Red Claw Crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus Cultivation Influences the Dynamics and Assembly of Benthic Bacterial Communities in Paddy Fields
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experiment
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Paddy Soil Properties Determination
2.4. Bacterial DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.5. Sequence Data Processing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
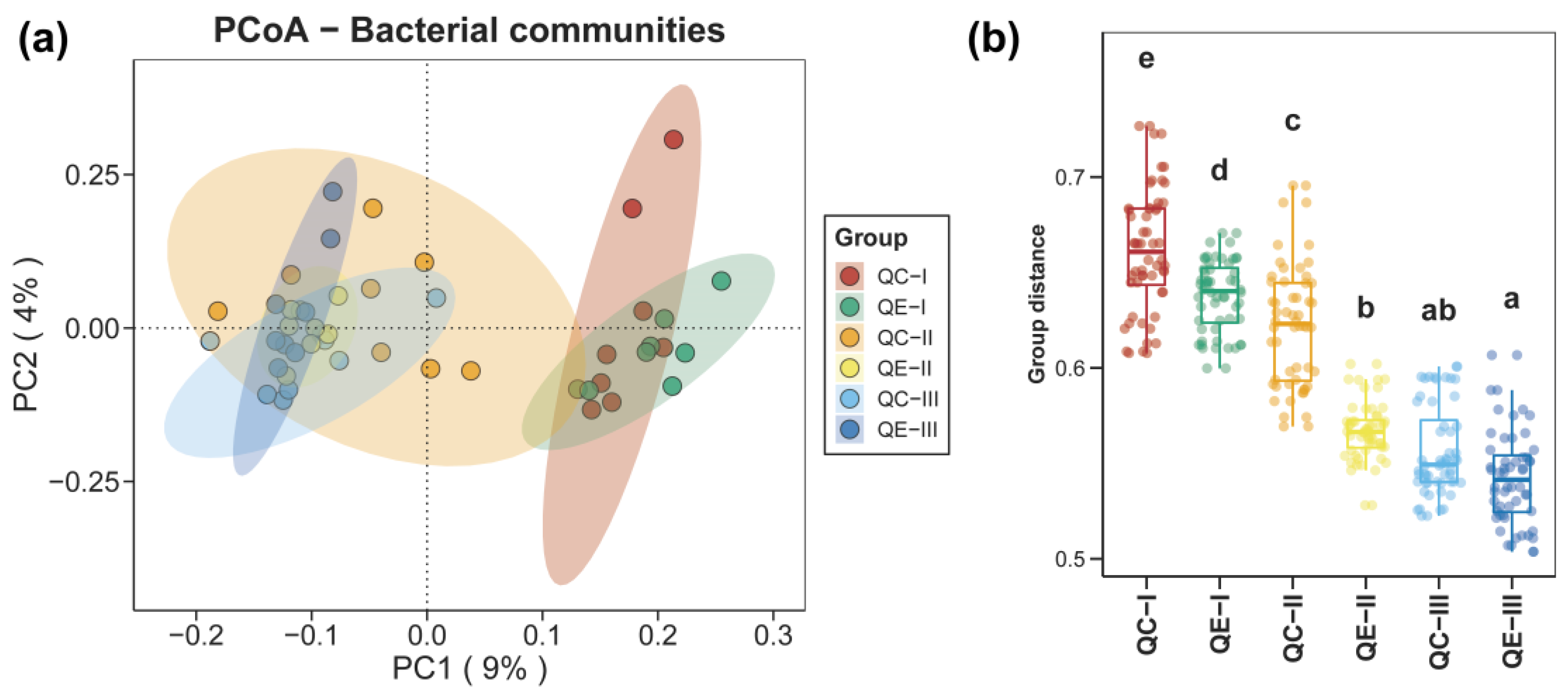
3.1. Alpha and Beta Diversities of Bacterial Communities in Paddy Soil
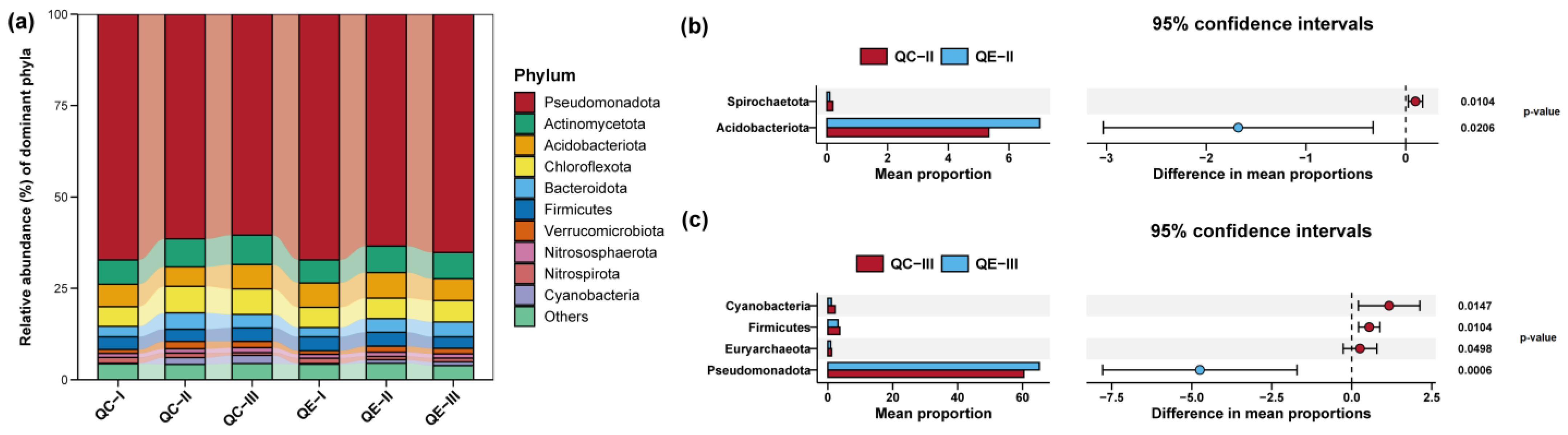
3.2. Compositions of Bacterial Communities in Paddy Soil
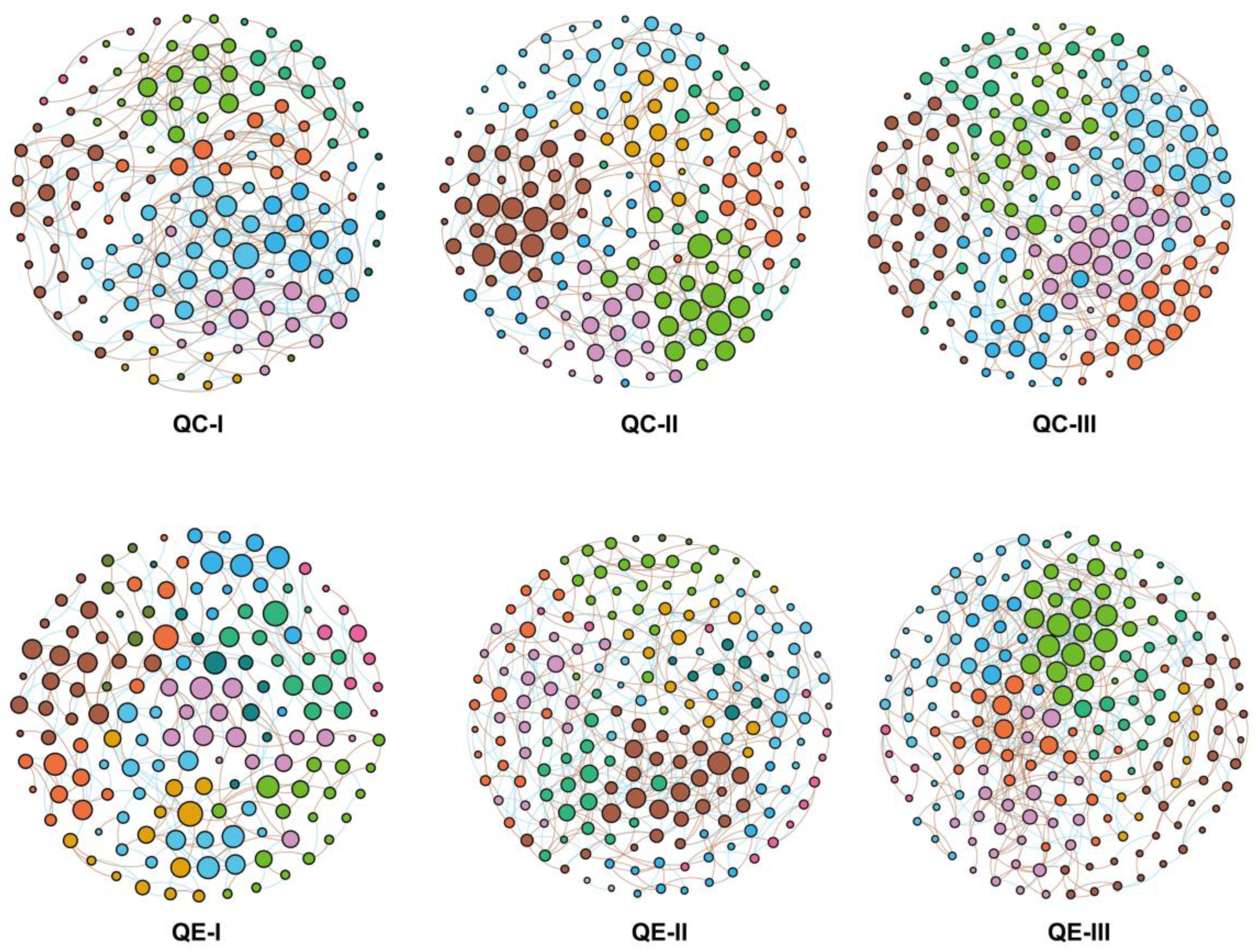
3.3. Co-Occurrence Patterns in the Soil Bacterial Communities
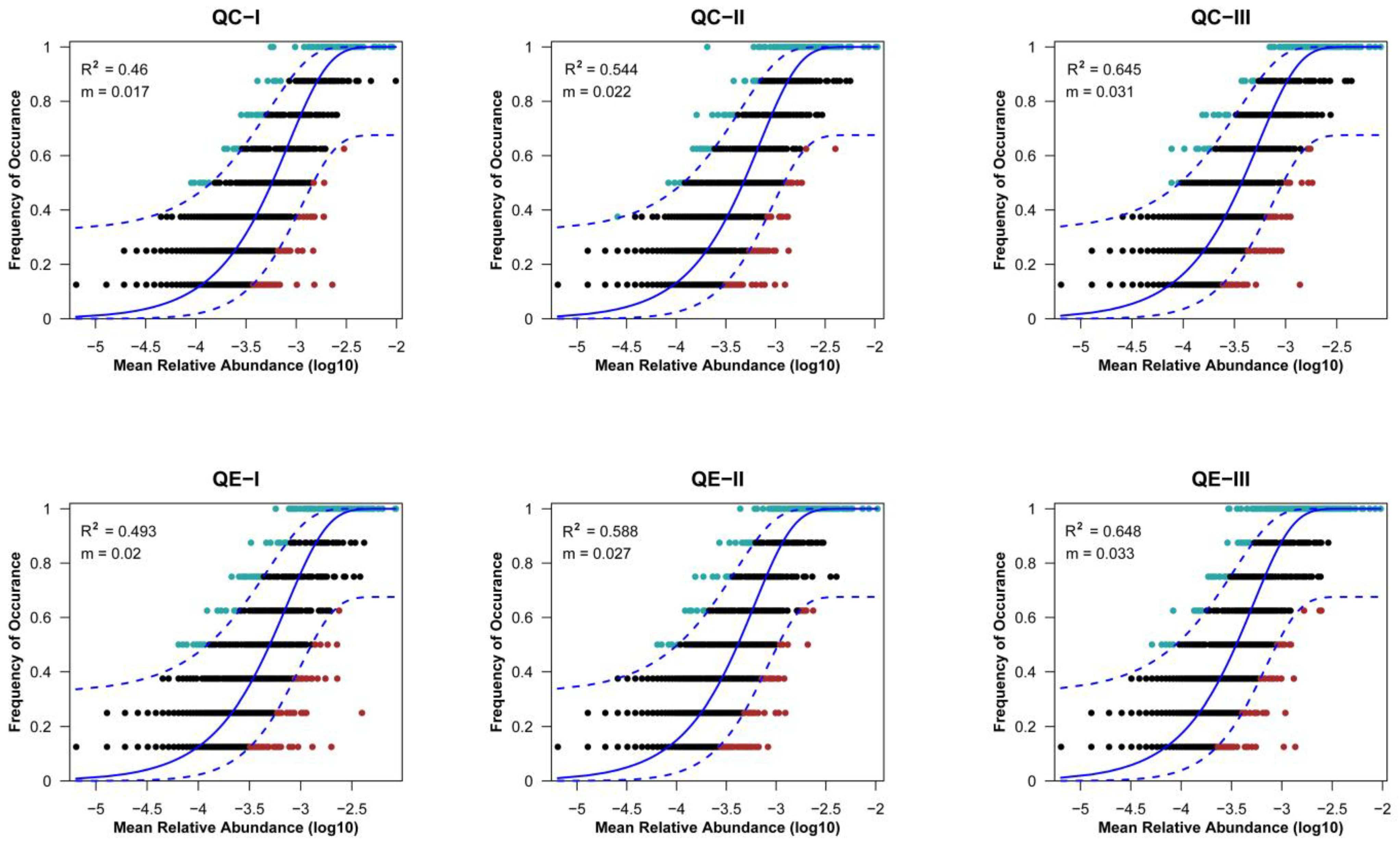
3.4. Assembly Processes in the Soil Bacterial Communities
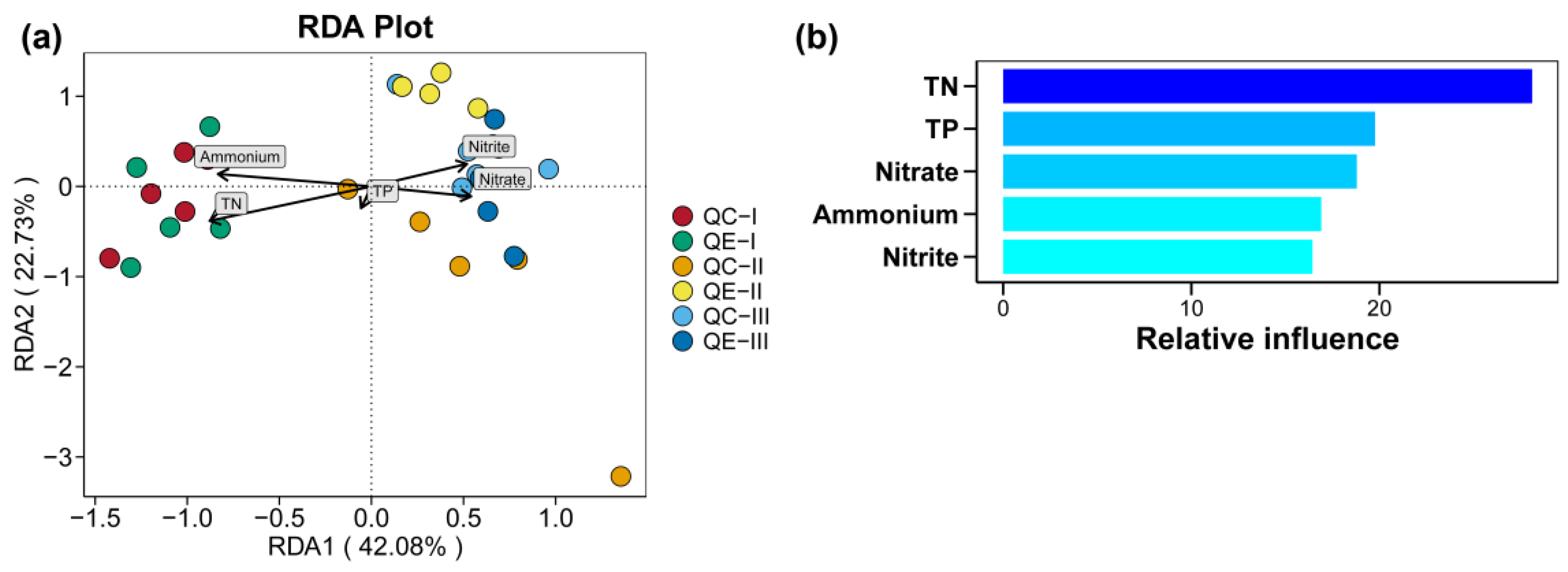
3.5. Effect of Environmental Factors on the Soil Bacterial Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Bacterial Community and Its Composition in Paddy Field Influenced by Red Claw Crayfish
4.2. Bacterial Community Assembly in Paddy Field Influenced by Red Claw Crayfish
4.3. Bacterial Community Co-Occurrence Pattern in Paddy Field Influenced by Red Claw Crayfish
4.4. Correlations of Environmental Factors with Soil Bacterial Community in Integrated Rice–Crayfish Farming System
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, N.; Hornbuckle, J.; Turchini, G.M. Blue–green water utilization in rice–fish cultivation towards sustainable food production. Ambio 2022, 51, 1933–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Ward, J.D.; Saint, C.P. Can integrated aquaculture-agriculture (IAA) produce “more crop per drop”? Food Secur. 2014, 6, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Lv, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, D.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, S. Effect of nitrogen application rate on soil fungi community structure in a rice-fish mutualistic system. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, X. Review of rice–fish-farming systems in China—One of the Globally Important Ingenious Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS). Aquaculture 2006, 260, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, M.; Li, H.; Guo, P. Microbiome Analysis Reveals Microecological Balance in the Emerging Rice–Crayfish Integrated Breeding Mode. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 669570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K. Rice fish culture in China—A review. Aquaculture 1988, 71, 173–186. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Hao, X.; Dang, Z.; Yang, L. Industrial development report on integrated rice-fish farming in China (2023). China Fish. News 2023, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NBS. Statistical Bulletin of the People’s Republic of China on National Economic and Social Development, 2022; National Bureau of Statistics: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Day, J.; Diener, C.; Otwell, A.; Tams, K.; Bebout, B.; Detweiler, A.; Lee, M.; Scott, M.; Ta, W.; Ha, M.; et al. Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) productivity influenced by microbial inocula under nitrogen-limited conditions in aquaponics. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlambang, A.; Murwantoko, M.; Istiqomah, I. Dynamic change in bacterial communities in the integrated rice–fish farming system in Sleman, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 5566–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, D. The role of microorganisms in aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture 1997, 151, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiang, J.; Pan, Y.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Gao, S.; Sun, H.; Guan, X.; Wang, B.; et al. Temporal dynamics of bacterial communities in the water and sediments of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) culture ponds. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, H.; Zhu, J.; Lin, X.; Feng, Y. Effects of elevated ground-level ozone on paddy soil bacterial community and assembly mechanisms across four years. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholaus, R.; Lukwambe, B.; Zhao, L.; Yang, W.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, Z. Bioturbation of blood clam Tegillarca granosa on benthic nutrient fluxes and microbial community in an aquaculture wastewater treatment system. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 142, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholaus, R.; Zheng, Z. The effects of bioturbation by the Venus clam Cyclina sinensis on the fluxes of nutrients across the sediment–water interface in aquaculture ponds. Aquac. Int. 2014, 22, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Hou, J.; Deng, M.; Liu, Q.; Wu, C.; Ji, Y.; He, X. Bacterial abundance and diversity in pond water supplied with different feeds. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Tang, J.; Zhang, C.; Qin, J.; Wang, Y. Bacterial composition, abundance and diversity in fish polyculture and mussel–fish integrated cultured ponds in China. Aquac. Res. 2016, 48, 3950–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Dai, Y. Bacterial communities in Chinese grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) farming ponds. Aquac. Res. 2013, 45, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C. Source-sink balance and carbon allocation below ground in plants exposed to ozone: Tansley review. New Phytol. 2003, 157, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellend, M. Conceptual Synthesis in Community Ecology. Q. Rev. Biol. 2010, 85, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, G.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Jia, R.; Li, Q.; Zhu, J. Dynamic and Assembly of Benthic Bacterial Community in an Industrial-Scale In-Pond Raceway Recirculating Culture System. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 797817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, P.; Huang, S.; Li, Z.; Gong, H.; Huang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, Z. Environmental filtering dominates bacterioplankton community assembly in a highly urbanized estuarine ecosystem. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Wilkins, M.J.; Konopka, A.E.; Nelson, W.C.; Arntzen, E.V.; Chrisler, W.B.; Chu, R.K.; Danczak, R.E.; Fansler, S.J.; et al. Groundwater-surface water mixing shifts ecological assembly processes and stimulates organic carbon turnover. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, Z. Ecological economic analysis of a rice-crab model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 13, 323–326. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Feng, J.; Zhou, X.; Wu, D.; Chen, F.; Xu, C.; Fang, F. Nutrients removal from fish pond by rice planting. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2015, 29, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, D.; Li, W. Evaluation of comprehensive benefit of rice-fish agriculture and rice monocropping—A case study of Qingtian County, Zhejiang Province. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2010, 18, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, Q.; He, T.; Luo, H.; Qian, X. Research on water quality dynamics of integrated rice-fish farming and rice growth and economic benefits. Tillage Cultiv. 2003, 5, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Si, G.; Peng, C.; Xu, X.; Xu, D.; Yuan, J.; Li, J. Effect of integrated rice-crayfish farming system on soil physico-chemical properties in waterlogged paddy soils. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2017, 25, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Fang, Y.; Han, G.; Fu, Y. Effects of rice -fish integrated ecosystem on physical and chemical properties of paddy soil. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2009, 4, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q. Regulation and mechanism of greenhouse gas emissions of circular agriculture ecosystem of planting and breeding in paddy. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2018, 26, 633–642. [Google Scholar]
- Ahyong, S.; Yeo, D. Feral populations of the Australian Red-Claw crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus von Martens) in water supply catchments of Singapore. Biol. Invasions 2007, 9, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, F.; Re, A.; Sierra, E.; Amador, A.N.D. Behavioral thermoregulation and critical limits applied to culture of red claw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus (Von Martens). Freshw. Crayfish 2004, 14, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, D.; Wu, D.-L.; Ma, C.-A.; Li, H.-X.; Youhui, H.; Wang, D.-L.; Zhao, Y.-L. Effects of white spot syndrome virus infection and role of immune polysaccharides of juvenile Cherax quadricarinatus. Aquaculture 2015, 437, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Li, B.; Yu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J. Effects of rice-crayfish integrated model on root exudates and microorganisms of rice during grain filling. J. Fish. China 2022, 46, 2122–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lv, M.; Yang, Y.; Lu, T.; Tong, T.; Liang, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Wang, R. Study on the correlation in Cherax quadricarinatus cultured in rice field between body size and intestinal microbiota. Freshw. Fish. 2022, 52, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Z.; Huang, F.; Cui, M. Integrated rice-red claw crayfish farming technology. Fish. Guide Be Rich. 2021, 24, 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, S. Effects of integrated rice-red claw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus on water environment. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2019, 47, 213–215. [Google Scholar]
- Angeler, D.; Sánchez-Carrillo, S.; Garcia, G.; Alvarez-Cobelas, M. The influence of Procambarus clarkii (Cambaridae, Decapoda) on water quality and sediment characteristics in a Spanish floodplain wetland. Hydrobiologia 2001, 464, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Yurrita, P.; Marténez, J.; Bravo-Utrera, M.; Montes, C.; Ilhéu, M.; Bernardo, J. The Status of Crayfish Populations in Spain and Portugal; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 161–192. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Yurrita, P.; Montes, C. Bioenergetics of juveniles of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2001, 130, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhéu, M.; Bernardo, J. Aspects of trophic ecology of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii Girard) in Alentejo, South of Portugal. In Proceedings of the Actas VI Congreso Español de Limnología, Granada, Spain, 9–13 September 1991; pp. 417–423. [Google Scholar]
- Lodge, D.; Hill, A.M. Factors governing species composition, population size and productivity of coolwater crayfishes. Nord. J. Freshw. Res. 1994, 69, 111–136. [Google Scholar]
- Momot, W. Redefining the Role of Crayfish in Aquatic Ecosystems. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1995, 3, 33–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.C. Benthic fauna and biogeochemical processes in marine sediments: The role of burrow structures. In Nitrogen Cycling in Coastal Marine Environments; Blackburn, T.H., Sorensen, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1988; pp. 301–338. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Li, B.; Luo, J.; Zhang, C.; He, J.; Zhu, J. Effect of Bellamya purificata on organic matter degradation in surface sediment as revealed by amino acids. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2021, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverock, B.; Smith, C.J.; Tait, K.; Osborn, A.M.; Widdicombe, S.; Gilbert, J.A. Bioturbating shrimp alter the structure and diversity of bacterial communities in coastal marine sediments. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1531–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermillodblondin, F.; Rosenberg, R.; Francoiscarcaillet, F.; Norling, K.; Mauclaire, L. Influence of bioturbation by three benthic infaunal species on microbial communities and biogeochemical processes in marine sediment. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 36, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.M.H.; Meadows, A.; Meadows, P.S. Biogeomorphological implications of microscale interactions between sediment geotechnics and marine benthos: A review. Geomorphology 2002, 47, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegrí, S.P.; Blackburn, T.H. Bioturbation effects of the amphipod Corophium volutator on microbial nitrogen transformations in marine sediments. Mar. Biol. 1994, 121, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugenski, A.T.; Murria, C.; Whiles, M.R. Tadpoles enhance microbial activity and leaf decomposition in a neotropical headwater stream. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 1904–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockdale, A.; Davison, W.; Zhang, H. Micro-scale biogeochemical heterogeneity in sediments: A review of available technology and observed evidence. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2009, 92, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tu, J.; Lin, F.; Guo, J.; Lu, D.; Guo, S. A preliminary study on the technology of integrated rice-red claw crayfish farming. Sci. Fish. Farming 2019, 3, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Soil-Determination of Total Phosphorus by Alkali Fusion–Mo-Sb Anti Spectrophotometric Method; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Norman, A.; Bremner, J. Inorganic Forms of Nitrogen; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Zang, W.; Yang, F.; Jiang, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, L. Aquaculture Water Environment Chemistry Experiment; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, J.; Brandt, K.; Abu Al-Soud, W.; Holm, P.; Hansen, L.; Sørensen, S.; Nybroe, O. Selection for Cu-Tolerant Bacterial Communities with Altered Composition, but Unaltered Richness, via Long-Term Cu Exposure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7438–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Jia, R.; Ji, P.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. Organic matter degradation and bacterial communities in surface sediment influenced by Procambarus clarkia. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 985555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2 ‘ s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberan, A.; Bates, S.T.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Using network analysis to explore co-occurrence patterns in soil microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Sansupa, C.; Kongsurakan, P.; Sereenonchai, S.; Hatano, R. Soil Microbial Diversity and Community Composition in Rice-Fish Co-Culture and Rice Monoculture Farming System. Biology 2022, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chu, C.B.; Zhou, D.P.; Wang, Q.F.; Wu, S.H.; Zheng, X.Q.; Song, K.; Lv, W.G. Soil bacterial community composition in rice-fish integrated farming systems with different planting years. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Maria Saez, J.; Davila Costa, J.S.; Leticia Colin, V.; Soledad Fuentes, M.; Antonio Cuozzo, S.; Susana Benimeli, C.; Alejandra Polti, M.; Julia Amoroso, M. Actinobacteria: Current research and perspectives for bioremediation of pesticides and heavy metals. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, A.T.; Stach, J.E.M.; Ward, A.C.; Goodfellow, M. Marine actinobacteria: Perspectives, challenges, future directions. Antonie Van. Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 87, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, A.; Garrity, G.M. Valid publication of the names of forty-two phyla of prokaryotes. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 005056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Xie, S. Bacterial communities in sediments of a drinking water reservoir. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.-Y.; Li, B.-B.; Yang, Z.-C.; Cheng, Y.-Y.; Liu, D.-F.; Yu, H.-Q. Mediation of functional gene and bacterial community profiles in the sediments of eutrophic Chaohu Lake by total nitrogen and season. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.W.; Zhou, R.J.; Zeng, S.Z.; Wei, D.D.; Deng, X.S.; Xing, C.G.; Weng, S.P.; He, J.G.; Huang, Z.J. Stochastic processes shape the bacterial community assembly in shrimp cultural pond sediments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 5013–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.R.; Jia, R.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. Apex Predators Enhance Environmental Adaptation but Reduce Community Stability of Bacterioplankton in Crustacean Aquaculture Ponds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.Y.; Xu, H.M.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, D.Y.; Yu, Z.B.; Wu, Q.L.L. Composition and assembly of bacterial communities in surface and deeper sediments from aquaculture-influenced sites in Eastern Lake Taihu, China. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 82, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Lin, Y.Q.; Zhao, D.Y.; Huang, R.; Xu, H.M.; Jiao, C.C. Seasonality overwhelms aquacultural activity in determining the composition and assembly of the bacterial community in Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. Microbial interactions: From networks to models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, Y.L.; Ye, S.D.; Liu, S.; Stirling, E.; Gilbert, J.A.; Faust, K.; Knight, R.; Jansson, J.K.; Cardona, C.; et al. Earth microbial co-occurrence network reveals interconnection pattern across microbiomes. Microbiome 2020, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Poulain, A.J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Abdelhafiz, M.A.; Meng, B.; Feng, X.B. Mercury drives microbial community assembly and ecosystem multifunctionality across a Hg contamination gradient in rice paddies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottjers, L.; Faust, K. From hairballs to hypotheses-biological insights from microbial networks. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 761–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.H.; Chen, N.; Ke, J.D.; Qi, Z.Y.; Chen, W.J.; Sun, S.Z.; Zheng, Z.M.; Xu, J.L.; Yang, W. Response of the rearing water bacterial community to the beneficial microalga Nannochloropsis oculata cocultured with Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2021, 542, 736895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.Y.; Xu, H.M.; Zhao, D.Y.; Zeng, J.; Wu, Q.L.L. Aquaculture drives distinct patterns of planktonic and sedimentary bacterial communities: Insights into co-occurrence pattern and assembly processes. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 4079–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, G.T.-W.; Liu, A.-C.; Weng, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Weng, F.C.-H.; Wang, D.; Chou, C.-Y. A network-based approach to deciphering a dynamic microbiome’s response to a subtle perturbation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, D.E.; Ward, C.S. A network-based approach to disturbance transmission through microbial interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaestecker, E.; Gaba, S.; Raeymaekers, J.A.M.; Stoks, R.; Van Kerckhoven, L.; Ebert, D.; De Meester, L. Host–parasite ‘Red Queen’ dynamics archived in pond sediment. Nature 2007, 450, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Hou, Y.; Jia, R.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. Effects of Bellamya purificata Cultivation at Different Stocking Densities on the Dynamics and Assembly of Bacterial Communities in Sediment. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Yurrita, P.; Sancho, G.; Bravo-Utrera, M.; Baltanas, A.; Montes, C. Diet of the Red Swamp Crayfish Procambarus clarkii in Natural Ecosystems of the Doñana National Park Temporary Fresh-Water Marsh (Spain). J. Crustac. Biol. 1998, 8, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, D.; Kershner, M.; Aloi, J.; Covich, A. Effects of an Omnivorous Crayfish (Orconectes rusticus) on a Freshwater Littoral Food Web. Ecology 1994, 75, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, P.V. Direct and Indirect Effects of Consumers on Benthic Algae in Isolated Pools of an Ephemeral Stream. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1990, 47, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NystrÖM, P.E.R.; Brönmark, C.; Graneli, W. Patterns in benthic food webs: A role for omnivorous crayfish? Freshw. Biol. 1996, 36, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Wong, M.H.; Xu, F.; Yang, X.; Xu, W.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, S. Characteristics of spatial and seasonal bacterial community structures in a river under anthropogenic disturbances. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, K.M.; Fierer, N.; Murphy, D.V.; Rousk, J. Linking bacterial community composition to soil salinity along environmental gradients. ISME J. 2019, 13, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Gao, S.; Sun, H.; Dong, Y.; Sun, P.; Guan, X.; Zhou, Z. Unrevealing variation of microbial communities and correlation with environmental variables in a full culture-cycle of Undaria pinnatifida. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 139, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wang, B.; Duan, P.; Tian, J.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, J.; Sun, B.; Zhou, Z. The dynamics of bacterial community in a polyculture aquaculture system of Penaeus chinensis, Rhopilema esculenta and Sinonovacula constricta. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolukirik, M.; Ince, O.; Cetecioglu, Z.; Celikkol, S.; Ince, B.K. Spatial and temporal changes in microbial diversity of the Marmara Sea Sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2384–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, F.; Bonin, P.; Stora, G. Effect of bioturbation on denitrification in a marine sediment from the West Mediterranean littoral. Hydrobiologia 1995, 304, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogaro, G.; Mermillod-Blondin, F.; Valett, H.; Carcaillet, F.; Gaudet, J.-P.; Lafont, M.; Gibert, J. Ecosystem engineering at the sediment-water interface: Bioturbation and consumer-substrate interaction. Oecologia 2009, 161, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, Y.; Jia, R.; Sun, W.; Ding, H.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. Red Claw Crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus Cultivation Influences the Dynamics and Assembly of Benthic Bacterial Communities in Paddy Fields. Environments 2023, 10, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10100178
Hou Y, Jia R, Sun W, Ding H, Li B, Zhu J. Red Claw Crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus Cultivation Influences the Dynamics and Assembly of Benthic Bacterial Communities in Paddy Fields. Environments. 2023; 10(10):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10100178
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Yiran, Rui Jia, Wei Sun, Houmeng Ding, Bing Li, and Jian Zhu. 2023. "Red Claw Crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus Cultivation Influences the Dynamics and Assembly of Benthic Bacterial Communities in Paddy Fields" Environments 10, no. 10: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10100178
APA StyleHou, Y., Jia, R., Sun, W., Ding, H., Li, B., & Zhu, J. (2023). Red Claw Crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus Cultivation Influences the Dynamics and Assembly of Benthic Bacterial Communities in Paddy Fields. Environments, 10(10), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10100178






