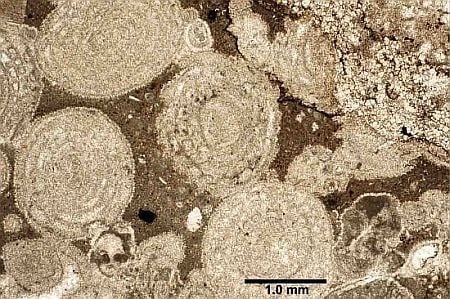
Ocean Acidification and the End-Permian Mass Extinction: To What Extent does Evidence Support Hypothesis?
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Background
2. Evidence of Ocean Acidification in the End-Permian Mass Extinction
2.1. Evidence in Sedimentary Rocks
2.1.1. Data Loss Resulting from Erosion and Pressure Solution
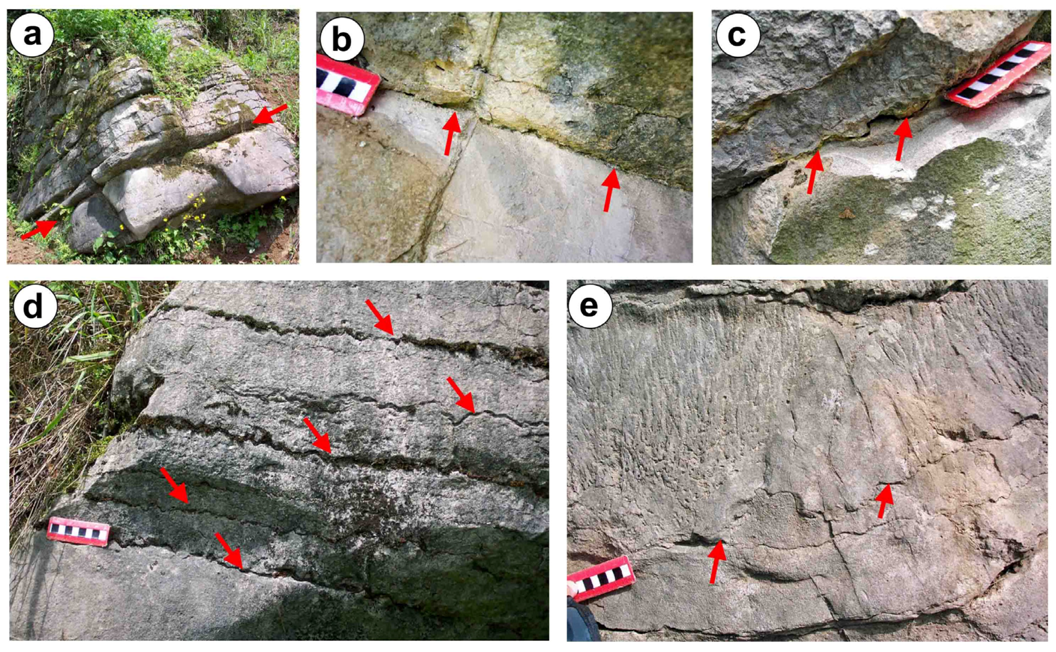
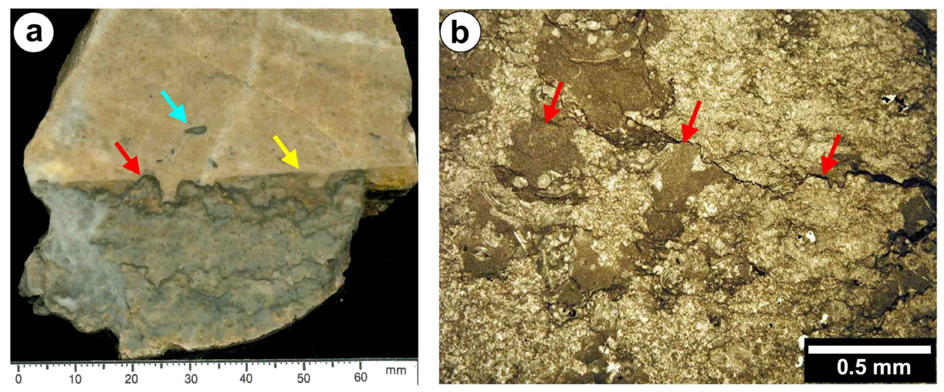
2.1.2. Possible Dissolution Surfaces in South China

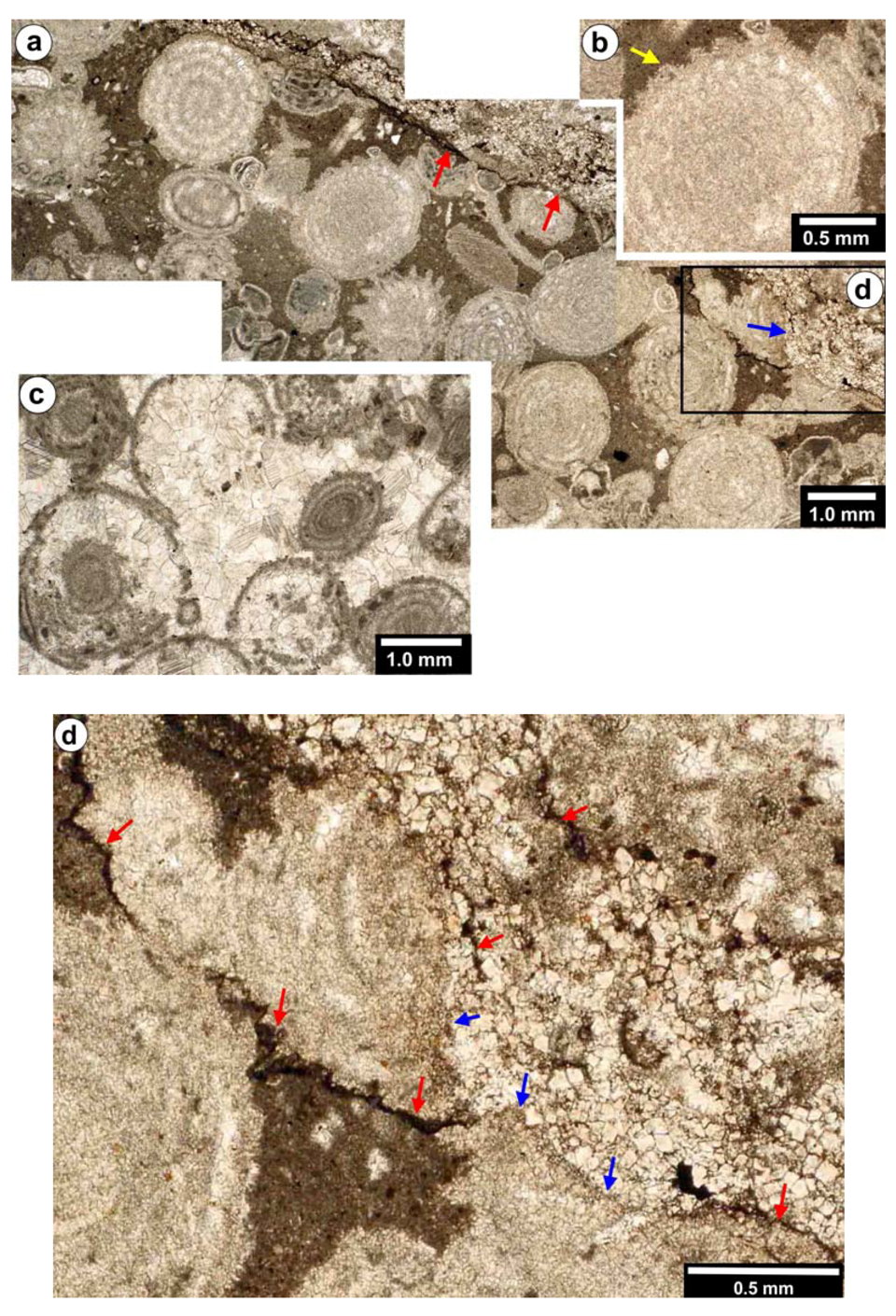
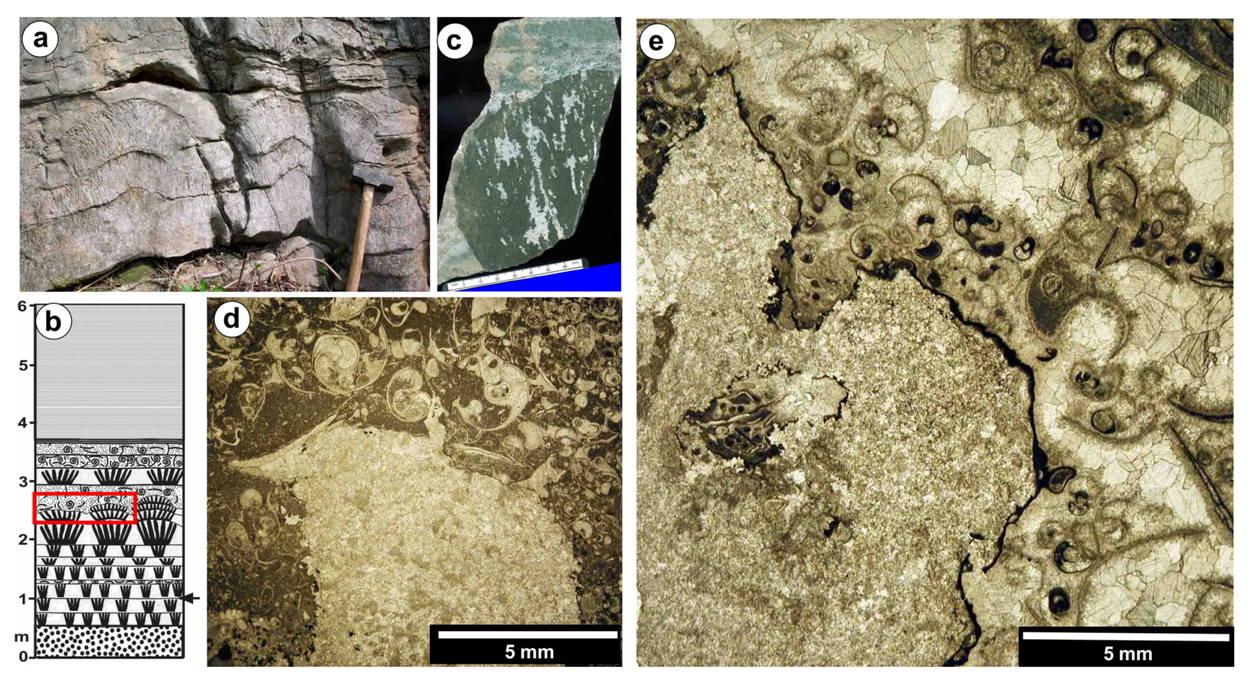
2.1.3. Other Areas
2.2. Evidence from Fossil Groups
3. Discussion
3.1. Petrographic Observations and Proxy Data in Sedimentary Rocks
3.2. Fossil Data
3.3. Rate of CO2 Increase, Dating Issues and Geography
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Erwin, D.H. Extinction: How Life on Earth Nearly Ended 250 Million Years Ago; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA; Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hörnisch, B.; Ridgwell, A.; Schmidt, D.N.; Thomas, E.; Gibbs, S.J.; Sluijs, A.; Zeebe, R.; Kump, L.; Martindale, R.C.; Greene, S.E.; et al. Geological record of ocean acidification. Science 2012, 335, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, J.L.; Turchyn, A.V.; Paytan, A.; DePaolo, D.J.; Lehrmann, D.J.; Yu, M.; Wei, J. Calcium isotope constraints on the end-Permian mass extinction. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8543–8548. [Google Scholar]
- Berner, R.A.; Kothavala, Z. GEOCARB III: A revised model of atmospheric CO2 over Phanerozoic time. Am. J. Sci. 2001, 301, 182–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattuso, J.-P.; Hansson, L. Ocean Acidification; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC Home Page. Available online: http://www.ipcc.ch/ (accessed on 19 September 2012).
- Orr, J.C.; Caldeira, K.C.; Fabry, V.; Gattuso, J-P.; Haughan, P.; Lehodey, P.; Pantoja, S.; Pörtner, H.-O.; Riebesell, U.; Trull, T.; Urban, E.; Hood, M.; Broadgate, W. Research priorities for understanding ocean acidification. Oceanography 2009, 22, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kleypas, J.A.; Yates, K.K. Coral reefs and ocean acidification. Oceanography 2009, 22, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, S.; Crasquin, S.; Li, Y.; Collin, P-Y.; Forel, M-B.; Mu, X.; Baud, A.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.; Maurer, F.; Guo, L. Microbialites and global environmental change across the Permian-Triassic boundary: A synthesis. Geobiology 2012, 10, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, J.L.; Lehrmann, D.J.; Follett, D.; Seibel, M.; Kump, L.R.; Riccardi, A.; Altiner, D.; Sano, H.; Wei, J. Erosional truncation of uppermost permian shallow-marine carbonates and implications for Permian-Triassic boundary events. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2007, 119, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, S.; Li, Y.; Crasquin-Soleau, S.; Feng, Q.; Mu, X.; Collin, P-Y.; Reynolds, A.; Guo, L. Earliest Triassic microbialites in the South China Block and other areas: Controls on their growth and distribution. Facies 2007, 53, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, S.; Crasquin, S.; Forel, M.-B.; Randon, C.; Collin, P.-Y.; Kosun, E.; Richoz, S.; Baud, A. Earliest Triassic microbialites in Çürük Dag, southern Turkey: Composition, sequences and controls on formation. Sedimentology 2010, 58, 739–755. [Google Scholar]
- Farabegoli, E.; Perri, M.C. Millenial physical events and the end-Permian mass mortality in the western Palaeotethys: timing and primary causes. In Earth and Life, International Year of Planet Earth; Talent, J.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germay, 2012; pp. 719–758. [Google Scholar]
- Flügel, E. Microfacies of Carbonate Rocks: Analysis Interpretation and Application; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Collin, P-Y.; Kershaw, S.; Crasquin, S.; Feng, Q. Facies changes and diagenetic processes across the Permian-Triassic boundary event horizon, Great Bank of Guizhou, South China: A controversy of erosion and dissolution. Sedimentology 2009, 56, 677–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wignall, P.; Kershaw, S.; Collin, P.-Y.; Crasquin, S. Erosional truncation of uppermost Permian shallow-marine carbonates and implications for Permian-Triassic boundary events: Comment. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2009, 121, 954–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, E.; Hassanzadeh, J. Deev Jahi Model of the Permian–Triassic boundary mass extinction: A case for gas hydrates as the main cause ofbiological crisis on Earth. Sediment. Geol. 2003, 163, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richoz, S.; Krystyn, L.; Baud, A.; Brandner, R.; Horacek, M.; Mohtat-Aghai, P. Permian–Triassic boundary interval in the Middle East (Iran and N. Oman): Progressive environmental change from detailed carbonate carbon isotope marine curve and sedimentary evolution. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2010, 39, 236–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, A.H.; Fischer, W.W. Skeletons and ocean chemistry: The long view. In Ocean Acidification; Gattuso, J.-P., Hansson, L., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hinojosa, J.L.; Brown, S.T.; Chen, J.; de Paolo, D.J.; Paytan, A.; Shen, S.-Z.; Payne, J.L. Evidence for end-Permian ocean acidification from calcium isotopes in biogenic apatite. Geology 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kershaw, S. Personal observations of samples from the Permian-Triassic boundary from the Meishan GSSP, Zhejiang, China, provided by Cao ChangQun, September 2010.
- Zachos, J.C.; Rohl, U.; Schellenberg, S.A.; Sluijs, A.; Hodell, D.A.; Kelly, D.C.; Thomas, E.; Nicolo, M.; Raffi, I.; Lourens, L.J.; et al. Rapid acidification of the ocean during the Paleocene–Eocene thermal maximum. Science 2005, 308, 1611–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Knoll, A.H.; Bambach, R.K.; Payne, J.L.; Pruss, S.; Fischer, W.W. Palaeophysiology and end-Permian mass extinction. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 256, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensen, H.; Schmidbauer, N.; Roscher, M.; Stordal, F.; Planke, S. Contact metamorphism, halocarbons, and environmental crises of the past. Environ. Chem. 2009, 6, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensen, H.; Planke, S.; Polozov, A.G.; Schmidbauer, N; Corfu, F.; Podladchikov, Y.Y.; Jamtveit, B. Siberian gas venting and the end-Permian environmental crisis. Earth Plan. Sci. Lett. 2009, 277, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerhayes, H. Dragon’s den: CO2, volcanic or anthropogenic. Geoscientist 2011, 2011, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Egleston, E.S.; Sabine, C.L.; Morel, F.M.M. Revelle revisited: Buffer factors that quantify the response of ocean chemistry to changes in DIC and alkalinity. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2010, 24, GB1002:1–GB1002:9. [Google Scholar]
- Feely, R.A.; Sabine, C.L.; Lee, K.; Berelson, W.; Kleypas, J.; Fabry, V.J.; Millero, F.J. Impact of anthropogenic CO2 on the CaCO3 system in the oceans. Science 2004, 305, 362–366. [Google Scholar]
- Sabine, C.L.; Feely, R.A.; Gruber, N.; Key, R.M.; Lee, K.; Bullister, J.L.; Wanningkhof, R.; Wong, C.S.; Wallace, D.W.R.; Tilbrook, B.; et al. The oceanic sink for anthropogenic CO2. Science 2004, 305, 367–371. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kershaw, S.; Crasquin, S.; Li, Y.; Collin, P.-Y.; Forel, M.-B. Ocean Acidification and the End-Permian Mass Extinction: To What Extent does Evidence Support Hypothesis? Geosciences 2012, 2, 221-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences2040221
Kershaw S, Crasquin S, Li Y, Collin P-Y, Forel M-B. Ocean Acidification and the End-Permian Mass Extinction: To What Extent does Evidence Support Hypothesis? Geosciences. 2012; 2(4):221-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences2040221
Chicago/Turabian StyleKershaw, Stephen, Sylvie Crasquin, Yue Li, Pierre-Yves Collin, and Marie-Béatrice Forel. 2012. "Ocean Acidification and the End-Permian Mass Extinction: To What Extent does Evidence Support Hypothesis?" Geosciences 2, no. 4: 221-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences2040221
APA StyleKershaw, S., Crasquin, S., Li, Y., Collin, P.-Y., & Forel, M.-B. (2012). Ocean Acidification and the End-Permian Mass Extinction: To What Extent does Evidence Support Hypothesis? Geosciences, 2(4), 221-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences2040221