Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Contribution to the Inventory of Infrastructure Susceptible to Earthquake and Flooding Hazards in North-Eastern Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Digital Image Processing
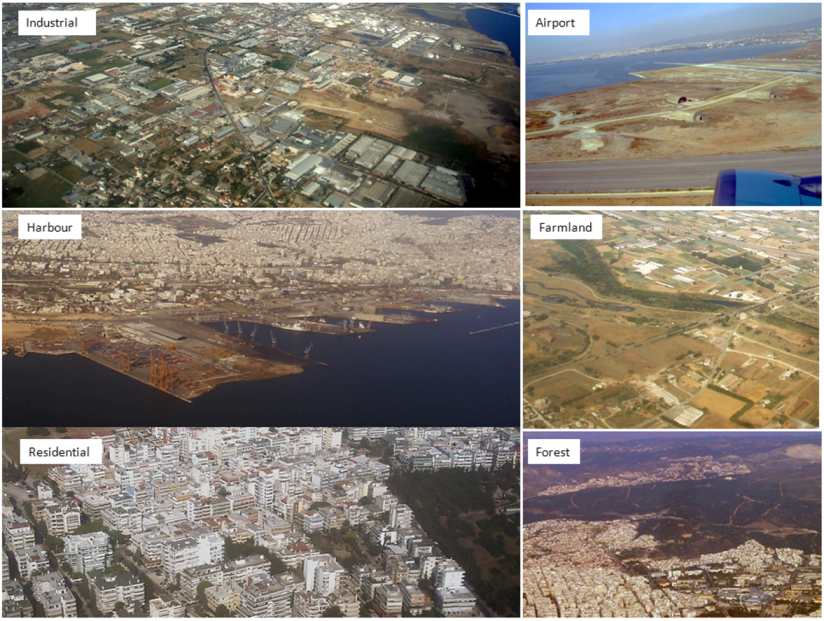
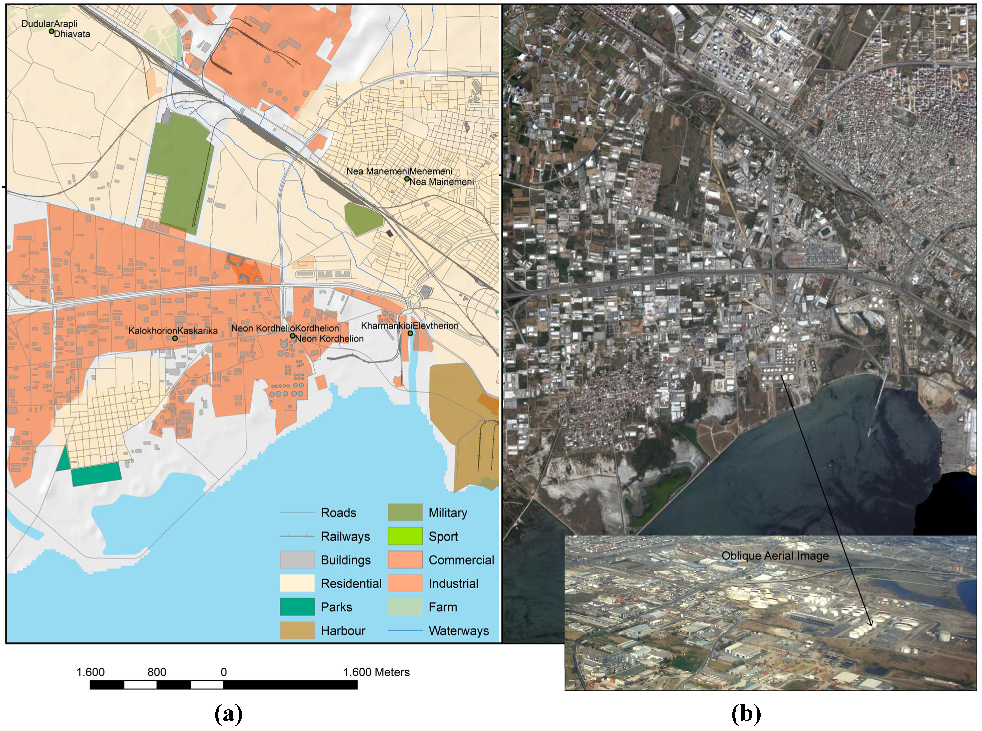
2.2. Evaluations of Digital Elevation Data for the Detection of Local Site Conditions and the Susceptibility to Flooding
- • slope degrees < 10°, indicating flat areas;
- • drop raster calculation <100.000 to 200.000 (calculated in ArcMap using the raster calculator), providing information of highest surface water flow input;
- • minimum curvature >250 (calculation in ENVI-software providing information upon flat, broader valleys, basins and depressions with younger sedimentary covers and higher groundwater tables, resulting in a grey-tone image with values between 0 and 255);
- • the lowest local height levels are indicating areas with relatively higher groundwater tables;
- • flow accumulation >1, highest flow-accumulations, providing information about areas with higher surface water-flow input.
- • from Quaternary sediment distributions and faults derived from geologic maps;
- • from lineaments derived visually from LANDSAT ETM+ and RapidEye imageries;
- • from earthquake data downloaded from International Earthquake Centres (International Seismological Centre, ISC, US Geological Survey, USGS, etc.);
- • Vs30-IDW-interpolation (data from USGS);
- • Shake maps, macroseismic observation records and further available data.
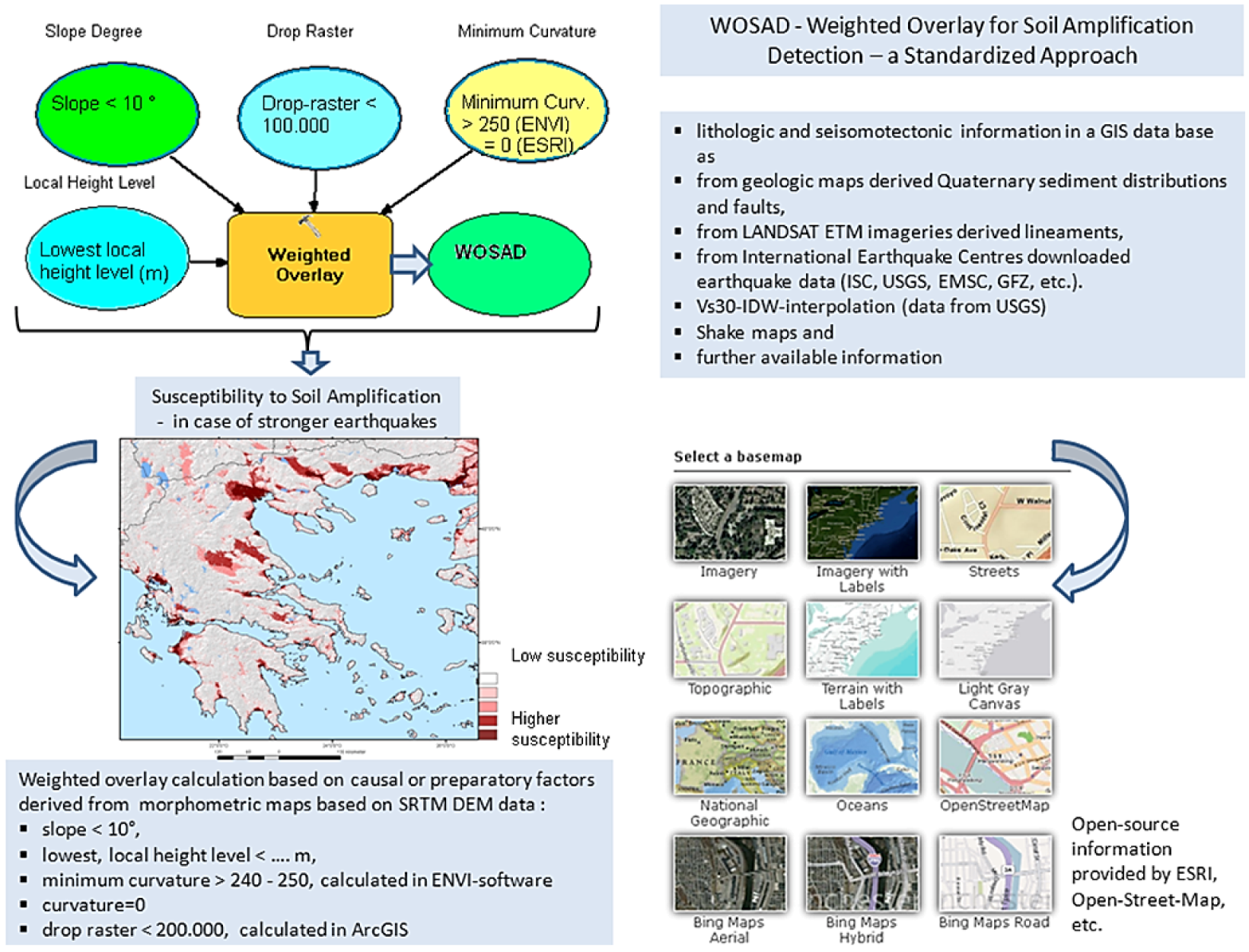

3. Seismotectonic Setting of Thessaloniki Area in NE-Greece
4. Susceptibility to Soil Amplification in Thessaloniki Area in NE-Greece
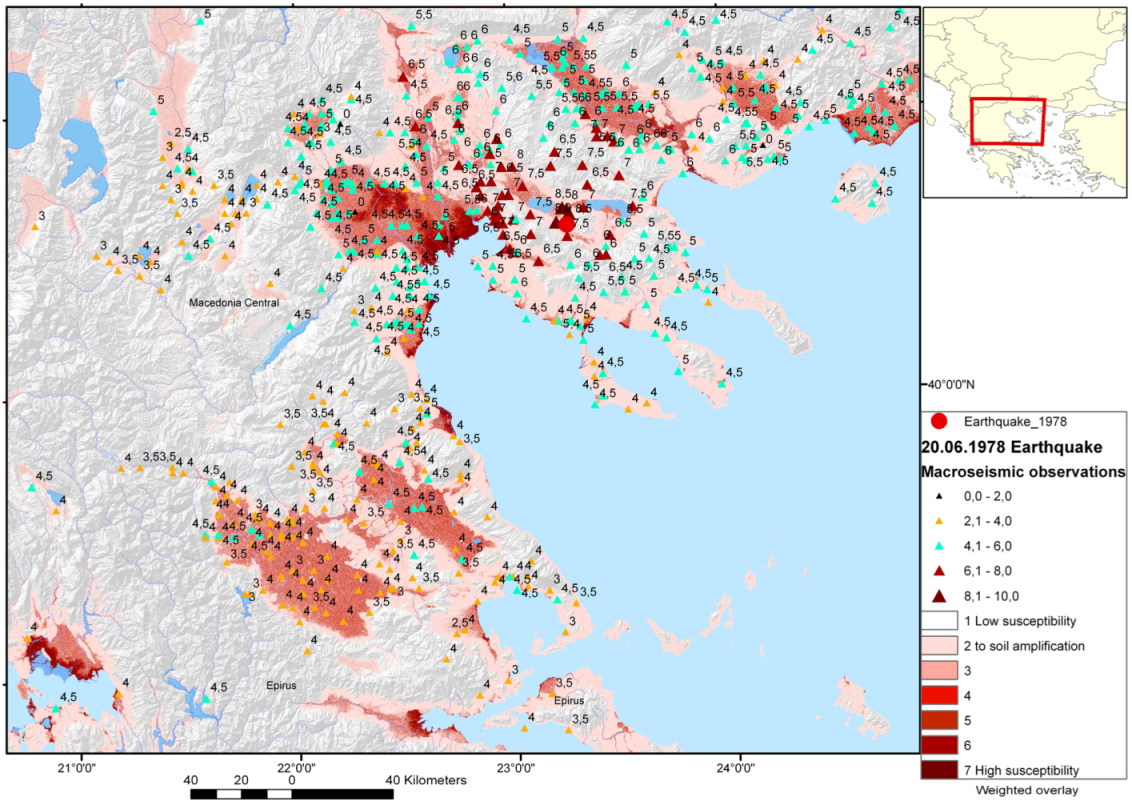

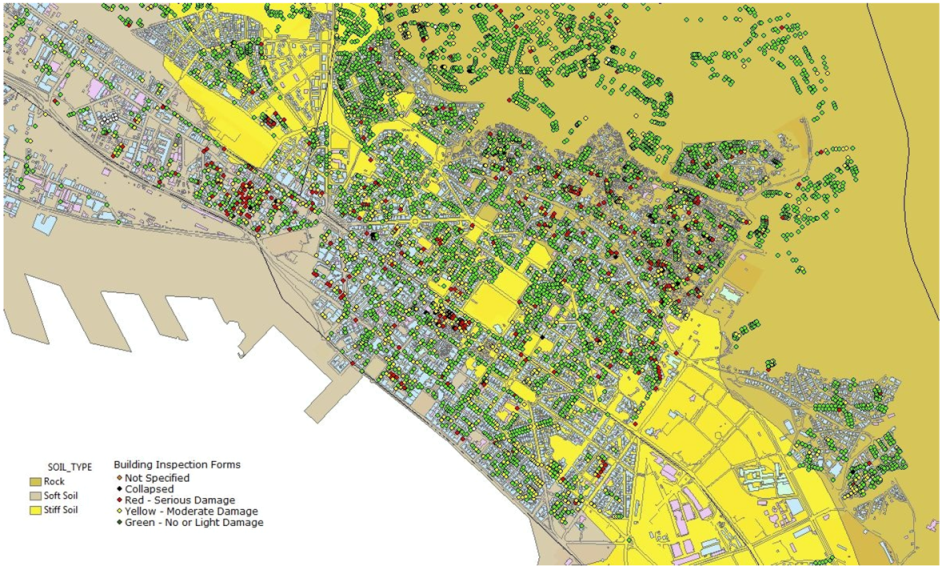
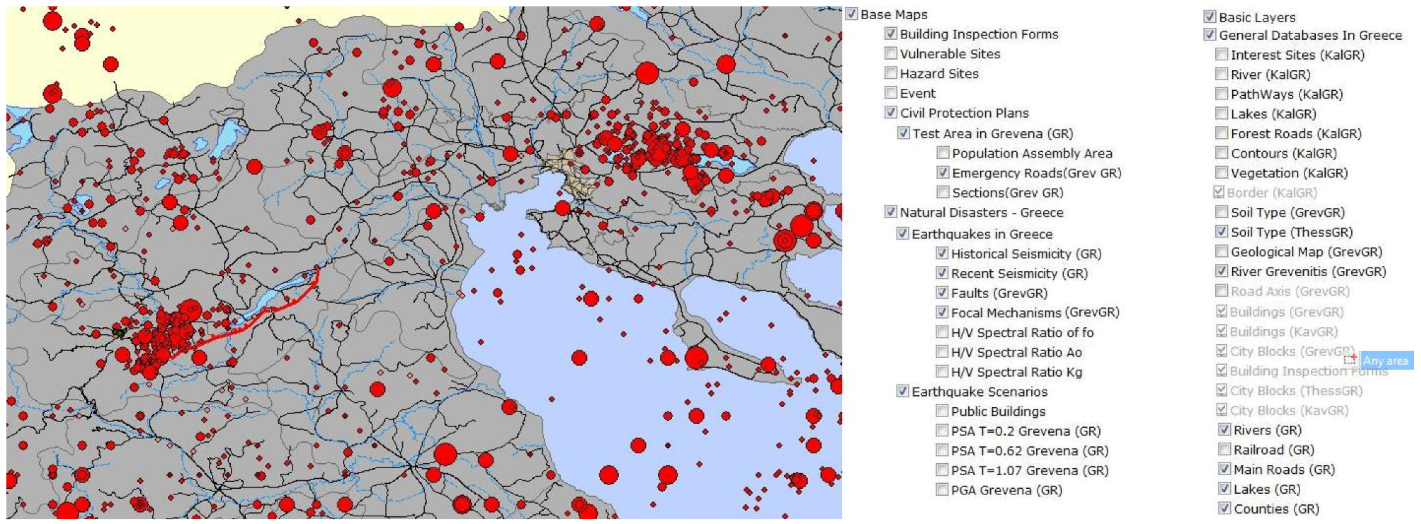
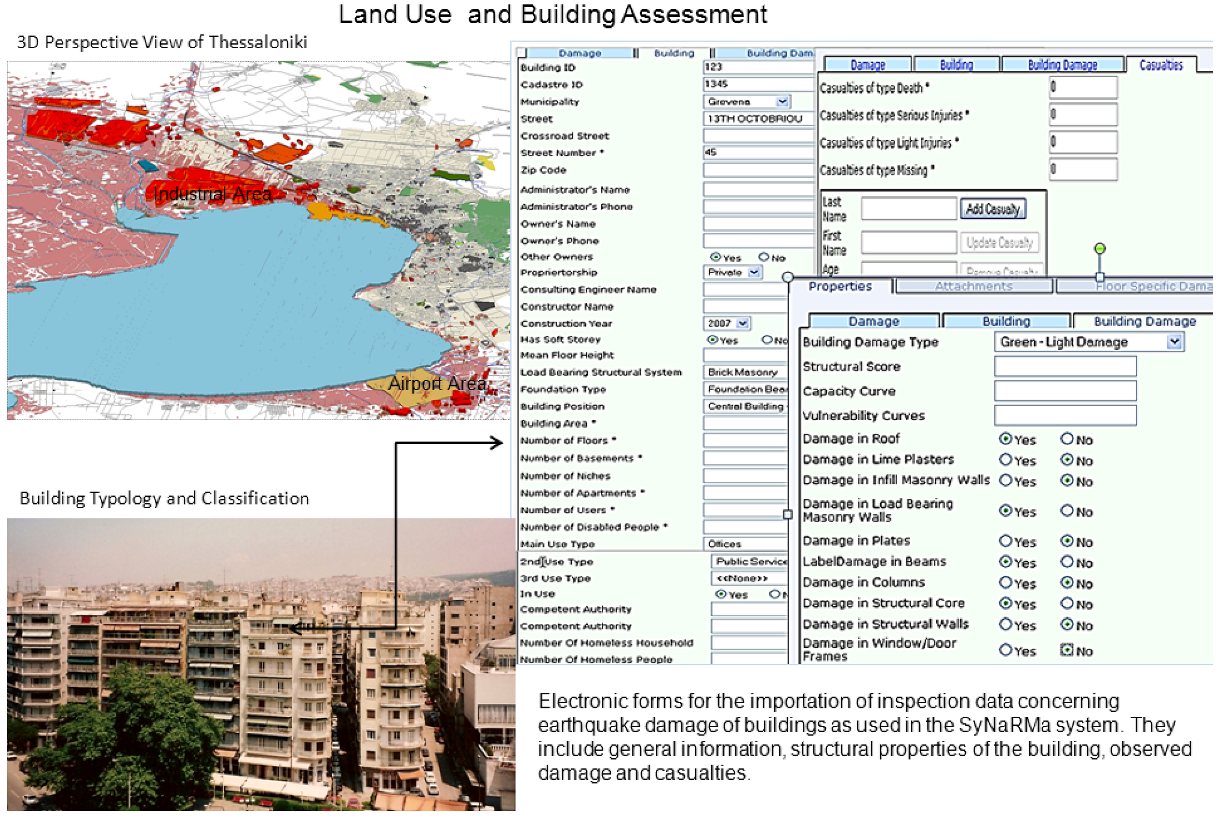
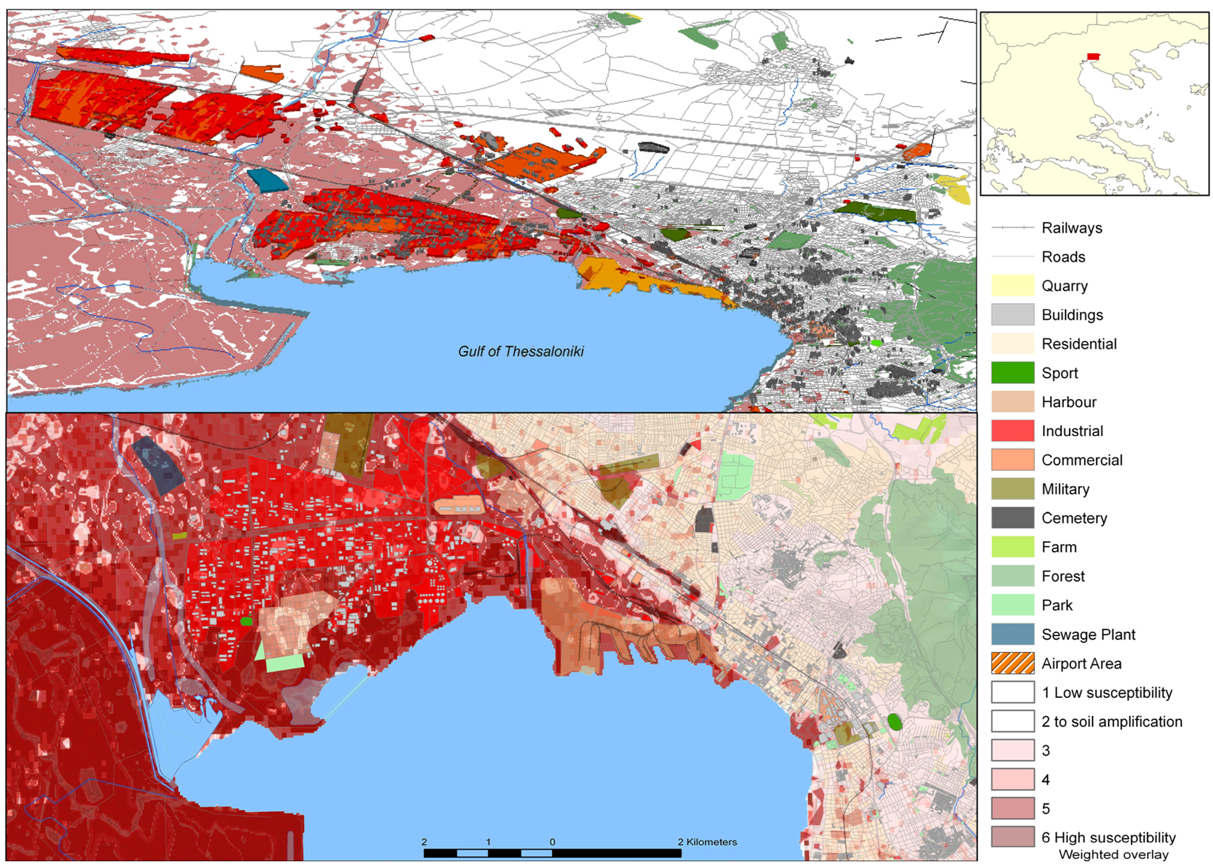
5. Flooding due to Flash Floods, Storm Surge and Tsunami Waves
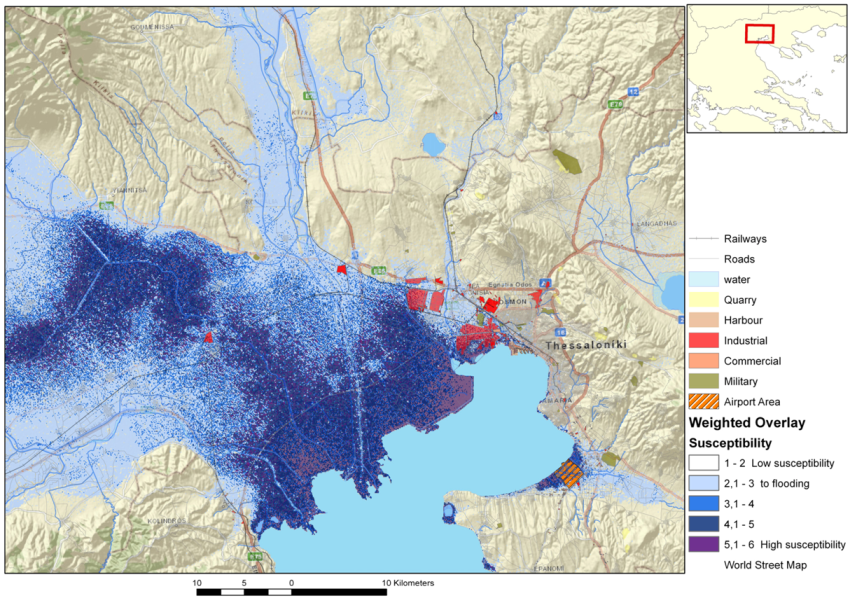
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Mas, E.; Koshimura, S.; Suppasri, A.; Matsuoka, M.; Matsuyama, M.; Yoshii, T.; Jimenez, C.; Yamazaki, F.; Imamura, F. Developing Tsunami fragility curves using remote sensing and survey data of the 2010 Chilean Tsunami in Dichato. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Strategy for Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP Strategy); Federal Ministry of the Interior, Federal Republic of Germany: Berlin, Germany, 2009. Available online: http://www.bmi.bund.de/cae/servlet/contentblob/598732/publicationFile/34423/kritis_englisch.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2012).
- United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction Secretariat (UNISDR). Living with Risk: A Global Review of Disaster Reduction Initiatives; UNISDR: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 2. Available online: http://www.unisdr.org/files/657_lwr21.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2012).
- Theilen-Willige, B.; Papadopoulou, I.D.; Savvaidis, P.; Tziavos, I.N. Use of Remote Sensing and GIS methods for mitigating the impact of earthquakes in cities. In Proceedings of the International Congress Natural Cataclysms and Global Problems of the Modern Civilization—GeoCataclysm, Istanbul, Turkey, 19–21 September 2011; International Committee on issues of Global Changes of the Geological Environment: Munich, Germany, 2012; pp. 587–596. [Google Scholar]
- Field, C.B.; Barros, V.; Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Dokken, J.; Ebi, K.L.; Mastrandrea, M.D.; Mach, K.J.; Plattner, G.-K.; Allen, S.K.; et al. IPCC: Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance ClimateChange Adaptation; A Special Report of Working Groups I and II of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Papathoma, M.; Dominey-Howes, D.; Zong, Y.; Smith, D. Assessing tsunami vulnerability, an example from Herakleio, Crete. Nat. Hazards Earth Sys. Sci. 2003, 3, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczuciński, W.; Chaimanee, N.; Niedzielski, P.; Rachlewicz, G.; Saisuttichai, D.; Tepsuwan, T.; Lorenc, S.; Siepak, J. Environmental and geological impacts of the 26 December 2004 Tsunami in coastal zone of Thailand—Overview of short and long-term effects. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 793–810. [Google Scholar]
- Szczuciński, W.; Niedzielski, P.; Kozak, L.; Frankowski, M.; Ziola, A.; Lorenc, S. Effects of rainy season on mobilization of contaminants from tsunami deposits left in a coastal zone of Thailand by the 26 December 2004 tsunami. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 253–264. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, G.A.; Daskalaki, E.; Fokaefs, A.; Giraleas, N. Tsunami hazards in the Eastern Mediterranean: Strong earthquakes and tsunamis in the East Hellenic Arc and Trench system. Nat. Hazards Earth Sys. 2007, 7, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradisopoulou, P.M.; Karakostas, V.G.; Papadimitriou, E.E.; Tranos, M.D.; Papazachos, C.B.; Karakaisis, G.F. Microearthquake study of the broader Thessaloniki area (Northern Greece). Ann. Geophys. 2006, 49, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Papazachos, B.C.; Mountrakis, D.M.; Papazachos, C.B.; Tranos, M.D.; Karakaisis, G.F.; Savvaidis, A.S. The fault which have caused the known major earthquakes in Greece and surrounding region between the 5th century BC and today. In Proceedings of 2nd National Conference Anti-Seismic Engineering and Technical Seismology, Thessaloniki, Greece, 28–30 November 2001; Technical Chamber of Greece; Aristotle University of Thessaloniki: Athens, Greece, 2001; pp. 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Skarlatoudis, A.A.; Papazachos, C.B.; Moczo, P.; Kristek, J.; Theodoulidis, N.; Apostolidis, P. Evaluation of ground motion simulations for the city of Thessaloniki, Greece using the FD method: The role of site effects and focal mechanism at short epicentral distances. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2007, 9, 10335:1–10335:2. [Google Scholar]
- Tranos, M.D.; Papadimitriou, Ε.Ε.; Kilias, A.A. Thessaliniki-Gerakarou Fault Zone (TGFZ): The western extension of the 1978 Thessaloniki earthquake fault (Northern Greece) and seismic hazard assessment. J. Struct. Geol. 2003, 25, 2109–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AUTH Thessaloniki Macroseismic Database. Available online: http://www.emidius.eu/AUTH/query_eq/?eq_group=1901_1999 (accessed on 24 July 2012).
- SyNaRMa Home Page. Available online: http://gserver.civil.auth.gr/synarma (accessed on 17 September 2012).
- Doukas, I.D.; Savvaidis, P.; Tziavos, I.N.; Grigoriadis, V.N.; Papadopoulou, I.; Vavassis, I. The use of a Web-based GIS for the management of databases related to natural disasters. Geod. Cartogr. 2007, 56, 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulou, I.D.; Savvaidis, P.; Tziavos, I.N. Using the SyNaRMa system as a disaster management tool. Nat. Hazards 2011, 57, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriadis, V.N.; Papadopoulou, I.D.; Spyridaki, P.; Doukas, I.D.; Tziavos, I.N.; Savvaidis, P. Presentation of a Web-based GIS system for the management of natural disasters. In Proceedings of Studying Modeling and Sense Making of Planet Earth, Mytilene, Greece, 1–6 June 2008; University of the Aegean: Mytilene, Greece, 2008. Available online: http://www.geo.aegean.gr/ earth-conference2008/papers/papers/ A06ID092.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2012). [Google Scholar]
- Spyridaki, P.; Papadopoulou, I.D.; Grigoriadis, V.N.; Tziavos, I.N.; Savvaidis, P. Methodology for identification of emergency assembly areas and road network in cities using GIS tools. In Proceedings of the 9th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference (SGEM), Albena, Bulgaria, 14–19 June 2009; SGEM Geoconferences: Sofia, Boulgaria, 2009; Volume II, pp. 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Karakostas, C.; Lekidis, V.; Salonikios, T.; Makarios, T.; Sous, I. Rapid visual screening of public buildings in the town of Grevena within a natural risk management system. In Proceedings of 3rd Panhellenic Congress on Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Seismology, Athens, Greece, 5–7 November 2008; Technical Chamber of Greece: Athens, Greece, 2008; pp. 1–14. Available online: http://library.tee.gr/digital/m2368/m2368_karakostas1.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2012). Paper No. 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Savvaidis, D. Towards an Effective EU Approach for Managing Floods in European Cities: The Thessaloniki Case Study. Master’s Thesis, University of Bradford, West Yorkshire, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Doukas, I.D.; Ifadis, I.M.; Savvaidis, P. Monitoring and analysis of ground subsidence due to water pumping in the area of Thessaloniki, Hellas. In Proceedings of FIG Working WeekTS16.4—Deformation Measurements and Analysis, Athens, Greece, 22–27 May 2004; International Federation of Surveyors: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Metzger, F.L.; Ikehara, M.E.; Howle, F.J. Vertical-Deformation, Water-Level, Microgravity, Geodetic, Water-Chemistry, and Flow-Rate Data Collected during Injection, Storage, and Recovery Tests at Lancaster, Antelope Valley, California, September 1995 through September 1998; Open-File Report 01-414; U.S. Geological Survey: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Stiros, S.; Psimoulis, P. Measurement of Land Subsidence Based on GPS and Historical Geodetic Data. 2008-2012 UNAVCO Proposal: Geodesy Advancing Earth Science Research; UNAVCO: Boulder, CO, USA, 2007; pp. 3–140. Available online: http://www.unavco.org/pubs_reports/ proposals/2007/facility2007/section3/UNV-GRID-SPREAD-R.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2012).
- Stiros, S. Rapid subsidence of the Thessaloniki (Northern Greece) coastal plain, 1960–1999. Eng. Geol. 2001, 61, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Theilen-Willige, B.; Savvaidis, P.; Tziavos, I.N.; Papadopoulou, I. Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Contribution to the Inventory of Infrastructure Susceptible to Earthquake and Flooding Hazards in North-Eastern Greece. Geosciences 2012, 2, 203-220. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences2040203
Theilen-Willige B, Savvaidis P, Tziavos IN, Papadopoulou I. Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Contribution to the Inventory of Infrastructure Susceptible to Earthquake and Flooding Hazards in North-Eastern Greece. Geosciences. 2012; 2(4):203-220. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences2040203
Chicago/Turabian StyleTheilen-Willige, Barbara, Paraskevas Savvaidis, Ilias N. Tziavos, and Ioanna Papadopoulou. 2012. "Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Contribution to the Inventory of Infrastructure Susceptible to Earthquake and Flooding Hazards in North-Eastern Greece" Geosciences 2, no. 4: 203-220. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences2040203
APA StyleTheilen-Willige, B., Savvaidis, P., Tziavos, I. N., & Papadopoulou, I. (2012). Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Contribution to the Inventory of Infrastructure Susceptible to Earthquake and Flooding Hazards in North-Eastern Greece. Geosciences, 2(4), 203-220. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences2040203




