Emissions and By-Products from Producing Torrefied Solid Recovered Fuel Using Pulp Industry Waste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Torrefaction of WPS and Sampling of Products
2.2. Gas Analysis
2.3. Liquid Analysis
3. Results & Discussion
3.1. Emissions and Gas Products from Manufacturing WPST1-573-20 and WPST2-593-20
3.1.1. Emissions of CO, NOx, SO2, and CO2
3.1.2. Hydrocarbons
3.1.3. Total Volume and Amount of Different Compounds in Emissions and Gas Products
3.1.4. Comparison of Gas Emissions with Standards for Air Pollutant Emissions
3.2. Characterizations of Liquid Products from the Torrefaction of WPS1 and WPS2
3.2.1. Yields of Liquid Products
3.2.2. Identification of Probable Constituents in Liquid Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature and Abbreviation
| Nomenclature | |
| CCOI | Instant emission concentration of CO (ppmv) |
| CCO2I | Instant emission concentration of CO2 (vol. %) |
| CI | Instant concentrations of gaseous products of HCs of Cn-HC (n = 1 to 6) (mmol/mL) |
| Cmax | Maximum emission concentration during torrefaction (ppmv) |
| CNOxI | Instant emission concentration of NOx (ppmv) |
| Cn | Number of carbons (−) |
| Cn-HC | Hydrocarbons exhibiting similar chemical polarity of the alkane of CnH2n+2, n = 1 to 6 (−) |
| CSO2I | Instant emission concentration of SO2 (ppmv) |
| ED | Energy densification ratio (−) |
| QN | Inlet flow rate of N2 to torrefaction reactor (mL/min) |
| T | Temperature (K) |
| TT | Torrefaction temperature (K) |
| t | Time (min) |
| tT | Torrefaction time (min) |
| WBCT-T-t | WBCT sample with torrefied T (K) and t (min), e.g., WBCT-563-40 (−) |
| WPST-T-t | WPST1 and WPST2 sample with torrefied T (K) and t (min), e.g., WPST1-573-20, WPST2-593-20 (−) |
| VG+N | Sum of volumes of inlet N2 and outlet gas products (mL) |
| VN | Volume of inlet N2 (mL) |
| YMG | Mass yield of gas product (−) |
| YML | Mass yield of liquid product (−) |
| YM or YMS | Mass yield of solid (−) |
| Abbreviation | |
| FID | Flame ionization detector |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| GC-MS | Gas chromatography-mass spectrophotometer |
| HCs | Hydrocarbons |
| SBF | Solid bio-fuel |
| SBFT | Torrefied SBF |
| SRF | Solid recovered fuel |
| SRFT | Torrefied SRF |
| WBCs | Waste bamboo chopsticks |
| WBCT | Torrefied waste bamboo chopsticks |
| WPS | Wood waste with pulp sludge |
| WPST | Torrefied WPS |
References
- TEPA (Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration). National Inventory Report. 2022. Available online: https://www.epa.gov.tw/eng/C822CC8F362AE1E2. (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- Promnuan, K.; O-Thong, S. Efficiency evaluation of biofilter for hydrogen sulfide removal from palm oil mill biogas. Energy Procedia 2017, 138, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegelmilch, M.; Streese, J.; Biedermann, W.; Herold, T.; Stegmann, R. Odour control at biowaste composting facilities. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papurello, D.; Gandiglio, M.; Kafashan, J.; Lanzini, A. Biogas purification: A comparison of adsorption performance in D4 siloxane removal between commercial activated carbons and waste wood-derived char using isotherm equations. Processes 2019, 7, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chang, C.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Yuan, M.H.; Ji, D.R.; Shie, J.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Chang, W.R.; Yang, T.Y.; Lee, C.H.; et al. Production of solid bio-fuel from waste bamboo chopsticks by torrefaction. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2017, 126, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Chang, C.C.; Yuan, M.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Wu, C.H.; Shie, J.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Ho, C.; Chang, W.R.; et al. Production of torrefied solid bio-fuel from pulp industry waste. Energies 2017, 10, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Ho, K.Y.; Lee, K.T.; Lu, D.; Lin, A.K.Y.; Rajendran, S.; Singh, Y.; Chang, J.S. Dual pretreatment of mixing H2O2 followed by torrefaction to upgrade spent coffee grounds for fuel production and upgrade level identification of H2O2 pretreatment. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, T.C.; Chang, C.C.; Yuan, M.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, C.F.; Ji, D.R.; Shie, J.L.; Manh, D.V.; Wu, C.H.; et al. Upgrading of Jatropha-seed residue after mechanical extraction of oil via torrefaction. Energy 2018, 142, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, D.; Yang, J.; Yuan, L. Kinetic mechanisms and emissions investigation of torrefied pine sawdust utilized as solid fuel by isothermal and non-isothermal experiments. Materials 2022, 15, 8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waheed, M.A.; Akogun, O.A.; Enweremadu, C.C. An overview of torrefied bioresource briquettes: Quality-influencing parameters, enhancement through torrefaction and applications. Bioresour. Bioproces. 2022, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.H.; Chang, C.C.; Hsu, T.C.; Shie, J.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Lin, C.F.; Yu, C.P.; Wu, C.H.; Do, M.V.; et al. A technical analysis of solid recovered fuel from torrefied jatropha seed residue via a two-stage mechanical screw press and solvent extraction process. Energies 2021, 14, 7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Waheed, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Al-Zahrani, A.A.; Nawaz, A.M.; Mahpudz, A.B. Synergistic evaluation of co-torrefaction performance of rice husk and coffee bean ground blends for biosolid production for industrial fuel sustainability. Fuel 2023, 343, 127891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, G.J.; Kuang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Luo, Y.H. Pretreatment of agricultural residues for co-gasification via torrefaction. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 86, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimchuai, A.; Dutta, A.; Basu, P. Torrefaction of agriculture residue to enhance combustible properties. Energy Fuel 2010, 24, 4638–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seithtanabutara, V.; Kaewmahawong, S.; Polvongsri, S.; Wang, J.; Wongwuttanasatian, T. Impact of positive and negative pressure on rice straw torrefaction: Optimization using response surface methodology. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 7, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.Y. Torrefaction of Rice Straw and Biofiber. Master’s Thesis, Graduate Institute of Environment Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2012. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Co-pyrolysis characteristics of raw/torrefied corn stalk and oil shale. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2023, 171, 105967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, B.; Pevida, C.; Fermoso, J.; Plaza, M.G.; Rubiera, F.; Pis, J.J. Influence of torrefaction on the grindability and reactivity of woody biomass. Fuel Process. Technol. 2008, 89, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgois, J.; Guyonnet, R. Characterization and analysis of torrefied wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 1988, 22, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Lu, K.M.; Lee, W.J.; Lin, T.C. Thermal pretreatment of wood (Lauan) block by torrefaction and its influence on the properties of the biomass. Energy 2011, 36, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensöz, S. Slow pyrolysis of wood barks from Pinus brutia Ten. and product compositions. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 89, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgeman, T.; Jones, J.; Williams, A.; Waldron, D. An investigation of the grindability of two torrefied energy crops. Fuel 2010, 89, 3911–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanphanich, M.; Mani, S. Impact of torrefaction on the grindability and fuel characteristics of forest biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balat, M.; Balat, M.; Kırtay, E.; Balat, H. Main routes for the thermo-conversion of biomass into fuels and chemicals. Part 1: Pyrolysis systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 3147–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, P.C.A.; Boersma, A.R.; Zwart, R.W.R.; Kiel, J.H.A. Torrefaction for Biomass Co-Firing in Existing Coal-Fired Power Stations. BIOCOAL; Energy Research Centre of the Netherlands: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2005.
- Huang, Y.F.; Chiueh, P.T.; Lo, S.L. A review on microwave pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2016, 26, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Li, W.; Chai, H.; Liu, K. Effect of temperature oscillation on torrefaction and pyrolysis of elm branches. Energy 2023, 271, 127055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentananunt, R.; Rahman, A.N.M.M.; Bhattacharya, S.C. Upgrading of biomass by means of torrefaction. Energy 1990, 15, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Lin, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Xiang, J.; Hu, X. Influence of torrefaction with microwave and furnace heating on pyrolysis of poplar sawdust. Fuel Process. Technol. 2023, 245, 107696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaka, S.; Negi, S. Improvements of biomass physical and thermochemical characteristics via torrefaction process. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2009, 28, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáiz-Jiménez, C.; De Leeuw, J.W. Lignin pyrolysis products: Their structures and their significance as biomarkers. Org. Geochem. 1986, 10, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumuluru, J.S.; Sokhansanj, S.; Hess, J.R.; Wright, C.T.; Boardman, R.D. A review on biomass torrefaction process and product properties for energy applications. Ind. Biotechnol. 2011, 7, 384–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Stelt, M.; Gerhauser, H.; Kiel, J.; Ptasinski, K. Biomass upgrading by torrefaction for the production of biofuels: A review. Biomass Bioenerg. 2011, 35, 3748–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.T.; Shih, Y.T.; Rajendran, S.; Park, Y.K.; Chen, W.H. Spent coffee ground torrefaction for waste remediation and valorization. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 324, 121330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.H.H.; Zhang, Y.; Pétrissans, A.; Pétrissans, M.; Ho, S.H.H. Superhydrophobic and superlipophilic biochar produced from microalga torrefaction and modification for upgrading fuel properties. Biochar 2023, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chang, C.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Yuan, M.H.; Ji, D.R.; Ho, C.; Chiou, C.S.; Shie, J.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Chang, W.R.; et al. The by-products and emissions from manufacturing torrefied solid fuel using waste bamboo chopsticks. Environments 2017, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, A.; Abbey, L.; Gunupuru, L.R. Production, prospects and potential application of pyroligneous acid in agriculture. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2018, 135, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Jang, E.S.; Kim, Y.M. The temperature effect on the production of liquid and solid fuel via wood pellet torrefaction. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- TEPA (Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration). Standards for Air Pollutant Emission from Stationary Pollution Sources. 2021. Available online: https://law.moj.gov.tw/ENG/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?pcode=O0020006 (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- Jeanmart, S.; Edmunds, A.J.F.; Lamberth, C.; Pouliot, M.; Morris, J.A. Synthetic approaches to the 2015–2018 new agrochemicals. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 39, 116162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Propane, 2-Chloro-2-nitro-. Available online: https://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductMSDSDetailCB3738690.htm (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- Acetamide, 2-Fluoro-. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fluoroacetamide (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- Mercaptamine. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cysteamine (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- 1,3-Dioxolane. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dioxolane (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- N,N-Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl)-2-aminoethanesulfonic Acid. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/N_N-Bis_2-hydroxyethyl_-2-aminoethanesulfonic-acid (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- Methyl Formate as Blowing Agent in the Manufacture of Polyurethane Foam Systems. 2021. Available online: https://www.undp.org/sites/g/files/zskgke326/files/publications/MethylalFormate_FINAL_WEB.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Decanol. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1-Decanol (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- Eucalyptol. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eucalyptol (accessed on 22 April 2023).
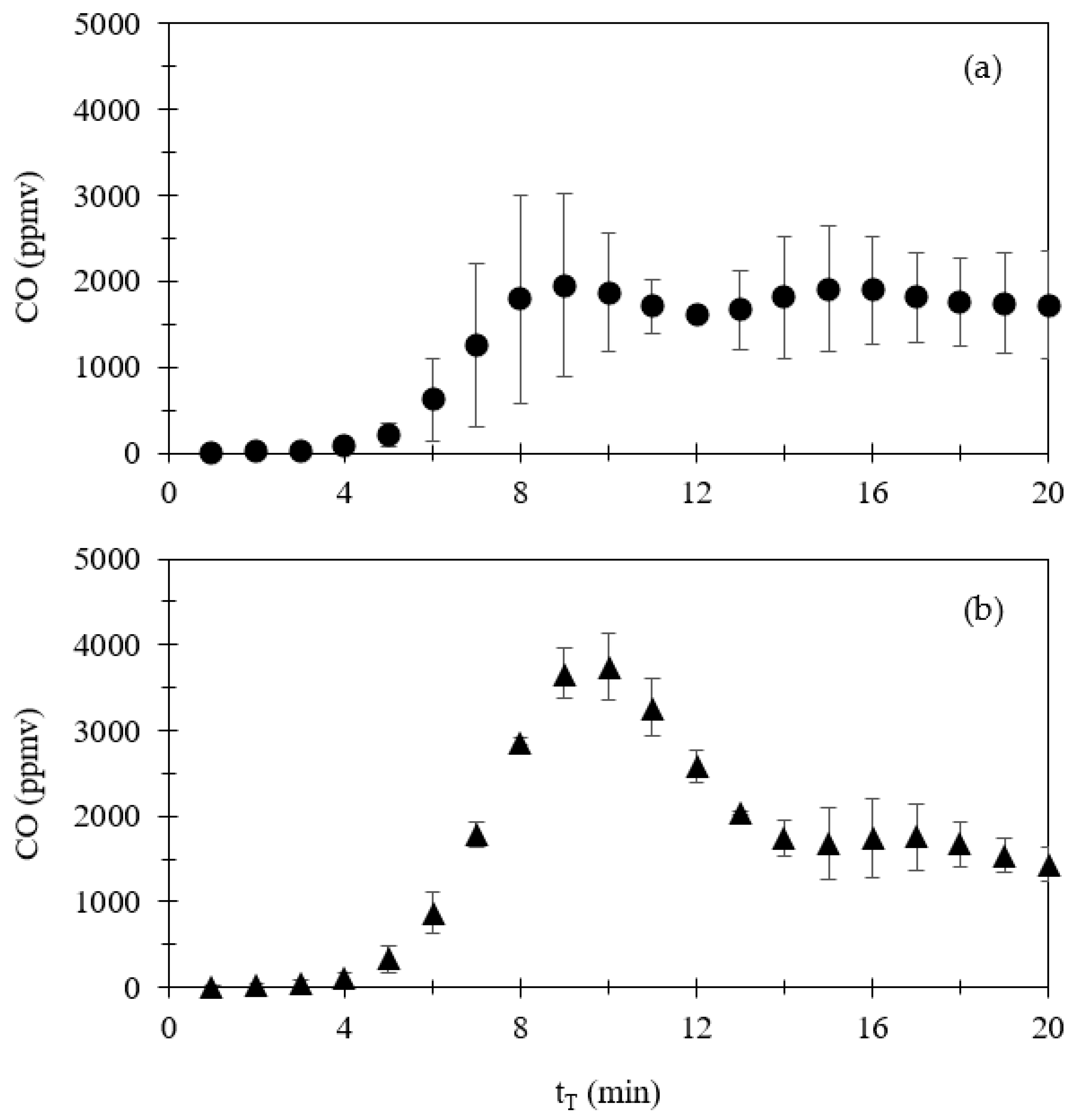
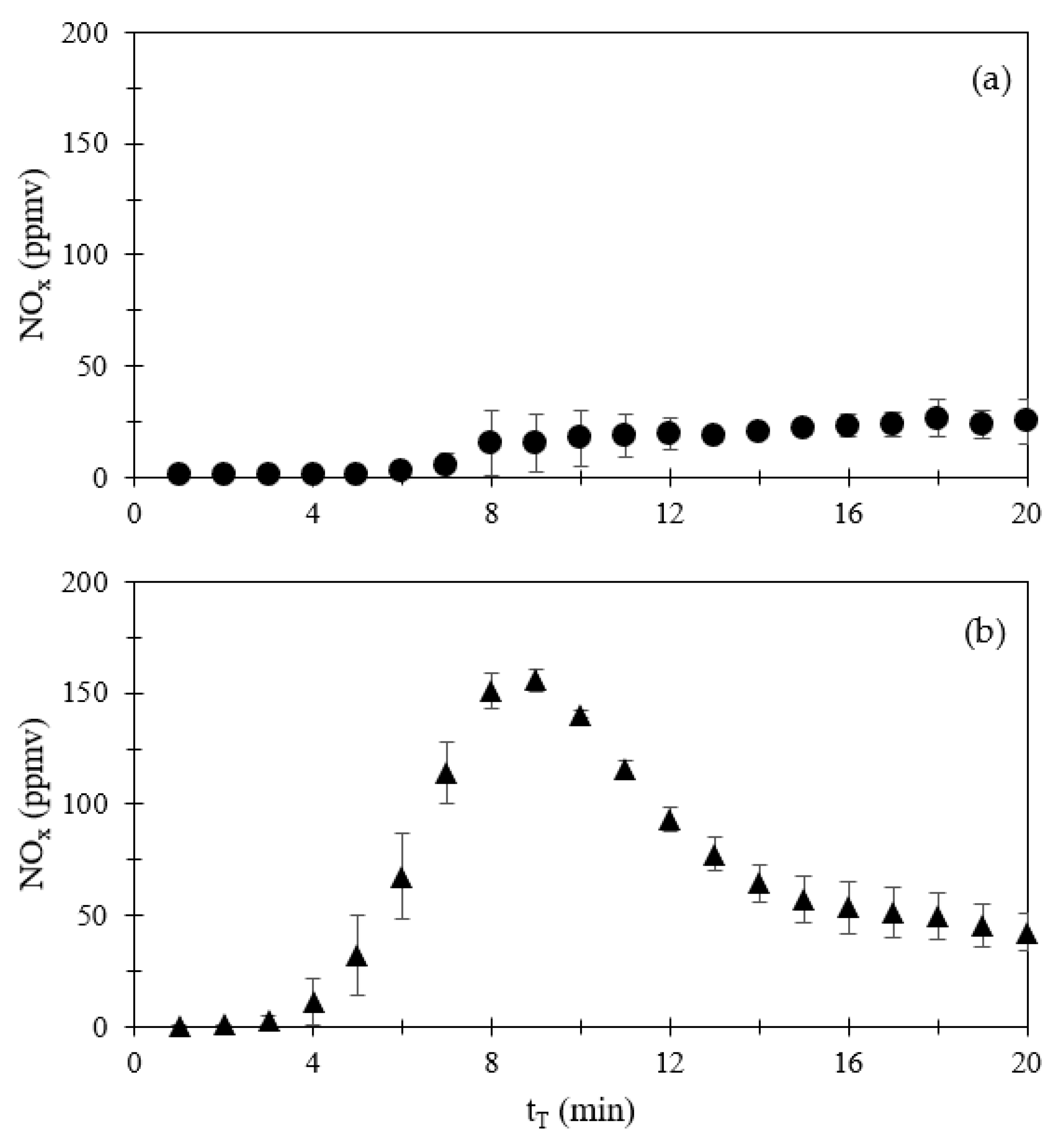
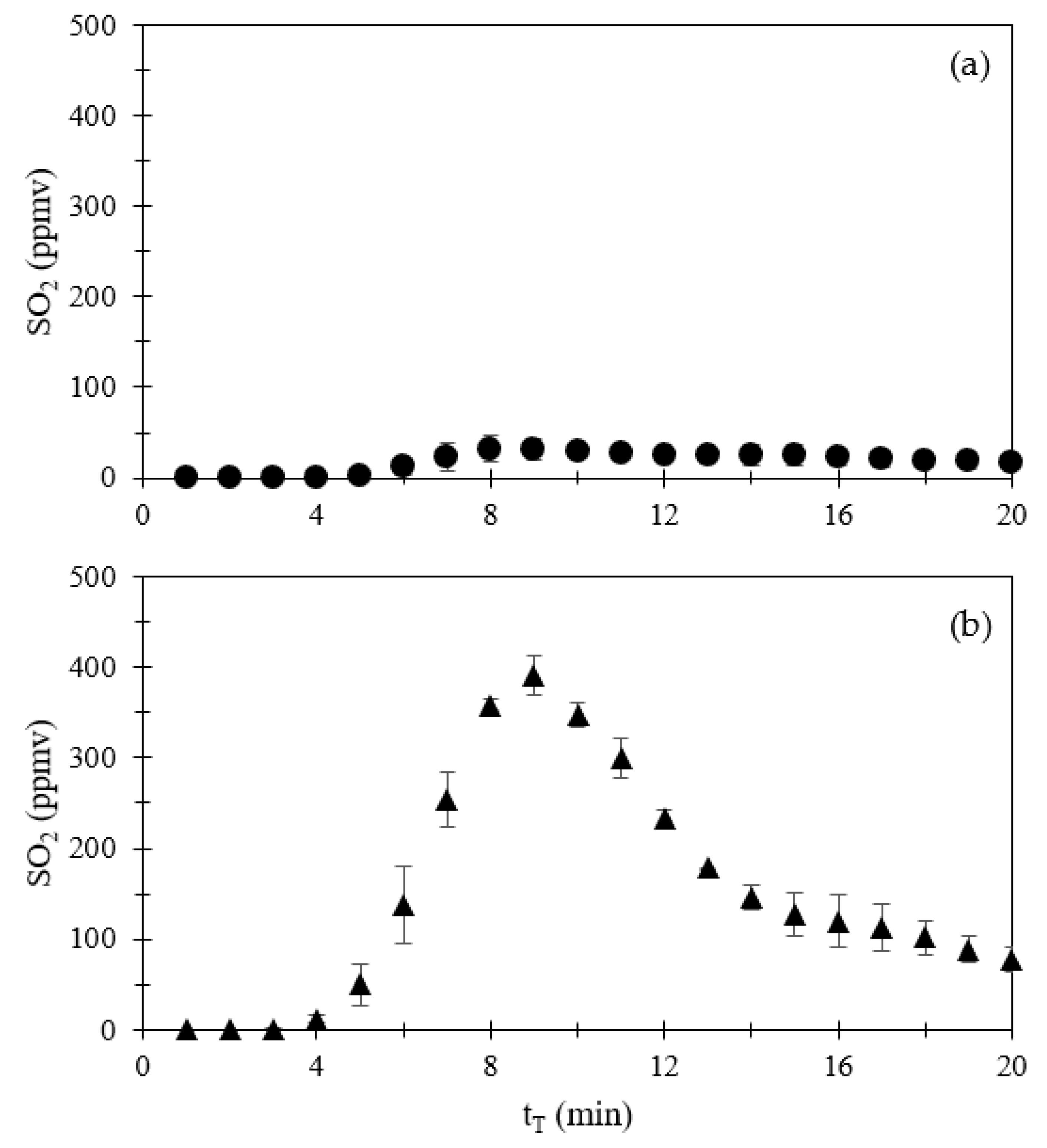
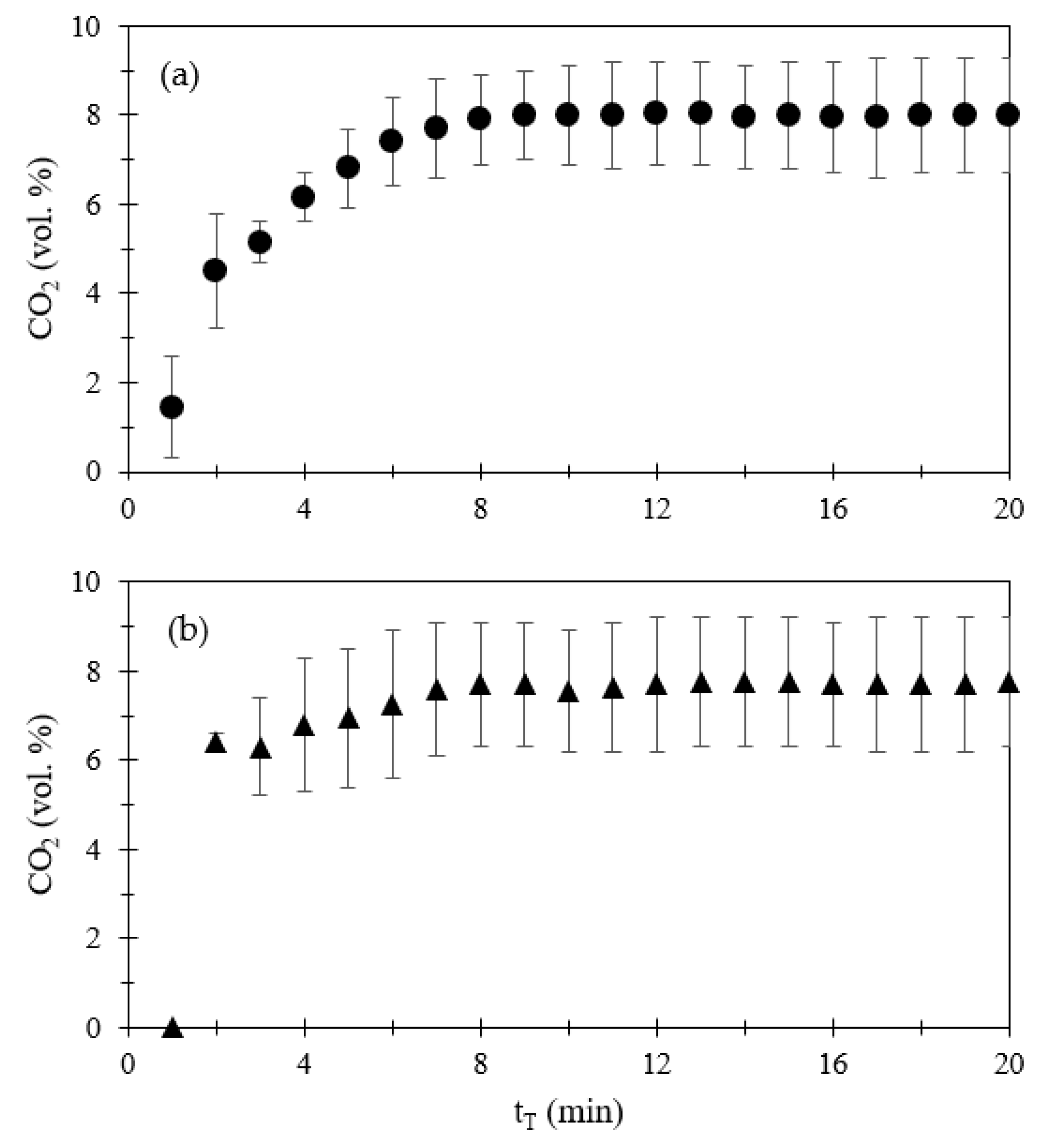

| Compound | Volume a (mL) | Volume (mL) | Amount (μmol) | Amount (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO * | 16.2 | 4.2 b,d; 5.43 b,e | 171.42 b,d; 221.63 b,e | 4.8 b,d; 6.21 b,e |
| NOx (NO2) | small | 0.047; 0.219 | 1.92; 8.94 | 0.088; 0.411 |
| SO2 | small | 0.059; 0.501 | 2.41; 20.45 | 0.154; 1.309 |
| CO2 * | 41.4 | 235.95; 233.31 | 9630.61; 9522.86 | 423.747; 419.006 |
| O2 * | 79.5 | 273.90; 278.36 | 11,179.59; 11,361.63 | 357.747; 363.572 |
| C1–C6 HCs * | 1.74 | 0.831 c,d; 0.918 c,e | 33.90 c,d; 37.48 c,e | 1.961 c,d; 1.995 c,d |
| C1–HC | 0.19 | 0.038; 0.135 | 1.56; 5.53 | 0.025; 0.089 |
| C4–HC | - | 0.704; 0.630 | 28.72; 25.71 | 1.666; 1.491 |
| C2, C3, C5, C6- HCs | 1.55 | 0.088; 0.153 | 3.61; 6.24 | 0.270; 0.415 |
| C2-C6 HCs | 1.55 | 0.793; 0.783 | 32.34; 31.95 | 1.936; 1.906 |
| H2O * | 51.2 | NM f | NM | NM |
| Total of terms with * | 190 | 514.88 d; 518.02 e | 21,015.52 d; 21,143.6 e | 788.26 d; 790.78 e |
| Total gases measured from flowmeter | 183 | NM | NM | NM |
| Item | Emission Standards a (ppmv) | Cmax b,c (ppmv) | Cmax b,d (ppmv) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SO2 | 650 | 58.0 | 31.5 e; 392 f |
| NO2 | 250 | 67.5 g | 26.5 e,g; 156 f,g |
| CO | 2000 | 4555.5 | 1952.5 e; 3743.5 f |
| TT-tT (K-min) | Mass (g) a | Mass Yield (-) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid b | Liquid | Gas c | Solid b YMS | Liquid YML | Gas c YMG | |
| 563-40 WBCT | 2.07 d | 0.43 d | 0.51 d | 0.69 d | 0.14 d | 0.17 d |
| 573-20 WPST1 | 2.82 e | 1.39 f | 0.788 g | 0.56 e | 0.28 f | 0.16 g |
| 593-20 WPST2 | 3.03 e | 1.18 f | 0.791 g | 0.61 e | 0.24 f | 0.16 g |
| WPST1-573-20 (5 Compounds) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | 2,3,6-Trichlorobenzaldehyde | Propane, 2-Chloro-2-Nitro- | Acetamide, 2-Fluoro- |
| Formula | Cl3C6H2CHO | C3H6ClNO2 | C2H4FNO |
| Structure | 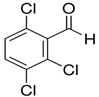 | 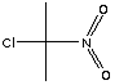 |  |
| Compound | Mercaptamine | 1,3-Dioxolane | |
| Formula | C2H7NS | C3H6O2 | |
| Structure |  | 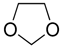 | |
| WPST2-593-20 (9 Compounds) | |||
| Compound | Hexadecane | N,N-Bis (2-hydroxyethyl)- 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid | Methyl formate |
| Formula | C16H34 | C6H15NO5S | HCO2CH3 |
| Structure |  |  |  |
| Compound | Eicosane | Undecane | 2-Heptanol, 3-methyl- |
| Formula | C20H42 | C11H24 | C8H18O |
| Structure |  | 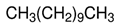 | 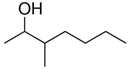 |
| Compound | 1-Decanol | Tetradecane | Eucalyptol |
| Formula | C10H22O | C14H30 | C10H18O |
| Structure |  |  |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, M.-H.; Chang, C.-C.; Huang, M.; Shie, J.-L.; Wu, C.-H.; Chang, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lin, F.-C.; Lin, C.-F.; Yu, C.-P.; et al. Emissions and By-Products from Producing Torrefied Solid Recovered Fuel Using Pulp Industry Waste. Environments 2023, 10, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10080135
Yuan M-H, Chang C-C, Huang M, Shie J-L, Wu C-H, Chang C-Y, Chen Y-H, Lin F-C, Lin C-F, Yu C-P, et al. Emissions and By-Products from Producing Torrefied Solid Recovered Fuel Using Pulp Industry Waste. Environments. 2023; 10(8):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10080135
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Min-Hao, Chia-Chi Chang, Michael Huang, Je-Lueng Shie, Chao-Hsiung Wu, Ching-Yuan Chang, Yi-Hung Chen, Far-Ching Lin, Cheng-Fang Lin, Chang-Ping Yu, and et al. 2023. "Emissions and By-Products from Producing Torrefied Solid Recovered Fuel Using Pulp Industry Waste" Environments 10, no. 8: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10080135
APA StyleYuan, M.-H., Chang, C.-C., Huang, M., Shie, J.-L., Wu, C.-H., Chang, C.-Y., Chen, Y.-H., Lin, F.-C., Lin, C.-F., Yu, C.-P., Chen, Y.-H., Chang, W.-R., Yang, T.-Y., & Liu, B.-L. (2023). Emissions and By-Products from Producing Torrefied Solid Recovered Fuel Using Pulp Industry Waste. Environments, 10(8), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10080135








