A Study of Role Stressors and Job Satisfaction: The Case of MNCs in Collectivist Context
Abstract
1. Background
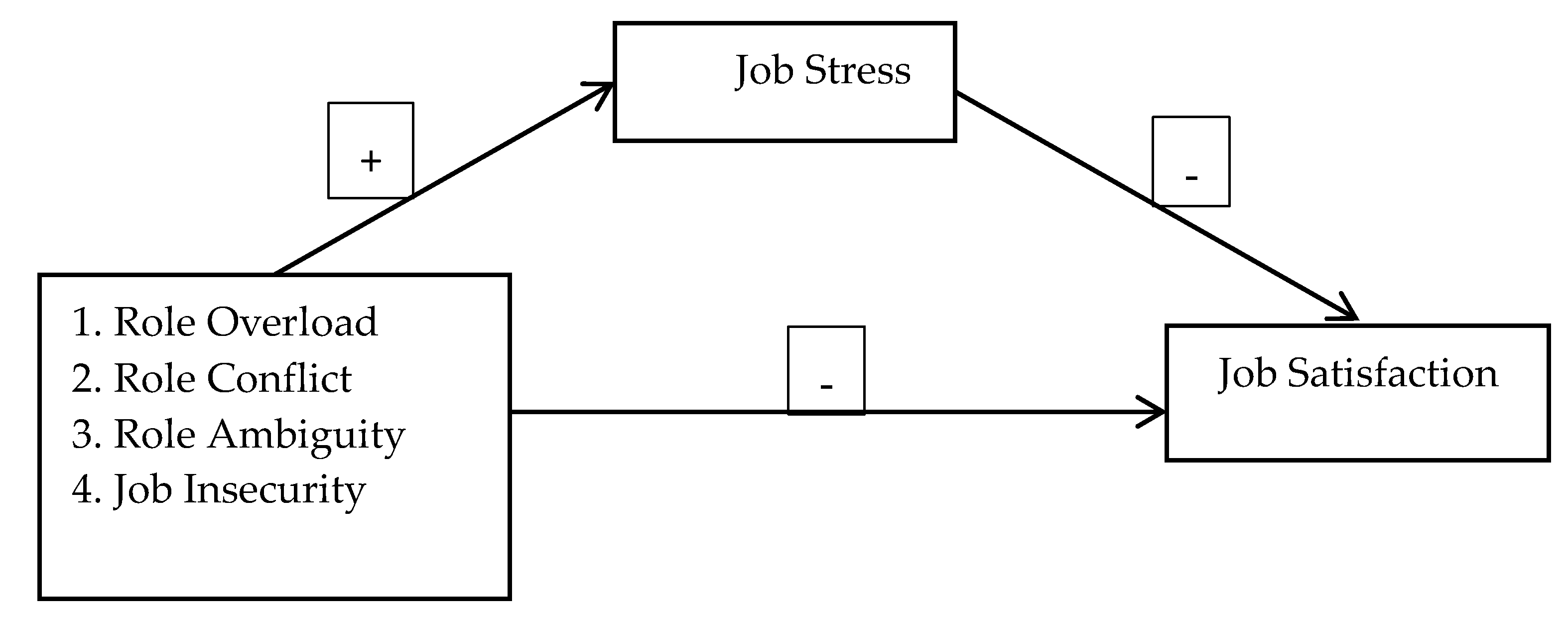
2. Theoretical Framework and Hypothesis
2.1. JS in Collectivist and Non-collectivist Societies
2.1.1. Relationship of Role stressors, JS and JSF
2.1.2. Mediating Role of JS
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Sample and Procedures
3.2. Measures
4. Results
4.1. Tests of Hypotheses
4.1.1. Role Stressors and JS (H1a–d)
4.1.2. Role Stressors and JSF (H2a–d)
4.1.3. JS and JSF (H3)
4.2. Mediation Test
4.2.1. RO and JSF (H4a)
4.2.2. RC and JSF (H4b)
4.2.3. RA and JSF (H4c)
4.2.4. JI and JSF (H4d)
5. Discussion
5.1. Limitations and Future Researches
5.2. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selye, H. Stress without Distress. In Psychopathology of Human Adaptation; Serban, G., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1976; pp. 137–146. ISBN 978-1-4684-2238-2. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Spector, P.E.; Jex, S.M. The relation of job control with job strains: A comparison of multiple data sources. J. Occup. Organ. Psychol. 2005, 78, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourigny, L.; Baba, V.V.; Wang, X. Stress episode in aviation: The case of China. Cross Cult. Manag. Int. J. 2010, 17, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.G.; Roger, A.; Asadullah, M.A. Imapct of Organizational Role Stressors on Faculty Stress & Burnout (An Exploratory Analysis of a Public Sector University of Pakistan); HAL: Lyon, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.T.; Lei, S. Role Stressors and Job Satisfaction in the Banking Industry: The Mediating Role of Job Stress. Int. Bus. Res. 2015, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, M.; Jinnah, M.A.; Fida, S.; Nasir, S.; Ahmad, Z. The Impact of Job Stress on Employee Job Satisfaction A Study on Telecommunication Sector of Pakistan. J. Bus. Stud. Q. 2011, 2, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, M. Role stress among women in the Indian information technology sector. Women Manag. Rev. 2004, 19, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Tariq, M.A.; Hussain, S.; Rashid, R.M.; Hussain, M.S.; Khawar, I.H. Antecedents of Job Stress and Its Impact on Job Satisfaction. Asian J. Empir. Res. 2013, 3, 175–190. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, R.L.; Wolfe, D.M.; Quinn, R.P.; Snoek, J.D.; Rosenthal, R.A. Organizational stress: Studies in role conflict and ambiguity; John Wiley: Oxford, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Hobfoll, S.E. Conservation of resources. A new attempt at conceptualizing stress. Am. Psychol. 1989, 44, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Örtqvist, D.; Wincent, J. Prominent consequences of role stress: A meta-analytic review. Int. J. Stress Manag. 2006, 13, 399–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidman, N.; Elisha, D. What generates the violation of psychological contracts at multinational corporations? A contextual exploratory study. Int. J. Cross Cult. Manag. 2016, 16, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quratulain, S.; Khan, A.K.; Crawshaw, J.R.; Arain, G.A.; Hameed, I. A study of employee affective organizational commitment and retention in Pakistan: The roles of psychological contract breach and norms of reciprocity. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2018, 29, 2552–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.F.; Thomas, D.C. Organizational behavior in multinational organizations. J. Organ. Behav. 2007, 28, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnall, P.L.; Dobson, M.; Landsbergis, P. Globalization, Work, and Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Health Serv. 2016, 46, 656–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshal, S.; Bartlett, C.A. The Multinational Corporation as an Interorganizational Network. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1990, 15, 603–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, E.G.; Hogan, N.L.; Paoline, E.A.; Clarke, A. The Impact of Role Stressors on Job Stress, Job Satisfaction, and Organizational Commitment among Private Prison Staff. Secur. J. 2005, 18, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, J.R.; House, R.J.; Lirtzman, S.I. Role Conflict and Ambiguity in Complex Organizations. Adm. Sci. Q. 1970, 15, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, J.; Campbell, K.M. Role Conflict and Role Ambiguity as Factors in Work Stress among Managers in Singapore: Some Moderator Variables. Res. Pract. Hum. Resour. Manag. 1994, 2, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tourigny, L.; Baba, V.V.; Han, J.; Wang, X. Emotional exhaustion and job performance: The mediating role of organizational commitment. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2013, 24, 514–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, K.; Azhar, S.; Ahmad, F. A Hidden Threat: Work Stress among Business Managers in Pakistan. Int. J. Econ. Manag. 2013, 7, 150–171. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.W.; Gwozdz, W. What makes MNCs succeed in developing countries?: An empirical analysis of subsidiary performance. Multinatl. Bus. Rev. 2015, 23, 224–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizaka, H.; Siu, A.; Chantasasawat, B.; Fung, K.C. Multinational enterprises in China, East Asia, Latin America and Eastern Europe: Moving out or moving in? J. Chin. Econ. Foreign Trade Stud. 2008, 1, 122–135. [Google Scholar]
- Spector, P.E.; Cooper, C.L.; Sanchez, J.I.; O’Driscoll, M.; Sparks, K.; Bernin, P.; Büssing, A.; Dewe, P.; Hart, P.; Lu, L.; et al. Locus of Control and Well-Being at Work: How Generalizable are Western Findings? Acad. Manag. J. 2002, 45, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, J. Working across Cultures; Stanford University Press: Stanford, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, O.F.; Malik, K. The Mediating Effects of Job Satisfaction on Role Stressors and Affective Commitment. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2010, 5, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trayambak, M.S.; Kumar, P.; Jha, A.N. A Conceptual Study on Role Stressors, their impact and Strategies to manage Role Stressors. IOSR J. Bus. Manag. 2012, 4, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, F.T.; Lemming, T.; Link, B.G.; Wozniak, J.F. The Impact of Social Supports on Police Stress. Criminology 1985, 23, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasek, R.A. Job Demands, Job Decision Latitude, and Mental Strain: Implications for Job Redesign. Adm. Sci. Q. 1979, 24, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, D.P.; Fairchild, A.J.; Fritz, M.S. Mediation Analysis. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2006, 58, 593–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, N.; Shar, A.H.; Shaikh, F.M.; Nazar, M.S. Causes of Stress in Organization, a Case Study of Sukkur. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2010, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beehr, T.A.; Newman, J.E. Job Stress, Employee Health, and Organizational Effectiveness: A Facet Analysis, Model, and Literature Review1. Pers. Psychol. 1978, 31, 665–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatough, E.M.; Chang, C.-H.; Miloslavic, S.A.; Johnson, R.E. Relationships of role stressors with organizational citizenship behavior: A meta-analysis. J. Appl. Psychol. 2011, 96, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judeh, M. Role Ambiguity and Role Conflict as Mediators of the Relationship between Socialization and Organizational Commitment. Int. Bus. Res. 2011, 4, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyemah, V. Role Ambiguity, Role Conflict, and Performance: Empirical Evidence of an Inverted-U Relationship. J. Pers. Sell. Sales Manag. 2008, 28, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongkang, Z.; Weixi, Z.; Yalin, H.; Yipeng, X.; Liu, T. The Relationship among Role Conflict, Role Ambiguity, Role Overload and Job Stress of Chinese Middle-Level Cadres. Chin. Stud. 2014, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Rashid, H. The Mediating Role of Work-Leisure Conflict on Job Stress and Retention of It Professionals. J. Manag. Inf. Decis. Sci. 2010, 13, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Palomino, M.N.; Frezatti, F. Role conflict, role ambiguity and job satisfaction: Perceptions of the Brazilian controllers. Rev. Adm. 2016, 51, 165–181. [Google Scholar]
- Soltani, I.; Hajatpour, S.; Khorram, J.; Nejati, M. Investigating the effect of role conflict and role ambiguity on employees’ job stress: Articulating the role of work-family conflict. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2013, 3, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.-D. Job Insecurity, Well-Being, and Job Performance: The Role of General Self-Efficacy: Job Insecurity, Well-Being, and Job Performance: The Role of General Self-Efficacy. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2008, 40, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, T.M.; Lawler, J. Cultural Values as Moderators of Employee Reactions to Job Insecurity: The Role of Individualism and Collectivism. Appl. Psychol. 2006, 55, 234–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, C.A.; Israel, B.A.; House, J.S. Chronic job insecurity among automobile workers: Effects on job satisfaction and health. Soc. Sci. Med. 1982 1994, 38, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, H.D. Job insecurity: Review of the international literature on definitions, prevalence, antecedents and consequences. SA J. Ind. Psychol. 2005, 31, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakis, N.; Goulimaris, D.; Koustelios, A. Role ambiguity, role conflict and job satisfaction among physical education teachers in Greece. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2004, 18, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, D.A. The Interactive Effects of Role Conflict and Role Ambiguity on Job Satisfaction and Attitudes Toward Organizational Change: A Moderated Multiple Regression Approach. Int. J. Stress Manag. 2000, 7, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarinto, K. Understanding Stress in Multinational Companies in Thailand; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Blau, P.M. Exchange and Power in Social Life; J. Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1964; ISBN 978-0-471-08030-5. [Google Scholar]
- Imam, A.; Shah, F.T.; Raza, A. Mediating Role of Job Stress between Workplace Discrimination Gender Discrimination-Glass Ceiling and Employee Attitudinal Outcomes Job Satisfaction and Motivation in Banking Sector of Pakistan. Middle-East J. Recent Sci. 2013, 18, 264–274. [Google Scholar]
- Krejcie, R.V.; Morgan, D.W. Determining Sample Size for Research Activities. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1970, 30, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, R.; Cobb, S.; French, J., Jr.; Harrison, R.; Pinneau, S. Job Demands and Worker Health: Main Effects and Occupational Differences; Research report series; Survey Research Center, University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Ashford, S.J.; Lee, C.; Bobko, P. Content, Cause, and Consequences of Job Insecurity: A Theory-Based Measure and Substantive Test. Acad. Manag. J. 1989, 32, 803–829. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, D.F.; DeCotiis, T.A. Organizational determinants of job stress. Organ. Behav. Hum. Perform. 1983, 32, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, H.; Oktay, E. Relations Between Pay, Career, Job Satisfaction And Performance: An Application In Karaman Governorship. Selcuk Univ. Soc. Sci. Inst. J. 2008, 21, 223. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, M.E. Asymptotic Confidence Intervals for Indirect Effects in Structural Equation Models. Sociol. Methodol. 1982, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, C.M.; Kenny, D.A. Process Analysis: Estimating Mediation in Treatment Evaluations. Eval. Rev. 1981, 5, 602–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Ahmed, Z.; Ahmed, I. Work Stress Experienced by the Teaching Staff of University of the Punjab, Pakistan: Antecedents and Consequences. Int. J. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2011, 2, 202–210. [Google Scholar]
- Coverman, S. Role Overload, Role Conflict, and Stress: Addressing Consequences of Multiple Role Demands. Soc. Forces 1989, 67, 965–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, L.; Rosenblatt, Z. Job Insecurity: Toward Conceptual Clarity. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1984, 9, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaşlıoğlu, M.; Karagülle, A.Ö.; Baran, M. An Empirical Research on the Relationship between Job Insecurity, Job Related Stress and Job Satisfaction in Logistics Industry. Procedia—Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 99, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ismail, A.; Yao, A.; Yunus, N.K.Y. Relationship Between Occupational Stress and Job Satisfaction: An Empirical Study in Malaysia. Romanian Econ. J. 2009, 12, 3–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hobfoll, S.E.; Freedy, J. Conservation of resources: A general stress theory applied to burnout. In Professional Burnout: Recent Developments in Theory and Research; Series in applied psychology: Social issues and questions; Taylor & Francis: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993; pp. 115–133. ISBN 978-1-56032-262-7. [Google Scholar]
- Roll, L.C.; De Witte, H.; Siu, O.; Li, S.Y.W. Job insecurity: Cross-cultural comparison between Germany and China. J. Organ. Eff. People Perform. 2015, 2, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif-ud-Din; Baba, V.V.; Tourigny, L. Emotional exhaustion and its consequences: A comparative study of nurses in India and China. Int. J. Comp. Manag. 2018, 1, 65–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | RO | RC | RA | JI | JS | JSF | Mean | SD | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RO | 1 | 3.84 | 0.288 | 0.71 | |||||
| RC | 0.658 ** | 1 | 3.89 | 0.510 | 0.71 | ||||
| RA | 0.582 ** | 0.447 ** | 1 | 4.67 | 0.872 | 0.79 | |||
| JI | 0.445 ** | 0.351 ** | 0.364 ** | 1 | 2.89 | 0.442 | 0.84 | ||
| JS | 0.560 ** | 0.563 ** | 0.479 ** | 0.596 ** | 1 | 3.34 | 0.474 | 0.81 | |
| JSF | −0.506 ** | −0.347 ** | −0.475 ** | −0.451 ** | −0.511 ** | 1 | 4.10 | 0.367 | 0.87 |
| Independent Variables | Step 1 | Step 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JS | JSF | |||||
| B | F | R2 | B | F | R2 | |
| Role Overload | 0.92 ** | 78.29 ** | 0.31 | −0.64 ** | 59.98 ** | 0.26 |
| Role Conflict | 0.52 ** | 79.51 ** | 0.31 | −0.25 ** | 23.46 ** | 0.12 |
| Role Ambiguity | 0.26 ** | 50.83 ** | 0.23 | −0.20 ** | 49.91 ** | 0.26 |
| Job Insecurity | 0.63 ** | 94.17 ** | 0.35 | −0.37 ** | 43.57 ** | 0.20 |
| Job Stress | −0.39 ** | 60.33 ** | 0.26 | |||
| Predictors | Step 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JSF | ||||||||
| B | F | R2 | R2 (from Step 2) | ∆R2 | Bootstrap Interval | Sobel Test p-Value | ||
| Block-1 | RO | −0.41 ** | 42.15 ** | 0.33 | 0.26 | 0.07 ** | −0.38 to −0.13 | 0.000 |
| Block-2 | JS | −0.25 ** | ||||||
| Block-1 | RC | −0.06 | 30.80 ** | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.14 ** | −0.27 to −0.11 | 0.000 |
| Block-2 | JS | −0.36 ** | ||||||
| Block-1 | RA | −0.13 ** | 41.85 ** | 0.33 | 0.23 | 0.10 ** | −0.12 to −0.05 | 0.000 |
| Block-2 | JS | −0.28 ** | ||||||
| Block-1 | JI | −0.19 ** | 35.38 ** | 0.29 | 0.20 | 0.09 ** | −0.28 to −0.11 | 0.000 |
| Block-2 | JS | −0.29 ** | ||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Din, S.-u.-; Ishfaq, M.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, M.A. A Study of Role Stressors and Job Satisfaction: The Case of MNCs in Collectivist Context. Behav. Sci. 2019, 9, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs9050049
Din S-u-, Ishfaq M, Khan MI, Khan MA. A Study of Role Stressors and Job Satisfaction: The Case of MNCs in Collectivist Context. Behavioral Sciences. 2019; 9(5):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs9050049
Chicago/Turabian StyleDin, Saif-ud-, Mohammad Ishfaq, Muhammad Imran Khan, and Muhammad Asif Khan. 2019. "A Study of Role Stressors and Job Satisfaction: The Case of MNCs in Collectivist Context" Behavioral Sciences 9, no. 5: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs9050049
APA StyleDin, S.-u.-, Ishfaq, M., Khan, M. I., & Khan, M. A. (2019). A Study of Role Stressors and Job Satisfaction: The Case of MNCs in Collectivist Context. Behavioral Sciences, 9(5), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs9050049





