Abstract
Meiofauna (body size within 30–1000 µm) are the community of microscopic invertebrates that live at the bottom of marine and freshwater ecosystems and play a key role in the food webs of these environments. Several studies have addressed the adverse effects of anthropic stressors on meiofauna; however, data on the presence and impact of plastic debris in wild meiofaunal organisms are scant. Since the amount of microplastic waste in sediments may surge rapidly, ascertaining the ingestion of these xenobiotics by the abundant micrometazoan community is necessary to understand their potential accumulation in aquatic food webs and their hazard to the health of the ecosystem. The absence of documentation in this regard may be due to the difficulty in detecting the small size of the plastic fragments meiofauna may potentially ingest. To overcome this difficulty, we developed an integrated approach based on different microscopic/spectroscopic techniques suitable for detecting plastic particles of sizes down to 200 nm.
1. Introduction
Meiofauna are the community of microscopic invertebrates that live on or within the sediments of marine and freshwater ecosystems. The community is highly diverse and represents a significant fraction of the biodiversity of water bodies. The recent literature in streams suggested that as meiofauna increase web complexity, taking into account their functional diversity may be crucial to the understanding of food web properties and ecosystem processes [1].
Moreover, although small-sized, meiofaunal organisms play a role of primary importance in food webs as they are responsible for the transfer of energy from low to higher trophic levels, i.e., from the microbial loop to the macrofauna and juvenile forms of fish [2,3,4]. Given its relevant contribution to the health of aquatic ecosystems, it is not surprising that several studies have dealt with the adverse effects of various anthropic stressors on meiofauna [5], with some noticeable gaps (see below).
Plastic fragments less than five millimeters in diameter are pervasive pollutants in marine environments throughout the globe. According to recent studies, plastic debris is defined as microplastic when in a size range of 5000–1 µm and nanoplastic if <1 µm (1000 nm) that is considered the typical border of colloids [6]. Nevertheless, a definition supported by all scientists is still far from being developed, as some researchers support a lower range of dimensions for nanoplastics (<100 nm) [7].
The amount of microplastic debris in sediments may surge rapidly, affecting organisms inhabiting marine sediments, and has become an emerging issue (e.g., [8,9,10]).
However, information regarding the presence of microplastics in meiofaunal organisms in the wild is practically non-existent. A bibliographic search in WoS and SCOPUS databases (years 2010–2022, keywords: meiofauna and microplastics) yielded a single work, which documented the presence of plastic microfibers in individuals of three interstitial polychaete species [11]. Among the so-called microplastics, microfibers are probably the most easily identifiable inside an organism by their larger size and color. The small-magnification image supplied with the cited article, showing a specimen of Saccocirrus pussicus with a microfiber inside its intestinal tract, demonstrates this [11]. Indeed, the ease of identifying relatively large fragments of microplastics inside the animals using a simple stereomicroscope guided the cited research. Although the study by Gusmão and collaborators [11] did not lead to the discovery of microfibers in other meiofaunal organisms, specifically in other meiobenthic annelids, it could not exclude the presence of other different types/shapes of microplastics in their gut.
Microplastics of different shapes and sizes are widespread contaminants in marine environments around the world, and their deposition may change the texture of the sediment, affecting meiofaunal distribution and diversity (e.g., [12,13]). Moreover, the ability of meiofaunal organisms, belonging to a broad taxonomic spectrum, to ingest microplastics has been demonstrated experimentally in microcosm studies (e.g., [14,15]). Notwithstanding, proof that in nature, meiofaunal organisms ingest microplastics regularly and not occasionally, as the work by Gusmão et al. [11] suggests, is still lacking.
Due to their anatomical constraints (e.g., the small mouth), the microscopic size of the plastic debris that meiofaunal organisms could potentially ingest makes the identification of the tiny pieces in their gut difficult and may explain the current absence of documentation. Nonetheless, ascertaining the ingestion in nature of these xenobiotics by the abundant meiofaunal organisms is necessary to understand their potential accumulation in aquatic food webs and the hazard they pose to the health of the ecosystem [16,17].
This research aims to develop an integrated methodology to detect the presence of nanoplastics and small-sized microplastics (1 and 3 µm, [18]) in experimental meiofaunal organisms and apply it to the natural populations to quantify the uptake of these pollutants in the wild.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Meiofauna Positive Controls
Meiofaunal organisms acting as positive control were prepared at Modena. These were represented by laboratory-reared adult harpacticoid copepods (Tigriopus fulvus) and chironomid larvae (Chironomidae sp.), initially found in the supralittoral rock pools near Livorno [19]. For the microplastic ingestion experiment, the specimens were placed in six 5 cm diameter vessels filled with 35‰ artificial seawater and fed liberally with a mixture of fish-flaked food and 1-; 3-; and 1 + 3 µm diameter Fluoresbrite® YellowGreen polystyrene microbeads (Polysciences Europe GmbH, Eppelheim, Germany).
During the experiment, the culture water was not changed or aerated, and food and microbeads were added at the beginning; the concentration of microbeads was not determined.
After four-day feeding, animals were fixed in either 96% ethanol or 10% borax-neutralized formalin. The ingestion of the plastic microspheres by the experimental meiofauna was ascertained under a fluorescence microscope (Nikon Eclipse 90i) using UV or FITC filters. After inspection, animals were transferred to 0.5 mL glass vials and sent to the Bioscience Research Center (Orbetello) for micro- and nanoplastic quantification.
2.2. Meiofauna from Natural Sites
We obtained natural meiofauna populations from the marine area facing the city of Livorno, Italy (western Mediterranean Sea). In particular, meiofauna in three sites with potentially different levels of plastic pollution were collected: inside the Marine-Protected Area, Secche della Meloria (site M, low pollution), at the Yacht Club port of Livorno, site Y, high pollution), and from a site located between the yacht club and the AMP (site I, intermediate pollution). Type and levels of plastic debris and other pollutants in the three investigated sites can be found in Furno et al. [20].
Six sediment replicates containing meiofauna were collected manually using HDPE corers in each of the three sites mentioned above (M, Y, and I). In sites Y and I, the top 3 cm of sediment (top layer, about 9 cm3) was collected, while in site M, characterized by a medium-coarse deposit, the top 10 cm (about 30 cm3) of sediment was sampled. The collected material was transferred to jars and fixed with at least three-times the volume of 95% alcohol (3 replicates from each site) or 10% borax-buffered formalin (3 repeats). The samples were then sent to the Modena laboratory, where the meiofauna were extracted using the multiple swirling and decantation technique [3]; in the case of the alcohol-preserved samples, we used fresh alcohol for each decantation.
Animals from the replicates of a given sampling site were sorted out by taxon and pooled to obtain two forecasted sets of at least 25–50 specimens each. Sets of sorted organisms were transferred to glass vials and sent to the Bioscience Research Center at Orbetello for analyses aimed at the specific search of microplastics and their chemical characterization.
2.3. Sample Treatment
Most of the tested animals are characterized by a thick, generally chitinous exoskeleton (Figure 1A) that must be completely digested before the determinations of the ingested microplastics may be achieved. After some trials, a complete digestion of the roughest original matrix (i.e., Copepoda) was achieved using a saturated solution of KOH + NaOH coupled with sonication at 40 Hz for 20 min (30 °C). Therefore, we used this digestion technique for all the samples.
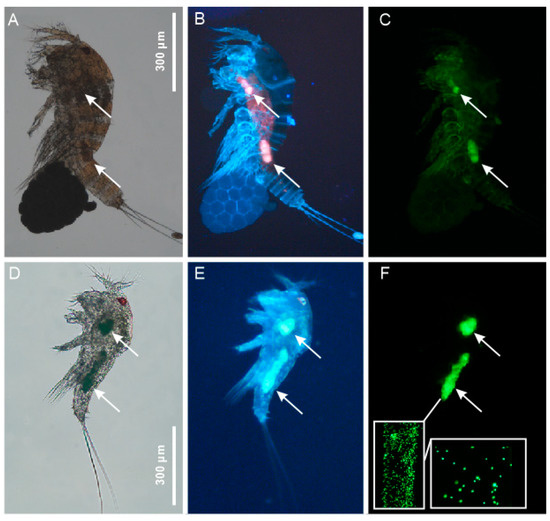
Figure 1.
Meiofauna positive control —photomicrographs of the experimental specimens of Tigriopus fulvus showing the intake of fluorescent-labelled polystyrene microspheres (arrows). (A–C) A gravid female; (D–F) a juvenile (copepodite); (A,D) bright-field microscopy; (B,E) florescence microscopy using UV filter; (C,F) florescence microscopy using an FITC filter; (F) inserts show the single 1 and 3 µm diameter microspheres.
Test samples were treated in a controlled area (glove box; Iteco engineering, mod. SGS20-13599, serial number 103,421) to ensure the absence, down to 200 nm of size, of contamination from air and other laboratory sources. Digested samples were filtered on Anodisc® (aluminum oxide membrane; 0.2 μm, Whatman, Maidstone, UK, lot A21184266) using a 13 mm PTFE syringe filter holder on a Luer-lock glass syringe (see [21]). Wet filters were collected under the glove box environment in a glass Petri dish and dried in an oven at 39 ± 1 °C. Positive controls (animals fed with 1–3 μm fluorescent polystyrene spherules) were carried out on single chironomid larva (n = 9 per treatment) and copepod (n = 20 per treatment). Negative controls (composed by a set of empty glass, unused Anodisc® filters) were performed in 5 replicates per batch of analysis according to the literature [22]. For details concerning the positive control treatments, see Quality Assurance and Quality Control (QA/QC) paragraph below. Finally, a standardized method for extraction and recovery of particles was applied on all tested samples such as positive/negative controls on environmental samples (animals collected from the two natural sites) [22]. All the tested samples were analyzed using three distinct, integrating techniques, as reported below.
2.4. Microscopy and Microchemical Analyses
Initially, the Anodisc® filters were analyzed under microscopy associated to Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy technique (μFT-IR; Nicolet™ iN™ 10 MX; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA); the analyzing system was equipped with a liquid-nitrogen-cooled MCT-A operating within a spectral range 7800–650 cm−1 and OMNIC™ Picta™ (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) user interface. This technique is mainly directed to the identification of relatively large plastic fragments. Particles within a dimensional range of 10–150 μm in length and <35 μm in width were analyzed via the Wizard-operating mode through transmission. All microplastics within this size range were recorded to allow for counting and measurements, using the “mosaic” software (Wizard section of OMNIC™ Picta™ software). The second analysis was carried out under RAMAN microscope spectroscopy (µRAMAN, DXR2, s/n AIY1716158, Thermo Scientific®), equipped with Olympus 10–1000× confocal microscopy for the chemical identification of the targeted particles using the Raman response (laser set emission source at 532 nm). This technique allows for the chemical identification of particles down to 1 μm of chemical resolution.
The third analysis was performed using Field emission Scanning Electron microscopy (FESEM model Zeiss, Merlin II). This technique allows for taking ultra-high-resolution pictures of the Anodisc® filter and performing chemical analyses by combining Energy-Dispersive (EDS) and Wavelength-Dispersive Spectroscopy (WDS) on the recovered particles in the dimensional size range down to 200 nm (the size of the filter pores). A special charge compensator allows to perform qualitative and quantitative elemental analysis of non-conductive specimen in high vacuum conditions required for high resolution imaging. Chemical analysis was carried out on all the recovered particles.
2.5. Quality Assurance and Quality Controls
Laboratory environment, equipment, and procedures were specifically devised to minimize sample contamination for this specific target of pollutant. The materials, equipment, bench surfaces, and gloves were carefully cleaned before and after the analysis of each sample; moreover, all glassware was accurately pre-rinsed to avoid potential contamination. Criteria for the QA/QC approach adopted in this study to ensure data quality follow criteria and procedures indicated mostly by Hermsen et al. [23]. Furthermore, quality controls on instruments were carried out to ensure data quality of chemical determinations performed on recovered particles. Finally, negative and positive controls were determined to ensure data quality.
Positive controls: Positive controls were performed to ensure the recovery of particles from animals actively fed with marked PS particles of the dimension of interest (1–3 μm and a mixture of both). The presence of fluorescence microbeads in digested material retained on Anodisc® was explored first using a fluorescence microscope (Intensilight HGFI) equipped with DAPI (EX340-380 DM 400 BA435-485), FITC (EX465-495 DM505 BA515-555), and TRITC (EX542/20 DM 570 BA620/52) filter sets and objectives 4–100 × CFI/DLL (Nikon). This analysis step aimed to detect, and count recovered nanoparticles within the dimensional range of 1–3 µm.
Negative controls: Negative controls were performed to ensure the absence of external and cross-over pollution of samples during the analytical process, including sample manipulation in laboratory, treatments occurred under the glove box, and drying and filter analyses under different instrument used (n = 5). Results on negative controls performed under the glove box (n = 5) per batch of analysis ensure the absence of external pollution within dimensional range of specific interest. Following testing of the filters, no particles larger than 1 µm were detected using RAMAN microscopy nor particles bigger than 200 nm by FESEM microscopy.
Quality controls on measurements: Double peak system ranging between 2350 and 2300 cm−1 was corrected using the “atmospheric correction” mode available in the OMNICTM PictaTM software. Collected spectra were back recognized using the Thermo® library integrated with the BsRC ones. The threshold for μFT-IR spectra, and RAMAN back-recognition was fixed over 80% of match. Limit of detection was 10 μm of maximum size (μFT-IR) and 1 μm (RAMAN); the size threshold in FESEM microscopy was limited by the size of pores of the Anodisc® used for sample filtrations (200 nm).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Meiofauna Positive Controls
Microscopical observation under a dissecting microscope (Wild M8) indicated that the alcohol-fixed copepods had relatively empty guts; therefore, subsequent analyses focused on the formalin-fixed animals. In fact, alcohol fixing may induce regurgitation/defecation in invertebrates, hence, the reason the guts of alcohol-preserved specimens may be empty. Formalin fixation is faster and, thus, less likely to result in regurgitation/defecation.
Fluorescence microscopy revealed that all the inspected animals (both Copepoda and chironomids larvae) had clusters of microbeads in their alimentary canal. In particular, juveniles and adults of Tigriopus fulvus invariably had two clusters of microbeads. A smaller one in the anterior midgut and a larger one in the posterior midgut [24] (Figure 1). The chironomid larvae exhibited more variability regarding the distribution and size of the bead clusters along their gut.
3.2. Meiofauna from Natural Sites
Observation under a dissecting microscope of the extracted meiofauna revealed a relatively low faunal richness, both in terms of major taxa present and the number of individuals. The only common taxonomic groups in the samples from the three sites were: Nematoda, harpacticoid Copepoda, and Polychaeta. However, the number of meiofaunal organisms from the intermediate site (site I) was so low as to suggest their exclusion from further analyses. Moreover, also in this case, the guts of the alcohol-fixed specimens were almost empty for the reason previously explained. Therefore, subsequent analyses focused on formalin-fixed fauna from site M and site Y only (Figure 2).
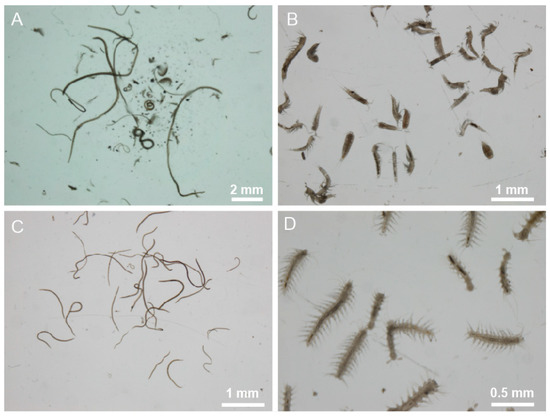
Figure 2.
Meiofauna from natural sites—photomicrographs of meiofaunal organisms tested for the intake of microplastics. (A), whole meiofauna community; (B), harpacticoid Copepoda; (C), Nematoda; (D), Polychaeta.
3.3. Microscopy and Microchemical Analyses
3.3.1. General Findings
Our analyses found microplastic elements associated only with the positive controls and to the meiofauna samples from natural sites; negative controls were completely blank/clean.
3.3.2. Positive Controls
As expected, polystyrene microbeads were found in all tested samples, i.e., single chironomid larvae and Tigriopus fulvus; moreover, the size of the microspheres mirrored the food protocols reported. The mean value of the recorded microplastic items per sample ranged from 2.73 to 4.03 × 106 particles per exposed animal, with little differences regarding tested taxa and size of the ingested microbeads (Table 1, Figure 1, Figure 3 and Figure 4). This numerical information assumes relevance concerning the discriminatory power of the used analytical techniques. While we caution on the use of these data for comparisons within and between the present taxa, these results open new avenues for studies aimed at shedding light on the foraging strategy and ingestion/egestion rates of tiny organisms, provided the amount of fish flakes and microbeads fed to the experimental animals is appropriately standardized, which was beyond the scope of the present research. In addition to the spherical particles, a polyester fiber (248.7 µm in length) was recorded in one of the positive control s, chironomid larvae. The source of this contamination remains unknown but very likely occurred outside the BsRC laboratory.

Table 1.
Meiofauna positive control. Estimation of PS-fluorescent microbeads recorded per animal. Mean (±standard variation).
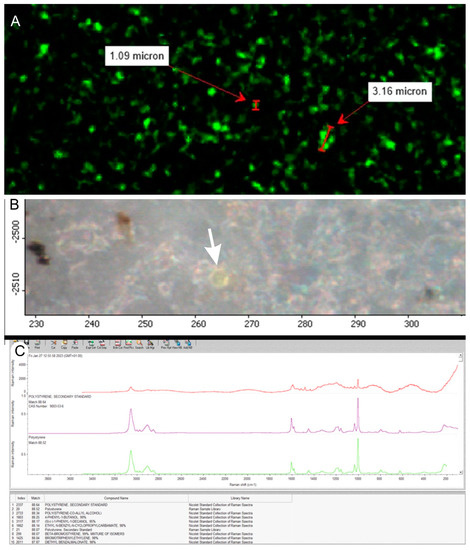
Figure 3.
Positive control analyses. (A) Fluorescent 1000–3000 nm sized nanoparticles on the Anodisc® filter and count of particles per filter; (B) analyses performed under RAMAN microscopy on fluorescent particles (white arrow); (C) chemical identification of recorded particles with spectral identification of polystyrene.
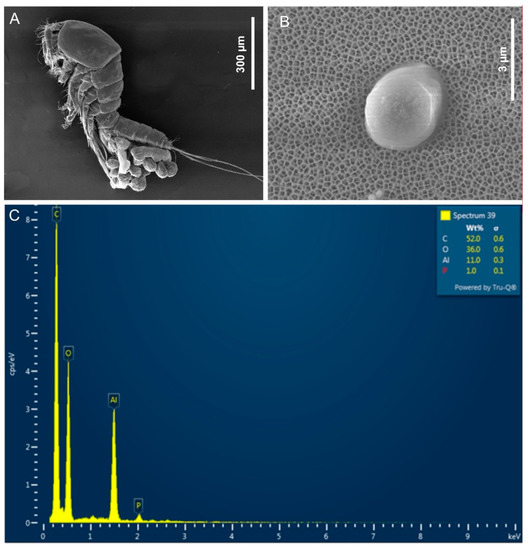
Figure 4.
Positive control analyses by FESEM microscopy: (A) Secondary electrons (morphoscopic) micrograph of a gravid female of Tigriopus fulvus; (B) image of targeted particle used as spiking nanoplastics; (C) chemical microanalyses combining FESEM with EDS of targeted particle supporting the presence of fluorescent plastic particles (C, P). The presence of Al and O in the reported spectrum is due to the contamination by surrounding Anodisc®.
The size range that determines the classification of plastic particles as micrometric, submicrometric, and nanometric has been repeatedly reviewed in the literature [25,26].
Currently, the size range that limits microplastics is 1 micrometer, while particles between 1 micrometer and 100 nanometers are called submicrometric [27]. However, some protocols still widely used, such as GESAMP, delineate nanoparticles starting at a size of <1000 nm [28]; in this size range, particles are said to exhibit colloidal behavior [25]. The detection of particles in a size range of less than 1000 nm requires high attention to control and clean the working environment [27].
Various extraction methods have been tested so far to optimize the extraction of tiny plastic particles from different matrices (i.e., water, sediments, soil, and biota), showing advantages and limitations [27].
Waddel [29] showed that the digestion of organic material with acids leads to the degradation of some plastics, such as PA and PU, while oxidation with H2O2 degrades plastics as a function of temperature [30]. On the other hand, alkaline digestions using KOH and NaOH lead to efficient and gentle particle degradation when performed at low temperatures, as in this study [30,31].
In addition, ultrasonic treatment has been reported in the literature to efficiently remove lipids and proteins without generating potassium salts [32] and can be used in combination with chemicals [33]. Furthermore, the direct filtration of digested animals on the Anodisc® allowed for the collection of particles down to 200 nm in size. Finally, the associated use of different techniques, such as µFT-IR, µRAMAN [28], and FESEM [34], improved the detection performance of the tested method down to the nano scale (200 nm). To conclude, the method proposed in this study appeared to be suitable, robust, fast, and cost-effective for quantification and chemical detection of plastic particles down to 200 nm in meiofauna samples.
3.3.3. Meiofauna from Natural Sites
Microscopic analysis of the specific Anodiscs® (i.e., retaining material from the digestion of meiofaunal organisms collected in nature) revealed the presence of few particles resembling microplastic debris in four filters only: two with material from Copepoda and two from Polychaeta (Table 2). Chemical determination of the ten particles found indicated that only two were microplastics, the other being of biological origin (likely cuticle fragments).

Table 2.
Meiofauna from natural sites. Analyzed taxa, individuals per batch, site of origin, analyzed items, type, composition, and length of the found microplastics. Only replicates with potential plastic items are reported. PP = Polypropylene; PE = Polyethylene.
The chemical composition and the elongated, thread-like shape identify the two plastic elements as microfibers (Table 2). The size and shape of the recovered plastic particles suggest they may have originally been attached externally to the body of some specimen rather than being ingested items. The fact that the microfibers have been found only in copepod samples supports the hypothesis of external contamination since the legs of these animals, provided with numerous setae, constitute a perfect filter within which the stray microfibers may remain trapped.
The absence on nano- and microplastics inside the tested organisms is somewhat surprising, considering the ability of meiofaunal taxa to ingest these contaminants ([14,15] and present study) and the pervasiveness of the microplastics in the marine system in general and in the sediment of the sites we sampled in particular [20]. Two main hypotheses explaining the absence of nano- and microplastics inside the tested organisms may be put forward: (i) the absence of particles of ingestible dimension in the sites from where the animals derive, (ii) specific feeding strategies of the analyzed animals.
To detect and precisely quantify nano- and microplastic particles in the wild is difficult [27], and we did not test our samples for this. On the other hand, the presence of larger microplastic debris at the same sites makes the absence of in situ smaller fragments very unlikely (Furno et al. [20]). Concerning the tested animals’ potential ability to avoid microplastic ingestion (implied by the second hypothesis) specifically, we highlight that various species of different taxa were analyzed (see the diversity of fauna in Figure 2); consequently, it is highly improbable that all these species have evolved the same ability to selectively avoid the ingestion of small microplastics. Lee et al. [35] showed that copepods (Tigriopus japonicas) ingested nanoplastics (50–500 nm of size). A further hypothesis explaining the absence of contaminants in our samples could be that the sites we sampled have relatively low levels of nano- and microplastic contamination. In this situation, the meiofauna can still find uncontaminated food (e.g., sediment patches without microplastics). It is worth mentioning that one of the sampling sites was located within the Meloria shoals, a protected marine area (MPA) of about 40 km2 sited at about 3 miles off the coast of Leghorn. Benthic assemblage and pollution levels in this natural reserve were studied, and the high biodiversity recorded is associated to low levels of human pressures [36,37]. On the other hand, the other sampled site (site Y) is located within the port of Leghorn, which is not immune to microplastic pollution (Furno et al. [20]).
4. Conclusions
The results from positive controls and the absence of contamination on the negative controls validate the integrated approach developed in this study for detecting plastic particles down to 1000 nm in size and suggest its usefulness for the discovery of contamination from nanoplastics down to 200 nm (Figure 4). The very low number of microplastics found in the meiofauna samples from natural sites and, in particular, the absence of particles in the dimensional range (200–1000 nm) that the tested organisms could potentially ingest indicate a negligible contamination by small-sized microplastics of these natural populations. This result could be due to the scarce sediment pollution of the studied MPA. Nevertheless, the same result was recorded in the harbor site (Y), leading to the supposition that meiofauna are inefficient for transferring microplastics to the higher trophic levels, thus decoupling the negative impacts of microplastics predicted from species-specific studies from the effects realized at the ecosystem scale [38]. Nevertheless, further research, possibly carried out in very impacted areas, is needed to better clarify the meiofauna–microplastic interaction and the role of natural meiofauna populations in transferring micro- and nanoplastics to the higher trophic levels.
Author Contributions
Contributions: M.A.T. and M.R.: conceptualization, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. S.A., investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. T.B., C.P. and A.C., investigation, writing—review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported by a grant ‘Far attrezzature 2021′ to M.A.T. from the University of Modena e Reggio Emilia, Italy.
Data Availability Statement
Most data presented in this study are available in the present paper; additional data may be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schmid-Araya, J.M.; Hildrew, A.G.; Robertson, A.; Schmid, P.E.; Winterbottom, J. The importance of meiofauna in food webs: Evidence from an acid stream. Ecology 2002, 83, 1271–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schratzberger, M.; Ingels, J. Meiofauna matters: The roles of meiofauna in benthic ecosystems. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2018, 502, 12−25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giere, O. Meiobenthology. The Microscopic Fauna in Aquatic Sediments; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; p. 328. [Google Scholar]
- Todaro, M.A.; Luporini, P. Not too big for its mouth: Direct evidence of a macrodasyidan gastrotrich preyed in nature by a dileptid ciliate. Eur. Zool. J. 2022, 89, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giere, O. Pollution and Meiofauna—Old Topics, New Hazards. In Perspectives in Meiobenthology; Springer Briefs in Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigault, J.; ter Hall, A.; Baudrimont, M.; Pascal P-y Gauffre, F.; Phi, T.-L.; El Hadri, H.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Current Opinion: What Is a Nanoplastic? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccardo, M.; Renzi, M.; Terlizzi, T. Nanoplastics in the oceans: Theory, experimental evidence and real world. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhof, H.K.; Schmid, J.; Niessner, R.; Ivleva, N.P.; Laforsch, C. A novel, highly efficient method for the separation and quantification of plastic particles in sediments of aquatic environments. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2012, 10, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masura, J.; Baker, J.; Foster, G.; Curtney, A. Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Recommendations for Quantifying Synthetic Particles in Waters and Sediments; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Kansas, MO, USA,, 2015.
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Vethaak, A.D.; Lavorante, B.R.B.O.; Lundebye, A.K.; Guilhermino, L. Marine microplastic debris: An emerging issue for food security, food safety and human health. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2018, 133, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusmão, F.; Di Domenico, M.; Amaral, C.Z.; Martínez, A.; Gonzalez, B.C.; Worsaae, K.; Ivar do Sul, J.A.; da Cunha Lana, P. In situ ingestion of microfibers by meiofauna from sandy beaches. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 216, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corinaldesi, C.; Canensi, S.; Carugati, L.; Lo Martire, M.; Marcellini, F.; Nepote, E.; Sabbatini, S.; Danovaro, R. Organic enrichment can increase the impact of microplastics on meiofaunal assemblages in tropical beach systems. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 292, 118415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, A.M.; Leon, V.; Colorado, A.; Giraldo, D.; Fragozo, L.; Quiroga, S.Y.; Martínez, A. Effects of microplastics pollution on the abundance and composition of interstitial meiofauna. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2023, 71, e50031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füser, H.; Mueller, M.-T.; Traunspurger, W. Ingestion of microplastics by meiobenthic communities in small-scale microcosm experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teawook, K.; Dongsung, K.; Je Hyeok, O. Ingestion of microplastics by free-living marine nematodes, especially Enoplolaimus spp., in Mallipo Beach, South Korea. Plankton Benthos Res. 2021, 16, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farady, S.E. Microplastics as a new, ubiquitous pollutant: Strategies to anticipate management and advise seafood consumers. Mar. Policy 2019, 104, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjani, M.; Veerasingam, S.; Venkatachalapathy, R.; Mugilarasan, M.; Bagaev, A.; Mukhanov, V.; Vethamony, P. Assessment of potential ecological risk of microplastics in the coastal sediments of India: A meta-analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.; Liu, X.; Qu, M. Nanoplastics and Human Health: Hazard Identification and Biointerface. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todaro, M.A.; Faranapova, O.; Onorati, F.; Pellegrini, D.; Tongiorgi, P. Tigriopus fulvus (Copepoda, Harpacticoida) a possible test-species in harbour sediment toxicity bioassessment: Life cycle and preliminary bioassays. Biol. Mar. Medit. 2001, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Furno, M.F.; Poli, A.; Ferrero, D.; Tardelli, F.; Manzini, C.; Oliva, M.; Pretti, C.; Campani, T.; Casini, S.; Fossi, M.C.; et al. The Culturable Mycobiota of Sediments and Associated Microplastics: From a Harbor to a Marine Protected Area, a Comparative Study. J. Fungi. 2022, 8, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzi, M.; Grazioli, E.; Bertacchini, E.; Blaskovic, A. Microparticles in table salt: Levels and chemical composition of the smallest dimensional fraction. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoli, M.; Renzi, M.; Pastorino, P.; Lesa, D.; Mele, A.; Anselmi, S.; Barcelò, D.; Prearo, M.; Pizzul, E. Microplastics and leaf litter decomposition dynamics: New insight from a lotic ecosystem (Northeastern Italy). Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermsen, E.; Mintening, S.M.; Besseling, E.; Koelmans, A.A. Quality criteria for the analysis of microplastic in biota samples: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10230–10240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, D.S.; Bisalputra, T. The morphology of a harpacticoid copepod gut: A review and synthesis. J. Morphol. 1980, 164, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangkham, S.; Faikhaw, O.; Munkong, N.; Sakunkoo, P.; Arunlertaree, C.; Chavali, M.; Mousazadeh, M.; Tiwari, A. A review on microplastics and nanoplastics in the environment: Their occurrence, exposure routes, toxic studies, and potential effects on human health. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2022, 181, 113832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autgoda, T.; Piyumali, H.; Wijesekara, H.; Sonne, C.; Lam, S.S.; Mahatantila, K.; Vithanage, M. Nanoplastic occurrence, transformation, and toxicity: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, J.; Taladriz-Blanco, P.; Lehner, R.; Lubskyy, A.; Ortuso, R.D.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Petri- Fink, A. The micro-, submicron-, and nanoplastic hunt: A review of detection methods for plastic particles. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GESAMP. Guidelines for the Monitoring and Assessment of Plastic Litter and Microplastics in the Ocean; Kershaw, P.J., Turra, A., Galgani, F., Eds.; GESAMP Reports and Studies, No. 99; GESAMP Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection: London, UK, 2019; 130p. [Google Scholar]
- Waddel, E.N. Development and Use of a Tissue-Destruction Method to Extract Microplastics Inblue Crabs (Callinectes sapidus). Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi, Corpus Christi, TX, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Choo, C.K.; Romano, N.; Ho, Y.B.; Salamatinia, B. A high-performance protocol for extraction of microplastics in fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, S.; van Werven, B.; van Oyen, A.; Meijboom, A.; Bravo Rebolledo, E.L.; van Franeker, J.A. The use of potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution as a suitable approach to isolate plastics ingested by marine organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Wang, Z.M.; Ghosal, S.; Rochman, C.; Gassel, M.; Wall, S. Novel method for the extraction and identification of microplastics in ocean trawl and fish gut matrices. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Webb, H.; Lindeque, P.K.; Fileman, E.S.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Isolation of microplastics in biota-rich seawater samples and marine organisms. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladár, A.E.; Hodoroaba, V.-D. Chapter 2.1.1—Characterization of nanoparticles by scanning electron microscopy. In Micro and Nano Technologies, Characterization of Nanoparticles; Hodoroaba, V.-D., Unger, W.E.S., Shard, A.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 7–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.W.; Shim, W.J.; Kwon, O.Y.; Kang, J.H. Size-Dependent Effects of Micro Polystyrene Particles in the Marine Copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11278–11283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huys, R.; Todaro, M.A. Meloriastacus ctenidis gen. et sp. nov.: A primitive interstitial copepod (Harpacticoida, Leptastacidae) from Tuscany. Ital. J. Zool. 1997, 64, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, M.A. Meiofauna from the Meloria Shoals: Gastrotricha, biodiversity and seasonal dynamics. Biol. Mar. Medit. 1998, 5, 587–590. [Google Scholar]
- Marchant, D.J.; Martínez Rodríguez, A.; Francelle, P.; Jones, J.I.; Kratina, P. Contrasting the effects of microplastic types, concentrations and nutrient enrichment on freshwater communities and ecosystem functioning. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 255, 114834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).