Abstract
Delphinus delphis uses the Algeciras–Gibraltar Bay (BA-G) as a feeding and breeding ground, but heavy maritime traffic and recreational fishing increase its exposure to injuries and anthropogenic threats. Over three years, more than 110,000 photographs were collected during 593 sampling days, resulting in a catalogue of 1356 adult individuals identified by dorsal fin markings and the species’ characteristic white patch. The posterior sectors and distal tip of the fin were the most affected by lesions, confirming the impact of local human activities. In addition, 104 putative mother–calf pairs were recorded, highlighting the importance of the BA-G as a breeding area. Individuals with greater dorsal fin damage showed significantly higher recapture frequencies, suggesting that exposure to anthropogenic pressures is associated with greater recurrent detectability. This catalogue, one of the most comprehensive catalogues available for D. delphis worldwide, represents a key tool for long-term monitoring of this population and provides a methodological framework that can be extrapolated to other regions where human pressure increases the marking of individuals. The results reinforce the need for specific management measures in the BA-G, including the establishment of protected areas, as a fundamental step towards conserving this endangered species.
1. Introduction
Identifying individuals within animal populations is crucial to understanding their ecology, behaviour, and dynamics, particularly in large, long-lived species exhibiting stable, individual-specific markings [1,2,3]. In cetaceans, the presence of scars, pigmentation patterns, or body injuries facilitates individual recognition through photo-identification, a non-invasive technique that enables the study of social structure, movements, life history, and both natural and anthropogenic threats [2,4,5,6,7]. Photo-identification has been applied to at least fifty-seven cetacean species [8] and has proven particularly effective in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus), which show high proportions of identifiable markings [9,10]. However, its application is more challenging in species with fewer markings or less specific pigmentation patterns, such as the common dolphin (Delphinus delphis, hereafter D. delphis), which exhibits one of the lowest known proportions of natural body marks [7,11,12]. Many of the nicks and notches in this species are small and less distinctive than in species traditionally used in photo-identification, making consistent individual recognition more difficult and reducing the number of recognisable specimens [13,14,15].
Photo-identification studies on D. delphis have been relatively scarce [11,16,17,18,19,20,21], possibly due to the gregarious behaviour of the species, its large populations, and its predominantly pelagic distribution, which hinders the acquisition of high-quality photographs [1,4,15]. Even so, catalogues of D. delphis have been developed in different regions, such as the central Mediterranean and the Pacific [11,19,21,22], demonstrating the potential of this technique even in species with limited marking.
Although some previous studies have employed photo-identification in Delphinus populations from different regions, most published catalogues have been attributed generically to Delphinus sp. (e.g., [6,20,21]). In the case of studies conducted on D. delphis in the north-eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean [11,16,17,19,22], photo-identification has been applied as a methodological tool, but without the publication of complete catalogues including all identified individuals.
Various dorsal fin features have been used as diagnostic markers in the literature: permanent nicks or tears on the leading or trailing edge [4,5,23,24,25], body scars in species such as Grampus griseus [26,27], colouration patterns on the fluke in rorquals such as Megaptera novaeangliae [28,29], or dorsal cartilage collapse and deformations resulting from disease, stress, ageing, or interaction with fishing gear or vessels [30,31,32].
In addition, skin lesions and mutilations can serve as indicators of anthropogenic pressures, such as entanglements in fishing gear or vessel strikes [33,34,35].
Xenobalanus globicipitis is an epibiotic barnacle exclusive to cetaceans, recorded in numerous odontocete and mysticete species in temperate and tropical waters, with an almost cosmopolitan distribution [36,37,38]. Its attachment occurs preferentially in areas where hydrodynamic flow favours boundary-layer separation, such as the trailing edge of the caudal, pectoral, and dorsal fins [39,40]. Moreover, its prevalence and location have been proposed to reflect differences in swimming hydrodynamics and, in some cases, to act as indicators of host physiological status [38,41].
In D. delphis, the presence of a variably sized white patch on the dorsal fin has been reported as a useful feature to support photo-identification [11,18]. In populations such as that of the Hauraki Gulf, this pigmentation trait has proven to be prevalent, stable over time, and sufficiently discriminative to be used even as a primary identification marker [20].
The Mediterranean subpopulation of D. delphis has undergone a marked decline since the mid-20th century [42,43] and is currently listed as “Endangered” (EN) on the IUCN Red List [44]. Genetic studies support some degree of differentiation between Mediterranean and Atlantic populations, with limited gene flow across the Strait of Gibraltar [45]. This status highlights the need for detailed studies to identify critical habitats, assess threats, and strengthen conservation strategies in the region. The Bay of Algeciras–Gibraltar (hereafter BA-G) has been recognised as a critical area for the species, with frequent records of feeding and breeding activity, where females with calves and juveniles are recurrently observed [46,47]. However, until now, no formal catalogue of D. delphis existed in this area, nor a detailed analysis of the morphological and pigmentation traits associated with photo-identification. Although [18] described the morphology and frequency of dorsal edge markings in D. delphis from the BA-G and the Moray Firth, their study focused on the typology and potential causes of these marks rather than on the development of a structured photo-identification catalogue. The present work therefore constitutes the first comprehensive catalogue of the species in the western Mediterranean, providing a baseline tool for population monitoring and for assessing anthropogenic impacts in the BA-G.
The objectives of this study were: (i) to produce the first comprehensive and structured photo-identification catalogue of adult D. delphis in a region of the western Mediterranean, with each individual documented by a unique alphanumeric code and associated photographs and metadata; (ii) to record and locate mutilations, nicks, and notches (DEMs) on the dorsal fin in order to infer the degree of exposure of individuals to natural or anthropogenic threats in the study area, and to analyse the white patch, when present, as a complementary feature for individual identification; (iii) to assess the relationship between recapture frequency and the degree of physical damage to the dorsal fin, as an indirect indicator of exposure to anthropogenic pressures and the apparent fidelity of individuals to specific coastal areas; (iv) to evaluate the diagnostic utility of these natural marks in population studies and their application in conservation proposals at regional scales; and (v) to document putative mother–calf pairs among the photo-identified individuals, in order to reinforce the evidence for the use of the area as a potential breeding ground.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study was conducted over three consecutive years (March 2017–March 2020) in the BA-G, located on the northern shore of the Strait of Gibraltar, at the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula (Figure 1). This is a semi-enclosed system subject to high anthropogenic pressure, particularly in summer, due to intense commercial and passenger maritime traffic. Covering an area of approximately 7500 ha, it reaches depths of up to 450 m as a result of the presence of a submarine canyon that crosses the bay from north to south in a mirror-image S-shape [48].
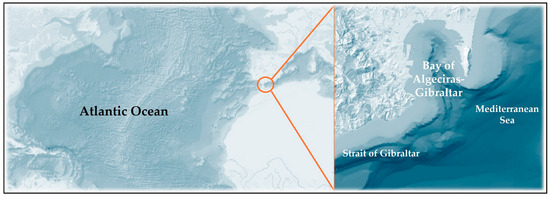
Figure 1.
Study area, Algeciras Bay (BA-G), southern Spain.
Dolphin sightings were conducted using Nikon 7 × 50 binoculars, and images were captured with two Nikon DSLR cameras equipped with 300 mm lenses, following standard photo-identification protocols [1].
2.2. Photo-Identification System and Diagnostic Criteria
The catalogue was compiled considering only adult individuals, given that calves and juveniles have a very low proportion of permanent markings useful for photo-identification [15,25]. Individual identification was based on unique and stable dorsal fin traits, mainly the morphology of the edges and the pigment pattern.
Each photo-identification event was defined as obtaining at least one photograph of usable quality of the dorsal fin of an individual on a given date. Recaptures obtained on the same day were considered a single event, regardless of the side photographed. Lateral coverage was classified as: right side (R), left side (L), or both sides (R + L). Whenever possible, bilateral images were selected, as these increase the reliability of recaptures and reduce matching errors [11,49]. Field sampling was opportunistic aboard licensed whale-watching platforms between 2017 and 2020, with year-round coverage when sea conditions allowed. In total, 593 sampling days yielded > 110,000 photographs; the year-by-year breakdown of effort and image filtering is provided in Table S2.
Photographic quality (PQ) was classified into three levels—PQ1 (high or very high), PQ2 (medium), and PQ3 (low, accepted only if containing unequivocal diagnostic features)—following criteria described in previous cetacean photo-identification studies [15,50,51]. In parallel, the distinctive character of the marks (DC) was coded as: DC1 (highly distinctive), DC2 (distinctive), or DC3 (not distinctive), following standards applied to poorly marked cetaceans [15,50,51]. Only individuals classified as DC1 or DC2 were included in the catalogue, while those assigned to DC3 were excluded.
Each photo-identified individual was recorded using a complete alphanumeric code (Code_ID_Date_Angle_Name), which included the reference number, sighting date, the side of the dorsal fin photographed, and, optionally, a name. The coding system implemented enabled the association of individual sightings and resightings with the observation calendar. The resulting data were organised into three Excel spreadsheets, all of which were deposited in Zenodo (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17183966). The files “(1) Catalogue_Ddelphis_BA_G_2017_20”, “(2) Number_Captures_Recaptures_Ddelphis_BA_G_2017_20”, and “(3) Captures_Recaptures_Ddelphis_BA_G_2017_20” contain, respectively: photographic identification of individuals, including image quality and distinctiveness; the number of sightings and resightings per dolphin, along with the dates of first and last observation, as well as a list of putative mothers photographed alongside a calf or neonate; and alphanumeric codes for all sightings and resightings, with representative photographs of each individual highlighted in bold.
2.3. Captures, Recaptures, and Classification of Putative Mother–Calf Pairs
To assess the recurrence of individuals within the study area, detection frequency (FR) was calculated as the number of days on which the same adult was photographed. Each detection on a different date was considered an independent event, whereas recaptures on the same day were integrated as a single event, regardless of whether the right, left, or both sides were photographed. Individuals were then grouped into frequency categories (1, 2, 3–5, 6–10, 11–15, 16–20, and >20 events), which allowed us to distinguish between those observed only once and those showing some degree of temporal recurrence.
Individual identification was based on independent photographic matching, whereby images were first evaluated by the lead author and, in cases of doubt, cross-checked with two other qualified researchers. Questionable matches were discussed until consensus was reached, with the aim of reducing the likelihood of identification errors. All matching and verification procedures were consistently performed by the same core team (the lead author and two trained collaborators) to ensure methodological consistency throughout the study period. This procedure sought to minimise false positives (when two different individuals are catalogued as the same) and false negatives (when a single individual is recorded as two different ones) following established methodological recommendations [3,15,52].
To estimate the error rate in recaptures, a random subsample comprising 20% of the catalogue was selected, and a blind test was conducted in which an external evaluator attempted to match images without prior knowledge of the assigned IDs. This approach, applied in previous studies of D. delphis and other species [3,15], allowed verification of the internal consistency of the catalogue.
In addition, the stability of markings was assessed in individuals recaptured on more than one occasion, which made it possible to confirm the persistence of nicks and notches over time through systematic comparisons between successive sightings, in line with methodological approaches used in previous studies [15,21].
In addition, cases of putative mother–calf pairs were identified. These were defined as adults observed in close association with a clearly smaller individual, in at least one photograph. Classification was based on visual criteria commonly accepted in the literature, including the presence of foetal folds [53,54], reduced body size of the neonate (≈<½ of the mother) [54,55,56], differences in dorsal fin morphology between age classes [57], and the calf’s close and coordinated position relative to the adult, usually swimming in echelon [58,59,60]. This procedure was applied in a functional manner and, although no longitudinal monitoring protocol was established, a systematic record was consolidated through a structured database and a photographic archive documenting all identified cases of putative mother–calf association.
All activities were conducted under a non-invasive observation protocol, without handling the animals or employing intrusive techniques. Data collection was carried out from a whale watching platform familiar with the applicable regulations, which in most cases allowed compliance with the established approach distances. Fieldwork was conducted in accordance with Spanish legislation (Royal Decree 1727/2007 of 21 December), which regulates approaches to cetaceans, and in compliance with the 2014 Marine Regulations of Gibraltar. The study was approved by the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee of the Gibraltar Ministry of Education, Heritage, Environment, Energy and Climate Change.
2.4. Morphological and Lesion Characterisation of the Dorsal Fin
Individual characterisation included the analysis of permanent marks on the dorsal fin edge (Dorsal Edge Marks, DEMs), as well as complementary morphological traits such as fin shape, the termination of the distal tip, and the presence of the characteristic white patch of D. delphis. DEMs were recorded according to their sectoral location on the fin, together with their number, size, and visible external morphology. In individuals with multiple lacerations distributed across different sectors, the types of wounds present in the individual as a whole were documented, without specifying the exact sectoral correspondence of each one. When a mark crossed two sectors, both were recorded.
An operational classification of eleven morphological categories was established: triangular (T), square or trapezoidal (S), elongated (E), rounded (R), parallel (P), chain-like (C), L-shaped or hooked (L), irregular (I), apical cut (A), deformations (D), and mutilations (M). This typology was based on previous descriptions, for example [35,61], as well as on new forms observed in the local population (Table 1). Mutilations included both partial amputations and total tissue loss, with collapse or bending also recorded when associated with partial amputation. This framework enabled the characterisation of the diversity of damaged profiles and facilitated individual identification. Lesion sizes were categorised as very small (VS), small (S), medium (M), large (L), and very large (VL), according to their relative extension on the fin surface. For subsequent statistical analyses, L and VL were merged into a single category (L+).

Table 1.
Types of dorsal edge markings (DEMs) described in the dorsal fins of common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) in BA-G, classified according to their external morphology into eleven main categories: triangular (T), square or trapezoidal (S), elongated (E), curved or semicircular (R), parallel (P), chain-shaped (C), L-shaped or hook-shaped (H), irregular (I), apical cut (A), deformations (D) and mutilations (M). Note: Partial mutilations accompanied by bending or collapse of the dorsal fin were included in the “mutilations” category.
The visual classification process was conducted with maximum rigour through repeated inspections and comparisons with reference images. Nevertheless, in the present study additional difficulties were encountered, associated with the relatively small size of D. delphis compared with other species used in photo-identification, the predominance of markings that were difficult to discern, and technical factors related to the angle, focus, or lighting of the photographs. These circumstances limited, in some cases, the precise assignment of the shape, number, and size of DEMs—an issue noted in the literature, although rarely made explicit [6,34]—and one that should be taken into account when interpreting the results.
In addition, the general morphology of the dorsal fin was recorded, classified as straight-triangular (ST), falcate (F), or highly falcate (HF), and the termination of the distal tip, defined as pointed (PDE), rounded (RDE), or intermediate (IDE), following criteria adapted from [69]. Although not diagnostic on their own, these attributes provide useful information in individuals with few lesion-related or pigmentation traits.
The white patch present in some individuals was also recorded as a pigmentation trait characteristic of the species [11,70] (illustrated in the Results section, where examples of this pigmentation pattern are shown). Its coverage was coded into four ranges (1–25%, 26–50%, 51–75%, and 76–100%), intensity as high, medium, or low, and type as compact, diffuse, or mixed. In cases where photographic conditions did not allow a reliable assessment, the variable was recorded as “not identifiable”. Evaluation was only carried out when the presence of the patch was unequivocal, and in individuals with extensive mutilations or other severe alterations, only the visible portion of the dorsal fin was considered. The presence of X. globicipitis on the dorsal fin was systematically recorded during the review of the photographs and used as an auxiliary photo-identification feature, following previous descriptions of its typical location on cetacean dorsal fins [39] (Moreno-Colom et al., 2020).
2.5. Image Processing and Filtering
The classification of DEMs was carried out through direct visual inspection and comparison with reference images. Photo quality (PQ) and distinctiveness (DC) were independently evaluated by two experienced observers, and discrepancies were discussed until consensus was reached to ensure inter-observer consistency. To minimise bias, assessments were conducted independently and doubtful cases were discussed until consensus was reached, following the quality control recommendations described in methodological photo-identification studies [6,71]. Only photographs meeting the minimum established quality thresholds (PQ1–PQ2) were included, and, exceptionally, those classified as PQ3 were accepted when they provided unequivocal diagnostic features. When the information was ambiguous or insufficient, the feature was recorded as “not identifiable” (ni) and excluded from the corresponding analysis.
Given the characteristics of D. delphis—reduced body size and the predominance of small nicks—notably rigorous control was required to ensure the accurate assignment of the shape, number, and size of DEMs. This type of methodological limitation is widely recognised in the literature and should be considered when interpreting the results [6,15,34]. Transparency in data processing is a key aspect in population studies based on photo-identification, where false positives and negatives may affect the robustness of the conclusions [1,3,5,52,72].
Photographs were evaluated according to quality criteria widely accepted in photo-identification studies, considering factors such as blurring, exposure, excessive distance, splashes, partial submersion, inadequate angles, or cases corresponding only to calves without adults [3,71]. Digital processing was carried out using Adobe Photoshop CS5 (Adobe Systems Inc., San José, CA, USA), ACDSee Pro (ACD Systems International Inc., Victoria, BC, Canada), and the Microsoft Windows Photos application. During the analysis, only basic adjustments of light and contrast were applied to improve the visibility of markings or the white blaze, without altering the original morphology under any circumstances [71,73]. When a single photograph included several photo-identifiable individuals, the dorsal fins were cropped independently, generating separate files with the suffix “_cut”.
Finally, to ensure consistency between the alphanumeric codes of photo-identified individuals and the image file names, automatic verification of both records was performed, correcting any discrepancies detected. The images were organised into four PDF files deposited in the Zenodo repository (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17186724) (Table S1). This material is not publicly available but can be provided upon request to the authors. This procedure ensured a refined set of comparable images, reinforcing the diagnostic robustness of the catalogue and its usefulness as a reference for longitudinal studies.
2.6. Statistical Analyses
2.6.1. Descriptive Analyses
Descriptive statistics (absolute frequencies, percentages, medians, and interquartile ranges, IQR) were calculated for the main variables recorded: (i) presence, number, shape, and size of marks on the dorsal fin edge (DEMs); (ii) general fin morphology (ST, F, HF) and distal termination (PDE, RDE, IDE); and (iii) white blaze (presence, coverage within the ranges 1–25%, 26–50%, 51–75%, 76–100%; high/medium/low intensity; and compact/diffuse/mixed type).
Recapture frequency (FR) was defined as the number of different days on which an individual was detected (captures + recaptures). When possible, length of stay (AE) was also calculated, defined as the number of days between the first capture and the last recapture. Only individuals with evaluable information according to the criteria established in Section 2.2 were included in each analysis.
2.6.2. Inferential Analyses
To evaluate the relationship between apparent occurrence in the bay (FR) and the degree of dorsal damage, non-parametric tests were applied. The Kruskal–Wallis test was used with FR as the response variable and three factors analysed independently: (a) number of sectors with DEMs (1, 2, ≥3); (b) number of DEMs per individual (1, 2, 3–5, ≥6; with rare categories such as 6–10 and >10 merged); and (c) dominant lesion size (VS, S, M, L+; with L and VL merged into L+).
Pairwise comparisons were carried out using Dunn’s tests with Holm adjustment to control for family-wise error. The Kruskal–Wallis ε2 statistic was reported as a measure of effect size.
Additionally, Spearman correlations (ρ) were calculated between FR and ordinal variables (number of sectors, number of DEMs, lesion size heterogeneity). Two additional indicators of severity were also included: (i) presence of at least one large lesion (L+), tested with Mann–Whitney, and (ii) lesion size heterogeneity, defined as the intrapersonal range between the minimum and maximum observed sizes, correlated with FR using Spearman.
Finally, exploratory analyses were performed on the possible association between FR and fin morphology (ST/F/HF) or distal termination (PDE/RDE/IDE), again applying Kruskal–Wallis with post hoc Holm adjustment. All analyses were implemented in Python 3.11, using the packages pandas, SciPy, and scikit-posthocs for statistical tests, and matplotlib for figure generation. GLMMs were not considered because there were no repeated measures per individual and effort covariates for detection were unavailable; rank-based non-parametric tests were therefore used. All analyses were two-tailed, with α = 0.05 as the threshold for statistical significance.
3. Results
3.1. Composition of the Photo-Identification Catalogue and Data Quality
During the study period, a total of 110,501 photographs were collected, of which 71,164 (64.4%) were discarded for not meeting the quality criteria. A total of 39,337 images (35.6%) were retained as suitable for evaluation; ultimately, only 7.5% of these suitable images were used in the development of the photo-identification catalogue (see Table S2 in the Supplementary Material).
The final catalogue included 1356 adult D. delphis individuals photo-identified in the BA-G between March 2017 and March 2020. Of these, 1348 exhibited at least one visible laceration or some type of mutilation and were included in the lesion analyses (some examples are shown in Figure 2). Eight individuals, without evident DEMs, were incorporated on the basis of distinctive morphological or pigmentation traits (e.g., atypical fin morphology, conspicuous white patch) but were excluded from the lesion analyses. The proportion of profiles photographed was approximately 46% on the right side (R), 38% on the left side (L), and 17% on both sides (R + L).

Figure 2.
Examples of D. delphis individuals with the highest number of recaptures photo-identified in the Bay of Algeciras–Gibraltar (BA-G). The number of confirmed recaptures for each individual is shown in the upper label of each panel. Individual codes correspond to the adult catalogue.
In terms of image quality, of the 1695 photographs comprising the catalogue, 72.4% corresponded to PQ1, 23.6% to PQ2, and 4.0% to PQ3 (the latter only when providing unequivocal diagnostic information). Distinctiveness was predominantly high (DC1), while DC2 cases represented only 1.6% of the total evaluated (see criteria in Section 2.2).
The distribution of independent events (number of days with detection) showed that 65.8% of individuals were detected only once, 14.3% on 2 days, 13.5% on 3–5 days, 4.1% on 6–10 days, 1.5% on 11–15 days, 0.7% on 16–20 days, and 0.1% on more than 20 days (see Figure S1 in the Supplementary Material).
A total of 104 putative mother–calf pairs were identified, representing 7.6% of the total photo-identified individuals (n = 1356). These cases were primarily recognised by the relatively small size of the calf, the occasional presence of foetal folds or typical neonatal colouration, and the neonatal/infant position in close proximity to the mother. Some examples of these mother–calf pairs documented during the study are provided in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Putative mother–calf pairs of D. delphis photo-identified in the Bay of Algeciras–Gibraltar (BA-G). Adult codes correspond to individuals included in the photo-identification catalogue.
The temporal distribution of sightings for the putative mother–calf pairs illustrated in Figure 3 is detailed in Table S4, which summarises the months in which adults were photographed with a calf. In addition to these 104 putative mothers–calf pairs, other cases were observed during the surveys in which the lack of distinctive features, together with limitations in image quality, individual positioning, or lighting, prevented their assignment to identified specimens (Figure S3). Although these cases were not included, they reinforce the role of the BA-G as a breeding area.
3.2. Dorsal Fin Traits (Descriptive)
Lesions on the dorsal fin were distributed mainly across two sectors (44.8% of individuals), followed by a single sector (33.9%) and three sectors (19.8%). Cases with four or five lacerated sectors, as well as mutilations, accounted for <1% (Figure 4a).
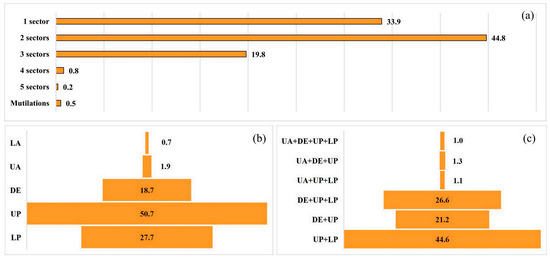
Figure 4.
Individuals of D. delphis in the Bay of Algeciras–Gibraltar (BA-G) showing external dorsal-edge marks (DEMs): (a) number of affected sectors per individual (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) and mutilations; (b) frequency by sector (LA, UA, DE, UP, LP); (c) most frequent sector combinations. Categories < 1% are not displayed. Boxes = distribution summaries as indicated in the panels.
By sector, the most affected was the upper posterior (UP, 50.7%), followed by the lower posterior (LP, 27.7%) and the distal edge (DE, 18.7%). The anterior sectors showed low frequencies (<2%) (Figure 4b). Among the most frequent combinations were UP + LP (44.6%), DE + UP + LP (26.6%), and DE + UP (21.2%) (Figure 4c).
Eleven morphological categories of DEMs were distinguished (Table 1). The most frequent were Rounded (R, 36.8%), Irregular (I, 12.3%), In a chain (C, 10.7%), and L-shaped/hook (L, 10.3%). Square (S, 9.1%), Triangular (T, 8.2%), and Elongated (E, 8.0%) showed similar proportions. Parallel (P, 2.3%), Apical cut (A, 1.0%), Deformations (D, 1.0%), and Mutilations (M, 0.3%) were uncommon (Figure 5). Seven individuals with mutilations were recorded: two with total amputations, two with partial amputations, and three with partial amputations accompanied by bending or collapse of the fin. Rounded and irregular DEM shapes were the most frequent, indicating the coexistence of lesions possibly derived from natural social interactions and from anthropogenic sources (e.g., fishing gear, vessel propellers).
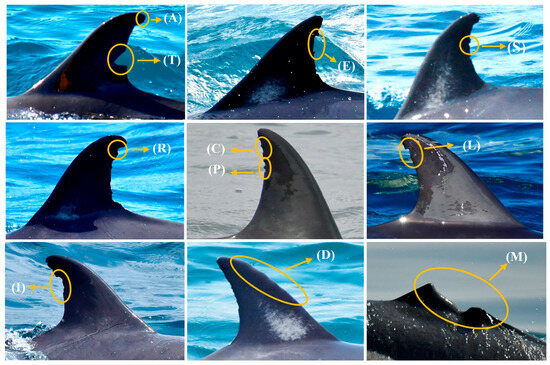
Figure 5.
Representative dorsal fins of D. delphis illustrating the 11 DEMs shape categories used in this study: Triangular (T), Square (S), Elongated (E), Rounded (R), Parallel (P), In a chain (C), L-shaped/hook-shaped (L), Irregular (I), Apical cut (A), Deformations (D) and Mutilations (M).
In terms of the number of DEMs per individual, the 3–5 class predominated (61.8%), followed by 1 (15.7%), 2 (12.1%), 6–10 (10.0%), and >10 (0.4%). Regarding size, the values corresponded to vs. (32.4%), S (38.7%), M (23.2%), L (5.3%), and VL (0.4%).
Although the general morphology of the dorsal fin and the presence of the white patch do not constitute primary photo-identification characters, they were systematically recorded in this study due to their comparative interest and potential value as complementary diagnostic traits, particularly in individuals with few permanent marks. Their inclusion in this section allows the morphological and pigmentation variability of the population to be described in an integrated manner alongside lesion patterns.
With respect to the general morphology of the dorsal fin (n = 1350), the shape was straight/triangular (ST) in 24.5%, falcate (F) in 67.9%, and highly falcate (HF) in 7.6% (Figure 6a–c). The distal tip was classified mainly as intermediate (IDE, 82.9%), followed by rounded (RDE, 11.0%) and pointed (PDE, 6.1%) (Figure 6d–f).

Figure 6.
(a–c) Different dorsal fin shapes: straight/triangular (ST), falcate (F), and highly falcate (HF); (d) pointed distal tip, (e) intermediate, and (f) rounded; (g–l) Dorsal fin colouration patterns: (g) fin without a white patch, (h–l) fins with a diffuse or mixed white patch and progressively greater coverage.
The presence of a dorsal white patch was assessed in 1163 individuals. In some cases, image darkness or the presence of mutilations prevented full observation. Of the individuals evaluated, 916 (78.8%) displayed a patch and 247 (21.2%) did not. Among those with a patch (n = 913 with measurable coverage), the most frequent ranges were 1–25% (46.0%) and 26–50% (34.2%), followed by 51–75% (15.0%) and 76–100% (4.8%). Regarding intensity (n = 915), the high category predominated (57.8%), followed by medium (30.8%) and low (11.4%). The type of patch was classified as mixed (38.8%), compact (36.3%), or diffuse (24.9%) (Figure 6g–l).
3.3. Relationship Between Dorsal Damage and Recapture Frequency (FR)
Recapture frequency (FR), expressed as the number of days on which an individual was detected, varied according to the degree of dorsal damage.
First, FR differed significantly with the number of lacerated sectors (1, 2, ≥3) (Kruskal–Wallis H = 33.04, df = 2, n = 1342, p = 6.70 × 10−8, ε2 = 0.023). Multiple comparisons indicated differences between individuals with ≥ 3 sectors and those with 1 or 2 sectors, but not between 1 and 2 (Figure 7a).
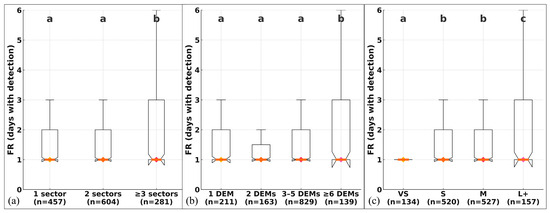
Figure 7.
Recapture frequency (FR; days with detection) according to (a) number of affected sectors, (b) number of DEMs per individual, and (c) dominant lesion size. Boxes show the interquartile range (IQR); the central line and diamond indicate the median; whiskers extend to 1.5 × IQR. Different letters indicate significant pairwise differences after Holm adjustment. Sample sizes (n) are shown below each category. Kruskal–Wallis tests (see Results Section 3.3) confirmed significant effects in all comparisons (p < 0.001).
Differences were also observed according to the total number of DEMs per individual (1, 2, 3–5, ≥6) (H = 23.12, df = 3, n = 1342, p = 3.81 × 10−5, ε2 = 0.015). Individuals with ≥6 DEMs showed higher FR values than those with 1, 2, or 3–5 DEMs (Figure 7b).
Finally, FR varied according to the dominant size of the marks (VS, S, M, L+) (H = 31.27, df = 3, n = 1338, p = 7.46 × 10−7, ε2 = 0.021). The L+ group showed higher FR than VS, S, and M, whereas S and M did not differ significantly from each other (Figure 7c).
3.4. Correlations and Severity Indicators (FR)
FR was positively correlated (small effect size) with the number of sectors (Spearman ρ = 0.135, p= 6.74 × 10−7) and with the number of DEMs (ρ = 0.100, p = 2.54 × 10−4).
Of the individuals with FR available (n = 1357), 157 (11.6%) presented at least one large lesion (L+). FR differed between L+ present/absent (Mann–Whitney U = 108,827, p = 1.72 × 10−4); the median was 1.0 in both groups (IQR: L+ = 2.0; non-L+ = 1.0) (Supplementary Material, Figure S2). The heterogeneity of lesion sizes (range > 0) was observed in 964 individuals (71.0%), showing a positive correlation with FR (ρ = 0.101, p = 2.26 × 10−4, N = 1338).
Dorsal fin shape (ST/F/HF) showed significant differences (H = 25.54, df = 2, n = 1349, p = 2.85 × 10−6, ε2 = 0.017), with ST ≠ F (p_adjusted = 2.0 × 10−6); HF did not differ from the other categories (p_adjusted ≥ 0.10) (Figure 8a). Distal tip (PDE/RDE/IDE) showed no differences (H = 0.11, p = 0.945) (Figure 8b).
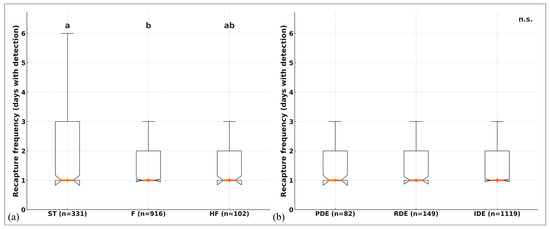
Figure 8.
(a) Recapture frequency (FR; days with detection) by dorsal-fin shape (ST, F, HF). Different letters indicate significant pairwise differences after Holm adjustment (ST ≠ F; HF not different). (b) FR by distal tip shape (PDE, RDE, IDE), n.s. Boxes show the IQR; the central line and diamond mark the median; whiskers = 1.5 × IQR. Sample sizes (n) are shown below each category. Kruskal–Wallis tests (see Results Section 3.4) showed a significant effect of fin shape (p < 0.001) but not of distal termination (p = 0.945).
3.5. Secondary Traits for Confirming Individual Identifications
Secondary traits were recorded in a substantial number of catalogue individuals. Overall, 48.8% of individuals exhibited visible rake marks. Among these, the distribution was: WR (white rakes) = 50.7%, BR (black rakes) = 9.7%, and WR + BR = 39.6%. Rake marks are often observed on various parts of the body, including but not limited to the dorsal fin; however, their visibility in dorsal fin images may be compromised when photographic quality is poor, lighting is suboptimal, or the fin is not fully visible.
The presence of X. globicipitis was detected in 22.6% of the evaluated individuals. In some cases, barnacles observed at first capture disappeared in subsequent recaptures, whereas in others new infestations were documented. In this population, the detection of this epibiont represents not only an additional trait for photo-identification but also a potential indicator of individual condition and local environmental pressures.
In addition, annular skin lesions consistent with tattoo skin disease (TSD) were recorded in 0.1% of individuals, and diffuse orange or yellowish patches, consistent with diatom colonisation, in 0.3% of the catalogue. Representative examples of these secondary traits are shown in Figure 9.
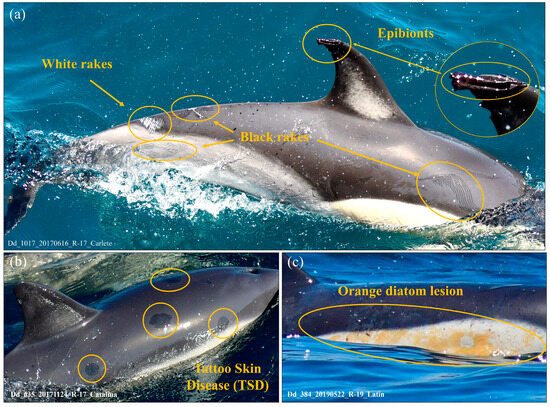
Figure 9.
Lesions and parasites in photo-identified individuals in the BA-G. (a) Rake mark lesions (white and black) and presence of the epibiont Xenobalanus globicipitis on the tip of the dorsal fin (close-up inset); (b) lesions consistent with tattoo skin disease (TSD); and (c) orange patches consistent with diatom colonisation.
4. Discussion
4.1. Catalogue and Relevance of the Study
To our knowledge, no photo-identification catalogue of D. delphis has previously been published for the BA-G. Although [18] described patterns of dorsal lesions in the species within this area, no catalogue with longitudinal tracking of individuals was produced. The present study therefore provides the first structured catalogue of the species in the region, based on three years of sampling. This catalogue represents a robust reference for long-term population monitoring and the evaluation of anthropogenic impacts, while also offering a solid foundation for management and conservation in the western Mediterranean.
Photo-identification of D. delphis is particularly challenging due to its smaller body size, fast movements, the low detectability of many dorsal marks, and the high proportion of individuals lacking permanent features [11,12,15]. Our results confirm this difficulty: more than half of the individuals in the catalogue were detected on a single occasion, which limits recaptures and the application of capture–recapture techniques for population estimates. This pattern may reflect both the mobility of dolphins—moving between the bay, the Alboran Sea, and the Strait of Gibraltar—and the difficulty of re-identifying poorly marked individuals. However, unlike in other regions where scarce marking has hindered catalogue construction, in this environment the strong anthropogenic pressure appears to have increased the prevalence of permanent marks, enabling the development of a robust catalogue of more than one thousand individuals.
This finding makes the area a unique case: the population’s vulnerability paradoxically translates into greater detectability, with methodological implications that may be extrapolated to similar contexts worldwide. Although D. delphis inhabits both open-ocean environments [74] and neritic coastal waters [75,76,77] and is typically associated with regions of high productivity and complex bathymetry [78,79], its regular presence in urbanised coastal areas has rarely been reported [19,80]. In our study, the repeated detection of identified individuals, together with the presence of a 450 m deep submarine canyon and high local productivity, suggests that these oceanographic features attract dolphins from the Strait of Gibraltar and the Alboran Sea, fostering site fidelity to the BA-G. These results are consistent with observations from other Mediterranean regions, where D. delphis also shows recurrent use of productive coastal areas under intense human activity [18,34]. The detection histories of the most frequently re-sighted individuals (Figure 2; Table S3) show that some dolphins were encountered in multiple months across the three consecutive years of monitoring. While these records point to potential seasonal patterns in bay use, they should be interpreted cautiously, as they may also reflect differences in sampling effort or environmental variability affecting detectability. Even so, the consistent re-sightings of certain individuals reinforce the evidence for spatial fidelity and highlight the value of re-sightings as a tool to explore both site use and possible seasonality. Despite these challenges, the species’ consistent occurrence in the bay throughout the year is confirmed, including its use as a breeding area [35,47,81]. This continued use fits into a wider context: photo-identification studies have shown that D. delphis can travel long distances within the Mediterranean, up to ~1000 km [80], while genetic analyses have revealed connectivity with north-eastern Atlantic populations, with gene flow across the Strait of Gibraltar [82,83]. Moreover, the importance of the Alboran Sea and the Strait as high-density areas essential for the conservation of the species has been emphasised [84,85].
Methodological consistency with other regional programmes supports comparability. Our photo-identification criteria and lesion-coding align with established efforts to monitor D. delphis in the eastern Ionian Sea [16], population studies from the Alboran Sea [84], and the multi-season Hauraki Gulf programme based on dorsal fin photo-identification [20]. Together, these parallels provide a coherent framework for assessing regional patterns of injury and site fidelity across different Mediterranean contexts.
In this context, the catalogue presented here not only expands knowledge of D. delphis in the western Mediterranean but also provides an essential tool for the temporal monitoring of anthropogenic interactions and the identification of critical management areas in the bay and its surroundings. In addition, the conservative classification of adults accompanied by calves as “putative mother–calf pairs” enables progress in the analysis of social bonds and association patterns without compromising methodological rigour, given the impossibility of confirming the sex of individuals under field conditions [11,86]. Beyond its regional scope, this catalogue offers a systematic and comprehensive reference for the species that can serve as a methodological model for photo-identification initiatives of D. delphis across its global distribution.
4.2. Dorsal Fin Features
Dorsal injuries were concentrated mainly along the trailing edge of the fin, particularly in the upper and lower posterior sectors (UP + LP), often in combination with the distal edge (DE). This pattern, previously reported in D. delphis from the bay [18], can be explained by anatomical factors: the leading edge is thicker and structurally reinforced, whereas the trailing edge is thinner and more flexible, making it more prone to cuts and tears [87,88,89]. This structural vulnerability, combined with exposure to recreational fishing gear, appears to underlie the observed patterns. In particular, the popping technique (a surface-casting method commonly used in sport fishing) is frequently employed in the area; this method involves surface lures towed from the stern of vessels in association with tuna and cetaceans, thereby increasing the likelihood of accidental contact with hooks and lines [47,81]. Injuries such as dorsal cuts, partial amputations, and structural irregularities have been linked to interactions with fishing gear in various small cetacean populations [34,61,62,67], consistent with the DEM patterns recorded in the area (Table 1).
The DEMs recorded showed a wide diversity, with rounded and irregular shapes, and small to medium-sized marks predominating. This pattern is consistent with descriptions from other populations of D. delphis and T. truncatus [18,21] and can be explained by the progressive regeneration of tissue, which masks larger injuries and favours repeated processes of interaction and healing [90].
Although dorsal fin shape does not constitute a primary photo-identification trait, its analysis provides valuable comparative ecological information. In T. truncatus, for example, the degree of fin curvature distinguishes between coastal and pelagic ecotypes [57]. In the BA-G, the oceanographic configuration—determined by the submarine canyon described in the Methods and the presence of shallow areas along its margins— creates a unique habitat gradient that combines coastal and oceanic features within a reduced space. This structure, together with the proximity of the Strait of Gibraltar and the Alboran Sea, makes it plausible that individuals with different habitat-use patterns coexist. Although this hypothesis cannot be directly tested from dorsal morphology alone and would require complementary studies (e.g., comparative photo-identification between areas, genetics, or stable isotopes), including this trait in the catalogue provides added value as a potentially informative variable for exploring intraspecific variation in D. delphis.
The dorsal white patch, in addition to its high frequency in the local population, has been described as a characteristic feature of D. delphis in different regions, showing considerable variability in both extent and intensity [11,91]. Although initially regarded as a secondary trait, several studies have demonstrated its temporal stability for more than a decade [20], reinforcing its value as a supportive marker for individual identification [19]. In previous catalogues, it has been used as a secondary trait and, in poorly marked populations, even as a diagnostic feature [15,20,21,49]. Moreover, the comparison of both flanks, as applied in this study, helps reduce matching errors and increases the number of recognisable individuals [11,49]. Thus, the systematic evaluation of the white patch in our catalogue provides a standardised framework to assess its diagnostic utility in populations subject to long-term monitoring.
The higher FR observed in individuals with more or larger dorsal lesions may reflect both biological and methodological factors. Dolphins with greater exposure to human activities may spend more time within the bay, leading to higher detectability. However, individuals with distinctive or severe marks are also easier to recognise in photo-identification, which could slightly inflate their apparent resighting frequency.
4.3. Lesion Causation and Secondary Traits
The diversity of dorsal edge marks recorded in this catalogue supports a dual origin involving natural social interactions [92,93,94] and anthropogenic impacts, particularly from vessels and fishing gear [18,33,34,35,47]. This pattern highlights the need to mitigate human-induced injuries in the BA-G population.
In addition to their diagnostic value, skin marks and epibionts can provide information on the health status of cetaceans and their exposure to environmental and anthropogenic pressures. The extent and intensity of epidermal lesions reflect the interaction of natural and human-driven factors in different populations [23,95,96,97]. Comparable injury distributions and causal mechanisms have been documented in D. delphis and other coastal odontocetes from areas with heavy maritime traffic, where trailing-edge fin tissues are particularly prone to lacerations associated with fishing gear and vessel interactions [34,61,62]. In this regard, the systematic recording of rake marks, epibionts, pigmentation patches, and lesions compatible with tattoo skin disease (TSD) in the BA-G contributes not only to individual identification but also to the detection of long-term environmental change and anthropogenic pressure.
The frequent detection of X. globicipitis reinforces this potential: this epibiotic barnacle, exclusive to cetaceans and with an almost cosmopolitan distribution, attaches to body areas exposed to turbulence and has been proposed as a bioindicator of host physiological condition [38,39,40,41].
Taken together, the incorporation of these secondary traits into longitudinal catalogues not only increases the diagnostic capacity of photo-identification but also broadens its utility as an integrated tool for population monitoring and conservation.
The effective sample size reflects the number of individuals that could be reliably photo-identified from all photographs collected during 2017–2020, according to strict inclusion criteria (adults only; PQ1–PQ3; DC1–DC2). These criteria prioritised diagnostic reliability over quantity, providing a consistent basis for the analyses. While the results of this study apply specifically to D. delphis in the BA-G, the relative patterns observed (such as sectoral distribution, lesion typologies, and the relationship between FR and damage) are consistent and provide valuable comparative insights for other populations of the species.
As in other photo-identification studies, the approach applied here is limited by potential matching errors and low recapture rates, yet the strict quality control ensures a reliable baseline for future monitoring and genetic connectivity assessments [45,98].
Recent advances in automated image-recognition algorithms, such as deep-learning architecture (e.g., YOLOv8, FinFindR), are emerging as promising tools to support photo-identification workflows. Their integration in future cataloguing efforts could enhance matching accuracy and processing efficiency, particularly in large datasets such as the present one.
4.4. Conservation Implications
The BA-G functions as a critical area for D. delphis, as demonstrated by the recurrent observation of feeding behaviour, breeding activity, and putative mother–calf pairs [46,47,81]. The high frequency and diversity of dorsal injuries, together with the appearance of new marks in resighted individuals, provide clear evidence of ongoing anthropogenic pressures [35,47,81]. The main threats include commercial and recreational vessel traffic, incidental interactions with fishing gear, and increasing nautical tourism, all identified as stressors for small cetaceans in other regions [99,100,101]. In the Mediterranean, the intensification of recreational traffic has been recognised as an emerging driver of ecological disturbance [102].
Climate change further compounds these impacts: projected shifts in the distribution of sardine, anchovy, and mackerel [103,104] are already linked to the latitudinal expansion of D. delphis [105]. Together, these factors highlight the vulnerability of the local population and the importance of considering both present and future pressures in conservation planning.
In this context, targeted management actions are recommended, including stricter regulation of maritime traffic in core areas, enforcement of fishing gear controls to reduce bycatch and entanglement risk, and the potential establishment of micro-sanctuaries or temporary exclusion zones during key breeding periods. These measures would help mitigate the cumulative impacts of human activities and support the long-term conservation of this endangered subpopulation.
5. Conclusions
This study provides the first structured catalogue of D. delphis in the BA-G, offering an innovative framework that combines dorsal fin lesion coding with recapture records. Although photo-identification of this species presents inherent challenges, the rigorous quality protocols applied support the reliability of the dataset and ensure its value as a baseline for future monitoring. The catalogue can be expanded through longer time series, the incorporation of computer-assisted tools, and complementary methods such as genetic analyses, thereby strengthening its role as a methodological model applicable beyond the study area.
From a conservation perspective, the BA-G is confirmed as a critical habitat for D. delphis. The prevalence of dorsal injuries, the recurrent detection of putative mother–calf pairs, and the appearance of new marks in resighted individuals reveal the intensity of anthropogenic pressures. Based on the lesion typologies documented in this catalogue, the most frequent dorsal-fin injuries in D. delphis from the BA-G are primarily associated with propellers and recreational fishing lines, while the most severe cases, including mutilations and deformities, are consistent with interactions with trawl gear. These patterns support targeted local management, including stricter control of trawling in core use areas and speed and approach limits for vessels operating near dolphin groups, to mitigate human-induced injuries.
These findings emphasise the urgent need for targeted management actions and the integration of climate change scenarios into conservation planning to protect this endangered species. The methodological framework developed here (combining lesion typology, individual photo-identification, and temporal monitoring) provides a transferable approach that can be applied to other D. delphis populations or similar species, supporting standardised assessments of injury patterns and anthropogenic pressures across regions.
This work lays the foundation for a regional photo-identification network integrating multiple Mediterranean sites, strengthening collaborative efforts for the monitoring and protection of D. delphis across its range.
Future studies could build on this framework by incorporating complementary genetic, behavioural, and environmental data to better assess connectivity, resilience, and long-term population dynamics.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/environments12110406/s1. Table S1. Details of the folders deposited in the institutional Zenodo repository, including their contents and number of photographs. Table S2. Total number of photographs taken, discarded, suitable, and used for photo-identification of individuals by year of study. Table S3. Monthly recaptures during the study period of the individuals shown in Figure 2. Table S4. Monthly records of putative mother–calf pairs shown in Figure 3, indicating the months in which adults were photographed with calves. Figure S1. Distribution of captures/recaptures categories. Figure S2. Distribution of recapture frequency (FR, number of days with detection) according to the presence of at least one large lesion (L+ yes/no). Median and IQR are shown; sample size is indicated under each box. Figure S3. Pairs of mothers (putative) and offspring not identified due to lack of distinctive characteristics.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.O.-P. and R.E.; methodology, L.O.-P. and R.E.; formal analysis, L.O.-P. and J.C.G.-G.; investigation, L.O.-P., R.E. and E.M.; data curation, L.O.-P.; writing—original draft preparation, L.O.-P. and J.C.G.-G.; writing—review and editing, L.O.-P., J.C.G.-G. and R.E.; funding acquisition, J.C.G.-G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Spanish legislation (Real Decreto 1727/2007) and the Marine Regulations 2014 of Gibraltar and was approved by the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee of the Ministry of Education, Heritage, Environment, Energy and Climate Change of Gibraltar. All observations were strictly non-invasive and did not involve capture, handling, or disturbance of dolphins.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. Access has been temporarily restricted because the files, owing to their volume, have been deposited in the Zenodo repository under restricted access and will not be made public until the final acceptance of the manuscript, in order to avoid premature dissemination. The dataset is available in Zenodo (DOIs: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17183966; https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17186724), and any request for access will be promptly authorised.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dolphin Adventure for the donation of their platforms, which made this project possible. We also thank Álvaro García Olaya for his support in developing database verification scripts. This work was supported by projects funded by the Fundación para la Investigación de la Universidad de Sevilla (FIUS), with additional support from the Port Authority of the Bay of Algeciras (APBA), Fundación CEPSA (now MOEVE), Red Eléctrica de España (REE), ACERINOX, the Provincial Council of Cádiz and the Marina of La Alcaidesa. We would also like to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions, which have contributed to improving the quality and clarity of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BA-G | Bay of Algeciras–Gibraltar |
| DEMs | Dorsal Edge Marks |
| PQ | Photographic quality |
| DC | Distinctive Character |
References
- Würsig, B.; Jefferson, T.A. Methods of photo-identification for small cetaceans. Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. Spec. Issue 1990, 12, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, B.; Thompson, P.M.; Hammond, P.S. Skin lesions and physical deformities in bottlenose dolphins in the Moray Firth: Population prevalence and age-sex differences. Ambio 1997, 26, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- Urian, K.; Gorgone, A.; Read, A.; Balmer, B.; Wells, R.S.; Berggren, P.; Durban, J.; Eguchi, T.; Rayment, W.; Hammond, P.S. Recommendations for photo-identification methods used in capture-recapture models with cetaceans. Mar. Mammal. Sci. 2015, 31, 298–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würsig, B.; Würsig, M. The photographic determination of group size, composition, and stability of coastal porpoises (Tursiops truncatus). Science 1977, 198, 755–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, P.S.; Mizroch, S.A.; Donovan, G.P. Individual recognition of cetaceans: Use of photo-identification and other techniques to estimate population parameters. Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. Spec. Issue 1990, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Hupman, K.E.; Pawley, M.D.M.; Lea, C.; Grimes, C.; Voswinkel, S.; Roe, W.D.; Stockin, K.A. Viability of photo-identification as a tool to examine the prevalence of lesions on free-ranging common dolphins (Delphinus sp.). Aquat. Mamm. 2017, 43, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczmarski, L.; Chan, S.C.; Rubenstein, D.I.; Chui, S.Y.; Cameron, E.Z. Individual identification and photographic techniques in mammalian ecological and behavioural research—Part 1: Methods and concepts. Mamm. Biol. 2022, 102, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichell, L.M.V.; Krzyszczyk, E.; Patterson, E.M.; Mann, J. The reliability of pigment pattern-based identification of wild bottlenose dolphins. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2018, 34, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmer, B.C.; Wells, R.S.; Nowacek, S.M.; Nowacek, D.P.; Schwacke, L.H.; McLellan, W.A.; Scharf, F.S.; Rowles, T.K.; Hansen, L.J.; Spradlin, T.R.; et al. Seasonal abundance and distribution patterns of common bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) near St. Joseph Bay, Florida, USA. J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 2008, 10, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrow, S.; O’Brien, J.; Groth, L.; Foley, A.; Voigt, K. Abundance Estimate of Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Lower River Shannon Candidate Special Area of Conservation, Ireland. Aquat. Mamm. 2012, 38, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, D.R.; Leitenberger, A.; Orams, M.B. Photo-identification of short-beaked common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) in north-east New Zealand: A photo-catalogue of recognisable individuals. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 36, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stockin, K.A.; Vella, A. Anomalous pigmentation in common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) from New Zealand waters. Aquat. Mamm. 2005, 31, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, A.; Hupman, K.; Stockin, K.A.; Pawley, M.D. Computer-assisted recognition of dolphin individuals using dorsal fin pigmentations. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Image and Vision Computing New Zealand (IVCNZ), Palmerston North, New Zealand, 28–29 November 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupman, K.; Stockin, K.A.; Pollock, K.; Pawley, M.D.; Dwyer, S.L.; Lea, C.; Tezanos-Pinto, G. Challenges of implementing mark-recapture studies on poorly marked gregarious delphinids. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliser, C.R.; van der Linde, K.; MacIver, K. Adapting photo-identification methods to study poorly marked cetaceans: A case study for common dolphins and harbor porpoises. Mamm. Biol. 2022, 102, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearzi, G.; Politi, E.; Agazzi, S.; Bruno, S.; Costa, M.; Bonizzoni, S. Occurrence and present status of coastal dolphins (Delphinus delphis and Tursiops truncatus) in the eastern Ionian Sea. Aquat. Conserv. 2005, 15, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearzi, G.; Bonizzoni, S.; Gonzalvo, J. Striped dolphins and short-beaked common dolphins in the Gulf of Corinth, Greece: Abundance estimates from dorsal fin photographs. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2011, 91, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamford, C.C.G.; Robinson, K.P. An analysis of dorsal edge markings in short-beaked common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) from the Bay of Gibraltar and the Moray Firth. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2016, 96, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.; Salgado Kent, C.; Donnelly, D.; Weir, J.; Bilgmann, K. Atypical residency of short-beaked common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) to a shallow, urbanized embayment in south-eastern Australia. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 160478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawley, M.D.; Hupman, K.E.; Stockin, K.A.; Dwyer, S.L.; Lea, C.; Tezanos-Pinto, G. Photo-identification of common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) in the Hauraki Gulf, New Zealand. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 52, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawley, M.D.M.; Hupman, K.E.; Stockin, K.A.; Gilman, A. Examining the viability of dorsal fin pigmentation for individual identification of poorly-marked delphinids. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihova, M.; Araújo, J.; Oliveira-Rodrigues, C.; Afonso, L.; Gil, Á.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; Correia, A.M. First Photo-ID Catalogue of Gregarious Oceanic Dolphins in the Northern Coast of Continental Portugal: Delphinus delphis and Tursiops truncatus; Internal Report; CIIMAR—Interdisciplinary Centre of Marine and Environmental Research: Porto, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, B.; Arnold, H.; Bearzi, G.; Fortuna, C.M.; Gaspar, R.; Ingram, S.; Berrow, S.; Tregenza, N.; Hammond, P.S.; Thompson, D. Auger-Méthé Epidermal diseases in bottlenose dolphins: Impacts of natural and anthropogenic factors. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1999, 266, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.; Ballardini, M.; Moulins, A.; Wurtz, M. Natural markings of Mediterranean bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus): Stability and implications for photo-identification studies. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2011, 91, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertulli, C.G.; Rasmussen, M.H.; Rosso, M. An assessment of the natural marking patterns used for photo-identification of common minke whales and white-beaked dolphins in Icelandic waters. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K. 2016, 96, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, R.; Bas, A.A.; Maglietta, R.; Renò, V.; Fanizza, C.; Rizzo, A.; Cipriano, G. Site fidelity, residency and habitat use of the Risso’s dolphin (Grampus griseus) in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-eastern Mediterranean Sea) by photo-identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea: Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Naples, Italy, 8–10 October 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Maglietta, R.; Bruno, A.; Renò, V.; Dimauro, G.; Stella, E.; Fanizza, C.; Carlucci, R. The promise of machine learning in the Risso’s dolphin (Grampus griseus) photo-identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea: Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Naples, Italy, 8–10 October 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, C.A.; Mayo, C.A.; Whitehead, H. Changes in the ventral fluke pattern of the humpback whale (Megaptera novaeangliae), and its effect on matching; evaluation of its significance to photo-identification research. Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. Spec. Issue 1990, 12, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, W.; Franklin, T.; Brooks, L.; Harrison, P.; Baverstock, P. Photo-identification of individual humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae) using all available natural marks: Implications for misidentification and automated algorithm matching technology. J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 2020, 21, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, I.N. Prolific body scars and collapsing dorsal fins on killer whales (Orcinus orca) in New Zealand waters. Aquat. Mamm. 1998, 24, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, R.W.; Gorgone, A.M. False killer whale dorsal fin disfigurements as a possible indicator of long-line fishery interactions in Hawaiian waters. Pac. Sci. 2005, 59, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, F.; Towers, J.R.; Baird, R.W.; Bearzi, G.; Bonizzoni, S.; Ferreira, R.; Halicka, Z.; Alessandrini, A.; Kopelman, A.H.; Yzoard, C.; et al. The incidence of bent dorsal fins in free-ranging cetaceans. J. Anat. 2018, 232, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, S.L.; Kozmian-Ledward, L.; Stockin, K.A. Short-term survival of severe propeller strike injuries and observations on wound progression in a bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 48, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luksenburg, J.A. Prevalence of External Injuries in Small Cetaceans in Aruban Waters, Southern Caribbean. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaya-Ponzone, L.; Espada-Ruiz, R.; Martín-Moreno, E.; Cárdenas-Marcial, I.; García-Gómez, J.C. Injuries, healing and management of common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) in human-impacted waters in the south Iberian Peninsula. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2020, 100, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwin, C. A Monograph on the Sub-Class Cirripedia: With Figures of All the Species; Ray Society: London, UK, 1854; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kane, E.A.; Olson, P.A.; Gerrodette, T.; Fiedler, P.C. Prevalence of the commensal barnacle Xenobalanus globicipitis on cetacean species in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean, and a review of global occurrence. Fish. Bull. 2008, 106, 395. [Google Scholar]
- Ten, S.; Fusar Poli, F.; Konishi, K.; Pastene, L.A.; Martín, V.; Raga, J.A.; Aznar, F.J. The epibiont Xenobalanus globicipitis indicates differences in swimming kinematics among cetaceans. Mar. Biol. 2025, 172, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Colom, P.; Ten, S.; Raga, J.A.; Aznar, F.J. Spatial distribution and aggregation of Xenobalanus globicipitis on the flukes of striped dolphins, Stenella coeruleoalba: An indicator of host hydrodynamics? Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2020, 36, 897–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezal, M.M.; Foroughirad, V.; Fish, F.E.; Jacoby, A.M.; Collier, M.A.; Murphy, C.J.; Mann, J. Some like it hot: Temperature and hydrodynamic factors influence Xenobalanus globicipitis attachment to cetaceans. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2023, 39, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, F.J.; Perdiguero, D.; Del Olmo, A.P.; Repullés, A.; Agustí, C.; Raga, J.A. Changes in epizoic crustacean infestations during cetacean die-offs: The mass mortality of Mediterranean striped dolphins Stenella coeruleoalba revisited. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005, 67, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearzi, G.; Reeves, R.R.; Notarbartolo di Sciara, G.; Politi, E.; Cañadas, A.; Frantzis, A.; Mussi, B. Ecology, status and conservation of short-beaked common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) in the Mediterranean Sea. Mammal. Rev. 2003, 33, 224–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, D.S.; Mussi, B.; Vella, J.G.; Vella, A. Conservation and Research Status of Mediterranean Delphinus delphis. Aquat. Conserv. 2021, 31 (Suppl. 1), 1–166. [Google Scholar]
- Bearzi, G. Delphinus delphis (Mediterranean subpopulation). In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2003: E.T41762A10556361; International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN): Gland, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Natoli, A.; Cañadas, A.; Vaquero, C.; Politi, E.; Fernandez-Navarro, P.; Hoelzel, A.R. Conservation Genetics of the Short-Beaked Common Dolphin (Delphinus delphis) in the Mediterranean Sea and in the Eastern North Atlantic Ocean. Conserv. Genet. 2008, 9, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, J.; Gauffier, P.; Verborgh, P.; Esteban, R.; Jiménez-Torres, C.; De Stephanis, R. The Bay of Algeciras: A Feeding and Breeding Ground for Common Dolphins? In Proceedings of the 25th Conference of the European Cetacean Society, Cádiz, Spain, 21–23 March 2011; Long-Term Datasets on Marine Mammals: Learning from the Past to Manage the Future. Gauffier, P., Verborgh, P., Eds.; TIDAC: Cádiz, Spain, 2011; p. 150. [Google Scholar]
- Olaya-Ponzone, L.; Ruíz, R.E.; Domínguez, D.P.; Moreno, E.M.; Marcial, I.C.; Santiago, J.S.; García-Gómez, J.C. Sport fishing and vessel pressure on the endangered cetacean Delphinus delphis. Towards an international agreement of micro-sanctuary for its conservation. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammartino, S.; Lafuente, J.G.; Garrido, J.S.; De los Santos, F.J.; Fanjul, E.Á.; Naranjo, C.; Calero, C. A numerical model analysis of the tidal flows in the Bay of Algeciras, Strait of Gibraltar. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 72, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearzi, G.; Agazzi, S.; Gonzalvo, J.; Costa, M.; Bonizzoni, S.; Politi, E.; Piroddi, C.; Reeves, R.R. Overfishing and the disappearance of short-beaked common dolphins from western Greece. Endang. Species Res. 2008, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, K.; Bejder, L.; Allen, S.J.; Krützen, M.; Pollock, K.H. Abundance, survival and temporary emigration of bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops sp.) of Useless Loop in the western Gulf of Shark Bay, Western Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 63, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyne, J.A.; Pollock, K.H.; Johnston, D.W.; Bejder, L. Abundance and survival rates of the Hawai’i Island associated spinner dolphin (Stenella longirostris) stock. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friday, N.A.; Smith, T.D.; Stevick, P.T.; Allen, J.; Fernald, T. Measurement of photographic quality and individual distinctiveness for the photographic identification of humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae). Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2000, 16, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, A.F.; Kritzler, H. Observations on pregnancy, parturition, and postnatal behavior in the bottlenose dolphin. J. Mammal. 1951, 32, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockcroft, V.G.; Ross, G.J.B. Observations on the early development of a captive bottlenose dolphin calf. In The Bottlenose Dolphin; Leatherwood, S., Reeves, R.R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 461–478. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, S.D.; Dawson, S.M.; Rayment, W.; Currey, R.J.C.; Slooten, E. Reproduction, Birth Seasonality, and Calf Survival of Bottlenose Dolphins in Doubtful Sound, New Zealand. Mar. Mammal. Sci. 2014, 30, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methion, S.; Díaz López, B. Spatial segregation and interspecific killing of common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) by bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Acta Ethol. 2021, 24, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, F.; Van Waerebeek, K.; Sanino, G.P.; Castro, C.; Van Bressem, M.-F.; Santillán, L. Variation in dorsal fin morphology in common bottlenose dolphin Tursiops truncatus (Cetacea: Delphinidae) populations from the Southeast Pacific Ocean. Pac. Sci. 2018, 72, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Smuts, B.B. Behavioral development in wild bottlenose dolphin newborns (Tursiops sp.). Behaviour 1999, 136, 529–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grellier, K.; Hammond, P.S.; Wilson, B.; Sanders-Reed, C.A.; Thompson, P.M. Use of photo-identification data to quantify mother–calf association patterns in bottlenose dolphins. Can. J. Zool. 2003, 81, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noren, S.R.; Edwards, E.F. Infant position in mother–calf dolphin pairs: Formation locomotion with hydrodynamic benefits. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 424, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machernis, A.F.; Stack, S.H.; Olson, G.L.; Sullivan, F.A.; Currie, J.J. External scarring as an indicator of fisheries interactions with bottlenose (Tursiops truncatus) and pantropical spotted (Stenella attenuata) dolphins in Maui Nui, Hawai‘i. Aquat. Mamm. 2021, 47, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiszka, J.; Pelourdeau, D.; Ridoux, V. Body scars and dorsal fin disfigurements as indicators of interaction between small cetaceans and fisheries around the Mozambique Channel island of Mayotte. West. Indian Ocean J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 7, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.S.; Allen, J.B.; Hofmann, S.; Bassos-Hull, K.; Fauquier, D.A.; Barros, N.B.; Scott, M.D. Consequences of injuries on survival and reproduction of common bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) along the west coast of Florida. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2008, 24, 774–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautek, J.; Smodlaka, H.; Pleslić, G.; Bearzi, G. A proposed categorization of external injuries observed on bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Adriatic Sea. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2019, 35, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.S.; Scott, M.D. Seasonal incidence of boat strikes on bottlenose dolphins near Sarasota, Florida. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 1997, 13, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechdel, S.E.; Mazzoil, M.S.; Murdoch, M.E.; Howells, E.M.; Reif, J.S.; McCulloch, S.D.; Bossart, G.D. Prevalence and impacts of motorized vessels on bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Indian River Lagoon, Florida. Aquat. Mamm. 2009, 35, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byard, R.W.; Winskog, C.; Machado, A.; Boardman, W. The assessment of lethal propeller strike injuries in sea mammals. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2012, 19, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Waerebeek, K.; Baker, A.N.; Felix, F.; Gedamke, J.; Iniguez, M.; Sanino, G.P.; Secchi, E.; Sutaria, D.; van Helden, A.; Wang, Y. Vessel Collisions with Small Cetaceans Worldwide and with Large Whales in the Southern Hemisphere: An Initial Assessment. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Mamm. 2007, 6, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morteo, E.; Rocha-Olivares, A.; Morteo, R.; Weller, D.W. Phenotypic variation in dorsal fin morphology of coastal bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) off Mexico. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, T.A.; Curry, B.E. Common dolphins: Delphinus delphis and D. capensis. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals, 3rd ed.; Würsig, B., Thewissen, J.G.M., Kovacs, K.M., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Read, A.J.; Urian, K.W.; Wilson, B.; Waples, D.M. Abundance of bottlenose dolphins in the bays, sounds, and estuaries of North Carolina. Mar. Mammal. Sci. 2003, 19, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevick, P.T.; Palsbøll, P.J.; Smith, T.D.; Bravington, M.V.; Hammond, P.S. Errors in identification using natural markings: Rates, sources, and effects on capture-recapture estimates of abundance. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosel, P.; Mullin, K.; Garrison, L.; Schwacke, L.; Adams, J.; Balmer, B.; Zolman, E. Photo-Identification Capture-Mark-Recapture Techniques for Estimating Abundance of Bay, Sound and Estuary Populations of Bottlenose Dolphins Along the US East Coast and Gulf of Mexico: A Workshop Report; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson, T.A.; Webber, M.A.; Pitman, R.L. Marine Mammals of the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Identification; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cañadas, A.; Sagrminaga, R.; García-Tiscar, S. Distribution of Cetaceans Related to Depth and Slope in the Mediterranean Waters off Southern Spain. Deep-Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 2053–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, L.M.; Valdez, P.F.; Allen, S.; Bilgmann, K.; Corrigan, S.; Beheregaray, L.B. Fine-Scale Genetic Structure in Short-Beaked Common Dolphins (Delphinus delphis) along the East Australian Current. Mar. Biol. 2011, 158, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgmann, K.; Möller, L.M.; Harcourt, R.G.; Gales, R.; Beheregaray, L.B. Common Dolphins Subject to Fisheries Interaction in Southern Australia Display Genetic Differences: Implications for Conservation. Anim. Conserv. 2008, 11, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, C.A. Submarine Topography and Distribution of the Genus Delphinus in the Southern California Bight. J. Mammal. 1979, 60, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo, L.; Esteves, M.A.; Acevedo, R.; Silva, N.; Bolaños-Jiménez, J.; Quevedo, A.M.; Fernández, M. Abundance, Distribution and Behaviour of Common Dolphins, Delphinus spp., off Northeastern Venezuela: Implications for Conservation and Management. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2010, 90, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genov, T.; Bearzi, G.; Bonizzoni, S.; Tempesta, M. Long-Distance Movement of a Solitary Short-Beaked Common Dolphin (Delphinus delphis) in the Central Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2012, 5, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaya-Ponzone, L.; García-Gómez, J.C. Effects of Vessels on Common Dolphin Activity Patterns in a Critical Area for the Species: Conservation Implications. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 207, 107081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natoli, A.; Cañadas, A.; Peddemors, V.M.; Aguilar, A.; Vaquero, C.; Fernández-Piqueras, J.; Hoelzel, A.R. Phylogeography and alpha taxonomy of the common dolphin (Delphinus delphis) based on mitochondrial DNA and microsatellite analyses. Mar. Biol. 2006, 148, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, A.R.; Sequeira, M.; Martínez-Cedeira, J.; Coelho, M.M. New Insights on Population Genetic Structure of Delphinus delphis from the Northeast Atlantic and Phylogenetic Relationships within the Genus Inferred from Two Mitochondrial Markers. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañadas, A.; Hammond, P.S. Abundance and Habitat Preferences of the Short-Beaked Common Dolphin (Delphinus delphis) in the Southwestern Mediterranean: Implications for Conservation. Endanger. Species Res. 2008, 4, 309–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, J.; Cañadas, A.; de Stephanis, R.; Ramírez, F. Expanding Protected Areas to Encompass the Conservation of the Endangered Common Dolphin (Delphinus delphis) in the Alboran Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 168, 105305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyning, J.E.; Perrin, W.F. Evidence for Two Species of Common Dolphins (Delphinus spp.) in the Eastern North Pacific. Contrib. Sci. 1994, 442, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.G. Preliminary Observations of the Form and Function of Cetacean Dorsal Fins and Flukes. In Whales, Dolphins, and Porpoises; Norris, K.S., Ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1966; pp. 55–90. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, V.V. Wing Design and Morphology of the Harbor Porpoise Dorsal Fin. J. Morphol. 2003, 258, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meagher, E.M.; McLellan, W.A.; Westgate, A.J.; Wells, R.S.; Frierson, D., Jr.; Pabst, D.A. The Relationship between Heat Flow and Vasculature in the Dorsal Fin of Wild Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 3475–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, S.L.; Visser, I.N. Cookie Cutter Shark (Isistius sp.) Bites on Cetaceans, with Particular Reference to Killer Whales (Orcinus orca). Aquat. Mamm. 2011, 37, 111–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.N.; Evans, P.G.H.; Collet, A. Common Dolphin Delphinus delphis. In Mammals of the British Isles: Handbook, 4th ed.; Harris, S., Yalden, D.W., Eds.; The Mammal Society: Southampton, UK, 2008; pp. 719–724. [Google Scholar]
- Lockyer, C.H.; Morris, R.J. Some Observations on Wound Healing and Persistence of Scars in Tursiops truncatus. Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 1990, 12, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, E.M.; Mann, J.; Watson-Capps, J.J.; Sargeant, B.L.; Connor, R.C. Aggression in Bottlenose Dolphins: Evidence for Sexual Coercion, Male–Male Competition, and Female Tolerance through Analysis of Tooth-Rake Marks and Behaviour. Behaviour 2005, 142, 21–44. [Google Scholar]
- Marley, S.A.; Cheney, B.; Thompson, P.M. Using Tooth Rakes to Monitor Population and Sex Differences in Aggressive Behaviour in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Aquat. Mamm. 2013, 39, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettis, H.M.; Rolland, R.M.; Hamilton, P.K.; Brault, S.; Knowlton, A.R.; Kraus, S.D. Visual Health Assessment of North Atlantic Right Whales (Eubalaena glacialis) Using Photographs. Can. J. Zool. 2004, 82, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bressem, M.F.; Van Waerebeek, K.; Aznar, F.J.; Raga, J.A.; Jepson, P.D.; Duignan, P.; Siebert, U. Epidemiological Pattern of Tattoo Skin Disease: A Potential General Health Indicator for Cetaceans. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 85, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.B.; Bonanno Ferraro, G.; Boitani, L.; Blasi, M.F. Skin Marks in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) Interacting with Artisanal Fishery in the Central Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasier, T.R.; Hamilton, P.K.; Brown, M.W.; Kraus, S.D.; White, B.N. Sources and Rates of Errors in Methods of Individual Identification for North Atlantic Right Whales (Eubalaena glacialis). J. Mammal. 2009, 90, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusseau, D.; Bejder, L. The Long-Term Consequences of Short-Term Responses to Disturbance: Experiences from Whale-Watching Impact Assessment. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2007, 20, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senigaglia, V.; Christiansen, F.; Bejder, L.; Gendron, D.; Lundquist, D.; Noren, D.P.; Lusseau, D. Meta-Analyses of Whale-Watching Impact Studies: Comparisons of Cetacean Responses to Disturbance. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 542, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, M.; Guerra, M.; Brough, T.; Carome, W.; Constantine, R.; Higham, J.; Dawson, S. Looking Back to Move Forward: Lessons from Three Decades of Research and Management of Cetacean Tourism in New Zealand. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 624448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño, A.; Lloret, J. Environmental Impacts of Increasing Leisure Boating Activity in Mediterranean Coastal Waters. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 209, 105693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Serra, I.; Edwards, M.; Genner, M.J. Warming Shelf Seas Drive the Subtropicalization of European Pelagic Fish Communities. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beare, D.; Burns, F.; Jones, E.; Peach, K.; Portilla, E.; Greig, T.; Reid, D. An Increase in the Abundance of Anchovies and Sardines in the North-Western North Sea since 1995. Glob. Change Biol. 2004, 10, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaya-Ponzone, L.; Ruíz, R.E.; Domínguez, D.P.; García-Gómez, J.C. Amphiatlantic Dolphins’ Prey: Indicators of Speciation, Trophic Competition and Global Warming? A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).