Abstract
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is characterized by the core domains of persistent deficits in social communication and restricted-repetitive patterns of behaviors, interests, or activities. A heterogeneous and complex set of neurodevelopmental conditions are grouped in the spectrum. Pro-inflammatory events and immune system dysfunctions are cellular and molecular events associated with ASD. Several conditions co-occur with ASD: seizures, gastro-intestinal problems, attention deficit, anxiety and depression, and sleep problems. However, language and speech issues are key components of ASD symptoms current therapies find difficult to face. Several speech-stimulating substances have been shown to be effective in increasing speech ability in ASD subjects. The need for large clinical trials to determine safety and efficacy is recommended.
1. Biological Aspects of Speech and Verbal Communication in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), with one of the prominent features being persistent deficits in social communication. These symptoms begin in early childhood, and produce clinically significant deficits in the social use of verbal and non-verbal communication [1]. The latest edition of the DSM, DSM-5, combined the previously separate subtypes of ASD listed in DSM-4. Autistic disorder, Asperger syndrome, pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS), and Childhood Disintegrative Disorder are now combined into one diagnosis of ASD with these categories indicating varying levels of severity and age of onset along the autism spectrum [1,2].
Some features of ASD, also commonly called autism, are seen in genetic and chromosomal abnormalities such as fragile X syndrome, Down Syndrome, as well as in many identified genomic insertions and deletions; however, most cases of ASD have an unknown etiology which indicates they could be due to environmental factors. Two of the prominent clinical features of ASD are inflammation and neuro-immune system dysregulation [3,4,5]. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that ASD occurs in one of every 59 children in the US aged eight years old [6], while an estimate from Xu and colleagues (2018) using data from the National Health Interview Survey puts the estimate of ASD higher when including children 3–17 years of age, where they found one child affected out of every 40 children in the US for the years 2014–2016 [7]. In a 2013 review article, we have summarized environmental factors which could contribute to ASD pathogenesis through epigenetic modifications [8]. Since the publication of that review, additional articles have continued to add to the evidence of epigenetic modifications in ASD. Some of these epigenetic modifications include DNA methylation, epigenetic proteins, gene polymorphisms associated with variation in diet, histone modifications, and microRNA dysregulation [9,10,11,12].
Some parents report regression in their children or a loss of previously acquired verbal skills with the subsequent diagnosis of ASD [13]. Parental reports of regression in children with ASD is estimated to occur in approximately 22% of cases [14]. Parental reports of regression have been validated with the use of videotape of children’s first and second birthdays [15]. Since these children did not initially present with symptoms of ASD, their verbal regression may be due to environmental factors to which a child is exposed, such as nutrition and medication use.
2. Speech-Stimulating Substances in ASD: Overview
Many substances have been proposed to improve speech in individuals with ASD. Vitamins in particular have been proposed as therapies. Vitamin B6 has been well-studied as a possible therapy after the Autism Research Institute in the US found that many parents saw improvements in their children with high Vitamin B6 doses [16]. Vitamin B12 has been much investigated showing its involvement in ASD [17]. Vitamin D has been suggested as a therapy to improve symptoms of ASD including speech [18]. Although various vitamins have shown positive results in some children, no vitamin has shown effectiveness in all children with ASD. Contrarily, a study published in 2018 by Bittker and Bell showed a weak positive association between Vitamin D drops and increased risk of ASD [19]. This study also showed increased risk for ASD from acetaminophen use and decreased use of breastfeeding as we have also seen [20,21].
Arachidonic acid (ARA), a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid, may improve the speech of children with ASD. Arachidonic acid (ARA) is considered a conditionally essential nutrient in infants which is present in breast milk but not all infant formulas [20]. Although infants can produce ARA, they do not produce as much as is required for their development and must acquire some from their diets [22]. ARA is required for production of the endocannabinoids anandamide and 2-arachidonylglycerol (2-AG). A study of piglets showed that arachidonic acid and other essential fatty acids in the diet affect the levels of anandamide and other endocannabinoids in the brain [23]. Anandamide and 2-AG are the primary signaling molecules in the endocannabinoid system (ECS) [24]. Anandamide is the primary ligand for cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) which is primarily found in the brain and is responsible for regulating neurite outgrowth in the brain as well as for synapse positioning [25]. 2-AG is the primary ligand for CB2 receptors which are primarily found on immune system cells and regulates their function [26]. A deficiency of ARA could lead to lower levels of anandamide and 2-AG, which could be the mechanism for the increased ASD risk we have shown due to a lack of sufficient amounts of breastfeeding or use of an infant formula without ARA supplementation [20].
We have recently shown that the atypical cannabinoid palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) improved speech in a report of two cases of ASD [27]. Messenger RNA (mRNA) for the production of CB2 receptors is up-regulated in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of individuals with ASD as we have shown [28]. This up-regulation of receptors could be the result of insufficient endocannabinoids in the blood. Our paper from 2008 shows an association of acetaminophen use with increased risk for ASD [21]. In this paper, reported use of acetaminophen at age 12–18 months significantly increased the odds of a child having ASD by more than eight times. Acetaminophen produces analgesia by indirectly stimulating CB1 receptors [29], which we suggested could produce dysregulation of the ECS to produce ASD [30]. Recently, it has been shown that anandamide levels are low in the blood of individuals with ASD [31], which supports our hypothesis of ECS dysregulation in ASD.
The following paragraphs will analyze the speech-stimulating substances methylcobalamin, tetrahydrobiopterin, folinic acid, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, flavonoids, and other medications with ASD in greater detail.
2.1. Methylcobalamin (Vitamin B12)
Methylcobalamin,(IUPAC:cobalt(3+);[(2~{R},3~{S},4~{R},5~{S})-5-(5,6-dimethylbenzimidazol-1-yl)-4-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-yl]1-[3[(1~{R},2~{R},3~{R},5~{Z},7~{S},10~{Z},12~{S},13~{S},15~{Z},17~{S},18~{S},19~{R})-2,13,18-tris(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-7,12,17-tris(3-amino-3-oxopropyl)-3,5,8,8,13,15,18,19-octamethyl-2,7,12,17-tetrahydro-1~{H}-corrin-24-id-3-yl]propanoylamino]propan-2-yl phosphate, mecobalamin, MeCbl, or MeB12) is the active form of cobalamin, also known as vitamin B12 [32]. It is a cofactor of the methionine synthase enzyme, which catalyzes the transfer of methyl groups [33]. Methylcobalamin is actively taken up by neurons, and it has been indicated for the treatment of nervous disorders through effective systemic or local delivery [32]. Its use in treating autism has been proposed as a complementary treatment [34]. Restoration of the impaired methylation capacity in children with ASD with the use of methylcobalamin, together with folinic acid and betaine, was demonstrated early [35]. However, vitamin B12 injected (64.5 µg/kg every three days, subcutaneously) in a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over clinical trial of 30 children with ASD showed no effect on overall outcomes [36]. Of note, a subset of treated children improved both behavioral and oxidative stress measures, indicating an active role of methyl B12 in reducing oxidative stress [36]. No speech analysis was performed in this study. A larger open-label trial with the use of 75 µg/Kg methylcobalamin, twice daily, together with folinic acid, demonstrated improvement in autistic symptoms, glutathione redox status and expressive communication. Receptive, expressive, and written language showed marked improvements [37]. These beneficial effects could be due to the re-balance in glutathione redox status and, thus, in redox metabolism [38].
2.2. Tetrahydrobiopterin (THB)
Tetrahydrobiopterin (THB) (IUPAC:(6~{R})-2-amino-6-[(1~{R},2~{S})-1,2-dihydroxypropyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1~{H}-pteridin-4-one, BH4, sapropterin) is a cofactor of the three aromatic amino acids, phenylalanine, tryptophan and tyrosine, hydroxylase enzymes [39]. These enzymes catalyze the hydroxylation of their respective substrates. Mutations in the genes encoding for these enzymes could be responsible for neurocognitive, neuropsychiatric, and developmental problems, as THB is required for the synthesis of several neurotransmitters [40]. An early study demonstrated that THB was reduced in the cerebrospinal fluid of children with ASD with respect to controls [41]. Using chromatographic techniques, the authors demonstrated that the brain of autistic subjects showed a dysregulated endogenous biosynthesis of THB. Following that research study, it was proposed that ASD could be a consequence of limited cofactor availability [42], and it was suggested that THB could be helpful in reducing autistic symptoms. Oral administration (1 mg/kg per day) of 6R-L-erythro-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin (R-THBP) in 14 autistic children was partially effective in improving autistic behavior, as seven children displayed improvements and seven children were non-responders [43]. A small group of autistic children was further treated for three months with THB [44]. The subjects reported improvements in social functioning, eye contact and interaction, as well as increased R-THB levels in cerebrospinal fluid. Interestingly and for the first time, speech improved after THB administration, as the number of words or sounds increased [44]. More recently, lower concentrations of THB were found in the spinal cords of autistic subjects [45]. The children were further treated with 3 mg/Kg per day of THB for six months alternating with placebo. After six months of treatment, they showed a significant improvement in the social interaction score [45]. In 2010, Frye et al. reviewed the clinical trials performed on the use of THB in autism [46]. Summarizing all the results, marked improvements were seen in cognitive ability, social interaction, communication, and verbal capacity. Side effects were not noted; however, a definitive, standard protocol needs to be defined to harmonize dose, time of treatment, and outcomes. Later, the same author performed an open-label clinical trial with the use of 20 mg/Kg per day of THB in 10 autistic children for 16 weeks [47]. Most notably, marked improvements in the Preschool Language Scale were seen. Nitric oxide metabolism parameters were also changed. Moreover, THB could be a critical element for the synthesis of the precursors of monoamine neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, and is vital in nitric oxide production [48]. It has been proposed that chronic environmental gestational exposure to nitrous oxide could impact ASD development [48].
A larger (46 Children with ASD) double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with the use of 20 mg/kg/day THB or placebo for 16 weeks demonstrated the effectiveness in reducing problems with social awareness, autism mannerisms, hyperactivity, and inappropriate speech [49]. A reanalysis of three clinical trials [50] has shown that THB does improve concomitant metabolic abnormalities in individuals with ASD; in particular, it has a significant effect on methylation and markers of chronic oxidative stress; however, additional clinical trials would be required to conclusively establish a beneficial effect on speech.
2.3. Folinic Acid
Folinic acid (IUPAC:2-[[4-[(2-amino-5-formyl-4-oxo-3,6,7,8-tetrahydropteridin-6-yl)methylamino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid, formyltetrahydrofolate, leucovorin) is a 5-formyl derivative of tetrahydrofolic acid which has similar effects to folic acid. Maternal folic acid and multivitamin supplementation before and during pregnancy are now well recognized as nutritional treatments for reducing ASD risk [51]. It has already been demonstrated that the use of folinic acid together with methylcobalamin as nutritional intervention is effective in reducing redox imbalances in autistic children [38]. It has been proposed that a subgroup of children with ASD, bearing the presence of folate receptor autoantibodies, would benefit of treatment with leucovorin calcium [52]. Indeed, four months of treatment has been able to improve verbal communication, receptive and expressive language. Folate receptor autoantibodies are able to block folate uptake, disrupting its pathway [53], causing cerebral folate deficiency [54]. This syndrome has been associated with autism [55]. A subgroup of children with ASD with these autoantibodies could represent as a particular ASD subset (but with high incidence, as at least 70% of autistic children show positivity for these autoantibodies [56]) of patients that could respond to high doses of folinic acid [57]. As stated in paragraph 2.1, synergistic treatment with methylcobalamin (subcutaneous injection) and folinic acid (400 μg as powder mixed in food, twice a day, orally) showed efficacy in ameliorating speech problems in children with ASD [37]. Consequently, a large double-blind placebo-controlled trial was initiated to determine if high doses of folinic acid were efficacious in improving verbal communication and language impairments [58]. Forty-eight autistic children received 2 mg/ kg per day, maximum 50 mg per day, of folinic acid for 12 weeks. Folinic acid improved verbal communication with respect to placebo; more importantly, greatest improvements in speech were seen in treated autistic children with high folate receptor autoantibodies [58]. As an explanation, folinic acid can easily cross the blood–brain barrier by using the reduced folate carrier when the folate receptors are blocked or dysfunctional. In addition, folinic acid does not require catalytic reduction by the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase and can readily enter the folate cycle to be used as a metabolite [58].
2.4. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
The term omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) indicates a group of carboxylic acids with three C-C double bounds (IUPAC: (4~{Z},7~{Z},10~{Z},13~{Z},16~{Z},19~{Z})-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic acid;(5~{Z},8~{Z},11~{Z},14~{Z},17~{Z})-icosa-5,8,11,14,17-pentaenoic acid;(9~{Z},12~{Z},15~{Z})-octadeca-9,12,15-trienoic acid). PUFAs are essential components of cellular membranes, and they are required by external intake from diet, such as from fish oil, as these biomolecules cannot be endogenously synthesized in the body.
In a typically developing population, it has been demonstrated that higher maternal fish intake during pregnancy is associated with higher language and communication skills, assessed in 15/18-month children [59]. Furthermore, lower levels of maternal seafood consumption in pregnancy has been associated with suboptimal levels of social and language development [60]. Maternal fish intake (more than twice weekly servings), compared with never consumed, has been directly associated with higher cognitive and language development at age three years [61]. However, to avoid the presence of potential neurotoxic substances, fish should be cleaned from environmental pollutants. Complementary supplementation of omega(ω)-3 in ASD is still an open research debate [62], as many trials have achieved conflicting results. In the valproic acid (VPA)-induced autism animal model, it has been demonstrated that there is a neuro-protective effect mediated by ω-3/-6 acids [63] that possesses immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory capabilities [64]. Furthermore, blood levels of ω-3 fatty acids are decreased in children with ASD [65]. Whereas ω-3 fatty acid supplementation (eight weeks) improved autistic behaviors in a randomized, crossover, placebo-controlled study [66], as well as improved hyperactivity, lethargy, and stereotypy in children with ASD [67], ω-3/-6/-9fatty acids were effective in ameliorating language abilities in preterm children with ASD [68]. In this randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial, the authors demonstrated that three months of oral treatment with ω-3/-6/-9 fatty acids were able to increase the number of words produced, the combined gesture and word use, and the broader social communicative gesture in 18–38 months, preterm born, ASD toddlers. They concluded that supplementation with PUFAs positively affected overall social communication [68]. Interestingly, possible explanation of these positive effects of PUFAs arose from an animal study demonstrating that dietary ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation was able to restore alterations in the expression of several genes [69]. Most recently, a randomized, large (n = 73), placebo-controlled trial demonstrated the efficacy of combined treatment with vitamin D and ω-3 PUFAs in increasing social communicative functions in children with ASD [70]. In general, ω-3 PUFAs demonstrated beneficial effects on metabolic function and in reducing inflammation [71].
2.5. Flavonoids (Luteolin) and Corticosteroids (Prednisolone and Prednisone)
The flavonoids-derived compound mixture (luteolin, quercetin and rutin) Neuroprotek® has a high gut absorption because of its olive kernel oil formulation, and many studies have assessed its properties. A trial was performed with ASD individuals (37 pediatric subjects) who were enrolled in a four-month regime with an administration of at least 2 capsules/20 kg weight, equivalent to at least 400 mg total flavonoid (each capsule contains 200mg of flavonoids). An important outcome was observed by the authors, which was the resumption of speech in 10% of the children [72]. A chemical feature particularly of luteolin is the capacity to cross the blood-brain barrier [73] and to exert its biological effects in the central nervous system. The resumption of speech may be due to luteolin’s antioxidant (reducing brain oxidative stress), anti-inflammatory (reducing gut and brain inflammation), anti-allergy (inhibiting mast cells and microglia) and neuroprotective properties. It also stabilizes blood vessels and promotes neuronal recovery. This compound mixture of flavonoids is safe [74], well-tolerated and may ameliorate ASD symptoms with an improvement in verbal language capabilities [72].
Corticosteroids exert their effect by affecting gene transcription and translation and modulating enzyme activity. The clinical roles of corticosteroids are related to their anti-inflammatory effects and immune-modulating properties due to their inhibitory effects on phospholipase A2, an enzyme required for the production of inflammatory compounds [75].
A few authors have studied corticosteroid therapy in the treatment of neurodevelopmental diseases with language improvements noted after treatment. A two-case clinical trial of children diagnosed with Childhood Disintegrative Disorder (CDD) was performed [76]. The first case was treated with prednisolone (2 mg/kg/day) and started speaking again by day 11, and afterwards showed normal academic school progress at a 30-month follow-up. The second case was also treated with prednisolone (2 mg/kg for two weeks, tapered over one week), and over the next month she started developing a little speech; improvement continued at 48-month follow-up [76].
The corticosteroid specific pathway that could explain how these molecules improve verbal language remains unclear, although most neurodevelopmental disorders, including ASD, have physiological, metabolic, and neuropsychologically similar disturbances among them [77]. In an early clinical case, the authors studied a child with language and behavior regression at 22 months diagnosed with pervasive developmental disorder. An empirical course of corticosteroid treatment was initiated after initial evaluation at six years of age when a 28-week trial of corticosteroid (starting with 2mg/kg of prednisone) was begun. Over several weeks of treatment, there was a significant increase in spontaneous speech and greater improvement in verbal communication skills. Language regression may be due to a neuropathogenic alteration and corticosteroid response may be optimal in early onset of the disorder, but without amelioration of nonverbal cognitive abilities. However, corticosteroid therapy could be a possible therapy for speech resumption in neurodevelopmental disorders such as ASD.
2.6. Other Medications (Alzheimer’s Medications and Beta-Adrenergic Antagonism (Propranolol))
ASD treatments are highly individualized, and include biomedical drug treatments, special education, and targeted speech therapy. People with ASD have bloodstream hyperserotonemia in contrast to decreased levels of serotonin in the central nervous system [78]. Some study cases have reported the usage of Alzheimer’s medications to treat ASD symptoms especially those related to language and speech. Hertzman (2003) reported three clinical cases of autistic adults treated with galantamine (4 mg daily at bedtime). All of them, within the first month started active speech, production of sounds, responding appropriately, and had improved cognition [79]. It had a positive effect on verbalization, socially appropriate behavior or both, in two cases; however, many side effects were reported in the second case. Speech improvement was not observed in the third case although some other beneficial effects were seen, such as diminished aggressive behavior [79].
Galantamine is a cholinomimetic compound; its dual effects combine competitive inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and allosteric modulation of nicotinic receptors. This produces increased acetylcholine in the neural synapse, while also increasing allosterically sodium and calcium influx. This leads to the release of glutamate, dopamine, and serotonin into the synaptic cleft [80]. Despite the positive effects observed in the treatment of autism, biochemical pathways need further research in order to decrease chances for harm.
In another report, novel Alzheimer drugs have been assessed in ASD treatment, including galantamine, rivastigmine, tacrine, and memantine; these studies reported improvements in receptive language, social interaction expressive language and communication [81], positioning these medications as promising drugs to future treatment of ASD.
Noradrenergic receptors play a role in a broad range of brain functions such as arousal, stress response, memory consolidation, sleep/wakefulness, learning, signal detection, and more [82,83,84]. Noradrenergic activity has been suggested to be increased in the ASD population [85,86]. Autistic features include problems in utilization of contextual information and processing semantic information [87,88]. Mehler and Purpura (2009) proposed a developmental dysregulation of the noradrenergic system in ASD individuals, relating it to improved behaviors and enhanced communication seen sometimes during fever in these individuals [89]. Indeed, they postulated that ASD core behaviors are the result of the developmental dysregulation of the noradrenergic system and neural network deployment.
Propranolol is a ß1,2-adrenoreceptor antagonist clinically used to target peripheral sites of the noradrenergic system and can be deployed to block ß-adrenoreceptors in the central nervous system, since as a lipophilic compound it readily crosses the blood–brain barrier [90]. It appears to affect flexibility of access to lexical, semantic and associative networks on verbal problem-solving tasks in neurotypical individuals [87]. Propranolol has been tested within the ASD population in clinical assays, showing cognitive benefits on verbal problem solving without significant effects on anxiety levels [91,92]. In an open trial with eight autistic adults, subjects received propranolol for a period of 11–19 months [93]; four of them improved their speech and another patient learned to point. Authors believe that these effects are a result of a decrease in the autistic individual’s state of hyperarousal. Recently, a single-dose trial reported an improvement in performance on conversational reciprocity without modifications of anxiety levels [94]. Even though there are few studies on propranolol as a supplement for ASD and speech, and their sample sizes are very small, the existing evidence suggests that propranolol could be a pharmacological agent to diminish these processing network problems and have cognitive benefits.
3. Future Perspectives of a Protocol to Stimulate Verbal Communication in ASD
We have correlated acetaminophen use at the time of childhood vaccination with the prevalence of ASD [21] and have proposed that the endocannabinoid system of children with ASD could have been dysregulated from acetaminophen use [95]. We have shown that children with ASD have more mRNA for type 2 cannabinoid receptors in their PBMCs compared to the typically-developing population [28]. In a further study, we showed that acetaminophen use for fever is associated with ASD and hypothesized that children with ASD would have lower endocannabinoid tone after frequent over-activation of the endocannabinoid system from acetaminophen use [30]. Recent studies have shown that this is correct: children with ASD have lower levels of three key cannabinoids in their blood: anandamide (N-arachidonoylethanolamine or AEA), N-palmitoylethanolamine (PEA), and N-oleoylethanolamine (OEA) [96]. PEA and OEA can be orally administered to increase blood levels of these endocannabinoids; however, anandamide is rapidly metabolized in the body and can be increased only indirectly. Administration of CBD of up to 600 mg/day in adults has been shown to increase blood levels of anandamide, perhaps by competitive inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), the enzyme responsible for anandamide degradation [97].
We have previously shown the beneficial effects PEA administration in two subjects [26]. Administration of CBD and THC to individuals with ASD has been shown to be safe and efficacious as well as to improve ASD symptoms in a recent parental survey [98]. We propose a clinical trial to study the effects of orally administered CBD, PEA, and OEA to raise the blood levels of anandamide, PEA, and OEA to normal levels in individuals with ASD. We believe our study would have the most desirable effects on speech by including OEA and PEA in addition to CBD in the treatment regimen. Further, we expect that normalizing the blood levels of OEA, PEA, and anandamide by this treatment will have beneficial effects on behavior in individuals with ASD.
4. Conclusions
This review considers all the substances that have been proposed to improve core ASD features, specifically those related with the speech (Figure 1). Before claiming enthusiastic outcomes, it is noteworthy to consider the need of large clinical trials to determine the speech-stimulating substances efficacy and safety. However, remarkable results are based on case reports, small size samples and often open-label studies. These studies show that the efficacy of speech-stimulating substances in ASD appears to be encouraging. As of today, scientist and clinicians have enough knowledge about vitamin B6, arachidonic acid, methylcobalamin, tetrahydrobiopterin, folinic acid, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, luteolin, prednisolone, prednisone, propranolol and Alzheimer drugs (galantamine, rivastigmine, tacrine, memantine).
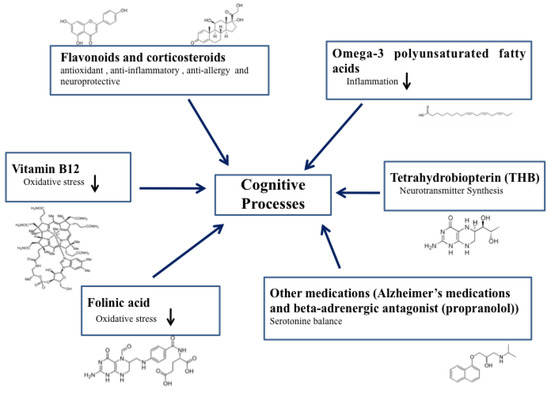
Figure 1.
Key elements of cognitive process regulation through substances discussed in the manuscript and their chemical structures.
The use of these substances is also encouraged by their low rate of side effects. In addition, all these vitamins, lipids, steroids, beta blockers, Alzheimer drugs and other metabolites have an oral route of administration with safe dosage ranges. Knowing the pharmacological mechanisms of action of these substances, we hypothesize that immunological alterations are involved in the lack of speech pathogenesis. Hence, through ameliorating the dysregulated inflammatory responses, a better treatment for ASD core features could be addressed. Therefore, translational medicine studies should be performed using these substances in order to establish a safe new protocol to treat ASD-mediated lack of speech ability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S.-H. and D.S.; methodology, N.A.; software, A.L.B.; validation, N.S.-H., S.S. and D.S.; resources, N.A.; data curation, A.L.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.C., K.E.U., N.S.-H., S.S., D.S.; writing—review and editing, D.S. and S.S.; visualization, A.L.B.; supervision, D.S. and S.S.; project administration, N.S.-H.; funding acquisition, D.S.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
To Valentina Patterson for motivating us to make revisions related to the translational medicine of autism.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed.; (DSM-IV); American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; (DSM-V); American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Onore, C.; Careaga, M.; Ashwood, P. The role of immune dysfunction in the pathophysiology of autism. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Li, X.; Zhong, Y. Inflammatory cytokines: Potential biomarkers of immunologic dysfunction in autism spectrum disorders. Med. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 531518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siniscalco, D.; Schultz, S.; Brigida, A.L.; Antonucci, N. Inflammation and Neuro-Immune Dysregulations in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2018, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2010, Surveillance Summaries. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2010, 63, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zablotsky, B.; Black, L.I.; Maenner, M.J.; Schieve, L.A.; Blumberg, S.J. Estimated Prevalence of Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities Following Questionnaire Changes in the 2014 National Health Interview Survey. Natl. Health Stat. Rep. Number 2015, 87, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Siniscalco, D.; Cirillo, A.; Bradstreet, J.J.; Antonucci, N. Epigenetic findings in autism: New perspectives for therapy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4261–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladd-Acosta, C.; Hansen, K.D.; Briem, E.; Fallin, M.D.; Kaufmann, W.E.; Feinberg, A.P. Common DNA methylation alterations in multiple brain regions in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.; Shen, Y.; Wu, J. Association between MTHFR gene polymorphisms and the risk of autism spectrum disorders: A meta-analysis. Autism Res. 2013, 6, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Poschmann, J.; Cruz-Herrera Del Rosario, R.; Parikshak, N.N.; Hajan, H.S.; Kumar, V.; Ramasamy, R.; Belgard, T.G.; Elanggovan, B.; Wong, C.C.Y.; et al. Histone Acetylome-wide Association Study of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Cell 2016, 167, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.E.; Parikshak, N.N.; Belgard, T.G.; Geschwind, D.H. Genome-wide, integrative analysis implicates microRNA dysregulation in autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.; Shulman, C.; DiLavore, P. Regression and word loss in autistic spectrum disorders. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2004, 45, 936–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siperstein, R.; Volkmar, F. Brief report: Parental reporting of regression in children with pervasive developmental disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2004, 34, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, E.; Dawson, G. Validation of the phenomenon of autistic regression using home videotapes. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005, 62, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent Ratings of Behavioral Effects of Biomedical Interventions, Publication 34, Autism Research Institute. Available online: https://www.autism.com/pdf/providers/ParentRatings 2009.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2018).
- Belardo, A.; Gevi, F.; Zolla, L. The concomitant lower concentrations of vitamins B6, B9 and B12 may cause methylation deficiency in autistic children. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 70, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannell, J.J. Autism and vitamin D. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 70, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittker, S.S.; Bell, K.R. Acetaminophen, antibiotics, ear infection, breastfeeding, vitamin D drops, and autism: An epidemiological study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 1399–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, S.T.; Klonoff-Cohen, H.S.; Wingard, D.L.; Akshoomoff, N.A.; Macera, C.A.; Ji, M.; Bacher, C. Breastfeeding, infant formula supplementation, and Autistic Disorder: The results of a parent survey. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2006, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schultz, S.T.; Klonoff-Cohen, H.S.; Wingard, D.L.; Akshoomoff, N.A.; Macera, C.A.; Ji, M. Acetaminophen (paracetamol) use, measles-mumps-rubella vaccination, and autistic disorder: The results of a parent survey. Autism 2008, 12, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO (Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations)/WHO (World Health Organization). Joint Expert Consultation Fats and Oils in Human Nutrition; FAO Food and Nutrition Paper No 57; Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1994; pp. 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, A.; Crozier, G.; Bisogno, T.; Cavaliere, P.; Innis, S.; Di Marzo, V. Anandamide and diet: Inclusion of dietary arachidonate and docosahexaenoate leads to increased brain levels of the corresponding N-acylethanolamines in piglets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6402–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertwee, R.G. Endocannabinoids and their pharmacological actions. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2015, 231, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keimpema, E.; Barabas, K.; Morozov, Y.M.; Tortoriello, G.; Torii, M.; Cameron, G.; Yanagawa, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Mackie, K.; Harkany, T. Differential subcellular recruitment of monoacylglycerol lipase generates spatial specificity of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol signaling during axonal pathfinding. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 13992–14007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, E.J.; Patel, S.; Hillard, C.J. Endocannabinoids in neuroimmunology and stress. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2005, 4, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, N.; Cirillo, A.; Siniscalco, D. Beneficial Effects of Palmitoylethanolamide on Expressive Language, Cognition, and Behaviors in Autism: A Report of Two Cases. Case Rep. Psychiatry 2015, 2015, 325061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniscalco, D.; Sapone, A.; Giordano, C.; Cirillo, A.; de Magistris, L.; Rossi, F.; Fasano, A.; Bradstreet, J.J.; Maione, S.; Antonucci, N. Cannabinoid receptor type 2, but not type 1, is up-regulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of children affected by autistic disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2013, 43, 2686–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högestätt, E.D.; Jönsson, B.A.; Ermund, A.; Andersson, D.A.; Björk, H.; Alexander, J.P.; Cravatt, B.F.; Basbaum, A.I.; Zygmunt, P.M. Conversion of acetaminophen to the bioactive N-acylphenolamine AM404 via fatty acid amide hydrolase-dependent arachidonic acid conjugation in the nervous system. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31405–31412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, S.T.; Gould, G.G. Acetaminophen Use for Fever in Children Associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Open Access. 2016, 6, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhson, D.S.; Krasinska, K.M.; Dallaire, J.A.; Libove, R.A.; Phillips, J.M.; Chien, A.S.; Garner, J.P.; Hardan, A.Y.; Parker, K.J. Plasma anandamide concentrations are lower in children with autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Autism 2018, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Han, W.; Hu, S.; Xu, H. Methylcobalamin: A potential vitamin of pain killer. Neural Plast. 2013, 2013, 424651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, K.; Puffer, B.; Kräutler, B. Vitamin B12-derivatives-enzyme cofactors and ligands of proteins and nucleic acids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4346–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendren, R.L. Autism: Biomedical complementary treatment approaches. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 22, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.J.; Cutler, P.; Melnyk, S.; Jernigan, S.; Janak, L.; Gaylor, D.W.; Neubrander, J.A. Metabolic biomarkers of increased oxidative stress and impaired methylation capacity in children with autism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoglio, K.; Jill James, S.; Deprey, L.; Brule, N.; Hendren, R.L. Pilot study of the effect of methyl B12 treatment on behavioral and biomarker measures in children with autism. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2010, 16, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.E.; Melnyk, S.; Fuchs, G.; Reid, T.; Jernigan, S.; Pavliv, O.; Hubanks, A.; Gaylor, D.W.; Walters, L.; James, S.J. Effectiveness of methylcobalamin and folinic Acid treatment on adaptive behavior in children with autistic disorder is related to glutathione redox status. Autism Res. Treat. 2013, 2013, 609705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.J.; Melnyk, S.; Fuchs, G.; Reid, T.; Jernigan, S.; Pavliv, O.; Hubanks, A.; Gaylor, D.W. Efficacy of methylcobalamin and folinic acid treatment on glutathione redox status in children with autism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hole, M.; Jorge-Finnigan, A.; Underhaug, J.; Teigen, K.; Martinez, A. Pharmacological Chaperones that Protect Tetrahydrobiopterin Dependent Aromatic Amino Acid Hydroxylases Through Different Mechanisms. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapatos, G. The neurobiology of tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthesis: A model for regulation of GTP cyclohydrolase I gene transcription within nigrostriatal dopamine neurons. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, Y.; Fernell, E.; Watanabe, Y.; Kanai, T.; Långström, B. Decrease in 6R-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin content in cerebrospinal fluid of autistic patients. Neurosci. Lett. 1994, 181, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thöny, B.; Auerbach, G.; Blau, N. Tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthesis, regeneration and functions. Biochem. J. 2000, 347 Pt 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, H.; Matsuishi, T.; Yamada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ohtaki, E.; Kato, H. Cerebrospinal fluid biopterin and biogenic amine metabolites during oral R-THBP therapy for infantile autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1995, 25, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernell, E.; Watanabe, Y.; Adolfsson, I.; Tani, Y.; Bergström, M.; Hartvig, P.; Lilja, A.; von Knorring, A.L.; Gillberg, C.; Långström, B. Possible effects of tetrahydrobiopterin treatment in six children with autism—Clinical and positron emission tomography data: A pilot study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1997, 39, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danfors, T.; von Knorring, A.L.; Hartvig, P.; Langstrom, B.; Moulder, R.; Stromberg, B.; Torstenson, R.; Wester, U.; Watanabe, Y.; Eeg-Olofsson, O. Tetrahydrobiopterin in the treatment of children with autistic disorder: A double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 25, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.E.; Huffman, L.C.; Elliott, G.R. Tetrahydrobiopterin as a novel therapeutic intervention for autism. Neurotherapeutics 2010, 7, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.E.; DeLatorre, R.; Taylor, H.B.; Slattery, J.; Melnyk, S.; Chowdhury, N.; James, S.J. Metabolic effects of sapropterin treatment in autism spectrum disorder: A preliminary study. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluegge, K. A reply to ‘Metabolic effects of sapropterin treatment in autism spectrum disorder: A preliminary study’. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaiman, C.; Huffman, L.; Masaki, L.; Elliott, G.R. Tetrahydrobiopterin as a treatment for autism spectrum disorders: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 23, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhey, L.M.; Tippett, M.; Rose, S.; Bennuri, S.C.; Slattery, J.C.; Melnyk, S.; James, S.J.; Frye, R.E. Comparison of Treatment for Metabolic Disorders Associated with Autism: Reanalysis of Three Clinical Trials. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.Z.; Kodesh, A.; Viktorin, A.; Smith, L.; Uher, R.; Reichenberg, A.; Sandin, S. Association of Maternal Use of Folic Acid and Multivitamin Supplements in the Periods Before and During Pregnancy with the Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Offspring. JAMA Psychiatry 2018, 75, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.E.; Sequeira, J.M.; Quadros, E.V.; James, S.J.; Rossignol, D.A. Cerebral folate receptor autoantibodies in autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, J.M.; Ramaekers, V.T.; Quadros, E.V. The diagnostic utility of folate receptor autoantibodies in blood. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2013, 51, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaekers, V.; Sequeira, J.M.; Quadros, E.V. Clinical recognition and aspects of the cerebral folate deficiency syndromes. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2013, 51, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaekers, V.T.; Sequeira, J.M.; Quadros, E.V. The basis for folinic acid treatment in neuro-psychiatric disorders. Biochimie 2016, 126, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Sequeira, J.M.; Quadros, E.V. Prevention of behavioral deficits in rats exposed to folate receptor antibodies: Implication in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.E.; Slattery, J.C.; Quadros, E.V. Folate metabolism abnormalities in autism: Potential biomarkers. Biomark. Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.E.; Slattery, J.; Delhey, L.; Furgerson, B.; Strickland, T.; Tippett, M.; Sailey, A.; Wynne, R.; Rose, S.; Melnyk, S.; et al. Folinic acid improves verbal communication in children with autism and language impairment: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, J.L.; Longnecker, M.P.; Rowland, A.S.; Golding, J.; ALSPAC Study Team. University of Bristol Institute of Child Health. Fish intake during pregnancy and early cognitive development of offspring. Epidemiology 2004, 15, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbeln, J.R.; Davis, J.M.; Steer, C.; Emmett, P.; Rogers, I.; Williams, C.; Golding, J. Maternal seafood consumption in pregnancy and neurodevelopmental outcomes in childhood (ALSPAC study): An observational cohort study. Lancet 2007, 369, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, E.; Radesky, J.S.; Wright, R.O.; Bellinger, D.C.; Amarasiriwardena, C.J.; Kleinman, K.P.; Hu, H.; Gillman, M.W. Maternal fish intake during pregnancy, blood mercury levels, and child cognition at age 3 years in a US cohort. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 167, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posar, A.; Visconti, P. Omega-3 supplementation in autism spectrum disorders: A still open question? J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2016, 11, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Tiwari, V.; Singh, M.; Yadav, R.K.; Roy, S.; Devi, U.; Gautam, S.; Rawat, J.K.; Ansari, M.N.; Saeedan, A.S.; et al. Comparative efficacy of alpha-linolenic acid and gamma-linolenic acid to attenuate valproic acid-induced autism-like features. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 73, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madore, C.; Leyrolle, Q.; Lacabanne, C.; Benmamar-Badel, A.; Joffre, C.; Nadjar, A.; Layé, S. Neuroinflammation in Autism: Plausible Role of Maternal Inflammation, Dietary Omega 3, and Microbiota. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 3597209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazahery, H.; Stonehouse, W.; Delshad, M.; Kruger, M.C.; Conlon, C.A.; Beck, K.L.; von Hurst, P.R. Relationship between Long Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Autism Spectrum Disorder: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control and Randomised Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2017, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parellada, M.; Llorente, C.; Calvo, R.; Gutierrez, S.; Lázaro, L.; Graell, M.; Guisasola, M.; Dorado, M.L.; Boada, L.; Romo, J.; et al. Randomized trial of omega-3 for autism spectrum disorders: Effect on cell membrane composition and behavior. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 27, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.S.; Tseng, P.T.; Chen, Y.W.; Stubbs, B.; Yang, W.C.; Chen, T.Y.; Wu, C.K.; Lin, P.Y. Supplementation of omega 3 fatty acids may improve hyperactivity, lethargy, and stereotypy in children with autism spectrum disorders: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 2531–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, K.W.; Boone, K.M.; Gracious, B.; Klebanoff, M.A.; Rogers, L.K.; Rausch, J.; Bartlett, C.; Coury, D.L.; Keim, S.A. Effect of Omega-3 and -6 Supplementation on Language in Preterm Toddlers Exhibiting Autism Spectrum Disorder Symptoms. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 3358–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basil, P.; Li, Q.; Gui, H.; Hui, T.C.K.; Ling, V.H.M.; Wong, C.C.Y.; Mill, J.; McAlonan, G.M.; Sham, P.C. Prenatal immune activation alters the adult neural epigenome but can be partly stabilised by a n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid diet. Transl. Psychiatry. 2018, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazahery, H.; Conlon, C.A.; Beck, K.L.; Mugridge, O.; Kruger, M.C.; Stonehouse, W.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Meyer, B.J.; Tsang, B.; Jones, B.; et al. A Randomised-Controlled Trial of Vitamin D and Omega-3 Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in the Treatment of Core Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, D.; Cook, C.; Santanam, N. Omega 3 rich diet modulates energy metabolism via GPR120-Nrf2 crosstalk in a novel antioxidant mouse model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 466–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Asadi, S.; Panagiotidou, S. A case series of a luteolin formulation (NeuroProtek®) in children with autism spectrum disorders. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2012, 25, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bai, L.; Li, X.; Xiong, J.; Xu, P.; Guo, C.; Xue, M. Transport of active flavonoids, based on cytotoxicity and lipophilicity: An evaluation using the blood-brain barrier cell and Caco-2 cell models. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, M.; Nielewska-Nikiel, B.; Borzelleca, J.F.; Flamm, G.W.; Williams, G.M.; Lines, T.C. A critical review of the data related to the safety of quercetin and lack of evidence of in vivo toxicity, including lack of genotoxic/carcinogenic properties. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2179–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericson-Neilsen, W.; Kaye, A.D. Steroids: Pharmacology, complications, and practice delivery issues. Ochsner J. 2014, 14, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mordekar, S.R.; Prendergast, M.; Chattopadhyay, A.K.; Baxter, P.S. Corticosteroid treatment of behaviour, language and motor regression in childhood disintegrative disorder. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2009, 13, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanatos, G.A.; Grover, W.; Geller, E. Case study: Corticosteroid treatment of language regression in pervasive developmental disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1995, 34, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugani, D.C. Role of altered brain serotonin mechanisms in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2002, 7 (Suppl. 2), S16–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertzman, M. Galantamine in the Treatment of Adult Autism: A Report of Three Clinical Cases. Int. J. Psychiatry Med. 2003, 33, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prvulovic, D.; Hampel, H.; Pantel, J. Galantamine for Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2010, 6, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossignol, D.A.; Frye, R.E. The use of medications approved for Alzheimer’s disease in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzori, M.; Cuevas-Olguin, R.; Esquivel-Rendon, E.; Garcia-Oscos, F.; Salgado-Delgado, R.C.; Saderi, N.; Miranda-Morales, M.; Treviño, M.; Pineda, J.C.; Salgado, H. Locus Ceruleus Norepinephrine Release: A Central Regulator of CNS Spatio-Temporal Activation? Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2016, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harley, C.W. A role for norepinephrine in arousal, emotion and learning?: Limbic modulation by norepinephrine and the Kety hypothesis. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1987, 11, 419–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, C.W.; Waterhouse, B.D. The locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system: Modulation of behavioral state and state-dependent cognitive processes. Brain Res. Rev. 2003, 42, 33–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, C.R.; Ziegler, M.G.; Murphy, D.L. Increased norepinephrine levels and decreased dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity in primary autism. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1977, 34, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Launay, J.M.; Bursztejn, C.; Ferrari, P.; Dreux, C.; Braconnier, A.; Zarifian, E.; Lancrenon, S.; Fermanian, J. Catecholamines metabolism in infantile autism: A controlled study of 22 autistic children. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1987, 17, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beversdorf, D.Q.; Hughes, J.D.; Steinberg, B.A.; Lewis, L.D.; Heilman, K.M. Noradrenergic modulation of cognitive flexibility in problem solving. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 2763–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minshew, N.J.; Goldstein, G. The pattern of intact and impaired memory functions in autism. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2001, 42, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehler, M.F.; Purpura, D.P. Autism, fever, epigenetics and the locus coeruleus. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 59, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenen, S.A.; van Wijk, A.J.; van der Heijden, G.J.; van Westrhenen, R.; de Lange, J.; Jongh, A. Propranolol for the treatment of anxiety disorders: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 30, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beversdorf, D.Q.; Carpenter, A.L.; Miller, R.F.; Cios, J.S.; Hillier, A. Effect of propranolol on verbal problem solving in autism spectrum disorder. Neurocase 2008, 14, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzow, R.M.; Ferguson, J.B.; Ragsdale, A.S.; Lewis, M.L.; Beversdorf, D.Q. Effects of acute beta-adrenergic antagonism on verbal problem solving in autism spectrum disorder and exploration of treatment response markers. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2017, 39, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratey, J.J.; Bemporad, J.; Sorgi, P.; Bick, P.; Polakoff, S.; O’Driscoll, G.; Mikkelsen, E. Brief Report: Open Trial Effects of Beta Blockers on Speech and Social Behaviors in 8 Autistic Adults. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1987, 17, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzow, R.M.; Ferguson, B.J.; Stichter, J.P.; Porges, E.C.; Ragsdale, A.S.; Lewis, M.L.; Beversdorf, D.Q. Effects of propranolol on conversational reciprocity in autism spectrum disorder: A pilot, double-blind, single-dose. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2016, 233, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, S.T. Can autism be triggered by acetaminophen activation of the endocannabinoid system? Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2010, 70, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Aran, A.; Eylon, M.; Harel, M.; Polianski, L.; Nemirovski, A.; Tepper, A.; Schnapp, A.; Cassuto, H.; Wattad, N.; Tam, J. Lower circulating endocannabinoid levels in children with autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Autism 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leweke, F.M.; Piomelli, D.; Pahlisch, F.; Muhl, D.; Gerth, C.W.; Hoyer, C.; Klosterkötter, J.; Hellmich, M.; Koethe, D. Cannabidiol enhances anandamide signaling and alleviates psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Lev Schleider, L.; Mechoulam, R.; Saban, N.; Meiri, G.; Novack, V. Real life Experience of Medical Cannabis Treatment in Autism: Analysis of Safety and Efficacy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).