Distribution, Characterization and Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Two Rivers in West Central Scotland: The Black Cart Water and White Cart Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Study Area | Density Separation Reagent | Organic Matter Removal | Abundance (Items/kg) | Polymers Found |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yongjiang River, Nanning City, South China [28] | NaCl/NaI | Fenton’s reagent | 90–550 | PA, PE, PET, PP, PS |
| Ganga River, India [16] | NaCl | Fenton’s reagent | 17–36 | Cellophane, PE, PEs, PP, PS, PVC |
| River Tame, Northwest England UK [26] | NaI | None | 24–138,400 | PA, PET, PS, styrene acrylonitrile |
| Red River Delta, Vietnam [29] | NaCl | H2O2 | 1450–56,000 | EVA, PE, PET, PP |
| Yamaguchi Prefecture, Japan [22] | ZnCl2 | Fenton’s reagent | 8–1010 | PE, PP, PS, PVC |
| Selangor River Basin, Malaysia [25] | ZnCl2 | H2O2 | 10–55 | LDPE, PE, PET, PP, PS, PVC |
| Ganges River Basin, Bangladesh [30] | ZnCl2 | H2O2 | 2950–4010 | Cellulose, PA, PE, PET, PP, PS, PVC |
| Kamniška Bistrica (KB) and Ljubljanica, Slovenia [19] | NaCl | Fenton’s reagent | 5–40 | PA, PE, PET, PS, PU |
| Liangfeng River, Guilin City, China [31] | NaCl | H2O2 | 10,300–82,900 | PA, PE, PP, PS, PVC |
| Mahanadi River, India [18] | NaCl | Fenton’s reagent | 49–354 | PA, PE, Pes, PVC, PP, PS |
| Nanming River, Guiyang, China [21] | NaCl | H2O2 | 1000–5500 | PE, PEG, PP, PVAc, PVM/MA |
| River Jinjiang, China [32] | NaCl | Fenton’s reagent | 21–924 | PE, PET, PP, PS, rayon |
| Wei River, China [17] | CaCl2 | H2O2 | 120–840 | PE, PET, PP, PS, PVC |
| Nanming River, Guizhou China [33] | NaCl, NaI | KOH:NaClO | 870–7500 | EVA, PC, PE, PVC |
| Yitong River, China [34] | NaCl | H2O2 | 300–850 | PE, PET, PP, PS |
| River Kelvin, Glasgow, Scotland [11] | NaCl | H2O2 | 50–244 | PE, PP |
| Jungnang Stream, South Korea [12] | ZnCl2 | Fenton’s reagent | 820–8060 | Cellophane, PE, PP |
| Wolf River, Memphis, Tennessee, USA [23] | ZnCl2 | H2O2 | 250–3000 | Acrylic, PE, PET, PP, PU, PVA, PVC |
| Mahaweli River, Sri-Lanka [15] | NaCl | H2O2 | 3.1–247 | PE, PET, PS, PU |
| Chichiriviche de la Costa, Venezuela [20] | NaCl | KOH:H2O2 | 10–150 | EPDM, PA, PE, PET, PP, PVA |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Pre-Treatment and Extraction of Microplastics
2.4. Microplastic Observation and Identification
2.5. Contamination and Risk Evaluation of Microplastics
2.5.1. Contamination Factor
2.5.2. Pollution Load Index
2.5.3. Polymer Hazard Index
2.5.4. Potential Ecological Risk Index
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Quality Control and Contamination Avoidance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Water
3.2. Sediments
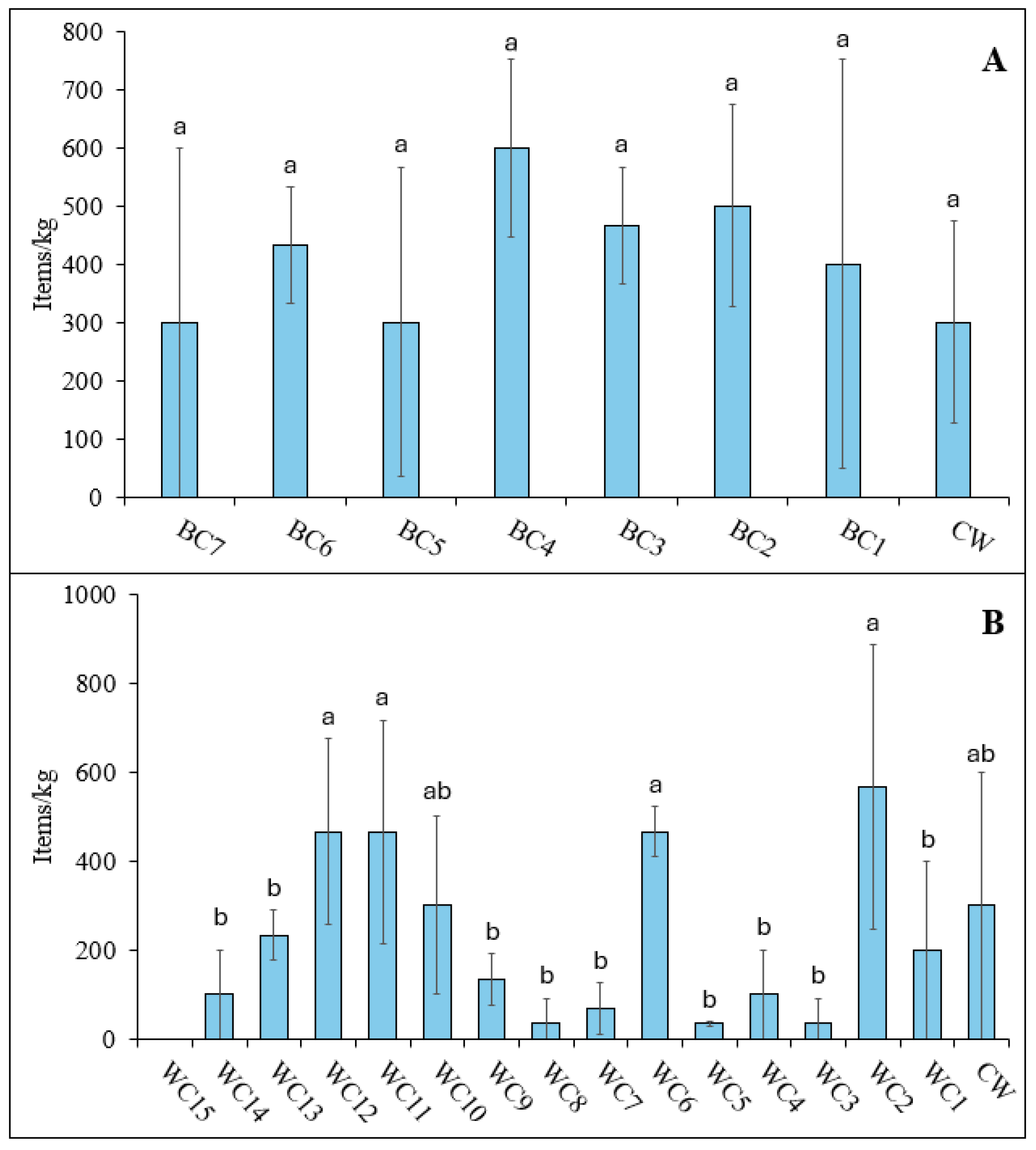
3.2.1. Microplastic Abundance
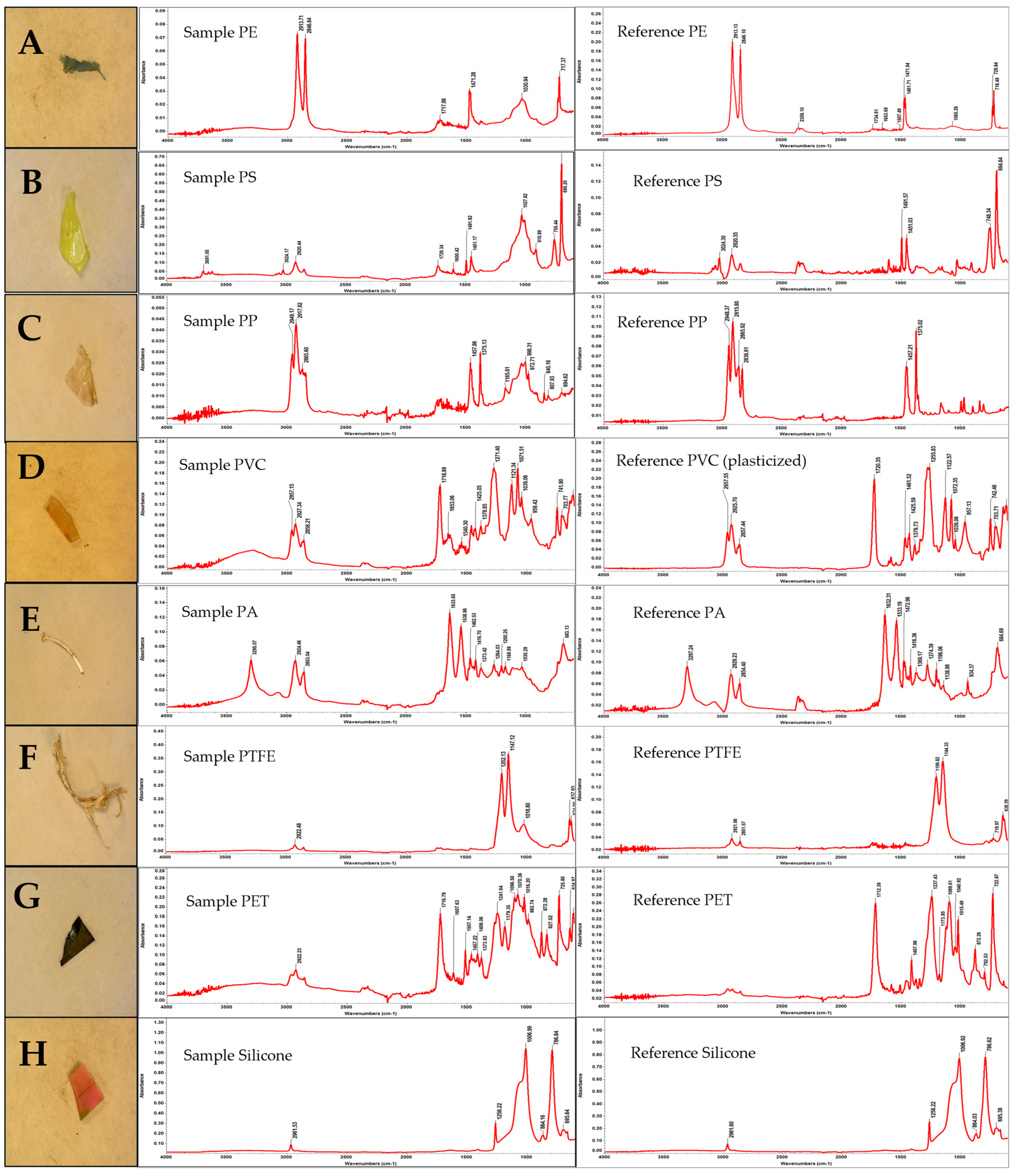
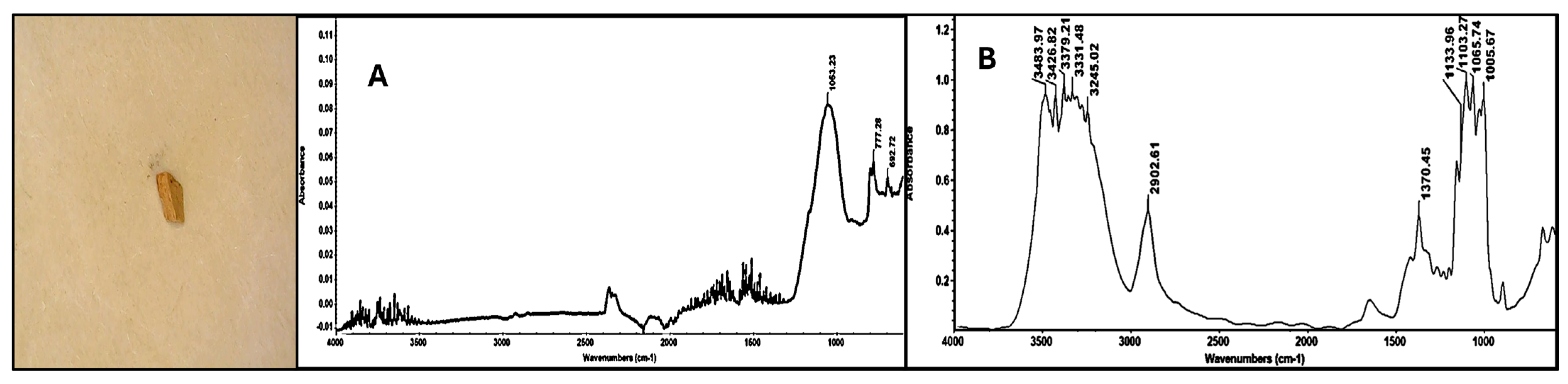
3.2.2. Identification of Microplastics by ATR-FTIR
3.2.3. Characteristics of Isolated Microplastics
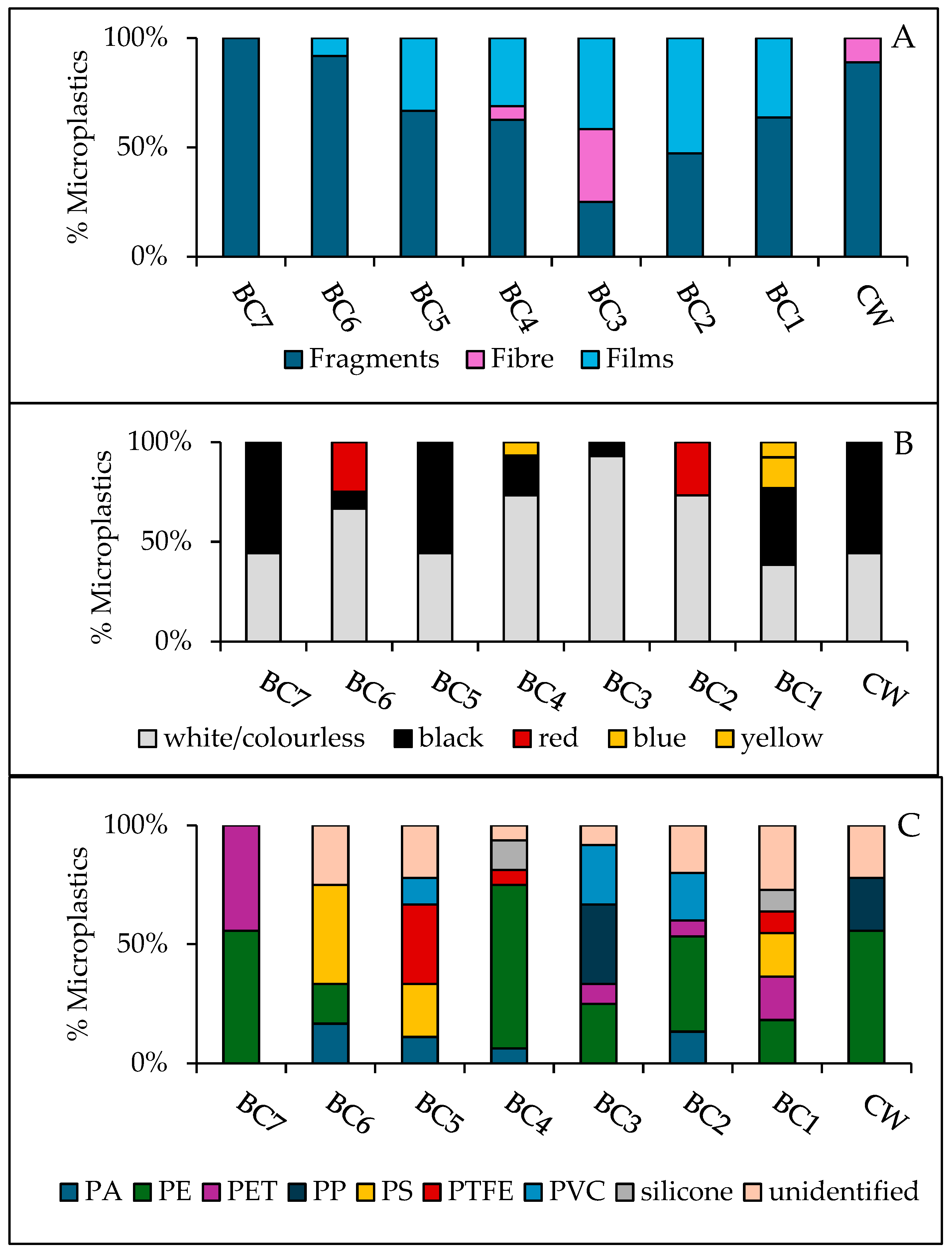
Black Cart Water
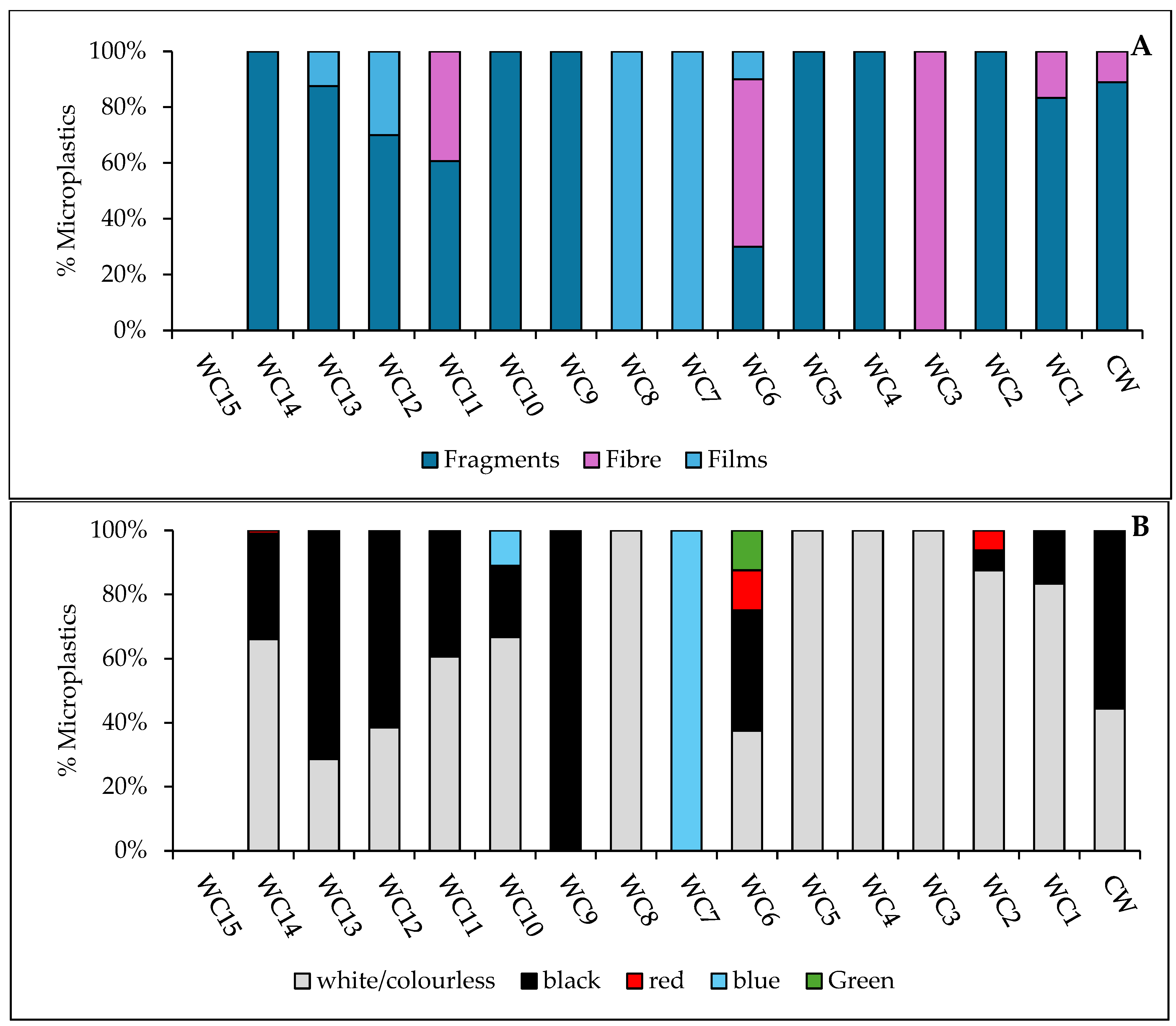
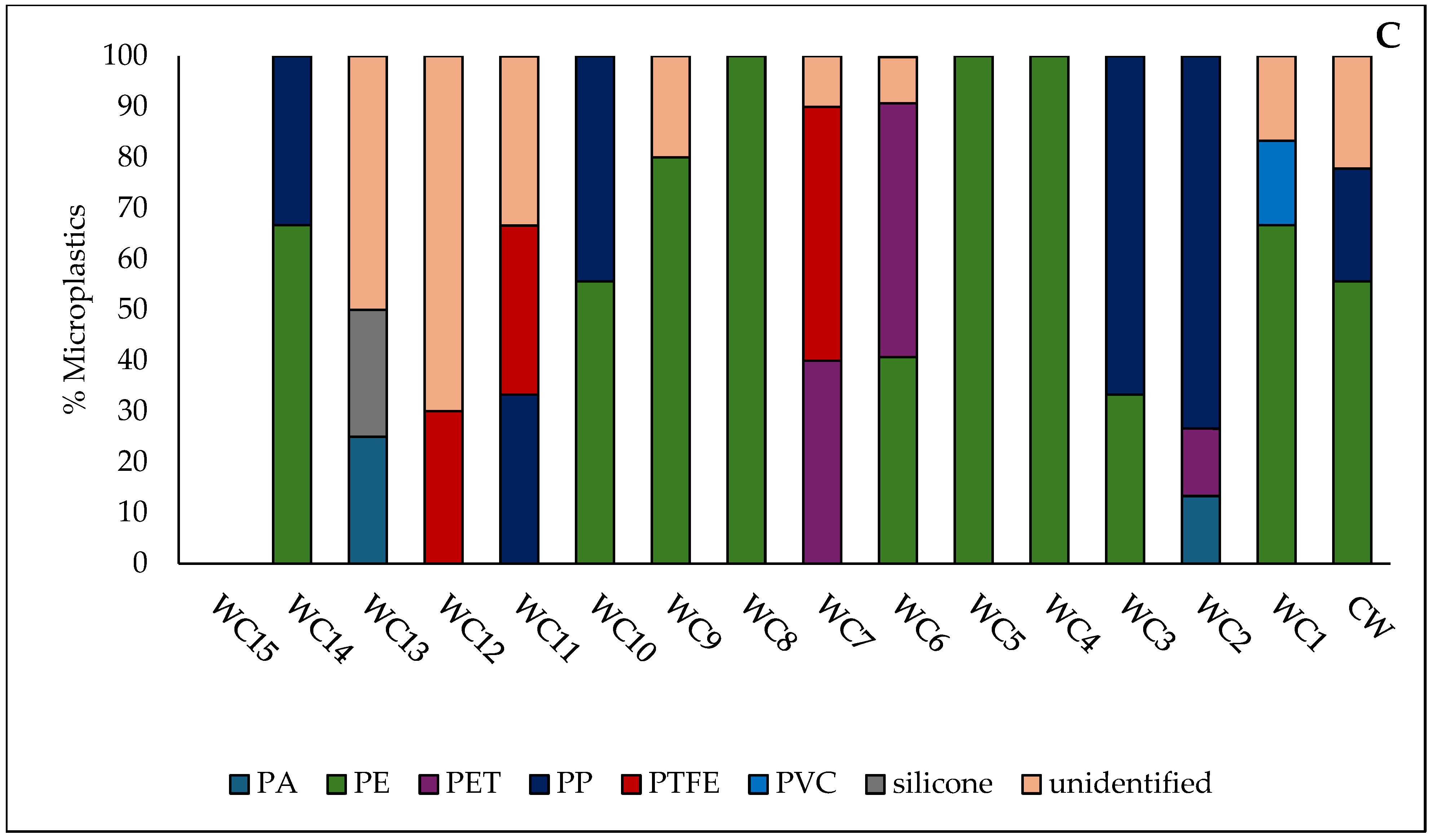
White Cart Water
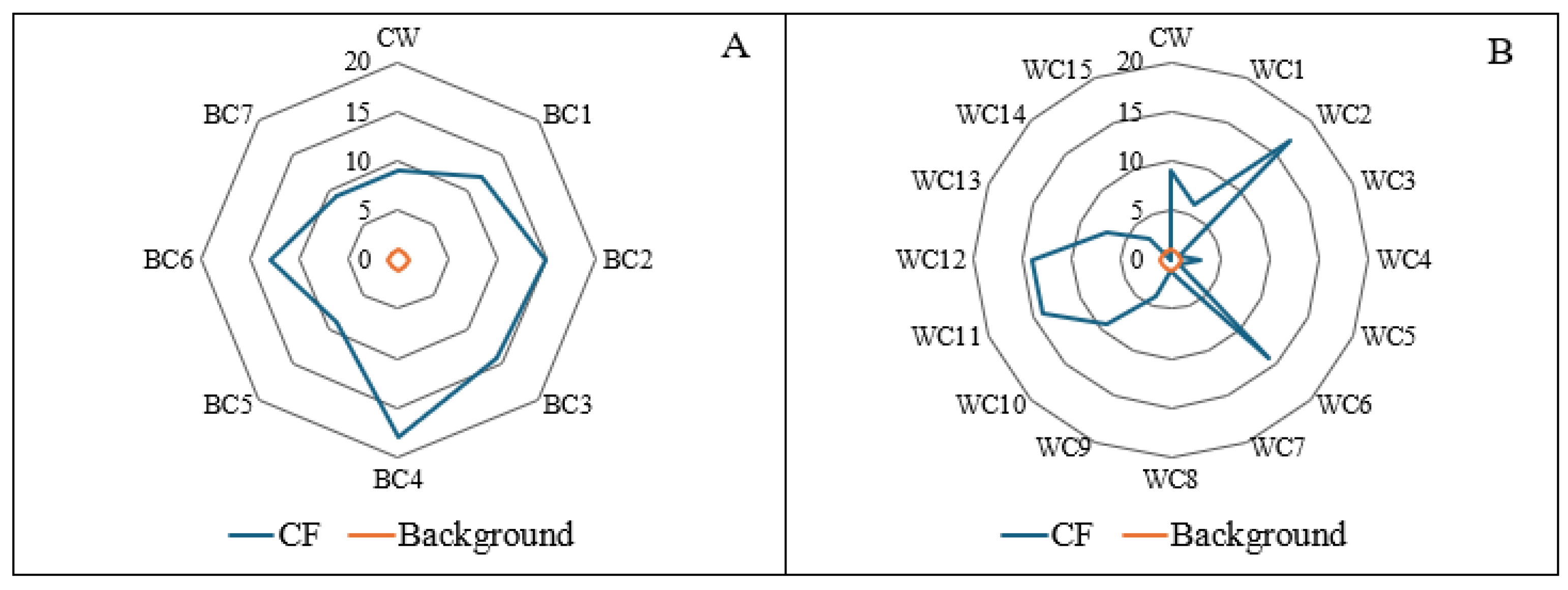
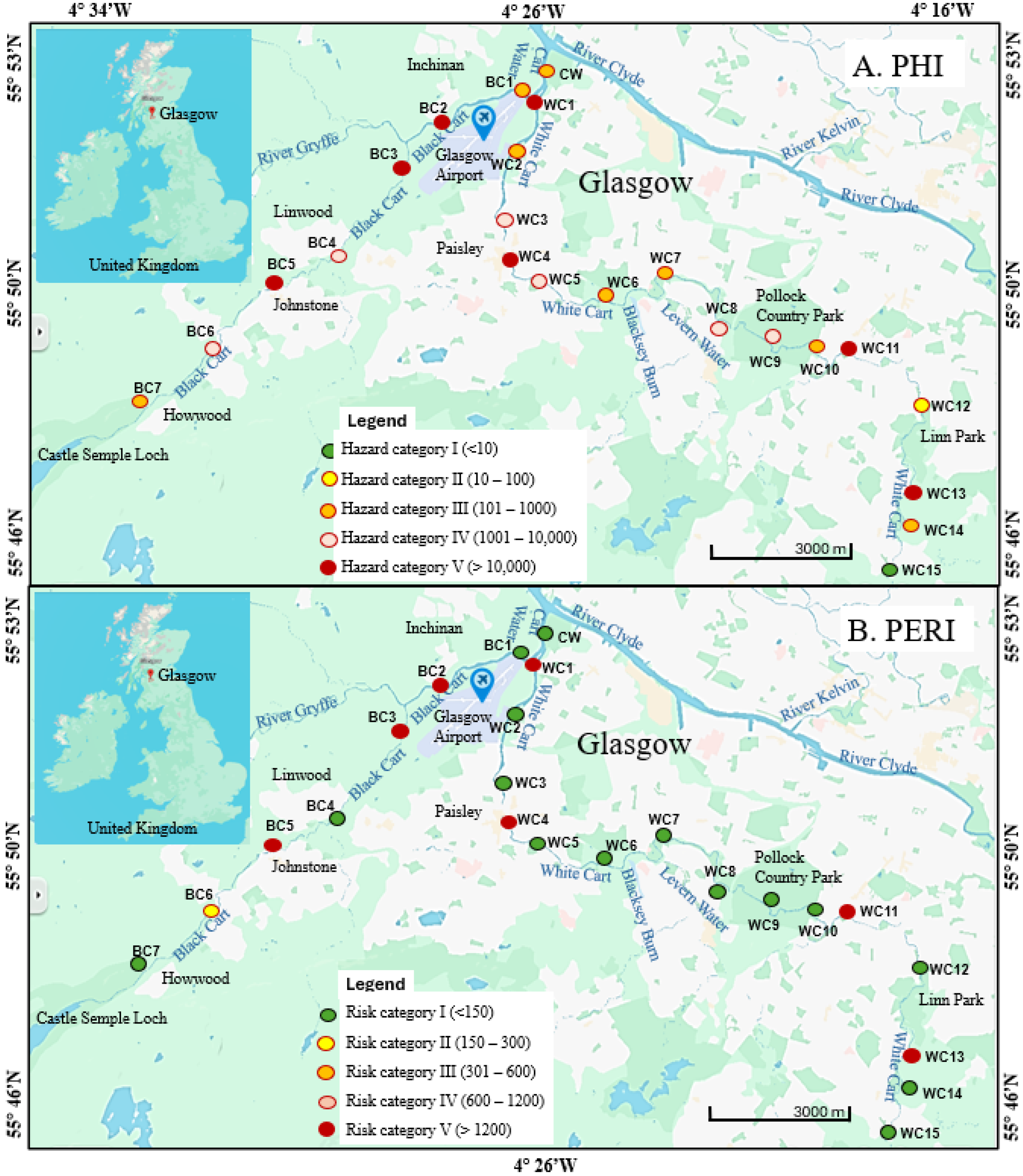
3.3. Contamination and Risk Indices
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Karak, P.; Parveen, A.; Modak, A.; Adhikari, A.; Chakrabortty, S. Microplastic Pollution: A Global Environmental Crisis Impacting Marine Life, Human Health, and Potential Innovative Sustainable Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.; Andrady, A. Future scenarios of global plastic waste generation and disposal. Palgrave Commun. 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handbook of Microplastics in the Environment; Corcoran, P.L., Rios-Mendoza, L.M., Costa, M.F., Rocha-Santos, T., Mouneyrac, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Liu, A.; Ayoko, G.; Egodawatta, P.; Wijesiri, B.; Goonetilleke, A. Environmental Risks Posed by Microplastics in Urban Waterways; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kataria, N.; Yadav, S.; Garg, V.K.; Rene, E.R.; Jiang, J.-J.; Rose, P.K.; Kumar, M.; Khoo, K.S. Occurrence, transport, and toxicity of microplastics in tropical food chains: Perspectives view and way forward. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Vidili, G.; Casu, G.; Navarese, E.P.; Sechi, L.A.; Chen, Y. Microplastics and nanoplastics in cardiovascular disease—A narrative review with worrying links. Front. Toxicol. 2024, 6, 1479292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D. Effects of Microplastics on Bioavailability, Persistence and Toxicity of Plant Pesticides: An Agricultural Perspective. Agriculture 2025, 15, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, M.S. The Microplastic Cycle: An Introduction to a Complex Issue; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Chia, R.W.; Veerasingam, S.; Uddin, S.; Jeon, W.-H.; Moon, H.S.; Cha, J.; Lee, J. A comprehensive review of urban microplastic pollution sources, environment and human health impacts, and regulatory efforts. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokunbi, O.S.; Idowu, G.A.; Aiyesanmi, A.F.; Davidson, C.M. Assessment of Microplastics and Potentially Toxic Elements in Surface Sediments of the River Kelvin, Central Scotland, United Kingdom. Environ. Manag. 2024, 73, 932–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, D.T.; Choi, S.-H.; Kwon, J.-H. Year-round spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics in water and sediments of an urban freshwater system (Jungnang Stream, Korea). Environ. Pollut. 2024, 357, 124362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, T.; Fórián, S.; Szatmári, G.; Sipos, G. Spatial distribution of microplastics in the fluvial sediments of a transboundary river—A case study of the Tisza River in Central Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Zhou, S.; Wang, K.; Li, D.; Liu, H.; Li, F. Distribution characteristics and pollution risk assessment of microplastics in urban rivers: A case study in Yitong River, China. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 61, 105277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapukotuwa, G.K.; Jayasena, N.; Weerakoon, K.C.; Abayasekara, C.L.; Rajakaruna, R.S. Microplastic Pollution of Stream Water and Sediment in a Tributary of a Major Drinking Water Supplying River in Sri Lanka. ACS EST Water 2025, 5, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Mondal, A.; Bagri, A.; Tiwari, E.; Khandelwal, N.; Monikh, F.A.; Darbha, G.K. Characteristics and spatial distribution of microplastics in the lower Ganga River water and sediment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Xia, X.; Zhang, H. The effects of land use types on microplastics in river water: A case study on the mainstream of the Wei River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patidar, K.; Ambade, B.; Verma, S.K.; Mohammad, F. Microplastic contamination in water and sediments of Mahanadi River, India: An assessment of ecological risk along rural-urban area. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matjašič, T.; Mori, N.; Hostnik, I.; Bajt, O.; Kovač Viršek, M. Microplastic pollution in small rivers along rural–urban gradients: Variations across catchments and between water column and sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, J.F.; López-Ordaz, A.; Hernández, A.J.; Gómez, F.B.; Sabino, M.A.; Ramos, R. Rural village as a source of microplastic pollution in a riverine and marine ecosystem of the southern Venezuelan Caribbean. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2025, 269, 104511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Wu, Q.; Gao, S.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Ruan, Y. Distribution and characteristics of microplastics in an urban river: The response to urban waste management. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 166638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, A.H.M.E.; Sekine, M.; Imai, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kanno, A.; Higuchi, T. Microplastics in the sediments of small-scale Japanese rivers: Abundance and distribution, characterization, sources-to-sink, and ecological risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrea Murrell, J.A.; Gálvez-Blanca, V.; Petre, A.L.; Alvarez, B.R.; Moya, D.L.; Rojas Badía, M.M.; Perdigón-Melón, J.A.; Boltes, K.; Rosal, R. Microplastics in Cuban freshwaters: Diversity, temporal changes, and effects on extracellular enzymatic activity. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 368, 125764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.O.; Abrantes, N.; Goncalves, F.J.M.; Nogueira, H.; Marques, J.C.; Goncalves, A.M.M. Spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics in water and sediments of a freshwater system (Antua River, Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, M.R.M.; Sukatis, F.F.; Roslan, M.Q.J.; Isa, N.M.; Yusoff, F.M.; Aris, A.Z. Microplastic Pollution in Freshwater Sediments: Abundance and Distribution in Selangor River Basin, Malaysia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, J.; Li, J.; Rothwell, J.; Hurley, R. Acute riverine microplastic contamination due to avoidable releases of untreated wastewater. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enenche, D.E.; Davidson, C.M.; Liggat, J.J. Towards a Consensus Method for the Isolation of Microplastics from Freshwater Sediments. Environments 2024, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Leng, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, K.; Wang, J. Microplastics’ Pollution and Risk Assessment in an Urban River: A Case Study in the Yongjiang River, Nanning City, South China. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.T.; Le, P.T.; Nguyen, T.N.H.; Hoang, T.Q.; Ngo, H.M.; Doan, T.O.; Le, T.P.Q.; Bui, H.T.; Bui, M.H.; Trinh, V.T.; et al. Selection of a density separation solution to study microplastics in tropical riverine sediment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.; Shammi, M.; Tareq, S.M. Distribution of microplastics in shoreline water and sediment of the Ganges River Basin to Meghna Estuary in Bangladesh. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2023, 266, 115537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Tan, Q.; Qin, H.; Wang, D.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, J. Sequestration and export of microplastics in urban river sediments. Environ. Int. 2023, 181, 108265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhao, Q.; Jin, J.; Lang, J.; Li, L.; Huang, L.; Long, L.; Xu, M.; Chen, C.; Yang, G. Microplastics in Sediments of the Urban River Jinjiang: Sources, Distribution, and Risk Assessment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Cao, Y. Characteristics, sources, and distribution of microplastics in sediments and their potential ecological risks: A case study in a typical urban river of China. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, R.; Zhang, B.; Meng, X.-Z.; Zhang, S. Seasonal variations of microplastics in surface water and sediment in an inland river drinking water source in southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renfrewshire Local History Forum. 2017. Available online: https://rlhf.info/ (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- The National Library of Scotland. The Fresh-Water Lochs of Scotland. 2024, Volume 2024. Available online: https://maps.nls.uk/dcn6/7443/74433404.6.pdf (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Douglas, B.M.; McGowan, A. River & Coastal Flood Alleviation; UK Water Projects: Glasgow, Scotland, 2014; Available online: https://waterprojectsonline.com/wp-content/uploads/case_studies/2013/White-Cart-Flood-Prevention-Scheme-2013.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- Water Overflow Maps, Scottish Water: Glasgow, Scotland. Available online: https://www.scottishwater.co.uk/Your-Home/Your-Waste-Water/Overflows/Live-Overflow-Map (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Omnic Library Spectral Indexes; Thermo Fisher Scientific: Loughborough, UK, 2025.
- Enyoh, C.E.; Verla, A.W.; Rakib, M.R.J. Application of index models for assessing freshwater microplastics pollution. World News Nat. Sci. 2021, 38, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Lu, J.; Li, W.; Ning, J.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Xiayihazi, N. Seasonal variation and risk assessment of microplastics in surface water of the Manas River Basin, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2021, 208, 111477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakib, M.R.J.; Hossain, M.B.; Kumar, R.; Ullah, M.A.; Al Nahian, S.; Rima, N.N.; Choudhury, T.R.; Liba, S.I.; Yu, J.; Khandaker, M.U.; et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessments due to the microplastics pollution in sediments of Karnaphuli River Estuary, Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manik, M.; Hossain, M.T.; Pastorino, P. Characterization and risk assessment of microplastics pollution in Mohamaya Lake, Bangladesh. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2025, 269, 104487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithner, D.; Larsson, Å.; Dave, G. Environmental and health hazard ranking and assessment of plastic polymers based on chemical composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjani, M.; Veerasingam, S.; Venkatachalapathy, R.; Mugilarasan, M.; Bagaev, A.; Mukhanov, V.; Vethamony, P. Assessment of potential ecological risk of microplastics in the coastal sediments of India: A meta-analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fordyce, F.; O Dochartaigh, B.; Lister, T.; Cooper, R.; Kim, A.; Harrison, I.; Vane, C.; Brown, S. Clyde Tributaries: Report of Urban Stream Sediment and Surface Water Geochemistry for Glasgow; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vane, C.H.; Lopes dos Santos, R.A.; Kim, A.W.; Moss-Hayes, V.; Fordyce, F.M.; Bearcock, J.M. Persistent organic pollutants (PAH, PCB, TPH) in freshwater, urban tributary and estuarine surface sediments of the River Clyde, Scotland, UK. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 2019, 108, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Li, Y. A study on limit velocity and its mechanism and implications for alluvial rivers. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 31, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, I.; Moggridge, H.; Warren, P.; Shucksmith, J. Regional flow–ecology relationships in small, temperate rivers. Water Environ. J. 2022, 36, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contaminants of the Great Lakes; Helm, P.A., Crossman, J., Weisener, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, A.; Schneider, F.; Anthony, N.; Lin, H.-T. Microplastics in rivers along an urban-rural gradient in an urban agglomeration: Correlation with land use, potential sources and pathways. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 321, 121096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrank, I.; Löder, M.G.J.; Imhof, H.K.; Moses, S.R.; Heß, M.; Schwaiger, J.; Laforsch, C. Riverine microplastic contamination in southwest Germany: A large-scale survey. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 794250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, T.; Li, D. Suspended microplastics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary System, China: First observations on occurrence, distribution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovall, J.K.; Bratton, S.P. Microplastic Pollution in Surface Waters of Urban Watersheds in Central Texas, United States: A Comparison of Sites With and Without Treated Wastewater Effluent. Front. Anal. Sci. 2022, 2, 857694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeque, P.K.; Cole, M.; Coppock, R.L.; Lewis, C.N.; Miller, R.Z.; Watts, A.J.R.; Wilson-McNeal, A.; Wright, S.L.; Galloway, T.S. Are we underestimating microplastic abundance in the marine environment? A comparison of microplastic capture with nets of different mesh-size. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovač Viršek, M.; Palatinus, A.; Koren, Š.; Peterlin, M.; Horvat, P.; Kržan, A. Protocol for Microplastics Sampling on the Sea Surface and Sample Analysis. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 118, 55161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devereux, R.; Ayati, B.; Westhead, E.K.; Jayaratne, R.; Newport, D. “The great source” microplastic abundance and characteristics along the river Thames. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, K.H.; Cucknell, A.-C.; Smith, B.D.; Clark, P.F.; Morritt, D. London’s river of plastic: High levels of microplastics in the Thames water column. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikareva, N.; Simon, K.S. Microplastic pollution in streams spanning an urbanisation gradient. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Svendsen, C.; Williams, R.J.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E. Large microplastic particles in sediments of tributaries of the River Thames, UK—Abundance, sources and methods for effective quantification. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Dixon, S.J. Microplastics: An introduction to environmental transport processes. WIREs Water 2018, 5, e1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Huang, X. Distribution and characteristics of microplastics in urban waters of seven cities in the Tuojiang River basin, China. Environ. Res. 2020, 189, 109893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, R.M.; Waldron, S.; Phoenix, V.R.; Gauchotte-Lindsay, C. Microscopy and elemental analysis characterisation of microplastics in sediment of a freshwater urban river in Scotland, UK. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12491–12504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendell-Bhatti, F.; Bull, C.; Cross, R.; Cox, R.; Adediran, G.A.; Lahive, E. From the environment into the biomass: Microplastic uptake in a protected lamprey species. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbetts, J.; Krause, S.; Lynch, I.; Smith, G.H.S. Abundance, distribution, and drivers of microplastic contamination in urban river environments. Water 2018, 10, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, H.A.; Dalu, T.; Wasserman, R.J. Sinks and sources: Assessing microplastic abundance in river sediment and deposit feeders in an Austral temperate urban river system. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Su, B.; Xu, X.; Di, D.; Huang, H.; Mei, K.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M.; Shang, X. Preferential accumulation of small (<300 μm) microplastics in the sediments of a coastal plain river network in eastern China. Water Res. 2018, 144, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, V.F.; Aneyo, I.A.; Fatunsin, O.T.; Enyoh, C.E.; Yahaya, T.O.; Emeronye, I.G.; Amolegbe, O.A.; Amaeze, N.H.; Anyiam, F.E.; Oloidi, A.A.; et al. Assessment of fishes, sediment and water from some inland rivers across the six geopolitical zones in Nigeria for microplastics. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2024, 39, e2024018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Choi, I.; Lee, S.; Hong, S.-j.; Kim, A.; Shin, J.; Kang, H.-C.; Kim, Y.-W. Renewable malic acid-based plasticizers for both PVC and PLA polymers. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 88, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.Y.; Chung, R.J.; Chang, P.P.; Tsai, T.H. Identification of Hydroxyl and Polysiloxane Compounds via Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy with Targeted Noise Analysis. Polymers 2025, 17, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anshari, R.; Tsuboi, M.; Sato, H.; Tashiro, K.; Ozaki, Y. Raman and ATR-FTIR unmask crystallinity changes and carboxylate group and vinyl group accumulation in natural weathering polypropylene microplastics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeseman, S.; Shaw, Z.L.; Vongsvivut, J.; Crawford, R.J.; Dupont, M.F.; Boyce, K.J.; Gangadoo, S.; Bryant, S.J.; Bryant, G.; Cozzolino, D.; et al. Analysis of Pathogenic Bacterial and Yeast Biofilms Using the Combination of Synchrotron ATR-FTIR Microspectroscopy and Chemometric Approaches. Molecules 2021, 26, 3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, J. Innovative New Method Speeds Up Correction of ATR Infrared Spectra. 2024. Available online: https://www.spectroscopyonline.com/view/innovative-new-method-speeds-up-correction-of-atr-infrared-spectra (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Jitkaew, P.; Pradit, S.; Noppradit, P.; Sengloyluan, K.; Yucharoen, M.; Suwanno, S.; Tanrattanakul, V.; Sornplang, K.; Nitiratsuwan, T. Occurrence of microplastics in freshwater gastropods from a tropical river U-Taphao, southern Thailand. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewicka, K.; Szymanek, I.; Rogacz, D.; Wrzalik, M.; Łagiewka, J.; Nowik-Zając, A.; Zawierucha, I.; Coseri, S.; Puiu, I.; Falfushynska, H.; et al. Current Trends of Polymer Materials’ Application in Agriculture. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Mao, R.f.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C. Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Wei River, in the northwest of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.B.; Yin, L.S.; Wen, X.F.; Du, C.Y.; Wu, L.X.; Long, Y.N.; Liu, Y.Z.; Ma, Y.; Yin, Q.D.; Zhou, Z.Y.; et al. Microplastics in Sediment and Surface Water of West Dongting Lake and South Dongting Lake: Abundance, Source and Composition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.L.; Hartl, M.G.J.; Bell, M.C.; Capper, A. Microplastic accumulation in a Zostera marina L. bed at Deerness Sound, Orkney, Scotland. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 152, 110883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenroeder, J.; Sechet, P.; Kakkonen, J.E.; Hartl, M.G.J. Microplastic contamination of intertidal sediments of Scapa Flow, Orkney a first assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
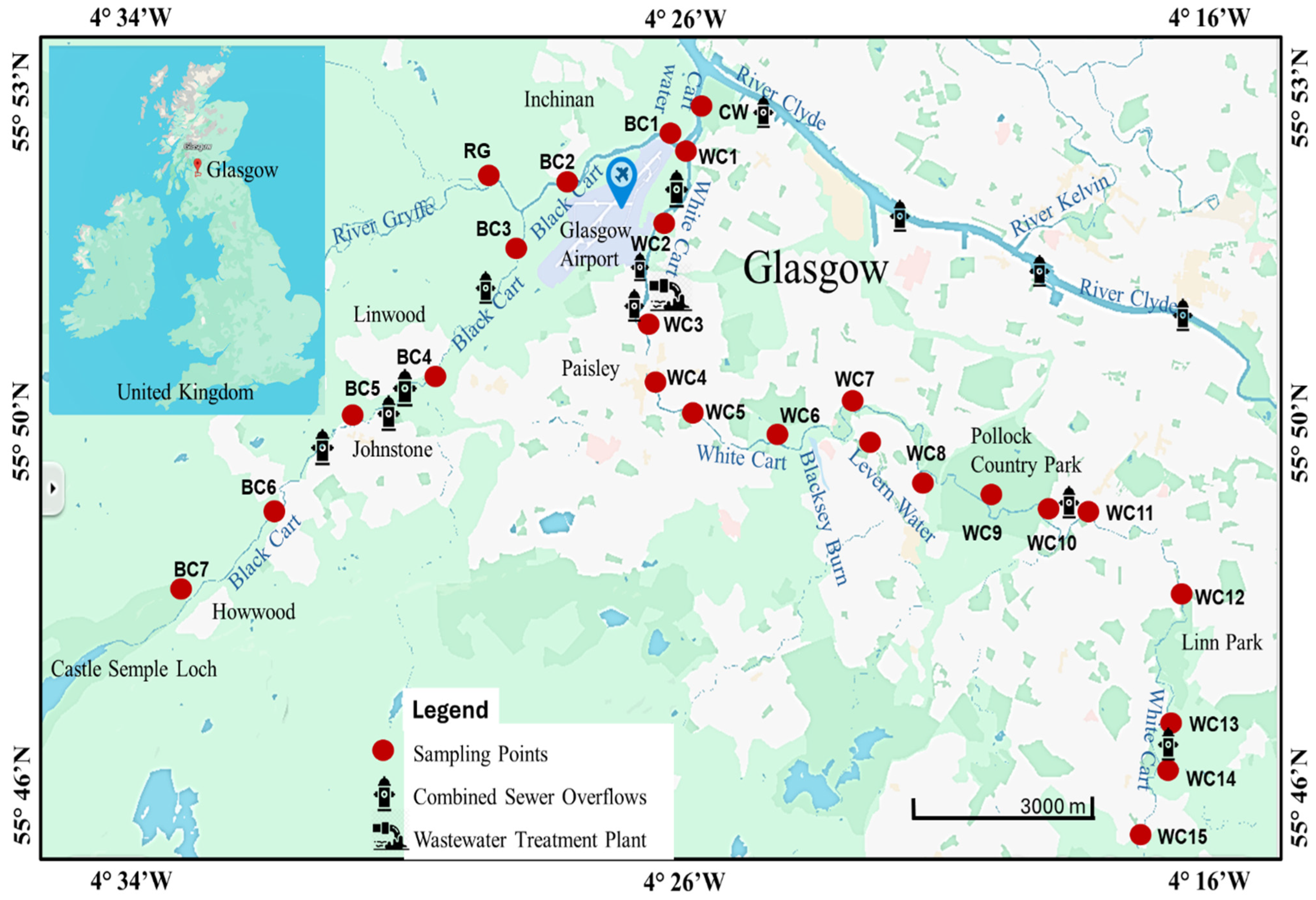
| Site Name | Site Coordinates | Current Land Use Within 500 m |
|---|---|---|
| CW | 55°53′00″ N, 4°24′54″ W | Agricultural land, boat club, hotel |
| BC1 | 55°52′51″ N, 4°24′45″ W | Agricultural land, airport runway |
| BC2 | 55°52′30″ N, 4°26′34″ W | Agricultural land, airport runway, residential buildings |
| BC3 | 55°51′43″ N, 4°27′42″ W | Agricultural land with few buildings |
| BC4 | 55°50′41″ N, 4°29′11″ W | Park playground, car parks and major motorway |
| BC5 | 55°50′16″ N, 4°30′45″ W | Shopping complex and museum |
| BC6 | 55°49′35″ N, 4°32′05″ W | Agricultural land with few buildings, parks and shopping complex |
| BC7 | 55°48′38″ N, 4°33′52″ W | Agricultural land, railway station, residential buildings |
| RG | 55°52′30″ N, 4°28′03″ W | Agricultural land with few buildings |
| WC1 | 55°52′41″ N, 4°24′34″ W | Residential buildings with large green areas |
| WC2 | 55°52′15″ N, 4°24′54″ W | Industrial estates with wastewater treatment plant |
| WC3 | 55°51′05″ N, 4°25′19″ W | Industrial estate, old shipping yard, shopping complex |
| WC4 | 55°50′34″ N, 4°25′08″ W | Shopping complex, hotel, major road bridge |
| WC5 | 55°50′19″ N, 4°24′11″ W | Residential buildings, green areas and ongoing building projects |
| WC6 | 55°50′06″ N, 4°22′45″ W | Agricultural land, residential buildings |
| WC7 | 55°50′30″ N, 4°21′39″ W | School, sparse residential buildings and park playgrounds |
| WC8 | 55°49′53″ N, 4°20′09″ W | Developed and ongoing residential building projects, sports park |
| WC9 | 55°49′35″ N, 4°19′03″ W | Country Park |
| WC10 | 55°49′25″ N, 4°17′57″ W | Residential buildings with green areas. |
| WC11 | 55°49′28″ N, 4°17′06″ W | Densely populated residential areas |
| WC12 | 55°48′47″ N, 4°15′29″ W | Densely populated residential areas, park playground |
| WC13 | 55°47′28″ N, 4°16′04″ W | Densely populated residential area, park playgrounds |
| WC14 | 55°46′52″ N, 4°15′57″W | Residential settlement, major road bridge, shopping complex |
| WC15 | 55°46′14″ N, 4°16′39″ W | Agricultural land with few buildings |
| LW | 55°50′11″ N, 4°21′30″ W | Sparse settlements, major motorway, park playground |
| Site | Abundance (Items/m3) | Shapes | Colours | Polymer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC6 | 200 | * Fragments (75%) † Films (25%) | Black, green, white | * PE (75%) † PP (25%) |
| WC9 | 100 | ‡ Fibres (50%) * Fragments (50%) | Black, white | ‡ Cellulose (50%) * PP (50%) |
| WC12 | 150 | * Fragments (100%) | Red, white | * LDPE (33%) * PP (67%) |
| WC13 | 100 | ‡ Fibres (50%) * Fragments (50%) | Blue, white | ‡ Cellulose (50%) * PP (50%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Enenche, D.E.; Davidson, C.M.; Osungbemiro, W.B.; Liggat, J.J. Distribution, Characterization and Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Two Rivers in West Central Scotland: The Black Cart Water and White Cart Water. Environments 2025, 12, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100342
Enenche DE, Davidson CM, Osungbemiro WB, Liggat JJ. Distribution, Characterization and Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Two Rivers in West Central Scotland: The Black Cart Water and White Cart Water. Environments. 2025; 12(10):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100342
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnenche, Daniel E., Christine M. Davidson, Walter B. Osungbemiro, and John J. Liggat. 2025. "Distribution, Characterization and Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Two Rivers in West Central Scotland: The Black Cart Water and White Cart Water" Environments 12, no. 10: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100342
APA StyleEnenche, D. E., Davidson, C. M., Osungbemiro, W. B., & Liggat, J. J. (2025). Distribution, Characterization and Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Two Rivers in West Central Scotland: The Black Cart Water and White Cart Water. Environments, 12(10), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100342








