Speed of Processing and Personality: The Influence of Personality and Extrinsic Feedback on the Performance of Cognitive Tasks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Outcome Measures
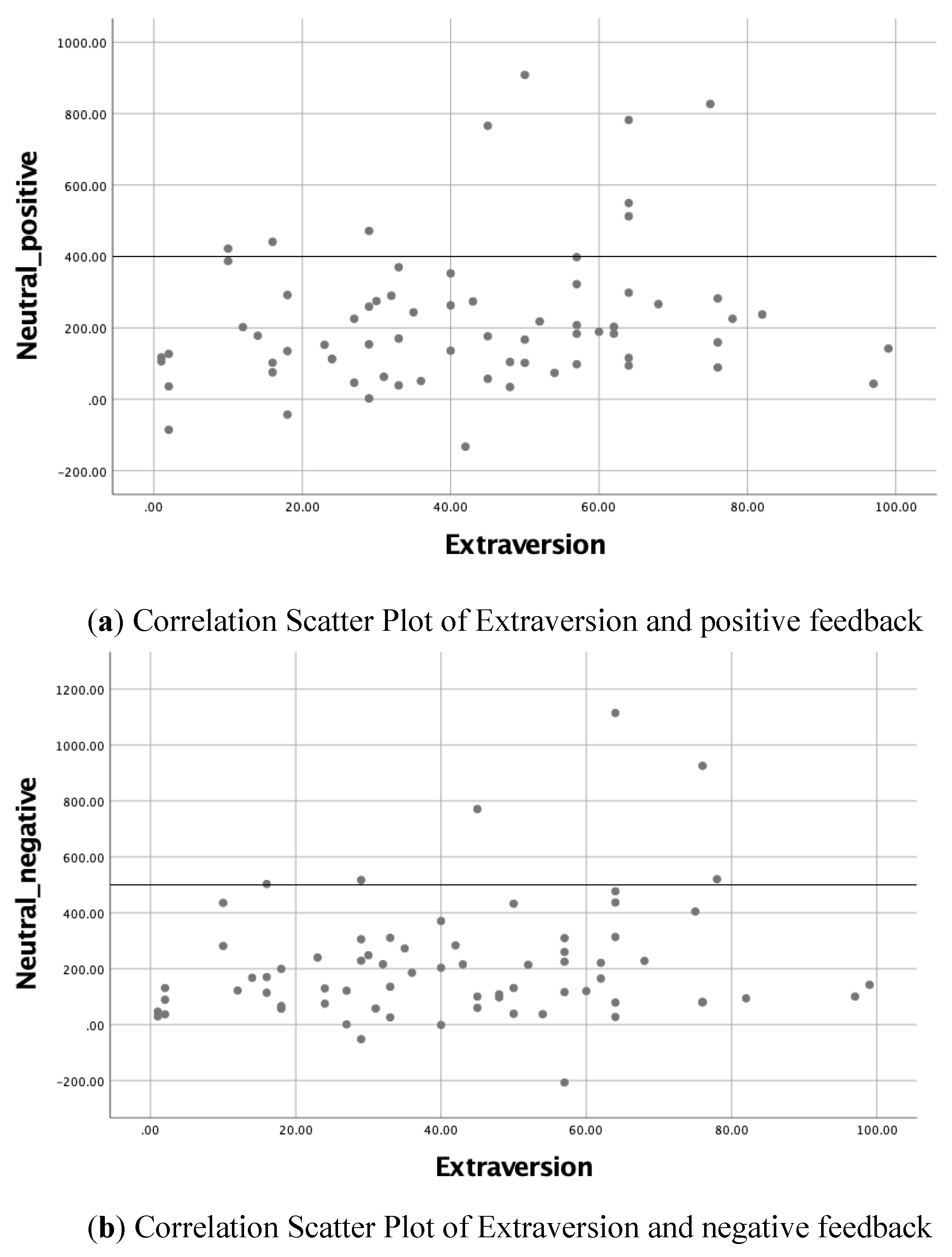
2.4. Statistical Method
3. Results
3.1. General Findings
3.2. Major Findings
3.2.1. Hypothesis 1a
3.2.2. Hypothesis 2
3.2.3. Hypothesis 4
3.3. Other Influences and Validity of the Sample
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sequence 1 | Sequence 2 | Sequence 3 | Sequence 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Filling in the demographic questions displayed by Open Sesame | |||
| Step 2 | Randomized Stroop Task | Randomized Stroop Task | Randomized Stroop Task | Randomized Stroop Task |
| Step 3 | TMT Version A | TMT Version A | TMT Version B | TMT Version B |
| Step 4 | Positive Feedback | Negative Feedback | Positive Feedback | Negative Feedback |
| Step 5 | Randomized Stroop Task | Randomized Stroop Task | Randomized Stroop Task | Randomized Stroop Task |
| Step 6 | TMT Version B | TMT Version B | TMT Version A | TMT Version A |
| Step 7 | Negative Feedback | Positive Feedback | Negative Feedback | Positive Feedback |
| Step 8 | Randomized Stroop Task | Randomized Stroop Task | Randomized Stroop Task | Randomized Stroop Task |
| Step 9 | Complete The International Personality Item Pool Presentation of the NEO PI-R (IPIP-NEO 120) questionnaire | |||
| Mean | Median | Std. Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extraversion | 41.88 | 74 | 23.64 |
| Agreeableness | 51.47 | 52.5 | 27.87 |
| Conscientiousness | 45.48 | 46 | 25.69 |
| Neuroticism | 46.41 | 45 | 26.07 |
| Openness | 39.27 | 43 | 24.20 |
| Neutral_RT | 1087 | 952 | 676.53 |
| Positive_RT | 866 | 748 | 1458.89 |
| Negative_RT | 876 | 794 | 2407.02 |
| Neutral_positive(RT) | 220 | 177 | 200.19 |
| Neutral_negative(RT) | 210 | 153 | 212.80 |
| Neutral_RT | Beta | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extraversion | 0.194 | 1.456 | 0.150 |
| Agreeableness | −0.204 | −1.607 | 0.113 |
| Conscientiousness | −0.093 | −0.706 | 0.483 |
| Neuroticism | −0.142 | −1.136 | 0.260 |
| Openness | 0.157 | 1.268 | 0.210 |
| Positive_RT | |||
| Extraversion | 0.147 | 1.075 | 0.287 |
| Agreeableness | −0.120 | −0.919 | 0.361 |
| Conscientiousness | −0.096 | −0.708 | 0.481 |
| Neuroticism | −0.138 | −1.066 | 0.291 |
| Openness | 0.125 | 0.981 | 0.330 |
| Negative_RT | |||
| Extraversion | 0.159 | 1.166 | 0.248 |
| Agreeableness | −0.156 | −1.201 | 0.234 |
| Conscientiousness | −0.076 | −0.561 | 0.577 |
| Neuroticism | −0.105 | −0.817 | 0.417 |
| Openness | 0.137 | 1.083 | 0.283 |
References
- Kearsley, G. Feedback/Reinforcement. In Explorations in Learning & Instruction: The Theory into Practice Database; Jacksonville State University Encyclopedia of Psychology: Jacksonville, AL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Krenn, B.; Würth, S.; Hergovich, A. The Impact of Feedback on Goal Setting and Task Performance: Testing the Feedback Intervention Theory. Swiss J. Psychol. 2013, 72, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, C.; Scheier, M. Control theory: A useful conceptual framework for personality–social, clinical, and health psychology. Psychol. Bull. 1982, 92, 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huitt, W. The Importance of Feedback in Human Behavior; Valdosta State University: Valdosta, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Brunot, S.; Huguet, P.; Monteil, J.M. Performance feedback and self-focused attention in the classroom: When past and present interact. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 2000, 3, 271–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNisi, A.; Kluger, A. Feedback effectiveness: Can 360-degree appraisals be improved? Acad. Manag. Exec. 2000, 14, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrae, R.R.; John, O. An Introduction to the Five-Factor Model and Its Applications. J. Personal. 1992, 60, 175–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.T., Jr.; McCrae, R.R. Personality in Adulthood: A Five-Factor Theory Perspective; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, G.; Deary, I.J.; Whiteman, M.C. Personality Traits; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, W.; Shoda, Y. A cognitive-affective system theory of personality: Re-conceptualizing situations, dispositions, dynamics, and invariance in personality structure. Psychol. Rev. 1995, 102, 246–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, T.A.; Zapata, C.P. The person-situation debate revisited: Effect of situation strength and trait activation on the validity of the big five personality traits in predicting job performance. Acad. Manag. J. 2015, 58, 1149–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, B.W.; Kuncel, N.R.; Shiner, R.L.; Caspi, A.; Goldberg, L.R. The power of personality: The comparative validity of personality traits, socioeconomic status, and cognitive ability for predicting important life outcomes. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2007, 2, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.; Tellegen, A. Toward a consensual structure of mood. Psychol. Bull. 1985, 98, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.; Moeller, S.; Fetterman, A. Neuroticism and Responsiveness to Error Feedback: Adaptive Self-Regulation Versus Affective Reactivity. J. Personal. 2010, 78, 1469–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluger, A.N.; DeNisi, A. The effects of feedback interventions on performance: A historical review, a meta-analysis, and a preliminary feedback intervention theory. Psychol. Bull. 1996, 119, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fremont, T.; Means, G.H.; Means, R.S. Anxiety as a Function of Task Performance Feedback and Extra Version-Introversion. Psychol. Rep. 1970, 27, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lischetzke, T.; Eid, M. Why extraverts are happier than introverts: The role of mood regulation. J. Personal. 2006, 74, 1127–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdfelder, E.; Faul, F.; Buchner, A. GPOWER: A general power analysis program. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 1996, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenn, B.; Wuerth, S.; Hergovich, A. Individual differences concerning the impact of feedback-specifying the role of core self-evaluations. Studia Psychol. 2013, 55, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, T.A.; Ilies, R. Relationship of personality to performance motivation: A meta-analytic review. J. Appl. Psychol. 2002, 87, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroop, J.R. Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J. Exp. Psychol. 1935, 18, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, C.M. The stroop effect. Encycl. Colour Sci. Technol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitan, R.M. The relation of the trail making test to organic brain damage. J. Consult. Psychol. 1955, 19, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotek, W.; Łyskawa, W.; Kluzik, A.; Grześkowiak, M.; Podlewski, R.; Żaba, Z.; Drobnik, L. Evaluation of the Trail Making Test and interval timing as measures of cognition in healthy adults: Comparisons by age, education, and gender. Med Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2014, 20, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Alloway, T.P. Working memory and executive function profiles of individuals with borderline intellectual functioning. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2010, 54, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Cubillo, I.; Perianez, J.A.; Adrover-Roig, D.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, J.M.; Rios-Lago, M.; Tirapu, J.E.E.A.; Barcelo, F. Construct validity of the Trail Making Test: Role of task-switching, working memory, inhibition/interference control, and visuomotor abilities. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2009, 15, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, L.R. International Personality Item Pool: A Scientific Collaboratory for the Development of Advanced Measures of Personality and Other Individual Differences. Available online: ipip.ori.org/ipip/1999 (accessed on 14 August 2002).
- Hoddes, E.; Dement, W.; Zarcone, V. The history and use of the Stanford Sleepiness Scale. Psychophysiology 1972, 9, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Maples, J.L.; Guan, L.; Carter, N.T.; Miller, J.D. A test of the International Personality Item Pool representation of the Revised NEO Personality Inventory and development of a 120-item IPIP-based measure of the five-factor model. Psychol. Assess. 2014, 26, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, S.T.; Arthur, W., Jr. Feedback acceptance in developmental assessment centers: The role of feedback message, participant personality, and affective response to the feedback session. J. Organ. Behav. Int. J. Ind. Occup. Organ. Psychol. Behav. 2008, 29, 681–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.S.; Amin, M.N. Personality and students’ academic achievement: Interactive effects of conscientiousness and agreeableness on students’ performance in principles of economics. Soc. Behav. Personal. Int. J. 2006, 34, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Reus, T.H.; Zhu, P.; Roelofsen, E.M. The acquisitive nature of extraverted CEOs. Adm. Sci. Q. 2018, 63, 370–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterston, E. Age-Related Differences in Negative Emotion Identification: The Effects of Cognitive Ability, Emotional Intelligence and Personality. In Psychology Undergraduate Thesis Collection; The University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dauvier, B.; Pavani, J.B.; Le Vigouroux, S.; Kop, J.L.; Congard, A. The interactive effect of neuroticism and extraversion on the daily variability of affective states. J. Res. Personal. 2019, 78, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keng, S.L.; Lee, Y.; Drabu, S.; Hong, R.Y.; Chee, C.Y.; Ho, C.S.; Ho, R.C. Construct Validity of the McLean Screening Instrument for Borderline Personality Disorder in Two Singaporean Samples. J. Personal. Disord. 2019, 33, 450–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.F.; Tang, T.B.; Yu, R.; Tam, W.W.; Tran, B.; Quek, T.T.; Hwang, S.-H.; Chang, C.W.; Ho, C.S.; Ho, R.C. Cortical haemodynamic response measured by functional near infrared spectroscopy during a verbal fluency task in patients with major depression and borderline personality disorder. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrick, M.R.; Mount, M.K.; Strauss, J.P. Conscientiousness and performance of sales representatives: Test of the mediating effects of goal setting. J. Appl. Psychol. 1993, 78, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajor, B. The relationship between selection optimization with compensation, conscientiousness, motivation, and performance. J. Vocat. Behav. 2003, 63, 347–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, V.; Peterson, J.B. Improving the effectiveness of performance feedback by considering personality traits and task demands. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197810. [Google Scholar]
- Gellatly, I.R. Conscientiousness and task performance: Test of cognitive process model. J. Appl. Psychol. 1996, 81, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, L.; Burke, L.; Barrick, M.; Mount, M. The interactive effects of conscientiousness and agreeableness on job performance. J. Appl. Psychol. 2002, 87, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, L.F. Occupational stress, coping and strain: The combined/interactive effect of the Big Five traits. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2006, 41, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.Y.; Tam, W.W.; Lu, Y.; Ho, C.S.; Zhang, M.W.; Ho, R.C. Prevalence of Depression in the Community from 30 Countries between 1994 and 2014. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniapillai, M.; Mansur, R.B.; Zuckerman, H.; Park, C.; Lee, Y.; Iacobucci, M.; Cao, B.; Ho, R.; Lin, K.; Phan, L. Association between cognitive function and performance on effort based decision making in patients with major depressive disorder treated with Vortioxetine. Compr. Psychiatry 2019, 94, 152113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRS Scotland Statistics. Mid-Year Population Estimates Scotland, Mid-2017; National Records of Scotland: Edinburgh, UK, 2018.
| Median Mean | t | df | p | 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Neutral_positive(RT)_ Neutral_negative(RT) | 9 | 0.485 | 69 | 0.629 | −30 | 49 |
| Positive_RT_ Negative_RT | −9 | −0.485 | 69 | 0.629 | −49 | 30 |
| Neutral_RT_ Positive_RT | 220 | 9.221 | 69 | 0.000 | 172 | 268 |
| Neutral_RT_ Negative_RT | 221 | 8.293 | 69 | 0.000 | 160 | 261 |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Neutral_positive | 0.673 ** | −0.059 | −0.037 | −0.022 | 0.156 | −0.003 | 0.205 * | −0.212 * | −0.041 | −0.110 | 0.153 |
| 2. Neutral_negative | 0.002 | −0.019 | 0.009 | 0.150 | 0.046 | 0.201 * | −0.162 | −0.050 | −0.162 | 0.139 | |
| 3. Age | −0.086 | −0.044 | −0.303 ** | −0.096 | 0.175 | 0.292 ** | −0.008 | −0.051 | 0.076 | ||
| 4. Gender | 0.142 | 0.001 | 0.029 | −0.097 | −0.053 | 0.044 | −0.030 | 0.011 | |||
| 5. Employment | −0.103 | 0.393 ** | −0.112 | −0.268 * | −0.150 | −0.089 | −0.021 | ||||
| 6. Education | 0.096 | 0.089 | −0.033 | 0.136 | −0.127 | 0.294 ** | |||||
| 7. Sleepiness | 0.003 | 0.014 | −0.098 | 0.012 | 0.150 | ||||||
| 8. Extraversion | 0.149 | 0.315 ** | −0.339 ** | 0.309 ** | |||||||
| 9. Agreeableness | 0.382 ** | −0.137 | 0.167 | ||||||||
| 10. Conscientiousness | −0.235 * | 0.163 | |||||||||
| 11. Neuroticism | −0.063 | ||||||||||
| 12. Openness |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wong, M.Y.C.; Chung, P.K.; Leung, K.M. Speed of Processing and Personality: The Influence of Personality and Extrinsic Feedback on the Performance of Cognitive Tasks. Behav. Sci. 2020, 10, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10040076
Wong MYC, Chung PK, Leung KM. Speed of Processing and Personality: The Influence of Personality and Extrinsic Feedback on the Performance of Cognitive Tasks. Behavioral Sciences. 2020; 10(4):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10040076
Chicago/Turabian StyleWong, Ming Yu Claudia, Pak Kwong Chung, and Ka Man Leung. 2020. "Speed of Processing and Personality: The Influence of Personality and Extrinsic Feedback on the Performance of Cognitive Tasks" Behavioral Sciences 10, no. 4: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10040076
APA StyleWong, M. Y. C., Chung, P. K., & Leung, K. M. (2020). Speed of Processing and Personality: The Influence of Personality and Extrinsic Feedback on the Performance of Cognitive Tasks. Behavioral Sciences, 10(4), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10040076





