Contrasting Nickel Binding Mechanisms in Water-Column and Sediment Organic Matter: The Critical Role of Molecular Size and Chemical Composition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Description and Sampling
2.2. AEOM Extraction and Size Fractionation
2.2.1. AEOM Extraction
2.2.2. Size Fractionation
2.2.3. System Cleaning Protocol
2.3. Analysis of Dissolved Organic Carbon and Metals
2.4. UV-Visible and Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.5. Calculation of Optical Indices and Nickel Binding Affinity
2.5.1. Optical Indices
2.5.2. Nickel Binding Affinity (NiBA)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
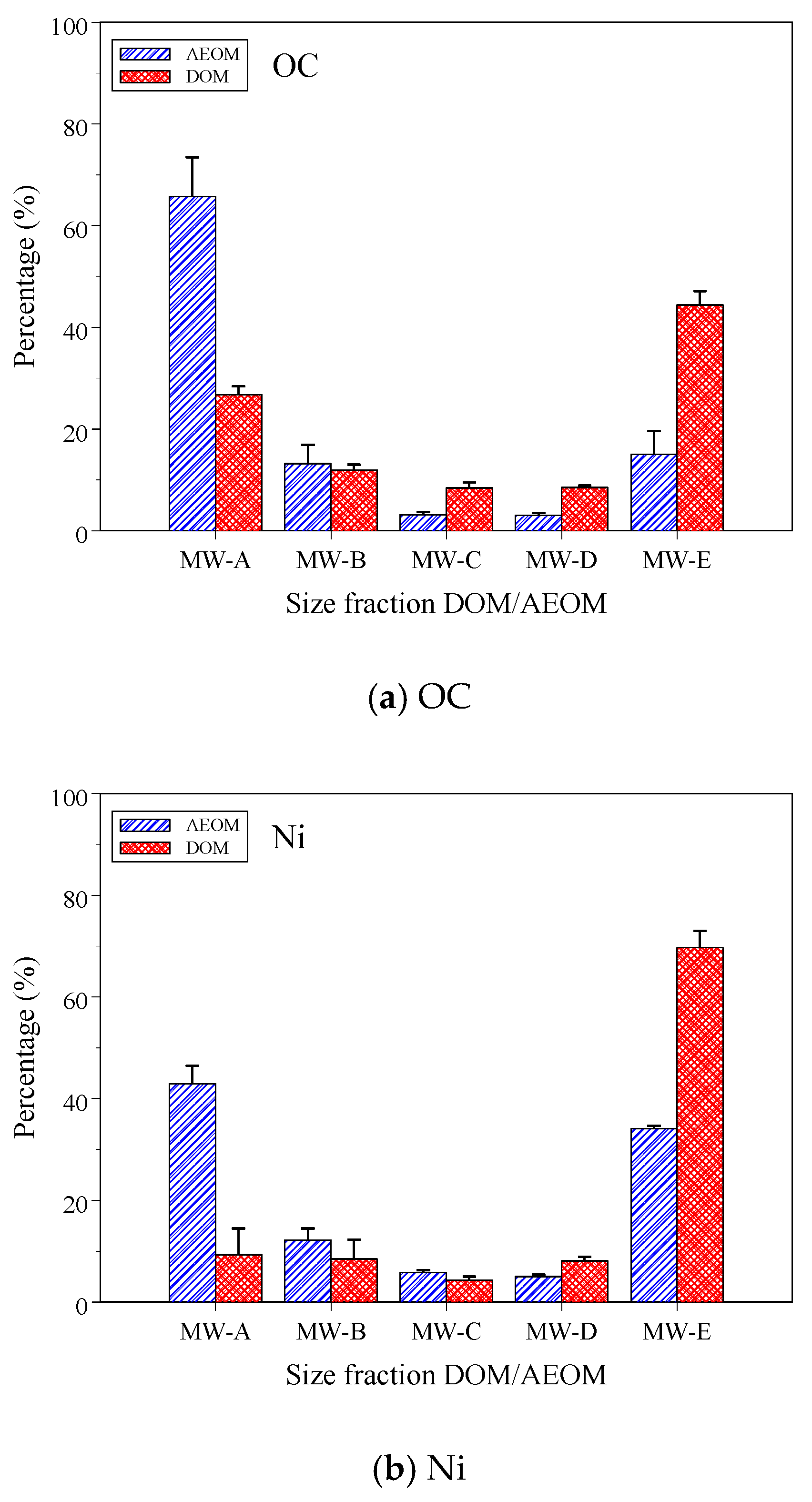
3.1. DOC and Ni Concentrations and Distribution in Size-Fractioned DOM/AEOM
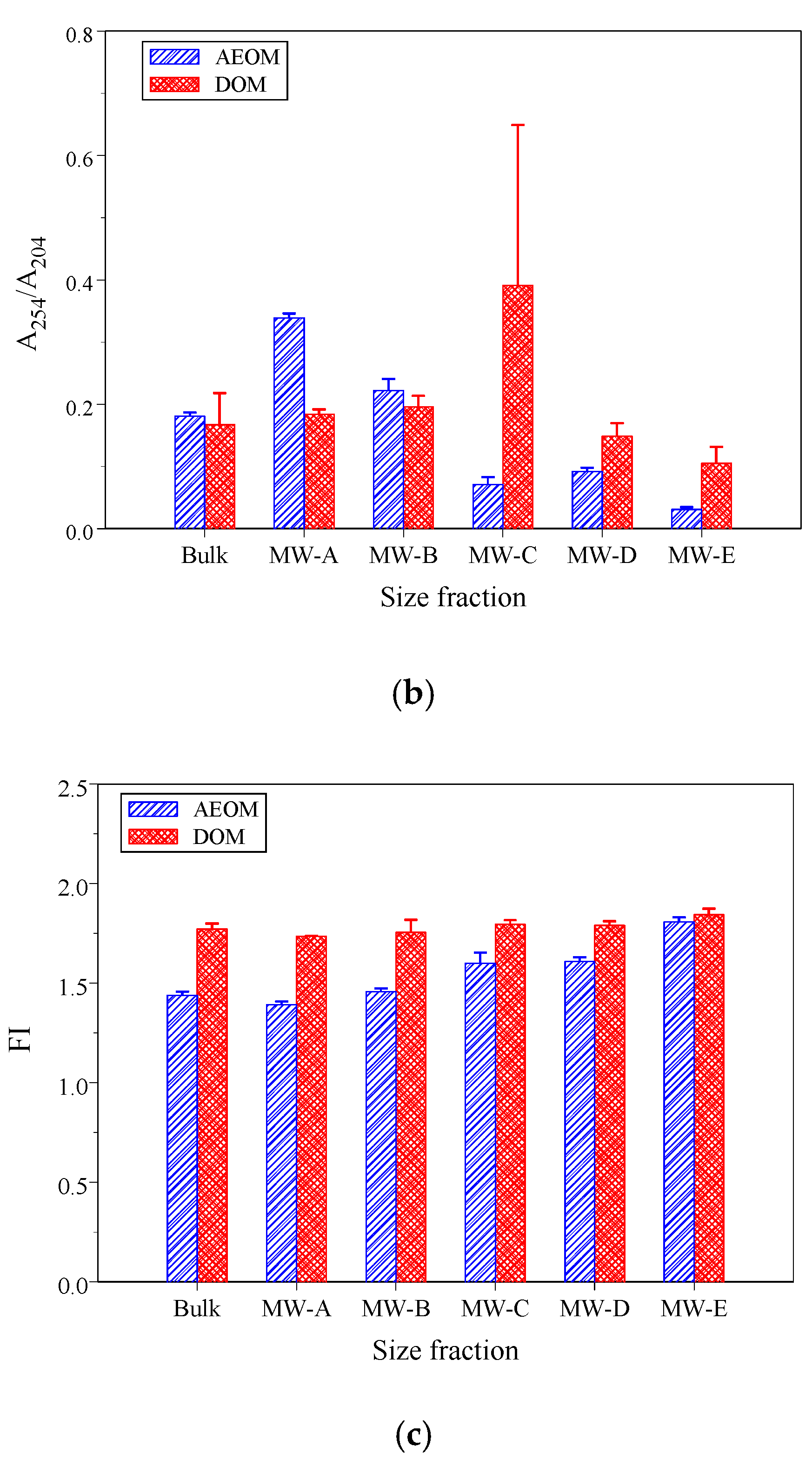
3.2. Optical Properties of DOM and POM
3.3. Ni Binding Affinity to Size-Fractionated DOM and AEOM
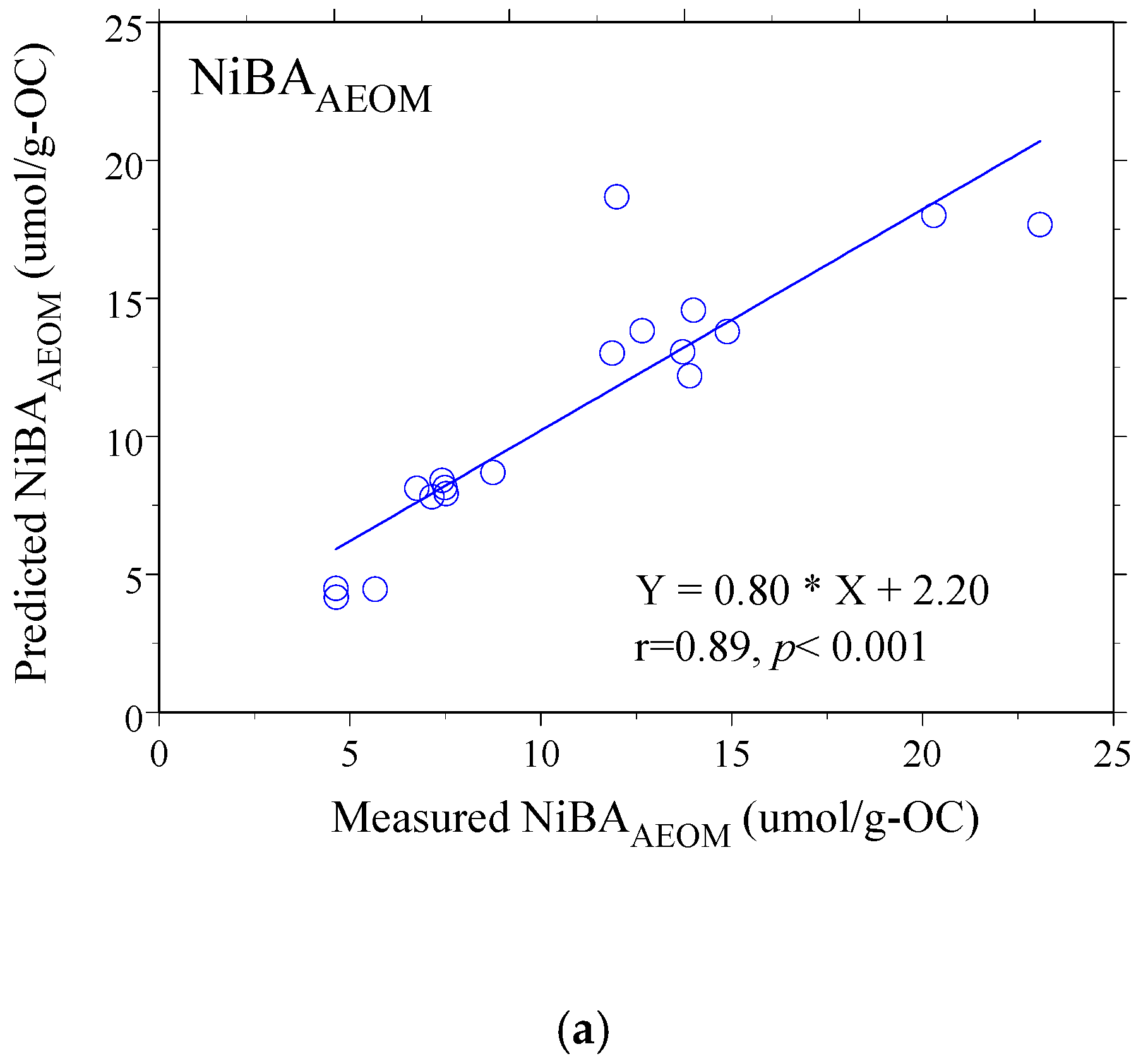
3.4. Modeling Nickel Binding Affinity: From Simple Correlations to Multiple Regression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Mol. Clin. Environ. Toxic. 2012, 3, 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdige, D.J.; Komada, T. Sediment pore waters. In Biogeochemistry of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, VT, USA, 2015; Chapter 12; pp. 535–577. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Chen, M.; Schlautman, M.A.; Hur, J. Dynamic exchanges between DOM and POM pools in coastal and inland aquatic ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Sun, G.-X.; Chen, S.-C.; Fang, Z.; Yuan, H.-Y.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, Y.-G. Molecular chemodiversity of dissolved organic matter in paddy soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.D.; Bianchi, T.S.; Medeiros, P.M.; Seidel, M.; Richey, J.E.; Keil, R.G.; Sawakuchi, H.O. Where carbon goes when water flows: Carbon cycling across the aquatic continuum. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Lao, Q. Source, distribution, and transformation of dissolved and particulate organic matters in Qinzhou Bay, Northern Beibu Gulf. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1163899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, G.R.; Hsu-Kim, H.; Ryan, J.N. Influence of dissolved organic matter on the environmental fate of metals, nanoparticles, and colloids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3196–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, K.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Zou, G.; Wang, Z. Occurrence, risk, and source of heavy metals in lake water columns and sediment cores in Jianghan Plain, Central China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baken, S.; Degryse, F.; Verheyen, L.; Merckx, R.; Smolders, E. Metal complexation properties of freshwater dissolved organic matter are explained by its aromaticity and by anthropogenic ligands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2584–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, G.; Lee, X. Concentrations, distribution, and pollution assessment of metals in river sediments in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, M.; Yu, K.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Hassan, M.; He, Y. Heavy metals in a typical city-river-reservoir system of East China: Multi-phase distribution, microbial response and ecological risk. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 112, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.R.; Shafer, M.M.; Armstrong, D.E. Strong colloidal and dissolved organic ligands binding copper and zinc in rivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6996–7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh-Nho, N.; Strady, E.; Nhu-Trang, T.T.; David, F.; Marchand, C. Trace metals partitioning between particulate and dissolved phases along a tropical mangrove estuary (Can Gio, Vietnam). Chemosphere 2018, 196, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worms, I.A.; Szigeti, Z.A.-G.; Dubascoux, S.; Lespes, G.; Traber, J.; Sigg, L.; Slaveykova, V.I. Colloidal organic matter from wastewater treatment plant effluents: Characterization and role in metal distribution. Water Res. 2010, 44, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Gjessing, E.T.; Lahtinen, T.; Hed, L.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. An overview of the methods used in the characterisation of natural organic matter (NOM) in relation to drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korak, J.A.; McKay, G. Meta-Analysis of Optical Surrogates for the Characterization of Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 7380–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weishaar, J.L.; Aiken, G.R.; Bergamaschi, B.A.; Fram, M.S.; Fujii, R.; Mopper, K. Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4702–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshin, G.V.; Li, C.-W.; Benjamin, M.M. Monitoring the properties of natural organic matter through UV spectroscopy: A consistent theory. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Lievens, C. Assessment of UV-VIS spectra analysis methods for quantifying the absorption properties of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM). Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1152536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, D.M.; Boyer, E.W.; Westerhoff, P.K.; Doran, P.T.; Kulbe, T.; Andersen, D.T. Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellman, J.B.; Spencer, R.G.; Hernes, P.J.; Edwards, R.T.; D’Amore, D.V.; Hood, E. The impact of glacier runoff on the biodegradability and biochemical composition of terrigenous dissolved organic matter in near-shore marine ecosystems. Mar. Chem. 2010, 121, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; Vacher, L.; Relexans, S.; Saubusse, S.; Froidefond, J.-M.; Parlanti, E. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.-W.; Hsu, L.-F.; Tsai, H.-C.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Huang, W.-S.; Chen, T.-C. Nickel Binding Affinity with Size-Fractioned Sediment Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter and Correlation with Optical Indicators. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, M.-Y.; Huang, W.-H.; Tsai, H.-C.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Chen, T.-C. Copper distribution and binding affinity to size-fractioned dissolved and particulate organic matter in river sediment. Environments 2024, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Wang, D.; Hou, Q.; Yu, T. Dissolved and particulate partitioning of trace elements and their spatial–temporal distribution in the Changjiang River. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 145, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korak, J.A.; McKay, G. Critical review of fluorescence and absorbance measurements as surrogates for the molecular weight and aromaticity of dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2024, 26, 1663–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y. Hydroclimatic controls on dissolved organic matter (DOM) characteristics and implications for trace metal transport in Hwangryong River Watershed, Korea, during a summer monsoon period. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 3025–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zou, L.; Guan, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, H. Molecular weight-dependent spectral and metal binding properties of sediment dissolved organic matter from different origins. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.-H.; Chiu, T.-P.; Huang, W.-S.; Chen, T.-C.; Yeh, Y.-L. Cadmium (Cd) and Nickel (Ni) Distribution on Size-Fractioned Soil Humic Substance (SHS). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Choi, I.; Lee, J.-J.; Hur, J. Coupling effects of abiotic and biotic factors on molecular composition of dissolved organic matter in a freshwater wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Carocci, A.; Lauria, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Catalano, A. Nickel: Human health and environmental toxicology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, P.; Saravanan, V.; Rajeshkannan, R.; Arnica, G.; Rajasimman, M.; Baskar, G.; Pugazhendhi, A. Comprehensive review on toxic heavy metals in the aquatic system: Sources, identification, treatment strategies, and health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2024, 258, 119440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.-Y.; Zhou, T.-H.; Du, Y.; Ye, B.; Wang, W.-L.; Hu, H.-Y. Characterizing the molecular weight distribution of dissolved organic matter by measuring the contents of electron-donating moieties, UV absorbance, and fluorescence intensity. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Jung, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Hur, J. Differences in spectroscopic characteristics between dissolved and particulate organic matters in sediments: Insight into distribution behavior of sediment organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.-S.; Huang, W.-S.; Hsu, L.-F.; Yeh, Y.-L.; Chen, T.-C. Fluorescence of Size-Fractioned Humic Substance Extracted from Sediment and Its Effect on the Sorption of Phenanthrene. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrin, A.; Roulier, J.-L.; Coquery, M. Colloidal and truly dissolved metal (oid) fractionation in sediment pore waters using tangential flow filtration. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.R.; Stubbins, A.; Ritchie, J.D.; Minor, E.C.; Kieber, D.J.; Mopper, K. Absorption spectral slopes and slope ratios as indicators of molecular weight, source, and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, N.; Baker, A.; Reynolds, D. Fluorescence analysis of dissolved organic matter in natural, waste and polluted waters—A review. River Res. Appl. 2007, 23, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Kinniburgh, D. An R script for visualising and analysing fluorescence excitation–emission matrices (EEMs). Comput. Geosci. 2009, 35, 2160–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hur, J. Pre-treatments, characteristics, and biogeochemical dynamics of dissolved organic matter in sediments: A review. Water Res. 2015, 79, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, M.-Y.; Huang, W.-H.; Hsu, L.-F.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Chen, T.-C. Investigation of the Distribution and Binding Affinity of Copper to Size-Fractioned Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) in a Constructed Wetland. Separations 2024, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-H.; Lin, T.-C.; Huang, C.-M.; Chen, T.-C.; Yeh, Y.-L. Copper distribution and binding affinity of size-fractioned humic substances taken from paddy soil and correlation with optical characteristics. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilina, S.M.; Lapitskiy, S.A.; Alekhin, Y.V.; Viers, J.; Benedetti, M.; Pokrovsky, O.S. Speciation, size fractionation and transport of trace elements in the continuum soil water–mire–humic lake–river–large oligotrophic lake of a Subarctic watershed. Aquat. Geochem. 2016, 22, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettweis, M.; Schartau, M.; Desmit, X.; Lee, B.J.; Terseleer, N.; Van der Zande, D.; Parmentier, K.; Riethmüller, R. Organic matter composition of biomineral flocs and its influence on suspended particulate matter dynamics along a nearshore to offshore transect. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2022, 127, e2021JG006332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiwei, L.; Xin, Y.; Keqiang, S.; Baohua, Z.; Guang, G. Unraveling the sources and fluorescence compositions of dissolved and particulate organic matter (DOM and POM) in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4027–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, K.; Chon, K.; Cho, J. Characterization of size fractionated dissolved organic matter from river water and wastewater effluent using preparative high performance size exclusion chromatography. Org. Geochem. 2017, 103, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontoni, L.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Pechaud, Y.; Fabbricino, M.; Esposito, G.; Pirozzi, F. Colloidal mobilization and fate of trace heavy metals in semi-saturated artificial soil (OECD) irrigated with treated wastewater. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Tanoue, E. Molecular mass distribution and fluorescence characteristics of dissolved organic ligands for copper (II) in Lake Biwa, Japan. Org. Geochem. 2001, 32, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Vadas, T.M. Size characterization of dissolved metals and organic matter in source waters to streams in developed landscapes. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 197, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.K.; Baker, A.; Murphy, K.; Hambly, A.; Stuetz, R.; Khan, S. Fluorescence as a potential monitoring tool for recycled water systems: A review. Water Res. 2009, 43, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, M.; Guo, L.; Wang, W.-X. Size partitioning and mixing behavior of trace metals and dissolved organic matter in a South China estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.M.; Dai, M.H.; Cauwet, G. Significance of colloids in the biogeochemical cycling of organic carbon and trace metals in the Venice Lagoon (Italy). Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Fujii, M.; Terao, K.; Jiwei, R.; Lee, Y.P.; Yoshimura, C. Correlations between aromaticity of dissolved organic matter and trace metal concentrations in natural and effluent waters: A case study in the Sagami River Basin, Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, B.P.; Ranville, J.F.; Bertsch, P.M.; Sowder, A.G. Characterization of colloidal and humic-bound Ni and U in the “dissolved” fraction of contaminated sediment extracts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2478–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-J.; He, X.-S.; Li, C.-W.; Li, N.-X. The binding properties of copper and lead onto compost-derived DOM using Fourier-transform infrared, UV–vis and fluorescence spectra combined with two-dimensional correlation analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Han, F.; Li, L.; Guo, J.; Ai, L.; Fang, L.; Liu, L.; Du, B. Extracellular polymeric substances for Zn (II) binding during its sorption process onto aerobic granular sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Shao, L.-M.; He, P.-J. Fluorescent characteristics and metal binding properties of individual molecular weight fractions in municipal solid waste leachate. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yue, D.; Liu, J.; Nie, Y. Size fractionation of organic matter and heavy metals in raw and treated leachate. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2527–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Ding, Z.; Liu, F.; Shi, Z. Theoretical modeling of molecular fractionation of dissolved organic matter on ferrihydrite and its impact on proton and metal binding properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, K.V.; DeForest, D.K.; Tear, L.; Grosell, M.; Adams, W.J. Use of multiple linear regression models for setting water quality criteria for copper: A complementary approach to the biotic ligand model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5182–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, K.V.; Tear, L.; Santore, R.C.; Croteau, K.; DeForest, D.K. Comparative performance of multiple linear regression and biotic ligand models for estimating the bioavailability of copper in freshwater. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeForest, D.K.; Ryan, A.C.; Tear, L.M.; Brix, K.V. Comparison of multiple linear regression and biotic ligand models for predicting acute and chronic zinc toxicity to freshwater organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, Y.; He, S. Multivariate Linear Regression Models to Predict Monomer Poisoning Effect in Ethylene/Polar Monomer Copolymerization Catalyzed by Late Transition Metals. Inorganics 2022, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallister, S.L.; Bauer, J.E.; Ducklow, H.W.; Canuel, E.A. Sources of estuarine dissolved and particulate organic matter: A multi-tracer approach. Org. Geochem. 2006, 37, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ni (μg/L) | DOC (mg/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOM | AEOM | DOM | AEOM | |
| Bulk | 9.1 ± 0.2 | 137 ± 6 | 3.3 ± 0.4 | 297 ± 25 |
| MW-A | 9.1 ± 4.5 | 610 ± 113 | 7.9 ± 1.3 | 2122 ± 555 |
| MW-B | 9.5 ± 4.2 | 190 ± 20 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | 455 ± 62 |
| MW-C | 5.3 ± 0.3 | 100 ± 0 | 3.1 ± 0.4 | 120 ± 5 |
| MW-D | 11.2 ± 1.9 | 97 ± 6 | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 129 ± 5 |
| MW-E | 10.7 ± 2.0 | 73 ± 6 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 72 ± 23 |
| R (%) | 111 ± 16 | 103 ± 9 | 89 ± 2 | 107 ± 9 |
| A254/204 | SUVA254 | FI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A254/204 | 0.82 *** | −0.87 *** | |
| SUVA254 | 0.96 *** | −0.83 *** | |
| FI | −0.01 | 0.21 |
| NiBA | A254/204 | SUVA254 | FI |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiBAAEOM | −0.86 *** | −0.74 *** | 0.87 *** |
| NiBADOM | −0.40 | −0.22 | 0.58 * |
| Mutiple Linear Regression Equation | r | p |
|---|---|---|
| NiBAAEOM = −14.53–19.80⋅A254/204 + 18.43⋅FI | 0.89 | <0.001 |
| NiBADOM = 50.71–470.5⋅A254/204 + 36.96⋅SUVA254 | 0.70 | 0.006 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.-H.; Huang, W.-H.; Hsu, L.-F.; Tsai, H.-C.; Chen, T.-C. Contrasting Nickel Binding Mechanisms in Water-Column and Sediment Organic Matter: The Critical Role of Molecular Size and Chemical Composition. Environments 2025, 12, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100352
Yang K-H, Huang W-H, Hsu L-F, Tsai H-C, Chen T-C. Contrasting Nickel Binding Mechanisms in Water-Column and Sediment Organic Matter: The Critical Role of Molecular Size and Chemical Composition. Environments. 2025; 12(10):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100352
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kuo-Hui, Wei-Hsiang Huang, Liang-Fong Hsu, Hsiang-Chun Tsai, and Ting-Chien Chen. 2025. "Contrasting Nickel Binding Mechanisms in Water-Column and Sediment Organic Matter: The Critical Role of Molecular Size and Chemical Composition" Environments 12, no. 10: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100352
APA StyleYang, K.-H., Huang, W.-H., Hsu, L.-F., Tsai, H.-C., & Chen, T.-C. (2025). Contrasting Nickel Binding Mechanisms in Water-Column and Sediment Organic Matter: The Critical Role of Molecular Size and Chemical Composition. Environments, 12(10), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100352





