From Cradle to Grave: Microplastics—A Dangerous Legacy for Future Generations
Abstract
1. Generation and Composition of Macro-, Micro- and Nanoplastic Particles
2. Presence of Microplastics in the Environment
2.1. Drinking Water
2.2. Food Products
2.3. Articles of Daily Use and (Leisure) Activities
2.4. Leaching Chemicals and Additives
3. Uptake and Accumulation of Microplastics in Human Tissues and Organs
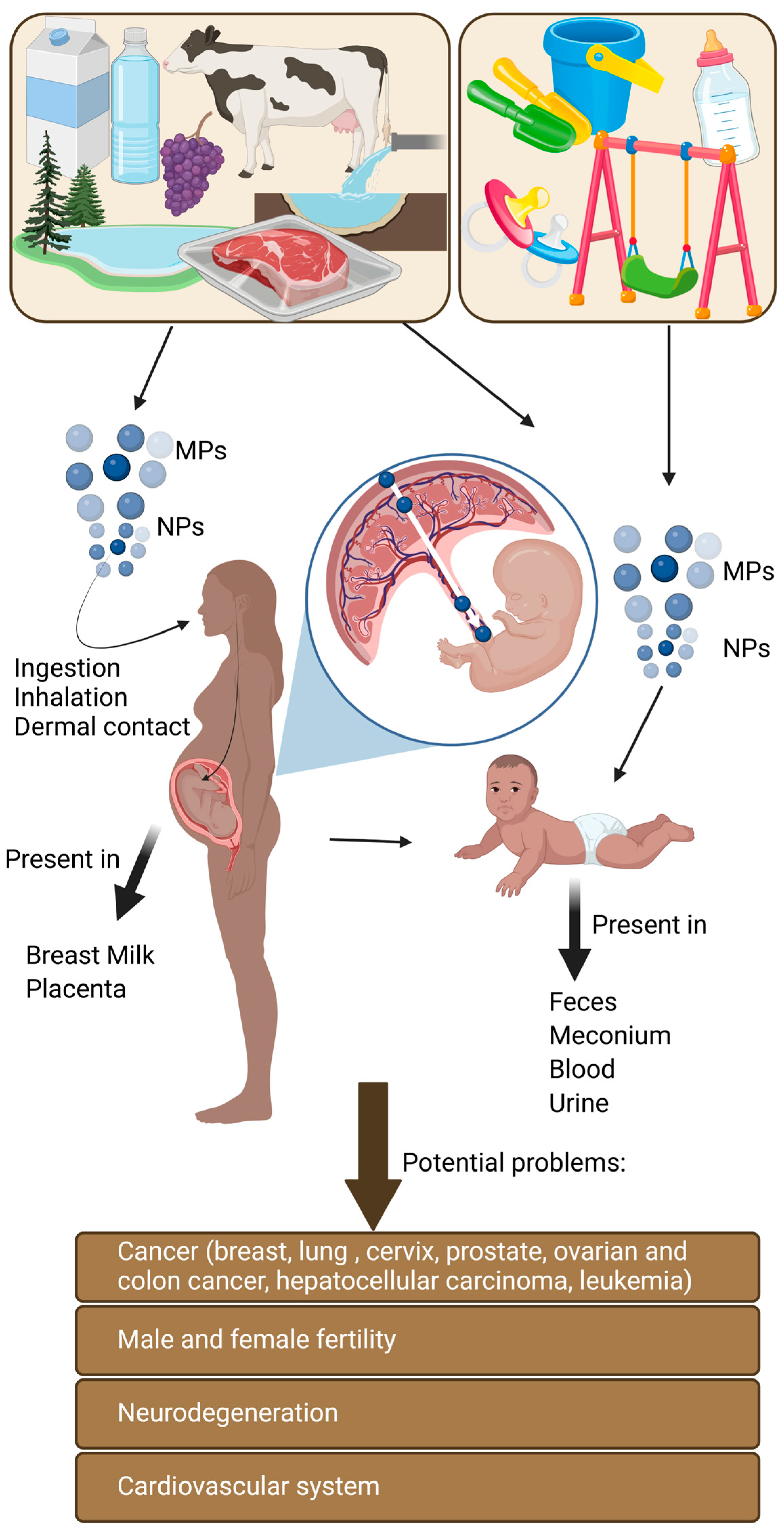
3.1. Routes of Exposure
3.1.1. Ingestion
3.1.2. Inhalation
3.1.3. Dermal Contact
3.2. Particle Uptake and Transport Mechanisms Across Tissue Barriers
4. Physiological Consequences of Microplastics Exposure During Human Development
4.1. Critical Stages During Early Human Development Affected by Microplastics
4.1.1. Fetal Exposure to Microplastic Particles via the Placental Route
4.1.2. Microplastics and the Neonatal Stage
4.1.3. The Prepubertal Stage
4.2. The Problem of Lifetime Accumulation of Microplastic Particles
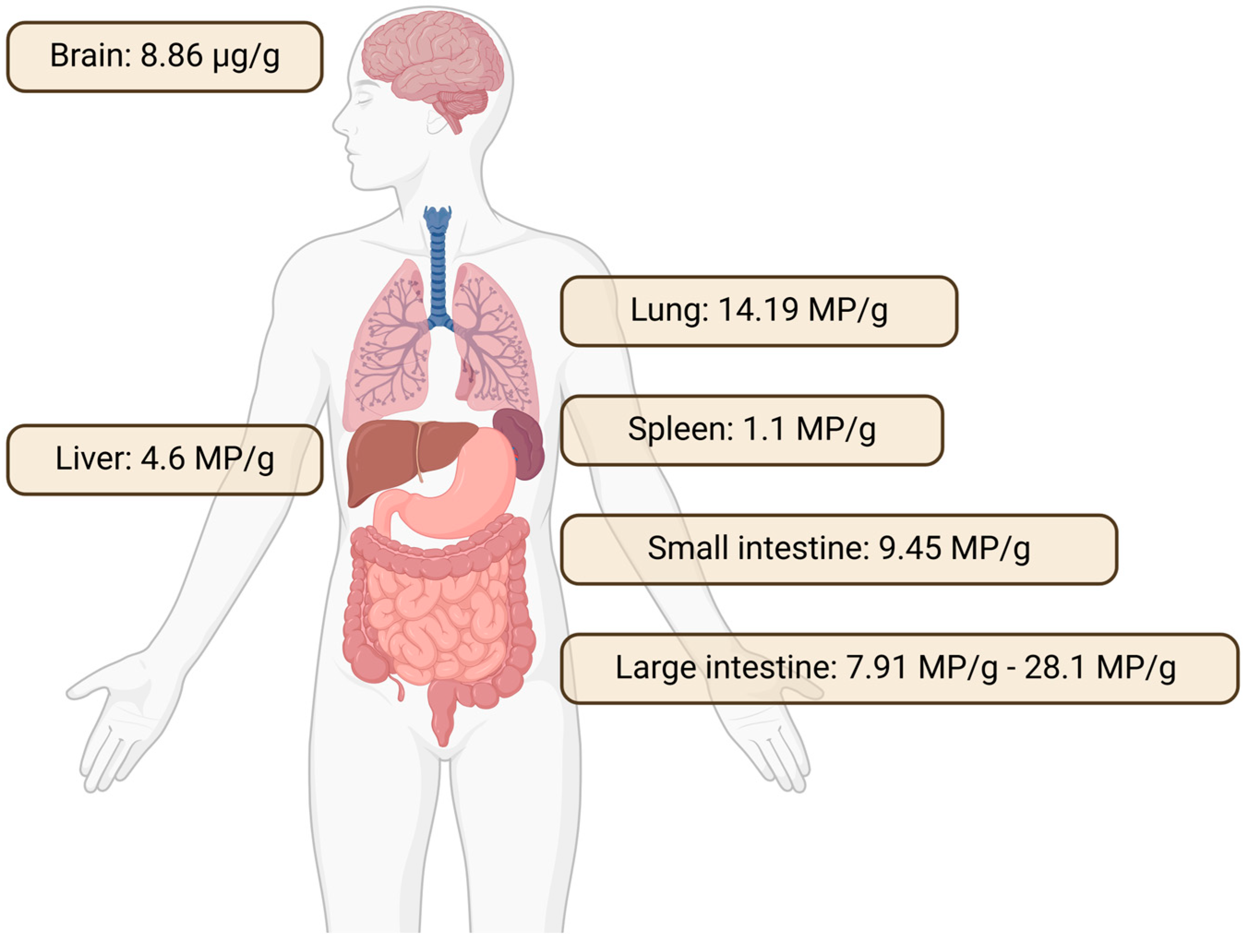
4.2.1. Accumulation of Microplastics in Different Tissues of the Human Body
4.2.2. Pathophysiological Consequences of Microplastics Exposure
4.2.3. Types of Cancer Linked to Microplastic Particles and Associated Chemicals
- Breast Cancer
- Lung Cancer
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Cervical Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Leukemia
- Ovarian Cancer
- Colon Cancer
4.2.4. Microplastics and Cardiovascular Diseases
4.2.5. Microplastics and the Nervous System
4.2.6. Microplastics and Reproductive Health—Fertility Issues
- Male Fertility
- Female Fertility
5. Microplastic Particles Do Not Disappear After the End of Biological Life
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Available Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sipe, J.M.; Bossa, N.; Berger, W.; von Windheim, N.; Gall, K.; Wiesner, M.R. From bottle to microplastics: Can we estimate how our plastic products are breaking down? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vdovchenko, A.; Resmini, M. Mapping Microplastics in Humans: Analysis of Polymer Types, and Shapes in Food and Drinking Water-A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Júnior, G.R.; Dos Santos Galvão, L.; Ando, R.A.; Mauad, T. Presence of airborne microplastics in human lung tissue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, T.; Rico, A.; Vighi, M. Occurrence, Fate and Fluxes of Plastics and Microplastics in Terrestrial and Freshwater Ecosystems. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 250, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, E.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.; Foekema, E.M.; Koelmans, A.A. Quantifying ecological risks of aquatic micro- and nanoplastic. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 32–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.; Bao, L.-J.; Shi, L.; Wong, C.S.; Zeng, E.Y. A review of methods for measuring microplastics in aquatic environments. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11319–11332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarfl, C. Promising techniques and open challenges for microplastic identification and quantification in environmental matrices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 3743–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. The plastic in microplastics: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendall, L.S.; Sewell, M.A. Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: Microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Microplastic--an emerging contaminant of potential concern? Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2007, 3, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Ma, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, F. Microbial degradation and other environmental aspects of microplastics/plastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J. Microplastic degradation methods and corresponding degradation mechanism: Research status and future perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpia, A.A.; Chen, W.-H.; Ubando, A.T.; Naqvi, S.R.; Culaba, A.B. Microplastic degradation as a sustainable concurrent approach for producing biofuel and obliterating hazardous environmental effects: A state-of-the-art review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toapanta, T.; Okoffo, E.D.; Ede, S.; O’Brien, S.; Burrows, S.D.; Ribeiro, F.; Gallen, M.; Colwell, J.; Whittaker, A.K.; Kaserzon, S.; et al. Influence of surface oxidation on the quantification of polypropylene microplastics by pyrolysis gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamweru, P.K.; Ndiritu, F.G.; Kinyanjui, T.K.; Muthui, Z.W.; Ngumbu, R.G.; Odhiambo, P.M. Study of Temperature and UV Wavelength Range Effects on Degradation of Photo-Irradiated Polyethylene Films Using DMA. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2011, 50, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delre, A.; Goudriaan, M.; Morales, V.H.; Vaksmaa, A.; Ndhlovu, R.T.; Baas, M.; Keijzer, E.; de Groot, T.; Zeghal, E.; Egger, M.; et al. Plastic photodegradation under simulated marine conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Yan, D.; Fu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ou, H. Ultraviolet-C and vacuum ultraviolet inducing surface degradation of microplastics. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesa, F.S.; Turra, A.; Checon, H.H.; Leonardi, B.; Baruque-Ramos, J. Laundering and textile parameters influence fibers release in household washings. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubarenko, I.; Efimova, I.; Bagaeva, M.; Bagaev, A.; Isachenko, I. On mechanical fragmentation of single-use plastics in the sea swash zone with different types of bottom sediments: Insights from laboratory experiments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziani, K.; Ioniță-Mîndrican, C.-B.; Mititelu, M.; Neacșu, S.M.; Negrei, C.; Moroșan, E.; Drăgănescu, D.; Preda, O.-T. Microplastics: A Real Global Threat for Environment and Food Safety: A State of the Art Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, R.C.; Seeley, M.E.; La Guardia, M.J.; Mai, L.; Zeng, E.Y. A Global Perspective on Microplastics. JGR Ocean. 2020, 125, e2018JC014719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, E.S.; Stadlbauer, V.; Pichler, V.; Resch-Fauster, K.; Todorovic, A.; Meisel, T.C.; Trawoeger, S.; Hollóczki, O.; Turner, S.D.; Wadsak, W.; et al. To Waste or Not to Waste: Questioning Potential Health Risks of Micro- and Nanoplastics with a Focus on Their Ingestion and Potential Carcinogenicity. Expo. Health 2023, 15, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sinha, J.K.; Ghosh, S.; Vashisth, K.; Han, S.; Bhaskar, R. Microplastics as an Emerging Threat to the Global Environment and Human Health. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelle, S.B.; Ringma, J.; Law, K.L.; Monnahan, C.C.; Lebreton, L.; McGivern, A.; Murphy, E.; Jambeck, J.; Leonard, G.H.; Hilleary, M.A.; et al. Predicted growth in plastic waste exceeds efforts to mitigate plastic pollution. Science 2020, 369, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PlasticsEurope. Association of Plastics Manufacturers Plastics—The Facts 2017: An Analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data; PlasticsEurope: Brussels, Belgium, 2017; Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/2015-Plastics-the-facts.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Yu, Q.; Hu, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Ling, W. Distribution, abundance and risks of microplastics in the environment. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.S.; Liu, Y.F. The distribution of microplastics in soil aggregate fractions in southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, M.; Bigalke, M. Microplastics in Swiss Floodplain Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3591–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, B.; Russell, C.W.; Green, D.S. Effects of Microplastics in Soil Ecosystems: Above and Below Ground. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11496–11506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Jarvis, P.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Tan, Q.; Tian, Y. Occurrence, removal and potential threats associated with microplastics in drinking water sources. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccarello, P.; Ferrante, M.; Cristaldi, A.; Copat, C.; Grasso, A.; Sangregorio, D.; Fiore, M.; Oliveri Conti, G. Exposure to microplastics (<10 μm) associated to plastic bottles mineral water consumption: The first quantitative study. Water Res. 2019, 157, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, E.G.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Ma, L.; Zeng, E.Y.; Shi, H. A Review of Microplastics in Table Salt, Drinking Water, and Air: Direct Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3740–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meizoso-Regueira, T.; Fuentes, J.; Cusworth, S.J.; Rillig, M.C. Prediction of future microplastic accumulation in agricultural soils. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 359, 124587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelis, J.L.; Schacht, V.J.; Dawson, A.L.; Bose, U.; Tsagkaris, A.S.; Dvorakova, D.; Beale, D.J.; Can, A.; Elliott, C.T.; Thomas, K.V.; et al. The measurement of food safety and security risks associated with micro- and nanoplastic pollution. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 161, 116993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aardema, H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Kamstra, J.H.; Legler, J. Farm animals as a critical link between environmental and human health impacts of micro-and nanoplastics. Micropl. Nanopl. 2024, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, R.Z.; Kindi, R.A.; Salem, F.A.; Kittaneh, W.F.; Poulose, V.; Iftikhar, S.H.; Mourad, A.-H.I.; Thiemann, T. Microplastic Contamination of Chicken Meat and Fish through Plastic Cutting Boards. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 13442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, E.; Niero, G.; Benetti, F.; Perini, A.; Zanella, M.; Pozza, M.; de Marchi, M. Preliminary characterization of microplastics in beef hamburgers. Meat Sci. 2024, 217, 109626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Basantes, M.F.; Conesa, J.A.; Fullana, A. Microplastics in Honey, Beer, Milk and Refreshments in Ecuador as Emerging Contaminants. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, E.; Manuelian, C.L.; Niero, G.; Benetti, F.; Perini, A.; Zanella, M.; Pozza, M.; de Marchi, M. Characterization of microplastics in skim-milk powders. J. Dairy. Sci. 2024, 107, 5393–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitko, V.; Hanlon, M. Another source of pollution by plastics: Skin cleaners with plastic scrubbers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1991, 22, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopewell, J.; Dvorak, R.; Kosior, E. Plastics recycling: Challenges and opportunities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, M.R. Plastic ‘scrubbers’ in hand cleansers: A further (and minor) source for marine pollution identified. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1996, 32, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruter, A.T. Sources, quantities and distribution of persistent plastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1987, 18, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.T.; Simmons, S.L. Estuarine Litter at the River/Beach Interface in the Bristol Channel, United Kingdom. J. Coast. Res. 1997, 13, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Sun, C.; Teng, J.; Chen, L.; Shan, E.; Zhao, J. Microplastics in fish meals: An exposure route for aquaculture animals. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-S.; Koongolla, J.B.; Li, H.-X.; Lin, L.; Pan, Y.-F.; Liu, S.; He, W.-H.; Maharana, D.; Xu, X.-R. Microplastic accumulation in fish from Zhanjiang mangrove wetland, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, C.; Burton, H. Origins and biological accumulation of small plastic particles in fur seals from Macquarie Island. Ambio 2003, 32, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; Luzardo, O.P.; Gómez, M.; Acosta-Dacal, A.; Martínez, I.; La Felipe de Rosa, J.; Macías-Montes, A.; Suárez-Pérez, A.; Herrera, A. Microplastics ingestion and chemical pollutants in seabirds of Gran Canaria (Canary Islands, Spain). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-L.; Duan, Y.; Zhong, H.-N.; Lin, Q.-B.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, C.-C.; Chen, S.; Dong, B.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; et al. Analysis of microplastics released from plastic take-out food containers based on thermal properties and morphology study. Food Addit. Contam. Part. A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2023, 40, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-P.; Huang, X.-H.; Chen, J.-N.; Dong, M.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Qin, L. Pouring hot water through drip bags releases thousands of microplastics into coffee. Food Chem. 2023, 415, 135717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Xu, L.; Yu, K.; Wei, F.; Zhang, M. Release of microplastics from disposable cups in daily use. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shruti, V.C.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G. Migration testing of microplastics in plastic food-contact materials: Release, characterization, pollution level, and influencing factors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 170, 117421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Jia, P.; He, S.; Dai, H.; Deng, S.; Han, J. Release of microplastics from breastmilk storage bags and assessment of intake by infants: A preliminary study. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savva, K.; Llorca, M.; Borrell, X.; Bertran-Solà, O.; Farré, M.; Moreno, T. Granulated rubber in playgrounds and sports fields: A potential source of atmospheric plastic-related contaminants and plastic additives after runoff events. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 479, 135697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.N.; Lara, L.Z.; de Falco, F.; Turner, A.; Thompson, R.C. Effect of the age of garments used under real-life conditions on microfibre release from polyester and cotton clothing. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 348, 123806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthammer, T. Microplastics and their Additives in the Indoor Environment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2022, 61, e202205713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, J.D.; Swarthout, R.F.; Turner, A.; Hendren, C.O. Bringing sex toys out of the dark: Exploring unmitigated risks. Micropl. Nanopl. 2023, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, L.P.; Baez, A.G.; Purchase, D.; Jones, H.; Garelick, H. Release of microplastic fibres and fragmentation to billions of nanoplastics from period products: Preliminary assessment of potential health implications. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; de Ruijter, V.N.; Mintenig, S.M.; Verschoor, A.; Koelmans, A.A. Ingestion and Chronic Effects of Car Tire Tread Particles on Freshwater Benthic Macroinvertebrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13986–13994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieber, R.; Kawecki, D.; Nowack, B. Dynamic probabilistic material flow analysis of rubber release from tires into the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, F.; Dietze, V.; Baum, A.; Sauer, J.; Gilge, S.; Maschowski, C.; Gieré, R. Tire Abrasion as a Major Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2014–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, M.; Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Kroeze, C. Export of microplastics from land to sea. A modelling approach. Water Res. 2017, 127, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, A. European Chemical Agency’s Perspective: An Evaluation of the Possible Health Risks of Recycle Rubber Granules used as Infill in Synthetic Turf Fields. ISEE Conf. Abstr. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.; Sibai, A. Rubber/crete: Mechanical properties of scrap to reuse tire-derived rubber in concrete; A review. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2019, 17, 2280800019835486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechselberger, C.; Messner, B.; Bernhard, D. The Role of Trace Elements in Cardiovascular Diseases. Toxics 2023, 11, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vázquez, J.; Miró, M.; Quintana, J.B.; Cela, R.; Ferriol, P.; Rodil, R. Bioaccessibility of plastic-related compounds from polymeric particles in marine settings: Are microplastics the principal vector of phthalate ester congeners and bisphenol A towards marine vertebrates? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Savino, I.; Locaputo, V.; Uricchio, V.F. A Detailed Review Study on Potential Effects of Microplastics and Additives of Concern on Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solleiro-Villavicencio, H.; Gomez-De León, C.T.; Del Río-Araiza, V.H.; Morales-Montor, J. The detrimental effect of microplastics on critical periods of development in the neuroendocrine system. Birth Defects Res. 2020, 112, 1326–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Kang, Y.; Ma, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hu, R.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Gu, X.; An, L. Tissue accumulation of microplastics and potential health risks in human. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 170004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Y.S.; Tuan Anuar, S.; Azmi, A.A.; Wan Mohd Khalik, W.M.A.; Lehata, S.; Hamzah, S.R.; Ismail, D.; Ma, Z.F.; Dzulkarnaen, A.; Zakaria, Z.; et al. Detection of microplastics in human colectomy specimens. JGH Open 2021, 5, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvatits, T.; Tamminga, M.; Liu, B.; Sebode, M.; Carambia, A.; Fischer, L.; Püschel, K.; Huber, S.; Fischer, E.K. Microplastics detected in cirrhotic liver tissue. EBioMedicine 2022, 82, 104147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campen, M.; Nihart, A.; Garcia, M.; Liu, R.; Olewine, M.; Castillo, E.; Bleske, B.; Scott, J.; Howard, T.; Gonzalez-Estrella, J.; et al. Bioaccumulation of Microplastics in Decedent Human Brains Assessed by Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, A.L.; Kawaguchi, S.; King, C.K.; Townsend, K.A.; King, R.; Huston, W.M.; Bengtson Nash, S.M. Turning microplastics into nanoplastics through digestive fragmentation by Antarctic krill. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human Consumption of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7068–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Size, source and chemical composition as determinants of toxicity attributable to ambient particulate matter. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 504–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falakdin, P.; Lopez-Rosales, A.; Andrade, J.; Terzaghi, E.; Di Guardo, A.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S. Comparison of microplastic type, size, and composition in atmospheric and foliage samples in an urban scenario. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 349, 123911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kau, D.; Materić, D.; Holzinger, R.; Baumann-Stanzer, K.; Schauer, G.; Kasper-Giebl, A. Fine micro- and nanoplastics concentrations in particulate matter samples from the high alpine site Sonnblick, Austria. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materić, D.; Kjær, H.A.; Vallelonga, P.; Tison, J.-L.; Röckmann, T.; Holzinger, R. Nanoplastics measurements in Northern and Southern polar ice. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, S.; Mahagamage, Y. Microplastics in personal care products and cosmetics in Sri Lanka. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhu, M.; Nahid Pervez, M.; Wu, B.; Zhao, Y. Fabric structure and polymer composition as key contributors to micro(nano)plastic contamination in face masks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.; Simpson, K.; Brzezinski, M.; Watt, J.; Xu, W. Cellular response of keratinocytes to the entry and accumulation of nanoplastic particles. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2024, 21, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, C.M.; Singer, D.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S. Immune and inflammatory responses of human macrophages, dendritic cells, and T-cells in presence of micro- and nanoplastic of different types and sizes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganhör, C.; Rezk, M.; Doppler, C.; Ruthmeier, T.; Wechselberger, C.; Müller, M.; Kotnik, M.; Puh, Š.; Messner, B.; Bernhard, D. Aluminum, a colorful gamechanger: Uptake of an aluminum-containing food color in human cells and its implications for human health. Food Chem. 2024, 442, 138404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, V.; Böhmert, L.; Lisicki, E.; Block, R.; Cara-Carmona, J.; Pack, L.K.; Selb, R.; Lichtenstein, D.; Voss, L.; Henderson, C.J.; et al. Uptake and effects of orally ingested polystyrene microplastic particles in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1817–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, S.; Ramsperger, A.F.R.M.; Gross, W.; Lehmann, M.; Witzmann, T.; Caspari, A.; Obst, M.; Gekle, S.; Auernhammer, G.K.; Fery, A.; et al. Nominally identical microplastic models differ greatly in their particle-cell interactions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourian, P.; Yazdani, G.; Ashraf, S.S.; Frounchi, M.; Mashayekhan, S.; Kiani, S.; Kakkar, A. Effect of Physico-Chemical Properties of Nanoparticles on Their Intracellular Uptake. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, N.D.; Acar, H.; Wilhelm, S. Concepts of nanoparticle cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and kinetics in nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 143, 68–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vácha, R.; Martinez-Veracoechea, F.J.; Frenkel, D. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of nanoparticles of various shapes. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5391–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, F.; Torres-Arias, M. Nanoparticles cellular uptake, trafficking, activation, toxicity and in vitro evaluation. Curr. Res. Immunol. 2023, 4, 100073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Auth, T.; Gompper, G. Shape and orientation matter for the cellular uptake of nonspherical particles. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustine, R.; Hasan, A.; Primavera, R.; Wilson, R.J.; Thakor, A.S.; Kevadiya, B.D. Cellular uptake and retention of nanoparticles: Insights on particle properties and interaction with cellular components. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yameen, B.; Choi, W.I.; Vilos, C.; Swami, A.; Shi, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Insight into nanoparticle cellular uptake and intracellular targeting. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkers, J.M.; Höppener, E.M.; Grigoriev, I.; Will, L.; Melgert, B.N.; van der Zaan, B.; van de Steeg, E.; Kooter, I.M. Advanced epithelial lung and gut barrier models demonstrate passage of microplastic particles. Micropl. Nanopl. 2022, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Adhikary, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Agarwal, R.; Ganguly, A.; Nanda, S.; Rajak, P. The alarming link between environmental microplastics and health hazards with special emphasis on cancer. Life Sci. 2024, 355, 122937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Park, J.H.; Lee, I.; Jung, G.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, M.J.; Im, W.; Cho, S.; Choi, Y.S. Investigation of Cell-to-cell Transfer of Polystyrene Microplastics Through Extracellular Vesicle-mediated Communication. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 734, 150719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, B.H.; Ando, H.Y.; Gupta, P.K. Circulation time and body distribution of 14C-labeled amino-modified polystyrene nanoparticles in mice. J. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 84, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arturson, P.; Laakso, T.; Edman, P. Acrylic microspheres in vivo IX: Blood elimination kinetics and organ distribution of microparticles with different surface characteristics. J. Pharm. Sci. 1983, 72, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edman, P.; Sjöholm, I. Acrylic microspheres in vivo VIII: Distribution and elimination of polyacryldextran particles in mice. J. Pharm. Sci. 1983, 72, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illum, L.; Davis, S.S.; Müller, R.H.; Mak, E.; West, P. The organ distribution and circulation time of intravenously injected colloidal carriers sterically stabilized with a block copolymer--poloxamine 908. Life Sci. 1987, 40, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, K.; Zhang, B.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, W. Cellular internalization and release of polystyrene microplastics and nanoplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterland, R.A.; Michels, K.B. Epigenetic epidemiology of the developmental origins hypothesis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2007, 27, 363–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, F.; Sarker, D.B.; Jocelyn, J.A.; Sang, Q.-X.A. Molecular and Cellular Effects of Microplastics and Nanoplastics: Focus on Inflammation and Senescence. Cells 2024, 13, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Palić, D. Micro- and nano-plastics activation of oxidative and inflammatory adverse outcome pathways. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Han, J.; Liu, X.; Li, K.; Lai, W.; Bian, L.; Yan, J.; Xi, Z. Exposure to Polypropylene Microplastics via Oral Ingestion Induces Colonic Apoptosis and Intestinal Barrier Damage through Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Mice. Toxics 2023, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterland, R.A.; Jirtle, R.L. Transposable elements: Targets for early nutritional effects on epigenetic gene regulation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 5293–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, K.M.; Barker, D.J. Fetal programming and adult health. Public. Health Nutr. 2001, 4, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafmueller, S.; Manser, P.; Diener, L.; Diener, P.-A.; Maeder-Althaus, X.; Maurizi, L.; Jochum, W.; Krug, H.F.; Buerki-Thurnherr, T.; von Mandach, U.; et al. Bidirectional Transfer Study of Polystyrene Nanoparticles across the Placental Barrier in an ex Vivo Human Placental Perfusion Model. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syme, M.R.; Paxton, J.W.; Keelan, J.A. Drug transfer and metabolism by the human placenta. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 43, 487–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, P.; Malek, A.; Manser, P.; Meili, D.; Maeder-Althaus, X.; Diener, L.; Diener, P.-A.; Zisch, A.; Krug, H.F.; Mandach, U. von. Barrier capacity of human placenta for nanosized materials. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Razansky, D.; Estrada, G.G.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Beyerle, A.; Kreyling, W.; Ntziachristos, V.; Stoeger, T. Surface modification and size dependence in particle translocation during early embryonic development. Inhal. Toxicol. 2009, 21 (Suppl. S1), 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, S.B.; D’Errico, J.N.; Adler, D.S.; Kollontzi, S.; Goedken, M.J.; Fabris, L.; Yurkow, E.J.; Stapleton, P.A. Nanopolystyrene translocation and fetal deposition after acute lung exposure during late-stage pregnancy. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, D.J.; Das Sarkar, S.; Das, B.K.; Sahoo, B.K.; Das, A.; Nag, S.K.; Manna, R.K.; Behera, B.K.; Samanta, S. Occurrence, fate and removal of microplastics as heavy metal vector in natural wastewater treatment wetland system. Water Res. 2021, 192, 116853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Kalogerakis, N.; Ji, R.; Ma, Y. Interactions between microplastics and organic pollutants: Effects on toxicity, bioaccumulation, degradation, and transport. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 142427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, B.; Hutchinson, E.; Unwin, J.; Fletcher, T. Lung cancer risk after exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Xiao, L.; Kehoe, D.K.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Boland, J.J.; Wang, J.J. Microplastic release from the degradation of polypropylene feeding bottles during infant formula preparation. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Jaghbir, M.; Salam, M.; Al-Kadamany, G.; Damsees, R.; Al-Rawashdeh, N. Testing baby bottles for the presence of residual and migrated bisphenol A. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 191, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, B.; Dong, R. Detection of various microplastics in placentas, meconium, infant feces, breastmilk and infant formula: A pilot prospective study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; Da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Environmental exposure to microplastics: An overview on possible human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Turner, A.; Kelly, F.J.; Dominguez, A.O.; Jaafarzadeh, N. Distribution and potential health impacts of microplastics and microrubbers in air and street dusts from Asaluyeh County, Iran. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonca, K.; Hauser, R.; Calafat, A.M.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Duty, S.M. Bisphenol A concentrations in maternal breast milk and infant urine. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2014, 87, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celeiro, M.; Armada, D.; Dagnac, T.; de Boer, J.; Llompart, M. Hazardous compounds in recreational and urban recycled surfaces made from crumb rubber. Compliance with current regulation and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.; Scott, J.W.; Green, L.A. Rare earth elements in plastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Just, A.C.; Miller, R.L.; Perzanowski, M.S.; Rundle, A.G.; Chen, Q.; Jung, K.H.; Hoepner, L.; Camann, D.E.; Calafat, A.M.; Perera, F.P.; et al. Vinyl flooring in the home is associated with children’s airborne butylbenzyl phthalate and urinary metabolite concentrations. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Martínez, Y.; Caravaca, M.; Soto-Meca, A. Determination of Very Low Concentration of Bisphenol A in Toys and Baby Pacifiers Using Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction by In Situ Ionic Liquid Formation and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shen, J.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Deng, X.; Wu, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, R.; et al. Exposure to irregular microplastic shed from baby bottles activates the ROS/NLRP3/Caspase-1 signaling pathway, causing intestinal inflammation. Environ. Int. 2023, 181, 108296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietert, R.R. Developmental immunotoxicology: Focus on health risks. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Bai, J.; Ning, B.; Fan, L.; Sun, T.; Fang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Duan, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Effects of bisphenol A and nanoscale and microscale polystyrene plastic exposure on particle uptake and toxicity in human Caco-2 cells. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, A.; Lange, R.; Lemke, N.; Zimmermann, P.; Peisker, J.; Rucic, E.; Hahn, D.; Dębiakund, M.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. Ergebnisbericht—Deutsche Umweltstudie zur Gesundheit von Kindern und Jugendlichen 2014-2017 (GerES V): Teil 1: Human-Biomonitoring; Umweltbundesamt: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2023; Available online: https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:gbv:3:2-949390 (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Dodds, E.C.; Lawson, W. Synthetic strogenic Agents without the Phenanthrene Nucleus. Nature 1936, 137, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, A.M.; Sonnenschein, C. Environmental causes of cancer: Endocrine disruptors as carcinogens. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segovia-Mendoza, M.; Nava-Castro, K.E.; Palacios-Arreola, M.I.; Garay-Canales, C.; Morales-Montor, J. How microplastic components influence the immune system and impact on children health: Focus on cancer. Birth Defects Res. 2020, 112, 1341–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-F.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lu, T.-H.; Liao, C.-M. Toxicity-based toxicokinetic/toxicodynamic assessment for bioaccumulation of polystyrene microplastics in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyles, J.; Alpar, O.; Field, W.N.; Lewis, D.A.; Keswick, M. The transfer of polystyrene microspheres from the gastrointestinal tract to the circulation after oral administration in the rat. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyles, J.E.; Bramwell, V.W.; Williamson, E.D.; Alpar, H.O. Microsphere translocation and immunopotentiation in systemic tissues following intranasal administration. Vaccine 2001, 19, 4732–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Larpruenrudee, P.; Arsalanloo, A.; Beni, H.M.; Islam, M.A.; Gu, Y.; Sauret, E. How microplastics are transported and deposited in realistic upper airways? Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 063319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirinzi, G.F.; Pérez-Pomeda, I.; Sanchís, J.; Rossini, C.; Farré, M.; Barceló, D. Cytotoxic effects of commonly used nanomaterials and microplastics on cerebral and epithelial human cells. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lemos, B.; Ren, H. Tissue accumulation of microplastics in mice and biomarker responses suggest widespread health risks of exposure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackintosh, C.E.; Maldonado, J.; Hongwu, J.; Hoover, N.; Chong, A.; Ikonomou, M.G.; Gobas, F.A.P.C. Distribution of phthalate esters in a marine aquatic food web: Comparison to polychlorinated biphenyls. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2011–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.-W.; Xia, T.; Lee, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Tsai, J.-C.; Wang, Y.-J. Cationic polystyrene nanospheres induce autophagic cell death through the induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çobanoğlu, H.; Belivermiş, M.; Sıkdokur, E.; Kılıç, Ö.; Çayır, A. Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of polyethylene microplastics on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brynzak-Schreiber, E.; Schögl, E.; Bapp, C.; Cseh, K.; Kopatz, V.; Jakupec, M.A.; Weber, A.; Lange, T.; Toca-Herrera, J.L.; Del Favero, G.; et al. Microplastics role in cell migration and distribution during cancer cell division. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casella, C.; Ballaz, S.J. Genotoxic and neurotoxic potential of intracellular nanoplastics: A review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 44, 1657–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.-M.; Ran, B.; Zhang, C.-L.; Yan, D.-M.; Li, X.-H. Estrogen and progesterone promote breast cancer cell proliferation by inducing cyclin G1 expression. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitrascu, M.C.; Mares, C.; Petca, R.-C.; Sandru, F.; Popescu, R.-I.; Mehedintu, C.; Petca, A. Carcinogenic effects of bisphenol A in breast and ovarian cancers. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Hong, S.; Kim, O.-H.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.-W.; Hong, S.; Lee, H.J. Polypropylene microplastics promote metastatic features in human breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gao, J.; Yu, H.; Su, H.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Hollert, H.; Shi, H.; et al. An emerging role of microplastics in the etiology of lung ground glass nodules. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, K.E.; Hare, J.T.; Khamis, Z.I.; Hua, T.; Sang, Q.-X.A. Exposure of Human Lung Cells to Polystyrene Microplastics Significantly Retards Cell Proliferation and Triggers Morphological Changes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Mao, W.; Liao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, H. Association between urinary bisphenol analogue concentrations and lung cancer in adults: A case-control study. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Miao, X.; Li, G.; He, Q.; Xu, H.; Li, H.; Wei, Y. Cytotoxic effects of polystyrene nanoplastics with different surface functionalization on human HepG2 cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce hepatotoxicity and disrupt lipid metabolism in the liver organoids. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E.; Kueznik, T.; Samberger, C.; Roblegg, E.; Wrighton, C.; Pieber, T.R. Size-dependent effects of nanoparticles on the activity of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 242, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, A.; Mishra, S.P.; Pradhan, S.; Choudhary, S.; Singla, S.; Zahra, K.; Aggarwal, L.M. An assessment of serum oxidative stress and antioxidant parameters in patients undergoing treatment for cervical cancer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 167, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medellín-Garibay, S.E.; Alcántara-Quintana, L.E.; Rodríguez-Báez, A.S.; Sagahón-Azúa, J.; Rodríguez-Aguilar, M.; Hernández Cueto, M.d.L.A.; Muñoz Medina, J.E.; Del Milán-Segovia, R.C.; Flores-Ramírez, R. Urinary phthalate metabolite and BPA concentrations in women with cervical cancer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 21033–21042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbs, R.W.; Malhotra, N.R.; Greenwald, D.T.; Wang, A.Y.; Prins, G.S.; Abern, M.R. Estrogens and prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2019, 22, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Tao, L. Cytotoxicity study of polyethylene glycol derivatives. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 18252–18259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, G.S.; Tang, W.-Y.; Belmonte, J.; Ho, S.-M. Perinatal exposure to oestradiol and bisphenol A alters the prostate epigenome and increases susceptibility to carcinogenesis. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 102, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wu, J.; Su, X.; Yan, H.; Sun, Z. Effects of low dose of bisphenol A on the proliferation and mechanism of primary cultured prostate epithelial cells in rodents. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2635–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapore, P.; Ying, J.; Ouyang, B.; Burke, B.; Bracken, B.; Ho, S.-M. Exposure to bisphenol A correlates with early-onset prostate cancer and promotes centrosome amplification and anchorage-independent growth in vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.-M.; Tang, W.-Y.; Belmonte de Frausto, J.; Prins, G.S. Developmental exposure to estradiol and bisphenol A increases susceptibility to prostate carcinogenesis and epigenetically regulates phosphodiesterase type 4 variant 4. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5624–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, G.S.; Hu, W.-Y.; Xie, L.; Shi, G.-B.; Hu, D.-P.; Birch, L.; Bosland, M.C. Evaluation of Bisphenol A (BPA) Exposures on Prostate Stem Cell Homeostasis and Prostate Cancer Risk in the NCTR-Sprague-Dawley Rat: An NIEHS/FDA CLARITY-BPA Consortium Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Xu, K.; Yu, L.; Pu, Y.; Xiong, F.; He, Y.; Huang, Q.; Tang, M.; Chen, M.; Yin, L.; et al. Preliminary study on impacts of polystyrene microplastics on the hematological system and gene expression in bone marrow cells of mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 218, 112296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Fan, J.; Wu, X. Bisphenol A triggers the malignancy of acute myeloid leukemia cells via regulation of IL-4 and IL-6. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-K.; Tan, Y.-Y.; Yao, M.; Lin, H.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Li, Y.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Huang, T.-T.; Chang, C.-W.; Cheng, C.-M.; et al. Bisphenol A-induced DNA damages promote to lymphoma progression in human lymphoblastoid cells through aberrant CTNNB1 signaling pathway. iScience 2021, 24, 102888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, D.; McLachlan, J.A. Epigenetics, evolution, endocrine disruption, health, and disease. Endocrinology 2006, 147, S4–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafei, A.; Ramzy, M.M.; Hegazy, A.I.; Husseny, A.K.; El-Hadary, U.G.; Taha, M.M.; Mosa, A.A. The molecular mechanisms of action of the endocrine disrupting chemical bisphenol A in the development of cancer. Gene 2018, 647, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, X.; Yan, F.; Xu, L.; Ye, X. Modulation of Gut Microbial Metabolism by Cyanidin-3- O -Glucoside in Mitigating Polystyrene-Induced Colonic Inflammation: Insights from 16S rRNA Sequencing and Metabolomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 7140–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velcich, A.; Yang, W.; Heyer, J.; Fragale, A.; Nicholas, C.; Viani, S.; Kucherlapati, R.; Lipkin, M.; Yang, K.; Augenlicht, L. Colorectal cancer in mice genetically deficient in the mucin Muc2. Science 2002, 295, 1726–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xu, S.; Yang, X. Standardizing methodologies to study microplastics and nanoplastics in cardiovascular diseases. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Weng, H.; Liu, S.; Li, F.; Xu, K.; Wen, S.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Nie, Y.; Liao, B.; et al. Embryonic exposure of polystyrene nanoplastics affects cardiac development. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, N.; Chen, Y.; Ling, Z.; Xiang, P. Microplastics in the human body: A comprehensive review of exposure, distribution, migration mechanisms, and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Q.; Wei, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene microplastics cause cardiac fibrosis by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and promoting cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A.; Singh, A.; Kumar Gupta, V.; Mishra, Y.K. Nano/micro-plastic, an invisible threat getting into the brain. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, K.; Johnson, E.V.; Malmendal, A.; Linse, S.; Hansson, L.-A.; Cedervall, T. Brain damage and behavioural disorders in fish induced by plastic nanoparticles delivered through the food chain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Yang, C.; Jiang, C.; Li, L.; Pan, M.; Li, D.; Han, X.; Ding, J. Evaluation of Neurotoxicity in BALB/c Mice following Chronic Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 107002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojnits, K.; de León, A.; Rathore, H.; Liao, S.; Zhao, M.; Gibon, J.; Pakpour, S. ROS-dependent degeneration of human neurons induced by environmentally relevant levels of micro- and nanoplastics of diverse shapes and forms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 134017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, A.; Pioro, E.P.; Goutman, S.A.; Kiernan, M.C. Nanoplastics and Neurodegeneration in ALS. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, B.; Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; Song, E.; Liu, C.; Song, Y.; Jiang, G. Polystyrene nanoparticles trigger aberrant condensation of TDP-43 and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-like symptoms. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2024, 19, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, G.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M. The hidden threat: Unraveling the impact of microplastics on reproductive health. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borumandnia, N.; Alavi Majd, H.; Khadembashi, N.; Alaii, H. Worldwide trend analysis of primary and secondary infertility rates over past decades: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2022, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Ma, T.; Sha, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Ding, J. Polystyrene microplastics induced male reproductive toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Yu, H.; Yang, L.; Sun, Y.; Xu, N.; Wang, N.; Lei, Z.; Hou, J.; Jin, Y.; et al. Polystyrene microplastics induce blood-testis barrier disruption regulated by the MAPK-Nrf2 signaling pathway in rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47921–47931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z. Reproductive toxicity of polystyrene microplastics: In vivo experimental study on testicular toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, R.; Troisi, J.; Richards, S.; Scafuro, M.; Fasano, S.; Guida, M.; Pierantoni, R.; Meccariello, R. Bisphenol A in Reproduction: Epigenetic Effects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 748–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yu, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, R.; Yu, R.; Liu, J.; Su, J. Reproductive toxicity of microplastics in female mice and their offspring from induction of oxidative stress. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhuan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Meng, L.; Fu, X.; Hou, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induced female reproductive toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, W.; Ru, S. Polystyrene microplastics cause tissue damages, sex-specific reproductive disruption and transgenerational effects in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yan, Z.; Shen, R.; Huang, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced reproductive toxicities induced by phthalates contaminated microplastics in male mice (Mus musculus). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.R.; Syberg, K.; Shashoua, Y.; Bury, N.R. Influence of polyethylene microplastic beads on the uptake and localization of silver in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lü, F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Shao, L.; Ye, J.; He, P. Is incineration the terminator of plastics and microplastics? J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maafa, I.M. Pyrolysis of Polystyrene Waste: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yermán, L.; Wall, H.; Carrascal, J.; Browning, A.; Chandraratne, D.; Nguyen, C.; Wong, A.; Goode, T.; Kyriacou, D.; Campbell, M.; et al. Experimental study on the fuel requirements for the thermal degradation of bodies by means of open pyre cremation. Fire Saf. J. 2018, 98, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Degradation Process | Mechanism | Key Factors Involved | Resulting Changes | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIOTIC | Biodegradation | Enzymatic breakdown | Microorganisms (fungal, multiple bacteria, algae) | Enzymatic oxidation, hydrolysis, chain scission, polymer fragmentation | [12,13] |
| ABIOTIC DEGRADATION | Chemical degradation | Chemical reactions catalyzed by environmental agents | Hydrolysis, oxidation, solubilization | Oxidation, dehydrochlorination, chain scission, cross-linking, polymer fragmentation | [13] |
| Thermal degradation | Slow thermal oxidation in combination with photodegradation | Thermal oxidation | [11,14,15,16] | ||
| Photo-degradation | Exposure to UV radiation | UV radiation, oxygen, temperature | [13,17,18] | ||
| Mechanical degradation | Physical forces | Abrasion, friction, pressure | Ablation, particle fragmentation | [19,20] |
| Source | Chemical | Amount | Detection via | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baby bottles | PP | 14,600–4,550,000 particles per person per day Or 16.2 million particles per liter especially after heating in microwave | Water incubated in baby bottles | [119] |
| PC/BPA | 0.8 to 23.8% of their safe TDI of BPA by using plastic bottles | Ethanol/water mixture in baby bottles | [120] | |
| Baby formula | PP, PE | Not specified | Formula preparations in plastic bottles | [119] |
| mostly PU | 17.3 particles/g | Infant formula | [121] | |
| Household dust → crawling/hand-to-mouth activities | PA, PS | 20–60 particles/m3 | Indoor air sampling | [122] |
| Environmental dust | n.a. | 15 MPs per day via inhalation | Street dust | [123] |
| Toys | n.a. | By friction, heat or light, MNPs may be released directly onto the hands, mouths and noses of children | [34] | |
| Breastmilk | Various, mostly PU | 20.2 particles/g | Breastmilk | [121] |
| Breastmilk | BPA | 75% of breastmilk samples 0.4–1.4 µg/L | Breastmilk | [124] |
| Diverse sources | Various, mostly PA | 18.0 particles/g | Placenta | [121] |
| Football pitches and playgrounds | PAH, phthalates, adipates | 9–91 µg/g | Rubber samples | [125] |
| Children’s toys | Bromine and antimony | Toy Samples | [126] | |
| Vinyl Flooring | BBzP, DEHP | 23.9 ng/m3 BBzP in air samples (compared to 10.6 ng/m3) | Indoor Air Sample | [127] |
| Pacifiers Toys | BPA | Below LOD—0.33 µg/L | 11 Toy and Pacifier Samples | [128] |
| Chemical | Amount | Detection via | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Various, mostly PA | 54.1 particles/g | Meconium | [121] |
| Various, mostly PA | 26.6 particles/g Correlation of exposure to plastic toys | Infant feces | [121] |
| MPs with 11 out of 15 plastic ingredients traced | 1.2–3.3 µg/L In 93% of urine samples | Children (age 3–17) urine and blood samples | [132] |
| BPA | 1.2–4.4 μg/L | Infant urine (3–15 months) without known BPA exposure | [124] |
| MBzP | 32.6 ng/mL Urinary MBzP (compared to 18.3 ng/mL) | Urine metabolites from children living in homes with vinyl flooring | [127] |
| Category | Affected Organs/Tissues | Key Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accumulation in tissues | Lung, spleen, liver, brain, intestine, etc. | Significant accumulation documented in animal studies; translocation to distant organs observed | [72,73,74,97,137,138,139] |
| Pathophysiology/toxicity and inflammation | Various tissues | Induces oxidative stress, inflammation and cytotoxicity; exacerbated by additives like BPA | [140,141,142,143,144] |
| Carcinogenic potential | Breast, lung, liver, cervical, prostate, colon, blood | Chronic exposure linked to cancer risk via inflammation and genotoxicity | [97,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164,165,166,167,168,169,170,171,172] |
| Cardiovascular system | Heart | Accumulation leads to oxidative stress, heart fibrosis and heart damage | [173,174,175,176] |
| Nervous system | Brain | Leads to neuroinflammation and cognitive deficits | [94,98,177,178,179,180,181,182] |
| Reproductive health | Testes, ovaries | DNA damage, reduced fertility rates and impaired sperm and oocyte quality | [183,184,185,186,187,188,189,190,191] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lang, T.; Jelić, F.; Wechselberger, C. From Cradle to Grave: Microplastics—A Dangerous Legacy for Future Generations. Environments 2024, 11, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11120263
Lang T, Jelić F, Wechselberger C. From Cradle to Grave: Microplastics—A Dangerous Legacy for Future Generations. Environments. 2024; 11(12):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11120263
Chicago/Turabian StyleLang, Tamara, Filip Jelić, and Christian Wechselberger. 2024. "From Cradle to Grave: Microplastics—A Dangerous Legacy for Future Generations" Environments 11, no. 12: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11120263
APA StyleLang, T., Jelić, F., & Wechselberger, C. (2024). From Cradle to Grave: Microplastics—A Dangerous Legacy for Future Generations. Environments, 11(12), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11120263








