosystems such as the Zahuapan River in Puebla State, the Escanela–Jalpan Rivers in Querétaro State, and cenotes in Solidaridad, Quintana Roo State. [23,88,89]. In other parts of the world, MP concentrations of up to 15.6 items L−1, 36 items L−1 and 50 items L−1 have been reported in water from Thames River in UK, Yangtze River in Chinese and Cooum River in India, respectively [90,91,92]. In sediment, concentrations of up to 158.5 items kg−1 in Suquía River, Argentina and 208 items kg−1 in Elbe and Mulde Rivers, Germany [93,94]. The estimated MP pollution load scores (PLI) for each environmental matrix were 2.71 (October 2022) and 1.18 (April 2023) in surface water, and 1.54 (October 2022) and 1.61 (April 2023) in sediment. The highest PLI scores for surface water were observed in ES, EN, AH and PI during October 2022 (PLI > 3, “very high pollution load”), while for sediment were recorded in ES (Octobre 2022, PLI = 3.74), EN, AH and JL (April 2023, PLI = 3.31, 3.60 and 3.16, respectively) (Figure 6).
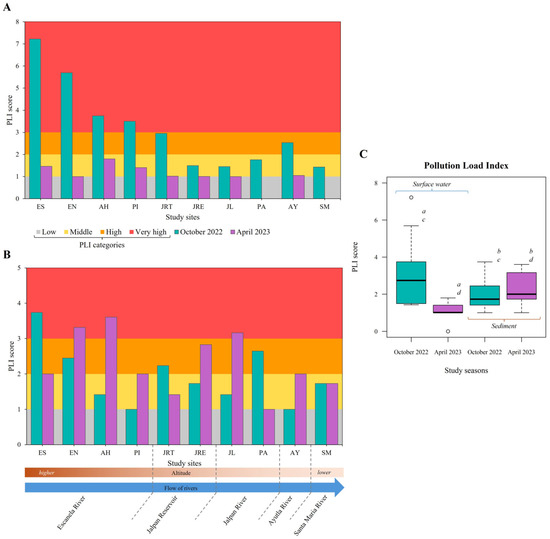
Figure 6.
MP Pollution Load Index (PLI). (A) PLI surface water values of study sites during each study season; (B) PLI sediment values of study sites during each study season; (C) PLI comparation between study seasons (Kruskal–Wallis’s test, p = 0.001); Dunn’s post hoc test: a (p < 0.0001), b (p = 0.348), c (p < 0.099), d (p = 0.003).
The high MP load in surface water in October 2022 (rainy season) likely resulted from terrestrial and atmospheric inputs favoured by wet deposition, runoff, and flooding. MP levels have been reported to increase during and after the rainy season (wet season) [95]. Rainfall can mobilise 24–77% of MPs in runoff, as reported in Chinese rivers [96]. The decrease in MP load in the Jalpan Reservoir suggests that lentic systems may act as sinks for upstream materials. Increased river flow and turbulence can release MPs trapped in sediments, transporting them downstream [97,98]. Freshwater sediments have been found to be primary long-term sinks for MPs, with concentrations 1–2 orders of magnitude higher than in water. This is due to the density and hydrophobicity of MPs [99,100,101]. These patterns and influences may explain the temporal variations observed in surface water and sediment.
Additionally, the polymers identified with FTIR were polypropylene (PP, 45%), polystyrene (PS, 17%), polyethylene (PE, 10%), high-density polyethylene (HDPE, 10%), polyethylene terephthalate (PET, 7%), polyester (PES, 3%), polyacrylamide (PAM, 3%) and polylactic acid (PLA, 3%) (Supplementary Figure S2). PP, PE, PES, PET, PS and HDPE have been widely detected in aquatic systems and attributed to various anthropogenic sources such as packaging, household products, laundry, fishing tools, and textile waste [102,103,104]. PLA and PAM have been identified at lower proportions of 3.84–23.16%. PLA is classified as a biodegradable polymer and its application is relatively recent, particularly in packaging products. In contrast, PAM is manufactured from acrylamide and is used as a flocculant in wastewater treatment; however, it raises environmental concerns due to its toxicity [105,106,107].
On the other hand, the most abundant forms in surface water and sediment were fibres (October 2022, 93.13% and 100%, respectively; April 2023, 90.9% and 80%, respectively). These findings suggest that the main MPs collected were secondary, derived from clothing or abrasion of larger materials. It is estimated that washing contributes up to 35% of these fibres to the environment [108,109]. In river and lake waters of China, Finland, Argentina and Vietnam, 44.25–96.4% of the reported MPs were fibres [110]. In studies of MPs in Mexico, fibres have been the most reported form (67%), as well as the colours blue (27%), colourless (27%), white (24%) and black (22%) [87]. The main source of fibres is related to domestic activities and industrial products such as laundry and fabric waste. Furthermore, the collected MPs showed different colourations; blue (October 2022, 31% in surface water and 29% in sediment; April 2023, 50% in surface water and 24% in sediment), black (October 2022, 29% in sediment; April 2023, 27% in sediment) and colourless (October 2022, 29% in surface water and 21% in sediment; April 2023, 50% in surface water) were the most abundant (Supplementary Figure S3). Similarities with food and dangerous chemical additives such as pigments can promote the intake of MPs and increase their toxicity in organisms [104,111].
3.4. Validation Outcomes of the IECI
As part of validation process, the multiple regression analysis between the IECI and the MPI (for surface water and sediment) was significant, showing a multiple R2 = 0.677 (p < 0.05). The equation that expresses this relationship is:
Thus, the adjusted model of IECIobserved versus IECIexpected (Supplementary Figure S5) also returned a value of R2 = 0.677 (p < 0.05) and the Willmott index resulted in d = 0.94, indicating a well-fitted model. Therefore, the IECI is accurately reflecting the environmental conditions of the study area.
3.5. Environmental Integrity Assessment by the IECI
The IECI showed spatial changes along the rivers of the SGBR. The superior limits of the IECI categorical scale (Q1–Q4) were Minor 4.16, Slight 6.35, High 10.22, and Critical 15.12. On the one hand, the ES, EN, and JRT sites obtained the highest values in October 2022 (IECI = 13.81, 11.41, and 13.58, respectively) and in April 2023 these values were observed at sites ES and AH (IECI = 14.19 and 15.12, respectively), suggesting a greater impact from pollutants and a decline in environmental health (“critical concern”). This may imply that these sites require urgent attention. The sites that reflected the least impairment to environmental conditions (IECI < 4.16) in ascending order were SM and AY in October 2022 and SM, PA, and AY in April 2023, which represents “minor concern” (Figure 7A). On the other hand, the average IECI scores were similar between study seasons (October 2022, = 7.48 ± 4.17; April 2023, = 7.27 ± 4.68) (t test, p = 0.916). However, the radar plots, in addition to showing that the environmental conditions evaluated exceed the threshold condition (there was environmental deterioration), reflected evident differences in some branches between seasons: in October 2022, the pollution load of MPs (PLI) in surface water was higher, while in April 2023, the pollution load of MPs (PLI) in sediment were higher (Figure 7B). Radar plots also revealed outstanding points of environmental and pollution conditions that differed temporarily at each study site (Figure 7C–L); for example, the ES site, MP pollution load (PLI) in surface water and sediment higher in October 2022 and water quality (WQI) and TM pollution (HPI) in surface water higher in April 2023.
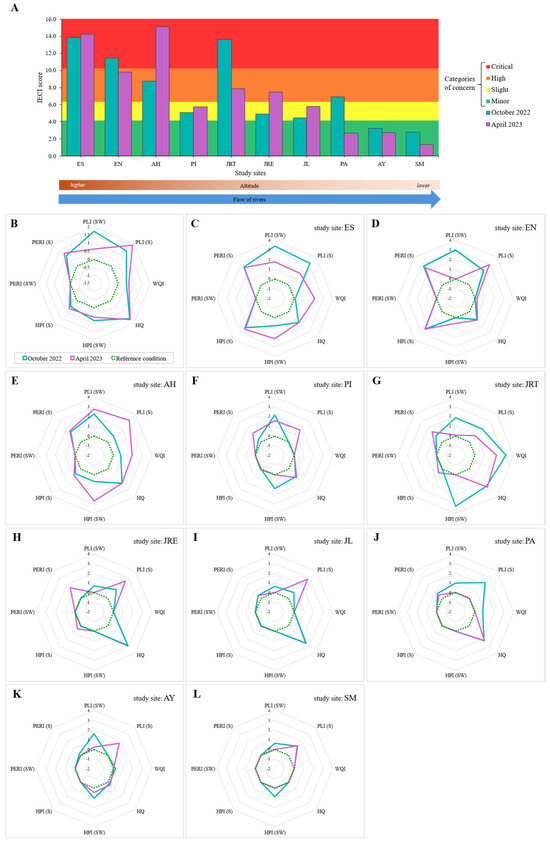
Figure 7.
Integrated Environmental Conditions Index (IECI). (A) IECI values in study sites during each study season; (B) patterns of the indices evaluated by the IECI in the study seasons; (C–L) patterns of the indices evaluated by the IECI in each study site during study seasons. Study sites: ES, Escanela; EN, Escanelilla; PI, Pizquintla; AH, Ahuacatlán; JRT: Jalpan Reservoir Tributary; JRE: Jalpan Reservoir Effluent; PA, Purísima; JL, Jalpan; AY, Ayutla; SM, Santa María.
The correlation analysis revealed that the IECI has a negative relationship with habitat and water quality and a directly proportional increase with the pollution indices by TMs and MPs (Supplementary Figure S4). On the other hand, the temporal contributions of the assessed environmental conditions showed the same pattern: MP pollution > detrimental habitat quality > TM pollution > TM risk > detrimental water quality (Figure 8A,B). The spatial contributions of the evaluated environmental conditions in sections of the river system (Upstream, sites ES-PI; Reservoir, JRT and JRE; Downstream, sites JL–SM) were different. In October 2022: MP pollution > TM pollution > TM risk > detrimental habitat quality > detrimental water quality; MP pollution > detrimental habitat quality > detrimental water quality and TM pollution > TM risk; and MP pollution > detrimental habitat quality > TM pollution > TM risk > detrimental water quality, respectively (Figure 8C). In April 2023: MP pollution > TM pollution > TM risk > detrimental habitat quality > detrimental water quality; detrimental habitat quality > MP pollution > TM risk > detrimental water quality > TM pollution; and MP pollution > detrimental habitat quality > TM risk > TM pollution, respectively (Figure 8D).

Figure 8.
Contributions of the assessed environmental conditions. (A,B) Percentage contribution in October 2022 and April 2023, respectively; (C,D) percentage contributions in sections of the river system in October 2022 and April 2023, respectively. SW, surface water; S, sediment.
Mainly upstream sites may be of greater concern due to the presence of TMs and MPs. Several studies mention that MPs act as carriers (vectors) of TMs, facilitating their transport through bodies of water and sediments [14,112]. The interaction between MPs and TMs is fundamentally governed by adsorption and desorption processes through electrostatic bonding with functional groups, such as carbonyl, carboxyl and hydroxyl groups [113,114]. The ageing of the MPs and the physicochemical properties of environmental matrices condition these processes [115,116]. Among the most abundant TMs adsorbed by MPs in freshwater are Cu, Ni, Pb, Cd, Zn, and Cr. MPs can act as an alternative route of exposure for TMs [117]. Therefore, the co-occurrence of MPs and TMs may cause synergistic effects, threatening ecosystem integrity [15,118,119]. These effects could be intensified in bodies of water near mining areas [120].
In contrast, the decrease observed in the IECI values in PI site (55.62% lower than the average value for ES–AH) could be indicative of environmental buffering and resilience processes in the area. Upstream from the PI, the Escanela River has an underground section that springs from the cave called “Río Adentro”, which can act as a natural filter. Karst aquifers are susceptible to the accumulation of pollutants such as MPs due to their structure and geological characteristics. Average concentration of 2570 items kg−1 has been reported in cave sediments from Italy [121,122]. MP-TM pollution also affects reservoirs and downstream areas, with habitat degradation as a further environmental concern. Loss of habitat heterogeneity reduces biodiversity, niches, and ecosystem resilience [123,124]. These stressors can significantly impact various areas, compromising essential environmental services. The findings underscore the vulnerability of protected natural areas, such as the SGBR. According to the IECI, AY and SM were sites that despite experiencing environmental impacts, exhibited the best environmental integrity. They were categorized as having “minor concern,” with the IECI values decreasing by 70.71% compared to ES–PA. The condition of these sections of the river may be attributed to their proximity to, and location within, core areas designated for conservation, where human activities are restricted.
The IECI represents a significant advancement in integrated environmental assessment. It combines diagnostic information from several indices that typically focus on specific pollutant groups, environmental parameters, or biotic components. For instance, the Integrated Biomarker Response Index targets organism-level biochemical responses [38], while Water Quality Indices typically include limited physicochemical parameters and often exclude emerging pollutants [20]. In turn, Multi-metric Indices of Biotic Integrity evaluate the ecological status of ecosystems based on local biological communities. Nevertheless, these traditional approaches can limit the comprehensiveness of holistic environmental evaluations [21,125].
Unlike previous indices, the IECI mathematically integrates multiple diagnostic perspectives into a single, interpretable metric through a standardised procedure that preserves the diagnostic sensitivity of each contributing index and enables cross-comparison among heterogeneous datasets. Consequently, the IECI synthesises complex environmental information into a comprehensive value that identifies the dominant environmental pressures. By providing both integrative and diagnostic capabilities, the IECI supports the development of more holistic, multi-pressure frameworks for environmental monitoring and assessment. However, its accuracy depends on the robustness of the component indices and the availability of local data, which may limit transferability without prior adaptation. A colour-classified scale was employed to provide both quantitative and categorical outputs based on percentile distributions from the study area; for other regions, a new scale should be established.
4. Conclusions
Spatio-temporal variations in environmental stressors were evident across the evaluated sites in the SGBR river systems. The IECI identified pollution from MPs and TMs in surface water and sediment as the primary adverse pressure during both seasons, followed by habitat degradation. The highest risk from pollutants occurred in upstream areas, whereas alterations to habitat were also evident in the reservoir and downstream sections. Factors such as human interventions, mining activities, and hydrometeorological influences may shape the presence and distribution of MPs and TMs in the SGBR, although their effects on pollutant mobility require further investigation. Conversely, PI, AY, and SM posed minor concerns, indicating environmental resilience and integrity. These findings underscore the importance of integrated monitoring frameworks to address multi-pressure threats and support sustainable management of aquatic ecosystems.
Practical Implications and Future Outlooks
The IECI can be a valuable instrument for government agencies that need to integrate dispersed environmental data into a unified, comprehensible indicator for informed decision-making and public policy management. Additionally, it facilitates the comparison of environmental conditions across distinct temporal periods, which could assist in the discernment of gradual changes or cumulative impacts. Regarding the IECI, the following qualities and future considerations can be mentioned:
- Integration and representativeness: The IECI framework enables the integration of multiple diagnostic indices into a single, interpretable measure of environmental integrity. When numerous variables are available, a representative subset should be selected according to the study objectives, supported by pre-selection and exploratory statistical analyses to ensure relevance and minimise redundancy.
- Reproducibility and adaptability: Through its standardised mathematical structure, the IECI can be reproduced across diverse ecosystems and geographical regions. It may also be extended to other environmental matrices or pollutant groups by incorporating diagnostic indices relevant to the target medium (e.g., air, soil, or biota). If index calculation is limited by a reduced number of variables, key environmental or pollutant values can be directly integrated using historically reported minimum and maximum levels and thresholds limits of the guidelines. Recalibration of the colour-classified scale (Q1–Q2) is recommended to maintain interpretability across different contexts, and integrated indices should be carefully evaluated to ensure consistency and diagnostic reliability.
- Communication and application: By condensing complex environmental information into a single metric, the IECI facilitates straightforward communication of ecosystem condition and identification of priority hotspots (e.g., critical variables, locations, or periods), thereby supporting evidence-based environmental management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded from https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/environments12110442/s1, Figure S1. Percentages of TM contributions to HPI and PERI; Figure S2. Spectra of polymers detected by FTIR in MPs extracted from surface water and river sediments of the SGBR; Figure S3. Microplastics from rivers within SGBR; Figure S4. Correlation matrix of Spearman’s test; Figure S5. Regression model of IECIobserved versus IECIexpected; Table S1. Limits of detection and quantification.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.R.G.-S., J.E.S.-D. and E.L.-L.; methodology, R.R.G.-S., J.E.S.-D. and E.L.-L.; formal analysis, R.R.G.-S.; investigation, R.R.G.-S., J.E.S.-D. and E.L.-L.; resources, J.E.S.-D. and E.L.-L.; data curation, R.R.G.-S.; writing—original draft preparation, R.R.G.-S.; writing—review and editing, R.R.G.-S., J.E.S.-D. and E.L.-L.; visualization, R.R.G.-S.; supervision, E.L.-L.; funding acquisition, E.L.-L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research and the APC was funded by the National Polytechnic Institute, Secretariat for Research and Postgraduate Studies, grant number SIP20221711, SIP20221886, and SIP20250148.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request to the corresponding author due to institutional restrictions related to the confidentiality of information.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Polytechnic Institute (IPN) for its financial support, Sandra Soledad Morales-García of CMPL–IPN for her support in the analysis of metallic elements in environmental samples, and Argelia López-Bonilla of CEPROBI–IPN for her support in the FTIR analyses. We gratefully acknowledge the postgraduate scholarship granted by the Secretariat of Science, Humanities, Technology, and Innovation (SECIHTI).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, X.; Shen, X.; Jiang, W.; Xi, Y.; Li, S. Comprehensive Review of Emerging Contaminants: Detection Technologies, Environmental Impact, and Management Strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhappan, J.S.; Kalaiselvan, N.; Assis, S.M.; Amjith, L.R.; Glivin, G.; Mathimani, T. Origin, Types, and Contribution of Emerging Pollutants to Environmental Degradation and Their Remediation by Physical and Chemical Techniques. Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Sze-Yin Leung, K.; Elsner, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, B.; Sun, H.; An, T.; Ying, G.; et al. Emerging Contaminants: A One Health Perspective. Innovation 2024, 5, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhariya, M.K.; Banerjee, A.; Meena, R.S. Importance of Natural Resources Conservation: Moving toward the Sustainable World. In Natural Resources Conservation and Advances for Sustainability; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, S.; Garg, N.; Paudel, R. Environmental Degradation: Causes and Consequences. Eur. Res. 2014, 81, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadaa, W.; Mohammed, H. Heavy Metals—Definition, Natural and Anthropogenic Sources of Releasing into Ecosystems, Toxicity, and Removal Methods—An Overview Study. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angon, P.B.; Islam, M.S.; KC, S.; Das, A.; Anjum, N.; Poudel, A.; Suchi, S.A. Sources, Effects and Present Perspectives of Heavy Metals Contamination: Soil, Plants and Human Food Chain. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elnabi, M.K.; Elkaliny, N.E.; Elyazied, M.M.; Azab, S.H.; Elkhalifa, S.A.; Elmasry, S.; Mouhamed, M.S.; Shalamesh, E.M.; Alhorieny, N.A.; Abd Elaty, A.E.; et al. Toxicity of Heavy Metals and Recent Advances in Their Removal: A Review. Toxics 2023, 11, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laoye, B.; Olagbemide, P.; Ogunnusi, T.; Akpor, O. Heavy Metal Contamination: Sources, Health Impacts, and Sustainable Mitigation Strategies with Insights from Nigerian Case Studies. F1000Research 2025, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, P.; Saravanan, V.; Rajeshkannan, R.; Arnica, G.; Rajasimman, M.; Baskar, G.; Pugazhendhi, A. Comprehensive Review on Toxic Heavy Metals in the Aquatic System: Sources, Identification, Treatment Strategies, and Health Risk Assessment. Environ. Res. 2024, 258, 119440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilapitiya, P.G.C.N.T.; Ratnayake, A.S. The World of Plastic Waste: A Review. Clean. Mater. 2024, 11, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastics Europe Plastics-the Facts 2025. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/PE_TheFacts_25_digital-1pager-scrollable.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; Van Der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River Plastic Emissions to the World’s Oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Brookson, C.; Bikker, J.; Djuric, N.; Earn, A.; Bucci, K.; Athey, S.; Huntington, A.; McIlwraith, H.; Munno, K.; et al. Rethinking Microplastics as a Diverse Contaminant Suite. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Ma, X.; Song, Y.; Zuo, S.; Li, H.; Deng, W. A Critical Review on the Interactions of Microplastics with Heavy Metals: Mechanism and Their Combined Effect on Organisms and Humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Singh, V.P. Environmental and Social Considerations. In Water Resources Systems Planning and Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 393–459. [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly, A.; Jones, M.; O’Mahony, T.; Byrne, G. Selecting Environmental Indicator for Use in Strategic Environmental Assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2007, 27, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; da Silva, J.B.; dos Santos, I.F.; de Oliveira, O.M.C.; Cerda, V.; Queiroz, A.F.S. Use of Pollution Indices and Ecological Risk in the Assessment of Contamination from Chemical Elements in Soils and Sediments—Practical Aspects. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 35, e00169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbie, M.J.; Dail, D. Environmental Indices. In Encyclopedia of Environmetrics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chidiac, S.; El Najjar, P.; Ouaini, N.; El Rayess, Y.; El Azzi, D. A Comprehensive Review of Water Quality Indices (WQIs): History, Models, Attempts and Perspectives. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 22, 349–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellemeyer, J.C.; Perkin, J.S.; Fore, J.D.; Boyd, C. Comparing Assembly Processes for Multimetric Indices of Biotic Integrity. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 590–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Sánchez, A.E.; Rodríguez-Romero, A.J.; Sedeño-Díaz, J.E.; López-López, E.; Sundermann, A. Aquatic Macroinvertebrate Assemblages in Rivers Influenced by Mining Activities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados-Sánchez, R.R.; Sedeño-Díaz, J.E.; López-López, E. Microplastic Pollution and Associated Trace Metals in Freshwater Ecosystems within Protected Natural Areas: The Case of a Biosphere Reserve in Mexico. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1441340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, A.; López-López, E.; Sedeño-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Picos, R.; Macchi, P.; Kohlmann, B.; Correa-Araneda, F.; Boyero, L.; Bernal-Vega, J.; Ríos, T. Protocolo de Biomonitoreo Para la Vigilancia de la Calidad del Agua en Afluentes Superficiales de Panamá; Instituto Conmemorativo Gorgas de Estudios de la Salud: Panama City, Panama, 2019; p. 81. [Google Scholar]
- Barbour, M.T.; Stribling, J.B.; Verdonschot, P.F.M. The Multihabitat Approach of USEPA’s Rapid Bioassessment Protocols: Benthic Macroinvertebrates. Limnetica 2006, 25, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinius, S.H. Desing of an Index of Water Quality. Water Resour. Bull. 1987, 23, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the Assessment of Heavy-Metal Levels in Estuaries and the Formation of a Pollution Index. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Li, Y.L.; Lin, C.; Bui, X.T.; Vo, T.D.H.; Ngo, H.H. Seasonal Influence on Pollution Index and Risk of Multiple Compositions of Microplastics in an Urban River. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.V.; Nithila, P.; Reddy, S.J. Estimation of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water and Development of Heavy Metal Pollution Index. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Environ. Sci. Eng. Toxicol. 1996, 31, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control: A Sedimentological. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabias, J.; Provencio, E.; de la Maza Elvira, J.; Ruíz Corso, M.I. Programa de Manejo Reserva de La Biosfera Sierra Gorda Mexico. Available online: https://paot.org.mx/centro/ine-semarnat/anp/AN15.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Pedraza-Ruiz, R. Ficha Informativa de Los Humedales de Ramsar (FIR). Available online: https://rsis.ramsar.org/RISapp/files/RISrep/MX1352RIS.pdf?language=es (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Ejecutivo, P. Decreto de La Reserva de La Biosfera Sierra Gorda. Available online: https://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=4879875&fecha=19/05/1997#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- INEGI Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática. México en Cifras. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/app/areasgeograficas/?ag=22#collapse-Resumen (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- SGM Servicio Geológico Mexicano. GeoInfoMex. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/sgm/articulos/conoce-el-sistema-de-consulta-de-informacion-geocientifica-geoinfomex?idiom=es (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- INEGI Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática. Simulador de Flujos de Agua de Cuencas Hidrográficas. Available online: https://antares.inegi.org.mx/analisis/red_hidro/siatl/ (accessed on 21 February 2025).
- Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Rice, E.W. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; ISBN 9780875532875. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, W.; Burgeot, T.; Porcher, J.M. A Novel “Integrated Biomarker Response” Calculation Based on Reference Deviation Concept. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2721–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisano, R.; Hall, K.; Griggs, J.; Willison, S.; Reimer, S.; Mash, H.; Magnuson, M.; Boczek, L.; Rhodes, E. Selected Analytical Methods for Environmental Remediation and Recovery (SAM). Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/si/si_public_file_download.cfm?p_download_id=535984&Lab=NHSRC (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Imhof, H.K.; Schmid, J.; Niessner, R.; Ivleva, N.P.; Laforsch, C. A Novel, Highly Efficient Method for the Separation and Quantification of Plastic Particles in Sediments of Aquatic Environments. Limnol. Ocean. Methods 2012, 10, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debraj, D.; Lavanya, M. Microplastics Everywhere: A Review on Existing Methods of Extraction. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Frond, H.; O’Brien, A.M.; Rochman, C.M. Representative Subsampling Methods for the Chemical Identification of Microplastic Particles in Environmental Samples. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute for Environment and Sustainability, MSFD Technical Subgroup on Marine Litter. Guidance on Monitoring of Marine Litter in European Seas; Publications Office of European Commission: Luxembourg, 2013; ISBN 9789279327094. [Google Scholar]
- Cowger, W.; Steinmetz, Z.; Gray, A.; Munno, K.; Lynch, J.; Hapich, H.; Primpke, S.; De Frond, H.; Rochman, C.; Herodotou, O. Microplastic Spectral Classification Needs an Open Source Community: Open Specy to the Rescue! Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7543–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAGUA Comisión Nacional Del Agua. Ley Federal de Derechos: Disposiciones Aplicables en Materia de Aguas Nacionales. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/915768/Ley_Federal_de_Derechos_2024.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- CCME Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. Canadian Sediment Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life. Available online: https://ccme.ca/en/current-activities/canadian-environmental-quality-guidelines (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Ahirvar, B.P.; Das, P.; Srivastava, V.; Kumar, M. Perspectives of Heavy Metal Pollution Indices for Soil, Sediment, and Water Pollution Evaluation: An Insight. Total Environ. Res. Themes 2023, 6, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, A.; Singh, P.K.; Chandra Sharma, Y. Metallic Contamination of Global River Sediments and Latest Developments for Their Remediation. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-García, S.S.; Pérez-Escamilla, P.d.A.; Sujitha, S.B.; Godwyn-Paulson, P.; Zúñiga-Cabezas, A.F.; Jonathan, M.P. Geochemical Elements in Suspended Particulate Matter of Ensenada de La Paz Lagoon, Baja California Peninsula, Mexico: Sources, Distribution, Mass Balance and Ecotoxicological Risks. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 136, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Zhao, Y. Microplastics Pollution in Freshwater Sediments: The Pollution Status Assessment and Sustainable Management Measures. Chemosphere 2023, 314, 137727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.H.M.E.; Sekine, M.; Imai, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kanno, A.; Higuchi, T. Assessing Small-Scale Freshwater Microplastics Pollution, Land-Use, Source-to-Sink Conduits, and Pollution Risks: Perspectives from Japanese Rivers Polluted with Microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelavannan, K.; Sen, I.S.; Lone, A.M.; Gopinath, K. Microplastics in the High-Altitude Himalayas: Assessment of Microplastic Contamination in Freshwater Lake Sediments, Northwest Himalaya (India). Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiddink, J.G.; Valanko, S.; Delargy, A.J.; van Denderen, P.D. Setting Thresholds for Good Ecosystem State in Marine Seabed Systems and Beyond. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2023, 80, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, N. Justified Design Evaluation for Percentile Standards. Environ. Model. Softw. 2001, 16, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the Validation of Models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usero, J.; González-Regalado, E.; Gracia, I. Trace Metals in the Bivalve Mollusc Chamelea Gallina from the Atlantic Coast of Southern Spain. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1996, 32, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedeño-Díaz, J.E.; López-López, E.; Mendoza-Martínez, E.; Rodríguez-Romero, A.J.; Morales-García, S.S. Distribution Coefficient and Metal Pollution Index in Water and Sediments: Proposal of a New Index for Ecological Risk Assessment of Metals. Water 2019, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, N.M.; Wah, Y.B. Power Comparisons of Shapiro-Wilk, Kolmogorov-Smirnov, Lilliefors and Anderson-Darling Tests. J. Stat. Model. Anal. 2011, 2, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hector, A. The New Statistics with R; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2021; ISBN 9780198798170. [Google Scholar]
- Heumann, C.; Schomaker, M.; Shalabh. Introduction to Statistics and Data Analysis; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-46160-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bermúdez-González, M.P.; Ramírez-García, A.; Velázquez-García, E.d.C.; Queijeiro-Bolaños, M.E.; Ramírez-Herrejón, J.P. Population Structure of Poecilia Mexicana (Native) and Poeciliopsis Gracilis (Non-Native) in a Subtropical River. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 48, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.A.; Menninger, H.L.; Bernhardt, E. River Restoration, Habitat Heterogeneity and Biodiversity: A Failure of Theory or Practice? Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, G.; Pérez, J.; Bennett-Vaz, R.M.; Araúz, G.; Boyero, L.; Cornejo, A. Impacts of Land Use Changes on Leaf Litter Decomposition in Tropical Streams. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2025, 62, e03814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Romero, A.J.; Rico-Sánchez, A.E.; Sedeño-Díaz, J.E.; López-López, E. Characterization of the Multidimensional Functional Space of the Aquatic Macroinvertebrate Assemblages in a Biosphere Reserve (Central México). Diversity 2021, 13, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, E.; Sedeño-Díaz, J.E.; Rico-Sánchez, A.E.; Zariñana-Andrade, E.A.; Reyes-Flores, F.; Soriana-Flores, L. Indigenous People Doing Citizen Science to Assess Water Quality Using the BMWP in Rivers of an Arid Semi-Arid Biosphere Reserve in Mexico. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gutiérrez, J.M.; Ramírez-Mosqueda, E.; Cea-Barcia, G.E.; Ruiz-Aguilar, G.M.L.; Castro-Ramírez, I.; Camarena-Martínez, S.; Ilizaliturri-Hernández, C.A.; Rocha-Amador, D.O.; Costilla-Salazar, R. A Comparative Assessment of Surface Water Quality in Lake Yuriria, Guanajuato, Using the Water Quality Index. Water 2025, 17, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S. Influences of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors on Surface and Groundwater Quality in Rural and Urban Areas. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botté, A.; Zaidi, M.; Guery, J.; Fichet, D.; Leignel, V. Aluminium in Aquatic Environments: Abundance and Ecotoxicological Impacts. Aquat. Ecol. 2022, 56, 751–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Heavy Metals: Toxicity and Human Health Effects. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 99, 153–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, S.; Prakash, T.; Madhu, K.D.; Goli, D. Multifaceted Effects of Aluminium in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Borah, S.S.; Kalamdhad, A. A Modified Indexing Approach for Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Deepor Beel, India. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.R.; Raj, D. Distribution and Probabilistic Human Health and Ecological Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Water, Sediments and Aquatic Plants: A Comprehensive Study to Understand the Impacts of Active Coal Mine on the Lentic Ecosystem. Environ. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Khatun, B.; Jewel, M.A.S.; Ara, J.; Kazal, M.S.I.; Hasan, J. Assessment of Water Quality and Heavy Metal Indices in a Tropical Freshwater River for Aquatic Life and Public Health Standard. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, M.; Palarea-Albaladejo, J.; Albanese, S.; Lin, X.; Ciarcia, S.; Cicchella, D. Assessing Natural Background Concentrations of Chemical Elements in Urban Soils: A Case Study in Benevento (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 975, 179298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Hua, J. Heavy Metal Pollution in Aquatic Systems of the Hunhe River Basin, China: Source Apportionment, Ecological and Health Risk Assessments. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 201, 107478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, A.; Török, A.I.; Kovacs, E.; Cadar, O.; Mirea, I.C.; Micle, V. Metal Contents and Pollution Indices Assessment of Surface Water, Soil, and Sediment from the Arieș River Basin Mining Area, Romania. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo-Sánchez, E.R.; Martínez, J.M.E.; Morales, M.M.; Talavera Mendoza, O.; Alberich, M.V.E. Ecological and Health Risk Assessment of Potential Toxic Elements from a Mining Area (Water and Sediments): The San Juan-Taxco River System, Guerrero, Mexico. Water 2022, 14, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dadzie, A.A.; Yuan, L.; Xing, S.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, S. Analysis and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of the Freshwater Ecosystem in Zhenjiang City, China. SN Appl. Sci. 2022, 4, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soetan, O.; Viteritto, M.; Qian, Y.; Feng, H. Evaluation of Toxic Metal Pollution in Freshwater Surficial Sediments Using Environmental Indices and Multivariate Statistical Approaches—A Systematic Review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Proshad, R.; Ahmed, S. Ecological Risk of Heavy Metals in Sediment of an Urban River in Bangladesh. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 24, 699–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnala, S.; Tiwari, S.; Nayak, A.; Bhushan, B.; Chandra, S.; Medeiros, C.R.; Coutinho, H.D.M. Impact of Heavy Metal Toxicity on the Human Health and Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 987, 179785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Lamb, D.; Naidu, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Yan, Y.; Ok, Y.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Choppala, G. Cadmium Solubility and Bioavailability in Soils Amended with Acidic and Neutral Biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, J.P.; Ferrari, L.; Eissa, B.L. Acute Toxicity of Cadmium to Freshwater Fishes and Its Relationship with Body Size and Respiratory Strategy. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 248, 109109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Miao, A.-J.; Wang, N.-X.; Li, C.; Sha, J.; Jia, J.; Alessi, D.S.; Yan, B.; Ok, Y.S. Arsenic Bioaccumulation and Biotransformation in Aquatic Organisms. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah; Abbas, A.; Al-Amer, A.M.; Laoui, T.; Al-Marri, M.J.; Nasser, M.S.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M.A. Heavy Metal Removal from Aqueous Solution by Advanced Carbon Nanotubes: Critical Review of Adsorption Applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro-Martínez, D.M.; Niño-Torres, C.A.; Charruau, P.; Rendón-von Osten, J.; Castelblanco-Martínez, D.N.; Rios Mendoza, L.M.; Frausto-Martínez, O.; Blanco-Parra, M.d.P. The State of Microplastic Pollution in México: A Review and Evolving Perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 988, 179772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, V.C.; Jonathan, M.P.; Rodriguez-Espinosa, P.F.; Rodríguez-González, F. Microplastics in Freshwater Sediments of Atoyac River Basin, Puebla City, Mexico. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Olea, I.J.; Leal-Bautista, R.M.; Cejudo, E.; Cervantes-Uc, J.M.; Rodríguez-Fuentes, N.; Acosta-González, G. Contaminación Por Microplásticos En El Acuífero Kárstico de La Península de Yucatán. Ecosistemas Recur. Agropecu. 2022, 9, e3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, K.H.; Cucknell, A.-C.; Smith, B.D.; Clark, P.F.; Morritt, D. London’s River of Plastic: High Levels of Microplastics in the Thames Water Column. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, J.M.; Selvam, S.; Saravanan, P.; Roy, P.D.; Sanju, P.; Muthukumar, P. Microplastics in Water from the Cooum River, Chennai, India: An Assessment of Their Distribution, Composition, and Environmental Impact. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 27, 101362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, C.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, C. Microplastic Pollution in the Yangtze River Basin: Heterogeneity of Abundances and Characteristics in Different Environments. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laermanns, H.; Reifferscheid, G.; Kruse, J.; Földi, C.; Dierkes, G.; Schaefer, D.; Scherer, C.; Bogner, C.; Stock, F. Microplastic in Water and Sediments at the Confluence of the Elbe and Mulde Rivers in Germany. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 794895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansoar-Rodríguez, Y.; Bertrand, L.; Colombo, C.V.; Rimondino, G.N.; Rivetti, N.; Bistoni, M.d.l.A.; Amé, M.V. Microplastic Distribution and Potential Ecological Risk Index in a South American Sparsely Urbanized River Basin: Focus on Abiotic Matrices and the Native Fish Jenynsia Lineata. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 18, 100685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Rao, Q.; Deng, X.; Chen, J.; Xie, P. Rainfall Is a Significant Environmental Factor of Microplastic Pollution in Inland Waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.; Xueying, L.; Xinrong, S.U. Microplastic Pollution in Chinese Rivers: A Detailed Analysis of Distribution, Risk Factors, and Ecological Impact. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2026, 222, 118676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Dixon, S.J. Microplastics: An Introduction to Environmental Transport Processes. WIREs Water 2018, 5, e1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, H.A.; Dalu, T.; Wasserman, R.J. Sinks and Sources: Assessing Microplastic Abundance in River Sediment and Deposit Feeders in an Austral Temperate Urban River System. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Xing, R.; Sun, M.; Gao, Y.; An, L. Microplastics in Sediments from an Interconnected River-Estuary Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolaosho, T.L.; Rasaq, M.F.; Omotoye, E.V.; Araomo, O.V.; Adekoya, O.S.; Abolaji, O.Y.; Hungbo, J.J. Microplastics in Freshwater and Marine Ecosystems: Occurrence, Characterization, Sources, Distribution Dynamics, Fate, Transport Processes, Potential Mitigation Strategies, and Policy Interventions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 294, 118036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naying, L.; Xintong, M.; Bo, Z.; Xiaofeng, W.; Xin, L.; Zao, Y.; Honghui, L.; Yixin, H. Potential Ecological Risk of Microplastics Contamination to Environment in Protect Area Lakes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 485, 136863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C. Microplastics in Freshwater Sediment: A Review on Methods, Occurrence, and Sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouchene, K.; da Costa, J.P.; Chamkha, M.; Ksibi, M.; Sayadi, S. Effects of Microplastics’ Physical and Chemical Properties on Aquatic Organisms: State-of-the-Art and Future Research Trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 166, 117192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdipour, H.; Asgari, G.; Shokoohi, R. A Review of Microplastics Pollution in Dams Globally: Consequences and Future Outlook. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2026, 276, 104730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Loss, R.D.; Shields, D.; Pawlik, T.; Hochreiter, R.; Zydney, A.L.; Kumar, M. Polyacrylamide Degradation and Its Implications in Environmental Systems. NPJ Clean. Water 2018, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueñas-Moreno, J.; Mora, A.; Capparelli, M.V.; González-Domínguez, J.; Mahlknecht, J. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Environmental Compartments in Mexico: A Meta-Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 361, 124812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swetha, T.A.; Bora, A.; Mohanrasu, K.; Balaji, P.; Raja, R.; Ponnuchamy, K.; Muthusamy, G.; Arun, A. A Comprehensive Review on Polylactic Acid (PLA)—Synthesis, Processing and Application in Food Packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.; Nguyen, K.Q.N.; Nguyen, P.T.; Duong, H.C.; Bui, X.T.; Hoang, N.B.; Nghiem, L.D. Microfibers in Laundry Wastewater: Problem and Solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 141948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surana, D.; Vinay; Patel, P.; Ghosh, P.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S. Microplastic Fibers in Different Environmental Matrices from Synthetic Textiles: Ecotoxicological Risk, Mitigation Strategies, and Policy Perspective. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Kim, H.-M.; Jung, Y.; Park, J.-W.; Moon, H.G.; Kim, S. Assessment of Potential Ecological Risk for Microplastics in Freshwater Ecosystems. Chemosphere 2025, 370, 143995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.H.; Kaykhaii, M. Azo Dyes: Sources, Occurrence, Toxicity, Sampling, Analysis, and Their Removal Methods. In Emerging Freshwater Pollutants; Dalu, T., Tavengwa, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 267–287. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Shi, L.; Yi, K.; Yu, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Li, J. Microplastics as a Vehicle of Heavy Metals in Aquatic Environments: A Review of Adsorption Factors, Mechanisms, and Biological Effects. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 113995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cao, W.; Hu, Y.; Shen, W. The Influence of Pb(II) Adsorption on (Non) Biodegradable Microplastics by UV/O3oxidation Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; He, G.; Liu, W. Adsorption Mechanism of Cadmium on Microplastics and Their Desorption Behavior in Sediment and Gut Environments: The Roles of Water PH, Lead Ions, Natural Organic Matter and Phenanthrene. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wangjin, X.; Wang, Y.; Meng, G.; Chen, Y. The Adsorption Behavior of Metals in Aqueous Solution by Microplastics Effected by UV Radiation. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 87, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenea, A.-G.; Dinu, C.; Rus, P.A.; Ionescu, I.A.; Gheorghe, S.; Iancu, V.I.; Vasile, G.G.; Pascu, L.F.; Chiriac, F.L. Exploring Adsorption Dynamics of Heavy Metals onto Varied Commercial Microplastic Substrates: Isothermal Models and Kinetics Analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Jin, L.; Peng, R. Factors Affecting the Adsorption of Heavy Metals by Microplastics and Their Toxic Effects on Fish. Toxics 2023, 11, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Ma, Q.; Xing, S.; Yuan, L.; Ma, Y. Distribution and Effects of Microplastics as Carriers of Heavy Metals in River Surface Sediments. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2024, 266, 104396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, M.; Gandhimathi, R.; Nidheesh, P.V. The Cause, Fate and Effect of Microplastics in Freshwater Ecosystem: Ways to Overcome the Challenge. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khant, N.A.; Chia, R.W.; Moon, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, H. Review on the Relationship between Microplastics and Heavy Metals in Freshwater near Mining Areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 66009–66028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestra, V.; Bellopede, R. Microplastic Pollution in Show Cave Sediments: First Evidence and Detection Technique. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestra, V.; Bellopede, R. Microplastics in Caves: A New Threat in the Most Famous Geo-Heritage in the World. Anal. Comp. Ital. Show. Caves Deposits. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadaki, M.; Brierley, G.; Cullum, C. River Classification: Theory, Practice, Politics. WIREs Water 2014, 1, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Niu, L.; Hui, C.; Lei, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Determination of the Direct and Indirect Effects of Bend on the Urban River Ecological Heterogeneity. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canning, A.D.; Death, R.G. Ecosystem Health Indicators—Freshwater Environments. In Encyclopedia of Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 46–60. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).