Abstract
The Marano and Grado Lagoon (Adriatic Sea, Italy) is an important transitional environment that furnishes numerous ecosystem services and is under protection as Site of Community Importance. It suffers from an excess of nutrients, especially nitrate (NO3−), and has been designated as a nitrate vulnerable zone. In this work, sixteen water bodies were seasonally monitored for physicochemical parameters and nutrients, to elucidate the trophic state of the lagoon and to check the occurrence of significant temporal trends in a time series from 2011 to 2021. Steep gradients of spatial and seasonal distribution were observed for all parameters with elevated concentration of N-NO3− (up to 360 µM) in the western sector. The whole lagoon was in phosphorous limitation (P-PO43− mean ± s.d. = 0.15 ± 0.22 µM) with a mean Redfield ratio of 1130. The concentration of nutrients was significantly correlated with the degree of both freshwater inputs and precipitation. The calculation of trophic indices shows that the lagoon is in an oligotrophic to hypertrophic condition (i.e., TRIX 1.9–6.8). The analysis of the temporal series showed that despite some significant trends, the time span considered is too short to detect significant changes in the trophic state of this dynamic environment.
1. Introduction
The Marano and Grado Lagoon (MGL) belongs to an extensive network of transitional environments in the northern Adriatic Sea, covering an area of approximately 160 km2 between the deltas of the Tagliamento and Isonzo rivers [1]: it is formally divided into the Marano and Grado Basins [2]. The Marano Basin is the oldest part (5550–4200 years ago), with the current morphology reached around 1600 years ago. The Grado Basin is more recent (4th–6th century AD), and the morphology of its easternmost part was reached after the massive land reclamation that took place since the beginning of the 20th century [3]. The MGL is classified as a microtidal lagoon of large dimension and is one of the 57 Italian sites under the protection of the Ramsar Convention since 1971 (Valle Cavanata site number 169/1978 and Foci dello Stella number 190/1979) (https://www.ramsar.org/ accessed on 9 May 2024). As part of the implementation of the Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), the MGL has been designated as a Site of Community Importance (SCI-IT3320037).
Similar to others Mediterranean coastal areas, the MGL suffers from numerous anthropogenic pressures, such as the presence of industrial sites, marinas, fishing, fish and clam farming and tourism [4]. However, one of the main concerns is the excess nutrients, particularly nitrate (NO3−), deriving from upland farming practices [5], and the MGL has been designated as a Nitrate Vulnerable Zone (NVZ) since 2008 [6]. Saccon et al. [5] reported NO3− concentration ranging from 400 to 31,000 µg L−1 depending on the water circulation and influencing factors (i.e., mixing between seawater, freshwater and rainwater, tidal oscillation, wave motion, water flow direction, wind speed, atmospheric pressure, tributary discharge, lagoon bottom morphology, and bathymetry). Recently, Acquavita et al. [1] described a variable range, from oligotrophic to hypertrophic, for the trophic state of the MGL in a 1-year cycle of physicochemical measurements carried out throughout the lagoon using a series of trophic indices (i.e., Carlson Trophic Index, TRIX and ASSETS) [7,8,9]. In addition, more specific efforts have been attempted to study the concentration of nutrients in confined areas, such as dismissed fish farms, and the nutrient recycling at the sediment–water interface throughout benthic chamber deployment [2,10].
It is well known that the excess of nutrients (mainly nitrogen and phosphorus) leads to an imbalance of the pristine trophic state, resulting in problems of eutrophication [11], which is currently defined as “a process driven by the enrichment of water with nutrients, especially compounds of nitrogen and/or phosphorus, leading to: increased growth, primary production and biomass of algae, changes in the balance of organisms and water quality degradation”. The consequences of eutrophication are undesirable if they appreciably degrade ecosystem health and/or the sustainable provision of goods and services [12]. Fertiliser use, soil leaching, land clearing, livestock farming, wastewater discharge and the burning of fossil fuels are the main sources of nutrients [13], and, considering the eutrophication problems reported in Europe [14,15], policies have been adopted and translated into regional and communitarian programs, to control nutrient inputs and their effects on the environment. These include the Oslo–Paris Convention for the Protection of the Northeast Atlantic [16], the Helsinki Convention [17] for the Protection of the Baltic Sea, the Barcelona Convention (MEDPOL) for the Mediterranean, and legislative instruments such as the Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive [18] and the Nitrates Directive [19] in the European Union (EU). In recent decades, two more comprehensive pieces of legislation have been introduced: The Water Framework Directive (WFD/2000/60/EC) and the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD/2008/56/EC) [20,21]. Specifically, the WFD/2000/60/EC covers all surface waters and groundwater, while the MSFD/2008/56/EC provides a policy framework up to the 200 nautical miles’ limit of the European Exclusive Economic Zone [22].
The primary goal of the WFD/2000/60/CE is to achieve conditions of “good ecological status” in selected water bodies by 2015 (or 2027 if certain exemptions are invoked). The Directive takes account of biological, chemical, and morphological elements—which must be supported by physicochemical parameters—and in particular currently sets the limit for DIN (dissolved inorganic nitrogen as the sum of NO3−, NO2−, and NH4+) and phosphorus (as total phosphorus, TP). In Italy, the WFD/2000/60/CE was put into law via Italian Legislative Decree no 152/2006 and by decrees for typing (DM 131/2008), monitoring (DM 56/2009) and classification (DM 260/2010). The analysis of specific descriptors (i.e., geomorphology, tides and salinity) coupled with the application of the DPSIR (driver, pressure, state impact, response) model [23] is the first tool required by the WFD for the individualisation of water bodies that—based on salinity—corresponds to three types, namely mesohaline, polyhaline, and euhaline.
The objective of this study was to assess the spatial distribution and seasonal variability of physicochemical parameters and nutrients in order to characterise the water quality of the lagoon and to classify it in accordance with the implementation of the WFD/2000/60/CE. Given that the primary pressure on the system is the input of riverine freshwater, an analysis was conducted to assess the degree of precipitation at two selected inland sites. The occurrence of a correlation between precipitation and physicochemical parameters and nutrients was also tested. To assess the trophic status, numerous multimetric indices are available, as reported in Bonometto et al. [24]. The metrics related to macrophytes—macroalgae cover, seagrass cover, and benthic macrophytes—were not fully available. Therefore, the simpler and widely applied TSI and TRIX [7,8] were used. Based on evidence from previous studies conducted in an abnormally rainy year and considering that temporal variability is a key issue in monitoring and explaining the dynamics of ecological systems [25], especially in transitional environments [26], the time-series was also discussed to detect the occurrence of significant positive or negative trends of the considered parameters. This is of paramount importance considering that the prediction that emissions of N, a major contributor, will increase significantly between now and 2050 [27] and that the concomitant effect of climate change [28,29] calls for special attention in the monitoring and control of trophy in marine–coastal systems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area, Sampling Strategy and Analysis
The MGL is one of the 37 largest lagoons in the Mediterranean [30] and the second largest in the Adriatic Sea in terms of surface area, after the Lagoon of Venice. It is located between 45.46 and 45.40 N latitude and between 13.04 and 13.26 E longitude and has a total perimeter of about 80 km, a width of 1.8 km, and a maximum depth of 6 m. In terms of hydrology, six main sub-basins (Lignano, Sant’Andrea, Buso, Morgo, Grado, and Primero) were identified by morphologic features and modelling approach [31,32]. The morphology varied from limited areas just above the sea level, numerous channels connecting the plain to the open sea, mudflats, tidal channel, and subtidal zones [33].
The Stella and Cormor Rivers (36.1 and 10.7 m3 s−1, respectively) are responsible for the freshwater input in the Marano sector, while other rivers make a minor contribution. Consequently, the MGL shows a net salinity gradient [1,34]. Salinity is also influenced through the seawater exchange that occurs at the tidal inlets of Lignano, Porto Buso, and Grado during the semidiurnal tides that have a mean range of 0.65 m and spring and neap ranges of 1.05 and 0.22 m, respectively [34]. In addition, about thirty drainage pumps located in the low Friulian plain give a variable contribution.
2.2. Water Monitoring and Samples Analysis
As part of the implementation of the WFD/2000/60/CE, 17 water bodies were identified on the basis of salinity (mesohaline-TME, polyhaline-TPO and euhaline-TEU) using the DPSIR model [23]. In addition, some water bodies have been identified as heavily modified (FM) if they have been significantly altered from their original condition by human activities (i.e., hydrodynamic and morphological alterations, fish farms). It should be noted that the water body FM1 was not considered in this study, because it does not belong to the MGL: its hydrology is manually regulated through the opening of a single sluice gate that connect the water body with the open sea. The sketch map of the water bodies is shown in Figure 1. In Table 1 are reported the coordinates of sampling stations and the areas of the water bodies.
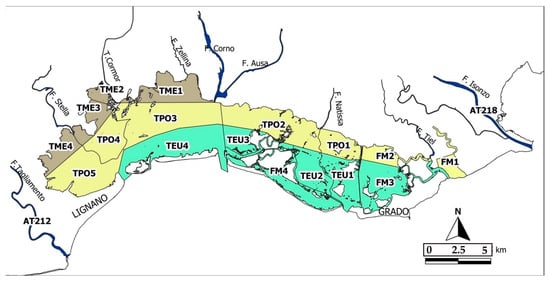
Figure 1.
The Marano and Grado Lagoon water bodies with the corresponding sampling stations. (TME: mesohaline; TPO: polyhaline; TEU: euhaline: FM: heavily modified).

Table 1.
The water bodies identified in the Lagoon of Marano and Grado, with the corresponding geographical coordinates of the sampling stations and surface areas.
Water sampling was initially carried out on a monthly basis (from 2011 to 2015), while the frequency was changed to a seasonal basis from 2016 to 2021. Therefore, in order to analyse a homogeneous database for the whole period, only the data collected in February, May, August, and November were considered in this work.
Samples for nutrient analysis were collected using a telescopic rod coupled to the specific pre-cleaned (HCl treated) polyethylene containers. The dissolved inorganic nutrients (ammonium, N-NH4+, nitrite, N-NO2−, nitrate, N-NO3−, phosphorus, P-PO43−) were analysed after filtration of the sample using GF/F 0.45-μm filters according to standard protocols [35] using an auto analyser (SEAL Analytical QuAAtro). The total nitrogen and phosphorus (TN and TP) were analysed tal quale with the same method after persulphate oxidation [36]. The calculated quantification limits (LOQ) were as follows: 0.025 µM for N–NO2−, 0.71 µM for N–NO3− and TN, 0.05 µM N–NH4+, and 0.01 µM for P-PO43− and TP. The accuracy of the method was verified in each analytical batch using certified standards (Inorganic Ventures standard solutions and MOOS-2, NRC) and spike samples, and analytical performance was regularly checked by proficiency testing (PT) organised by the European network of PT providers (QUASIMEME programmes AQ1 and AQ2).
In addition, the main physicochemical descriptors of the water column, temperature (°C), salinity, dissolved oxygen (expressed as % saturation and mg L−1), and chlorophyll a (µg L−1) were measured directly in situ with a CTD multiparameter probe (Idronaut Ocean Seven 316). It is noteworthy that the salinity was measured using the Practical Salinity Scale, and—as decided by the Joint Panel of Oceanographic Tables and Standards—it is reported in the paper without any symbol or indicator. The instrumental characteristics of the probe provided by the parent company are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Main sensor specifications of the Idronaut 316Plus CTD probe (www.idronaut.it accessed on 9 May 2024).
2.3. Source of Environmental Data
Monthly mean and decadal precipitation in the MGL, expressed as mm of cumulative rain, were obtained by the data provided by OSMER (Osservatorio Meteorologico Regionale del Friuli Venezia Giulia) at the website: https://www.osmer.fvg.it/clima.php?ln= (accessed on 9 May 2024). Due to the wide surface area of the MGL, two different meteorological stations were selected: Cervignano del Friuli (45°49′23″ N 013°20′06″ E) and Palazzolo dello Stella (45°48′ N 013°05′ E), which are referred to the Grado and Marano sectors, respectively.
2.4. Application of Trophic Indices
Trophic status was assessed using the Carlson’s trophic state index (TSI) [7] and the TRIX index [8]. The first index takes into consideration the concentrations of chlorophyll, a, and total phosphorous following the “Phase 1 approach” of eutrophication defined by Cloern [11]. It is expressed as µg L−1, using the following equations [37]:
TSI (Chl a) = 9.81 ln [Chl a] + 30.6
TSI (TP) = 14.42 ln [TP] + 4.15
The TRIX is calculated as follows [8,38]:
where Chl a is the concentration of the chlorophyll a (µg L−1), DO is the concentration of oxygen (% deviation from the saturation level), DIN is the sum of dissolved nitrogen species (µg L−1), TP is total phosphorous (µg L−1), and a and b are constant coefficient (1.5 and 1.2, respectively).
TRIX = [log10(Chl a) × (%DO) × (DIN) × (TP) + a]/b
2.5. Statistical Assessment
The final dataset was statistically analysed using the EXCEL™ and PAST (Paleontological Statistics); version 4.08 [39] software packages. The seasonal trends have been presented using a box and whisker plot: the median is represented by the horizontal bold line inside the box and the 25th and 75th percentiles are at the top and bottom. In this plot, the presence of outliers is indicated by circles. The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to test the normal distribution [40], and the non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis H test (K-W) [41] was used to test for the presence of significant differences of the medians in the parameters considered between the water bodies and in the selected seasons. The Spearman correlation coefficient (r) was used to test the linear relationship between variables. r was considered significant if the p-value was <0.05 [42]. The Mann–Kendall trend test (M-K) was used to assess the positive or negative time trend of selected parameters [43]. Distribution maps were produced as contour plots based on GIS technology (QGIS version 3.16.3 “Hannover”).
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Distribution and Seasonal Variability of Physicochemical Parameters
The univariate statistics of the physicochemical parameters are presented in Table 3, and the spatial distribution is presented in Figure 2.

Table 3.
Univariate statistics of physicochemical variables.
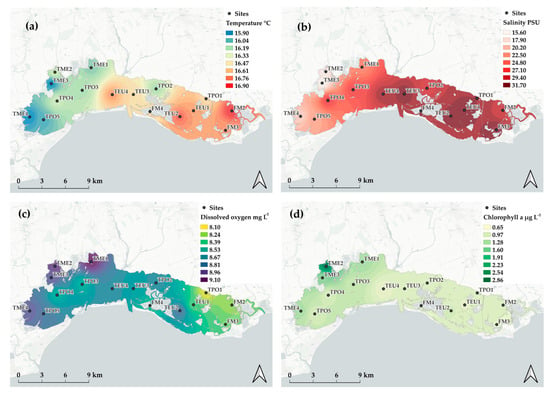
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of physicochemical parameters: (a) temperature, (b) salinity, (c) dissolved oxygen, and (d) chlorophyll a.
Surface water temperature averaged 16.4 ± 7.2 °C and ranged from 3.4 °C measured at TME1 in winter 2021 to the maximum of 30.1 °C found in summer 2013 at TPO5. On average, the highest value was found at FM2 (16.9 ± 6.9 °C) and the lowest at TME3 and TME4 (15.9 ± 7.1 and 15.9 ± 7.5 °C, respectively). Salinity averaged 26.8 ± 7.0, thus suggesting the occurrence of poly- to euhaline characteristics. However, some water bodies in the northwestern area display mesohaline characteristics (TME2, TM3, and TME4 with 16.9 ± 7.0, 15.6 ± 7.6 and 19.0 ± 5.6, respectively) with the lowest value (1.3) recorded at TME3 in November 2013. Dissolved oxygen covered a wide range of concentrations (3.8–15.0 mg L−1; mean = 8.61 ± 1.76 mg L−1) with the highest value found at TME1 (9.1 ± 2.3 mg L−1) and the lowest at TPO1 (8.1 ± 1.8 mg L−1). Chlorophyll a showed the highest mean value at TME2 and the lowest at TEU4 (2.86 ± 3.25 and 0.65 ± 0.36 µg L−1, respectively) as well as a remarkable peak in August 2021 (TME2 16.19 µg L−1).
A pronounced seasonal variability was observed for temperature with minima recorded in winter (7.8 ± 1.6 °C, median = 7.8 °C) and maxima in summer (25.9 ± 2.1 °C, median = 26.3 °C) (Figure 3) and, similarly, for salinity, which showed the highest mean value in summer (29.3 ± 5.7) and the lowest in autumn (25.0 ± 8.0). Dissolved oxygen showed a significant decrease from winter (10.4 ± 1.2 mg L−1) to summer (7.0 ± 1.2 mg L−1), followed by a sudden increase in autumn. Conversely, chlorophyll a showed the opposite pattern, with a maximum in summer (1.48 ± 1.75 µg L−1) and minimum values in autumn and winter (0.72 ± 0.49 and 0.79 ± 1.40 µg L−1, respectively).
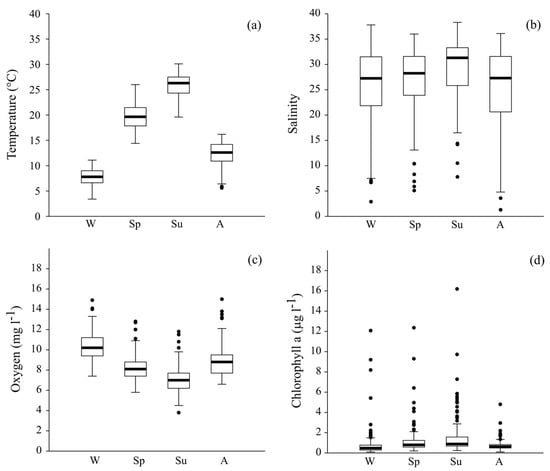
Figure 3.
Seasonal variability of physicochemical parameters: (a) temperature, (b) salinity, (c) dissolved oxygen, and (d) chlorophyll a.
3.2. Spatial Distribution and Seasonal Variability of Dissolved and Total Nutrients
The univariate statistics of dissolved and total nutrients are presented in Table 4 and the spatial distribution in Figure 4 and Figure 5.

Table 4.
Univariate statistics of dissolved and total nutrients.
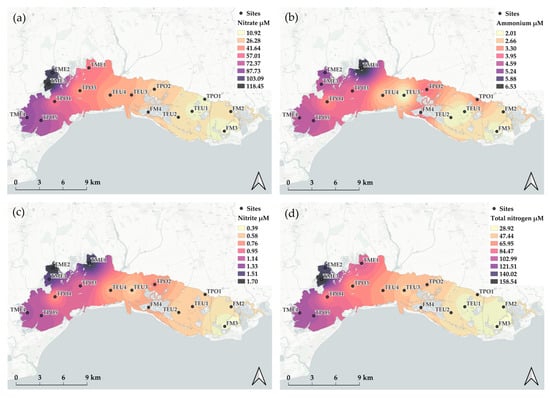
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of nitrogen species: (a) nitrate, (b) ammonium, (c) nitrite, and (d) total nitrogen.
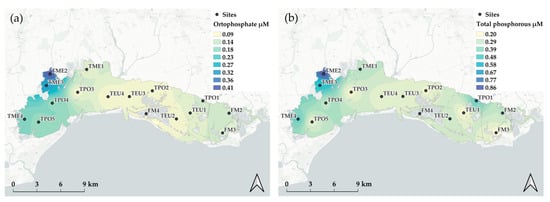
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of phosphorous species: (a) phosphate and (b) total phosphorous.
Nitrate (N-NO3−) was the dominant dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) form over N-NH4+ and N-NO2− in all water bodies (88.6 ± 4.6%, 9.3 ± 4.0% and 2.1 ± 0.7%, respectively) with a mean concentration of 45.9 ± 52.3 µM. The highest value was measured at TME3 (366.6 µM in February 2021), and this water body also had the highest mean during the monitoring period (118.5 ± 81.0 µM), while FM3 had the lowest average concentration (10.9 ± 9.7 µM) (Figure 4). On average, the level of N-NH4+ was an order of magnitude lower than that of N-NO3−, with 3.56 ± 3.13 µM. TME1 had the highest value both in absolute and average terms, with 29.3 µM in August 2017 and 6.53 ± 6.04 µM. On average, FM3 and TEU1 had the same minima with 2.01 ± 1.10 and 2.01 ± 1.20 µM, respectively. Nitrite (N-NO2−), with a mean of 0.88 ± 0.72 µM, was the less present form. TME1 and TME2 were the most enriched water bodies (1.61 ± 1.19 and 1.70 ± 0.86 µM, respectively), while FM3 displayed the lowest mean concentration (0.39 ± 0.49 µM). Total nitrogen (TN) accounted for 33.9% of the nitrogen pool and ranged from 5.7 to 459.9 µM at FM3 and TPO5 in August 2013 and February 2011, respectively (69.9 ± 54.1 µM). On average, FM3 was the less enriched water body with 28.9 ± 15.2 µM and TME3 was characterised by the highest concentration with 158.6 ± 60.9 µM.
The whole lagoon showed quite low concentration of P-PO43− (mean 0.15 ± 0.22 µM) with many values below the LOQ, except for the water body TME2. This latter had the highest mean concentration for the whole period (0.41 ± 0.39 µM), while TEU2, TEU4, and TPO2 had the lowest, with values of 0.09 ± 0.09, 0.09 ± 0.07, and 0.09 ± 0.12 µM, respectively. Total phosphorous (TP) accounted for 38.6% of the pool and ranged from 0.01 to 4.68 µM with a mean concentration of 0.33 ± 0.47 µM. The highest mean value was found at TME2 (0.86 ± 0.78 µM) and the lowest at TEU1 (0.20 ± 0.22 µM) (Figure 5).
The seasonal trend for the species of nutrient considered are depicted in Figure 6.
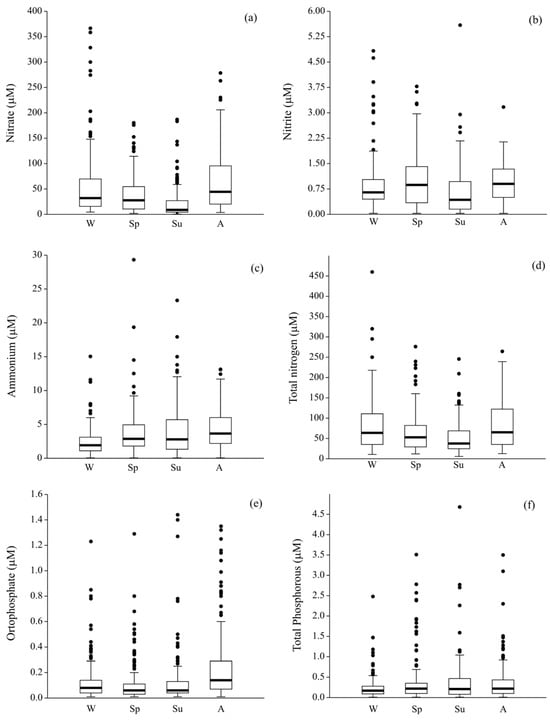
Figure 6.
Seasonal variability of: (a) nitrate, (b) nitrite, (c) ammonium, (d) total nitrogen, (e) orthophosphate, and (f) total phosphorous.
As observed in the case of physicochemical parameters, nutrients also showed peculiar seasonal trends. In the case of N-NO3−, peaks of concentration were centred in both autumn and winter (63.0 ± 56.8 and 56.0 ± 65.3 µM, respectively), while summer displayed levels approximately half. This trend was paralleled by TN that ranged from 82.0 ± 65.1 to 51.3 ± 39.4 µM in winter and summer, respectively. On the contrary, the reduced form showed important peaks in summer (N-NH4+, 3.94 ± 3.82 µM) and autumn (N-NH4+, 4.27 ± 2.82 µM). Regarding the phosphorous species, the trend of P-PO43− was quite similar to those of N-NO3− and TN, with the highest average value found in autumn (0.24 ± 0.28 µM), while for TP from spring to autumn, the mean concentrations were quite similar (from 0.36 to 0.38 µM) and higher when compared to those recorded in winter (0.24 ± 0.29 µM).
3.3. Analysis of Precipitation
The analysis of precipitation was conducted by considering the accumulated rainfall (mm), calculated as the sum of daily precipitation occurring ten days before each sampling operation. The highest value was recorded in autumn 2019 at Cervignano del Friuli (rainfall = 477 mm), while the lowest was recorded in summer 2011 (rainfall = 1 mm) at the same site. Cervignano was also characterised by the highest mean annual value, 129 ± 109 mm, whereas Palazzolo dello Stella was 103 ± 83 mm on average. However, no significant difference was found between the median at the two sites (K-W = 0.2581). When considering the seasons, autumn exhibited the greatest precipitation levels, with an average of 155 ± 121 mm, while summer exhibited the lowest levels, with an average of 78 ± 46 mm.
3.4. Relationship between Physicochemical Parameters, Nutrients, and Precipitation
Spearman rank order correlations between variables and the accumulation of precipitation are reported in Table 5 where the occurrence of significant correlation is reported in bold.

Table 5.
Spearman rank order correlation between all variables during the study period.
Temperature was negatively correlated with the level of dissolved oxygen (r = −0.9032) and with both N-NO3− and TN (r = −0.5678 and −0.6096, respectively) and was positively correlated with chlorophyll a (r = 0.5334). Salinity was negatively correlated with all nutrient species, with the exception of N-NH4+ and TP and also with the degree of precipitations. The latter were positively correlated with the oxidised form of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (except for N-NH4+). Chlorophyll a was positively correlated with TP and negatively correlated with O2 and N-NO3−.
3.5. Application of Trophic State Indices
The calculation of the TSI (Chl a/TP) and TRIX indices is reported in Figure 7.
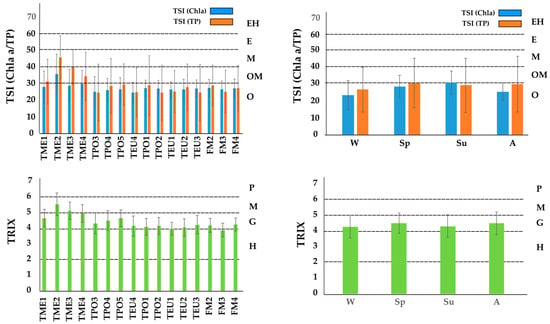
Figure 7.
Trophic state of the Marano and Grado Lagoon with the application of the Carlson’s [7] and TRIX indices [8,44]. For TSI index O = oligotrophic; OM = oligomesotrophic; M = mesotrophic; E = eutrophic; EH = eutrophic to hypereutrophic. For TRIX index H = high; G = good; M = moderate; and P = poor.
The range of the TSI is usually 0–100 and defines conditions from oligotrophic (<30) to hypereutrophic (>70) states. The mean values calculated for the whole basin were 27.6 ± 7.6 and 29.7 ± 15.5 for the TSI (Chl a) and TSI (TP), respectively, thus suggesting a classification as oligotrophic. However, it is noteworthy the wide variability and the system experienced, in some cases, conditions that range from oligomesotrophic to eutrophic. Taking into consideration the mean values, all the water bodies can be classified as oligotrophic, with the exceptions of TME2 and TME3 (only by the application of TP concentrations). Overall, the values were slightly higher during spring and summer periods.
The classification with the TRIX follows the criteria introduced by Penna et al. [44], where the system has quality that varies from high, characteristic of a system with low productivity and low trophic levels (TRIX: 2–4), to poor, typical of a highly productive system with high trophic levels (TRIX: 6–8). On average, the calculated value for TRIX was 4.41 ± 0.71, which suggests a trophic status ranging from high to moderate condition. As observed for the TSI (Chl a/TP) the water bodies TME2 and TME3 had the highest mean level (5.52 ± 0.73 and 5.11 ± 0.56, respectively), while TEU1 had the lowest (3.97 ± 0.42). Taking into consideration the seasonal trend, it is noteworthy that spring and autumn displayed levels slightly higher than winter and summer.
3.6. Temporal Trends of Physicochemical Parameters, Nutrients, Trophic Indices and Rainfall (2011–2021)
The analysis of the temporal series considered decadal values for all parameters. These values were yearly averaged over the entire lagoon. Positive and negative slopes of the regression line were found for all parameters except for TN. To distinguish statistically significant trends, the Mann-Kendall trend test was applied. Statistically significant increases were observed for P-PO43− (S = 27; pno trend = 0.0417), TSI (TP) (S = 29; pno trend = 0.0292), TSI (Chla) (S = 27; pno trend = 0.0429), and TRIX (S = 27; pno trend = 0.0429). Conversely, a significant decrease was found for N-NH4+ (S = −35; pno trend = 0.0077). Although positive trends were observed for temperature, chlorophyll a, N-NO3−, and TN, they were not statistically significant. Slightly negative trends were observed for salinity and dissolved oxygen. The related plots are reported in Figure S1. Time series of precipitation showed dry years (2011, 2015, 2018) alternate with wet period (i.e., 2019), but overall, no significant trend was observed (Figure S2).
4. Discussion and Conclusions
As a member state of the European Union, Italy has implemented the WFD 2000/60/CE. Since 2010, the Friuli Venezia Giulia region, which includes the Marano and Grado lagoon, has been conducting a monitoring programme. The programme focuses on collecting surface water samples seasonally to define the physicochemical conditions that support the biological quality elements. This allows for a better understanding of the trophic state of the lagoon. Furthermore, long-term studies have not been conducted in the MGL, and it is well known that physicochemical parameters that describe the water column are susceptible to significant changes, both positive and negative, in response to climate change and anthropogenic pressures [45,46,47,48,49,50].
The Mediterranean Sea is renowned for its significant spatiotemporal variability of physicochemical parameters and nutrients in coastal marine areas. Fluctuations in lagoons are typically substantial due to their location between land and sea, shallow depth, tidal effects, wind action, and runoff from inland. This has been observed in numerous studies [26,51,52,53]. Similar observations were made in the MGL, where steep spatial distribution gradients and fluctuations in the form of outliers were found for all parameters except water temperature and dissolved oxygen concentration (see Figures S3 and S4). Additionally, clear seasonal variability was detected, except for total phosphorus. The observed variabilities were statistically significant, as confirmed by the application of the Kruskal–Wallis test for equal medians (see Table 6).

Table 6.
Kruskal–Wallis test for comparison of medians. Significant differences are reported in bold.
The spatial variability in the MGL is mainly influenced by freshwater input and morphology. The impact of river discharge is supported by the significant inverse correlation between salinity and all nutrient species (except for N-NH4+ and TP) as well as the positive correlation with accumulated rainfall. However, the pattern of rainfall with nutrient level could be limited by the active exchange with the more diluted seawater through the tidal channel (Grado (390 m wide/10 m deep) 22% of the total water exchange, Porto Buso (430 m, 30%), and Lignano (310 m/11 m, 35%) [54]. The Marano basin is characterised by the flow of the Stella and Cormor rivers, which have average discharges of 36.1 and 10.7 m3 s−1 respectively. This basin has the lowest salinity values and the highest nutrient concentration. The morphology of the basin affects the water residence time, which can be up to 20 days under certain conditions [32]. As a result, the surface water temperature is higher on average within the confined water bodies.
The primary cause of nutrient loading in the upper Friulian Plain is runoff resulting from intensive agricultural activity [6]. This is evidenced by the high levels of the main dissolved nitrogen form, N-NO3−, which derives from lixiviate enriched in plant fertilisers [55,56,57,58]. Additionally, there are direct and inverse significant correlations between N-NO3− and accumulated rainfall and salinity. The reduced form, N-NH4+, displays the highest values in summer and is inversely correlated with the O2 content. This is likely due to intense biogeochemical processes, such as uptake by phytoplankton, excretion by zooplankton, bacterial remineralisation, and denitrification processes, which are favoured in low oxygen conditions and stimulated by high temperatures [59,60,61] and have already been observed in different lagoon environments [62,63,64]. The concentration of PO43− was significantly lower (three orders of magnitude) than that of N-NO3−. However, its spatial distribution was similar to that of nitrogen species, thus supporting the common origin of nutrients. The anthropogenic impact in the MGL is well evident if the level of nutrients is compared to that observed outside of the lagoon area in the adjacent Gulf of Trieste and in the northern Adriatic Sea. Cozzi et al. [65] analysed a long-term series of data (1992–2018) at the station C1, which belongs to the Long-term Ecosystem Research Network (http://www.lteritalia.it/ accessed on 9 May 2024). On average, DIN was mostly lower than 4 µM (value integrated over water column), which is one order of magnitude lower than that observed in the MGL (surface waters). In addition, Giani et al. [66] reported a typical range from <lod to 16 µM of N-NO3− for all the northern Adriatic. On the contrary, P-PO43− was comparable, with a minimum of 0.18 and a maximum of 1.5 µM. This suggests that the main concern in the MGL is the anthropogenic input of N species. It is noteworthy that due to the exchange of water masses, there is an active export of nutrients from the MGL to the Gulf of Trieste. In fact, two external water bodies recently considered by Bellese [67] showed values of N-NO3− up to 130 µM (mean 15.92 ± 17.73 μM), which is a dilution of about one third respect to the value found in the lagoon basin.
The Redfield N:P ratio (RR) is commonly used to describe the relative importance of N and P as factors capable of limiting the growth of phytoplankton [68]. It is important to note that the ratio of 16:1, originally calculated, can be significantly deviated due to the uncontrolled supply of nutrients, as observed in our lagoon. However, it is worth mentioning that the RR is currently being continuously revised, as reported in [69]. In this work the RR showed a wide range (3–55,967) and was, on average, 1130 ± 3033. These data are comparable to those observed in the nearby Gulf of Trieste and Isonzo River basin, thus confirming that the northern Adriatic Sea is experiencing P-limitation that is extreme in some cases [65,67,70,71]. This is a common occurrence in coastal environments with anthropogenic inputs that are enriched in N compared to P [72,73] and is a well-recognised characteristic of the Mediterranean Sea [74,75] and of other Mediterranean coastal lagoons [56,75,76,77]. The RR significantly decrease in summer due to the reduced inputs of dissolved nitrogen form and to the hypoxic conditions that cause the sediment to be an internal source of nutrients (e.g., ammonium and phosphates) [78].
Since the early 1970s, the European Council has introduced several environmental directives to establish threshold values for the concentration of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) species in various aspects of water quality. These include drinking water, protection from dangerous substances, support of fish life, and regulation of urban wastewater (74/440/EEC; 76/464/EC; 78/659/E; 80/68/EC; 98/15/EC). Despite the high DIN concentrations, the recommended values have never been exceeded. The WFD/2000/60/CE is currently in force and sets limits for DIN and P-PO43− as physicochemical elements that support ecological status. Proposed thresholds differentiate between euhaline water bodies and poli- and mesohaline ones. In euhaline water bodies, the limits for DIN and P-PO43− are 18 and 0.48 µM, respectively. For poli- and mesohaline ones, the limit for DIN is 30 µM. For P-PO43−, the limit value was never exceeded. However, all water bodies in the Marano basin were affected by DIN, including TEU2, TEU3, FM2, and FM4 in the Grado Basin.
The detection of eutrophication-related issues commonly involves measuring the concentration of chlorophyll a. In our transitional system, both the average and maximum values are lower than those reported for other Mediterranean lagoons, which in some cases reached extreme values close to 50 µg L−1 [57,61,76,79,80] and are indication of oligotrophic/mesotrophic conditions [81,82]. Phytoplankton growth rate is commonly sustained by the absolute concentration of nitrogen and phosphorus [83] and limited by light availability [84,85]. Despite P-limitation, chlorophyll a concentration in our lagoon is correlated with TP but not with dissolved and total nitrogen species, as the signal of the latter is superimposed with respect to that of phosphorus [61]. In shallow-water systems like the MGL, turbidity caused by suspended solid material may limit the production of chlorophyll a. This is due to reduced availability of light for photosynthesis and soluble phosphorus, which adheres to solid particles [86]. It is possible that this is the reason for the observed correlation with TP, but unfortunately no direct measurements of total suspended matter are available in this study to confirm the hypothesis. Overall, the traditional models that assume a direct response of phytoplankton to nutrient load (Phase I sensu Cloern) [11] is not applicable in this lagoon environment and at the same time indicates that phytoplankton do not efficiently control nutrient concentrations [87].
The use of indices can assess eutrophication based on a few diagnostic physical and biogeochemical variables. To account for the variability of physicochemical parameters in the lagoon environment, such as salinity, this work applies criteria suitable for fresh, marine–coastal, and transitional waters [7,8,38]. When more variables that act as drivers (i.e., different species of nutrients) and well-known responses (i.e., chlorophyll a, dissolved oxygen) are considered for the calculation, the application of Carlson’s indices can result in a wide range of classifications. This is a common finding, as reported by Acquavita et al. and Coelho et al. [1,57], which is also supported by the present study. The MGL exhibited greater eutrophication when the TSI (TP) was applied, as opposed to the TSI (CHla). This finding is consistent with the results reported in [57,76,88]. Specifically, 8.5% of the samples were in a eutrophic condition in the former case, while only 1.34% were in a eutrophic condition in the latter. The multimetric TRIX considers both drivers and responses in the same formula, making it more suitable for assessing the trophic state of coastal environments. However, TRIX was calibrated on the coastline of the Adriatic and Tyrrhenian Seas [8,32,38]. As previously suggested [57], specific classification criteria should be proposed to assess the correspondence between TRIX and water quality in lagoons. The trophic condition of the MGL varied, but the system is mostly oligo-mesotrophic. This suggests that several factors may contribute to buffering the input of nutrients that limit primary production (i.e., P-limitation, mineralization processes, water transparency, active exchange of water with the open sea, presence of microphytobenthos and macroalgae) [11,61,89,90]. It is important to note that the assessment of trophic conditions in transitional environments is critical. It is challenging to distinguish between the effects of anthropogenic pressures and the trophic status that is supported by the natural background of the system (EC, 2024) [24]. The indices TSI (TP and Chl-a) and TRIX have been a significant influence in the past literature [24] due to the ease of collection of the parameters that compose the indices. In this context, it is evident that the simplicity of these indices—particularly that of the TSI, which functions as a linear cause-and-effect mode (as defined by Phase-1 Cloern [11]) and which was calibrated for freshwater ecosystems—provides only a preliminary indication of the trophic state. This is primarily applicable to mesohaline water types. It is evident that the state of the art of the previous multimetric indices assessed for transitional waters [9,91,92,93,94] must be surpassed in order to reach the more recent TWEAM (transitional water eutrophication assessment method) [24]. It is recommended that further parameters, particularly biological ones, be considered in order to provide a more accurate assessment of the water quality of the Marano and Grado Lagoon. However, this is complicated by the difficulty of collecting samples at an appropriate frequency.
Temporal patterns observed for physicochemical parameters and nutrients suggests that significant changes can also be detected, if a long-term series of data is available, without human intervention (i.e., land reclamation, restoration). The latter are in fact causes of significant improvement of the trophic state, or better reoligotrophication, in such sensitive environments [95,96,97]. For natural systems that have not been disturbed by human intervention, there is a limited body of scientific literature on the remediation of environmentally degraded conditions, but two works similar to ours have been carried out in the nearby Lagoon of Venice [98,99]. The authors described a general increase in DIN and a decrease in PO43− because of the reduced amounts of phosphorous compounds, from 8% to 1%, in domestic and industrial Italian detergents, following Italian laws enforced in 1983. There is no overlap between the time periods under consideration and the time period of our study, and therefore, no direct comparison can be made. In fact, it is surprising that in our case P-PO43− significantly increase, but the improvement effects observed in water quality of marine coastal environment [100] was followed by a slight counter-trend [67,101]. Positive and significant increases were also found for the indices TSI (Chla) and TRIX. This evidence reflects the positive trend observed for Chl a, TP, and N-NO3− (see Supplementary Materials). On the other hand, N-NH4+ showed a significant negative trend, which could be related to improvement in the efficiency of the local sewage treatment plants. A positive trend was observed for the temperature which is in accordance with the evidence reported for the whole Mediterranean area [102] and in the adjacent Gulf of Trieste [103,104], whereas salinity showed a decrease. This latter parameter was found to generally increase in the Mediterranean Sea [105], the Gulf of Trieste [103], the Venice Lagoon [106], and—considering the presence of macrozoobenthos in relation with salinity—the MGL [107]. Thus, the negative pattern found in our study is probably influenced by the limited time series and by the recent anomaly of rainfall that occurred in 2019.
This study concludes that the MGL shows clear patterns in the distribution and seasonal variation of environmental parameters, with high nutrient levels, especially nitrogen, in the western part due to anthropogenic (effluent) sources and, as a consequence, high variability of trophic state using both TSI and TRIX indices depending on where and when the indices are applied. The current state of the lagoon requires careful management given its importance as an ecosystem service and should consider the maintenance of long-term series to better define future strategies, especially in the light of actual climate change. Future works and research programmes dedicated to the biogeochemical budget, biological processes, and integration with a modelling approach could provide further understanding, and this will be part of our future study.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/environments11070152/s1, Figure S1: Temporal trends of physicochemical parameters, nutrients, trophic indices and rainfall in the Marano and Grado Lagoon from 2011 to 2021. Figure S2: Mean monthly value of rainfall over the period 2011–2021. Figure S3: Spatial distribution of physicochemical parameters in the Marano and Grado Lagoon. A dashed line separates the water bodies of the Marano Basin (on the left) from those of the Grado Basin (on the right). Figure S4: Spatial distribution of nutrients in the Marano and Grado Lagoon. A dashed line separates the water bodies of the Marano Basin (on the left) from those of the Grado Basin (on the right).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A. and C.O.; methodology, A.A., O.B., N.B. and C.O.; software, A.A. and F.P.; formal analysis, A.A. and N.B.; investigation, A.A.; resources, A.A., F.P. and C.O.; data curation, A.A., N.B., O.B. and F.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.; writing—review and editing, A.A., O.B., N.B., F.P. and C.O.; visualization, A.A. and N.B.; supervision, C.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are partially openly available at the following website: https://www.dati.friuliveneziagiulia.it/Ambiente/Acqua-Acque-di-classificazione-Superficiali-marino/qcsf-bwk5/about_data, accessed on 9 May 2024. Further requests should be submitted to: urp@arpa.fvg.it and to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The Authors would like to thank all the staff of the Friuli Venezia Giulia Environmental Protection Agency (Arpa FVG) involved in the sampling operations and laboratory analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Acquavita, A.; Aleffi, I.F.; Benci, C.; Bettoso, N.; Crevatin, E.; Milani, L.; Tamberlich, F.; Toniatti, L.; Barbieri, P.; Licen, S.; et al. Annual characterization of the nutrients and trophic state in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon: The Marano and Grado Lagoon (northern Adriatic Sea). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vittor, C.; Faganeli, J.; Emili, A.; Covelli, S.; Predonzani, S.; Acquavita, A. Benthic fluxes of oxygen. carbon and nutrients in the Marano and Grado Lagoon (northern Adriatic Sea. Italy). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 113, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontolan, G.; Pillon, S.; Bezzi, A.; Villalta, R.; Lipizer, M.; Triches, A.; D’Aietti, A. Human impact and the historical transformation of saltmarshes in the Marano and Grado Lagoon, northern Adriatic sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 113, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramieri, E.; Barbanti, A.; Picone, M.; Menchini, G.; Bressan, E.; Dal Forno, E. Integrated Plan for the Sustainable Management of the Lagoon of Marano and Grado. In Proceedings of the Littoral 2010—Adapting to Global Change at the Coast: Leadership, Innovation, and Investment, London, UK, 21–23 September 2010; Available online: http://coastnet-littoral2010.edpsciences.org/articles/litt/pdf/2011/01/litt-05008.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Saccon, P.; Leis, A.; Marca, A.; Kaiser, J.; Campisi, L.; Böttcher, M.E.; Savarino, J.; Escher, P.; Eisenhauer, A.; Erbland, J. Multisotope approach for the identification and characterisation of nitrate pollution sources in the Marano lagoon (Italy) and parts of its catchment area. App. Geochem. 2013, 34, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RAFVG. S.A.R.A. Sistema Aree Regionali Ambientali Costituzione Sistema Regionale delle Aree Naturali. Piano di Gestione del SIC/ZPS IT3320037 Laguna di Marano e Grado. Available online: https://www.regione.fvg.it/rafvg/export/sites/default/RAFVG/ambiente-territorio/tutela-ambiente-gestione-risorse-naturali/FOGLIA203/allegati/documenti_tecnici/PdG_Laguna_testo.pdf (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limonol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollenweider, R.A.; Giovanardi, F.; Montanari, G.; Rinaldi, A. Characterisation of the trophic conditions of marine coastal waters with special reference to the NW Adriatic Sea: Proposal for a trophic state, turbidity and generalized water quality index. Environments 1998, 9, 329–357. [Google Scholar]
- Bricker, S.B.; Ferreira, J.G.; Simas, T. An integrated methodology for assessment of estuarine trophic status. Ecol. Model. 2003, 169, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petranich, E.; Covelli, S.; Acquavita, A.; De Vittor, C.; Faganeli, J.; Contin, M. Benthic nutrient cycling at the sediment-water interface in a lagoon fish farming system (northern Adriatic Sea, Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J.E. Our evolving concept of the coastal eutrophication problem. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 210, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.G.; Andersen, J.H.; Borja, A.; Bricker, S.B.; Camp, J.; Cardoso da Silva, M.; Garcés, E.; Heiskanen, A.S.; Humborg, C.; Ignatiades, L.; et al. Marine Strategy Framework Directive Task Group 5 Report Eutrophication; EUR 24338 EN e Joint Research Centre, Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2010; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Nixon, S.W. Coastal marine eutrophication: A definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 1995, 41, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karydis, M.; Kitsou, D. Eutrophication and environmental policy in the Mediterranean Sea: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 4931–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. Nutrient Enrichment and Eutrophication in Europe’s Seas—Moving towards a Healthy Marine Environment; EEA Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- OSPAR. Common Assessment Criteria, Their Assessment Levels and Area Classification within the Comprehensive Procedure of the Common Procedure. OSPAR Commission for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the North-East Atlantic. Available online: http://www.ospar.org/eng/html/welcome.html (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- HELCOM. HELCOM Baltic Sea Action Plan; Helsinki Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2021; p. 103. Available online: http://www.helcom.fi/BSAP/ (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- 91/271/EEC; Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive. European Community: Maastricht, The Netherlands, 1991.
- 91/676/EEC; Nitrates Directive. European Community: Maastricht, The Netherlands, 1991.
- European Community. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community actions in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Union 2000, L 237, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- European Community. Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008 establishing a framework for Community actions in the field of marine environmental policy (Marine Strategy Framework Directive). Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, L 164, 19–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, J.G.; Andersen, J.H.; Borja, A.; Bricker, S.B.; Camp, J.; Cardoso da Silva, M.; Garcés, E.; Heiskanen, A.-S.; Humborg, C.; Ignatiades, L.; et al. Overview of eutrophication indicators to assess environmental status within the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, Á.; Galparsoro, I.; Solaun, O.; Muxika, I.; Tello, E.M.; Uriarte, A.; Valencia, V. The European Water Framework Directive and the DPSIR, a methodological approach to assess the risk of failing to achieve good ecological status. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 66, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonometto, A.; Ponis, E.; Cacciatore, F.; Riccardi, E.; Pigozzi, S.; Parati, P.; Novello, M.; Ungaro, N.; Acquavita, A.; Manconi, P. A new Multi-Index Method for the eutrophication assessment in transitional waters: Large-Scale implementation in Italian lagoons. Environments 2022, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, A. Timescales, dynamics and ecological understanding. Ecology 2010, 91, 3471–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena-Moya, P.; Gómez-Rodríguez, C.; Pardo, I. Spatio-temporal variability in water chemistry of Mediterranean coastal lagoons and its management implications. Wetlands 2012, 32, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jickells, T.D.; Buitenhuis, E.; Altieri, K.; Baker, A.R.; Capone, D.; Duce, R.A. A revaluation of the magnitude and impacts of anthropogenic atmospheric nitrogen inputs on the ocean. Biogeochem. Cycles 2017, 31, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, E.T.; Díaz, R.J.; Justić, B. Global change and eutrophication of coastal waters. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, E.; Michalak, A.M.; Balaji, V. Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science 2017, 357, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.; Pérez, R.; Sòria-Pepinyà, X. Mediterranean coastal lagoon review: Sites to visit before disappearance. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambati, A. Metalli Pesanti nelle Lagune di Marano e Grado: Piano di Studi Finalizzato All’accertamento della Presenza di Eventuali Sostanze Tossiche Persistenti nel Bacino Lagunare di Marano e Grado ed al suo Risanamento; Technical Report; Regione Autonoma Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Servizio Idraulica: Trieste, Italy, 1996; 174p. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarin, C.; Umgiesser, G.; Bajo, M.; Bellafiore, D.; De Pascalis, F.; Ghezzo, M.; Mattassi, G.; Scroccaro, I. Hydraulic zonation of the lagoons of Marano and Grado, Italy, A modelling approach. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 87, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triches, A.; Pillon, S.; Bezzi, A.; Lipizer, M.; Gordini, E. Carta Batimetrica della Laguna di Marano e Grado; Regione Autonoma Friuli Venezia Giulia—A Cura di: Autorità di Bacino Regionale del Friuli Venezia Giulia, Commissario Delegato per L’emergenza Socioeconomico Ambientale Determinatasi nella Laguna di Marano Lagunare e Grado; Dipartimento di Geoscienze dell’Università di Trieste: Trieste, Italy; OGS—Istituto Nazionale di Oceanografia e di Geofisica Sperimentale: Sgonico, Italy; Arti Grafiche Friulane, Imoco spa (Ud): Fagagna, Italy, 2011; Available online: https://www.regione.fvg.it/rafvg/export/sites/default/RAFVG/ambiente-territorio/tutela-ambiente-gestione-risorse-naturali/FOGLIA202/allegati/Note_illustrative_Carta_batimetrica.pdf (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Pittaluga, F.; Aleffi, I.F.; Bettoso, N.; Blasutto, O.; Celio, M.; Codarin, A.; Cumani, F.; Faresi, L.; Guiatti, D.; Orlandi, C.; et al. The Shape Project: An innovative approach to understanding seasonal and diel dissolved oxygen dynamics in the Marano and Grado Lagoon (Adriatic Sea) under the WFD/2000/60/CE. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasshoff, K.; Ehrhardt, M.; Kremling, K. Methods of Seawater Analyses; Verlag Chemie: Weinheim, Germany, 1983; p. 419. [Google Scholar]
- Valderrama, J.C. The simultaneous analyses of total phosphorus and total nitrogen in natural waters. Mar. Chem. 1981, 10, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E.; Simpson, J. A Coordinator’s Guide to Volunteer Lake Monitoring Methods; North American Lake Management Society: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Giovanardi, F.; Vollenweider, R.A. Trophic conditions of marine coastal waters: Experience in applying the Trophic Index TRIX to two areas of the Adriatic and Tyrrhenian seas. J. Limnol. 2004, 63, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes in C; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, R.O. Statistical Methods for Environmental Pollution Monitoring; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Penna, N.; Cappellacci, S.; Ricci, F. The influence of the Po River discharge on phytoplankton bloom dynamics along the coastline of Pesaro (Italy) in the Adriatic Sea. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2004, 48, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marullo, S.; Artale, V.; Santoleri, R. The SST multidecadal variability in the Atlantic–Mediterranean region and its relation to AMO. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 4385–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltout, M.; Omstedt, A. Recent sea surface temperature trends and future scenarios for the Mediterranean Sea. Oceanologia 2014, 56, 411–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunstan, P.K.; Foster, S.D.; King, E.; Risbey, J.; O’Kane, T.J.; Monselesan, D.; Hobday, A.J.; Hartog, J.R.; Thompson, P.A. Global patterns of change and variation in sea surface temperature and chlorophyll a. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoni, S.; Bantan, R.A.; Al-Dubai, T.A.; Lubis, M.Z.; Anurogo, W.; Silaban, R.D. Chlorophyll-a, and sea surface temperature (SST) as proxies for climate changes: Case study in Batu Ampar waters, Riau Islands. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 273, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaffey, C.; Palmer, M.; Greenwood, N.; Sharples, J. Impacts of climate change on dissolved oxygen concentration relevant to the coastal and marine environment around the UK. MCCIP Sci. Rev. 2020, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewska, T.; Wilman, B.; Łapeta, B.; Marosz, M.; Biernacik, D.; Wochna, A.; Saniewski, M.; Grajewska, A.; Iwaniak, M. Seawater temperature changes in the southern Baltic Sea (1959–2019) forced by climate change. Oceanologia 2023, 66, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, J.; Aronson, J.; Bodiou, J.-Y. The Mediterranean Region: Biological Diversity in Space and Time, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wilke, M.; Boutiere, H. Hydrobiological, physical and chemical characteristics and spatio-temporal dynamics of an oligotrophic Mediterranean lagoon: The Etang de La Palme (France). Vie Milieu 2000, 50, 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Dhib, A.; Brahim, M.B.; Ziadi, B.; Akrout, F.; Turki, S.; Aleya, L. Factors driving the seasonal distribution of planktonic and epiphytic ciliates in a eutrophicated Mediterranean Lagoon. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2013, 74, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancero-Mosquera, I. Water flow in the inlets of the Marano-Grado lagoon system (NE Italy). Il Nuovo Cim. 2013, 36, 132–144. [Google Scholar]
- Kormas, K.A.; Nicolaidou, A.; Reizopoulou, S. Temporal variations of nutrients, chlorophyll a and particulate matter in three coastal lagoons of Amvrakikos Gulf (Ionian Sea). Mar. Ecol. 2001, 22, 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, A.; Mudge, S.M. Lagoon-sea exchanges, nutrient dynamics and water quality management of the Ria Formosa (Portugal). Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2005, 62, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, S.; Gamito, S.; Pérez-Ruzafa, A. Trophic state of Foz de Almargem coastal lagoon (Algarve, South Portugal) based on the water quality and the phytoplankton community. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaldívar, J.M.; Cardoso, A.C.; Viaroli, P.; Newton, A.; de Wit, R.; Ibañez, C.; Reizopoulou, S.; Somma, F.; Razinkovas, A.; Basset, A.; et al. Eutrophication in transitional waters: An overview. Transitional Waters Monogr. 2008, 1, 11–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, W.M.; Smith, E.M.; Marvin-Dipasquale, M.; Boynton, W.R. Organic carbon metabolism in Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 150, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belias, C.; Dassenakis, M.; Scoullos, M. Study of the N, P and Si fluxes between fish farm sediment and seawater, Results of simulation experiments employing a benthic chamber under various redox conditions. Mar. Chem. 2007, 103, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselli, L.; Fabbrocini, A.; Manzo, C.; D’Adamo, R. Hydrological heterogeneity, nutrient dynamics and water quality of a non-tidal lentic ecosystem (Lesina Lagoon, Italy). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 84, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretus, J.L. Limnología de la Albufera de Menorca (Menorca, España). Limnetica 1989, 5, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapelle, A.; Ménesguen, A.; Deslous-Paoli, J.M.; Souchu, P.; Mazouni, N.; Vaquer, A. Impact of oysters farming and inputs from the watershed in a Mediterranean lagoon. Ecol. Modell. 2000, 127, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizzoli, D.; Bartoli, M.; Cooper, M.; Welsh, D.T.; Underwood, G.J.C.; Viaroli, P. Implications for oxygen, nutrient fluxes and denitrification rates during the early stage of sediment colonisation by the polychaete Nereis spp., in four estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 75, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, S.; Cabrini, M.; Kralj, M.; De Vittor, C.; Celio, M.; Giani, M. (2020) Climatic and anthropogenic impacts on environmental conditions and phytoplankton community in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea). Water 2020, 12, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, M.; Pavlidou, A.; Kralj, M.; Varkitzi, I.; Borja, A.; Menchaca, I.; Lipizer, M.; Partescano, E.; Urbini, L.; Francé, J.; et al. Assessment of the eutrophication status at Mediterranean sub-basin scale, within the European Strategy Framework Directive. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 173876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellese, F. Stato Trofico del Golfo di Trieste: Applicazione di Indici Trofici e Analisi Preliminare della Serie Temporale 2010–2021 nel Contesto di Cambiamento Climatico. Master’s Thesis, University of Trieste, Trieste, Italy, 2024; p. 102. (In Italian). [Google Scholar]
- Redfield, A.C. The biological control of chemical factors in the environments. Am. Sci. 1958, 46, 205–221. [Google Scholar]
- Eighty years of Redfield. Nature Geosci. 2014, 7, 849. [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, S.; Giani, M. River water and nutrient discharges in the Northern Adriatic Sea: Current importance and long term changes. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipizer, M.; De Vittor, C.; Falconi, C.; Comici, C.; Tamberlich, F.; Giani, M. Effects of intense physical and biological forcing factors on CNP pools in coastal waters (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krom, M.D.; Herut, B.; Mantoura, R.F.C. Nutrient budget for the Eastern Mediterranean: Implications for phosphorus limitation. Limnol. Ocean. 2004, 49, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, W.; Dumont, E.; Meybeck, M.; Heussner, S. River discharges of water and nutrients to the Mediterranean and Black Sea: Major drivers for ecosystem changes during past and future decades? Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 80, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herut, B.; Krom, M.D.; Pan, G.; Mortimer, R. Atmospheric input of nitrogen and phosphorus to the Southeast Mediterranean: Sources, fluxes, and possible impact. Limnol. Ocean. 1999, 44, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujo-Pay, M.; Conan, P.; Oriol, L.; Cornet-Barthaux, V.; Falco, C.; Ghiglione, J.F.; Goyet, C.; Moutin, T.; Prieur, L. Integrated survey of elemental stoichiometry (C, N, P) from the western to eastern Mediterranean Sea. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Rieradevall, M.; Farrés-Correll, R.; Newton, A. Annual characterisation of four Mediterranean coastal lagoons subjected to intense human activity. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 114, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.; Icely, J.D.; Falcao, M.; Nobre, A.; Nunes, J.P.; Ferreira, J.G.; Vale, C. Evaluation of eutrophication in the Ria Formosa coastal lagoon, Portugal. Cont. Shelf Res. 2003, 23, 1945–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanni, P.; Caprioli, R.; Ghiara, E.; Mignuzzi, C.; Orlandi, C.; Paganin, G.; Monti, A. Sediment and interstitial water chemistry of the Orbetello lagoon (Grosseto, Italy); nutrient diffusion across the water-sediment interface. Hydrobiologia 1992, 235, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specchiulli, A.; Focardi, S.; Renzi, M.; Scirocco, T.; Cilenti, L.; Breber, P.; Bastianoni, S. Environmental heterogeneity patterns and assessment of trophic levels in two Mediterranean lagoons: Orbetello and Varano, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 402, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Specchiulli, A.; Scirocco, T.; D’Adamo, R.; Cilenti, L.; Fabbrocini, A.; Cassin, D.; Penna, P.; Renzi, M.; Bastianoni, S. Benthic vegetation, chlorophyll α and physical-chemical variables in a protected zone of a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Lesina, Italy). J. Coast. Conserv. 2016, 20, 363–374. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, F.; Teixeira, H.; Marcos, C.; Marques, J.C.; Pérez-Ruzafa, A. Applicability of the trophic index TRIX in two transitional ecosystems: The Mar Menor lagoon (Spain) and the Mondego estuary (Portugal). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngadi, H.; Layachi, M.; Azizi, G.; Baghour, M.; Essefar, S.; Loukili, H.; Moumen, A. Evaluation of the water quality and the eutrophication risk in Ramsar site on Moroccan northern Mediterranean (Marchica lagoon): A multivariate statistical approach. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2003, 194, 115373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, G.; Nimmo-Smith, R.J.; Glegg, G.A.; Tappin, A.D.; Worsfold, P.J. Estuarine eutrophication in the UK: Current incidence and future trends. Aq. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosys. 2009, 19, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocum, E.; Nedwell, D.B.; Underwood, G.J.C. Simultaneous measurement of phytoplanktonic primary production, nutrient and light availability along a turbid, eutrophic UK east coast estuary (the Colne Estuary). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 231, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocum, E.; Nedwell, D.B.; Underwood, G.J.C. Regulation of phytoplankton primary production along a hypernutrified estuary. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 231, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, J.M.; Tyler, P.A. Chlorophyll–total phosphorus relationships in Lake Burragorang, New South Wales, and some other Southern Hemisphere lakes. Aust. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1985, 36, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Fernandez, A.; Marcos, C.; Gilabert, J.; Quispe, J.; Garcia-Charton, A. Spatial and temporal variations of hydrological conditions, nutrients and chlorophyll a in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Mar Menor, Spain). Hydrobiologia 2005, 550, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysoula, C.; Giordani, G.; Papastergiadou, E. Assessment of ecological quality of coastal lagoons with a combination of phytobenthic and water quality indices. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2014, 86, 411–423. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, A.C.; McGlatery, K.J. Benthic algae control sediment–water column fluxes of inorganic nitrogen compounds in a temperate lagoon. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 2125–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlathery, K.J.; Sundbäck, K.; Anderson, I.C. Eutrophication in shallow coastal bays and lagoons: The role of plants in the coastal filter. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 348, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souchu, P.; Ximenes, M.C.; Lauret, M.; Vaquer, A.; Dutriex, E. Mise a Jour D’indicateurs du Niveau D’eutrophisation des Milieux Lagunaires Mediterraneens; Ifremer-Creocean-Universite Montpellier II: Montpellier, France, 2000; Volume II, 412p. [Google Scholar]
- Giordani, G.; Zaldivar, J.M.; Viaroli, P. Simple tools for assessing water quality and trophic status in transitional water ecosystems. Ecol. Ind. 2009, 9, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Song, X.; Yuan, Y.; Cao, X.; Liang, Y. Application of an integrated methodology for eutrophication assessment: A case study in the Bohai Sea. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 2013, 31, 1064–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertig, B.; Kennish, M.J.; Sakowicz, G.P.; Reynolds, G. Mind the Data Gap: Identifying and Assessing Drivers of Changing Eutrophication Condition. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 198–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, M.; Ben Amor, R.; Gueddari, M. Assessment of the trophic status of the South Lagoon of Tunis (Tunisia, Mediterranean Sea): Geochemical and statistical approaches. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 9859546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Fur, I.; De Wit, R.; Plus, M.; Oheix, J.; Derolez, V.; Simier, M.; Malet, N.; Ouisse, V. Re-oligotrophication trajectories of macrophytes assemblages in Mediterranean coastal lagoons based on 17-year time-series. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 608, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derolez, V.; Bec, B.; Munaron, D.; Fiandrino, A.; Pete, R.; Simier, M.; Souchu, P.; Laugier, T.; Aliaume, C.; Malet, N. Recovery trajectories following the reduction of urban nutrient inputs along the eutrophication gradient in French Mediterranean lagoons. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 171, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acri, F.; Bernardi Aubry, B.; Berton, A.; Bianchi, F.; Boldrin, A.; Camatti, E.; Comaschi, A.; Rabitti, S.; Socal, G. Plankton communities and nutrients in the Venice Lagoon, Comparison between current and old data. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 51, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastres, R.; Solidoro, C.; Ciavatta, S.; Petrizzo, A.; Cossarini, G. Long-term changes of inorganic nutrients in the Lagoon of Venice (Italy). J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 51, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degobbis, D.; Precali, R.; Ivančić, I.; Smodlaka, N.; Fuks, D.; Kveder, S. Long-term changes in the northern Adriatic ecosystem related to anthropogenic eutrophication. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 13, 495–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, M.; Djakovac, T.; Degobbis, D.; Cozzi, S.; Solidoro, C.; Umani, S.F. Recent changes in the marine ecosystems of the northern Adriatic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, A.; Marullo, S.; Artale, V.; Falcini, F.; Yang, C.; Leonelli, F.E.; Santoleri, R.; Buongiorno Nardelli, B. New evidence of Mediterranean climate change and variability from sea surface temperature observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malačič, V.; Celio, M.; Čermelj, B.; Bussani, A.; Comici, C. Interannual evolution of seasonal thermohaline properties in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic) 1991–2003. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, C08009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondelli, L. Fitoplancton Potenzialmente Tossico nelle Mitilicolture del Golfo di Trieste: Analisi Preliminari della Serie Temporale in Rapporto al Contesto Ambientale e Climatico. Master’s Thesis, University of Trieste, Trieste, Italy, 2023; p. 105. (In Italian). [Google Scholar]
- Vargas-Yáñez, M.; Moya, F.; Serra, M.; Juza, M.; Jordà, G.; Ballesteros, E.; Alonso, C.; Pascual, J.; Salat, J.; Moltó, V.; et al. Observations in the Spanish MediterraneanWaters: A Review and Update of Results of 30-Year Monitoring. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, C.; Bonaldo, D.; Bergamasco, A.; Ghezzo, M. Sea level and temperature extremes in a regulated Lagoon of Venice. Front. Clim. 2023, 5, 1330388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettoso, N.; Aleffi, I.F.; Faresi, L.; Acquavita, A.; Orlandi, C. Il macrozoobenthos di fondo mobile nella laguna di Marano e Grado: Un confronto tra gli anni ’90 e lo stato attuale. In Proceedings of the Congresso del Centro Italiano Studi di Biologia Ambientale (CISBA), Ravenna, Italy, 2–3 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).