Impulsivity and Stillness: NADA, Pharmaceuticals, and Psychotherapy in Substance Use and Other DSM 5 Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Impulsivity and DSM 5 Diagnoses
3. Neurobiology and Impulsivity
4. Treatment Option: Medication
5. Treatment Option: Mindfulness Based Therapies
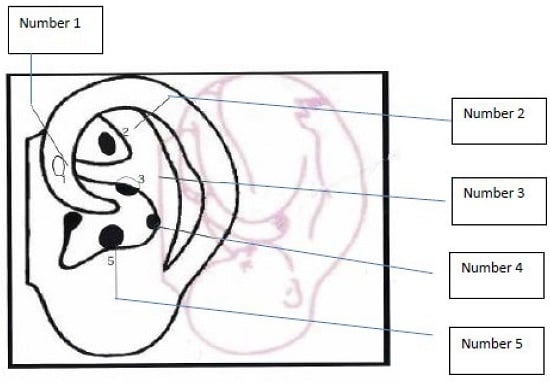
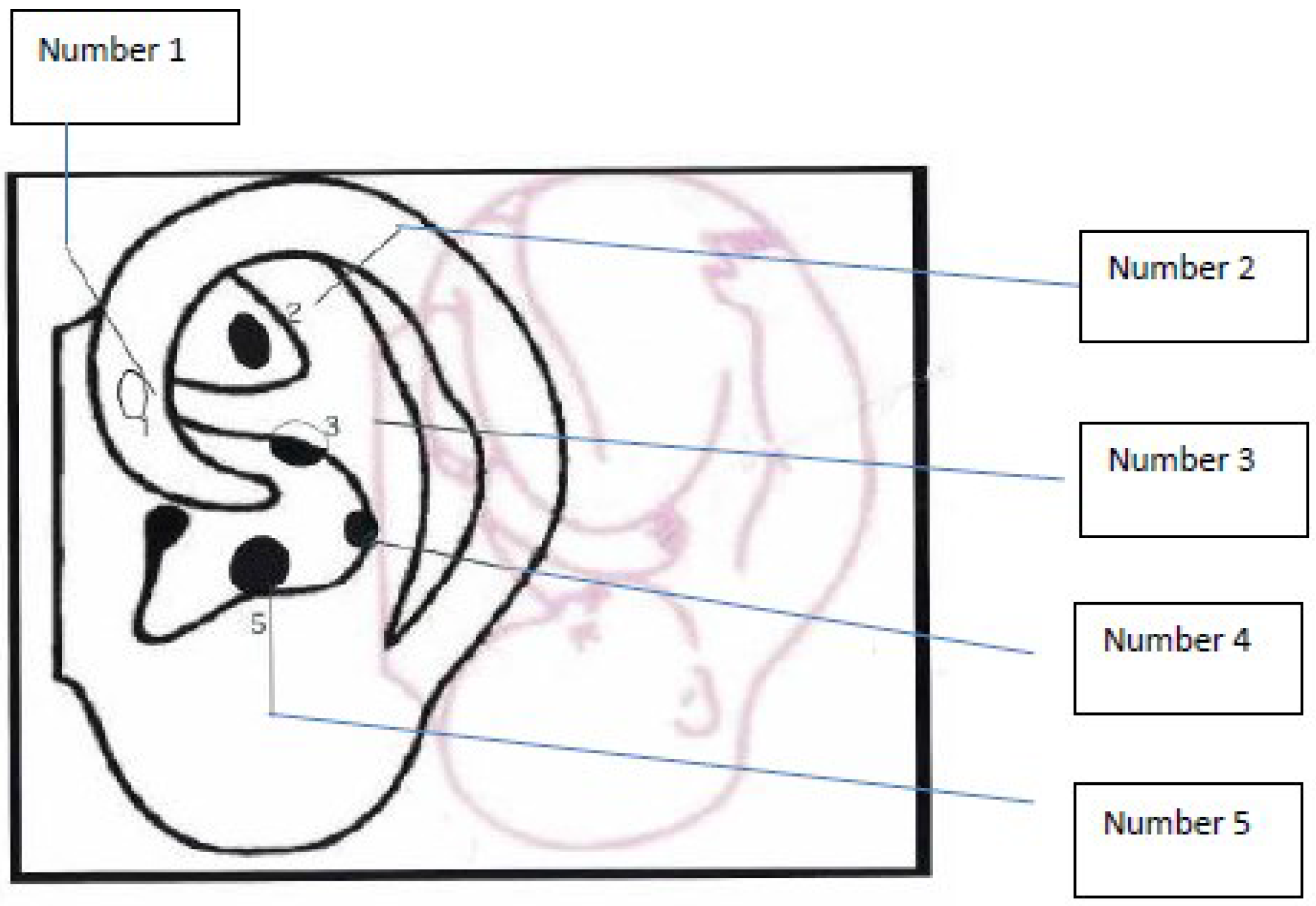
6. Treatment Option: NADA Ear Acupuncture Protocol
7. Summary
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Center for Substance Abuse Treatment. Center for Substance Abuse Treatment Detoxification and Substance Treatment: TIP Series 45 (DHHS Publication No. [SMA] 06–4131); Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services: Rockville, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, W.; Peters, J.R.; Adams, Z.W.; Lynam, D.R.; Milich, R. Identifying the facets of impulsivity that explain the relation between ADHD symptoms and substance use in a nonclinical sample. Addict. Behav. J. 2014, 39, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5™, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, J.E.; Chamberlain, S.R. Impulsive action and impulsive choice across substance and behavioral addictions: Cause or consequence? Addict. Behav. 2014, 39, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barratt, E. Impulsiveness Substrates; Arousal and Information Processing; Spence, J.T., Izard, C.E., Eds.; Motivation, Emotion, and Personality; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, J.; Sanford, M.; Barratt, E. Factor structure of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale. J. Clin. Psychol. 1995, 51, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L. Predicting relapse and recover in alcoholism and addiction: Neuropsychology, personality, and cognitive style. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 1991, 8, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, F.; Barratt, E.; Dougherty, D.R.; Schmitz, J.; Swann, A. Reviews and Overviews: Psychiatric aspects of impulsivity. Am. J. Psychiatry 2001, 158, 1783–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, F.; Dougherty, D.; Barratt, E.; Schmitz, J.; Swann, A.; Grabowski, J. The impact of impulsivity on cocaine use and retention in treatment. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2001, 21, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, A.; Lijffijt, M.; Lane, S.; Steinberg, J.; Moeller, F. Increased trait like impulsivity and course of illness in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2009, 11, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swann, A.; Lijffijt, M.; Lane, S.; Steinberg, J.; Moeller, F. Interacting mechanisms of impulsivity in bipolar disorder and antisocial personality disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swann, A.; Daugherty, D.; Pazzaglia, P.; Pham, M.; Steinberg, J.; Moeller, F. Increased impulsivity associated with severity of suicide attempt history in patients with bipolar disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.; Collins, R.; Kent, T. Language and the Modulation of Impulsive Aggression. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 20, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Elst, L.; Woermann, F.; Lemieux, L.; Thompson, P.J.; Trimble, M.R. Affective aggression in patients with temporal epilepsy: A quantitative MRI study of the amygdala. Brain 2000, 123, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barratt, E.; Sandford, M.; Felthous, A.; Kent, T.A. The effects of phenytoin on impulsive and premediated aggression: A controlled study. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1997, 17, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barratt, E.S.; Stanford, M.S.; Kent, T.A.; Felthous, A. Neuropsychological and cognitive psychophysiological substrates of impulsive aggression. Biol. Psychiatry 1997, 41, 1045–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, A.S.; Buchsbaum, M.S.; Hazlett, E.A.; Goodman, M.; Koenigsberg, H.W.; Lo, J.; Iskander, L.; Newmark, R.; Brand, J.; O’Flynn, K.; et al. Fluoxetine increases relative metabolic rate in prefrontal cortex in impulsive aggression. Psychopharmacology 2004, 176, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheard, M.; Marini, J.L.; Bridges, C.; Wagner, E. The effects of lithium on impulsive behavior in men. Am. J. Psychiatry 1976, 133, 1409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mattres, J.S. Oxcarbazepine in patients with implusive aggression: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 25, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritt, K.; Nickel, C.; Lahmann, C.; Leiberich, P.K.; Rother, W.K.; Loew, T.H.; Nickel, M.K. Lamotrigine treatment of aggression in female borderline-patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 19, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, M.K.; Nickel, C.; Mitterlehner, F.O.; Tritt, K.; Lahmann, C.; Leiberich, P.K.; Rother, W.K.; Loew, T.H. Topiramate treatment of aggression in female border personality disorder patients: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2004, 65, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, M.K.; Nickel, C.; Kaplan, P.; Lahmann, C.; Muhlbacher, M.; Tritt, K.; Krawczyk, J.; Leiberich, P.K.; Rother, W.K.; Loew, T.H. Treatment of aggression with topiramate in male borderline patients. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollander, E.; Tracy, K.A.; Swann, A.C.; Coccaro, E.F.; McElroy, S.L.; Wozniak, P.; Summerville, K.W.; Nemeroff, C.B. Divalproex in the treatment of impulsive aggression: Efficacy in cluster B personality disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003, 28, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreier, H.A. Risperidone for young children with mood disorders and aggressive behavior. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 1998, 8, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccaro, E.F.; Lee, R.J.; Kavoussi, R.J. A double blind randomized placebo controlled trial of fluoxetine in patients with intermittent explosive disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2009, 70, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccaro, E.F.; Kavoussi, R.J. Fluoxetine and impulsive aggressive behavior in personality disorder subjects. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1997, 54, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, R.A.; Smith, G.T.; Hopkins, J.; Krietemeyer, J.; Toney, L. Using self-report methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment 2006, 13, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.; MacKlillop, J. Living in the here and now: Interrelationship between impulsivity, mindfulness and alcohol misuse. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marlatt, G.A. Buddhist philosophy and the treatment of addictive behavior. Cogn. Behav. Pract. 2002, 9, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkiewitz, K.; Lustyk, M.; Bowen, S. Re-training the addicted brain: A review of hypothesized neurobiological mechanisms of mindfulness-based relapse prevention. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2013, 2027, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppes, K. The application of mindfulness-based cognitive interventions in the treatment of co-occurring addictive and mood disorders. CNS Spectr. 2006, 11, 829–851. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carter, K.; Olshan-Perlmutter, M.; Norton, H.J.; Smith, M.O. NADA acupuncture prospective trial in patients with substance use disorders and seven common health symptoms. Med. Acupunct. 2011, 23, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Acupuncture Detoxification Association (NADA). Acupuncture Detoxification Specialist (ADS) Training Resource Manual: A Handbook for Individual Training in the National Acupuncture Detoxification Association’s 5-needle Acudetox Protocol, 4th ed.; NADA: Columbia, MO, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, M. Letter from the AAC provided by Schroeder; American Acupuncture Council: Orange, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Brewington, V.; Smith, M.; Lipton, D. Acupuncture as a detoxification treatment: An analysis of controlled research. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 1994, 11, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, M.; Shim, I.; Kim, K.; Lee, M.; Lee, Y.; Golden, G.; Yang, C. Acupuncture-mediated inhibition of ethanol-induced dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens through the GABAb receptor. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 369, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.; Carter, K.; Landgren, K.; Stuyt, E. Addiction Medicine: Science and Practice. In Ear Acupuncture in Addiction Treatment; Johnson, B., Ed.; Springer Science & Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stux, G.; Pomeranz, B. Basics of Acupuncture, 5th ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Landgren, K. Ear Acupuncture: A Practical Guide; Elsevier: Chatswood, Australia, 2008; pp. 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- White, A. Trials of acupuncture for drug dependence; a recommendation for hypothesis based on the literature. Acupunct. Med. 2013, 31, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, P.; Barrowclough, C. Mental health problems: Are they or are they not a risk factor for drop out from drug treatment? A systemic review of the evidence. Drug Educ. Prev. Policy 2009, 16, 7–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuyt, E. Ear acupuncture for co-occuring substance abuse and borderline personality disorder; an aid to encourage treatment retention and tobacco cessation. Acupunct. Med. 2014, 32, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, J. Acupuncture Energetics: A Clinical Approach for Physicians, 2nd ed.; Medical Acupuncture: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1997; pp. 153–154. [Google Scholar]
- Santasiero, R.; Neussle, G. Cost effectiveness of auricular acupuncture for treating substance abuse in an HMO setting: A pilot study. Med. Acupunct. 2005, 16, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bergdahl, L.; Berman, A.H.; Haglund, K. Patient’s experience of auricular acupuncture. J. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs. 2014, 21, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, M.L.; Culliton, P.D.; Olander, R.T. Controlled trial of acupuncture for severe recidivist alcoholism. Lancet 1989, 1, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolin, A.; Avants, K.; Holford, T.R. Interpreting conflicting findings from clinical trials of auricular acupuncture for cocaine addiction: Does treatment influence outcome? J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2002, 8, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakur, M.; Smith, M.O. The use of acupuncture in the treatment of drug addiction. Am. J. Acupunct. 1979, 7, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Bursac, S. Missouri Acu Community Mobilizes for Joplin. Guidepoints: News from NADA; National Acupuncture Detoxification Association: Laramie, WY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- VA/DoD Practice Management Guideline for the Management of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Available online: http://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/MH/ptsd/ (accessed on 23 November 2015).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carter, K.; Olshan-Perlmutter, M. Impulsivity and Stillness: NADA, Pharmaceuticals, and Psychotherapy in Substance Use and Other DSM 5 Disorders. Behav. Sci. 2015, 5, 537-546. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs5040537
Carter K, Olshan-Perlmutter M. Impulsivity and Stillness: NADA, Pharmaceuticals, and Psychotherapy in Substance Use and Other DSM 5 Disorders. Behavioral Sciences. 2015; 5(4):537-546. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs5040537
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarter, Kenneth, and Michelle Olshan-Perlmutter. 2015. "Impulsivity and Stillness: NADA, Pharmaceuticals, and Psychotherapy in Substance Use and Other DSM 5 Disorders" Behavioral Sciences 5, no. 4: 537-546. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs5040537
APA StyleCarter, K., & Olshan-Perlmutter, M. (2015). Impulsivity and Stillness: NADA, Pharmaceuticals, and Psychotherapy in Substance Use and Other DSM 5 Disorders. Behavioral Sciences, 5(4), 537-546. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs5040537