Conceptual Framework for Nutritional Psychology as a New Field of Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Historical Background
3. Methodology (Developing Nutritional Psychology as a Conceptual Framework)
3.1. Mapping the Selected Data Sources
3.2. Reading and Categorizing of the Selected Data
3.3. Identifying and Naming Concepts
3.4. Deconstructing and Categorizing Concepts
3.5. Integrating Concepts
3.6. Synthesis and Resynthesis
3.7. Validating the Conceptual Framework
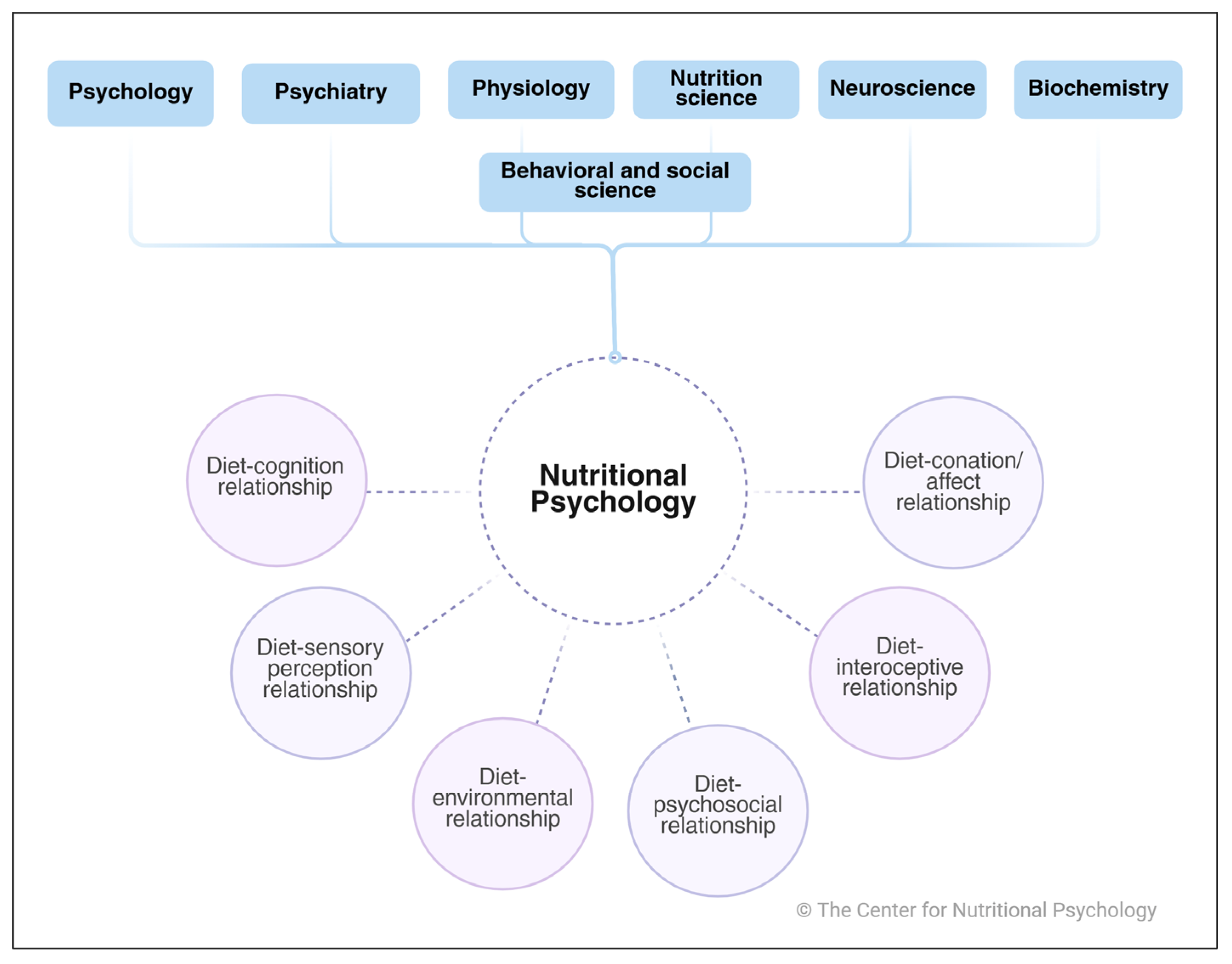
4. Results (Six Core Areas of Nutritional Psychology)
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adan, R. A. H., van der Beek, E. M., Buitelaar, J. K., Cryan, J. F., Hebebrand, J., Higgs, S., Schellekens, H., & Dickson, S. L. (2019). Nutritional psychiatry: Towards improving mental health by what you eat. European Neuropsychopharmacology: The Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 29(12), 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlAmmar, W. A., Albeesh, F. H., & Khattab, R. Y. (2020). Food and mood: The corresponsive effect. Current Nutrition Reports, 9(3), 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlBreiki, M., Middleton, B., Ebajemito, J., & Hampton, S. (2015). The effect of light on appetite in healthy young individuals. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 74(OCE1), E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychological Association (APA). (2025). APA dictionary of psychology. Available online: https://dictionary.apa.org/ (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- An, R. (2016). Fast-food and full-service restaurant consumption and daily energy and nutrient intakes in US adults. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 70(1), 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arno, A., & Thomas, S. (2016). The efficacy of nudge theory strategies in influencing adult dietary behaviour: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health, 16(1), 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atasoy, D., Betley, J. N., Su, H. H., & Sternson, S. M. (2012). Deconstruction of a neural circuit for hunger. Nature, 488(7410), 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassul, C., A Corish, C., & M Kearney, J. (2020). Associations between the home environment, feeding practices and children’s intakes of fruit, vegetables and confectionary/sugar-sweetened beverages. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(13), 4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayes, J., Schloss, J., & Sibbritt, D. (2022). The effect of a Mediterranean diet on the symptoms of depression in young males (The “AMMEND: A mediterranean diet in MEN with depression” study): A randomized controlled trial. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 116(2), 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermingham, K. M., May, A., Asnicar, F., Capdevila, J., Leeming, E. R., Franks, P. W., Valdes, A. M., Wolf, J., Hadjigeorgiou, G., Delahanty, L. M., Segata, N., Spector, T. D., & Berry, S. E. (2024). Snack quality and snack timing are associated with cardiometabolic blood markers: The ZOE PREDICT study. European Journal of Nutrition, 63(1), 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, M. C., Li, P., Allison, D. B., & Gohlke, J. M. (2015). Warm ambient temperature decreases food intake in a simulated office setting: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Frontiers in Nutrition, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, D. M., Laney, C., Morris, E. K., & Loftus, E. F. (2005). False beliefs about fattening foods can have healthy consequences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 102(39), 13724–13731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthoud, H., Lenard, N. R., & Shin, A. C. (2011). Food reward, hyperphagia, and obesity. AJP Regulatory Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 300(6), R1266–R1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bédard, A., Lamarche, P.-O., Grégoire, L.-M., Trudel-Guy, C., Provencher, V., Desroches, S., & Lemieux, S. (2020). Can eating pleasure be a lever for healthy eating? A systematic scoping review of eating pleasure and its links with dietary behaviors and health. PLoS ONE, 15(12), e0244292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackman, M. C., & Kvaska, C. (2011). Nutrition psychology: Improving dietary adherence. Jones and Bartlett Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, D. A. (1994). Psychology of nutrition. Taylor & Francis. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braune, T., Kudlek, L., Xiao, C., Tang, H., Demers-Potvin, É., Harris, H. A., Fitzsimons-West, E., Adams, J., & Winpenny, E. M. (2024). Interpersonal determinants of diet quality and eating behaviors in people aged 13–30 years: A systematic scoping review. Obesity Reviews, 26(1), e13835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bschaden, A., Dörsam, A. F., Cvetko, K., Kalamala, T., & Stroebele-Benschop, N. (2020). The impact of lighting and table linen as ambient factors on meal intake and taste perception. Food Quality and Preference, 79, 103797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camprodon-Boadas, P., Gil-Dominguez, A., De La Serna, E., Sugranyes, G., Lázaro, I., & Baeza, I. (2024). Mediterranean diet and mental health in children and adolescents: A systematic review. Nutrition Reviews, 83(2), 43–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, W. B., & Washburn, A. L. (1912). An explanation of hunger. American Journal of Physiology-Legacy Content, 29(5), 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M., Scirocco, A., Maselli, M. A., & Severi, C. (2015). The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Annals of Gastroenterology: Quarterly Publication of the Hellenic Society of Gastroenterology, 28(2), 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Caspi, C. E., Sorensen, G., Subramanian, S., & Kawachi, I. (2012). The local food environment and diet: A systematic review. Health & Place, 18(5), 1172–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Nutritional Psychology [CNP]. (2025a). Center for nutritional psychology. Available online: https://www.nutritional-psychology.org/ (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Center for Nutritional Psychology [CNP]. (2025b). Encyclopedia of nutritional psychology. Available online: https://www.nutritional-psychology.org/encyclopedia/ (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Center for Nutritional Psychology [CNP]. (2025c). Nutritional psychology research library. Available online: https://www.nutritional-psychology.org/np-research-library/ (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Chandon, P., & Wansink, B. (2002). When are stockpiled products consumed faster? A convenience–salience framework of postpurchase consumption incidence and quantity. Journal of Marketing Research, 39(3), 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawner, L. R., & Filippetti, M. L. (2024). A developmental model of emotional eating. Developmental Review, 72, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P. S., Yang, Y. K., Yeh, T. L., Lee, I., Yao, W. J., Chiu, N. T., & Lu, R. B. (2008). Correlation between body mass index and striatal dopamine transporter availability in healthy volunteers—A SPECT study. NeuroImage, 40(1), 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, W.-J., Lee, M.-F., Hou, M.-L., Hsiao, L.-S., Lee, M.-J., Chou, M.-C., & Wang, L.-J. (2018). Dietary and nutrient status of children with attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder: A case-control study. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 27(6), 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, N., Pechey, E., Pechey, R., Ventsel, M., Mantzari, E., De-Loyde, K., Pilling, M. A., Morris, R. W., Marteau, T. M., & Hollands, G. J. (2021). Size and shape of plates and size of wine glasses and bottles: Impact on self-serving of food and alcohol. BMC Psychology, 9(1), 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente-Suárez, V. J., Redondo-Flórez, L., Martín-Rodríguez, A., Curiel-Regueros, A., Rubio-Zarapuz, A., & Tornero-Aguilera, J. F. (2025). Impact of vegan and vegetarian diets on neurological health: A Critical review. Nutrients, 17(5), 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooksey-Stowers, K., Schwartz, M., & Brownell, K. (2017). Food swamps predict obesity rates better than food deserts in the United States. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(11), 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, M. (2014). Association of ambient indoor temperature with body mass index in England. Obesity, 22(3), 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashti, H. S., Gómez-Abellán, P., Qian, J., Esteban, A., Morales, E., Scheer, F. A. J. L., & Garaulet, M. (2021). Late eating is associated with cardiometabolic risk traits, obesogenic behaviors, and impaired weight loss. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 113(1), 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, T. L., & Stevenson, R. J. (2022). Appetitive interoception, the hippocampus and western-style diet. Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders, 23(4), 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leon, A., Jahns, L., Roemmich, J. N., Duke, S. E., & Casperson, S. L. (2022). Consumption of dietary guidelines for Americans types and amounts of vegetables increases mean subjective Happiness Scale scores: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 122(7), 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Osso, L., Abelli, M., Carpita, B., Pini, S., Castellini, G., Carmassi, C., & Ricca, V. (2016). Historical evolution of the concept of anorexia nervosa and relationships with orthorexia nervosa, autism, and obsessive-compulsive spectrum. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 12, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devonport, T. J., Nicholls, W., & Fullerton, C. (2017). A systematic review of the association between emotions and eating behaviour in normal and overweight adult populations. Journal of Health Psychology, 24(1), 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmas, C., & Kabaran, S. (2023). Is repeated taste exposure an effective strategy to increase vegetable acceptance and liking among neophobic tendency children? Child & Family Behavior Therapy, 45(4), 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriquez, J. P., & Archila-Godinez, J. C. (2022). Social and cultural influences on food choices: A review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 62(13), 3698–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espel-Huynh, H. M., Muratore, A. F., & Lowe, M. R. (2018). A narrative review of the construct of hedonic hunger and its measurement by the Power of Food Scale. Obesity Science & Practice, 4(3), 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evers, C., Dingemans, A., Junghans, A. F., & Boevé, A. (2018). Feeling bad or feeling good, does emotion affect your consumption of food? A meta-analysis of the experimental evidence. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 92, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernqvist, F., Spendrup, S., & Tellström, R. (2024). Understanding food choice: A systematic review of reviews. Heliyon, 10(12), e32492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firth, J., Gangwisch, J. E., Borisini, A., Wootton, R. E., & Mayer, E. A. (2020). Food and mood: How do diet and nutrition affect mental wellbeing? BMJ, 369, m2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, H. M., Stevenson, R. J., Chambers, J. R., Gupta, D., Newey, B., & Lim, C. K. (2019). A brief diet intervention can reduce symptoms of depression in young adults—A randomised controlled trial. PLoS ONE, 14(10), e0222768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesteiro, E., García-Carro, A., Aparicio-Ugarriza, R., & González-Gross, M. (2022). Eating out of home: Influence on nutrition, health, and policies: A scoping review. Nutrients, 14(6), 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, H., Gill, B., Lipsitz, O., Rodrigues, N. B., Cha, D. S., El-Halabi, S., Mansur, R. B., Rosenblat, J. D., Cooper, D. H., Lee, Y., Nasri, F., & McIntyre, R. S. (2021). The impact of overweight/obesity on monetary reward processing: A systematic review. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 137, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanz, K., Sallis, J. F., Saelens, B. E., & Frank, L. D. (2005). Healthy nutrition environments: Concepts and measures. American Journal of Health Promotion, 19(5), 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluck, M. E., Venti, C. A., Salbe, A. D., & Krakoff, J. (2008). Nighttime eating: Commonly observed and related to weight gain in an inpatient food intake study. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 88(4), 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godet, A., Fortier, A., Bannier, E., Coquery, N., & Val-Laillet, D. (2022). Interactions between emotions and eating behaviors: Main issues, neuroimaging contributions, and innovative preventive or corrective strategies. Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders, 23(4), 807–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godos, J., Currenti, W., Angelino, D., Mena, P., Castellano, S., Caraci, F., Galvano, F., Del Rio, D., Ferri, R., & Grosso, G. (2020). Diet and mental health: Review of the recent updates on molecular mechanisms. Antioxidants, 9(4), 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, E. C. L. (2013). “You must finish your dinner”: Meal time dynamics between grandparents, parents and grandchildren in urban China. British Food Journal, 115(3), 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C. E. F., Chávez-Servín, J. L., De La Torre-Carbot, K., González, D. R., De Los Ángeles Aguilera Barreiro, M., & Navarro, L. R. O. (2022). Relationship between emotional eating, consumption of hyperpalatable energy-dense foods, and indicators of nutritional status: A systematic review. Journal of Obesity, 2022, 4243868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, O., & Lim, S. (2023). The role of emotion in eating behavior and decisions. Frontiers in Psychology, 14, 1265074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampson, S. E., Vollrath, M. E., & Júlíusson, P. B. (2015). Personality and overweight in 6–12-year-old children. Pediatric Obesity, 10(5), e5–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampton, S., & Whitmarsh, L. (2023). Choices for climate action: A review of the multiple roles individuals play. One Earth, 6(9), 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, C. P. (2015). The social facilitation of eating. A review. Appetite, 86, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, K. A., Hudson, J. L., Hayes, A. M. R., Braun, E., Cheon, E., Couture, S. C., Gunaratna, N. S., Hill, E. R., Hunter, S. R., McGowan, B. S., Reister, E. J., Wang, Y., & Mattes, R. D. (2021). Systematic review and meta-analysis on the effect of portion size and ingestive frequency on energy intake and body weight among adults in randomized controlled feeding trials. Advances in Nutrition, 13(1), 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgs, S. (2008). Cognitive influences on food intake: The effects of manipulating memory for recent eating. Physiology & Behavior, 94(5), 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgs, S. (2015). Manipulations of attention during eating and their effects on later snack intake. Appetite, 92, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollands, G. J., Shemilt, I., Marteau, T. M., Jebb, S. A., Kelly, M. P., Nakamura, R., Suhrcke, M., & Ogilvie, D. (2013). Altering micro-environments to change population health behaviour: Towards an evidence base for choice architecture interventions. BMC Public Health, 13, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, J. M., Colucci, L., Baudewyns, D., Balkan, J., Hunt, T., Hunt, B., Kinney, M., Holcomb, L., Stratigakis, A., Chen, G., Moses, P. L., Mawe, G. M., Zhang, T., Li, Y., & Ishaq, S. L. (2023). Steamed broccoli sprouts alleviate DSS-induced inflammation and retain gut microbial biogeography in mice. mSystems, 8(5), e0053223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppu, U., Puputti, S., & Sandell, M. (2021). Factors related to sensory properties and consumer acceptance of vegetables. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 61(19), 1751–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, A. L., Robinson, M., Smith, G. J., Ambrosini, G. L., Piek, J. P., & Oddy, W. H. (2011). ADHD is associated with a “Western” dietary pattern in adolescents. Journal of Attention Disorders, 15(5), 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabareen, Y. (2009). Building a conceptual framework: Philosophy, definitions, and procedure. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 8(4), 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacka, F. N., O’Neil, A., Opie, R., Itsiopoulos, C., Cotton, S., Mohebbi, M., Castle, D., Dash, S., Mihalopoulos, C., Chatterton, M. L., Brazionis, L., Dean, O. M., Hodge, A. M., & Berk, M. (2017). A randomised controlled trial of dietary improvement for adults with major depression (the ‘SMILES’ trial). BMC Medicine, 15(1), 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, M., Rödiger, M., & Hamm, U. (2016). Labels for animal husbandry systems meet consumer preferences: Results froma meta-analyses of consumer studies. Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Ethics, 29, 1071–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, B. E., & Wansink, B. (2004). The influence of assortment structure on perceived variety and consumption quantities. Journal of Consumer Research, 30(4), 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamara, T., Dodos, K., Georgakopoulou, V., Fotakopoulos, G., Spandidos, D., & Kapoukranidou, D. (2025). Cognitive efficacy of omega-3 fatty acids in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomedical Reports, 22(4), 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelli, H. M., Kim, J. H., Samman Tahhan, A., Liu, C., Ko, Y., Hammadah, M., Sullivan, S., Sandesara, P., Alkhoder, A. A., Choudhary, F. K., Gafeer, M. M., Patel, K., Qadir, S., Lewis, T. T., Vaccarino, V., Sperling, L. S., & Quyyumi, A. A. (2019). Living in food deserts and adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. Journal of the American Heart Association, 8(4), e010694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleisiaris, C., Sfakianakis, C., & Papathanasiou, I. V. (2014). Health care practices in ancient Greece: The Hippocratic ideal. DOAJ (Directory of Open Access Journals), 7, 6. Available online: https://doaj.org/article/8584027c5c1c4816b62e8f511d6d57ac (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Kroll, J., & Bachrach, B. S. (1984). Sin and mental illness in the middle ages. Psychological Medicine, 14(3), 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laney, C., Morris, E. K., Bernstein, D. M., Wakefield, B. M., & Loftus, E. F. (2008). Asparagus, a love story. Experimental Psychology (Formerly Zeitschrift Für Experimentelle Psychologie), 55(5), 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfield, T., Pechey, R., Gilchrist, P. T., Pilling, M., & Marteau, T. M. (2020). Glass shape influences drinking behaviours in three laboratory experiments. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langlois, M., & Chandon, P. (2024). Experiencing nature leads to healthier food choices. Communications Psychology, 2(1), 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauer, A. A., Grimm, H. S., Apel, B., Golobrodska, N., Kruse, L., Ratanski, E., Schulten, N., Schwarze, L., Slawik, T., Sperlich, S., Vohla, A., & Grimm, M. O. W. (2022). Mechanistic link between vitamin B12 and Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules, 12(1), 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R. H. (2022). The status and significance of Paracelsus in the Modern Medical Revolution. Zhonghua Yi Shi Za Zhi, 52(3), 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y., Wang, S., Zhang, L., Dong, Q., Hu, X., Yang, Y., Liu, T., Wu, B., Shan, B., Yin, C., Xie, Q., Zhu, B., & Zheng, C. (2025). Sensory insights in aging: Exploring the impact on improving dietary through sensory enhancement. Food Science & Nutrition, 13(3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z., Luo, Y., Liu, W., & Chen, H. (2025). A systematic review of the relationship between taste and personality traits: Phenomena and possible mechanisms. Appetite, 207, 107875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippert, R. N., Hess, S., Klemm, P., Burgeno, L. M., Jahans-Price, T., Walton, M. E., Kloppenburg, P., & Brüning, J. C. (2020). Maternal high-fat diet during lactation reprograms the dopaminergic circuitry in mice. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 130(7), 3761–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H., Bean, J. C., Li, Y., Yu, M., Ginnard, O. Z., Conde, K. M., Wang, M., Fang, X., Liu, H., Tu, L., Yin, N., Han, J., Yang, Y., Tong, Q., Arenkiel, B. R., Wang, C., He, Y., & Xu, Y. (2024). Distinct basal forebrain-originated neural circuits promote homoeostatic feeding and suppress hedonic feeding in male mice. Nature Metabolism, 6(9), 1775–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logue, A. (2014). The psychology of eating and drinking (4th ed.). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loxton, N. J. (2018). The role of reward sensitivity and impulsivity in overeating and food addiction. Current Addiction Reports, 5(2), 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, B. (1989). A psychology of food: More than a matter of taste. Van Nostrand Reinhold. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G. (2015). Food, eating behavior, and culture in Chinese society. Journal of Ethnic Foods, 2(4), 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macht, M. (2008). How emotions affect eating: A five-way model. Appetite, 50(1), 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, A., Chabanet, C., Schaal, B., Issanchou, S., & Leathwood, P. (2007). Effects of repeated exposure on acceptance of initially disliked vegetables in 7-month old infants. Food Quality and Preference, 18(8), 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L. E., Holsen, L. M., Chambers, R. J., Bruce, A. S., Brooks, W. M., Zarcone, J. R., Butler, M. G., & Savage, C. R. (2010). Neural mechanisms associated with food motivation in obese and healthy weight adults. Obesity, 18(2), 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massicotte, E., Deschênes, S.-M., & Jackson, P. L. (2019). Food craving predicts the consumption of highly palatable food but not bland food. Eating and Weight Disorders: EWD, 24(4), 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, A. L., Gardiner, E., & Loxton, N. J. (2020). Investigating the relationship between reward sensitivity, impulsivity, and food addiction: A systematic review. European Eating Disorders Review, 28(4), 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClain, A. D., van den Bos, W., Matheson, D., Desai, M., McClure, S. M., & Robinson, T. N. (2014). Visual illusions and plate design: The effects of plate rim widths and rim coloring on perceived food portion size. International Journal of Obesity, 38(5), 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougle, M., De Araujo, A., Singh, A., Yang, M., Braga, I., Paille, V., Mendez-Hernandez, R., Vergara, M., Woodie, L. N., Gour, A., Sharma, A., Urs, N., Warren, B., & De Lartigue, G. (2024). Separate gut-brain circuits for fat and sugar reinforcement combine to promote overeating. Cell Metabolism, 36(2), 393–407.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiselman, H. L., Johnson, J. L., Reeve, W., & Crouch, J. E. (2000). Demonstrations of the influence of the eating environment on food acceptance. Appetite, 35(3), 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meléndez-Fernández, O. H., Liu, J. A., & Nelson, R. J. (2023). Circadian rhythms disrupted by light at night and mistimed food intake alter hormonal rhythms and metabolism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méjean, C., & Recchia, D. (2022). Urban foodscape and its relationships with diet and health outcomes. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 81(4), 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller-Stierlin, A. S., Cornet, S., Peisser, A., Jaeckle, S., Lehle, J., Mörkl, S., & Teasdale, S. (2022). Implications of dietary intake and eating behaviors for people with serious mental illness: A qualitative study. Nutrients, 14(13), 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nederkoorn, C., Braet, C., Van Eijs, Y., Tanghe, A., & Jansen, A. (2006). Why obese children cannot resist food: The role of impulsivity. Eating Behaviors, 7(4), 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y., Wu, L., Jiang, J., Yang, T., Wang, Z., Ma, L., Zheng, L., Yang, X., Wu, Z., & Fu, Z. (2019). Late-night eating-induced physiological dysregulation and circadian misalignment are accompanied by microbial dysbiosis. Molecular Nutrition and Food Research, 63(24), e1900867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygaard, M. E. (2019). Swedish fermented herring as a marker of rural identity: The Alfta surströmmingsskiva. Food, Culture & Society, 22(4), 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocean, N., Howley, P., & Ensor, J. (2019). Lettuce be happy: A longitudinal UK study on the relationship between fruit and vegetable consumption and well-being. Social Science & Medicine, 222, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, J. (2010). The psychology of eating: From healthy to disordered behavior (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Oltersdorf, U. (1984). Methodische Probleme der Erfassung von Ernährungsverhalten [Methodological problems in the assessment of nutrition behavior]. AID Verbraucherdienst, 29(9), 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, S., Minehan, M., Knight-Agarwal, C. R., & Turner, M. (2022). Depression, is it treatable in adults utilising dietary interventions? A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Nutrients, 14(7), 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oriach, C. S., Robertson, R. C., Stanton, C., Cryan, J. F., & Dinan, T. G. (2016). Food for thought: The role of nutrition in the microbiota-gut–brain axis. Clinical Nutrition Experimental, 6, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oustric, P., Gibbons, C., Beaulieu, K., Blundell, J., & Finlayson, G. (2018). Changes in food reward during weight management interventions—A systematic review. Obesity Reviews, 19(12), 1642–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parent, M. B., Higgs, S., Cheke, L. G., & Kanoski, S. E. (2022). Memory and eating: A bidirectional relationship implicated in obesity. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 132, 110–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C., Pagnini, F., & Langer, E. (2020). Glucose metabolism responds to perceived sugar intake more than actual sugar intake. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 15633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, G., Parker, I., & Brotchie, H. (2006). Mood state effects of chocolate. Journal of Affective Disorders, 92(2–3), 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, S., Correia-de-Sá, T., Sampaio-Maia, B., Vasconcelos, C., Moreira, P., & Ferreira-Gomes, J. (2022). Eating patterns and dietary interventions in ADHD: A narrative review. Nutrients, 14(20), 4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polivy, J., & Herman, C. P. (2005). Mental health and eating behaviours: A bi-directional relation. Canadian Journal of Public Health, 96(Suppl. S3), S43–S46, S49–S53. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, L. M., & Nguyen, B. T. (2013). Fast-food and full-service restaurant consumption among children and adolescents: Effect on energy, beverage, and nutrient intake. JAMA Pediatrics, 167(1), 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pristyna, G., Mahmudiono, T., Rifqi, M. A., & Indriani, D. (2022). The relationship between Big Five Personality Traits, eating habits, physical activity, and obesity in Indonesia based on analysis of the 5th wave Indonesia Family Life Survey (2014). Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 881436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, A., Meule, A., Reichenberger, J., & Blechert, J. (2017). Food cravings in everyday life: An EMA study on snack-related thoughts, cravings, and consumption. Appetite, 113, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, P. J., Appleton, K. M., Kessler, D., Peters, T. J., Gunnell, D., Hayward, R. C., Heatherley, S. V., Christian, L. M., McNaughton, S. A., & Ness, A. R. (2008). No effect ofn-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (EPA and DHA) supplementation on depressed mood and cognitive function: A randomised controlled trial. British Journal of Nutrition, 99(2), 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romaní-Pérez, M., Bullich-Vilarrubias, C., López-Almela, I., Liébana-García, R., Olivares, M., & Sanz, Y. (2021). The microbiota and the gut-brain axis in controlling food intake and energy homeostasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(11), 5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, N. D., Epstein, L. H., & Salvy, S.-J. (2009). Peer modeling influences girls’ snack intake. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 109(1), 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, C. J., & Margolis, R. L. (2018). Research domain criteria: Cutting edge neuroscience or galen’s humors revisited? Complex Psychiatry, 4(3), 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Sabate, R., & Sabaté, J. (2019). Consumer attitudes towards environmental concerns of meat consumption: A systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(7), 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K., & Hoffmann, I. (2011). Nutrition Ecology—A concept for systemic nutrition research and integrative problem solving. Ecology of Food and Nutrition, 50(1), 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S., Schilling, L., & Osenbrügge, N. (2021). Determinants of soft drink consumption among children and adolescents in developed countries—A systematic review. Central European Journal of Public Health, 29(4), 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnorr, S. L., Candela, M., Rampelli, S., Centanni, M., Consolandi, C., Basaglia, G., Turroni, S., Biagi, E., Peano, C., Severgnini, M., Fiori, J., Gotti, R., de Bellis, G., Luiselli, D., Brigidi, P., Mabulla, A., Marlowe, F., Henry, A. G., & Crittenden, A. N. (2014). Gut microbiome of the Hadza hunter-gatherers. Nature Communications, 5, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, E., Lee, S.-Y., & Prescott, M. P. (2022). Chili pepper preference development and its impact on dietary intake: A narrative review. Frontiers in Nutrition, 9, 1039207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J. J., Skunde, M., Sinno, M. H., Brockmeyer, T., Herpertz, S. C., Bendszus, M., Herzog, W., & Friederich, H. (2014). Impaired cross-talk between mesolimbic food reward processing and metabolic signaling predicts body mass index. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, P. A. M., Erkner, A., & de Graaf, C. (2010). Cephalic phase responses and appetite. Nutrition Reviews, 68(11), 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, C. (2021). What is the link between personality and food behavior? Current Research in Food Science, 5, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, C., & Piqueras-Fiszman, B. (2014). The perfect meal: The multisensory science of food and dining. John Wiley & Sons Ltd. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R. J. (2024). The psychological basis of hunger and its dysfunctions. Nutrition Reviews, 82(10), 1444–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, R. J., Bartlett, J., Wright, M., Hughes, A., Hill, B. J., Saluja, S., & Francis, H. M. (2023). The development of interoceptive hunger signals. Developmental Psychobiology, 65(2), e22374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, R. J., Francis, H. M., Attuquayefio, T., Gupta, D., Yeomans, M. R., Oaten, M. J., & Davidson, T. (2020). Hippocampal-dependent appetitive control is impaired by experimental exposure to a Western-style diet. Royal Society Open Science, 7(2), 191338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stice, E., Yokum, S., Bohon, C., Marti, N., & Smolen, A. (2010). Reward circuitry responsivity to food predicts future increases in body mass: Moderating effects of DRD2 and DRD4. NeuroImage, 50(4), 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwalska, J., & Bogdański, P. (2021). Social modeling and eating behavior: A narrative review. Nutrients, 13(4), 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swami, V., Hochstöger, S., Kargl, E., & Stieger, S. (2022). Hangry in the field: An experience sampling study on the impact of hunger on anger, irritability, and affect. PLoS ONE, 17(7), e0269629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szypula, J., Ahern, A., & Cheke, L. (2023). Imagine this: Visualising a recent meal as bigger reduces subsequent snack intake. Appetite, 181, 106411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H. S. G., Fischer, A. R. H., Tinchan, P., Stieger, M., Steenbekkers, L. P. A., & Van Trijp, H. C. M. (2015). Insects as food: Exploring cultural exposure and individual experience as determinants of acceptance. Food Quality and Preference, 42, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, F., Pretner, G., Iovina, R., Bainchie, G., Tessitore, S., & Iraldo, F. (2021). Drivers to green consumption: A systematic review. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23, 4826–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanarajah, S. E., DiFeliceantonio, A. G., Albus, K., Kuzmanovic, B., Rigoux, L., Iglesias, S., Hanßen, R., Schlamann, M., Cornely, O. A., Brüning, J. C., Tittgemeyer, M., & Small, D. M. (2023). Habitual daily intake of a sweet and fatty snack modulates reward processing in humans. Cell Metabolism, 35(4), 571–584.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trucco, E. M., Colder, C. R., Wieczorek, W. F., Lengua, L. J., & Hawk, L. W. (2014). Early adolescent alcohol use in context: How neighborhoods, parents, and peers impact youth. Development and Psychopathology, 26(2), 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, S., Maldonado-Araque, C., García-Torres, F., Goday, A., Bosch-Comas, A., Bordiú, E., Calle-Pascual, A., Carmena, R., Casamitjana, R., Castaño, L., Castell, C., Catalá, M., Delgado, E., Franch, J., Gaztambide, S., Girbés, J., Gomis, R., Gutiérrez, G., López-Alba, A., … Rojo-Martínez, G. (2014). Ambient temperature and prevalence of obesity in the Spanish population: The Di@bet.Es study. Obesity, 22(11), 2328–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Alvarez, M. A., Navas-Carretero, S., Palla, L., Martínez, J. A., & Almiron-Roig, E. (2021). Impact of portion control tools on portion size awareness, choice and intake: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients, 13(6), 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vartanian, L. R., Spanos, S., Herman, C. P., & Polivy, J. (2015). Modeling of food intake: A meta-analytic review. Social Influence, 10(3), 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzijl, C. L., Ahlich, E., Schlauch, R. C., & Rancourt, D. (2018). The role of craving in emotional and uncontrolled eating. Appetite, 123, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.-J., Shokri Kojori, E., Yuan, K., Wiers, C. E., Manza, P., Wong, C. T., Fowler, J. S., & Volkow, N. D. (2020). Inhibition of food craving is a metabolically active process in the brain in obese men. International Journal of Obesity, 44(3), 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardle, J. (1993). Psychology, food, health and nutrition. British Food Journal, 95(9), 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, L. L., & Brunstrom, J. M. (2016). Sensory specific satiety: More than ‘just’ habituation? Appetite, 103, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C., Zhu, H., Huang, C., Liang, X., Zhao, K., Zhang, S., He, M., Zhang, W., & He, X. (2022). Does a beautiful environment make food better—The effect of environmental aesthetics on food perception and eating intention. Appetite, 175, 106076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X., Ravichandran, S., Gee, G. C., Dong, T. S., Beltrán-Sánchez, H., Wang, M. C., Kilpatrick, L. A., Labus, J. S., Vaughan, A., & Gupta, A. (2024). Social isolation, brain food cue processing, eating behaviors, and mental health symptoms. JAMA Network Open, 7(4), e244855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X., Wang, H., Kilpatrick, L. A., Dong, T. S., Gee, G. C., Labus, J. S., Osadchiy, V., Beltran-Sanchez, H., Wang, M. C., Vaughan, A., & Gupta, A. (2023). Discrimination exposure impacts unhealthy processing of food cues: Crosstalk between the brain and gut. Nature Mental Health, 1(11), 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stroebele-Benschop, N.; Hedrih, V.; Behairy, S.; Pervaiz, N.; Morphew-Lu, E. Conceptual Framework for Nutritional Psychology as a New Field of Research. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15081007
Stroebele-Benschop N, Hedrih V, Behairy S, Pervaiz N, Morphew-Lu E. Conceptual Framework for Nutritional Psychology as a New Field of Research. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(8):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15081007
Chicago/Turabian StyleStroebele-Benschop, Nanette, Vladimir Hedrih, Shereen Behairy, Nabila Pervaiz, and Ephi Morphew-Lu. 2025. "Conceptual Framework for Nutritional Psychology as a New Field of Research" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 8: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15081007
APA StyleStroebele-Benschop, N., Hedrih, V., Behairy, S., Pervaiz, N., & Morphew-Lu, E. (2025). Conceptual Framework for Nutritional Psychology as a New Field of Research. Behavioral Sciences, 15(8), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15081007







