The Intention to be Physically Active in Sedentary Obese Children: A Longitudinal Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
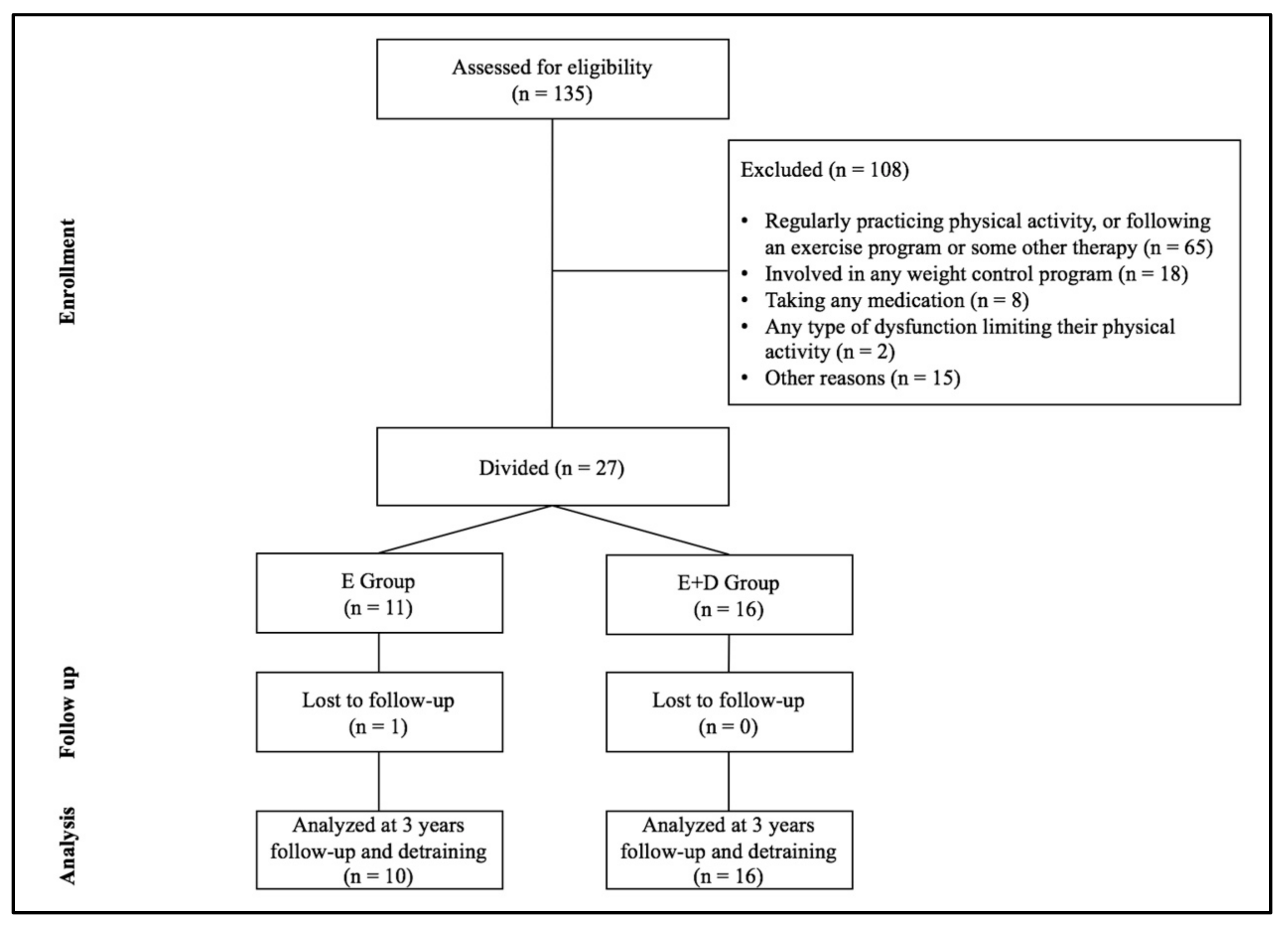
2.1. Participants
2.2. Physical Exercise Program
2.3. Diet Program
2.4. Measures
2.5. Intention to be Physically Active
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; ISBN 978-92-4-159-997-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, M. The GBD 2013 Obesity Collaboration. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, R.; Eneli, I. Severe childhood obesity: An under-recognised and growing health problem. Postgrad. Med. J. 2015, 91, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, E.; de Silva-Sanigorski, A.; Hall, B.J.; Brown, T.; Campbell, K.J.; Gao, Y.; Armstrong, R.; Prosser, L.; Summerbell, C.D. Interventions for preventing obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 7, CD001871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, L.; Wu, Y.; Wilson, R.; Weston, C.; Fawole, O.; Bleich, S.N.; Cheskin, L.J.; Showell, N.N.; Lau, B.D.; et al. What childhood obesity prevention programmes work? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annesi, J.J.; Johnson, P.H. Relative effects of reduced weight and increased physical activity on hemoglobin A1c: Suggestions for behavioral treatments. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2013, 13, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, B.; Serra-Majem, L.; Ribas-Barba, L.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta, J. How many children and adolescents in Spain comply with the recommendations on physical activity? J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2008, 48, 380–387. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.; Kim, Y. Physical activity and its related motivational attributes in adolescents with different BMI. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2013, 20, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deforche, B.I.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.M.; Tanghe, A.P. Attitude toward physical activity in normal-weight, overweight and obese adolescents. J. Adolesc. Health. 2006, 38, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabinski, M.F.; Saelens, B.E.; Stein, R.I.; Hayden-Wade, H.A.; Wilfley, D.E. Overweight children’s barriers to and support for physical activity. Obes. Res. 2003, 11, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra, J.M.; García-Hermoso, A.; Escalante, Y.; Domínguez, A.M. Self-determined motivation, physical exercise and diet in obese children: A three-year follow-up study. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2014, 14, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I.; Fishbein, M. Understanding Attitudes and Predicting Behaviour; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1980; ISBN 0-13-936435-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, M.; Castellet, J.; Narvaiza, J.L.; Rincón, J.M.; Ruiz, I.; Sánchez, E.; Sobradillo, B.; Zurimendi, A. Curvas y Tablas de Crecimiento; Garsi: Madrid, Spain, 1988; ISBN 84-607-9967-9. [Google Scholar]
- Maliszewski, A.F.; Freedson, P.S.; Ebbeling, C.J.; Crussemeyer, J.; Kastango, K.B. Validity of the Caltrac accelerometer in estimating energy expenditure and activity in children and adults. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 1991, 3, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, Y.; Backx, K.; Saavedra, J.M.; García-Hermoso, A.; Domínguez, A.M. Play area and physical activity in recess in primary schools. Kineziologija 2012, 44, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Sallis, J.F.; Buono, M.J.; Roby, J.J.; Carlson, D.; Nelson, J.A. The Caltrac accelerometer as a physical activity monitor for school-age children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1990, 22, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, L.H.; Myers, M.D.; Raynor, H.A.; Saelens, B.E. Treatment of pediatric obesity. Pediatrics 1998, 101, 554–570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Golan, M.; Crow, S. Targeting parents exclusively in the treatment of childhood obesity: Long-term results. Obes. Res. 2004, 12, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, J.M.; Whitehouse, R.H.; Takaishi, M. Standards from birth to maturity for height, weight, height velocity, and weight velocity: British children, 1965. I. Arch. Dis. Child. 1966, 41, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hein, V.; Müür, M.; Koka, A. Intention to be physically active after school graduation and its relationship to three types of intrinsic motivation. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2004, 10, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.A.; Moreno, R.; Cervelló, E. El autoconcepto físico como predictor de la intención de ser físicamente activo. Psicol. Salud 2007, 17, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Trost, S.G.; Kerr, L.M.; Ward, D.S.; Pate, R.R. Physical activity and determinants of physical activity in obese and non-obese children. Int. J. Obes. Relat Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juvancic-Heltzel, J.A.; Glickman, E.L.; Barkley, J.E. The effect of variety on physical activity: A cross-sectional study. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Hermoso, A.; Saavedra, J.M.; Olloquequi, J.; Ramírez-Vélez, R. Associations between the duration of active commuting to school and academic achievement in rural Chilean adolescents. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2017, 22, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardle, J.; Cook, L. The impact of obesity on psychological well-being. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 19, 421–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.K.; Shroff, H.; Herbozo, S.; Cafri, G.; Rodriguez, J.; Rodrigues, M. Relations among multiple peer influences, body dissatisfaction, eating disturbance, and selfesteem: A comparison of average weight, at risk of overweight, and overweight adolescent girls. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2007, 31, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampasa-Kanyinga, H.; Hamilton, H.A.; Willmore, J.; Chaput, J.P. Perceptions and attitudes about body weight and adherence to the physical activity recommendation among adolescents: The moderating role of body mass index. Public Health 2017, 146, 75–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, P.J.; Going, S.B.; Houtkooper, L.B.; Cussler, E.C.; Metcalfe, L.L; Blew, R.M; Sardinha, L.B; Lohman, T.G. Exercise motivation, eating, and body image variables as predictors of weight control. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| E Group (M ± SD) | E + D Group (M ± SD) | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (boys/girls) | 11 (8/3) | 16 (10/6) | - | - |
| Age (years) | 10.73 ± 0.90 | 10.19 ± 1.02 | 2.630 | 0.085 |
| Tanner stage (pubic hair) | 2.01 ± 0.63 | 1.81 ± 0.54 | 0.068 | 0.796 |
| Eating habits (kcal/day) | 1912.96 ± 204.10 | 1906.26 ± 210.92 | 0.017 | 0.897 |
| Height (m) | 1.49 ± 0.10 | 1.46 ± 0.10 | 0.530 | 0.473 |
| Weight (kg) | 62.15 ± 9.86 | 57.68 ± 11.20 | 0.257 | 0.617 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.85 ± 3.42 | 27.32 ± 3.88 | 0.507 | 0.483 |
| Fat mass (%) | 25.47 ± 6.90 | 25.89 ± 5.71 | 0.376 | 0.545 |
| Intervention | Detraining | ANOVA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 3rd Year | 6 Months | ||||||
| M ± SD | M ± SD | M ± SD | ||||||
| n | a | b | c | F | p | Diff. | ||
| MIFA | E | 10 | 2.33 ± 1.01 | 4.34 ± 0.40 | 4.66 ± 0.47 | 26.154 | <0.001 | a < b, c |
| E + D | 16 | 2.82 ± 0.81 | 4.32 ± 0.71 | 4.51 ± 0.62 | 11.553 | <0.001 | a < b, c | |
| p | 0.232 | 0.954 | 0.636 | |||||
| Daily PA | E | 10 | 443.13 ± 106.45 | 611.81 ± 159.29 | 724.30 ± 124.33 | 10.185 | 0.001 | a < b, c |
| E + D | 6 | 442.65 ± 99.56 | 526.18 ± 120.97 | 771.49 ± 91.84 | 23.966 | <0.001 | a < b, c | |
| p | 0.981 | 0.259 | 0.439 | |||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Hermoso, A.; Saavedra, J.M.; Escalante, Y.; Domínguez, A.M. The Intention to be Physically Active in Sedentary Obese Children: A Longitudinal Study. Behav. Sci. 2018, 8, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs8010009
García-Hermoso A, Saavedra JM, Escalante Y, Domínguez AM. The Intention to be Physically Active in Sedentary Obese Children: A Longitudinal Study. Behavioral Sciences. 2018; 8(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs8010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Hermoso, Antonio, Jose M. Saavedra, Yolanda Escalante, and Ana M. Domínguez. 2018. "The Intention to be Physically Active in Sedentary Obese Children: A Longitudinal Study" Behavioral Sciences 8, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs8010009
APA StyleGarcía-Hermoso, A., Saavedra, J. M., Escalante, Y., & Domínguez, A. M. (2018). The Intention to be Physically Active in Sedentary Obese Children: A Longitudinal Study. Behavioral Sciences, 8(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs8010009





