Abstract
Monthly meteorological data from 27 observation stations provided by the Presidency of Meteorology and Environment (PME) of Saudi Arabia were used to analyze the spatial and temporal distribution of atmospheric dust in Saudi Arabia between 2000 and 2016. These data were used to analyze the effects of environmental forcing on the occurrence of dust storms across Saudi Arabia by considering the relationships between dust storm frequency and temperature, precipitation, and wind variables. We reveal a clear seasonality in the reported incidence of dust storms, with the highest frequency of events during the spring. Our results show significant positive relationships (p < 0.005) between dust storm occurrence and wind speed, wind direction, and precipitation. However, we did not detect a significant relationship with temperature. Our results reveal important spatial patterns, as well as seasonal and inter-annual variations, in the occurrence of dust storms in Saudi Arabia. For instance, the eastern part of the study area experienced an increase in dust storm events over time, especially in the region near Al-Ahsa. Similarly, an increasing trend in dust storms was also observed in the west of the study area near Jeddah. However, the occurrence of dust storm events is decreasing over time in the north, in areas such as Hail and Qaisumah. Overall, the eastern part of Saudi Arabia experiences the highest number of dust storms per year (i.e., 10 to 60 events), followed by the northern region, with the south and the west having fewer dust storm events (i.e., five to 15 events per year). In addition, our results showed that the wind speeds during a dust storm are 15–20 m/s and above, while, on a non-dust day, the wind speeds are approximately 10–15 m/s or lower. Findings of this study provide insight into the relationship between environmental conditions and dust storm occurrence across Saudi Arabia, and a basis for future research into the drivers behind these observed spatio-temporal trends.
1. Introduction
Dust storms are natural phenomena which usually occur in desert areas [1,2,3]. These events happen as a result of strong winds which raise dust and sand from deserts and surrounding areas and carry it over large distances. The African and Asian deserts are the major sources of dust worldwide [4,5,6]. In addition to the African Sahara region, the Middle East is the world region most affected by dust storms [3,7,8,9], and within the Middle East, it is well known that the Arabian Peninsula is one of the largest source areas of dust storms [10,11]. The vast dunes and deserts on the Arabian Peninsula and surrounding topographically complex terrain, characterized by very low amounts of precipitation and sparse vegetation cover, are the essential ingredients to rouse dust into the air [12,13,14,15]. Furthermore, the dominant northwesterly winds contribute to the extensive mobilization of dust across the peninsula (e.g., the Al Shamaal winds) [16,17,18,19].
Recent studies showed that dust storm outbreaks are associated with high wind speeds in the regions of Saudi Arabia and Iraq [3], as well as in Southwest Asia [20]. Overall, the highest frequency of dust storms is recorded in the spring, mostly originating from the Karakum desert, located in in the west of Turkmenistan and considered as one of the main sources of dust within Asia [21]. Also, the Sistan Basin in Iran is an important dust storm source area in southwest Asia [20]. Awad et al. [22] and Mashat et al. [23] illustrated that the characteristics of synoptic weather conditions (i.e., the configuration of high-pressure and low-pressure systems) are associated with dust storm activity over the north and southwest of Saudi Arabia. Furthermore, Rashki et al. [24] highlighted that the Jazmurian basin, located in the southeast of Iran, produces dust storms which affect the northern part of the Arabian Sea and the surrounding areas. Recent evidence suggests that the occurrence of dust storm events is correlated with the Asian summer monsoon system, as well as the activity of both the Shamal and Levar winds over the Arabian Sea during the summer season [25].
Anthropogenic activities such as the construction of dams are likely to be associated with increasing dust storm incidence [26,27]. For instance, research showed that the construction of the Ilisu Dam in Turkey reduced the downstream discharge of the Tigris and Euphrates River, which resulted in more periods of extensive drought, triggering dust storms in the wider region [28,29,30,31]. Moreover, overgrazing by cattle and off-road driving, which can lead to serious soil degradation, are considered as important additional contributing factors in mobilizing sand and dust [1,32,33,34]. Finally, recent and ongoing conflicts in the Middle East region (e.g., Syrian civil war) and associated failures in land management, such as the abandonment of cultivated land, should also be considered as important factors contributing to the occurrence of dust storms in the region.
Although dust storms can occur throughout the entire year in Saudi Arabia [10,31,35,36,37], on the local scale, these phenomena are known to be variable in space and time. Previous studies showed that the peak in dust storm activity occurs at different times of year in different regions; for instance, in the southern region near the Red Sea coast, dust storms mostly occur during the middle of the winter season (December–January–February); whereas in the Northern region around the An Nafud desert it peaks in the spring season (March–April–May) [38]. However, there is limited systematic understanding of how variations in environmental drivers lead to spatial and temporal variations in the occurrence of dust storms across the entire Arabian Peninsula. Hence, this study aims to improve our understanding of how climate variables—specifically temperature, precipitation, wind speed, and wind direction—influence the incidence of dust storms in Saudi Arabia. This study also seeks to provide a comprehensive characterization of the seasonal variation in the frequency and the distribution of dust storms over different regions in the study area.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Saudi Arabia is located in the southwest of the Asian continent. Most of its territory is covered by vast arid deserts, with the exception of the southwestern part of the country [39]. The largest desert is the Empty Quarter (or Rub’ al Khali), which dominates the southern part of the Arabian Peninsula and covers more than 650,000 km2. Other important deserts are found in the north, including the An Nafud desert with an area of 57,000 km2, and in the east of Saudi Arabia, including the Ad Dahna desert, with an area of 1450 km2 [13,40,41] (see Figure 1).
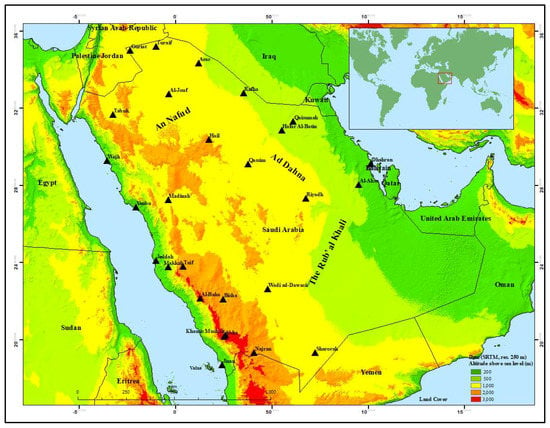
Figure 1.
Elevation map of the Arabian Peninsula with annotation of major cities and deserts, as well as the location of the in situ dust storm measurement stations.
Climatologically, Saudi Arabia is known to be one of the driest places in the world, with an average annual precipitation of less than 100 mm per year [42]. The temperatures are in excess of 50 °C in the summer season. On the other hand, in the winter season, the average maximum temperature drops to 8–17 °C [43], at which time most of the annual rainfall occurs, especially in the western and southern regions. Central regions are relatively cold and dry in the winter.
2.2. Dust Storm and Climate Variable Data
2.2.1. Monthly Dust Storm Observations
Monthly dust storm data for 27 in situ stations were obtained from the Presidency of Meteorology and Environment (PME) of Saudi Arabia, which is the official governmental climate agency in Saudi Arabia [44] for the period 2000–2016 (Figure 1). Incomplete observational records were available for two years in this period (2002 and 2009); thus, these records were omitted from the analysis. This dataset was used to analyze the spatio-temporal distribution of dust storm events across Saudi Arabia, including seasonal and inter-annual variations. The raw data for each station were analyzed in Microsoft Excel, including temporal linear trend fitting and five-pass filtering. The stations are situated across all of the 13 regions of Saudi Arabia (i.e., Riyadh, Makkah, Madinah, Al-Qassim, Eastern Province, Asir, Tabuk, Hail, Northern Borders, Jizan, Najran, Baha, and Al-Jouf). Moreover, the Pandas package for Python (WinPython-64bit-3.5.2.3) [45] was used to analyze the seasonal variation in the frequency of dust storms, as well as meteorological conditions (precipitation, temperature, and wind).
Vector dust storm data from all 27 stations were spatially interpolated by using the “spline with barrier” tool in ArcGIS 10.5.1, producing continuous raster layers representing the spatio-temporal variability of dust storms across the entire study area. The spline with barrier interpolation method estimates values using a mathematical algorithm which minimizes the surface curvature with a barrier of a chosen area, producing a smooth surface based on the input points [46]. The interpolation was applied to provide the rate of the change of the frequency of dust storms over the study period.
2.2.2. Climate Variable Data
We also used monthly averaged climate data provided by PME for 27 in situ meteorological stations, covering the period 2000–2016, in order to determine the correlation between specific climate variables and the occurrence frequency of dust storms. These climate variables were average temperature (°C) and average numbers of rain events per station. To investigate the wind speed and direction at each in situ station, we used daily data from the METAR/TAF (Meteorological Terminal Aviation Routine and Terminal Aerodrome Forecast) aviation routine weather report at hourly or half-hourly intervals. These data contain observations of the meteorological elements such as surface wind, visibility, and present weather (e.g., dust storm, haze, mist, and thunderstorm), clouds of operational significance, air temperature, dew-point temperature, and atmospheric pressure. These reports are based on the coding of the present weather, which is observed and forecasted by the World Meteorological Organization [47,48,49].
In order to understand the relationship between the wind velocity and the occurrence of the dust storms at each of the five monitoring stations, we compared wind patterns under dust-free weather conditions versus dust storm conditions for the period 2005–2017. To do so, we created wind rose diagrams to compare the prevailing wind directions and wind speed under these two conditions across different regions within Saudi Arabia.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
To gain a stronger understanding of the variability in the observed occurrence of dust storms, we analyzed the possible existence of temporal trends across several Saudi Arabia stations between 2000 and 2016 by conducting regression analyses [50]. The associated coefficients of determination (R2) and model uncertainty were considered to evaluate the goodness of these fits. Moreover, a Pearson correlation coefficient (r) analysis was used to investigate the potential existence of significant relationships between the weather variables and the frequency of dust storm occurrence (Figure 2).
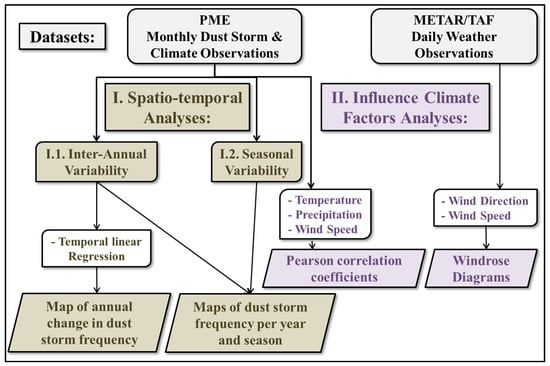
Figure 2.
Methodological flowchart of spatio-temporal variability in dust storms over Saudi Arabia.
3. Results
3.1. Inter-Annual Variation of Dust Storms
Figure 3 presents a moving average (five-pass) filter applied to the total number of dust storms recorded across all in situ stations within the study area between the years 2000 and 2016. This figure highlights the temporal trend of the annual number of dust events as recorded over all the in situ stations across entire Saudi Arabia by using the linear regression line with associated model error bounds (at 95% confidence interval) method. Figure 4 shows the linear regression analysis with associated model error bounds (at 95% confidence interval) which was applied to the dataset of the total dust events per PME station between the years 2000 and 2016, including the five-pass filter. This figure illustrates the temporal trend in the frequency of dust events in each station. Furthermore, Table 1 shows the slope coefficient values of the temporal linear regression analysis (annual change in the number of dust storms) with associated standard error value (and level of confidence) for each station over the study area. Figure 5 shows the results of the spatial interpolation analysis, highlighting inter-annual variability in dust storms and their spatial distribution between the years 2000 and 2016.
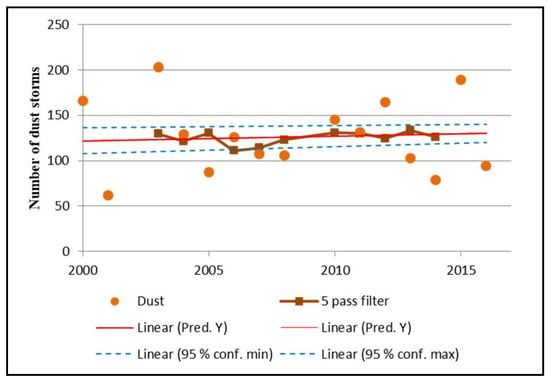
Figure 3.
Temporal trend analysis of the total annual number of dust storm events as recorded over all the in situ stations across entire Saudi Arabia between the years 2000 and 2016, including a five-pass filter and linear regression line with associated model error bounds (at 95% confidence interval).
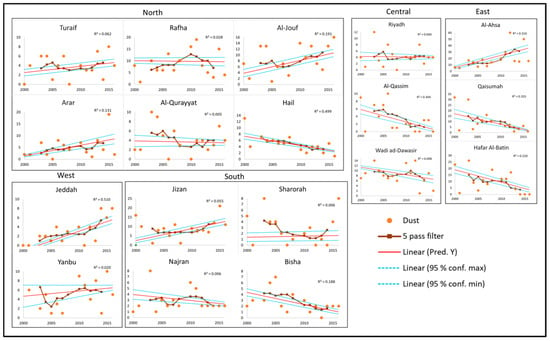
Figure 4.
Scatter plots showing the total annual number of dust storm events per Presidency of Meteorology and Environment (PME) station between the years 2000 and 2016, including a five-pass filter and linear regression line with associated model error bounds (at 95% confidence interval).

Table 1.
Slope coefficient values of the temporal linear regression analysis (annual change in number of dust storms) with associated standard error value (and level of confidence). Rows are colored by the sign of the trend (yellow for positive, blue for negative) and significance of trend (darker is more significant).
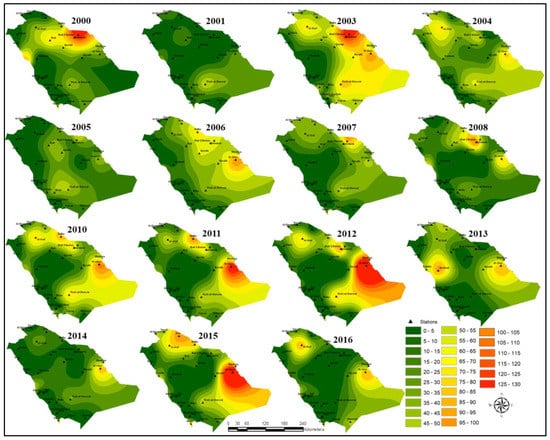
Figure 5.
Spatially interpolated dust storm frequency per year over Saudi Arabia for the period 2000–2016. Note that the highest frequency of total dust event occurrences varies from year to year with a concentration mostly in the east region.
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Variability Analysis of Dust Storms in Saudi Arabia
Figure 6 presents the inter-annual trend in dust storm event occurrence over entire Saudi Arabia after interpolating the associated slope parameter value from each station.
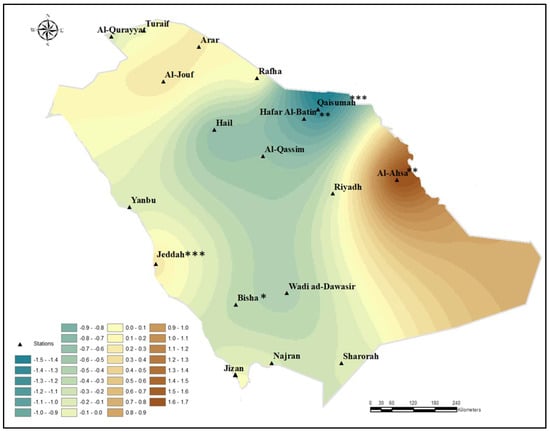
Figure 6.
Annual change in dust storm frequency (number of events/year) over Saudi Arabia. Increasing trends are shown in brown, while decreasing trends are shown in blue (Table 1).
3.3. Regional Differences in Seasonality of Dust Storms
Figure 7 indicates the spatial distribution of the total number of dust storms per season as being recorded over the entire period 2000–2016.
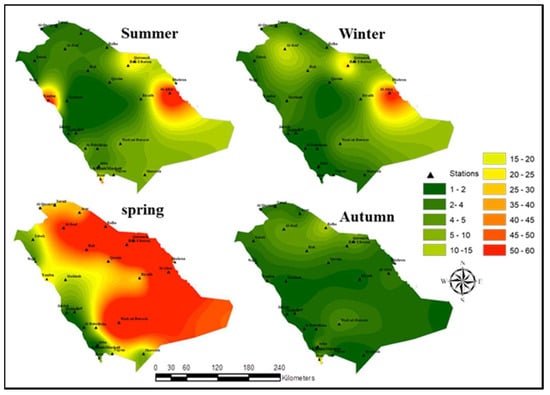
Figure 7.
Map of the total amount of dust storms per season recorded over the period 2000–2016.
3.4. Seasonal Variations across All Stations
The graphs below show the seasonal variation in the frequency of dust storms, temperature, frequency of precipitation, and wind speed for all PME stations and for each station (Figure 8 and Figure 9).
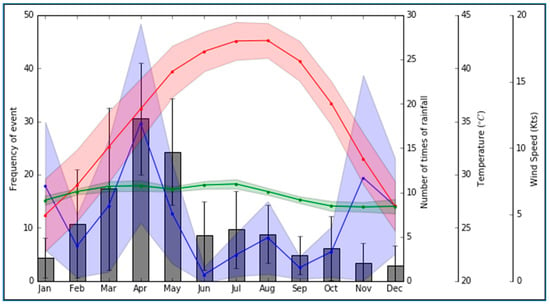
Figure 8.
Seasonal variation in (i) the frequency of dust storms in gray, (ii) temperature in red, (iii) frequency of precipitation in blue, and (iv) wind speed in green for all PME stations. The values in the graph represent the average and the associated standard deviation (by error bars or shaded surface) for the period 2000–2016.
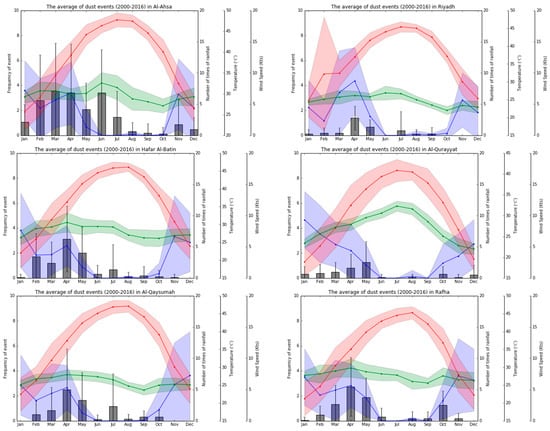
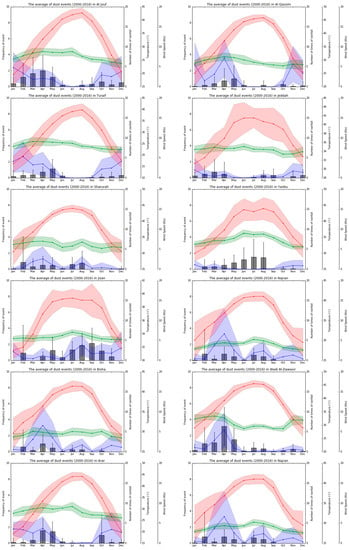
Figure 9.
Scatter plots showing the total annual number of dust storm events per PME station between the years 2000 and 2016, including a five-pass filter and linear regression line with associated model error bounds (at 95% confidence interval).
3.5. Spatio-Temporal Variations in Wind Speed and Direction
Figure 10 illustrates the wind speed and direction for two dust presence conditions, dust free and dust storms for the period 2005–2017. To make this comparison across entire Saudi Arabia, we chose the following five main cities, Riyadh representing the central region, Al-Ahsa representing the eastern region, Jeddah representing the western region, Arar representing the northern region, and Jizan representing the northern region.
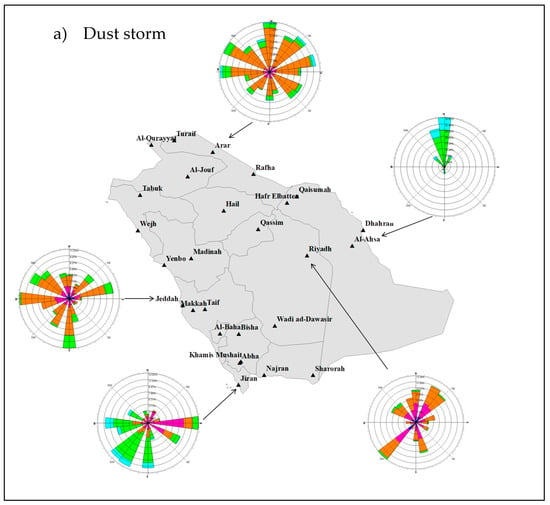
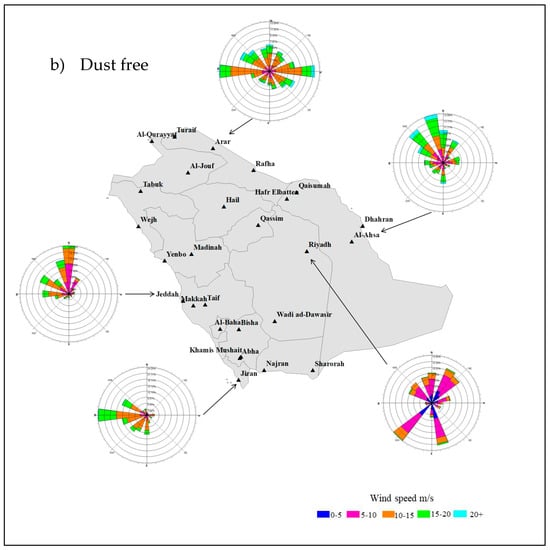
Figure 10.
Wind roses representing wind direction and wind speed covering the period 2005–2017 under dust storm conditions (a) and dust-free conditions (b).
4. Discussion
4.1. Inter-Annual Variation of Dust Storms
Figure 3 shows that, when considering all the dust storms recorded in the 27 in situ stations across Saudi Arabia, 2013 had the highest five-pass filter value. However, when looking at the unfiltered data, the highest annual total number of dust storm events was recorded in 2003 with 203 events (Figure 3). From the temporal analysis of each station (i.e., graphs in Figure 4), both the frequency of occurrence of dust storms and the long-term trends varied to a large extent depending on the location. A gradual increase in dust events with an associated significant linear regression slope was noted in Al-Ahsa (1.71 ± 0.71 y−1) and Jeddah (0.37 ± 0.10 y−1). Furthermore, our analysis revealed a considerable increase in the frequency of dust storms in Arar (0.32 ± 0.24 y−1), Turaif (0.11 ± 0.13 y−1), Al-Jouf (0.38 ± 0.24 y−1), Rafha (0.17 ± 0.27 y−1), and Jizan (0.24 ± 0.27 y−1); however, the analysis did not show a significant linear regression slope parameter in these cases (Table 1). Moreover Figure 4 suggests a decrease in the number of dust storms over more recent years with fewer dust storms in 2013, 2015, and 2016, resulting in a long-term decreasing trend of dust storm occurrences across multiple stations, as indicated by significant negative regression slope parameters in Hail (−0.39 ± 0.11 y-1), Qaisumah (−1.10 ± 0.42 y−1), Hafar Al-Batin (−0.80 ± 0.41 y−1), Al Qassim (−0.36 ± 0.16 y−1), and Bisha (−0.15 ± 0.09 y−1) (Table 1).
From Figure 5, it is evident that the highest annual frequency of dust events varies in space and, depending on the year, may occur either in the east (i.e., near Qaisumah, Hafar Al-Batin, and Al-Ahsa), north (i.e., near Turaif, Arar, Al-Qurayyat, Al-Jouf, and Rafha), and the center (i.e., near Wadi ad-Dawasir, Riyadh, and Al-Qassim). The highest frequency of dust storms in Saudi Arabia occurred in 2003, which accounted for 10.74% of the total events recorded between 2000 and 2016. Notably, in 2003, dust storms were concentrated in the eastern region with 30, 26, and 17 events recorded in Qaisumah, Hafar Al-Batin, and Al-Ahsa, respectively. The second highest frequency was recorded in 2015 which accounted for 9.99% of the total dust storm events during the study period, which were particularly concentrated in the region around Al-Ahsa. Figure 5 also highlights that the lowest number of dust storm events were recorded in the years 2005, 2014, and 2016, which is in line with the observations made for Figure 3 and Figure 4.
4.2. Spatio-Temporal Variability Analysis of Dust Storms in Saudi Arabia
In general, our results showed that, despite the rather high inter-annual variability of dust events across entire Saudi Arabia, there exist some remarkable long-term trends in total annual number of dust storms, i.e., (i) an increasing trend in the east toward southeastern, and (ii) a decreasing trend in the northeast toward central and southern parts of the country, as illustrated in Figure 6. More precisely, Al-Ahsa in the east and Jeddah in the west were marked by a significant increases (p < 0.05) in dust storms over the past 16 years, whereas, for the same period of time, significant decreases in dust storm occurrence were recorded in Hail, Qaisumah, Hafar Al-Batin, and Al-Qassim in the northeast–center (p < 0.05) and Bisha in the south (p < 0.1).
4.3. Regional Differences in Seasonality of Dust Storms
Findings of this study demonstrated a strong spatial variability in dust storm occurrence in Saudi Arabia, with the highest frequency of dust storm events in the eastern region, especially in Hafr Al-Batin, Qaisumah, and Al-Ahsa, which is in line with other findings in the literature (e.g., [35,51,52]). In addition to the eastern region, the north part of the study area was also characterized by a high frequency of dust storm events, in particular, Al-Jouf and Rafha. Furthermore, it can be seen that the dust storm frequency reduced from the center to the southwest and increased slightly to the west (e.g., Yanbu) (Figure 7). However, Figure 7 reveals some remarkable seasonal differences. In general, when considering the entire country, our results emphasized that the highest frequency of dust occurs during the spring and summer (i.e., March–August), whereas the lowest number of dust storms events took place in the autumn and winter (i.e., September–November). More precisely, Figure 7 highlights that, in most regions, except the west, the dust storm frequency reached its maximum during the spring (i.e., March–May). However, during the summer the very high frequency of dust storm occurrence was restricted to the areas around Al-Ahsa in the east and Yanbu in the west [53]. Furthermore, we also identified a high frequency of dust events during the winter season in the eastern and northern parts of the study area (i.e., near Al-Ahsa, Hafar Al-Batin, and Al-Jouf), as well as two regions characterized by a slightly higher frequency of dust storms over the autumn, of which one is located in the north of the Arabian Peninsula (i.e., near Rafha) and the other is located in the southern region (i.e., near Jizan) (Figure 7).
4.4. Seasonal Variations across All Stations
According to our analysis of the seasonality of dust storms for the entire study site, dust storm events across Saudi Arabia occur throughout the entire year; however, similar to observations at the regional scale, there is a clear seasonal variability, with a maximum peak in dust storm occurrence (30 ± 11) in April (Figure 8). The monthly incidence of dust storms remains high (25 ± 10) during May, then drops significantly to less than 10 per month for the remainder of the calendar year. The period with the fewest dust storms is November to January (~4 ± 3). Between January and April, there is a steady increase in dust storm frequency, rising to the peak in April.
Considering the bar graphs for the individual stations in Figure 9, the most noticeable feature is that the mean dust storm frequency reaches its maximum peak in April in most of the regions (e.g., Riyadh, Jeddah, Hail, Al-Jouf, Bisha, Hafr Al-Batin, Arar, Rafha, and Al-Ahsa). Moreover, it is evident that, in Al-Ahsa, there is a longer period of high-frequency dust storm occurrence, i.e., between the months of February and June, after which the frequency of dust storms dramatically declines to fewer than two per month in August–October. Furthermore, the plots for Yanbu and Jizan, both located on the west coast, do not follow the general intra-annual distribution of dust storms, but have the highest frequency in dust storms around September for Jizan and for the period July–August for Yanbu. However, their frequency of dust storms is low overall (Figure 9).
4.4.1. The Relationship between Dust Storms and Temperature
There is a clear and robust seasonal variation in air temperature across the peninsula, with a peak of 42 ± 2 °C in August, decreasing steadily to a minimum around 26 ± 4 °C in December (Figure 8). Pearson correlation coefficient analysis (Table 2) was used to investigate the relationship between air temperature and dust storm occurrence. Our results (Table 1) indicated that, although there was a positive correlation (i.e., value of 0.24) between the two variables, it was not statistically significant. However, Figure 8 shows that the seasonal maximum temperature occurs in a period (July to September) characterized by a relatively small number of dust storms.

Table 2.
The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) of the frequency of dust storms versus temperature, precipitation and wind speed considering each Presidency of Meteorology and Environment (PME) station from 2000 until 2016.
A very similar intra-annual trend in temperature can be observed across all individual stations (Figure 9). Hence, the relationship between dust storms and temperature was not significant in most of the regions, except for the three stations located along the western coast of Saudi Arabia. However, across these locations, no consistent pattern could be identified, because Jeddah was characterized by a significant negative correlation (i.e., r = −0.55), whereas Yanbu and Jizan were characterized by significant positive correlations (i.e., r = 0.69 in both cases) (Table 2).
4.4.2. The Relationship between Dust Storms and Precipitation
In general, the rainy season in Saudi Arabia runs from November to April, and the dry season is primarily during the months of June to September [54]. The overall highest frequency of precipitation events occurs in April (i.e., an average monthly number of rain cases of 20), which coincides with the highest dust storm frequency. Moreover, our results illustrated that the peak in dust storms is clearly related to the peak in frequency of precipitation events in the period March–May. There is notably less precipitation in the period June–October, with an average of five rainfall occurrences per month, as well as a lower frequency in dust storm events as compared to the antecedent wetter period. A second peak in rainfall is situated in November, with an average frequency of 10 rainfall events per month, which does not coincide with a higher frequency in dust storm events; however, it is important to note that the average frequency of precipitation events for this particular month has greater variability.
Previous research highlighted a negative correlation between precipitation and dust storms [55,56,57]. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that dust events tend to suppress rainfall [58,59]. Also, Middleton [60] claimed that the correlation between annual numbers of dust events and the total annual amount of precipitation is weak. Nevertheless, our results showed a positive correlation between dust storms and precipitation, because the occurrence of dust storms was mostly followed by rainfall [61,62]. Moreover, Zender and Kwon [63] suggested that there is a significant positive correlation between precipitation and the increase of dust emissions in the same month, especially in Saudi Arabia, Oman, and the Thar Desert (in India) [64]. Yang et al. [65] also found that the relationship of dust storm event occurrence with precipitation is stronger than with temperature. Moreover, it is known that, in Central Asia, the seasonality of precipitation is strongly linked to intra-annual variability in the frequency of dust storms [66].
Furthermore, the associated correlation coefficient between dust storm frequency and average frequency of precipitation events was found to be positive and statistically significant at p < 0.005 in Riyadh, Hail, Bisha, Najran, Sharurah, and Wadi ad-Dawasir (i.e., r = 0.53, 0.51, 0.74, 0.81, 0.51, and 0.89, respectively) (Table 1). In addition, in many stations, a second peak can be observed in November with a figure approximately above 10 rainfall events per month (e.g., Riyadh, Hail, Al-Qassem, Arar, Rafha, Jeddah, Rafha, and Hafr Al-Batin). However, the correlation between dust occurrence and precipitation was negative and statistically significant at p < 0.005 in Yanbu, located along the western coast of Saudi Arabia, with an r-value of −0.696. Hence, this result showed that there is an inverse relationship between annual dust storms and the frequency of precipitation events in Yanbu, which is a clear difference as compared to other regions. However, it should be noted that this station is characterized by remarkably low precipitation throughout the year, with typically fewer than five events per month (Figure 9).
4.4.3. The Relationship between Dust Storms and Wind Speed
As highlighted in Figure 8, the average wind speed remained fairly constant below 10 m/s across all months with slightly higher values in the period March–July and slightly lower values in the period October–December. However, despite this limited variation in wind speed, Table 2 illustrates that there was a significant positive correlation (p < 0.005) between the frequency of dust events and wind speed (i.e., r = 0.69), which is in accordance with other studies (e.g., [3,67]). Moreover, it can be seen that the months with the highest frequency in dust storms, i.e., March–May accounted for more than 50% of the total annual number of dust storms, and they were characterized by both high wind speeds and high precipitation amounts [38,60]. In contrast, the lower frequency of dust storm events in the period November–January coincided with lower wind speeds [35]. The average wind speed remained fairly steady between 6 and 8 knots across all months in Riyadh, Jeddah, Hail, Al-Qassem, Jizan, and Al-Qaysumah, with slightly higher values between the period March–July and slightly lower values between the period October–December. On the other hand, in some other regions, the variability in average wind speed was larger, with monthly average values between 6 and 12 knots (e.g., Al Qurrayat and Al-Ahsa) (Figure 9). We found a significant positive correlation (p < 0.005) in Hail, Al-Qassem, Jizan, Yanbu, Turaif, Hafr Al-Batin, Rafha, Sharurah, Al-Ahsa, and Al-Qaysumah (r = 0.751, 0.748, 0.546, 0.842, 0.499, 0.799, 0.7051, 0.772, and 0.697, respectively) (Table 2).
Overall, the two meteorological variables of precipitation and wind speed were positively correlated with the occurrence of dust storms. Moreover, we found no correlation between temperature and dust events. However, the most surprising positive correlation was with the precipitation; few studies were published on the relationship between dust events and precipitation, and they found that dust storms are negatively correlated with precipitation, which means that dust storms are reduced due to precipitation [55,56,57,59]. A possible explanation for this result is that our analysis was based on the frequency of rainfall events, while other studies considered the amount of the precipitation. A further explanation is that rainfall might be caused or followed by the dust storms.
4.5. Spatio-Temporal Variations in Wind Speed and Direction
In order to understand the spatial changes in dust storm frequency, we investigated wind speed and direction at each in situ station for dust-free conditions and during dust storms (Figure 10). To make this comparison across entire Saudi Arabia, we chose the following five main cities: Riyadh representing the central region, Al-Ahsa representing the eastern region, Jeddah representing the western region, Arar representing the northern region, and Jizan representing the northern region. It can be seen that, while the prevailing wind direction in Riyadh is from the southwest regardless of the conditions, the mean windspeed is between 5–10 m/s during dust-free days and 10–15 m/s during dust storm events (Figure 10). In the eastern part of Saudi Arabia (i.e., Al-Ahsa), the prevailing winds are from the north and the northwest with a mean speed of 10–15 m/s under dust-free conditions, whereas, during dust storms, the wind directions are the same with a mean speed above 20 m/s. Hence, the dust storms in this region are often linked to the Al Shamal wind, which has a predominately north-to-northwest wind direction, transporting dust from the Tigris and Euphrates plain over Syria and Iraq toward the northern and eastern part of the Arabian Peninsula [18,68,69,70,71]. However, Al Senafi and Anis [72] concluded that dust storm events in the east of Saudi Arabia are not always associated with the Al Shamal wind, but might also be a result of local unsettled weather systems. This may explain the high frequency of dust storm incidents in the eastern part of Saudi Arabia (Figure 5). In addition, Figure 10 shows that, in Arar, the prevailing winds are from all directions with a mean speed of 10–15 m/s and during both dust-free and dust storm conditions. This station is located on the border with the Syrian Desert, which is one of the dust storm source areas in the north [38]. Finally, the wind rose (Figure 10) revealed that the prevailing wind in Jeddah, located in the west, is from the north with a mean wind speed of 15–20 m/s during dust storm conditions and 10–15 m/s during dust-free conditions. The Sahara Desert can be considered as an important source area for the dust storms in the western and northwestern part of Saudi Arabia. This also may apply to Jizan, which is located along the southwestern coast of the Red Sea, and the prevailing wind is from the west during the dust storms with a mean speed above 20 m/s, while, for the dust-free days, the mean wind speed is between 10–15 m/s. In addition, as Doronzo et al. [73] concluded that buildings have a significant impact on dust storms with velocities between 10–20 m/s, an interesting future research avenue could be to investigate the potential of residential areas to function as dust storm corridors across Saudi Arabia.
4.6. Large-Scale Trends and Drivers
The observed temporal trends might be a result of large-scale land-use change dynamics within Saudi Arabia (e.g., urbanization and variability in vegetation coverage) [74,75], as well as in neighboring military conflict areas, such as Syria and Iraq, where a widespread abandonment of fields resulted in an enhanced dust erodibility of the soil [76]. As these regions are located on the most important dust trajectories reaching the northeastern part of the Arabian Peninsula [77], it is likely to result in a locally increased dust supply. Furthermore, climate change might also have an impact on the frequency of dust storms, as drier and hotter conditions may reduce the overall vegetation coverage and, therefore, intensify the desertification process [38,78]. This is particularly important, as recent studies showed that long-term drought conditions linked to synoptic weather conditions (i.e., the configuration of high-pressure and low-pressure systems) control dust storm activities over large areas (e.g., [22,23,79]). This underlines the urgent need for future research investigating the spatio-temporal trends of dust storms across the Arabian Peninsula taking into account large-scale influencing factors such as land-use change and climate change.
5. Conclusions
Our analysis shows that dust storms in Saudi Arabia occur most frequently in the eastern and northern regions of the country. These two regions are located near two major deserts in the study area, Ad-Dahna desert in the east and An Nafud in the north. The analysis illustrated that the dust storm frequency reached its maximum during the spring, whereas the lowest number of dust storms events took place in autumn. As dust storms are positively correlated with precipitation and wind speed p < 0.005, these two meteorological factors have an impact on the frequency of dust storms, although there is a negative correlation between dust events and temperature. The most notable result is that dust storms for the period 2000–2016 increased in the eastern part of the country, especially in the area around Al-Ahsa by 13.87%. Moreover, there was also a constant increase in the frequency of dust storms over time in Jeddah by 2.81%, which is located on the west coast. In contrast, dust storm frequency decreased over time in Hail, Qaisumah, Hafar Al-Batin, Al-Qassim, and Bisha. Also, our results showed a shift in dust storms from the northeast, possibly caused by the wind between the high pressure over the Mediterranean Sea and the low pressure in Saudi Arabia [80] to the southeast. The prevailing wind direction during dust-free and dust storm days varied across different parts of the country. The mean wind speeds during a dust storm are between 15 and 20 m/s, while, during non-dust days, they are around 10–15 m/s. Future research should seek to identify the drivers behind the observed spatio-temporal trends in dust storm event occurrence across Saudi Arabia, and aim to further explain the significant correlations with climatological factors such as the frequency of precipitation events.
Author Contributions
S.P. and J.M. designed the research and revised this manuscript. S.A. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. S.P., J.M., and J.C. provided comments and suggestions for the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a Jeddah University Scholarship and the University of Exeter.
Acknowledgments
I would like to express my deepest appreciation to all those who provided me the possibility to complete this paper. I am also grateful to the funding received through the Jeddah University Scholarship.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Goudie, A.S.; Middleton, N.J. Saharan dust storms: Nature and consequences. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2001, 56, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Hou, Q.; Zhou, C.H.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Niu, T. Sand/dust storm processes in Northeast Asia and associated large-scale circulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, M.; Irannejad, P.; Shao, Y. Climatology of the Middle East dust events. Aeolian Res. 2013, 10, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippertz, P.; Deutscher, C.; Kandler, K.; Müller, T.; Schulz, O.; Schütz, L. Dust mobilization due to density currents in the Atlas region: Observations from the Saharan Mineral Dust Experiment 2006 field campaign. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Kuciauskas, A.P.; Liu, M.; Ji, Q.; Reid, J.S.; Breed, D.W.; Walker, A.L.; Mandoos, A.A. Haboob dust storms of the southern Arabian Peninsula. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, K. Aeolian Dust and Dust Deposits; Elsevier, Academic Press: London, UK, 2015; p. 334. [Google Scholar]
- Furman, H.K.H. Dust storms in the Middle East: Sources of origin and their temporal characteristics. Indoor Built Environ. 2003, 12, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, R.; Todd, M.; Middleton, N.J.; Goudie, A.S. Dust-storm source areas determined by the total ozone monitoring spectrometer and surface observations. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2003, 93, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnum, B.H.; Winstead, N.S.; Wesely, J.; Hakola, A.; Colarco, P.R.; Toon, O.B.; Ginoux, P.; Brooks, G.; Hasselbarth, L.; Toth, B. Forecasting dust storms using the CARMA-dust model and MM5 weather data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2004, 19, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M.; Bullard, J.E.; Hodgkins, R. High-latitude dust over the North Atlantic: Inputs from Icelandic proglacial dust storms. Science 2012, 335, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Mahowald, N.; Jones, C. Temporal variability of dust mobilization and concentration in source regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sanad, H.A.; Ismael, N.F.; Nayfeh, A.J. Geotechnical properties of dune sands in Kuwait. Eng. Geol. 1993, 34, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgell, H.S. Arabian Deserts: Nature, Origin and Evolution; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 201–238. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Bassam, A.M.; Zaidi, F.K.; Hussein, M.T. Natural hazards in Saudi Arabia: Extreme Natural Events, Disaster Risks and Societal Implications. In An Introduction to Signal Detection and Estimation; Poor, H., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Chapter 4; pp. 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, G.; Terradellas, E.; Baklanov, A.; Kang, U.; Sprigg, W.; Nickovic, S.; Boloorani, A.D.; Al-Dousari, A.; Basart, S.; Benedetti, A.; et al. Global Assessment of Sand and Dust Storms; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Glennie, K.W.; Singhvi, A.K. Event stratigraphy, paleoenvironment and chronology of SE Arabian deserts. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2002, 21, 853–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.G.; Hatwar, H.R.; Al-Sulaiti, M.H.; Al-Mulla, A.H. Summer shamals over the Arabian Gulf. Weather 2003, 58, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, K.S. Dust Storm Forecasting for Al Udeid AB, Qatar: An Empirical Analysis. Master’s Thesis, Department of Engineering Physics, Air Force Institute of Technology, Air University, Islamabad, Pakistan, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Babikir, A.A.A. Some aspects of climate and economic activities in the Arab Gulf States. GeoJournal 1986, 13, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Sepehr, A. Statistical evaluation of the dust events at selected stations in Southwest Asia: From the Caspian Sea to the Arabian Sea. Catena 2018, 165, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlovsky, L.; Orlovsky, N.; Durdyev, A. Dust storms in Turkmenistan. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 60, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.M.; Mashat, A.W.S. Synoptic characteristics of spring dust days over northern Saudi Arabia. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2016, 9, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashat, A.W.S.; Alamoudi, A.O.; Awad, A.M.; Assiri, M.E. Seasonal variability and synoptic characteristics of dust cases over southwestern Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Arjmand, M.; Kaskaoutis, D.G. Assessment of dust activity and dust-plume pathways over Jazmurian Basin, southeast Iran. Aeolian Res. 2017, 24, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Mofidi, A.; Minvielle, F.; Chiapello, I.; Legrand, M.; Dumka, U.C.; Francois, P. Effects of Monsoon, Shamal and Levar winds on dust accumulation over the Arabian Sea during summer—The July 2016 case. Aeolian Res. 2019, 36, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S.; Middleton, N.J. The changing frequency of dust storms through time. Clim. Chang. 1992, 20, 197–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S. Dust storms: Recent developments. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastan, M.; Abdollahi, F.; Shokoufi, K. Analysis of Iran’s dust emission with system dynamics methodology. Tech. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2013, 3, 3515–3524. [Google Scholar]
- Pirsaheb, M.; Zinatizadeh, A.; Khosravi, T.; Atafar, Z.; Dezfulinezhad, S. Natural Airborne Dust and Heavy Metals: A Case Study for Kermanshah, Western Iran (2005–2011). Iran. J. Public Health 2014, 43, 460. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Amiraslani, F.; Liu, J.; Zhou, N. Identification of dust storm source areas in West Asia using multiple environmental datasets. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notaro, M.; Yu, Y.; Kalashnikova, O.V. Regime shift in Arabian dust activity, triggered by persistent Fertile Crescent drought. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.S.A. Dust Storm Phenomena and Their Environmental Impacts in Kuwait. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Gong, S.L.; Zhao, T.L.; Arimoto, R.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhou, Z.J. Sources of Asian dust and role of climate change versus desertification in Asian dust emission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbary, M.; Farahbakhshi, M. Analyzing and Tracing of Dust Hazard in Recent Years in Kermanshah Province. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 673–682. [Google Scholar]
- Notaro, M.; Alkolibi, F.; Fadda, E.; Bakhrjy, F. Trajectory analysis of Saudi Arabian dust storms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6028–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Notaro, M.; Liu, Z.; Kalashnikova, O.; Alkolibi, F.; Fadda, E.; Bakhrjy, F. Assessing temporal and spatial variations in atmospheric dust over Saudi Arabia through satellite, radiometric, and station data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albugami, S.; Palmer, S.; Meersmans, J.; Waine, T. Evaluating MODIS Dust-Detection Indices over the Arabian Peninsula. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Notaro, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Alkolibi, F.; Fadda, E.; Bakhrjy, F. Climatic controls on the interannual to decadal variability in Saudi Arabian dust activity: Toward the development of a seasonal dust prediction model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 1739–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, M.A. Introduction to Plant Ecology and Vegetation Types of Saudi Arabia; King Abdul Aziz University Press: Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Alaamer, A.S. Measurement of natural radioactivity in sand samples collected from Ad-Dahna desert in Saudi Arabia. World J. Nuclear Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthan Purakkal, J.; Kalenderski, S.; Stenchikov, G.L. Simulation of the Radiative Impact of High Dust Loading during a Dust Storm in March 2012. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- De Pauw, E. An Agroecological Exploration of the Arabian Peninsula; ICARDA: Aleppo, Syria, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, M.; Böer, B.; Michael, C.; Brook, Z.A.; Clüsener-Godt, M.; Wadid, S. Policy Perspectives for Ecosystem and Water Management in the Arabia Peninsula; UNESCO, Doha & United Nations University: Hamilton, ON, USA, 2006; Chapter 1; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, M.R.; Harmsen, E.W. (Eds.) Evapotranspiration: Principles and Applications for Water Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney, W. Pandas: A foundational Python library for data analysis and statistics. In Proceedings of the Python for High Performance and Scientific Computing, Tsukuba, Japan, 1–3 June 2011; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, S.; Pal, D.K.; Lohar, D.; Pal, B. Interpolation of climate variables and temperature modeling. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 107, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). International Codes—Volume, I.1 Part A: Alphanumeric Codes; Secretariat of the World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mahringer, G. Terminal aerodrome forecast verification in Austro Control using time windows and ranges of forecast conditions. Meteorol. Appl. 2008, 15, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.; Katsafados, P. Verification of operational weather forecasts from the POSEIDON system across the Eastern Mediterranean. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.R.; Rao, C.R.; Statistiker, M.; Rao, C.R.; Rao, C.R. Linear Statistical Inference and Its Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1973; Volume 2, pp. 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Alharbi, B.H.; Maghrabi, A.; Tapper, N. The March 2009 dust event in Saudi Arabia: Precursor and supportive environment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.O.; Haimberger, L.; Samimi, C. Climatology of dust distribution over West Asia from homogenized remote sensing data. Aeolian Res. 2016, 21, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashat, A. Study of Dust Storms over Yanbu City. J. King Abdulaziz Univ. Meteorol. Environ. Arid Land Agric. Sci. 2011, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanean, H.; Almazroui, M. Rainfall: Features and variations over Saudi Arabia, a review. Climate 2015, 3, 578–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littmann, T. Dust storm frequency in Asia: Climatic control and variability. Int. J. Climatol. 1991, 11, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTainsh, G.H.; Lynch, A.W.; Tews, E.K. Climatic controls upon dust storm occurrence in eastern Australia. J. Arid Environ. 1998, 39, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Quan, L.; Shi, S. Variations of the dust storm in China and its climatic control. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1216–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maley, J. Dust, clouds, rain types, and climatic variations in tropical North Africa. Quat. Res. 1982, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S. Dust storms in space and time. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1983, 7, 502–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.J. Dust storms in the Middle East. J. Arid Environ. 1986, 10, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuggio, V.M. How Dust Storms Work. 2012. Available online: http://science.howstuffwoks.com/nature/climate-wheather/storms/dust-storm1.htm (accessed on 28 March 2019).
- Vukovic, A.; Vujadinovic, M.; Pejanovic, G.; Andric, J.; Kumjian, M.R.; Djurdjevic, V.; Dacic, M.; Prasad, A.K.; El-Askary, H.M.; Paris, B.C.; et al. Numerical simulation of “An American Haboob”. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 26175–26215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zender, C.S.; Kwon, E.Y. Regional contrasts in dust emission responses to climate. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdari, S.; Karimi, N.; Sorooshian, A.; Mohammadi, G.; Sehatkashani, S. Impacts of climate and synoptic fluctuations on dust storm activity over the Middle East. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 173, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Bräuning, A.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Esper, J. Dust storm frequency and its relation to climate changes in Northern China during the past 1000 years. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 9288–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unescap.org. Sand and Dust Storms in Asia and the Pacific: Opportunities for Regional Cooperation and Action|United Nations ESCAP. 2018. Available online: https://www.unescap.org/resources/sand-and-dust-storms-asia-and-pacific-opportunities-regional-cooperation-and-action (accessed on 28 March 2019).
- Aili, A.; Oanh, N.T.K.; Abuduwaili, J. Variation Trends of Dust Storms in Relation to Meteorological Conditions and Anthropogenic Impacts in the Northeast Edge of the Taklimakan Desert, China. Open J. Air Pollut. 2016, 5, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Membery, D.A. Low level wind profiles during the Gulf Shamal. Weather 1983, 38, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.J. A geography of dust storms in South-west Asia. Int. J. Climatol. 1986, 6, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y. A model for mineral dust emission. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 20239–20254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S.; Middleton, N.J. Desert Dust in the Global System; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Al Senafi, F.; Anis, A. Shamals and climate variability in the Northern Arabian/Persian Gulf from 1973 to 2012. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 4509–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doronzo, D.M.; Khalaf, E.A.; Dellino, P.; de Tullio, M.D.; Dioguardi, F.; Gurioli, L.; Mele, D.; Pascazio, G.; Sulpizio, R. Local impact of dust storms around a suburban building in arid and semi-arid regions: Numerical simulation examples from Dubai and Riyadh, Arabian Peninsula. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 7359–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqurashi, A.F.; Kumar, L. Land use and land cover change detection in the Saudi Arabian desert cities of Makkah and Al-Taif using satellite data. Adv. Remote. Sens. 2014, 3, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T. Detection of land use/land cover changes and urban sprawl in Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia: An analysis of multi-temporal remote sensing data. ISPRS Int. J. GeoInf. 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomos, S.; Ansmann, A.; Mamouri, R.H.; Binietoglou, I.; Patlakas, P.; Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V. Remotesensing and modelling analysis of the extreme dust storm hitting the Middle East and eastern Mediterranean in September 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 4063–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dousari, A.; Doronzo, D.; Ahmed, M. Types, Indications and Impact Evaluation of Sand and Dust Storms Trajectories in the Arabian Gulf. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Yonemura, S.; Den, H.; Shen, Z.; Shen, Y. Relationship between the climate change and dust storm occurrence in China. J. Arid Land Stud. 2009, 19, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Parolari, A.J.; Li, D.; Bou-Zeid, E.; Katul, G.G.; Assouline, S. Climate, not conflict, explains extreme Middle East dust storm. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 114013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousta, I.; Doostkamian, M.; Taherian, A.; Haghighi, E.; Ghafarian Malamiri, H.; Ólafsson, H. Investigation of the spatio-temporal variations in atmosphere thickness pattern of iran and the middle east with special focus on precipitation in Iran. Climate 2017, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).