Variability and Trends in Dust Storm Frequency on Decadal Timescales: Climatic Drivers and Human Impacts
Abstract
1. Introduction
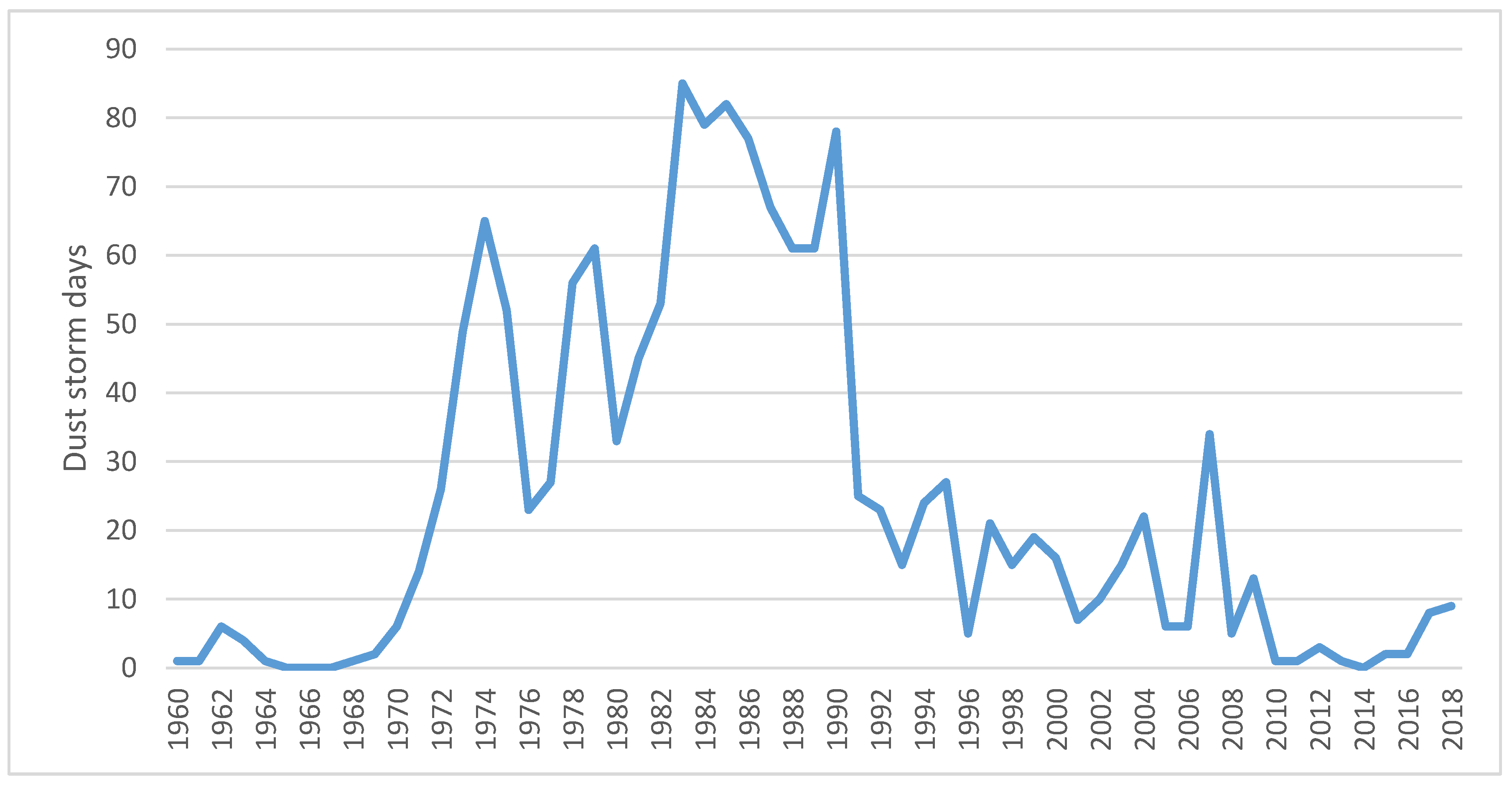
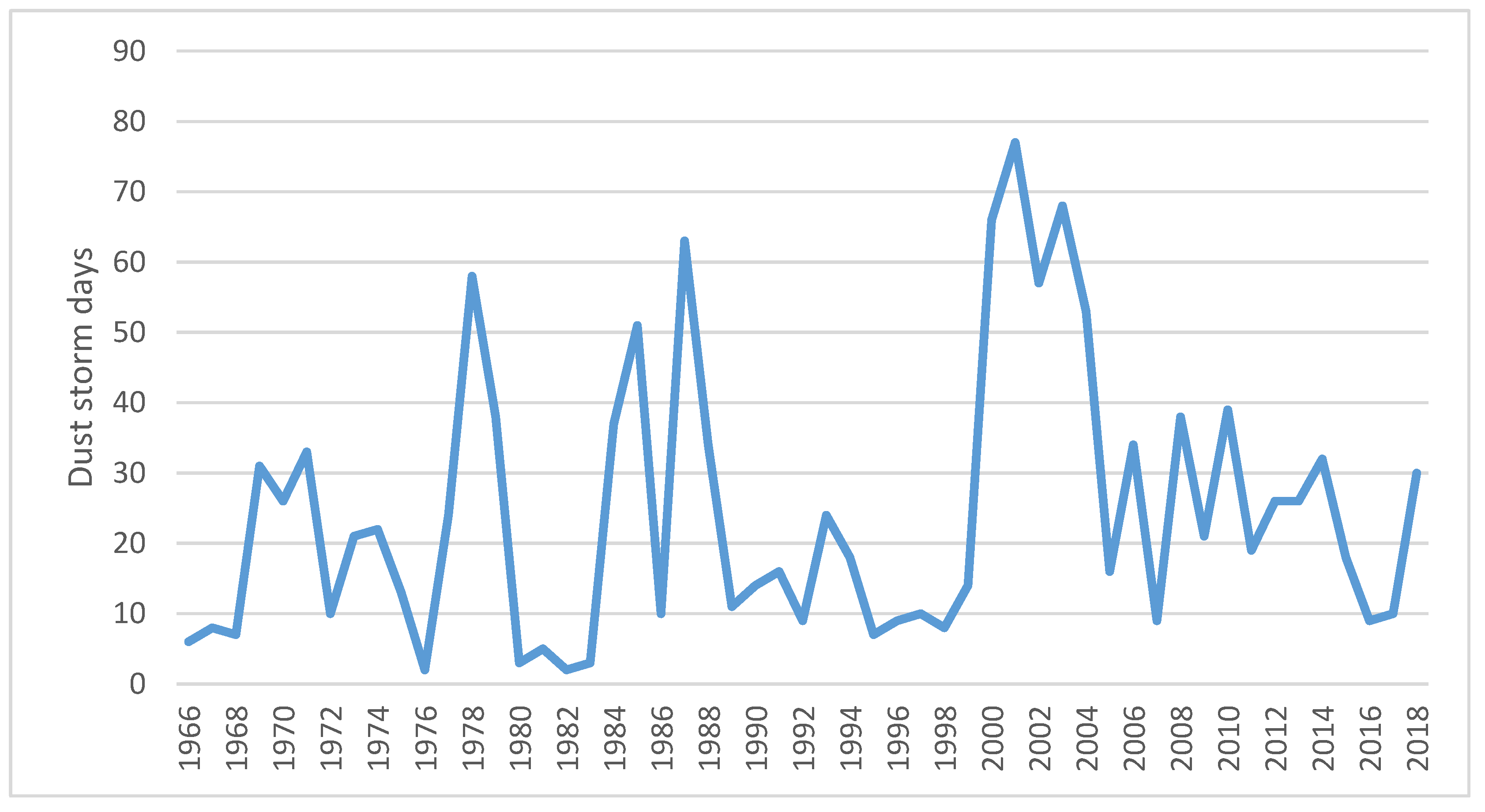
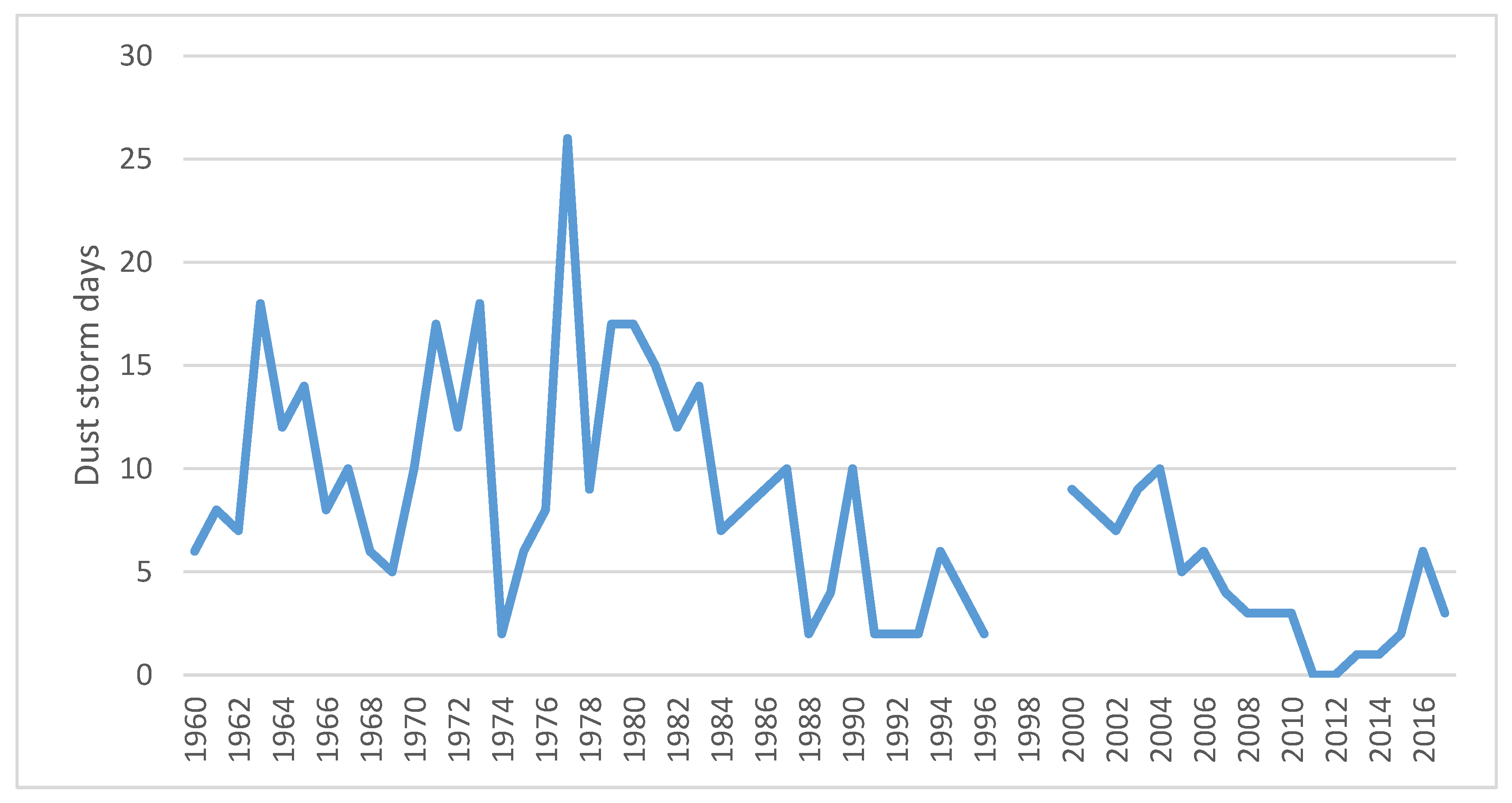
2. Sahel/Sahara: Nouakchott, Mauritania
3. Hamoun Basin: Zabol, Iran
4. Northeast Asia: Minqin, China
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goudie, A.S.; Middleton, N.J. Desert Dust in the Global System; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; McTainsh, G.H.; Mikami, M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Wang, X.; Yoon, S. Dust cycle: An emerging core theme in Earth system science. Aeolian Res. 2011, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepanski, K. Transport of mineral dust and its impact on climate. Geosciences 2018, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.J. Desert dust hazards: A global review. Aeolian Res. 2017, 24, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M.; Ginoux, P.; Torres, O.; Nicholson, S.E.; Gill, T.E. Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the Nimbus 7 Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) absorbing aerosol product. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 2-1–2-31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.; Gill, T. Challenges and opportunities in atmospheric dust emission, chemistry, and transport. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, ES115–ES118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S.; Middleton, N.J. The changing frequency of dust storms through time. Clim. Chang. 1992, 20, 197–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, C.; Lambert, C.E.; Dulac, F.; Dayan, U. Control of atmospheric export of dust from North Africa by the North Atlantic Oscillation. Nature 1997, 387, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, G.; Lambert, F. In and out of glacial extremes by way of dust−climate feedbacks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2026–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issanova, G.; Abuduwaili, J.; Galayeva, O.; Semenov, O.; Bazarbayeva, T. Aeolian transportation of sand and dust in the Aral Sea region. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3213–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegen, I.; Werner, M.; Harrison, S.P.; Kohfeld, K.E. Relative importance of climate and land use in determining present and future global soil dust emission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Luo, C. A less dusty future? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M.; Mayol-Bracero, O.L. Understanding the transport and impact of African dust on the Caribbean basin. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Kreycik, P. Dust generation and drought patterns in Africa from helium-4 in a modern Cape Verde coral. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L20820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evan, A.T.; Flamant, C.; Gaetani, M.; Guichard, F. The past, present and future of African dust. Nature 2016, 531, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Ballantine, J.A.; Feddema, J.; Ramankutty, N. Global trends in visibility: Implications for dust sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 3309–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Klose, M.; Wyrwoll, K.H. Recent global dust trend and connections to climate forcing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 11–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Fu, Q. Expansion of global drylands under a warming climate. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10081–10094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yu, H.; Guan, X.; Wang, G.; Guo, R. Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A. Increasing drought under global warming in observations and models. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, B.; Ginoux, P. Projection of American dustiness in the late 21 st century due to climate change. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuillée, P. 1721: Observation sur une pluie de sable dans la mer Atlantique pre´cede´e d’une aurore bore´ale. In Histoire de l’Academie Royale des Sciences avec les Mémoires de Mathématique et Physique; L’Imprimerie Royal: Paris, France, 1719; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Darwin, C. An account of the Fine Dust which often falls on Vessels in the Atlantic Ocean. Q. J. Geol. Soc. 1846, 2, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.J. Effect of drought on dust production in the Sahel. Nature 1985, 316, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M.; Lamb, P.J. African droughts and dust transport to the Caribbean: Climate change implications. Science 2003, 302, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folland, C.K.; Palmer, T.N.; Parker, D.E. Sahel rainfall and worldwide sea temperatures, 1901–1985. Nature 1986, 320, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, D.A.; Heald, C.L.; Prospero, J.M. What controls the recent changes in African mineral dust aerosol across the Atlantic? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5735–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Dong, S.; Evan, A.T.; Foltz, G.R.; Lee, S.K. Multidecadal covariability of North Atlantic sea surface temperature, African dust, Sahel rainfall, and Atlantic hurricanes. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 5404–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, M.; Mahowald, N.M.; Conley, A.J.; Collins, W.D.; Fillmore, D.W.; Zender, C.S.; Coleman, D.B. Impact of desert dust radiative forcing on Sahel precipitation: Relative importance of dust compared to sea surface temperature variations, vegetation changes, and greenhouse gas warming. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 1445–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kergoat, L.; Guichard, F.; Pierre, C.; Vassal, C. Influence of dry-season vegetation variability on Sahelian dust during 2002–2015. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 5231–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.J.; Goudie, A.S. Saharan dust: Sources and trajectories. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 2001, 26, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, S.M.; Knippertz, P.; Marsham, J.H. Are vegetation-related roughness changes the cause of the recent decrease in dust emission from the Sahel? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1868–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozlaker, A.; Prospero, J.M.; Price, J.; Chellam, S. Linking Barbados mineral dust aerosols to North African sources using elemental composition and radiogenic Sr, Nd, and Pb isotope signatures. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 1384–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.S.; Middleton, N.J. Desertification: Exploding the Myth; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Behnke, R.; Mortimore, M. The End of Desertification? Disputing Environmental Change in the Drylands; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Touré, A.A.; Tidjani, A.D.; Rajot, J.L.; Bouet, C.; Garba, Z.; Marticorena, B.; Ambouta, K.J.M. Quantification des flux d’érosion éolienne au cours d’une transition champ-jachère au Sahel (Banizoumbou, Niger). Physio-Géo. Géogr. Phys. Environ. 2018, 12, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, C.; Kergoat, L.; Hiernaux, P.; Baron, C.; Bergametti, G.; Rajot, J.L.; Abdourhamane Touré, A.; Okin, G.S.; Marticorena, B. Impact of agropastoral management on wind erosion in Sahelian croplands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, P.; Laghdaf, M.B.O.M.; Lemine, S.O.M.; Gassani, J. Estimation of air quality degradation due to Saharan dust at Nouakchott, Mauritania, from horizontal visibility data. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 178, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanguy, P. L’urbanisation irrégulière à Nouakchott: 1960–2000. L’institution de la norme légal/illégal. Insaniyat. Revue Algérienne d’anthropologie Sci. Soc. 2003, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N. Drought in the Sahel. Science 2003, 302, 999–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Fink, A.H.; Funk, C. Assessing recovery and change in West Africa’s rainfall regime from a 161-year record. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 3770–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littaye, A.; Ould Ahmed, S.C. The dynamics of the coastal landscapes over the last decades: Wind drivers for change along the North Western Mauritanian coast. J. Earth Sci. Clim. Chang. 2018, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berte, C.J. Fighting Sand Encroachment: Lessons from Mauritania; FAO Forestry Paper 158; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Na, Z.; Yongdong, W.; Jiaqiang, L.; Soule, A.O.; Xinwen, X.; Fall, A.; Mohamed, L.S. Determination of the Status of Desertification in the Capital of Mauritania and Development of a Strategy for Combating It. J. Resour. Ecol. 2018, 9, 306–316. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, N.J. A geography of dust storms in south-west Asia. J. Climatol. 1986, 6, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Choobari, O.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Sturman, A. The “wind of 120 days” and dust storm activity over the Sistan Basin. Atmos. Res. 2014, 143, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrooz, R.D.; Esmaili-Sari, A.; Bahramifar, N.; Kaskaoutis, D.G. Analysis of the TSP, PM10 concentrations and water-soluble ionic species in airborne samples over Sistan, Iran during the summer dusty period. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, A.; Ahmadi, H.; Ekhtesasi, M.R.; Panjehkeh, N.; Ghanbari, A. Environmental and socio-economic impacts of dust storms in Sistan Region, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2009, 66, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Eriksson, P.G.; Qiang, M.; Gupta, P. Dust storms and their horizontal dust loading in the Sistan region, Iran. Aeolian Res. 2012, 5, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaljahi, M.; Bagheri, S.; Keykhaei, K.R. The Effects of Haze on General Health of Women Employed in Zabol University of Medical Sciences in 2018. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2019, 16, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Goudie, A.S.; Kahn, R.A. Dryness of ephemeral lakes and consequences for dust activity: The case of the Hamoun drainage basin, southeastern Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 552–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharazmi, R.; Tavili, A.; Rahdari, M.R.; Chaban, L.; Panidi, E.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Monitoring and assessment of seasonal land cover changes using remote sensing: A 30-year (1987–2016) case study of Hamoun Wetland, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. History of Environmental Change in the Sistan Basin Based on Satellite Image Analysis: 1976–2005; United Nations Environment Programme: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Behrooz, R.D.; Gholami, H.; Telfer, M.W.; Jansen, J.D.; Fathabadi, A. Using GLUE to pull apart the provenance of atmospheric dust. Aeolian Res. 2019, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, E.; Bozorgy, B.; Vekerdy, Z.; Meijer, K. Limits to agricultural growth in the sistan closed inland delta, Iran. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2008, 22, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, J.W. Geology, water, and wind in the lower Helmand Basin, southern Afghanistan. In U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2006–5182; U.S. Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2006; 40p. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Q.; Sun, X.; Yang, J.; Pan, B.; Zhao, S.; Wang, L. Dust storms in northern China: Long-term spatiotemporal characteristics and climate controls. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6683–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Sohn, B.J. Recent increasing trend in dust frequency over Mongolia and Inner Mongolia regions and its association with climate and surface condition change. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4611–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Guo, L.; Li, N.; Chen, J.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, M.; Rao, Y.; Wang, C.; Ma, L. Earlier vegetation green-up has reduced spring dust storms. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Wang, B.; Qian, W. Why do dust storms decrease in northern China concurrently with the recent global warming? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L18702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Quan, L.; Shi, S. Variations of the dust storm in China and its climatic control. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1216–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Wang, H.J. Antarctic Oscillation and the Dust Weather Frequency in North China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L10201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Washington, R. Arctic oscillation and the interannual variability of dust emissions from the Tarim Basin: A TOMS AI based study. Clim. Dyn. 2010, 35, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.J.; Han, Z.W.; Wang, M.X.; Zhang, X.Y. Dust storm weather in China: New characteristics and origins. Quat. Sci. 2002, 22, 374–380. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, N.J. Rangeland management and climate hazards in drylands: Dust storms, desertification and the overgrazing debate. Nat. Hazards 2016, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhang, C.X.; Hasi, E.; Dong, Z.B. Has the Three Norths Forest Shelterbelt Program solved the desertification and dust storm problems in arid and semiarid China? J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalintai, B.; Yanbo, L.; Jianjun, C. The Eurasian Steppe: History of Utilization and Policies on the Rangeland. In Restoring Community Connections to the Land; Ferna’ndez-Gime´nez, M.E., Wang, X., Baival, B., Klein, J., Reid, R., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2011; pp. 51–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, D.E.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Rui, L.I. Effects of the grain-for-green program on soil erosion in China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2015, 27, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Li, X. Does the Green Great Wall effectively decrease dust storm intensity in China? A study based on NOAA NDVI and weather station data. Land Use Policy 2015, 43, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.; Li, W.; Tian, L.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, H.; Fang, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, G.; Mu, X.; et al. Multiple afforestation programs accelerate the greenness in the ‘Three North’ region of China from 1982 to 2013. Ecol. Ind. 2016, 61, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; He, B.; Lei, T.; Wang, Q. Increasing terrestrial vegetation activity of ecological restoration program in the Beijing–Tianjin sand source region of China. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Fang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhu, B. NDVI-indicated decline in desertification in China in the past two decades. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, T.; Rueff, H.; Middleton, N. Contraction of the Gobi Desert, 2000–2012. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shen, S.; Yang, F.; He, Q.; Ali, M.; Huo, W.; Liu, X. Spatial and temporal variations of blowing dust events in the Taklimakan Desert. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 125, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Man, D.; Luo, W.; Qian, G.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, S.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, S. Horizontal aeolian sediment flux in the Minqin area, a major source of Chinese dust storms. Geomorphology 2010, 116, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Shang, K. Effects of Long-Term Dust Exposure on Human Respiratory System Health in Minqin County, China. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2015, 70, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Lu, B. Dust events as a risk factor for daily hospitalization for respiratory and cardiovascular diseases in Minqin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7048–7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Qu, J.; Zu, R.; Fang, H. Temporal variations of sandstorms in Minqin oasis during 1954–2000. Environ. Geol. 2005, 49, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Liao, J.; Hsing, Y.; Huang, C.; Liu, F. Policies, land use, and water resource management in an arid oasis ecosystem. Environ. Manag. 2015, 55, 1036–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.W.; Chen, F.H. Study on the change of Minqin Oasis since recent twenty years on digital Rs images. Arid. Zone Res. 2002, 19, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.C.; Qu, J.J.; Liu, Q.H. Environmental degradation in the Minqin oasis in northwest China during recent 50 years. J. Environ. Syst. 2004, 31, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhao, S.; Pan, B.; Liu, C.; Zhang, D.; Wu, T. Climatological analysis of dust storms in the area surrounding the Tengger Desert during 1960–2007. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemi, T.; Seino, N. Dust storms and cyclone tracks over the arid regions in east Asia in spring. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D18S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crofts, R. Healing the Land; Soil Conservation Service of Iceland: Reykjavik, Iceland, 2011; p. 212.
- Fox, T.A.; Barchyn, T.E.; Hugenholtz, C.H. Successes of soil conservation in the Canadian Prairies highlighted by a historical decline in blowing dust. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 014008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Middleton, N. Variability and Trends in Dust Storm Frequency on Decadal Timescales: Climatic Drivers and Human Impacts. Geosciences 2019, 9, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9060261
Middleton N. Variability and Trends in Dust Storm Frequency on Decadal Timescales: Climatic Drivers and Human Impacts. Geosciences. 2019; 9(6):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9060261
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiddleton, Nick. 2019. "Variability and Trends in Dust Storm Frequency on Decadal Timescales: Climatic Drivers and Human Impacts" Geosciences 9, no. 6: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9060261
APA StyleMiddleton, N. (2019). Variability and Trends in Dust Storm Frequency on Decadal Timescales: Climatic Drivers and Human Impacts. Geosciences, 9(6), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9060261




